
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Soyuz
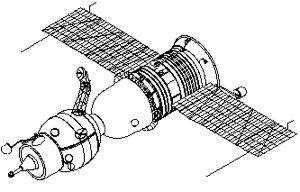 Soyuz 7K-OK Credit: © Mark Wade |
The fundamental concept of the design can easily be summarized as obtaining minimum overall vehicle mass for the mission. This is accomplished by minimizing the mass of the re-entry vehicle. There were two major design elements to achieve this:
- Put all systems and space not necessary for re-entry and recovery outside of the re-entry vehicle, into a separate jettisonable 'living section', joined to the re-entry vehicle by a hatch. Every gram saved in this way saves two or more grams in overall spacecraft mass - for it does not need to be protected by heat shields, supported by parachutes, or braked on landing.
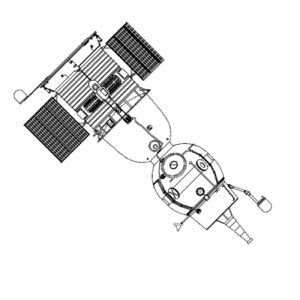
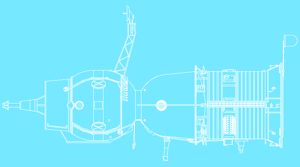
- Use a re-entry vehicle of the highest possible volumetric efficiency (internal volume divided by hull area). Theoretically this would be a sphere. But re-entry from lunar distances required that the capsule be able to bank a little, to generate lift and 'fly' a bit. This was needed to reduce the G forces on the crew to tolerable levels. Such a maneuver is impossible with a spherical capsule. After considerable study, the optimum shape was found to be the Soyuz 'headlight' shape - a hemispherical forward area joined by a barely angled cone (7 degrees) to a classic spherical section heat shield.
This design concept meant splitting the living area into two modules - the re-entry vehicle, with just enough space, equipment, and supplies to sustain the crew during re-entry; and a living module. As a bonus the living module provided an airlock for exit into space and a mounting area for rendezvous electronics.
The end result of this design approach was remarkable. The Apollo capsule designed by NASA had a mass of 5,000 kg and provided the crew with six cubic meters of living space. A service module, providing propulsion, electricity, radio, and other equipment would add at least 1,800 kg to this mass for the circumlunar mission. The Soyuz spacecraft for the same mission provided the same crew with 9 cubic meters of living space, an airlock, and the service module for the mass of the Apollo capsule alone!
The modular concept was also inherently adaptable. By changing the fuel load in the service module, and the type of equipment in the living module, a wide variety of missions could be performed. The superiority of this approach is clear to see: the Soyuz will remains in use at least 70 years later, while the Apollo was quickly abandoned. After studying a range of designs, the Chinese elected to copy the Soyuz layout for their Shenzhou spacecraft, rather than Apollo. Perversely, NASA copied the Apollo spacecraft layout for their Orion CEV, set to replace the shuttle after 2015. The Orion was in turn delayed. If Orion ever flies, will Soyuz still be flying when Orion is retired?
Origin
In the Soviet Union, manned spacecraft design in the late 1950's was solely handled by engineers within Sergei Korolev's design bureau. Korolev had designed the Vostok manned spacecraft that gave Russia the lead in the space race in the first half of the 1960's. Studies for a follow-on to Vostok, with the objective of sending a manned capsule on a circumlunar flight, began in 1959 under Tikhonravov. At this point it was assumed that any such flight would require use of launch vehicles derived from Korolev's R-7 ICBM. Since planned derivatives of the R-7 could not put more than six metric tons into orbit, it was immediately obvious that a circumlunar spacecraft would have to be assembled in low earth orbit from several R-7 launches. Therefore it would be necessary to perfect techniques for rendezvous, docking, and refueling of rocket stages in orbit. By 1960 to 1961 the studies, now dubbed 'L1', were expanded to cover automatic rendezvous and docking of several stages, and use of manipulators to assemble the stages.
Meanwhile the configuration of the re-entry vehicle for a Vostok follow-on was being investigated by other departments of Korolev's bureau. Lead for work on the re-entry problem was OKB-1's Gas Dynamics Department. There was no shortage of ideas. In 1959 Chief Designer Tsybin and Solovyev of the Spacecraft Department both offered designs for a winged manned spacecraft with a hypersonic lift-to-drag ratio of over 1.0. Prugnikov of the Warhead Department and Feoktistov of the Spacecraft Department proposed development of a ballistic capsule composed of variations of 'segmented spheres'. Korolev requested TsAGI, the state's Central Aerodynamic/Hydrodynamic Institute, to investigate all possible configurations. In a letter from A I Makarevskiy to Korolev on 9 September 1959 TsAGI set out its study plan. Aerodynamic characteristics at various angles of attack for a wide range of winged, spherical, elliptical, sphere-with cones, and conical shapes were to be analyzed at velocities from Mach 0.3 to Mach 25. The ballistic vehicle was to have a basic diameter of 2.5 m, a total internal volume of 3 to 3.5 cubic meters, and a living volume of 2 to 3 cubic meters. Separately considered for all configurations were aerodynamics of ejection seats or capsules with a diameter of 0.9 cubic meters and a length of 1.85 meters. Most of the work was promised for completion by the end of 1959. To exploit this database, Reshetin started a project group to conduct trade-off studies of the various configurations at the beginning of 1960. It was upgraded to a project sector, under the leadership of Timchenko, in 1961.
The 1960 studies considered various configurations of ballistic capsule, wing-canard schemes of conventional aircraft layout, and tailless hybrid configurations. As was done at General Electric, each configuration had a complete theoretical study, from the standpoint of aerodynamics, trajectories, resulting spacecraft masses, thermal protection requirements, and so on. By the end of 1960 it was found that the winged designs were too heavy for launch by the R-7 and in any case presented difficult re-entry heating problems that were beyond the existing technology. Studies of re-entry trajectories from lunar distances showed that a modest lift-to-drag ratio of 0.2 would be sufficient to lower G forces and allow the capsule to fly 3,000 to 7,000 km from its re-entry point and land on the Soviet territory. When the existing guidance accuracy were taken into account, this was increased to 0.3 to allow sufficient maneuverability to ensure the capsule could land within 50 km of the aim point.
These studies were the most complex ever undertaken, and Korolev obtained assistance from the most brilliant Soviet aerodynamicists, notably Likhushin at NII-1, and those refugees from Chelomei's take-over of their bureaus, Myasishchyev at TsAGI, and Tsybin at NII-88. In 1962 the classic Soyuz 'headlight' configuration was selected: a hemispherical forebody transition in a barely conical (7 degree) section to the section-of-a-sphere heat shield.
The Gas Dynamics Department had conceived of the modular scheme to reduce the mass of the re-entry vehicle in 1960. The Spacecraft Department's competing design was two modules, like Apollo. Further iterative studies in 1961 to 1962 reached the conclusion that the Soyuz should consist of four sections. From fore to aft these were the living module; the landing module; the equipment-propulsion module; and an aft jettisonable module, that would contain the electronics for earth orbit rendezvous (this was to be jettisoned after the last docking was completed and before translunar injection. Until the 1990's this compartment on the early Soyuz models was misidentified as a 'toroidal fuel tank' by Western space experts).
This configuration was selected only after considerable engineering angst. From the point of view of pulling the capsule away from the rocket in an emergency, positioning the capsule at the top of the spacecraft was ideal. But to use this layout with the living module concept, a hatch would have to be put through the heat shield to connect the two living areas. Korolev's engineers just could not accept the idea of violating the integrity of the shield (and would later get in bitter battles with other design bureaus when competing manned spacecraft - Kozlov's Soyuz VI and Chelomei's TKS - used such hatches).
Allegations have been made that the Korolev Soyuz design was based on General Electric's losing Apollo proposal. However study of the chronology of the two projects shows that early development work was almost simultaneous. Independently of General Electric, Korolev had arrived at the modular spacecraft approach and a similar capsule concept before the General Electric proposal was published. However there was plenty of time to incorporate detailed features of the General Electric design into Soyuz before it was finalized.
On May 7, 1963 Korolev signed the final draft project for Soyuz. The baseline consisted of a circumlunar Soyuz A (7K) manned spacecraft. This would be boosted around the moon by the Soyuz B (9K) rocket stage, which was fueled by the Soyuz V (11K) tanker. However Korolev understood very well that financing for a project of this scale would only be forthcoming from the Ministry of Defense. Therefore his draft project proposed two additional modifications of the Soyuz 7K: the Soyuz-P (Perekhvatchik, Interceptor) space interceptor and the Soyuz-R (Razvedki, intelligence) command-reconnaissance spacecraft. The Soyuz-P would use the Soyuz B rocket motor to boost it to intercepts in orbits of up to 6,000 km.
The Soyuz draft project was submitted to the expert commission on 20 March 1963. However only the reconnaissance and interceptor applications of the Soyuz could be understood and supported by the VVS air force and RVSN rocket forces. Korolev wanted to concentrate on the manned space exploration mission and felt he had no time to work on a Soyuz military 'side-line'. In 1963 his OKB-1 was working on the three-crew 3KV Voskhod, the two-crew 3KD Voskhod-2, the immense N1 11A52 launch vehicle , its smaller derivatives 11A53 (N11) and 11A54 (N111), and a large number of other unmanned spacecraft. Therefore it was decided that OKB-1 would concentrate only on development of the 7K spacecraft, while development of the 9K and 11K spacecraft would be passed to other design bureaus. The military projects Soyuz-P and Soyuz-R were ‘subcontracted' to OKB-1 Filial number 3, based in Samara.
To Korolev's frustration, while Filial 3 received budget to develop the military Soyuz versions, his own Soyuz-A did not receive adequate financial support. The 7K-9K-11K plan would have required five successful automatic dockings to succeed. This seemed impossible at the time. Instead the road to the moon advocated by Vladimir Nikolayevich Chelomei was preferred. Chelomei was Korolev's arch-rival, and had the advantage of having Nikita Khrushchev's son in his employ. He attempted to break the stranglehold that ‘Korolev and Co.', also known as the ‘Podpilki' Mafia, had on the space program. Chelomei's LK-1 single-manned spacecraft, to be placed on a translunar trajectory in a single launch of his UR-500K rocket, was the preferred approach. Chelomei issued the advanced project LK-1 on 3 August 1964, the same day the historic decree was issued that set forth the Soviet plan to beat the Americans to the moon. Under this decree Chelomei was to develop the LK-1 for the manned lunar flyby while Korolev was to develop the N1-L3 for the manned lunar landing. The 7K-9K-11K system was canceled. But the Soyuz A itself would be developed by Korolev as the 7K-OK manned earth orbit spacecraft. Korolev kept his options open and had versions of it designed which would in the end be flown for manned orbital (7K-LOK) and circumlunar (7K-L1) missions.
The Soyuz spacecraft was initially designed for rendezvous and docking operations in near earth orbit, leading to piloted circumlunar flight. In the definitive December 1962 Soyuz draft project, the Soyuz-A appeared as a two-place spacecraft. The Soyuz would have been launched on a lunar flyby after successive launches of 11K tanker spacecraft with a 9K translunar injection stage.
To Korolev's frustration, while Filial 3 received budget to develop the military Soyuz versions, his own Soyuz-A did not receive the support of the leadership for inclusion in the space program of the USSR. The 7K-9K-11K plan would have required five successful automatic dockings to succeed. This seemed impossible at the time. Instead Chelomei's LK-1 single-manned spacecraft, to be placed on a translunar trajectory in a single launch of his UR-500K rocket, was the preferred approach. According to the historic decree of 3 August 1964 that set forth the Soviet plan to beat the Americans to the moon, Chelomei was to develop the LK-1 for the manned lunar flyby while Korolev was to develop the N1-L3 for the manned lunar landing. The Soyuz-A was cancelled.
In the second quarter of 1963, when Korolev had begun design of the Voskhod multi-manned spacecraft, he instructed his bureau to begin design of a three-manned orbital version of the Soyuz A, the 7K-OK. But the crush of work on other projects and the new lunar landing project resulted in development of the 7K-OK being stopped by the fall of 1964. Soyuz was pushed into the background.
On 14 October 1964 Khrushchev was ousted from power, and Chelomei lost his patron. Soon thereafter, Korolev quietly reanimated his Soyuz-A project - not the circumlunar version, but a 7K-OK orbital spacecraft. Korolev's stated plan was for two of these spacecraft to demonstrate rendezvous and docking in earth orbit - but this was really a cover in preparation for wresting the circumlunar program back from Chelomei.
On 25 October 1965, less than three months before his death, Korolev regained the project for manned circumlunar flight. This would use a derivative of the 7K-OK, the 7K-L1, launched by Chelomei's UR-500K, but with a Block D translunar injection stage from the N1. Originally Korolev considered that the 7K-L1, for either safety or mass reasons, could not be boosted directly by the UR-500K toward the moon. He envisioned launch of the unmanned 7K-L1 into low earth orbit, followed by launch and docking of a 7K-OK with the 7K-L1. The crew would then transfer to the L1, which would then be boosted toward the moon. This was his hidden reason for the development of the 7K-OK.
On the first orbital launch of the 7K-OK in November 1966 a large number of failures occurred, indicating many errors in construction. The spacecraft was uncontrollable and was finally destroyed by the on-board APO destruct system.
On the second launch attempt on 14 December, the Soyuz incorrectly detected a failure of the launch vehicle at 27 minutes after an aborted launch attempt. The launch escape system activated while the vehicle was still fuelled on the pad, pulling the capsule away from the vehicle but exploding the launch vehicle and killing and injuring several people. Analysis of the failure indicated numerous problems in the escape system.
The 7K-OK, after sinking to the bottom of the Aral Sea after a trouble-ridden third flight, was taken into space by cosmonaut Komarov in April 1967. This disastrous flight ended in the cosmonaut being killed when the parachute failed to deploy. The 7K-OK parachute system was redesigned to the extent possible given the constraints of the moon race and went on to accomplish 13 relatively successful manned and unmanned earth orbital flights. After the Soviets lost the moon race, a plan to beat the Americans in the space station race was conceived. The 7K-OK was modified to the space station ferry configuration 7K-OKS with the addition of a docking tunnel. This configuration killed three cosmonauts aboard Soyuz 11 in 1971. Thereafter the spacecraft underwent a complete redesign, resulting in the substantially safer 7K-T, which flew dozens of times to Salyut and Almaz space stations until replaced by the Soyuz T in 1981. This was later replaced by the Soyuz TM and TMA models for the Mir and ISS stations, mainly involving electronics upgrades. These provided the only American/European/Russian access to space after the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011.
| Sever Russian manned spacecraft. Study 1959. Sever was the original OKB-1 design for a manned spacecraft to replace the Vostok. It was designed to tackle such problems as maneuvering in orbit, rendezvous and docking, and testing of lifting re-entry vehicles. |
| L1-1960 Russian manned lunar flyby spacecraft. Study 1960. Circumlunar manned spacecraft proposed by Korolev in January 1960. The L1 would a man on a loop around the moon and back to earth by 1964. |
| L4-1960 Russian manned lunar orbiter. Study 1960. Lunar orbiter proposed by Korolev in January 1960. The spacecraft was to take 2 to 3 men to lunar orbit and back to earth by 1965. |
| Soyuz A Russian manned spacecraft. Study 1962. The 7K Soyuz spacecraft was initially designed for rendezvous and docking operations in near earth orbit, leading to piloted circumlunar flight. |
| Soyuz B Russian space tug. Study 1962. In the definitive December 1962 Soyuz draft project, the Soyuz B (9K) rocket acceleration block would be launched into a 225 km orbit by a Soyuz 11A511 booster. |
| Soyuz V Russian logistics spacecraft. Cancelled 1964. In the definitive December 1962 Soyuz draft project, the Soyuz B (9K) rocket acceleration block would be launched into a 225 km orbit by a Soyuz 11A511 booster. |
| L1-1962 Russian manned lunar flyby spacecraft. Study 1962. Early design that would lead to Soyuz. A Vostok-Zh manned tug would assemble rocket stages in orbit. It would then return, and a Soyuz L1 would dock with the rocket stack and be propelled toward the moon. |
| Soyuz P Russian manned combat spacecraft. Study 1963. In December 1962 Sergei Korolev released his draft project for a versatile manned spacecraft to follow Vostok. The Soyuz A was primarily designed for manned circumlunar flight. |
| Soyuz R Russian manned spacecraft. Cancelled 1966. A military reconnaissance version of Soyuz, developed by Kozlov at Samara from 1963-1966. It was to consist of an the 11F71 small orbital station and the 11F72 Soyuz 7K-TK manned ferry. |
| Soyuz A SA Russian manned spacecraft module. Study 1962. Original Soyuz design, allowing crew of three without spacesuits. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz A BO Russian manned spacecraft module. Study 1962. Original design with notional docking system with no probe and internal transfer tunnel. Living section. |
| Soyuz A PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. Study 1962. Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system but with no base flange for a shroud. Equipment-engine section. |
| L3-1963 Russian manned lunar lander. Study 1963. Korolev's original design for a manned lunar landing spacecraft was described in September 1963 and was designed to make a direct lunar landing using the earth orbit rendezvous method. |
| L4-1963 Russian manned lunar orbiter. Study 1963. The L-4 Manned Lunar Orbiter Research Spacecraft would have taken two to three cosmonauts into lunar orbit for an extended survey and mapping mission. |
| Soyuz 7K-TK Russian manned spacecraft. Cancelled 1966. To deliver crews to the Soyuz R 11F71 station Kozlov developed the transport spacecraft 11F72 Soyuz 7K-TK. |
| Soyuz PPK Russian manned combat spacecraft. Study 1964. The Soyuz 7K-PPK (pilotiruemiy korabl-perekhvatchik, manned interceptor spacecraft) was a revised version of the Soyuz P manned satellite inspection spacecraft. |
| Soyuz VI Russian manned combat spacecraft. Cancelled 1965. To determine the usefulness of manned military space flight, two projects were pursued in the second half of the 1960's. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK Tether Russian manned spacecraft. Study 1965. Korolev was always interested in application of artificial gravity for large space stations and interplanetary craft. He sought to test this in orbit from the early days of the Vostok program. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK Russian manned spacecraft. Development of a three-manned orbital version of the Soyuz, the 7K-OK was approved in December 1963. Launched 1966 - 1969. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK (Soyuz 2, 5, passive) Null |
| Soyuz 7K-OK SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 17 launches, 1966.11.28 (Cosmos 133) to 1970.06.01 (Soyuz 9). Post-Soyuz 1 modification, allowing crew of three without spacesuits. Analogue sequencer and computers operate spacecraft. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK BO Russian manned spacecraft module. 17 launches, 1966.11.28 (Cosmos 133) to 1970.06.01 (Soyuz 9). Heavy-duty male/female docking system with no internal transfer tunnel. Igla automatic rendezvous and docking system. Living section. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 17 launches, 1966.11.28 (Cosmos 133) to 1970.06.01 (Soyuz 9). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK (Soyuz 9, non docking) Null |
| Soyuz 7K-L1 Russian manned lunar flyby spacecraft. The Soyuz 7K-L1, a modification of the Soyuz 7K-OK, was designed for manned circumlunar missions. Lunar flyby and return satellite, Russia. Launched 1967 - 1970. |
| Soyuz 7K-L1P Technology satellite, Russia. Launched 1967. |
| Soyuz OB-VI Russian manned space station. Cancelled 1970. In December 1967 OKB-1 chief designer Mishin managed to have Kozlov's Soyuz VI project killed. In its place he proposed to build a manned military station based on his own Soyuz 7K-OK design. |
| Soyuz 7K-L1 SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 12 launches, 1967.03.10 (Cosmos 146) to 1970.10.20 (Zond 8). Increased heat shield protection and presumably reaction control system propellant for re-entry from lunar distances. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz 7K-L1 SOK Russian manned spacecraft module. 12 launches, 1967.03.10 (Cosmos 146) to 1970.10.20 (Zond 8). Separates before trans-lunar injection. Jettisonable support cone. |
| Soyuz 7K-L1 PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 12 launches, 1967.03.10 (Cosmos 146) to 1970.10.20 (Zond 8). Modification of Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Aelita satellite Russian infrared astronomy satellite. Cancelled 1982. The Aelita infrared astronomical telescope spacecraft was derived from the Soyuz manned spacecraft and had an unusually long gestation. |
| Soyuz 7K-L1A Russian manned lunar orbiter. Hybrid spacecraft used in N1 launch tests. |
| Soyuz 7K-L1S Alternate designation for [Soyuz 7K-L1A] manned lunar orbiter. |
| Soyuz Kontakt Russian manned spacecraft. Cancelled 1974. Modification of the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft to test in earth orbit the Kontakt rendezvous and docking system. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK (Soyuz 6, non docking, special) Null |
| LK Russian manned lunar lander. The LK ('Lunniy korabl' - lunar craft) was the Soviet lunar lander - the Russian counterpart of the American LM Lunar Module. Manned Lunar lander test satellite, Russia. Launched 1970 - 1971. |
| Soyuz 7KT-OK Russian manned spacecraft. This was a modification of Soyuz 7K-OK with a lightweight docking system and a crew transfer tunnel. Launched 1971. |
| Soyuz 7K-LOK Russian manned lunar orbiter. The two-crew LOK lunar orbiting spacecraft was the largest derivative of Soyuz developed. Manned Lunar orbit and return satellite, Russia. Launched 1972. |
| Soyuz 7K-LOK SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 2 launches, 1971.06.26 (N-1 6L) to 1972.11.23 (LOK). Increased heat shield protection and presumably reaction control system propellant for re-entry from lunar distances. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz 7K-OKS SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 2 launches, 1971.04.23 (Soyuz 10) to 1971.06.06 (Soyuz 11). Post-Soyuz 1 modification, allowing crew of three without spacesuits. Analogue sequencer and computers operate spacecraft. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz 7K-LOK BO Russian manned spacecraft module. 2 launches, 1971.06.26 (N-1 6L) to 1972.11.23 (LOK). Living section. |
| Soyuz 7K-OKS BO Russian manned spacecraft module. 2 launches, 1971.04.23 (Soyuz 10) to 1971.06.06 (Soyuz 11). Lightweight male/female docking system with roller-type probe, internal transfer tunnel. Living section. |
| Soyuz 7K-OKS PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 2 launches, 1971.04.23 (Soyuz 10) to 1971.06.06 (Soyuz 11). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz 7K-T Russian manned spacecraft. Launched 1972 - 1981. |
| Soyuz 7K-T SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 23 launches, 1972.06.26 (Cosmos 496) to 1981.05.14 (Soyuz 40). Post-Soyuz 11 modification for crew of two in spacesuits. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz 7K-T BO Russian manned spacecraft module. 23 launches, 1972.06.26 (Cosmos 496) to 1981.05.14 (Soyuz 40). Lightweight male/female docking system with roller-type probe, internal transfer tunnel (Collar Length: 0.22 m. Probe Length: 0. Living section. |
| Soyuz 7K-T PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 23 launches, 1972.06.26 (Cosmos 496) to 1981.05.14 (Soyuz 40). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz 7K-T/AF (Soyuz 13) Null |
| Soyuz 7K-TM Russian manned spacecraft. The Soyuz 7K-T as modified for the docking with Apollo. Launched 1974 - 1975. |
| Soyuz 7K-T/A9 Russian manned spacecraft. Version of 7K-T for flights to Almaz. Known difference with the basic 7K-T included systems for remote control of the Almaz station and a revised parachute system. Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Soyuz 7K-S Russian manned spacecraft. The Soyuz 7K-S had its genesis in military Soyuz designs of the 1960's. Launched 1974 - 1976. |
| Soyuz ASTP SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 4 launches, 1974.04.03 (Cosmos 638) to 1975.07.15 (Soyuz 19 (ASTP)). Post-Soyuz 11 modification for crew of two in spacesuits. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz ASTP BO Russian manned spacecraft module. 4 launches, 1974.04.03 (Cosmos 638) to 1975.07.15 (Soyuz 19 (ASTP)). Universal docking system designed for ASTP with three petaled locating system and internal transfer tunnel. No automated rendezvous and docking system. Living section. |
| Soyuz ASTP PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 4 launches, 1974.04.03 (Cosmos 638) to 1975.07.15 (Soyuz 19 (ASTP)). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz 7K-MF6 Russian manned spacecraft. Soyuz 22. Soyuz 7K-T modified with installation of East German MF6 multispectral camera. Used for a unique solo Soyuz earth resources mission. Launched 1976. |
| Soyuz 7K-MF6 SA Russian manned spacecraft module. One launch, 1976.09.15, Soyuz 22. Post-Soyuz 11 modification for crew of two in spacesuits. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz 7K-MF6 BO Russian manned spacecraft module. One launch, 1976.09.15, Soyuz 22. MKF6 Camera replaced docking system and Igla automatic rendezvous and docking system deleted. Four windows, BO separated after retrofire. Living section. |
| Soyuz 7K-MF6 PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. One launch, 1976.09.15, Soyuz 22. Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Progress Russian logistics spacecraft. Progress took the basic Soyuz 7K-T manned ferry designed for the Salyut space station and modified it for unmanned space station resupply. Cargo satellite operated by RKK, Russia. Launched 1978 - 1990. |
| Soyuz T Russian manned spacecraft. Soyuz T had a long gestation, beginning as the Soyuz VI military orbital complex Soyuz in 1967. Launched 1978 - 1986. |
| Progress OKD Russian manned spacecraft module. 43 launches, 1978.01.20 (Progress 1) to 1990.05.06 (Progress 42). Fuel module for refueling space stations. |
| Progress GO Russian manned spacecraft module. 43 launches, 1978.01.20 (Progress 1) to 1990.05.06 (Progress 42). Igla automatic rendezvous and docking system. Cargo section. |
| Progress PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 43 launches, 1978.01.20 (Progress 1) to 1990.05.06 (Progress 42). Derived from Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz T SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 18 launches, 1978.04.04 (Cosmos 1001) to 1986.03.13 (Soyuz T-15). Significantly improved Soyuz re-entry capsule, based on development done in Soyuz 7K-S program. Accommodation for crew of three in spacesuits. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz T BO Russian manned spacecraft module. 18 launches, 1978.04.04 (Cosmos 1001) to 1986.03.13 (Soyuz T-15). Lightweight male/female docking system with flange-type probe, internal transfer tunnel. Igla automatic rendezvous and docking system. Living section. |
| Soyuz T PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 18 launches, 1978.04.04 (Cosmos 1001) to 1986.03.13 (Soyuz T-15). Improved PAO service module derived from Soyuz 7K-S with pressure-fed main engines and unitary RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz TM Russian manned spacecraft. Launched 1986 - 2002. |
| Soyuz TM SA Russian manned spacecraft module. 34 launches, 1986.05.21 (Soyuz TM-1) to 2002.04.25 (Soyuz TM-34). Significantly improved Soyuz re-entry capsule, based on development done in Soyuz 7K-S program. Accommodation for crew of three in spacesuits. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz TM BO Russian manned spacecraft module. 34 launches, 1986.05.21 (Soyuz TM-1) to 2002.04.25 (Soyuz TM-34). Lightweight male/female docking system with flange-type probe, internal transfer tunnel. Kurs automatic rendezvous and docking system . Living section. |
| Soyuz TM PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 34 launches, 1986.05.21 (Soyuz TM-1) to 2002.04.25 (Soyuz TM-34). Further improvement of Soyuz T PAO service module with pressure-fed main engines and unitary RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Progress M Russian logistics spacecraft. Progress M was an upgraded version of the original Progress. New service module and rendezvous and docking systems were adopted from Soyuz T. Cargo satellite operated by RKK > RAKA, Russia. Launched 1989 - 2009. |
| Progress M OKD Russian manned spacecraft module. Operational, first launch 1989.08.23 (Progress M-1). Fuel module for refueling space stations. |
| Progress M GO Russian manned spacecraft module. Operational, first launch 1989.08.23 (Progress M-1). Two Kurs-type rendezvous antennas. Cargo section. |
| Progress M PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. Operational, first launch 1989.08.23 (Progress M-1). Improved PAO service module derived from Soyuz 7K-S with pressure-fed main engines and unitary RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Progress-M-VDU 14, 38 (11F615A55, 7KTGM) Null |
| Soyuz TM (APAS, Soyuz TM 16) Null |
| Progress M2 Russian logistics spacecraft. Cancelled 1993. As Phase 2 of the third generation Soviet space systems it was planned to use a more capable resupply craft for the Mir-2 space station. |
| Progress M VBK Russian manned spacecraft module. Two launched, 1993-1994. This payload return capsule was brought to the Mir space station aboard a Progress M freighter. It was loaded by the cosmonauts aboard the station, then reinstalled in the Progress M. Ballistic landing capsule - return of experimental materials from Mir space station. |
| Progress M1 Russian logistics spacecraft. Progress M1 was a modified version of the Progress M resupply spacecraft capable of delivering more propellant than the basic model to the ISS or Mir. Cargo satellite operated by RAKA, Russia. Launched 2000 - 2004. |
| Progress M-SO Russian docking and airlock module for the International Space Station. Delivered to the station by the Progress service module, which was jettisoned after docking. |
| Soyuz TMA Russian three-crew manned spacecraft. Designed for use as a lifeboat for the International Space Station. After the retirement of the US shuttle in 2011, Soyuz TMA was the only conveying crews to the ISS. Except for the Chinese Shenzhou, it became mankind's sole means of access to space. Launched 2002 - 2011. |
| Soyuz TMA SA Russian manned spacecraft module. Operational. First launch 2002.10.30. Reentry capsule. |
| Soyuz TMA BO Russian manned spacecraft module. Operational. First launch 2002.10.30. Lightweight male/female docking system with flange-type probe, internal transfer tunnel. Kurs automatic rendezvous and docking system with two Kurs antennae, no tower. Living section. |
| Soyuz TMA PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. Operational. First launch 2002.10.30. Further improvement of Soyuz T PAO service module with pressure-fed main engines and unitary RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| DSE-Alpha Russian manned lunar flyby spacecraft. Study 2005. Potential commercial circumlunar manned flights were offered in 2005, using a modified Soyuz spacecraft docked to a Block DM upper stage. |
| Progress-M 1M - 29M (11F615A60, 7KTGM) Null |
| Soyuz TMA-M Manned spcecraft satellite, Russia. Launched 2010 - 2016. |
| Soyuz MS Russian three-crew manned spacecraft. Evolved from the Soyuz TMA incorporating numerous minor improvements identified over time. New digital computer, more redundancy in attitude control and docking systems, modernized electronics and solar power. Launched 2016 - on. |
| Progress MS Russian logistics spacecraft. Incorporated systems evolved from the Soyuz TMA. New digital computer, more redundancy in attitude control and docking systems, modernized electronics and solar power. Cargo satellite operated by RKK > RAKA, Russia. Launched 2015 - 2017. |
| Progress-M1 01M - 02M (11F615A70, 7KTGM) Null |
| Soyuz 7K-L3S Version of the Soyuz designed to be used in a combined lunar orbit / robot soil return mission to upstage the Americans prior to Apollo 11. |
| VBK-Raduga Reentry capsule which allowed returning materials from the space station Mir. They were launched and finally deorbited together with Progress-M cargo craft. |
People: Tsybin, Chelomei, Mishin, Mnatsakanian, Beregovoi, Komarov, Shatalov, Lazarev, Filipchenko, Nikolayev, Yazdovsky, Kolodin, Grechko, Khrunov, Gagarin, Yeliseyev, Gorbatko, Volynov, Kubasov, Sevastyanov, Shonin, Volkov. Country: Russia. Flights: Soyuz 1, Soyuz 2A, Soyuz s/n 3/4, Soyuz s/n 5/6, Soyuz s/n 7, Soyuz 3, Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5, Soyuz sn 14, Soyuz s/n 15+16, Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8, Soyuz 9. Launch Sites: Baikonur, Plesetsk. Agency: RVSN, MOM.
 | Soyuz 4 and 5 Soyuz 4 and 5 in docked configuration Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz TM cabin Soyuz TM cabin during ascent Credit: RKK Energia |
 | Soyuz TM from space Credit: RKK Energia |
 | Soyuz-MS 1 - 12 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Soyuz OM panel Detail of orbital module command panel of Soyuz OK Credit: © Mark Wade |
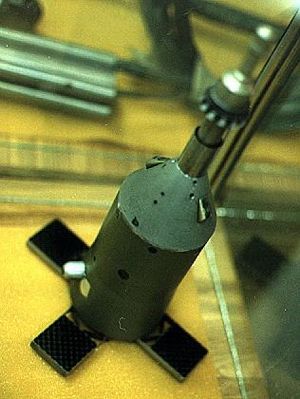 | Soyuz escape tower Soyuz launch escape system - air tunnel test model Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz OK panel Detail of left command panel of Soyuz OK Credit: © Mark Wade |
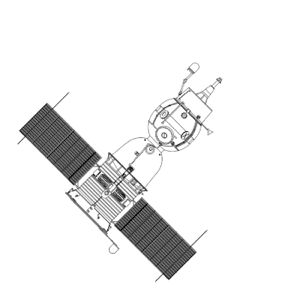 | Soyuz 7K-OK Bottom Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | LOK Descent Module LOK Descent Module and Orbital Module Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz 7K-OK probe Soyuz 7K-OK docking probe Credit: © Mark Wade |
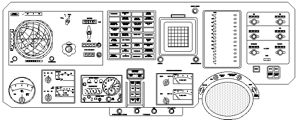 | Panel Soyuz 7K-OK Control panel of the initial earth orbit version of Soyuz. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Gas dynamic tunnel Gas dynamic tunnel tests Credit: © Mark Wade |
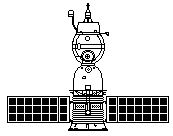 | Soyuz 7K-OK Icon Soyuz 7K-OK Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz 7K-OK Side Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz 7K-OK Top Credit: © Mark Wade |
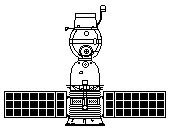 | Soyuz 7K-OK Icon Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz 7K-OK Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz Icon Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Background Soyuz Background Soyuz 7K-OK Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz orbital module Soyuz 7K-OKS passive docking orbital module Credit: Andy Salmon |
 | Soyuz OPS Soyuz escape tower (as used on early Soyuz launches) Credit: Andy Salmon |
 | Soyuz OM interior Interior view of Soyuz 4 orbital module (through open side hatch) Credit: Andy Salmon |
1959 March 1 - .
- OKB-1 preliminary work on circumlunar spacecraft - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Sever.
The first design sketched out was known as Sever (North). The reentry capsule had the same configuration as the ultimate Soyuz design but was 50% larger. By summer 1959 Feoktistov had reduced the size to that of the later Soyuz, while retaining the three-man crew size.
1961 April 10 - .
- Vostok preparations - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Korolev,
Moskalenko,
Nelyubov,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Rudnev,
Titov.
Program: Vostok.
Flight: Vostok 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Sever.
Kamanin plays badminton with Gagarin, Titov, and Nelyubov, winning 16 to 5. At 12:00 a meeting is held with the cosmonauts at the Syr Darya River. Rudnev, Moskalenko, and Korolev informally discuss plans with Gagarin, Titov, Nelyubov, Popovich, Nikolayev, and Bykovsky. Korolev addresses the group, saying that it is only four years since the Soviet Union put the first satellite into orbit, and here they are about to put a man into space. The six cosmonauts here are all ready and qualified for the first flight. Although Gagarin has been selected for this flight, the others will follow soon - in this year production of ten Vostok spacecraft will be completed, and in future years it will be replaced by the two or three-place Sever spacecraft. The place of these cosmonauts here does not indicate the completion of our work, says Korolev, but rather the beginning of a long line of Soviet spacecraft. Korolev predicts that the flight will be completed safely, and he wishes Yuri Alekseyevich success. Kamanin and Moskalenko follow with their speeches. In the evening the final State Commission meeting is held. Launch is set for 12 April and the selection of Gagarin for the flight is ratified. The proceedings are recorded for posterity on film and tape.
1962 February 10 - .
- Sever spacecraft trials - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Voronin. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Sever. Two officers start a 15 day test aboard a mock-up of the Sever spacecraft, but without the participation of the IAKM. The whole thing was planned by Voronin's OKB in GKNII..
1962 February 13 - .
- Sever trial - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Bushuyev, Vershinin, Voronin, Yazdovskiy. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Sever. Vershinin, Bushuev and others are at OKB-124 for Voronin's Sever experiment. It was a bit mistake not to include IAKM in the 15-day experiment. This is Yazdovskiy's doing. He wanted to get a second source due to problems with IAKM's equipment.
1962 August 8 - .
- Additional Vostok missions; launch preparations. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Korolev,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Rudenko,
Titov.
Program: Vostok,
Soyuz.
Flight: Vostok 3,
Vostok 4,
Vostok 5,
Vostok 6,
Vostok 6A,
Vostok 7,
Vostok 8,
Vostok 9.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V,
Vostok.
Kamanin discusses with Rudenko the need for construction and flight of ten additional Vostok spacecraft. Korolev still plans to have the first Soyuz spacecraft completed and flying by May 1963, but Kamanin finds this completely unrealistic. The satellite is still only on paper; he doesn't believe it will fly until 1964. If the Vostoks are not built, Kamanin believes the Americans will surpass the Russians in manned spaceflight in 1963-1964. From 13:00 to 14:00 Nikolayev spends an hour in his spacesuit in the ejection seat. Kamanin finds many mistakes in the design of the ejection seat. There is no room for error in disconnect of the ECS, in release of the seat, and so on. At 17:00 the State Commission holds a rally to fete Gagarin and Titov in the square in front of headquarters. Kamanin finds the event very warm but poorly organised. At 19:00 Smirnov chairs the meeting of the State Commission in the conference hall of the MIK. Korolev declares the spacecraft and launch vehicle ready; Kamanin declares the cosmonauts ready. Nikolayev is formally named the commanding officer of Vostok 3, and Popovich of Vostok 4. Rudenko gets Popovich's name wrong - his second serious mistake. He had earlier called the meeting for the wrong time.
1962 August 9 - .
- Vostok 3 rollout - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Korolev,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Smirnov.
Program: Vostok,
Soyuz.
Flight: Vostok 3,
Vostok 4.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V.
At the MIK Popovich finally trains in his suit in the seat 'as planned'. At 11:30 Smirnov, Korolev, and Keldysh inspect the new space food prepared for the flight, then meet with the cosmonauts. The Soyuz spacecraft is discussed - the cosmonauts want to have a mock-up commission. Afterwards the pilots conduct more training in their flight suits. At 21:00 Vostok 3 is rolled out from Area 10 to the pad. There was a two hour delay due to the need to reinspect the fasteners on the ejection seat - use of unauthorised substitutes was detected on other seats.
1962 November 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Chelomei takes over Lavochkin and Myasishchev OKBs - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei, Khrushchev, Lavochkin, Myasishchev. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. At Khrushchev's decision Chelomei takes over Lavochkin's OKB-301 and Myasishchev's OKB-23. Lavochkin had built objects 205, 207, 400 (SA-1,2,5); Chelomei UR-96 ABM-1..
1962 November 16 - .
- Meeting of the Soviet Ministers - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Vostok,
Soyuz.
Flight: Vostok 7,
Vostok 8,
Vostok 9.
They agree to a plan for a national centrifuge facility: specifications to be determined in 1963, and the facility completed by 1967. They are not if favour of building more Vostoks - they want to move on to the Soyuz spacecraft. But this will produce an 18 to 24 month gap in Soviet manned spaceflight, during which the Americans will certainly catch up (Cooper's one-day Mercury flight is already scheduled).
1962 December - .
- Soyuz draft project completed. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz A, Soyuz B, Soyuz P, Soyuz R, Soyuz V. The draft project for a versatile manned spacecraft included the Soyuz-A circumlunar spacecraft, the military Soyuz-P fighter and Soyuz-R reconn bird..
1962 December 6 - .
- Soviet Space Plans for 1963-1964 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz,
Vostok,
DS.
Flight: Vostok 7,
Vostok 8,
Vostok 9.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V,
Vostok,
Zenit-2 satellite,
Zenit-4.
Meeting of the Interdepartmental Soviet of the Academy of Sciences reviews space exploration plans. In the next two years, 5-6 Luna probes will be sent to the moon, including soft landers with a mass of 100 kg, and orbiters to map the surface. There will be flybys and landings of Mars and Venus. Two Zond spacecraft will study the space environment out to 20 million kilometres from the earth. In earth orbit, 10 Zenit spy satellites, 10 to 12 Vostok manned spacecraft, 4 to 6 Soyuz spacecraft, and 10 to 12 Kosmos satellites will be launched. The Kosmos will fly missions in meteorology, communications, television transmission, and heliographic, and geological studies. Kamanin finds this a good program, but it nearly all relies on a single launch pad and one-time transmission of data from a few satellites. The military plan is not reviewed; it must go through the VPK Military-Industrial Commission first. An Expert Commission is to be formed on the Soyuz spacecraft. Smirnov and Korolev have dictated a letter to Ustinov asking that eight more Vostoks be built. On the other hand, some on the general staff want 60 cosmonauts trained in the next two to three years, to support 8 to 10 flights of single-place spacecraft and 7 to 8 flights of multiplace spacecraft.
1963 January 21 - .
- VVS Review of Soyuz - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz P,
Soyuz R,
Soyuz V.
The primary objective of the design is to achieve docking to two spacecraft in earth orbit. Secondary objectives are the operation of scientific and military equipment from the spacecraft. Three different spacecraft, all launched by an R-7 derived booster, are required to achieve this:
- 7K spacecraft, capable of carrying three men into space and returning them to earth. The 5.5 tonne spacecraft has three modules, including the BO living module and the SA re-entry capsule
- 9K booster stage, with a fuelled mass of 18 tonnes. After docking with the 7K this is capable of boosting the combined spacecraft to earth escape velocity. The 9K is equipped with a 450 kgf main engine and orientation engines of 1 to 10 kgf. It will have 14 tonnes propellant when full loaded. Four sequential docking with a tanker spacecraft will be required to fill the tanks before the final docking with the 7K.
- 11K tanker, with a mass of 5 tonnes.
The system will conduct fuellings and dockings in a 250 km altitude parking orbit, and be boosted up to 400,000 km altitude on lunar flyby missions. The system will be ready in three years. Military variants proposed are the Soyuz-P and Soyuz-R. Each spacecraft will have 400 kg of automatic rendezvous and docking equipment. Manual docking will be possible once the spacecraft are within 300 m of each other.
Korolev still insists on an unguided landing and categorically rejects the use of wings. A parachute will deploy and slow the capsule to 10 m/s. Then a retrorocket will fire just before impact with the earth to provide a zero-velocity soft landing. Korolev still insists that spacesuits will not be carried for the crew. First test flight of the 7K, without docking, could not occur until the second half of 1964.
1963 February 1 - . LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 'leaves drafting boards' - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz A. Soyuz 'leaves drafting boards'..
1963 February 16 - .
- Plethora of projeects - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Vershinin. Program: Vostok, Soyuz. Flight: Vostok 5, Vostok 6, Vostok 6A, Vostok 7. Spacecraft: Raketoplan, Soyuz A, Vostok. Vershinin says the Soviet Union can't work on the Vostok, Soyuz, and Raketoplan manned spacecrafft all at the same time. But he still wants fo fly four Vostoks by the end of the year..
1963 March 21 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1 1964.
- Presidium of Inter-institution Soviet - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Glushko,
Keldysh,
Korolev.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V.
The expert commission report on Soyuz is reviewed by the Chief Designers from 10:00 to 14:00. The primary objective of the Soyuz project is to develop the technology for docking in orbit. This will allow the spacecraft to make flights of many months duration and allow manned flyby of the moon. Using docking of 70 tonne components launched by the N1 booster will allow manned flight to the Moon, Venus, and Mars. Keldysh, Chelomei and Glushko all support the main objective of Soyuz, to obtain and perfect docking technology. But Chelomei and Glushko warn of the unknowns of the project. Korolev agrees with the assessment that not all the components of the system - the 7K, 9K, and 11K spacecraft - will fly by the end of 1964. But he does argue that the first 7K will fly in 1964, and the first manned 7K flight will come in 1965.
1963 September - .
- Korolev earth orbit rendezvous L3 manned lunar lander design. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: L3-1963. This L3 design was a 200 tonne direct-lander requiring three launches of his giant N1 rocket and assembled in low earth orbit..
1963 November 30 - .
- 1964 Flight Plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Vostok,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Vostok 7,
Vostok 8,
Vostok 9.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V,
Voskhod.
Four Vostoks are planned for 1964, one of these with dogs and other biological specimens, which will fly for ten days at altitudes of up to 600 km. This is to be followed by an eight day manned flight, then two Vostoks on a ten-day group flight. The altitude for these latter flights will be decided after the results of the dog flight. Then, by the end of the year, the first Soyuz flights will be made. Two to three of the new spacecraft are being prepared. Therefore the crews must start training for circumlunar flights and cislunar navigation. Kamanin decides that he must select 3-4 navigators, 1-2 mathematicians, and 2-3 astronomers to make up a training group of cosmonaut-navigators for these flights.
1963 December 7 - .
- Crews for 1964 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Nikolayev,
Rudenko,
Tereshkova.
Program: Vostok,
Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4,
Vostok 7,
Vostok 8,
Vostok 9.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V,
Voskhod.
Kamanin meets with Rudenko, to discuss selection of three crews for Vostok and three crews for Soyuz flights in 1964. Ioffe reports that the Soyuz docking simulator will be completed by 25 December. Tereshkova, Nikolayev, and Bykovsky are in Indonesia on a public relations tour, to be followed by Burma.
1963 December 16 - .
- Yerkina wedding - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dementiev,
Korolev,
Ponomaryova,
Tereshkova,
Tsybin,
Yerkina.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A.
The cosmonaut weds at the TsPK cosmonaut centre, and 80 guests attend. Of the female cosmonauts, only Ponomaryova is not yet married. However the next female flight will be made no earlier than 1965-1966. Tereshkova looks tired after her tour to Southeast Asia - and she's supposed to go to Ghana on 10 January! Korolev claims that the Soyuz schedule, as laid out in the resolution of 4 December 1963, is still realistic. He will have the first Soyuz flight in August 1964 and the second and third in September 1964. Ivanovskiy doesn't believe it will be possible to make any flights until 1965. Korolev and Tsybin disccuss Shcherbakov's design for a rocket-propelled high-altitude glider. This concept was supported by the VVS, but Dementiev was against it and it was killed in the bureaucracy.
1964 February 12 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1 1962.
- Kremlin meeting on lunar landing plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: L3-1963.
VVS officers meet with O G Ivanovskiy for two hours. The Communist Party plans a lunar expedition in the 1968-1970 period. For this the N1 booster will be used, which has a low earth orbit payload of 72 tonnes. The minimum spacecraft to take a crew to the lunar surface and back will have a minimum payload of 200 tonnes; therefore three N1 launches will be required to launch components, which will have to be assembled in orbit. However all of these plans are only on paper, and Kamanin does not see any way the Soviet Union can beat the Americans to the moon, who are already flying Apollo hardware for that mission.
1964 June 23 - .
- Soyuz crews. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Beregovoi, Rudenko, Shatalov. Program: Lunar L1. Flight: Soyuz A-1, Soyuz A-2, Soyuz s/n 3/4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz A. Kamanin discusses candidates for the first five Soyuz flights. Rudenko wants Beregovoi and Shatalov named as flight commanders, but Kamanin wants the commanders to be cosmonauts with previous flight experience..
November 1964 - .
- No direction on space from new Soviet leadership. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Korolev,
Okhapkin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
After the triumph of the Voskhod-1 flight, Korolev gathers a group of his closest associates in his small office - Chertok, Bushuyev, Okhapkin, and Turkov. Firm plans do not exist yet for further manned spaceflights. Following the traditional Kremlin celebrations after the return of the Voskhod 1 crew, he has heard no more from the new political management. Khrushchev's old enthusiasm for space does not exist in the new leadership. Korolev is angry. "The Americans have unified their forces into a single thrust, and make no secret of their plans to dominate outer space. But we keep our plans secret even to ourselves. No one has agreed on our future space plans - the opinion of OKB-1 differs from that of the Minister of Defense, which differs from that of the VVS, which differs from that of the VPK. Some want us to build more Vostoks, others more Voskhods, while within this bureau our priority is to get on with the Soyuz. Brezhnev's only concern is to launch something soon, to show that space affairs will go better under his rule than Khruschev's." Korolev however does not think the new leadership will support continuation of Chelomei's parallel lunar project. Okhapkin speaks up. "Do not underestimate Chelomei. He is of the same design school as Tupolev and Myasishchev. If we give him the will and the means, his products will equal those of the Americans. Now is the right moment to combine forces with Chelomei".
1965 March 1 - .
- Soyuz 7K-PPK cancelled. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz PPK. Based on successful test flights of Chelomei's unmanned interceptor-sputnik prototypes (Polyot 1 and 2), the Soyuz 7K-PPK manned interceptor version is cancelled..
1965 April 2 - .
- VVS role in space - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Artyukhin,
Belyayev,
Beregovoi,
Brezhnev,
Demin,
Katys,
Korolev,
Leonov,
Ponomaryova,
Rudenko,
Shatalov,
Solovyova,
Tereshkova,
Volynov.
Program: Voskhod,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 4,
Voskhod 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A.
Kamanin visits Korolev and tells him that in an upcoming meeting between the cosmonauts and Brezhnev and Kosygin, they are going to push for the VVS to be given a leading role in the exploration of space, including the necessity to improve the cosmonaut training centre with 8 to 10 simulators for Voskhod and Soyuz spacecraft, and development within the VVS of competence in space technology. Korolev is not opposed to this, but says he doubts the VVS leadership will support acquiring the new mission. Kamanin then indicates to Korolev his proposed crews for the upcoming Voskhod missions: Volynov-Katys, Beregovoi-Demin, Shatalov-Artyukhin. Kamanin hopes that Korolev will support Volynov as the prime candidate against Marshall Rudenko's favouring of Beregovoi. Kamanin then raises the delicate issue of Korolev's unfavourable opinion of Tereshkova. After her flight, Korolev angrily said: "I never want to have anything to do with these women again". Kamanin does not believe his remarks were meant seriously, and broaches the subject of training Soloyova and Ponomaryova for a female version of Leonov's spacewalk flight. Korolev says he will seriously consider the suggestion.
1965 April 20 - .
- Cosmonaut tours - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Tereshkova.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz A.
The demand for cosmonaut appearances is constant; over 90% of such requests have to be denied. Tereshkova and Nikolayev are especially in demand - France wants them for two or three days, and there are also requests from Mongolia, Finland, Norway, Greece, Iran, Rumania, USA, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, and many others. As far as progress on cosmonaut trainers, General Ponomaryov, who has no interests in space, is hampering development efforts. So far his interference has delayed completion of the docking trainer by six months.
1965 July 6 - .
- Soyuz hot mock-up - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Chertok argues for the necessity of adding one Soyuz to production and using it as an iron bird - a hot mock-up on which avionics and electrical systems can be integrated and tested. Gherman Semenov and Turkov convince Korolev that this cannot be done within the existing schedules.
1965 August 18 - .
- Soyuz development program reoriented; Soyuz 7K-OK earth orbit version to be built in lieu of Soyuz A. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V.
Military-Industrial Commission (VPK) Decree 180 'On the Order of Work on the Soyuz Complex--approval of the schedule of work for Soyuz spacecraft' was issued. It set the following schedule for the new Soyuz 7K-OK version: two spacecraft to be completed in fourth quarter 1965, two in first quarter 1966, and three in second quarter 1966. Air-drop and sea trails of the 7K-OK spacecraft are to be completed in the third and fourth quarters 1965, and first automated docking of two unmanned Soyuz spacecraft in space in the first quarter of 1966. Korolev insists the automated docking system will be completely reliable, but Kamanin wishes that the potential of the cosmonauts to accomplish a manual rendezvous and docking had been considered in the design. With this decree the mission of the first Soyuz missions has been changed from a docking with unmanned Soyuz B and V tanker spacecraft, to docking of two Soyuz A-type spacecraft. It is also evident that although nothing is official, Korolev is confident he has killed off Chelomei's LK-1 circumlunar spacecraft, and that a Soyuz variant will be launched in its place.
1965 August 20 - .
- Soyuz crews - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Artyukhin,
Beregovoi,
Bykovsky,
Demin,
Feoktistov,
Gagarin,
Katys,
Komarov,
Korolev,
Nikolayev,
Volynov.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Voskhod.
Kamanin calls Korolev, finds he is suffering from very low blood pressure (100/60). Kamanin suggests that candidates for the commander position in the first two Soyuz missions would be Gagarin, Nikolayev, Bykovsky, or Komarov. Korolev agrees basically, but says that he sees Bykovsky and Nikolayev as candidates for the first manned lunar flyby shots. Kamanin suggests Artyukhin and Demin for the engineer-cosmonaut role on the first Soyuz flights, but Korolev disagrees, saying Feoktistov has to be aboard. However Korolev agrees with Kamanin's selection for the next Voskhod flight - Volynov/Katys as prime crew, Beregovoi/Demin as backups. Later Kamanin corresponds with Stroev over modification of an Mi-4 helicopter as a lunar lander simulator.
1965 August 24 - .
- Soyuz-VI program started.. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kozlov.
Flight: Gemini 4,
Soyuz VI Flight 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz VI,
Gemini,
MOL.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On expansion of military space research and on 7K-VI Zvezda' was issued. In June 1965 Gemini 4 began the first American experiments in military space. At the same time the large military Manned Orbital Laboratory space station was on the verge of being given its final go-ahead. These events caused a bit of a panic among the Soviet military, where the Soyuz-R and Almaz projects were in the very earliest stages of design and would not fly until 1968 at the earliest. VPK head Leonid Smirnov ordered that urgent measures be taken to test manned military techniques in orbit at the earliest possible date. Modifications were to be made to the Voskhod and Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft to assess the military utility of manned visual and photographic reconnaissance; of inspection of enemy satellites from orbit; attacking enemy spacecraft; and obtaining early warning of nuclear attack. The decree instructed Kozlov to fly by 1967 a military research variant of the Soyuz 7K-OK 11F615.
1965 August 28 - .
- Korolev secretly puts Voskhod production on back burner. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Flight: Gemini 5,
Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 4,
Voskhod 5,
Voskhod 6.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod,
Gemini.
It is becoming clear that in order to ever get Soyuz into space it is necessary to clear all decks at OKB-1. After Voskhod-2 the Soviet manned space plans are in confusion. The Americans have flown Gemini 5, setting a new 8-day manned space endurance record - the first time the Americans are ahead in the space race. They rubbed salt into the Soviet wound by sending astronauts Cooper and Conrad on a triumphal world tour. This American success is very painful to Korolev, and contributes to his visibly deteriorating health. In the absence of any coherent instructions from the Soviet leadership, Korolev makes a final personal decision between the competing manned spacecraft priorities. Work on completing a new series of Voskhod spacecraft and conducting experiments with artificial gravity are unofficially dropped and development and construction of the new Soyuz spacecraft is accelerated. The decision is shared only with the OKB-1 shop managers. One of Korolev's "conspirators" lays on Chertok's table the resulting new Soyuz master schedule. The upper left of the drawing has the single word "Agreed" with Korolev's signature. The only other signatures are those of Gherman Semenov, Turkov and Topol - Korolev has ordered all other signature blocks removed. Chertok is enraged. The plan provides for the production of thirteen spacecraft articles for development and qualification tests by December 1965! These include articles for thermal chamber runs, aircraft drop tests, water recovery tests, SAS abort systems tests, static and vibration tests, docking system development rigs, mock-ups for zero-G EVA tests aboard the Tu-104 flying laboratory, and a full-scale mock-up to be delivered to Sergei Darevskiy for conversion to a simulator. Chertok is enraged because the plan does not include dedicating one spaceframe to use as an 'iron bird' hot mock-up on which the electrical and avionics systems can be integrated and tested. Instead two completed Soyuz spacecraft are to be delivered to OKB-1's KIS facility in December and a third in January 1966. These will have to be used for systems integrations tests there before being shipped to Tyuratam for spaceflights.
1965 September 1 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1 1964.
- Voskhod/Soyuz crewing plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Artyukhin,
Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Katys,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Korolev,
Matinchenko,
Nikolayev,
Ponomaryova,
Solovyova,
Volynov.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 5.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Voskhod.
Kamanin meets with Korolev at 15:00 to discuss crew plans. As Soyuz pilot candidates, Kamanin proposes Gagarin, Nikolayev, Bykovsky, Komarov, Kolodin, Artyukhin, and Matinchenko. Korolev counters by proposing supplemental training of a supplemental group of engineer-cosmonauts from the ranks of OKB-1. He calls Anokhin, his lead test pilot, informs Korolev that there are 100 engineers working at the bureau that are potential cosmonauts candidates, of which perhaps 25 would complete the selection process. Kamanin agrees to assist OKB-1 in flight training of these engineer-cosmonauts. Kamanin again proposes Volynov and Katys as prime crew for the Voskhod 3 12-15 day flight. Korolev reveals that, even though Kamanin will have the crew ready by October, the spacecraft for the flight may not yet even be ready by November - Kamanin thinks January 1966 is more realistic. The discussion turns to the female EVA flight - Ponomaryova as pilot, Solovyova as spacewalker. It is decided that a group of 6 to 8 cosmonauts will begin dedicated training in September for lunar flyby and landing missions. Korolev advises Kamanin that metal fabrication of the N1 superbooster first article will be completed by the end of 1965. The booster will have a payload to low earth orbit of 90 tonnes, and later versions with uprated engines will reach 130 tonnes payload. Korolev foresees the payload for the first N1 tests being a handful of Soyuz spacecraft.
1965 September 8 - .
- American vs Soviet programs - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Kamanin reviews a speech by President Johnson to the US Congress. From 1954-1965 the USA spent 34 billion dollars on space, $ 26.4 billion of that in just the last four years. The Soviet Union has spent a fraction of that, but the main reason for being behind the US is poor management and organisation structure, in Kamanin's view. With the US now having the lead in space, and the Gemini 5 results showing they openly used the manned flight for military reconnaissance, the Soviet leadership has awakened to the threat. They are demanding answers - how many cosmonauts does the US have in training? What are Soviet plans for use of hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells in space? What are the flight schedules for Voskhod and Soyuz? In contradiction to these demands, Kamanin is finding it difficult to obtain funding to keep the Tu-104 weightlessness trainer flying....
1965 September 22 - .
- Tereshkova manoeuvres - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Korolev,
Ponomaryova,
Tereshkova.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Tereshkova confides to Kamanin that Ponomaryova is not ready for her scheduled spaceflight. Kamanin does not believe it - he has heard it from no other cosmonauts, and he has spoken to Ponomaryova often over the years. Flight plans for 1965-1966 are reviewed. The pluses and minuses of each cosmonaut in advanced training for Voskhod flights is reviewed. The latest plan for the Voskhod-3 flight is for a 20-day flight with two cosmonauts (in an attempt to upstage the planned Gemini 7 14-day flight). This is followed by another tense phone call from Korolev, then Feoktistov complaining about inadequate VVS support for the Soyuz landing system trials at Fedosiya (no Mi-6 helicopter as promised; incorrect type of sounding rockets for atmospheric profiles; insufficient data processing capacity; inadequate motor transport). When Kamanin appeals to Finogenov on the matter, he is simply told that if "Korolev is unhappy with out facilities, let him conduct his trials elsewhere". Without the support of the VVS leadership, it is up to Kamanin to try to improve the situation using only his own cajoling and contacts.
1965 October 22 - .
- Gagarin writes a letter to Brezhnev - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Belyayev, Biryuzov, Brezhnev, Bykovsky, Gagarin, Grechko, Leonov, Nikolayev, Titov. Program: Lunar L1, Voskhod, Soyuz. Gagarin has sent a letter to Brezhnev, complaining of the poor organisation of the Soviet space program. The Kremlin has received it... reaction is awaited. The letter specifically cites the multitude of space projects and de-emphasis of manned efforts.. Additional Details: here....
1965 October 26 - .
- Thoughts on Gemini 6 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Kamanin notes the aborted first launch attempt of Gemini 6, but expects the Americans to achieve the first space docking, using the crew as pilots to fly the spacecraft. He curses Korolev and Keldysh for wasting three years trying to develop a fully automated system for Soyuz, which has put the Soviet Union well behind the Americans. He does not see any equivalent Soviet achievement until the end of 1966...
1965 November 1 - .
- OKB-1 learns of Gagarin letter - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Gagarin,
Korolev,
Tsybin.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Tsybin has learned through his Ministry of Defence contacts of Gagarin's letter to Brezhnev. He hears that they have criticized the space policy of the Minister of Defence and proposed that the VVS manage Soviet manned spaceflight. The letter also reportedly requests production of a new series of Voskhods to fill in the manned spaceflight gap created by delays in the Soyuz program. Korolev is remarkably unperturbed that he had not heard of the letter, and that Gagarin never said anything to him about it.
1965 November 24 - .
- Kamanin and Korolev - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Korolev,
Pashkov,
Smirnov,
Tyulin.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 4,
Voskhod 5,
Voskhod 6.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
Kamanin has his first face-to-face meeting with Korolev in 3 months - the longest delay in three years of working together. Their relationship is at low ebb. Despite having last talked about the next Voskhod flight by the end of November, Korolev now reveals that the spacecraft are still incomplete, and that he has abandoned plans to finish the last two (s/n 8 and 9), since these would overlap with planned Soyuz flights. By the first quarter of 1966 OKB-1 expects to be completing two Soyuz spacecraft per quarter, and by the end of 1966, one per month. Voskhod s/n 5, 6, and 7 will only be completed in January-February 1966. Korolev has decided to delete the artificial gravity experiment from s/n 6 and instead fly this spacecraft with two crew for a 20-day mission. The artificial gravity experiment will be moved to s/n 7. Completion of any of the Voskhods for spacewalks has been given up; future EVA experiments will be conducted from Soyuz spacecraft. Korolev says he has supported VVS leadership of manned spaceflight in conversations with Tyulin, Afanasyev, Pashkov, and Smirnov.
1965 November 25 - .
- New cosmonauts - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babiychuk,
Korolev,
Voronin.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
.
Flight: Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Vostok.
Spacecraft: Voskhod.
Kamanin meets the 22 new cosmonaut candidates. Some higher officers have questioned the need for so many cosmonauts in training - 32 are already available. But Kamanin sees plans for 40 to 50 manned spaceflights over the next 3 to 4 years. He expects to see some of these cosmonauts walking on the moon, and others on expeditions to other planets. Later Kamanin has to call Korolev after a dispute breaks out between Voronin and Babiychuk and Frolov. Voskhod 3 will not be cleared for flight because the trials of the long-duration environmental control system will not be undertaken at designer Voronin's institute. Furthermore it is still the position of the military that Voskhod 4 should conduct some military experiments.
1965 November 30 - .
- Problems with the Igla system for Soyuz - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Korolev,
Mnatsakanian.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 4,
Voskhod 5,
Voskhod 6.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
After a meeting with Kamanin, Korolev tells Chertok in confidence that Gagarin is training for a flight on a Soyuz mission. Chertok responds that it will take him at least a year to complete training, but that doesn't matter, since Mnatsakanian's Igla docking system will not be ready than any earlier than that. Korolev explodes on hearing this. "I allowed all work on Voskhod stopped so that the staff can be completely dedicated to Soyuz. I will not allow the Soyuz schedule to slip a day further". Turkov had been completing further Voskhods only on direct orders from the VPK and on the insistence of the VVS. Aside from military experiments, further Voskhod flights were meant to take back the space endurance record from the Americans. Korolev has derailed those plans without openly telling anyone in order to get the Soyuz flying.
1965 December 4 - .
- Voskhod trainers - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gorbatko,
Popovich,
Volynov.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
At LII Kamanin reviews progress on the Voskhod trainer. It should be completed by 15 December, and Volynov and Gorbatko can then begin training for their specific mission tasks. The Volga docking trainer is also coming around. Popovich is having marital problems due to his wife's career as a pilot. Popovich will see if she can be assigned to non-flight duties.
1965 December 8 - .
- Soyuz VI - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gorbatko,
Volynov.
Flight: Gemini 7,
Soyuz VI Flight 1,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz VI,
Gemini.
Kamanin meets with an engineering delegation from Kuibyshev. They are seeking a close relationship with the cosmonaut cadre in development of the military reconnaissance version of Soyuz, which they are charged with developing. They have already been working with the IAKM for over a year in establishing he basic requirements. Kamanin finds this refreshing after the arms-length relationship with Korolev's bureau. Meanwhile Gemini 7 orbits above, and there is not the slightest word on the schedule for Volynov-Gorbatko's Voskhod 3 flight, which would surpass the new American record.
1965 December 31 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1 1964.
- Daunting year ahead - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing,
Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin looks ahead to the very difficult tasks scheduled for 1966. There are to be 5 to 6 Soyuz flights, the first tests of the N1 heavy booster, the first docking in space. Preparations will have to intensify for the first manned flyby of the moon in 1967, following by the planned first Soviet moon landing in 1967-1969. Kamanin does not see how it can all be done on schedule, especially without a reorganization of the management of the Soviet space program.
1966 January 8 - .
- Space trainers - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev,
Mozzhorin,
Tyulin.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 4,
Voskhod 5.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
Tyulin and Mozzhorin review space simulators at TsPK. The 3KV and Volga trainers are examined. Tyulin believes the simulators need to be finished much earlier, to be used not just to train cosmonauts, but as tools for the spacecraft engineers to work together with the cosmonauts in establishing the cabin arrangement. This was already done on the 3KV trainer, to establish the new, more rational Voskhod cockpit layout. Tyulin reveals that the female Voskhod flight now has the support of the Central Committee and Soviet Ministers. He also reveals that MOM has promised to accelerate things so that four Voskhod and five Soyuz flights will be conducted in 1966. For 1967, 14 manned flights are planned, followed by 21 in 1968, 14 in 1969, and 20 in 1970. This adds up to 80 spaceflights, each with a crew of 2 to 3 aboard. Tyulin also supports the Kamanin position on other issues - the Voskhod ECS should be tested at the VVS' IAKM or Voronin's factory, not the IMBP. The artificial gravity experiment should be removed from Voskhod and replaced by military experiments. He promises to take up these matters with Korolev.
1966 January 14 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Korolev's death - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Korolev,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Kuznetsova,
Mishin,
Petrovskiy,
Ponomaryova,
Shatalov,
Shonin,
Solovyova,
Tereshkova,
Volynov,
Yerkina.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
Korolev dies at age 59 during what was expected to be routine colon surgery in Moscow. The day began for Kamanin with firm plans finally in place for the next three Voskhod and first three Soyuz flights. Volynov and Shonin will be the crew for the first Voskhod flight, with Beregovoi and Shatalov as their back-ups. That will be followed by a female flight of 15-20 days, with the crew begin Ponomaryova and Solovyova, with their back-ups Sergeychik (nee Yerkina) and Pitskhelaura (nee Kuznetsova). Tereshkova will command the female training group. Training is to be completed by March 15. After this Kamanin goes to his dacha, only to be called by General Kuznetsov around 19:00, informing him that Korolev has died during surgery.
Kamanin does not minimise Korolev's key role in creating the Soviet space program, but believes the collectives can continue the program without him. In truth, Kamanin feels Korolev has made many errors of judgment in the last three years that have hurt the program. Mishin, Korolev's first deputy, will take over management of Korolev's projects. Kamanin feels that Mishin is a clever and cultured engineer, but he is no Korolev. Over the next three days the cosmonauts console Korolev's widow.
Korolev's surgery was done personally by Petrovskiy, the Minister of Health. Korolev was told the surgery would take only a few minutes, but after five hours on the operating table, his body could no longer endure the insult, and he passed away.
1966 January 24 - .
- New space schedules - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Chelomei,
Korolev,
Malinovskiy,
Petrovskiy.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing,
Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The VVS General Staff reviews a range of documents, authored by Korolev before his death, and supported by ministers Afanasyev and Petrovskiy. The schedules for the projects for flying around and landing on the moon are to be delayed from 1966-1967 to 1968-1969. A range of other space programs will similarly be delayed by 18 to 24 months. An institute for tests of space technology will be established at Chelomei's facility at Reutov. The IMBP will be made the lead organization for space medicine. Responsibility for space technology development will be moved from MOM to 10 other ministries. 100 million roubles have been allocated for the establishment of new research institutes. Kamanin is appalled, but Malinovskiy favours getting rid of the responsibility for these projects. The arguments over these changes - which reduce the VVS role in spaceflight - will be the subject of much of Kamanin's diary over the following weeks.
1966 February 19 - .
- Soyuz trainer - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Voskhod.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
A meeting is held with the Deputy Minister of MAP, OKB-1 leaders, and 20 developers of subsystems to nail down completion of the Soyuz trainer. It was supposed to be completed by 31 March, with cosmonaut training to start 15 April. In fact OKB-1 has not even begun work on it, and they only consider it long-term work. MOM in fact has insisted that the trainers be finished early, so that they can be used as development tools by the engineers in cooperation with the cosmonauts. OKB-1 engineers don't see it that way.
1966 March 12 - .
- Discussion of L1S Docking Complex / Landing System tests. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1S. Leave factory December 66; arrive test point January 67; Independent testing from March 67. (Mishin Diaries 1-220).
1966 March 12 - .
- Mishin lists the projects DI Kozlov was developing in Samara - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Soyuz VI,
Soyuz 7K-S.
1. Military research ship (e.g. 7K-VI)
2. Transport ship to the station "Almaz" (e.g. 7K-S)
3. MKBS multipurpose space base station (preliminary project) - specification requirements.
4. "Procyon" - Draft Project - classified (interesting unidentified military project)
5. Block "D" - (full responsibility) - including experimental work. (Mishin Diaries 1-219)
1966 March 18 - .
- Earth-to-Space equipment for the 7K-OK, 7K-L1, and 7K-L1S - . Related Persons: Mishin, Chertok. Spacecraft: Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-L1S, Soyuz 7K-OK. Message from BE Chertok on the development of Earth-to-Space equipment for the 7K-OK, 7K-L1, and 7K-L1S' (Mishin Diaries 3-9)..
1966 March 23 - .
- Inconsistent Soviet lunar program - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chertok.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt.
Acting director Mishin held a brainstorming session with this top managers to address "...our inconsistent lunar program". He noted then-current contradictory approaches: 1. Return to a two-launch scheme (podsadka, as baseline); 2. Keep with direct landing; 3. Use a Block D with storable propellants; 4. Use the 7K-OK as the designated return spacecraft. He noted that the L1 program was a diversion for the bureau to the core objective of landing a cosmonaut on the moon (the L3 program). Among the advantages of continuing with the L1, he noted that it "Utilizes the 7K-OK" - evidently there was no purpose for the spacecraft beyond the L1 mission in the podsadka scenario. He asks for frank opinions from his managers. V Rauschenbach noted that they "..have to do the L-1 … and therefore we will have to use a 2-launch scheme based on the L1-S". BE Chertok: discussed the rendezvous and docking systems for the various spacecraft: L1-S - "Igla"; LOK - "Kontakt" (since "Igla" cannot be used on the LOK (due to mass considerations); or a new system for the LOK. (Mishin Diaries 1-226) Here we have an indication that the L1 podsadka version did use the Igla system, which makes complete sense, since the Soyuz 7K-OK missions conducted dress rehearsals for podsadka using this system to rendezvous and dock two 7K-OK spacecraft in earth orbit.
1966 April 1 - .
- Production rates for the podsadka program. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Ministry of Defense directive laid out the production rate for both the L1, Block D, and 7K-OK for the podsadka program. Ministry of Defense directive (Mishin Diaries 1-234) laid out the production rate for both the L1, Block D, and 7K-OK for the podsadka program:
7K-L1: one unit per month beginning 15 Sept 66
7K-OK for podsadka delivery of crews to L1: 1 unit per month beginning Oct 66
Block D deliveries: 1 unit 15 Sept; 1 unit 15 Oct; 1 further unit in October; and 1 unit per month thereafter.(Mishin Diaries 1-234)
1966 April 10 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmonaut training for lunar flights announced - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Leonov. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Leonov announces that cosmonauts are in training for lunar missions..
1966 April 20 - .
- L1 accelerated program plan for 14 L1 and 6 7K-OK podsadka spacecraft. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
A VPK Military-Industrial Commission resolution on the L1 program plan was issued and included the total accelerated program for build of 14 L1 and 6 7K-OK podsadka spacecraft. The schedule:
7K-L1:
1 unit 3rd quarter 66
4 units 4th quarter 66
3 units 1st quarter 67
3 units 2nd quarter 67
3 units 3rd quarter 67
7K-OK for delivery of crews to L1:
3 units 4th quarter 66
3 units 1st quarter 67. (Mishin Diaries 1-234)
1966 April 26 - .
- Soyuz simulators - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Leonov,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Shonin,
Solovyova,
Titov,
Volynov,
Zaikin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The simulators and partial-task trainers continue very much behind schedule. There is talk of moving responsibility for them from Darevskiy's bureau to OKB-1. Popovich's fitness for future flight and command assignments is questionable. Nevertheless, he will join Titov, Leonov, Volynov, Shonin, Zaikin, Gagarin, and Solovyova at the Zhukovskiy Academy, from which they will be expected to graduate with advanced degrees in engineering in October 1967. Nikolayev, Bykovsky, and Gorbatko will finish one or two years later, since they will be preoccupied with flight assignments on the 7K-OK.
1966 April 27 - .
- VPK Resolution No. 101 (Mishin Diaries 1-266) mandated an aggressive L1 flight test program. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
No 1 - August - Proton-2 (this may refer to the Proton / Block D full-mass mockup that was tested in October 1966 but then abandoned for safety reasons).
2-4: Flyby of the moon with the unpiloted version:
No 2 - October
No 3 - November
No 4 - December
No 5 - No 9: 7K-L1 flyby of the moon at intervals of one month with crew delivery by 7K-OK
No 10 - No 14: Direct flyby of the moon at one month intervals.This indicates that podsadka was the baseline approach for early missions, for both safety and launch mass considerations. Only the last five missions would be direct flights. It was probably anticipated that by then the Proton booster would be reliable enough and that improvements to the Block D and the weight reduction on the L1 would make the single-launch approach feasible. (Mishin Diaries 1-266)
1966 April 29 - .
- Cosmonaut travels - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Leonov,
Popovich,
Tereshkova,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Spiral 50-50.
Spacecraft: Spiral OS.
Kamanin plans to make Popovich and Titov deputy commanders of cosmonaut detachments preparing for flight of the Soyuz 7K-OK and Spiral spaceplane. Leonov is back from a tour of France; Titov is preparing to go to Afghanistan, and Tereshkova to Armenia. But that night Titov does not come home - he is hanging out again with artists and other unacceptable types.
1966 May 3 - .
- Soviet recovery planning - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Kamanin is upset over the lack of resources he is given to plan and carry out manned spacecraft recovery for circumlunar missions, which may splash down in the ocean or land almost anywhere on earth. His staff dedicated to this are to be increased from 3 to 6, and he has another 8 dedicated to survival equipment. But he figures the Americans must have over 500 staff assigned to just this problem alone.
1966 May 10 - .
- Voskhod 3 spiked - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Burnazyan,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Tyulin.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Flight: Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
A meeting of the VPK Military Industrial Commission begins with Tyulin, Mishin, Burnazyan, and Kamanin certifying the readiness for launch of Voskhod 3 on 25-28 May. Then Smirnov drops a bombshell: Voskhod 3 should be cancelled because: an 18-day flight will be nothing new; further work on Voskhod 3 will only interfere with completion of the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft, which is to be the primary Soviet piloted spacecraft; and a new spaceflight without any manoeuvring of the spacecraft or a docking in orbit will only highlight the lead the Americans have. Kamanin argues that the long work of preparing for the flight is finally complete, and that it will set two new space records (in manned flight altitude and duration). Furthermore the flight will include important military experiments, which cannot be flown on early Soyuz flights. Smirnov and Pashkov appear not to be swayed by these arguments, but back down a bit. The State Commission for the flight may continue its work.
1966 May 15 - .
- Soyuz 7K-OK flight preparations. - . Nation: Russia. Flight: Soyuz 1, Soyuz 2A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Decree 144 'On assessing preparations for flights of the 7K-OK spacecraft' was issued..
1966 May 19 - .
- L1 flight plan - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Voskhod,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
VPK resolution number 101 dated 27 April 1966 finally hits Kamanin's desk. It issues the orders to industry for implementation of the Party resolution 655-268 of 3 August 1964. 14 7K-L1 spacecraft are to be completed: one in the third quarter of 1966, two in the fourth quarter, and the rest between January and September 1967. Final integration of the first spacecraft is to be completed in October 1966,and flight trials from December 1966 to March 1967. Detailed planning for completion of simulators and trainers for the L1, and for international recovery forces to recover spacecraft returning from the moon, are to be completed within two weeks to a month from the date of the resolution. Meanwhile Tyulin reports that the launch of Voskhod 3 in May is no longer possible, and likely will be delayed until July. It is clear to Kamanin that Smirnov has effectively killed off Voskhod 3 in order to concentrate on the Soyuz, L1, and L3 programs.
1966 May 20 - .
- L1 recovery issues - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Kamanin discusses with VVS management the huge task of organizing recovery forces that can find and pick up a manned spacecraft returning from the moon anywhere on the earth. Receivers for the spacecraft's homing beacons have to be installed on a fleet of ocean-going vessels and recovery aircraft. This requirement has been known for six years, but nothing has been done yet.
1966 May 31 - .
- Commonality of theme for the L1 and L1S. - . Related Persons: Mishin, Litvinov, . Spacecraft: Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-L1S, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Mishin makes a note for himself (Mishin Diaries 1-284-285): "Get photos for VYa Litvinov of Blok D, 7K-L-1, 7K-L1S", indicating a commonality of theme for the L1 and L1S..
1966 June 15 - .
- Soyuz 7K-OK crew training. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. OKB-1 Decree 144 'On preparation of crews ior the 7K-OK Spacecraft and civilian cosmonauts' was issued..
1966 June 21 - .
- Mishin asserts himself - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Burnazyan,
Bykovsky,
Frolov,
Gagarin,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Tyulin,
Volkov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Gagarin and Leonov visit Kamanin, who is on vacation at his dacha. They tell him of manoeuvres by Tyulin, Burnazyan, and Mishin in his absence. A VPK resolution will name crews for Soyuz missions that will consist of "invalid" engineers from OKB-1 (Anokhin, Frolov, Makarov, Volkov) instead of trained, flown cosmonauts (Gagarin, Nikolayev, Bykovsky).
1966 July 2 - .
- Soyuz crew manoeuvres - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Bykovsky,
Dolgopolov,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Khrunov,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Makarov,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Rudenko,
Smirnov,
Tsybin,
Tyulin,
Ustinov,
Volkov,
Voronov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin is back from leave and orients himself. VVS General Rudenko has been visited by Mishin, Tsybin, and Tyulin. They want to replace Kamanin's crews for the first Soyuz mission in September-October with a crew made up of OKB-1 engineers: Dolgopolov, Yeliseyev, and Volkov as the prime crew, Anokhin, Makarov, and Grechko as back-ups. Kamanin believes this absurd proposal, made only three months before the planned flight date, shows a complete lack of understanding on the part of OKB-1 management of the training and fitness required for spaceflight. Kamanin has had eight cosmonauts (Komarov, Gorbatko, Khrunov, Bykovsky, Voronov, Kolodin, Gagarin, and Nikolayev) training for this flight since September 1965. Yet Mishin and Tyulin have been shopping this absurd proposal to Smirnov, Ustinov, and Malinovskiy, who do not know enough to reject it.
1966 July 4 - .
- Soyuz simulators - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Burnazyan,
Keldysh,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The 7K-OK simulator consists of a mock-up of the BO living compartment and SA re-entry capsule only. The interiors are not yet fitted out with equipment, and development of the optical equipment to allow the cosmonauts to train with simulated dockings is proceeding very slowly. Mishin has promised a dozen times to speed up the work on the trainers, but produced nothing. Meanwhile Mishin is proceeding to train his cosmonaut team for Soyuz flights in September. It is said that he has other leaders, including Burnazyan and Keldysh, on his side.
1966 July 6 - .
- State Commission on Manned Spaceflight - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Belyayev,
Bugrov,
Bykovsky,
Dolgopolov,
Grechko,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Tyulin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Tyulin heads a meeting that brings the Soyuz crewing dispute into the open. The opposing crews are represented as follows:
- Soyuz s/n 3: VVS: commander: Komarov; backup Belyayev. MOM: commander: Dolgopolov; backup Grechko. Flight engineer: VVS: open; MOM: Makarov, Backup: Bugrov.
- Soyuz s/n 4: VVS: commander: Bykovsky; backup Nikolayev. MOM: commander: Yeliseyev; backup Anokhin. Flight engineer: VVS: open; MOM: Kubasov, Backup: Volkov.
Kamanin is furious. Mishin and Tyulin think an engineer can be trained to be a spacecraft commander in three months, without passing a flight physical, without being a qualifed pilot, without screening and training on the centrifuge or zero-G aircraft, and without parachute training. They put no value in six years of VVS experience in cosmonaut training. They give no weight to the years of general training, spaceflight experience, and ten months of Soyuz-specific training his candidates have already had. He notes that the United States trains crews for a minimum of one to two years before a flight. Kamanin says this decision will not stand.
1966 July 9 - .
- Struggle for space leadership - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Malinovskiy,
Rudenko,
Smirnov,
Ustinov,
Vershinin.
Program: Soyuz,
Voskhod.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 4,
Voskhod 5,
Voskhod 6.
Spacecraft Bus: Vostok.
Spacecraft: Voskhod.
In the previous days Kamanin has been preparing Vershinin and Rudenko for the struggle to ensure the Ministry of Defence's interests in space are preserved and defended. Malinovskiy, Smirnov, and Ustinov must be convinced of the righteousness of the VVS position on space crew preparation and training. At the beginning of 1966, Kamanin thought 1966 would be the year Russia would leap ahead again in the space race. At that time four manned Voskhod and four manned Soyuz flights were expected. Now the year is half over, and it is clear that the only remaining Voskhod flight will not go ahead, and it will be luck if even two Soyuz missions are flown. Instead of a year of triumph, 1966 will see the USA pulling far ahead in the space race. This is the fault of the incredibly poor management of the Soviet space program by Ustinov, Smirnov, Keldysh, and Malinovskiy -- but even more fundamentally due to the inept management of OKB-1 and TsUKOS. The Voskhod program was delayed, then destroyed by OKB-1's insistence on inclusion of their poorly thought-out and developed experiment in artificial gravity. VVS was always opposed to this experiment, yet OKB-1 dragged the program out for years trying to perfect it. Flights of the Soyuz spacecraft could already have occurred in 1962-1963, had Korolev not ignored VVS recommendations and insisted on perfecting a fully automatic rendezvous and docking system. Development of this system delayed the Soyuz project a minimum of three years.
1966 July 12 - .
- Soyuz crews - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Tsybin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Yastreb.
Kamanin meets with Tsybin (Mishin being unavailable on 'command' activities). For over two hours they argue about Soyuz crew plans. Kamanin finds it absurd that OKB-1 thinks they can turn engineers into spacecraft commanders with two to three months training, when it takes the VVS two to four years. He also declares himself categorically opposed to sending crew out on spacewalks with serious health defects. He tries to impress on Tsybin that it will be fatal to send men into space without medical screening, centrifuge and zero-gravity screening and training. It would be insane to send men out into open space to conduct work without training on representative equipment, dressed in a spacesuit, in a zero-G aircraft. He declares himself ready to train candidates selected by the Academy of Science and MOM as cosmonauts, but only on a sensible and professional basis, not a crash program. Kamanin senses that Tsybin realises the fallacy of MOM's position, but he is only following the orders of Mishin, Tyulin, and Korolev before them. He promises to discuss the matter again with Mishin.
1966 July 13 - .
- Struggle for space continues - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Rudenko,
Smirnov,
Vershinin.
Program: Soyuz.
Kamanin has prepared a draft letter from the Minister of Defence to the Central Committee decrying the lead of the United States in military space research and manned spaceflight. But the letter has not been forwarded. Rudenko has sought a meeting with Smirnov on the attempt by MOM and OKB-1 to take over all manned spaceflight functions, but Kamanin does not believe that he or Vershinin have Smirnov's ear.
1966 July 16 - .
- Cosmonaut meeting with Brezhnev - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Gagarin,
Leonov,
Malinovskiy,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Brezhnev has finally agreed to meet with Gagarin, Leonov, and Kamanin on 28 or 29 July. Gagarin will be in Czechoslovakia on 25 July, and Leonov in Hungary; they'll have to be back by the 27th to prepare for the meeting. Kamanin holds no great hope for the outcome - the cosmonauts' desire to reorganize and reprioritise Soviet spaceflight will meet powerful opposition from Ustinov, Smirnov, and Malinovskiy.
1966 July 20 - .
- Heated exchange with Mishin - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Darevskiy,
Komarov,
Mishin,
Severin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft: Yastreb.
Kamanin and VVS officers spend more than two hours in a heated exchange with Mishin and his staff at OKB-1. Mishin is attacked for delays in completion of Soyuz; his demand that OKB-1 cosmonauts be trained in VVS zero-G aircraft without any agreement on this having been reached; the lack of work on spacesuits for the Soyuz flights by Severin; and above all his "illegal" training of his own cosmonauts. Mishin responds with wild attacks against the competence of Kamanin's cosmonauts, saying that his engineers could better guide a spacecraft to a docking than Kamanin's pilots. Finally things cool down, and Mishin agrees to submit to Kamanin a list of OKB-1 candidates for cosmonaut training within two to three days. Kamanin agrees to consider how they may be prepared for flight on a two-month schedule.
Later Kamanin's group visits Darevskiy at MAP and reviews the status of Soyuz trainer completion. He promises to have them completed by the end of August. Finally Kamanin confronts Komarov over statements he made in Japan. Komarov admits telling the world press that the Soviet Union will, at the scheduled time, fly an automated spacecraft around the moon and return it to earth, to be followed by a dog flight, then a manned circumlunar flight. Kamanin has already had the Central Committee and Soviet Ministers calling him about this unauthorised disclosure.
1966 July 21 - .
- Soyuz crews - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Malinovskiy, Mishin. Program: Soyuz. Malinovskiy agrees to support Kamanin's objections to the attempt by Mishin to take over manned spaceflight, and documents are to be prepared for the General Staff and Central Committee staking out the Ministry of Defence's position..
1966 July 22 - . LV Family: N1.
- Revised L1 flight schedule is released. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
As a result of the review two days earlier (Mishin Diaries 1-266), a revised L1 flight schedule is released. No 1P - For 1M1 (N1 functional mockup) - 15 September
No 2P - 15 October & No 3P - October: Orbital flights with 2x (indecipherable) (1P, 2P and 3P were prototype L1's without heat shields and recovery possibilities).
Number 4 and 5: 2 units:Direct unpiloted flight with return to earth (November-December)
Numbers 6 to 10: 5 units: Flyby of the moon; 7K-L1 with crew transfer from 7K-OK (January to May 1967)
Numbers 11 to 14 (15): 4 units: Direct flyby of the moon by 7K-L1 (June-September) - launches every 1 to 1.5 months until completion (Mishin Diaries 1-266)
1966 July 25 - .
- VVS Victory on Soyuz crew issue - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Kolodin,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Severin,
Tyulin,
Voronov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft: Yastreb.
Tyulin advises Kamanin that Ustinov has instructed Mishin to accept that Soyuz spacecraft will be commanded by a VVS pilot cosmonaut, with OKB-1 providing cosmonauts for the engineering support role. Mishin is to immediately send four candidates from OKB-1 to Kamanin for cosmonaut training. Kamanin feels this is only a 50% victory, and vows to accelerate submission of the letter from Malinovskiy to the Central Committee, demanding that the support cosmonaut seats also be filled by trained VVS engineer cosmonauts (e.g. Khrunov, Gorbatko, Voronov, and Kolodin). Meanwhile spacesuit designer Severin informs Kamanin that OKB-1 has insisted that the outer hatch of Soyuz will remain at 660 mm diameter, even though he has told them for a long time that the minimum diameter for a cosmonaut in spacesuit with a life support system backpack is 700 mm. Kamanin agrees to support him, but notes the change can only be made in later spacecraft; it is too late to change the first production run.
1966 July 26 - .
- Soyuz hatch problem - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Alekseyev, Semyon,
Anokhin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Mishin,
Severin,
Sharafutdinov,
Shcheglov,
Skvortsov,
Smirnov,
Tsybin,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
Training of the new cosmonaut cadre is reviewed. English language courses are proving to be a particular problem. There have been some potential washouts - Sharafutdinov has done poorly in astronomy, Shcheglov suffered an injury at the beach, Skvortsov damaged his landing gear on a MiG-21 flight.
At 15:00 a major review is conducted, with Komarov, Khrunov, Gorbatko, Kamanin, and other VVS officer meeting with OKB-1 leaders Mishin, Tsybin, Severin, Alekseyev, Anokhin, and other engineers. Film is shown of the difficulties in the zero-G aircraft of cosmonauts attempting to exit from the 660 mm diameter hatch. In four sets of ten attempts, the cosmonaut was only to get out of the hatch half the time, and then only with acrobatic contortions - the inflated suit has a diameter of 650 mm, only 10 mm less than the hatch. Mishin finally concedes the point. But installation of the hatch in Soyuz s/n 3 and 4 is not possible - the spacecraft are essentially complete, and to add the hatch would delay their flight 6 to 8 months. Then Mishin makes the astounding assertion that Gorbatko and Khrunov are not adequately trained to be engineer-cosmonauts, and without this he will not allow them into space. He suggests OKB-1 engineers Anokhin and Yeliseyev instead. After outraged response, Severin finally sinks this suggestion by pointing out that no space suit has been prepared for Anokhin, and that it will take two to three months to make one. Kamanin is astounded that Mishin has pushed Anokhin all the way up to Smirnov and the VPK without even knowing he could not possibly fly due to this restriction. It again points out their poor management. Finally Mishin agrees that spacecraft s/n 5 and 6 and on will have 720 mm hatches. The ECS for the suits for those missions will have to be changed from a backpack configuration, with the equipment rearranged around the waist of the cosmonaut. The crews for the flight will be an experienced VVS pilot cosmonaut as commander, and (Kamanin realizes he may have to concede) a VVS engineer as flight engineer cosmonaut. They will have to complete training by 1 October 1966.
1966 July 27 - .
- VPK Meeting - L1 delays - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Mishin,
Severin,
Vershinin,
Voronin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Marshal Vershinin attends the meeting, where it is revealed that all systems in development - Chelomei's, Mishin's, Voronin's, Severin's, and others - are seriously behind schedule. The first unmanned circumlunar test of the L1 was to be made by 15 April 1967, but it seems unlikely it will even be completed by the end of 1967.
1966 July 30 - .
- Beregovoi pushed for Soyuz mission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Beregovoi,
Burnazyan,
Gagarin,
Keldysh,
Khrunov,
Krylov,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Rudenko,
Shonin,
Tsybin,
Tyulin,
Vershinin,
Volynov,
Zakharov.
Program: Soyuz,
Voskhod.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
Mishin, Rudenko, and others have met with Beregovoi and support his selection as commander for the first Soyuz mission. Kamanin does not believe he is fit for the assignment, due to his age, his height and weight (that are the limit of the acceptable for the Soyuz). Gagarin reports that during a visit to OKB-1 the day before, he discovered that they were still going all out to prepare their own crews and train their own cosmonauts for Soyuz flights. Kamanin reassures him that the full power of the VVS, the General Staff, and the Ministry of Defence is behind the position that only VVS pilots will command the missions. Mishin is gloating over the latest spacesuit tests. Khrunov tried exiting from the Soyuz hatch in the Tu-104 zero-G aircraft. Using his full dexterity and strength, he had more success than in earlier tests. But Kamanin notes that designing a spacecraft hatch only 10 mm wider than the cosmonaut is hardly the basis for practical spaceflight or training. Later Kamanin plays tennis with Volynov and Shonin. Their Voskhod 3 flight is still not officially cancelled. They have been fully trained for the flight for months now, but no go-ahead is given. On Saturday, Tsybin presents to the General Staff OKB-1's concept for training of engineer cosmonauts. Tyulin, Burnazyan, and Keldysh have approved the plan, except they have substituted VVS engineer cosmonauts for those from OKB-1 for the first Soyuz flights. So this is the result of months of controversy - a position that there is no fundamental opposition to cosmonaut candidates from OKB-1. Kamanin sees the absolute need for his draft letter to be sent from the four Marshals (Malinovskiy, Zakharov, Krylov, and Vershinin) to the Central Committee. Mishin continues to "assist" the situation - it has been two weeks since he promised to submit the names and documentation for his candidates to the VVS, and he has done nothing.
1966 August 2 - .
- Letter to Central Committee on OKB-1 actions. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Malinovskiy. Program: Soyuz, Lunar L1, Lunar L3. Malinovskiy decides to send the letter to the Central Committee complaining about MOM and OKB-1's after two days of indecision..
1966 August 3 - .
- Sea tests of Soyuz - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Brezhnev,
Gagarin,
Kubasov,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin sends a letter to Kamanin, linking acceptance of his eight cosmonaut candidates from OKB-1 to continuation of sea recovery tests of the Soyuz capsule at Fedosiya. Kamanin's early hopes for Mishin have been dashed - not only is he no Korolev, but his erratic management style and constant attempts to work outside of accepted channels and methods, are ruining the space program. Later Gagarin briefs Kamanin on the impossibility of meeting Brezhnev, who has flown south for vacation without reacting to Gagarin's letter. Most likely, the letter will be referred to Ustinov, who will pass it to Smirnov, with instructions to suppress this "revolt of the military". Gagarin requests permission to resume flight and parachute training in preparation for a space mission assignment. Kamanin agrees to allow him to begin three months before the mission to space. This will be no earlier than 1967, as Gagarin will not be assigned to the first Soyuz flights.
Kamanin decides to smooth over matters with OKB-1. He calls Mishin, and then Tsybin, and agrees to begin processing of Anokhin, Yeliseyev, Volkov, and Kubasov as soon as he receives their personnel files and security clearances. Mishin promises to deliver the Soyuz mock-up of the Tu-104 zero-G aircraft soon - it slid from 20 July, then from 7 August.
1966 August 5 - .
- Showdown on spacesuits - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Alekseyev, Semyon,
Anokhin,
Bushuyev,
Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Litvinov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Severin,
Tsybin,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
At a meeting at LII MAP Zazakov, Litvinov, Mishin, Tsybin, Bushuev, Severin, Alekseyev, and Komarov spar over the hatch and spacesuit problem. Severin only agrees to modifying the ECS under immense pressure, but the modified suit will not be ready until November. Severin could not get Mishin to agree to an increased hatch diameter from Soyuz s/n 8 - Mishin will only "study the problem". An arrangement of the ECS around the waist of the cosmonaut is finally agreed. Mishin and Litvinov categorically rejected any modification of the hatch in the first production run of Soyuz.
In turn, Factory 918 insisted on a final decision on Soyuz crews. They cannot build 16 of the custom-built spacesuits for all possible candidates for the flights (8 from VVS and 8 from OKB-1). It was therefore agreed that the commanders of the first two missions would be Komarov and Bykovsky, with Nikolayev and Gagarin as their backups. It was finally decided to assume that the other crew members would be either Khrunov and Gorbatko from the VVS, or Anokhin and Yeliseyev from OKB-1.
1966 August 8 - .
- Gagarin's letter buried. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Malinovskiy,
Rudenko,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
As expected, Gagarin's letter to Brezhnev was referred to Ustinov, then to Smirnov, who has now referred it to Afanasyev and Malinovskiy with the instructions that they are "to present a mutually agreed solution". Malinovskiy referred it in turn to his four marshals, and Rudenko immediately makes an error by conceding that TsPK will accept OKB-1 cosmonaut candidates for training aboard Soyuz.
1966 August 10 - .
- Soyuz schedule has been delayed again - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Demin,
Gagarin,
Mishin,
Tereshkova,
Tyulin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Soyuz s/n 5/6.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Soyuz s/n 1 and 2 will be flown unpiloted by October 1966 Manned flights aboard Soyuz s/n 3, 4, 5, 6 will not take place until the first quarter of 1967. Later Mishin tours the cosmonaut training centre - the first time in his life he has visited the place. Mishin admires the new construction from Demin's balcony on the 11th floor of cosmonaut dormitory, then goes to Tereshkova's apartment on the seventh floor, and then Gagarin's apartment. Mishin insists on drinking a toast of cognac on each visit. Tyulin reveals this is a peace mission - they want to normalize relations and get on with cosmonaut training. At Fedosiya the auxiliary parachute of a Soyuz capsule failed to open during a drop test. Kamanin believes that the Soyuz parachute system is even worse than that of Vostok. His overall impression of the Soyuz is poor: the entire spacecraft looks unimpressive. The small dimensions of hatch, antiquated communication equipment, and inadequate emergency recovery systems are only the most noticeable of many discrepancies. If the automatic docking system does not function, then the entire Soviet space program will collapse in failure.
1966 August 11 - .
- Lunar cosmonaut training - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Burnazyan,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Kamanin receives a document, signed by Mishin, Tyulin, Burnazyan and Keldysh, which declares that OKB-1 will be solely responsible for training of cosmonauts for L1 circumlunar missions. Only OKB-1 engineers and Academy of Science researchers will be considered for such missions, and no assistance is needed from VVS cosmonauts or its training centre.
1966 August 22 - .
- OKB-1 cosmonaut disputes - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Pravetskiy,
Tyulin.
Program: Soyuz.
Tyulin and Pravetskiy insist that Kamanin take the eight Soyuz cosmonaut candidates from OKB -1 based on their having passed physical examinations by the Ministry of Health. Kamanin rejects this; he will only accept candidates screened by VVS flight surgeons. He notes that Pravetskiy's ministry could not be conscientious in their examinations if they passed the 56-year-old, half-blind Anokhin for flight. Tyulin and Pravetskiy agree to withdraw Anokhin, and Kamanin agrees that a joint board of VVS and Ministry of Public Health physicians will screen the candidates together.
1966 August 23 - .
- Soyuz recovery training at sea - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Burnazyan,
Bykovsky,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Keldysh,
Khrunov,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Nikolayev,
Smirnov,
Volkov,
Voronov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
Nikolayev, Bykovsky, Komarov, Khrunov, Gorbatko, Kolodin, and Voronov complete two parachute jumps each, with landing at sea. Training in sea-recovery by helicopter, with the cosmonauts in spacesuits, will be completed over the next two days. Smirnov is ready to sign a letter from Afanasyev, Burnazyan and Keldysh creating a new civilian cosmonaut training centre under the Ministry of Medium Machine Building, separate from the VVS centre. The letter is not coordinated with the Defence Ministry, and contradicts the letter sent by the four marshals to the Central Committee. Kamanin prepares a vigorous refutation of the letter's position. The physicians' board on OKB-1 candidates has only cleared Yeliseyev for flight - they could not agree on Volkov, Kubasov, and Grechko. OKB-1 only submitted four candidates for review, not the eight promised.
1966 August 29 - .
- VVS - OKB-1 relations at low ebb - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Mishin,
Nikolayev.
Program: Soyuz.
Mishin invites Kamanin and his cosmonauts to the 20th Anniversary Party of OKB-1. Kamanin is so alienated he refuses to go, and sends only Nikolayev and Bykovsky as cosmonaut representatives. OKB-1 has wasted three months arguing about Soyuz crewing, and essential work to prepare for the flights has either not been done or kept from the VVS. No list of scientific experiments and procedures for the flights, adequate trainers, or information that would allow preparation of flight plans and log books has been provided. A minimum of four months will be required to prepare for flight after all these materials are delivered. Gagarin reports on the farce in sea recovery training at Fedosiya. It took eight days instead of the three planned to train 16 cosmonauts. Only after the VVS cosmonauts had left did Mishin sent 8 OKB-1 cosmonaut candidates, who were prohibited from training together with the VVS cosmonauts.
September 1966 - .
- N1 two-launch moon scenario proposed - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK,
Molniya-1,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Bushuyev proposed a two launch variation on Korolev's single-launch scheme. The increased-payload version of the N1 with six additional engines was not planned to fly until vehicle 3L. 1L and 2L were to be technology articles for ground test with only the original 24 engine configuration. At that time the first Apollo test flight was planned by the end of 1966, and the US moon landing no later than 1969. The Soviets expected the first test of their LK lander in 1969, and concluded they could not expect to land a Soviet man on the moon until 1972. Additional Details: here....
1966 September 2 - .
- Cosmonaut civilian program training groups - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Dobrovolsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Leonov,
Nikolayev,
Shatalov,
Volynov,
Voronov,
Zholobov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing,
Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Soyuz s/n 5/6,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin organises the cosmonauts into the following training groups:
- Soyuz 7K-OK: Gagarin, Komarov, Nikolayev, Bykovsky, Khrunov, Gorbatko, Voronov, Kolodin
- L1: Volynov, Dobrovolskiy, Voronov, Kolodin, Zholobov, Komarov, Bykovskiy
- L3: Leonov, Gorbatko, Khrunov, Gagarin, Nikolayev, Shatalov
Rudenko agrees with Kamanin's plan, except he urges him to assign more cosmonauts to the Soyuz 7K-OK group, and include OKB-1 cosmonauts in the 7K-OK, L1, and L3 groups, and Academy of Science cosmonauts in the L1 and L3 groups.
These cosmonaut assignments were in constant flux, and many cosmonauts were assigned to train for more than one program - resulting in multiple claims in later years that 'I was being trained for the first moon flight'.
1966 September 2 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Lunar flight cosmonauts assignments. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Artyukhin,
Beregovoi,
Bykovsky,
Dobrovolsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Khrunov,
Klimuk,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Rukavishnikov,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov,
Volkov,
Voloshin,
Volynov,
Voronov,
Yeliseyev,
Zholobov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
In the period 1966 to 1968 there were five simultaneous Soviet manned space projects (Soyuz 7K-OK orbital; Soyuz 7K-L1 circumlunar; Soyuz VI military; L3 manned lunar landing; Almaz space station). Cosmonaut assignments were in constant flux, resulting in many claims in later years that 'I was being trained for the first moon flight'. Additional Details: here....
1966 September 5 - .
- OKB-1 cosmonauts accepted for training. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Dolgopolov, Grechko, Kubasov, Makarov, Volkov, Yeliseyev. Program: Soyuz. Kubasov, Volkov, and Grechko have been accepted by the VVS for cosmonaut training, with some relaxation in health requirements. Yeliseyev, Dolgopolov and Makarov need more medical tests to be cleared. .
1966 September 7 - .
- Cosmonaut group leaders - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Belyayev,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Khrunov,
Kubasov,
Popovich,
Pravetskiy,
Severin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz,
Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz VI,
Yastreb.
Volkov, Grechko and Kubasov believe they can complete cosmonaut training in two months. Of course they know space technology, but Kamanin informs them that, with intensive training, they might be ready in one or two years. Popovich is assigned as leader of the Soyuz VI military spacecraft training group, and Belyayev as head of the Almaz military orbital station training group. Kaminin tells Severin to complete spaceuits for Khrunov and Gorbatko, but to ignore Mishin's orders to prepare suits for Anokhin and Yeliseyev. Anokhin has already been rejected due to his age and health, and Yeliseyev is still being tested. Kamanin reviews draft test programs for the UR-500K/L1 and N1-L3. He lines out statements inserted by Pravetskiy on joint training of cosmonauts by the MOM, Ministry of Public Health and VVS.
1966 September 8 - .
- Cosmonaut tour to Syria - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Leonov.
Program: Soyuz.
Belyayev and Leonov depart, after being briefed on correct responses to expected embarrassing questions (Why has there been no Soviet manned spaceflight for eighteen months? When will there be a Soviet rendezvous in space? Who now leads in the space race?)
1966 September 10 - .
- Soyuz crew selection dispute to be resolved - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kerimov,
Litvinov,
Pashkov,
Pravetskiy,
Rudenko,
Tregub.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
While Gemini 11 orbits above, the Soviet leadership argues about fundamental organisational details. Pashkov leads a meeting of the VPK, with Litvinov, Kerimov, Pravetskiy, Tregub, Tsarev, Bogdanov; Rudenko, and Moroz present. After prolonged debate, it is decided that Kiyasov, Kerimov and Kamanin will prepare a letter to the Central Committee. The TsPK Cosmonaut Training Centre will remain the only such centre in the country. However the VVS will agree to some modifications in existing selection and training arrangements. The Ministry of Public Health will be excluded from participation in selection and training of cosmonauts.
1966 September 21 - .
- Soyuz simulators still incomplete - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Darevskiy,
Tsybin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Darevskiy now reports that the 7K-OK will not be finished until the end of October at the earliest. Poor quality optic systems and unreliable equipment from OKB-1 are blamed. Tsybin promises to resolve all issues, with OKB-1-providing equipment within a week
1966 September 28 - .
- Delays in Soyuz spacesuit completion - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
The Tu-104 and TBK-60 Soyuz mock-ups for zero-G and vacuum EVA training will be finished, at best, by 10 October. Another holding item is production of the new spaceuists with the rearranged ECS systems. Due to continued delays in the optical subsystems, the Soyuz rendezvous trainer will not be completed until 20 October.
1966 September 29 - .
- Cosmonaut leave cancelled to support Soyuz missions in December - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin claims he will be ready to fly two piloted 7K-OK spacecraft in the second-half of December 1966. No one but Mishin believes this is possible. The tests of many subsystems are not finished, with the parachutes and ECS far from completion of qualification tests. However in order not to give Mishin any excuses, Kamanin orders Gagarin to cancel all cosmonaut leave for the rest of the year, and to accelerate training to be ready for Soyuz flights by 1 December.
1966 September 30 - .
- Kerimov to be Chairman of the State Commission for Manned Flights - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kerimov,
Rudnev,
Smirnov,
Tyulin,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
The government has decided to decrease rather than increase the authority of the Chairman of the State Commission for Manned Flights. Kerimov will be appointed to the post. He is now only Chief for the MOM Third Main Administration. His predecessors were Ministers or Deputy Ministers (Rudnev, Smirnov, Tyulin). Kerimov will not have the rank or authority to stand up to dozens of chief designers, deputy ministers, Marshals, Generals, or the President of the Academy of Sciences. Kamanin observes that Soviet space affairs continue to roll downhill under the "valiant" management of Ustinov and Smirnov.
1966 October 4 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Dummy Proton/Block D mounted on pad. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
A dummy 8K82K/Block D rocket was mounted at the launch site. The dummy was loaded with imitation propellants (kerosene as fuel and water/ethyl alcohol as oxidiser). The nitrogen tetroxide oxidiser had to be kept above -11 degrees C, and it was originally planned for a thermostatically-controlled electrical heating of the tank walls to achieve this. It was ultimately decided that the risk of explosion of such a system was too great, and the system was abandoned.
1966 October 5 - .
- Council for the Problem of the Conquest of the Moon - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Karas,
Sokolov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
A government resolution has created a Council for the Problem of the Conquest of the Moon. The chairman will be Minister Afanasyev; the members, other ministers, deputy ministers, academicians, and the chief designers. The only member from the Defense Ministry will be lieutenant generals Karas and Sokolov. There are no VVS members, but Kamanin has already received a request that General Ioffe report to the council on VVS plans for search and recovery of unmanned lunar precursor spacecraft.
1966 October 10 - .
- Grechko breaks his leg in parachute training. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Beregovoi, Bykovsky. Program: Soyuz, Lunar L1. Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Beregovoi has been named commander of the L1 training group in place of Bykovsky, who is busy with 7K-OK flight training..
1966 October 27 - .
- Soyuz launch plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Ustinov chairs a VPK meeting on the readiness of the Soyuz spacecraft for flight. The first unmanned launch of the spacecraft will not be possible until 20 November. Mishin considers a manned flight impossible before 10 January 1967, but Ustinov orders preparations for a 20 December 1966 launch date. Mishin attempts to blame the delay on crew training. But it is OKB-1 and Mishin who failed to deliver the necessary training equipment for the TBK-60 chamber, Tu-104 aircraft, and the Volga docking simulator.
1966 October 31 - .
- Soyuz crews have only 40 days for flight training. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Nikolayev,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
First snow of the winter in Moscow. The training of Soyuz crews has to be completed within 40 days, but there is still no assurance the trainers will be ready by 15 November. Komarov will command the active spacecraft, and Bykovsky the passive. Gagarin and Nikolayev are their back-ups. The 20 December flight date can only be met if Khrunov and Gorbatko serve as flight engineers. Training of Kubasov, Volkov and Yeliseyev in 40 days is impossible. Yet there is still no agreement on the crew composition.
1966 November 3 - .
- Soyuz parachute fails in drop test. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
In a test of the reserve parachute at Fedosiya, the Soyuz capsule was dropped from the aircraft at 10,500 m. The drogue chute deployed normally, as did the main parachute. They were then jettisoned and the reserve parachute deployed normally. However descent on both main and auxiliary chutes occurs only with noticeable pulsations of their cupolas, with the capsule revolving at one RPM. In this case it finally led to failure of the lines of the reserve chute at 1500 m, after which it crashed to earth. Contributing to the problem was the jettison of the remaining hydrogen peroxide reaction control system fuel from the capsule during the descent. It is normally expected that 30 kg of the 70 kg load of propellant will remain after re-entry. When this was vented, it burned the parachute lines. Each line will normally carry a load of 450 kg, but after being burnt by the peroxide, they can be torn apart by hand. Meanwhile there is still no agreement on crew composition. Komarov, Bykovsky, Khrunov and Gorbatko can be ready for flight by10 December. However the VPK representatives, Tyulin and Mishin insist that their OKB-1 candidates be flown in stead of Khrunov and Gorbatko.
1966 November 10 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Lunar coordination problems - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. Kamanin diary complains of lunar coordination problems..
1966 November 11 - .
- Soyuz crew dispute drags on - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kubasov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin visits OKB-1. Mishin certifies that unmanned Soyuz s/n 1 and 2 will fly by 26 November, and the manned spacecraft s/n 3 and 4 by the end of December. The departure of cosmonauts for the range must take place not later than 12-15 December. There remains only 30 days for training of the crews, the member of which have still have not been agreed. Mishin ignores common sense and still insists on the preparation of only his own engineers (Yeliseyev, Kubasov, Volkov, Makarov). The argument over the Soyuz crews continues without resolution up to the Central Committee level, then back down through the VPK and State Commission, over the next week.
1966 November 17 - .
- VVS told to surrender on crew assignments issue. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Kerimov,
Khrunov,
Kirillov,
Komarov,
Kuznetsov,
Mishin,
Rudenko,
Yeliseyev,
Zakharov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Kamanin is at Tyuratam for the first Soyuz launch. He and Rudenko are accommodated in the new hotel at Area 2. It has all conveniences - a local telephone, radio and television with Moscow programs, even a promise to install an HF telephone that will allow secure communications with Moscow. Also there for the launch are Kerimov, Kirillov, Kuznetsov, Bykovsky, Komarov, Khrunov, amd Yeliseyev. Rudenko reports that he has been chewed out by Marshal Zakharov. Zakharov told him "What are you and Kamanin doing, blocking OKB-1 candidates from flight? If Mishin wants to send his people to the Moon, let him do it and do not interefere!"
1966 November 18 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 facilities tour - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Rudenko,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Rudenko and Kamanin meet with Mishin at Area 31 (18-20 kilometers east of Area 2). Launch preparations are reviewed, and Mishin satisfies them that the two Soyuz will be launched on 26-27 November. The State Commission will meet officially tomorrow at 16:00. For today, they tour the N1 horizontal assembly building at Area 13. Korolev planned the N1 as early as 1960-1961. It will have a takeoff mass of 2700-3000 tonnes and will be able to orbit 90-110 tonnes. The first stage of rocket has 30 engines, and the booster's overall height is114 m. The construction of the assembly plant, considered a branch of the Kuibyshev factory, began in 1963 but is still not finished. Two factory shops are in use, and the adjacent main assembly hall is truly impressive - more than 100 m in length, 60 m high, and 200 wide. Work on assembly of the ground test version of the rocket is underway. Assembly will be completed in 1967, and it will be used to test the systems for transport to the pad, erection of the booster, servicing, and launch preparations. The booster is to be ready for manned lunar launches in 1968. The construction site of the N1 launch pads occupies more than one square kilometre. Two pads are located 500 meter from each other. Between and around them is a mutli-storied underground city with hundreds of rooms and special equipment installations.
Only late in the night Rudenko and Mishin finally agree that the crews for the first manned Soyuz flights will be: Basic crews: Komarov, Bykovsky, Khrunov, Yeliseyev; Back-up crews: Gagarin, Nikolayev, Gorbatko, Kubasov. Meanwhile poor weather in Moscow is delaying zero-G training for the flight. In the last week only one weightless flight on the Tu-104 was possible - and a minimum of 24 flights need to be flown before the launch. It was therefore decided to ferry one Tu-104 to Tyuratam and train the cosmonauts here - it made its first flight today.
1966 November 19 - .
- First Soyuz Launch Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Grechko,
Keldysh,
Kerimov,
Krylov,
Kurushin,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Mnatsakanian,
Pashkov,
Petrovskiy,
Pravetskiy,
Rudenko,
Ryazanskiy,
Serbin,
Smirnov,
Tkachev,
Ustinov,
Vershinin,
Zakharov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing,
Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Rudenko has reached agreement with Mishin that L1 and L3 crews will also consist of a VVS pilot as commander, and an OKB-1 flight engineer. Kamanin is depressed. Despite the support six marshals (Malinovskiy, Grechko, Zakharov, Krylov, Vershinin and Rudenko), Mishin has won this argument with the support of Ustinov, Serbin, Smirnov, Pashkov, Keldysh, Afanasyev, and Petrovskiy. Later the State Commission meets, for the first time in a long time at Tyuratam. Kerimov chairs the session, with more than 100 attendees, including Mishin, Rudenko, Krylov, Pravetskiy, Kurushin, Ryazanskiy, Mnatsakanian, and Tkachev. All is certified ready,. Launch of the active spacecraft is set for 26 November, and the passive vehicle on 27 November.
1966 November 20 - .
- Soyuz first flight plan - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Feoktistov,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Pravetskiy,
Rudenko,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
Feoktistov briefs the State Commission on the flight plan for the upcoming mission at 10:00. Each spacecraft will be in space for four days, and will demonstrate orbital manoeuvre, rendezvous and automatic spacecraft docking. If the passive vehicle can be placed in orbit within 20 kilometres of the previously launched active spacecraft, then docking can be accomplished on the first or second orbit of passive vehicle. If they are more than 20 kilometres apart, then 24 hours will be needed to manoeuvre the spacecraft to a rendezvous. Kamanin and Rudenko take a zero-G flight aboard the Tu-104 (Pravetskiy was bumped at the airfield "due to space limitations"). The Tu-104 needs good visibility of the horizon in order to fly the zero-G parabola. The aircraft is accelerated to maximum speed and then pulls up into a sharp climb (going from 7,000 to 10,000 m). At the end of the climb 20-25 seconds of weightlessness is available for training the cosmonauts. Komarov, Bykovsky, Khrunov and Yeliseyev are aboard today. Khrunov practiced moving from the BO living module of the passive vehicle to that of the active spacecraft. Yeliseyev practiced exiting and entering the BO hatches with his bulky spacesuit and 50- kilogram ECS system strapped to his leg.
Mishin receives an encrypted telegram from Okhapkin and Tsybin. They propose that one of the cosmonauts on the first mission will back away from the docked spacecraft on a 10-m long safety line and film the other cosmonaut moving from one spacecraft to the other. Kamanin believes only Khrunov (with more than 50 Tu-104 weightless flights), has enough training to accomplish the task. After a sauna with Rudenko and an attempt to watch a film (aborted due to projector failure), Kamanin takes a walk in a drizzly, evocative night. He visits the cottages used by Korolev and the cosmonauts for the first missions. A light burns in Korolev's cottage - Mishin is working late. Kamanin recalls his many confrontations with Korolev, but also remembers how well he managed people compared to Mishin. Even if he had already decided personally what to do, he took the time to listen to other opinions and everyone felt their views had been considered.
1966 November 21 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- First Proton/Soyuz L1 begins assembly. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The first flight rocket (serial number 22701) began assembly on 21 November 1966, with mechanical assembly completed by 29 November. Electrical connections and tests were completed by 4 December 1966. Due to New Year's holidays work did not resume until 28 January 1967. By 28 February the fully assembled booster / spacecraft unit was completed in the MIK, including the 7K-L1P boilerplate spacecraft.
1966 November 21 - .
- Soyuz crews agreed officially - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Bykovsky,
Feoktistov,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Kamanin,
Kerimov,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Rudenko,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The weather continues to deteriorate, and Kamanin considers moving the Tu-104 and cosmonauts to Krasnovodsk in order to get the 24 necessary zero-G flights before launch. At 11:00 the State Commission meets at Area 31. Present are Kerimov, Mishin, Rudenko, Kamanin, Komarov, Bykovsky, Khrunov, Yeliseyev, Anokhin and others. Mishin describes the status of preparations of Soyuz s/n 1, 2, 3, 4 for launch. He notes that the L1 and L3 lunar spacecraft are derived from the 7K-OK, and that these flights will prove the spacecraft technology as well as the rendezvous and docking techniques necessary for subsequent manned lunar missions. Feoktistov and the OKB-1 engineers say a launch cannot occur before 15 January, but Mishin insists on 25 December. That will leave only 20 days for cosmonaut training for the mission, including the spacewalk to 10 m away from the docked spacecraft. Faced with the necessity for the crews to train together as a team prior to flight, Mishin at long last officially agrees to the crew composition for the flights: Komarov, Bykovsky, Khrunov, and Yeliseyev as prime crews, with Gagarin, Nikolayev, Gorbatko, and Kubasov as back-ups. However a new obstacle appears. KGB Colonel Dushin reports that Yeliseyev goes by his mother's surname. His father, Stanislav Adamovich Kureytis , was a Lithuanian sentenced to five years in 1935 for anti-Soviet agitation. He currently works in Moscow as Chief of the laboratory of the Central Scientific Research Institute of the Shoe Industry. Furthermore Yeliseyev had a daughter in 1960, but subsequently annulled the marriage in 1966.
Later Feoktistov works with the crews on spacecraft s/n 1 to determine the feasibility of the 10-m EVA. The cosmonauts suggest a telescoping pole rather than a line be used to enable the cosmonaut to be in position to film the joined spacecraft. Bushuyev is tasked with developing the new hardware.
1966 November 22 - .
- Crash efforts to make manned Soyuz flight by end of December - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Kubasov,
Mishin,
Rudenko,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Faced with the possibility Yeliseyev will be bumped from the crew, Mishin requests accelerated training of Kubasov as a substitute. Kamanin asks the KGB for a definitive ruling on Yeliseyev's fitness. It will only be possible to meet a 25-29 December manned flight date by curtailing certain tests and supplementing the existing preparation and test staff with about 100 military staff from the Tyuratam range and 50 additional industrial technicians. Rudenko and Mishin have backed away from the agreement on the "final" crew compositions. Now they propose to assign as second cosmonauts the best two of Khrunov, Yeliseyev, and Kubasov. Kamanin adamantly opposes this latest deviation to plan.
1966 November 24 - .
- Apollo program delays give Soviets opportunity to leapfrog Americans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz,
Voskhod.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Soyuz s/n 5/6,
Soyuz s/n 7,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
Komarov, Bykovsky, Khrunov, and Yeliseyev have completed zero-G training in the Tu-104 at Tyuratam, and need to get back to Moscow to complete simulator training. But continued bad weather at Moscow means that they will have to be flown by Il-14 to Gorkiy, and then get to Moscow by train. Kamanin notes reports on NASA's reorganised flight program for the Apollo program. Under the new schedule, the first attempt at a manned lunar landing will be possible in the first half of 1968. The first manned flight of the Apollo CSM has slipped from December 1966 to the first quarter of 1967. This makes it possible that the Soviets can make 3 to 5 manned spaceflights before the first Apollo flight - the flights of Soyuz s/n 3 and 4 in December 1966, Voskhod 3 in January 1967, and Soyuz s/n 3 and 4 in February 1967.
1966 November 25 - .
- Soyuz launch commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belousov,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Kolodin,
Mishin,
Nikolayev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
Gagarin, Nikolayev, Gorbatko, Kolodin and Belousov arrive at Tyuratam for Tu-104 zero-G training, while the prime crews successfully arrive at Moscow for simulator training. The State Commission meets. After extensive detailed reports, Mishin certifies that the boosters and spacecraft at 09:00 on 26 November. S/N 2 would be launched first, on 28 November at 14:00, followed by s/n 2 24 hours later. The go-ahead is given for launch. In zero-G tests, the reserve cosmonauts find it is necessary to grip the handrail from above with both hands to move easily with the ECS strapped to the leg. The previously approved method, with one hand on top, the other below the handrail, was only good with the ECS configured as a backpack. The hardest part of the EVA will be getting on the spacesuits beforehand, especially in achieving a seal between the gloves and the suit
1966 November 26 - .
- Soyuz vehicles rolled out to pads for dual launch - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Rudenko,
Vershinin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The boosters were rolled out to the pads over eight hours late, at 17:30. There were delays in integrating the spacecraft in its fairing with the rocket, due to the much greater length of the Soyuz fairing and SAS abort tower (making the whole vehicle 46 m long). There was even concern that the assembled rocket would topple over in its horizontal carriage due to the forward centre of gravity. Mishin is getting out of control - publicly screaming at his staff. He demeans the competence of the cosmonauts and extols the quality of his own engineer-cosmonauts in front of the leadership. He yet again insists on crew changes. Kamanin discusses Mishin's public hysterics and tantrums with Rudenko. Rudenko agrees that the man is unstable and unsuitable, but says that he has powerful forces behind him on the Central Committee and Council of Ministers. No one except Vershinin dares oppose him. Rudenko's only course is to let the State Commission and government decide who will fly.
1966 November 28 - .
- Cosmos 133 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Gagarin,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Rudenko,
Yegorov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Four years behind Korolev's original promised schedule, the countdown is underway for the first Soyuz spacecraft. A new closed circuit television system allows the rocket to be observed from several angles during the final minutes. Mishin, as per tradition, personally stays with the rocket until the last moment. Rudenko, Kerimov, and Kamanin observe the launch from the bunker, while Gagarin, Nikolayev, Belyayev and Yegorov observe from the observation post. The launch is perfect, within 0.2 seconds of the 16:00 launch time. The separation of the first stage strap-ons can be seen with the naked eye in the clear sky. The spacecraft is given the cover designation Cosmos 133 after launch. By 22:00 the spacecraft is in deep trouble. For unknown reasons the spacecraft consumed its entire load of propellant for the DPO approach and orientation thrusters within a 15-minute period, leaving the spacecraft in a 2 rpm spin. At the insertion orbital perigee of 179 kilometres, the spacecraft will have a life of only 39 orbits. It is decided to attempt to stop the spin on the 13th orbit using other thrusters and the ion flow sensors to determine attitude. Then the re-entry sequence will be commanded on the 16th orbit, with the spacecraft to use solar sensors to orient itself for retrofire on the 17th orbit.
1966 November 28 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 133 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (A) s/n 2. Mass: 6,450 kg (14,210 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 1.97 days. Decay Date: 1966-11-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 2601 . COSPAR: 1966-107A. Apogee: 219 km (136 mi). Perigee: 173 km (107 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
First test flight of Soyuz 7K-OK earth orbit spacecraft. A planned 'all up' test, with a second Soyuz to be launched the following day and automatically dock with Kosmos 133. This was to be followed by a manned link-up in December 1966. However Kosmos 133's attitude control system malfunctioned, resulting in rapid consumption of orientation fuel, leaving it spinning at 2 rpm. After heroic efforts by ground control and five attempts at retrofire over two days, the craft was finally brought down for a landing on its 33rd revolution. However due to the inaccuracy of the reentry burn, it was determined that the capsule would land in China. The APO self destruct system detected the course deviation and the destruct charge of several dozen kilogrammes of explosive was thought to have destroyed the ship on November 30, 1966 at 10:21 GMT. But stories persisted over the years of the Chinese having a Soyuz capsule in their possession....
1966 November 29 - .
- Cosmos 133 fails to land on first attempt - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At 10:00 the re-entry command sequence is transmitted, but there is some doubt if the sequence was correct. Mishin decides to abort the landing attempt. Later telemetry shows that the command sequence was indeed correct. Attempts are made on orbits 18 and 19 to orient the spacecraft using data from the ion flow sensors, but these were not successful. After orbit 20 the spacecraft's orbital track no longer passed over Soviet ground stations, and another attempt for a solar-oriented re-entry would have to wait for orbit 32. But the spacecraft would possibly decay out of orbit before that time. Commands were transmitted to the spacecraft to raise its orbit, but from orbits 20 to 29 there was no tracking that allowed verification if the manoeuvres had been made. After an uncertain night, telemetry was received in the morning that showed the spacecraft had accepted all three commands for firing of the engines using the ion flow sensors for orientation. However on the first manoeuvre, the engines cut off after 10 seconds, after 13 seconds on the second, and 20 seconds on the third. In all three cases the spacecraft became unstable as soon as the engine firing began, developing large angular oscillations, which resulted in the engines being automatically shut down prior to delivering the total planned total impulse.
1966 November 30 - .
- Cosmos 133 lost on re-entry - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At 09:00 Cosmos 133 appears above the horizon of tracking stations on Soviet territory, but does not respond. On the next orbit, the 30th, it accepted and acknowledged receipt of a command sequence. On the 32nd orbit the retrofire command sequence was transmitted to the spacecraft and accepted. The sequence began on the 33rd orbit, but the engine again cut out after a few seconds firing. The sequence was transmitted for a re-entry with orientation using the ion flow sensors on the 34th orbit, and the spacecraft finally headed to earth. PVO radars tracked the capsule during re-entry from stations at Krasnodar, Gurevym, and Aktyubinsk, with the final track being 200 kilometres southeast of Orsk. Landing should have been at 14:32 Moscow time. There are reports of reception of the homing beacon and sightings of the parachute from areas around Orsk, but by nightfall the capsule has not been found. It is possible the capsule was destroyed by its APO self-destruct system. It is decided the search will be resumed in the morning. Four State Commissions are formed and charged with determining the causes of the failures by 6 December. Meanwhile preparation of spacecraft s/n 3 and 4; will continue, and s/n 1 will be removed from the pad and stored in readiness in the MIK for a possible launch in mid-December.
1966 December 1 - .
- No sign of Cosmos 133 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Kerimov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The search for the wreckage of Cosmos 133 continues without success. Mishin and Kerimov agree with Kamanin's opinion that if a cosmonaut had been aboard instead of a mannequin, the mission could have been successful. Kamanin has temporarily removed Gagarin from flight status after he missed a Tu-104 flight debriefing, then a 22:30 curfew, and did not show up at the Cosmonaut Dormitory at Tyuratam until 14:00 the next day. While on his escapade he also was found to have driven an automobile while intoxicated.
1966 December 2 - .
- Mishin discussion with NA Pilyugin - On the supply of (guidance) equipment for the 7K-L1S. - . Related Persons: Mishin, Pilyugin, . Spacecraft: Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-L1S. (Mishin Diaries 1-319).
1966 December 2 - .
- Mishin discussion with Tregub YaI on 7K-L1 with crew delivery via 7K-OK. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK. (Mishin Diaries 1-252).
1966 December 6 - .
- Cosmos 133 probably self-destructed - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The wreckage of Cosmos 133 has not been found. NII-4 has calculated, based on PVO tracking data that the re-entry capsule probably passed over Orsk at 70 to 100 kilometres altitude. The APO self-destruct system sensed the overshoot and exploded. The fragments would have fallen into the Pacific Ocean east of the Marianas Islands. Further searching is called off. Meanwhile, with only three months to go before the first flight of the L1 circumlunar spacecraft, the VPK has finally woken up to the total lack of preparation for location and recovery of the returning space capsule if it comes down outside of Soviet territory.
1966 December 7 - .
- Soyuz and L1 crew assignments. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Kerimov,
Khrunov,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Rudenko,
Shatalov,
Volkov,
Volynov,
Yeliseyev,
Yershov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Soyuz s/n 5/6,
Soyuz s/n 7.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Rudenko, Mishin, Kerimov and Kamanin agree on crews for upcoming flights. Komarov, Bykovsky, Khrunov, and Yeliseyev are assigned to Soyuz s/n 3 and 4; Gagarin, Nikolayev, Gorbatko, and Kubasov to Soyuz s/n 5 and 6, with Beregovoi, Shatalov, Volkov, and Makarov trained as back-ups. For Soyuz s/n 7, which will conduct space welding experiments with the Vulkan furnace, the commander will be either Komarov, Bykovsky, Gagarin, Nikolayev, Beregovoi, or Shatalov. The other two crewmembers will be either Lankin and Fartushniy from the Paton Institute, VVS cosmonaut Kolodin, or an engineer from OKB-1.
Crews for the L1 must be named in order to complete the five-month training program in time. Eight L1's are being completed to the manned configuration, but Mishin believes it is necessary to plan for only six manned missions. It is decided to train nine crews. Spacecraft commanders will be Komarov, Bykovsky, Nikolayev, Gagarin, Leonov, Khrunov, Volynov, Beregovoi, and Shatalov. Flight engineers will be Yeliseyev, Kubasov, Makarov, Volkov, and Grechko. Komarov, Bykovsky or Nikolayev will command the first circumlunar flight. Mishin promises to name the OKB-1 candidates for that flight by 8 December. Mishin and Kerimov agree that training of cosmonaut- researchers from the Academy of Sciences may begin, although both Mishin and Rudenko expressed doubts about cosmonaut candidate Yershov.
The failures of Cosmos 133 have been narrowed to entangled thrust vector vanes in the main engines and a single defective approach and orientation thruster. It is agreed to set the unmanned launch of Soyuz s/n 1 for 18 December as a final functional check of all systems. If this is successful, the date will then be set for the manned launch of Soyuz s/n 3 and 4. Flight control will be conducted from Yevpatoria.
1966 December 8 - .
- Soyuz parachute problems unresolved - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Shatalov,
Volkov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The newly named crew for Soyuz s/n 7 begin zero-G training on the Tu-104 (Beregovoi, Shatalov, Volkov and Makarov). A review will be held of the SAS emergency recovery system in Vladimirovka tomorrow. VVS engineers are worried about the hydrogen peroxide venting which has burned parachute lines on two occasions. It is not believed that Soyuz s/n 1 can complete all tests to verify the systems that failed on s/n 2 before 18 December. It is clear that Mishin cannot resist the pressure from the leadership to hurry, and is cutting out pre-launch tests, with an inevitable decrease in the chances for mission success. TsNII-30 has been given until the end of December complete plans for search and recovery of returning lunar spacecraft. But Mishin and OKB-1 have not provided the necessary trajectory data for such planning.
1966 December 9 - .
- Soyuz State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Mnatsakanian,
Smirnov,
Tsybin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The investigative committees unanimously concluded that the problems with Cosmos 133 were not due to any fundamental design defects, but rather poor pre-launch quality control and testing which did not reveal the problems. All Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft will be reworked to remove the problems by 15 December. The go-ahead is given to launch Soyuz s/n 1 between 15-18 December. Only Mnatsakanyan, designer of the automatic docking system, objects to the idea of a single spacecraft test flight. Tsybin reports that over four hundred system and subsystem qualification tests have been completed on Soyuz. However some vacuum tests in the TBK-60 chamber, and tests of the back-up parachute system and emergency recovery system will not be completed until 10 January 1967. Tsybin is ordered to accelerate the work so that the entire spacecraft is qualified for manned flight by 5 January. Mishin states that, assuming the flight of s/n 1 is successful, the manned flight of Soyuz s/n 3 and 4 can begin by 29 January 1967. Kamanin is reminded that Smirnov's cancellation of the Voskhod 3 launch in June, based on the promise that Soyuz would fly by October, has instead resulted in almost two years without a Soviet manned spaceflight.
Later Kamanin learns that Malinovskiy is dying of cancer and will not return to work. Kamanin prays for his own health in the remaining five to seven years until his retirement. He will be able to retire peacefully only once Soviet voyages to the lunar surface have become routine.
1966 December 10 - .
- L1 production and flight plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Mishin briefs the production plan for the L1 circumlunar spacecraft. Two spacecraft, s/n 1 and 2, have already been shipped to Tyuratam. These prototypes are not equipped with heat shields, and will be used to perfect orbital operation of the spacecraft without recovery of the capsule. L1 s/n 3 and 4 will be used for unmanned flights around the moon, with recovery on earth, in March to May 1967. The first manned flight around the moon is set for 25 June. All present, after examining the detailed production and training plans, object that they cannot be met. Mishin advises that Ustinov and Smirnov dictated the schedules and they are not subject to revision.
1966 December 10 - .
- Soviets view scope of American Apollo program with dismay - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko,
Ivashutin,
Rudenko,
Vershinin,
Zakharov.
Program: Soyuz,
Apollo,
Lunar L1.
Grechko, Zakharov, Shtemenko, Ivashutin, Vershinin, Rudenko and with dozens of other generals view a film prepared by the GRU on the American Apollo program. It gives the viewers a clear idea of the immense scale of the American program, which dwarfs the resources the Soviets have devoted to their counterpart. Kamanin believes it clearly demonstrates why the Soviet Union is lagging in the space race and how illusory is the hope of ever regaining the lead.
1966 December 12 - .
- Second Soyuz rolled out to pad - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kerimov,
Mishin,
Rudenko,
Smirnov,
Tyulin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
At Tyuratam, the staff views American films on the Gemini program. Kamanin notes the use of manual methods for rendezvous and docking, and the use of an umbilical cord to supply oxygen to the spacewalker as opposed to an autonomous backpack. Despite over a hundred training sessions, American astronauts have experienced pulse rates of over 160 per minute, immense fatigue and overwhelming perspiration on their spacewalks. Three of their four EVA's were curtailed because of these and other unforeseen complications. This clearly indicates how Mishin, Smirnov, Kerimov, Tyulin, and Rudenko have underestimated the danger and difficulty of this work. The booster for Soyuz s/n 1 has been erected at Area 31 and the missile crews have gone home for the weekend. Kamanin credits Mishin for being ahead of schedule for the first time ever - he believes he can launch on 14 December.
1966 December 14 - .
- Soyuz SAS firing destroys booster and pad - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The second attempt to launch a Soyuz spacecraft ends tragically. The State Commission had met at Area 31 at 11:00. Mishin reported complete readiness for launching, which was set for 16:00 local time. Fifteen minutes before launch the observers move to the observation post 300 metres from the pad. At the ignition command, a smaller-than-usual amount of flame and smoke appeared, and the rocket did not rise. Several seconds later orders to flood the pad with water were given. The fire subsided, and the rocket remained on the pad, steaming more than usual. Over a half hour later, the order to clear the area is given, and Kamanin goes to phone the airfield from the Cosmonaut Dormitory to cancel the planned takeoff of the aircraft that was to take the flight control team to Yevpatoriya. As Kamanin ascends the staircase to the dormitory's second floor, he hears a muffled explosion, runs outside, and sees a large parachute descending 600 to 700 m beyond the MIK assembly building. He understands immediately that the booster has exploded and the capsule has been hurled away from the pad by the SAS escape tower. From the third floor of the dormitory the burning rocket could be seen on the pad. Kamanin orders everyone away from the windows before the first stage blows, and two seconds later there is a flash, and a series of powerful explosions blow out all the windows and shower everyone with plaster from the ceiling. The dormitory was 700 m from the pad, but buildings even a kilometre from the pad were damaged. Telephone communications with the bunker and pad were cut, and the fate of Mishin, Kerimov, and Kirillov, and others near the pad was unknown. It is clear further Soyuz flights will be delayed by several months, especially due to the need to repair the pad for the two-spacecraft mission. In fact, the entire Soviet lunar flight schedule is questionable now.
1966 December 14 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511. FAILURE: Erroneous firing of launch escape tower ignited launch vehicle on the pad.. Failed Stage: P.
- Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 2 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (A) s/n 1. Mass: 6,560 kg (14,460 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Second attempted flight of Soyuz 7K-OK (the spacecraft planned for the linkup with Ksomos 133). An analogue to Mercury Redstone's 'day we launched the tower' but with more disastorous consequences. The core stage ignited, but the strap-ons did not. A booster shutdown was commanded. The service towers were brought back around the booster, and ground crew began work to defuel the launch vehicle. At 27 minutes after the original launch attempt, the Soyuz launch escape system, having received the signal that liftoff had occurred, detected that the booster was not on course (either because a tower arm nudged the booster or because the earth's rotation as detected by the gyros had moved the spacecraft out of limits relative to its original inertial position). The launch escape system ignited, pulling the Soyuz away from the booster, igniting the third stage fuel tanks, leading to an explosion that severely damaged the pad and killed at least one person (the Soviet Rocket Forces major supervising the launch team) and injured many others.
1966 December 15 - .
- Soyuz failure in detail - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kerimov,
Kirillov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kerimov, Mishin, and Kirillov were nearly scared to death but escaped unharmed. A fuller account of yesterday's events is available. At the command "ignition", only the second stage engines of the core vehicle ignited; the first stage strap-ons did not, therefore the rocket did not develop enough thrust to move an inch. On the order to flood the pad, all power was cut off to the rocket and equipment. 35-40 minutes after shutdown of the booster and the flooding, only steam and oxygen vapour were rising from the pad. Mishin and Kirillov emerged from the bunker and approached the rocket. They decided the danger was past, and gave the command for the service gantries to be raised, to protect the rocket from wind gusts. As the gantry arms reached the upper stage, and personnel were climbing up to service the rocket, one arm tilted the dislocated rocket more than seven degrees from the vertical. At such an angle the SAS abort sequence was activated. The solid rockets of the SAS abort motor suddenly ignited, pulling the Soyuz capsule 600 m into the sky, but also setting the third stage of the rocket on fire. This immediately alerted Mishin, Kerimov, and Kirillov to take cover in the bunker, while others were able to run to 100 to 200 m from the pad in the two minutes before the first stage exploded. A Major Korostylev and a group of soldiers decided instead to take cover behind the concrete wall of the pad, and paid for this decision with their lives or severe injuries. A preliminary accident commission meeting was convened at 09:00 at Area 2. An oxygen bypass valve failure several seconds after the ignition command is blamed for the shutdown of the first-stage engines. Although final acceptance tests of the SAS tower only began at Vladimirovka on 10 December, it is noted that the SAS system has actually just passed its most realistic test - it saved the Soyuz capsule, which landed 300 meters from the pad. Examining the blackened and smoking pad later, it is estimated it will take at least six months to get it back into operation.
1966 December 16 - .
- Manned Soyuz flights delayed to March - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The State Commission sets a new schedule, with the launch of a single unmanned Soyuz planned for 15 January 1967. Spacecraft s/n 3 and 5 will be prepared in parallel for this flight. The booster will be prepared at Area 2, and the spacecraft at Area 31. Launch of two manned Soyuz spacecraft will take place in March at the earliest.
1966 December 16 - .
- Soyuz post-mortem - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin views film of the Soyuz SAS failure and subsequent first stage explosion. The film is of little help, being taken from far away and the camera jiggling. Afanasyev arrives in Tyuratam that evening and is domiciled in the house in Area 17 used by Khrushchev and DeGaulle during their stay. Kamanin leaves for Moscow, but ends up having to take the train from Kuibyshev due to sustained poor weather. Meanwhile Afanasyev heads the State Commission at Tyuratam. Mishin bravely confesses that OKB-1's design of the SAS system had fundamental errors in logic. It was found that after power was removed from the SAS during the booster deactivation process, the gyroscopes would slowly rise to the stops of their supports, which in turn would trigger firing of the abort rocket. It had previously been thought there were only three ways to fire the SAS: by command from the flight director, when the flight angle of the rocket dropped below seven degrees, or when the combustion chamber pressure dropped below a specific level. The subsequent fire in the booster was inevitable since the separation of the descent module of Soyuz from the instrument compartment was accomplished by firing 32 squib charges. The commission hears with alarm that a test of the SAS on 11 December at Vladimirovka also started a small fire for about a minute, but it was restricted to the Soyuz instrument module since the dummy third stage was not fuelled. This was considered insignificant at the time, but the failure to report it prior to the launch attempt of 14 December is now seen as a major failure of communications. Mishin's resolve to accept the blame does not last long - he soon tries to blame the engine manufacturer. However Glushko's representative proves that the first stage shut down because of a failed oxygen valve in the Block G strap-on. Normally this could be repaired and the launch reattempted within three days. The reason for the catastrophe was the defective logic of Mishin's SAS system.
1966 December 20 - .
- Americans have understood true purpose of Cosmos 133 mission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Nikolayev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin meets with key personnel of the TsPK and explains the reasons for the Soyuz incident, noting inadequate understanding of the abort systems. Kamanin orders improved medical examination of cosmonauts immediately after flight at the recovery site. Gagarin and Nikolayev request that the Soyuz crews now be allowed to take leave. Reports in the American press show that their experts have correctly interpreted the true nature of Cosmos 133 as a manned precursor mission. The American press alleges that there were two other explosions of the spacecraft in the USSR during September and October.
1966 December 22 - .
- Recent failures blamed on Mishin - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin, Vershinin. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 1, Soyuz 2A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Vershinin has explained to the General Staff that recent Soviet space failures were due to poor development and testing by industry, and the personal deficiencies of Mishin..
1966 December 23 - .
- SAS abort system modifications ordered - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 1, Soyuz 2A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. The State Commission finds that the 14 December uncommanded SAS escape tower firing was the fault of the system designers. They directed that a number of the modifications of the SAS be made..
1966 December 28 - .
- Soyuz-VI to fly by end of 1967. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Kozlov. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz VI. Resolution 'On approval of work on the 7K-VI Zvezda and course of work on Almaz' no. 305 ordered Kozlov's filial 3 of OKB-1 to undertake first flight of the manned military research spacecraft 7K-VI - 11F73 Zvezda by the end of 1967..
1966 December 31 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- 18 cosmonauts in lunar training - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Artyukhin, Belousov, Bykovsky, Dobrovolsky, Gagarin, Gorbatko, Gubarev, Gulyayev, Khrunov, Kolesnikov, Kolodin, Komarov, Nikolayev, Popovich, Volynov, Voronov, Zholobov. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. Gagarin, Komarov, Nikolayev, Bykovsky, Khrunov, Gorbatko, Voronov, Kolodin, Popovich, Gubarev, Artyukhin, Gylyayev, Belousov, Kolesnikov, Volynov, Doborvolsky, Zhobolov..
1966 December 31 - .
- Second session of the L1 State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Chelomei,
Mishin,
Ryazanskiy,
Spitsa,
Zakharov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Mishin, Chelomei and Barmin report that the spacecraft, booster, and launch facilities are ready. The first unmanned launch of the L1 is set for the end of January, with the arrival of the members of state commission at Tyuratam on 10-12 January.
The commission then considers reports on improvements needed for command, control, and recovery of manned lunar spacecraft. General Spitsa and Chief Designer Ryazanskiy list needed improvements to tracking and communications stations. These will cost more than 100 million roubles, including 50 million to equipment tracking ships. Tracking stations at Yevpatoria and Ussuriysk will require extensive new equipment for control of lunar spacecraft. Officers from TsNII-30 report on enhancements required for search and recovery forces. Due to the worldwide requirement, this can no longer be handled by the VVS alone - naval, long-range aviation, and communications forces need to be involved. Returning lunar ships will be targeted for landing on Soviet territory, but there is a great probability in the event of guidance problems of a splashdown in the Indian Ocean or a landing in Iran, Pakistan, or India. The VVS only has very limited capability for sea search and rescue. On 21 December Marshal Zakharov split manned spacecraft recovery responsibility between the VVS and VMF. To enable search and recovery of spacecraft at sea or on land outside of Soviet territory will require 12,000 to 15,000 personnel and dozens of ships, aircraft, and helicopters. A new net of ground-based radio stations and direction finders will also be needed. This will cost hundreds of millions of roubles to implement. The cost must be borne - it is clearly unacceptable that a Soviet crew fly to the moon and back, only to perish on return to earth due to inadequate recovery forces. A special subcommittee under Marshal Rudenko is named to handle the matter. Kamanin reports on training plans for lunar spacecraft. Crew training will have to begin in January 1967 for crews to complete the five-month syllabus in time for the planned flight dates. L1 commanders must be pilots with prior spaceflight experience. The second cosmonaut need not have flown before. Training of L1 and 7K-LOK crews must be carried out in parallel and separately in order to meet schedules. Mishin, the Ministry of Public Health, and Kamanin should name the crews for thee flights within five days in order to make schedule.
1967 January - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- First L-1 Zond spacecraft mated to Proton - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1P #1. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Fit tests at Tyuratam. Not launched (Interavia SD)..
1967 January 5 - .
- Cosmonaut training status - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Titov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz VI,
Voskhod.
Crews are in training for Voskhod, Soyuz, Lunar L-1, Almaz, and 7K-VI missions. There will be 100 cosmonauts in training by February. Meanwhile the Americans have conducted 10 manned flights since the last Soviet manned flight in March 1965. The cosmonauts want Kamanin to be training 8 crews for L-1 translunar flights, but he only has 4 in training. He doesn't think it is worth to train more, since if one successful L-1 flight is conducted before the 50th Anniversary of the Soviet Union in November 1957, all subsequent flights will be cancelled. Additional Details: here....
1967 January 17 - .
- Manned space plans reviewed - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Artyukhin, Belyayev, Beregovoi, Bykovsky, Gagarin, Gorbatko, Grechko, Khrunov, Klimuk, Kolodin, Komarov, Kubasov, Leonov, Makarov, Nikolayev, Popovich, Rukavishnikov, Sevastyanov, Shatalov, Volkov, Volynov, Voronov, Yeliseyev. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 1, Soyuz 2A. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK. At a meeting of the VPK Military-Industrial Commission and Chief Designers current manned space plans are reviewed.. Additional Details: here....
1967 February 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Government approves landing on moon by end 1968 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Soviet government approves plan to land cosmonaut on moon by end 1968. N-1 test plan approved, envisioning third quarter 1967 as beginning of flight hardware construction. Fall-back project would be manned circumlunar mission. First manned L1 mission imagined as early as June 1967. First N1 launch by March 1968.
1967 February 4 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- UR-500K/L1 manned circumlunar design authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 115-46 'On the Progress of the Work on the Development of the UR500K-L1 --confirmation of schedule for piloted lunar missions' was issued..
1967 February 7 - . 03:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 140 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (P) s/n 3. Mass: 6,450 kg (14,210 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 1.98 days. Decay Date: 1967-02-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 2667 . COSPAR: 1967-009A. Apogee: 216 km (134 mi). Perigee: 169 km (105 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
After the self-destruction of the first Soyuz 7K-OK on re-entry, and the loss of the second one on the pad fire in December, the state commission ruled that the third 7K-OK model would be flown unpiloted on a solo mission. If this was successful then the fourth and fifth Soyuz would be flown on a manned docking mission. Once in orbit Cosmos 140 experienced attitude control problems due to a faulty star sensor resulting in excessive fuel consumption. The spacecraft couldn't keep the required orientation towards the sun to keep the solar panels illuminated, and the batteries discharged. Despite all of these problems the spacecraft remained controllable. An attempted manoeuvre on the 22nd revolution still showed problems with the control system. It malfunctioned yet again during retrofire, leading to a steeper than planned uncontrolled ballistic re-entry. The re-entry capsule itself had depressurised on separation from the service module due to a fault in the base of the capsule. A 300 mm hole burned through in the heat shield during re-entry. Although such events would have been lethal to any human occupants, the capsule's recovery systems operated and the capsule crashed through the ice of the frozen Aral Sea, 3 km from shore and 500 kilometres short of the intended landing zone. The spacecraft finally sank in 10 meters of water and had to be retrieved by divers. Still, the mission was deemed 'good enough' for the next mission to be a manned two-craft docking and crew transfer space spectacular. Mishin and Kamanin felt that a human crew could have sorted out the problems. They were also under intense pressure to achieve a manned circumlunar flight before the 50th Anniversary of the Soviet Revolution in October.
1967 March 10 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Cosmos 146 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1P s/n 2P. Mass: 5,017 kg (11,060 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Duration: 7.90 days. Decay Date: 1967-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 2705 . COSPAR: 1967-021A. Apogee: 312 km (193 mi). Perigee: 178 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 89.30 min.
Protoype Soyuz 7K-L1P launched by Proton into planned highly elliptical earth orbit. The first flight four-stage Proton rocket began assembly on 21 November 1966, with mechanical assembly completed by 29 November. Electrical connections and tests were completed by 4 December 1966. Due to New Year's holidays work did not resume until 28 January 1967. By 28 February the fully assembled booster / spacecraft unit was completed in the MIK, including the 7K-L1P boilerplate spacecraft. The launch tower was added on 2 March 1967 and the system was declared ready for launch. A serious potential problem during preparations was the discovery that fuel gases could lead to pump cavitation at the turbine exits. Tests on the ground showed that the problem was not the fuel itself, but in the monitoring equipment. The launch vehicle and Block D stage functioned correctly and put the spacecraft into a translunar trajectory. The spacecraft was not aimed at the moon, did not have a heat shield for reentry, and no recovery was planned or attempted. A successful launch that created false confidence just before the string of failures that would follow.
1967 March 12 - .
- Spiral and Soyuz training - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Spiral OS.
Titov visits Kamanin on leave from test pilot duties at Vladimirovka. Titov will spend a year training as a test pilot on MiG-21, Su-7, and Su-9 aircraft. He flies well, and has matured and changed for the better over the last two years. Kamanin has talked to him 3 or 4 times about his future plans. Titov has bound his future with the Spiral spaceplane programme. Additional Details: here....
1967 March 15 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- CIA reports on Soviet space developments - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. CIA reports accurately development of N-1, Almaz, Proton, etc.... even states 100,000 kg large space station in development for launch by N-1 by 1969. CIA does not expect lunar landing until early 1970's..
1967 March 16 - .
- Soyuz state commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Mishin,
Smirnov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soyuz 1/2 crews had planned to depart for Baikonur on 30 March, but Mishin wants to push this forward to the night of 17/18 March. This disrupts all of Kamanin's training plans and shows the poor planning and work of Mishin and his followers. A Soyuz state commission is held. Kamanin doesn't trust Mishin. The spacecraft is unreliable and incompletely tested. But it is decided all the conditions exist for a launch of the mission on 20-25 April. The question of Gagarin flying on the mission is brought up. The Communist Party says he is too valuable to risk on further spaceflights. Kamanin is against making him a living 'museum exhibit'. Smirnov agrees to raise the matter with the Politburo.
1967 March 20 - .
- Soyuz 1 preparations - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The cosmonauts have given up on further training at Baikonur due to the incomplete state of the spacecraft and returned to Moscow. Kamanin wanted to confront Mishin on the issue - this was all his fault, six days wasted - but Mishin never even showed up on the plane for the flight to Baikonur.
1967 March 22 - .
- L1 flight scenario undecided - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Kerimov,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Volynov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Kerimov argued with Mishin that without any logical reason his demand that the cosmonauts go to the cosmodrome for training has disrupted their preparation schedule. Later Kamanin met with Gagarin, Leonov, Volynov, and Makarov, all selected as pilots for L1 lunar flybys. The L1 flight scenario was still open. Variant 1 would involve launch of two spacecraft, with transfer of one to two crew to the translunar spacecraft in earth orbit. Variant 2 would be a direct flight to the moon. Additional Details: here....
1967 March 23 - .
- L1 State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
A State Commission is held on the impending L1 translunar flights. A major issue is the L1 tracking/recovery radio beacon and the Zarya-3 deep space communications system. Launches of prototype L1P spacecraft are planned for April and May, with the first all-up L1 in June. All commission members are confident a Soviet man will the first around the moon by the end of the year. The State Commission also considers the pending Soyuz 1 / Soyuz 2 flight.
1967 April 1 - .
- Manual docking for Soyuz 1/2 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Komarov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Ustinov reviews the cosmonauts. Kamanin urges that a manual docking be allowed on the Soyuz 1/2 mission - he had argued the same point with Korolev before his death. Komarov say he can accomplish a manual docking from 350 km range (once the Igla automatic system has brought him there from 23 km range). There follows a discussion of an all-female flight. Four female cosmonauts would be assigned to the mission, and Kamanin would need 5 to 6 months to complete there training. The mission is designated 'Voskhod-6'.
1967 April 8 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D ullage rocket failure; no restart.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 154 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1P s/n 3P. Mass: 5,020 kg (11,060 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Mishin,
Tsybin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Duration: 1.98 days. Decay Date: 1967-04-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 2745 . COSPAR: 1967-032A. Apogee: 203 km (126 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
Protoype Soyuz 7K-L1 manned circumlunar spacecraft. There are high winds for the L1 launch, 15-17 m/s. The official limit is 20 m/s, but Chelomei wants to scrub the launch if winds go over 15 m/s. Nevertheless the launch proceeds in 17-18 m/s winds and the L1 reached earth orbit. However the Block D translunar injection stage failed to fire (ullage rockets, which had to fire to settle propellants in tanks before main engine fired, were jettisoned prematurely). The failure is blamed on Mishin and has Tsybin seething in anger. Mishin is disorganised and has made many mistakes. Spacecraft burned up two days later when orbit decayed. Later in the day comes the news the RTS has to be replaced on one of the Soyuz 1/2 spacecraft. This will have a 3 to 4 day schedule impact, and push the launch back to 15-20 April. The crews arrive the same day for the upcoming Soyuz launch.
1967 April 12 - .
- Chaos at Area 31. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Kerimov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The cosmonauts began work at 10:30 in the morning, and didn't complete work until 23:30 at night. They spent 16 hours working on Cosmonaut's Day, due to the criminally chaotic performance of TsKBEM. The cosmonauts have to train simultaneously for the Soyuz and L1 missions. Kamanin warns Kerimov about the unacceptable situation. Grechko arrives to head the state commission. The launch of Soyuz 1 is set for 24-25 April - there will be only eight days to fix all of the problems. The energy and optimism of Korolev is sorely missed. Mishin was a poor deputy, and a worse leader - his constant mistakes and stupidity delay work and aggravate people. The cosmonauts have to keep in shape by playing tennis, but there is only one court at Tyuratam - a second court is to be built eventually (!)
1967 April 14 - .
- Huge blow-up at Tyuratam. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The cosmonauts are completely trained, ready for launch at any time with four hours notice. Then Mishin calls Ustinov and tells him that their training is what is holding up the Soyuz 1 launch! From the point of view of the military quality assurance inspectors, there are 100 unresolved discrepancies on Soyuz 1 - the spacecraft is a piece of shit.
1967 April 16 - .
- Soyuz 1 is moved to the integration hall. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soyuz 2 crew trains from 15:00 to 20:00 - they had to wait due to problems with the spacecraft, but then the training went all right. The argument continues on whether to do an automatic or a manual docking. The design bureau wants to use the Igla automatic system; the cosmonauts want to do it manually. They have done 800 dockings in the simulator, so they should know best, in Kamanin's opinion. They want to let the automatic system take the spacecraft up to 50 to 70 m from the target, then use manual maneuvering to proceed to dock. The number two valve on the Soyuz 1 spacecraft's nitrogen tank was inadvertently opened during preparation. It was said not to be serious, but the problems are getting on everyone's nerves.
1967 April 20 - .
- Soyuz 1/2 State Commission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
150 people attend. The readiness of the spacecraft and launch vehicles are confirmed. The final responsibilities and schedule are approved. Everything is go. Afterwards there is a meeting with Mishin. He is mainly worried about two things that could cause them to scrub the launch of the second Soyuz: a failure of the Igla automatic docking system or the solar panels on Soyuz 1.
1967 April 23 - . 00:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 1 - .
Call Sign: Rubin (Ruby ). Crew: Komarov.
Backup Crew: Gagarin.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 4. Mass: 6,450 kg (14,210 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 1.12 days. Decay Date: 1967-04-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 2759 . COSPAR: 1967-037A. Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 197 km (122 mi). Inclination: 50.80 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Space disaster that put back Soviet lunar program 18 months. Soyuz 1 as active spacecraft was launched first. Soyuz 2, with a 3 man crew would launch the following day, with 2 cosmonauts spacewalking to Soyuz 1. However immediately after orbital insertion Komarov's problems started. One of the solar panels failed to deploy, staying wrapped around the service module. Although only receiving half of the planned solar power, an attempt was made to manoeuvre the spacecraft. This failed because of interference of the reaction control system exhaust with the ion flow sensors that were one of the Soyuz' main methods of orientation. Additional Details: here....
1967 April 24 - .
- Crash of Soyuz 1. Cosmonaut Vladimir Mikhailovich Komarov is killed at age 40. - .
Return Crew: Komarov.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Komarov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
The decision was made to bring Komarov back due to an undeployed solar panel which reduced electrical power and blocked orientation sensors. Re-entry was successful and the drag chute deployed. However due to a flaw during manufacture, the parachute compartment housing was too rough and the main parachute would not deploy. Komarov released the reserve chute, but it became tangled with the drag chute. The descent module crashed into a field near Orenburg at 03:24 GMT. Additional Details: here....
1967 April 26 - .
- Komarov state funeral. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Komarov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 1. Komarov's ashes are interred in the wall of the Kremlin..
1967 April - .
- Soyuz 2A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Bykovsky,
Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Backup Crew: Gorbatko,
Kubasov,
Nikolayev.
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The first manned Soyuz flights were an attempt at an 'all up' manned rendezvous, docking, and crew transfer spectacular (eventually accomplished by Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5). Komarov was the pilot for the Soyuz 1 active spacecraft, which would be launched first. Soyuz 2, with the crew of Bykovsky, Khrunov, and Yeliseyev would launch the following day, with Khrunov and Yeliseyev space-walking to Soyuz 1 and returning to earth with Komarov. Komarov's spacecraft developed serious problems after launch, including the failure of one of the spacecraft's solar panels to deploy. The Soyuz 2 crew were given the order to rendezvous with Soyuz 1 and to try during the planned EVA to unfold the undeployed solar panel. But the launch of Soyuz 2 was cancelled due to heavy rain at the cosmodrome. Low on power and battery reserves, Komarov made an attempt to land the following day. Parachute failure led to the crash of Soyuz 1 and the death of Komarov. After the disaster the Soyuz 2 spacecraft was checked, and the parachute system had the same technical failure. If Soyuz 2 had launched, the docking may have been successful, but then both spacecraft would have crashed on landing, killing four cosmonauts instead of one.
1967 April 27 - .
- State Commission on Soyuz 1 crash. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Gagarin,
Serbin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Ustinov convened the commission at noon. The work was to be completed by 15 May, and the final report issued by 25 May. The members of the commission would be Ustinov, Smirnov, Serbin, Afanasyev, the Chief Designers, and Gagarin. 22 members would work in seven subcommittees that would:
- Investigate design and test of the spacecraft structures
- Investigate design and test of the landing and parachute systems
- Investigate design and test of the orientation and guidance systems
- Study the performance of the tracking, communications, and flight ground control systems
- Investigate design and test of the launch system
- Analyse the contents of the Mir-3 flight data recorder, telemetry, and space-to-earth communications
- Review the design and as-built documentation for the spacecraft, subsystems, training program, flight plan, and the on-board flight log
1967 April 29 - .
- L1 trainer review. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Darevskiy,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Review of progress on the L1 trainer MN-17, consisting of the SA and NO of the spacecraft It was built by the Factory Brigade headed by Darevskiy and was finished three to four weeks ago. But there is still the question of the cosmonauts conducting autonomous navigation. Tyulin and Mishin promised a solution long ago, but nothing has been delivered to date.
1967 May 5 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, N11.
- Recommendation that podsadka be dropped and L1 direct flight become the baseline. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soviet of Chief Designers met with the Civil Chief Designer UR500K-L1 and recommended that podsadka be dropped and direct flight become the baseline. This was evidently to make possible the objective of a Soviet man around the moon before 4 October 1967. The reasons given were:
a) The successful flights of the UR-500K and Block D on the L1 2P and 3P and the further 4 separate UR-500 launches provided confidence in the launch vehicle's reliability.
b) The main delays with L1 development will be in relation to development by BTsVM of the Argon-11 digital computer for its control system.
c) The failure of 7K-OK number 4 (Soyuz 1) indicated a delay in development of docking in earth orbit.
It was recommended that the 7K-L1 launch sequence be revised to two missions per month as follows:
- 4L - "Zond" unmanned 17 - 29 June 1966
- 5L - unmanned, circumlunar, 27 June - 5 July
- 6L - "Zond", unmanned, 12 - 17 July
- 7L - unmanned, circumlunar, 25 July - 3 August
Followed by manned launches according to astronomical constraints (which would mean 23 August, 21 September, 19 October). (Mishin Diaries 2-22)
1967 May 5 - .
- Gagarin and Leonov want Mishin cited in Soyuz crash report. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Leonov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Gagarin and Leonov meet with Kamanin. They discuss the complete inadequacy of Mishin - his excitability, poor knowledge of the Soyuz spacecraft and the details of its operation, his lack of cooperation in working with the cosmonauts in flight and training activities. They urge that these facts be documented in the Komarov crash commission report. Problems are discussed with getting an additional Tu-104 for zero-G/one sixth-G training. Three are needed, and only two have been made available. Even these two can only be used for 23 flights up to 10 August, after which they must be sent away for ejection seat modifications.
1967 May 6 - .
- Chief Designers favour direct L1 flight to the moon - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Tyulin calls Kamanin. He reports that all of the Chief Designers are in favour of direct L1 flight to the moon instead of the earth orbit rendezvous method. However the Central Committee wants to see four consecutive successful unmanned flights, rather than two, before a manned L1 flight can be made.
1967 May 7 - .
- Soyuz return-to-flight plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Aboard Mishin's aircraft, he discusses his plans with Kamanin. He plans to launch two unmanned Soyuz spacecraft in the second half of July. An automated docking will be attempted, but the mission will be considered successful if the spacecraft rendezvous in space and approach to within 50 to 70 m of each other. He expects to follow this in August with a manned rendezvous, docking, and crew transfer mission. Two further pairs of spacecraft will be available by November 1967. This means a total of eight crews, including back-up crews, will have to be trained. He wants Feoktistov to fly on one of these missions. Kamanin tells Mishin that it will take two to three months to prepare Feoktistov for flight and will be too disruptive to flight training. After arriving at Fedosiya they attend a Soyuz 1 State Commission meeting from 10:00 to 13:00. Tests of the Soyuz parachute system are to be conducted beginning 14 May, on two mass models and one Soyuz mock-up.
1967 May 15 - .
- Soyuz parachute test results. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
In the first drop, the reserve parachute didn't open. In the second test, it did inflate, but only after a delay of twenty seconds. TsAGI studies show the drogue chute is creating an area of turbulence in the wake of the capsule, and the reserve chute is deploying right into that zone of chaotic air, preventing it from inflating. Tests on the parachute show that while it was designed to deploy with 1.8 tonnes of drag force from the drogue chute, it actually requires 3-4 tonnes of force to pull the packed parachute out of the container and allow parachute deployment. The parachute fails at 8 tonne load. The Soyuz parachute system is supposed to have a reliability of 95% ... and this essential problem was unknown...
1967 May 20 - .
- LII Soyuz parachute findings - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The drop of the Soyuz 1 mock-up at Fedosiya was cancelled due to the great likelihood of loss of the spacecraft and the low likelihood of obtaining any new data as a result. The LII assessment of the parachute system has been completed:
- The likely cause of non-deployment of the primary parachute on Soyuz 1 was insufficient drag force created by the drogue chute to pull it out of the container (the drogue needs to produce 3 tonnes of force, but tests show only 1.1 to 1.8 tonnes of force are being produced at an ambient pressure of 0.67 atmospheres)
- The reliable operation of the reserve parachute and the drogue parachute at the same time was never demonstrated in trials. The chance of them getting tangled was actually very likely.
- Remove the reserve parachute and have a system of two main parachutes, with landing possible even if one of the main chutes does not deploy
- Develop through extensive actual testing reliable inflation of the drogue chute
- Add controls to allow manual parachute deployment by the crew, with appropriate cockpit instruments
- Increase the jettison time of the heat shield from 60.7 seconds to 100 seconds after parachute deployment to allow the full interval for operation of the automatic landing system.
1967 May 22 - .
- LII Soyuz parachute recommendations impractical. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The conclusions of the LII study are found to be sound, but it would take months or even years to implement such an extensive spacecraft redesign. Mishin is still under orders to fly a manned mission around the moon by the 50th Anniversary of the Russian Revolution in October.
1967 May 26 - .
- Soyuz 1 Commission report is reviewed. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Gagarin,
Kerimov,
Tyulin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Afanasyev, Kerimov, and Tyulin object to Kamanin's conclusion that problems exist with the automated landing system and that a manual backup is needed. They want to find fault only with the parachute. The findings of VVS LII, and TsAGI are discussed. Later Kamanin has an unpleasant conversation with Gagarin. He wants to remove control of the manned flight control centre away from the MOM. Kamanin believes this is contrary to the interests of the Ministry of Defence.
1967 May 29 - .
- Soviet of Chief Designers. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Tkachev,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Tkachev, chief designer of parachute systems, rejects the findings of the Soyuz 1 state commission. His objections are overruled. The final decision is to adopt the conclusions of the commission in their entirety. Two unmanned Soyuz flights will take place in August, followed by manned flight in September. However the manned flights will go ahead only if the unmanned flights are entirely 'clean' - without any deviations. Beregovoi and Volynov are to head the first two crews.
1967 June 16 - .
- Mishin's notes indicate the revision of the L1 test program for the rest of the year. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
From this it can be seen that the podsadka still is considered essential:
(Mishin Diaries 2-2)..
VII VIII IX X XI XII
7K-OK 2 2 2 2 -
7K-L1 1 1 2 1 1 -
1967 July 16 - .
- Soviet space setbacks - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Feoktistov, Korolev, Mishin. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK. Kamanin observes in his diary that there will be no way a Soviet cosmonaut will fly in space in 1967 and blames it all on Mishin.. Additional Details: here....
1967 July 21 - .
- Soyuz spacecraft programme review is conducted. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Problems are identified with the parachutes and oxygen regeneration system which must be solved before the first manned flight..
1967 July 24 - .
- Cosmonaut group meeting. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Mishin is seen as jeopardising Soviet manned lunar plans. He has no understanding of the necessity of providing proper training simulators to prepare the cosmonauts for flight. He is coarse, rude, doesn't listen to critics, and ignores the comments of those who will have to fly aboard his spacecraft. The cosmonauts agree they should request a meeting with Brezhnev and tell him flat out - there will be no moon landing as long as Mishin is in charge. Additional Details: here....
1967 July 29 - .
- Review of Soyuz trainer status. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Mishin,
Tsybin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soyuz simulator has not been functional for three months -- entirely the fault of Mishin and Tsybin. The L1 trainer has not been finished, and the autonomous navigation system has not completed development. There are two prototype electronic computers at TsKBEM, but they are not complete and don't work. The first L1 spacecraft was to fly in May, but it is now clear it won't be ready until September at the earliest. There will be no manned lunar flyby for the fiftieth anniversary of the October Revolution as was ordered by the Party. Additional Details: here....
1967 August - .
- First flight of Soyuz VI planned for 1968 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Kozlov. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz VI. Kozlov was predicting first flight of the VI in 1968, with the first all-up operational flight in 1970..
1967 August 2 - .
- Manned spacecraft trainer status - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Bykovsky, Feoktistov, Nikolayev. Program: Lunar L3, Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-LOK, Soyuz 7K-OK. The Volga and Soyuz trainers are to be finally operational on 10 and 20 August respectively. The L1 trainer is not progressing and the L3 trainer exists only on paper.. Additional Details: here....
1967 August 8 - .
- Gagarin grounded. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Gagarin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The Soviet leadership has decided Gagarin is too important a propaganda asset to take any risks with his life. He is removed from the list of cosmonauts to be selected for space flights, and will be allowed to fly aircraft only with an instructor aboard. This ruling overrules a promise made by Kamanin to Gagarin that he would be put back on the flight rosterthat after he obtained his engineering diploma from the Zhukovskiy Academy on 1 May 1968. A vote is taken of the cosmonaut selection commission on Feoktistov's fitness for duty. The vote is 4:4, but then a quorum of at least 12 commission members is demanded. Feoktistov passes 9:8 in the final vote.
1967 August 9 - .
- Gorbatko grounded. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Gorbatko. Program: Soyuz. Gorbatko shows heart abnormalities in his EKG during a run on the TBK-60 centrifuge..
1967 August 14 - .
- Gulyayev grounded; Feoktistov in training. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Feoktistov, Gulyayev. Program: Soyuz. Cosmonaut Gulyayev has hit his head on a stone when diving in the Kholodniy River. Feoktistov continues his attempt to complete 30 months of command cosmonaut training in 75 days. The makes ten dockings in the Volga trainer - 8 of the are rated as 'bad'..
1967 August 24 - .
- Soyuz launch commission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Over 200 recommendations were made for revision of the parachute system, and all of these had to be made over the last two to three months. There have been 30 drops of the FAB-3000 Soyuz capsule mass simulator and two drops of capsule mock-ups. The entire series of tests is due to be completed by 20 September. This will allow flight of the first two manned spacecraft on 15 to 20 October. The commission is split over the selection of Feoktistov for the flight. It has to be referred to Smirnov and Ustinov for a final decision.
1967 August 31 - .
- 7K-VI Zvezda program review. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Darevskiy,
Kozlov.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz VI.
The 7K-VI military Soyuz was supposed to have been built on the basis of the 7K-OK model, with a first flight in December 1967. After all the problems with the 7K-OK, Kozlov replaced most subsystems and ended up with a basically new spacecraft, the Zvezda, which will have a mass of 6.3 to 6.6 tonnes. Officially first flight was set for the second half of 1968, but Kozlov says that even a flight in 1969 may not be possible. They simply can't meet the 21 July 1967 decree to have the spacecraft in service in 1968 - they need a further 18 to 24 months of development time. In Kamanin's opinion, this whole approach has been mismanaged. Urgent military experiments could have been flying long ago on a series of Voskhod flights. Furthermore there is no trainer yet for the 7K-VI. Kozlov says simply that he is not responsible for providing a trainer. Resort has to be made to a new design bureau set up specifically to produce simulators, headed by Darevskiy.
1967 September 13 - .
- Smirnov told Feoktistov unready for command. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Feoktistov, Smirnov, Vershinin. Program: Soyuz. Vershinin writes a letter to Smirnov on the subject of Feoktistov. He tells Smirnov he is not ready to be a spacecraft commander..
1967 September 19 - .
- L1 Launch Commission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The cosmonauts are training at Area 113, and the launch will be from Area 81. The State Commission meets from 15:00 to 18:30. So far there have been six successful Proton flights and only one failure. The Proton assembly was completed in 71 working days. UR-500 s/n 7 for this launch had 138 systems requiring rework at the launch site and 120 discrepancies (an increase: Proton number 5 for the first L1 launch had 208 reworks/223 discrepancies, while Proton number 6 for the first L1 launch was down to 70 reworks/194 defects). The L1 spacecraft had 15 notable defects on delivery, but this had increased to 100 by the time of the commission. Therefore Mishin should not be certifying readiness for launch. Manned flight to the moon requires a total mission probability of 0.99 to 0.9999, and Mishin puts the current Proton/L1 system reliability at only 0.6. It certainly has to be better- this is an 'all-up mission'. It will be the world's first re-entry at parabolic velocity. On return from the moon the spacecraft has to hit a re-entry corridor only 30 km across. The range of possible touchdown points extends along a 400 km wide corridor stretching from the equator to the North Pole, and extending over the Indian Ocean, India, Central Asia, and Siberia.
1967 September 21 - .
- L1 launch delayed to November. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. The L1 in preparation at Area 31 will not be ready for the planned 20 October launch due to delays in qualification of the parachute system at Fedosiya. No launch attempt now expected until November..
1967 September 26 - .
- L1 Launch Commission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Proton s/n 229 and L1 s/n 4L are ready for launch. There remain communications problems, including the 3-channel telemetry and the SAS abort system. Launch is set for 28 September, landing after return from the moon on 4 October at 19:52, 200 to 300 km north of Dzhezkazgan. At Area 31 there is a problem with the solar cells on the Soyuz. They have to be replaced, which means acceptance tests will have to start all over. At Fedosiya parachute trials are still experiencing delays.
1967 September 27 - . 22:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: First stage -1 RD-253 failed, resulting at T+67 sec in deviation from flight path.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 4L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 4L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Mishin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1967-09-28 .
First attempted circumlunar flight. The UR-500K failed, crashing 50 to 60 km from the launch pad. The L1 radio beacon was detected 65 km north of the Baikonur aerodrome by an Il-14 search aircraft. An Mi-6 helicopter recovered the capsule and had it back to the cosmodrome by 13:30. Mishin's record: of seven launches of the Soyuz and L1, only one has been successful. Film of the launch shows that one engine of the first stage failed. Mishin still wants to launch the next L1 by 28 October. The other chief designers oppose the move. Barmin says at least five months are needed to diagnose the cause of the failures and makes fixes to ensure they don't happen again. Nevertheless the leadership sides with Mishin, and Barmin is ordered to prepare the left Proton pad for a launch within 30 to 40 days.
1967 October 4 - . LV Family: N1.
- Mishin conducts a rather grim review of the cut backs to his OKB's budget for 1968. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
MKBS,
LK.
Consider the shortfall in his request compared with the challenge of beating the Americans to the moon!
Review with Company Management on Occasion of Tenth Anniversary of Sputnik 1
Plan for 1968.
1. Funding:
R&D - 7.5 million Rubles. (26 million requested).
including YaRD nuclear rocket engine- 6 million., MKBS - 0.5 million., L-5 - 0.5 mln., Yantar - 0.5 million.
Experimental design work - 266 million. (Requested 333 million).
Funded 3 sets N1-L3 instead of 6 sets.
For 7K-OK - 11, 12, 13, 14 (shortfall 20%).
N1-L3 (3 sets - 207 million., Including 38 million experimental work. Stages A, B, V, G - 22.8 million. Payloads (LOK, LK, Block D, GO) - 9.5 million. Blocks E and I - free of charge. (under direct contract with Isayev).
2. Plan - does not meet the 5-year plan. Not included at all:
- Modernization of the N1-L3.
- In R&D - Modernization of the RT-2M (in full).
- EYaRD (nuclear electric propulsion)- instead of in R&D - to search for funding.
1967 October 6 - .
- Soyuz parachute trials at Fedosiya. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
They need to complete 70 drops, which normally would take five to six months. Mishin still insists that they be completed by 1 November. Three tests are made in one day, a record, including the drop of a Soyuz mock-up at 17:55 from an An-12. The parachute deployed correctly, but the soft landing system fired at 2000 m instead of 1.2 m. The spacecraft hit the ground on its side at 8 m/s. Because of the angle of impact the crew seat shock absorbers couldn't function. If any cosmonauts had been aboard, they would have suffered serious trauma.
1967 October 7 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Soviet of Chief Designers - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Dementiev,
Glushko,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
In Moscow, Mishin heads a meeting of all the Chief Designers (including Chelomei, Mishin, and Glushko). Glushko says that the last UR-500K failure was due to errors made during manufacture of an engine in 1965 at Factory 19 at Perm. Ustinov notes that the failure has cost the state 100 million roubles and has delayed the program two to three months. He brutally attacks Dementiev, Minister of Aviation Industry, for the poor work of his factories on the space program. Another issue is continued delays in the Salyut computer for the L1. Ustinov orders an alternate technical solution to be developed in parallel with the digital computer development. The next Soyuz flight is set for the end of December, the next L1 attempt for 21-22 November.
1967 October 13 - .
- Mishin seeks cancellation of 7K-VI. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Mishin,
Smirnov.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz VI.
Mishin sends a letter to Afanasyev and Smirnov, proposing to cancel the Kozlov's 7K-VI military version of Soyuz. It is an unnecessary new spacecraft design, he says. As an alternative Mishin proposes to double to 8 to 10 the number of flights of the existing Soyuz design planned for 1968. Kamanin is astounded. Mishin was never opposed to Kozlov's 7K-VI before. No one had ever indicated that the VI had to be a precise copy of the Soyuz. The military is opposed to the move. On another matter, Kamanin sends a letter to Mishin, complaining about the L1 trainer provided - the simulator is not representative of the actual spacecraft. Meanwhile the second test of a Soyuz mock-up is made at the parachute trials at Fedosiya. It proceeds normally, and the test clears the way for an unmanned space flight of the redesigned Soyuz.
1967 October 15 - .
- Meeting on crew selections for the L3 program. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Artyukhin,
Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Kubasov,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Rukavishnikov,
Voronov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Attending are Kuznetsov, Gagarin, Khlebnikov. There are three training groups: Soyuz, L1, and L3. Mishin and the MOM are holding up further training of cosmonauts until the VVS agrees to accept Mishin's candidates from TsKBEM. In any case, Mishin's attitude is that 'automation in space is everything. Humans in space are only supposed to monitor the operation of automated systems'. L3 cosmonauts selected by the VVS are: Leonov, Bykovsky, Nikolayev, Popovich, Voronov, Khrunov, Gorbatko, Artyukhin, Kubasov, Makarov, and Rukavishnikov. The official requirements: balanced composition of a crew according to mass requirements (no more than 70 kg weight per cosmonaut), and the ability to monitor fully automated function of the L3. According to official documents, the crew's primary function is to guide the flight, but now Mishin intends that their primary role will be as subjects of psychological and physical observations to establish the adaptation of the human organism to space flight).
1967 October 16 - .
- Continued problems with Soyuz landing system tests. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Tkachev.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
A further test of the Soyuz landing system went all right, if you don't consider the fact that the 'Tor' altimeter triggered the braking system 3.3 seconds early. One certainly couldn't say, as a result of only these two successful tests, that the system was reliable. The system uses a gamma altimeter, with redundant verification using pulses from HF and UHF antennae. The system has been approved for unmanned flights, but needs additional tests before it can be certified for manned flights. Kholdokov wants the VVS to take over not just trials, but all further development of the landing system, since Mishin and Tkachev are unable to deliver a reliable product. But such a decision can only be taken jointly by the VVS and RVSN.
1967 October 17 - .
- The return to flight of Soyuz is approved. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
There have been many improvements and additional qualification tests conducted since the Soyuz 1 crash, notably to the parachute system. MAP, TsAGI, LII, and the VVS want the L1 to have a reserve parachute as well, but Mishin rejects the recommendation -- it would cost 200 kg extra mass, and there are absolutely no reserves in the L1.
1967 October 21 - .
- Lunar crew controversy rages. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Feoktistov,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
First Mishin was pushing the 60-year-old Anokhin for spaceflight, now the invalid Feoktistov. Feoktistiov suffers from gastrointestinal ulcers. Tyulin and Kerimov are of one voice in the matter - this is not even a question that can be raised - sick is sick, period. The L1 and L3 crews will have to endure eight to ten days of orbital flight. They can only be between 170 and 175 cm tall, and can have a maximum weight of 70 kg. Mishin insists that he doesn't even need military pilots for the L1 and L3, and therefore doesn't need to decide crew compositions until the middle of 1968, and then only 'his' engineer cosmonauts from TsKBEM should be considered. The Marshal interrupts Mishin, angrily reminding him that the space program is a national enterprise, not something being accomplished by 'your' spacecraft or 'your' cosmonauts. A three hour-long bitter debate ensues, with no resolution on crew selections. The final conclusions are only that the crews will consist of one pilot, and one engineer, and that Feoktistov will never be allowed to go into space.
1967 October 23 - .
- Soyuz launches delayed. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. The Soyuz launches have been delayed two to three days because of rain. In any case a membrane in an orientation system propellant tank burst during fuelling of spacecraft number 6..
1967 October 24 - .
- Soyuz launch commission - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Soyuz launch commission is held at Area 31 at 17:00..
1967 October 27 - . 09:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 186 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (A) s/n 6. Mass: 6,530 kg (14,390 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 3.95 days. Decay Date: 1967-10-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 3014 . COSPAR: 1967-105A. Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 179 km (111 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Docked with Cosmos 188; first automated rendezvous and docking of two spacecraft. The dockings were timed to celebrate the 50th Anniversary of the October Revolution (in lieu of a succession of manned space feats that all had to be cancelled due to schedule delays). Achieved automatic rendezvous on second attempt. Capture achieved but hard docking and electric connections unsuccessful due to misallignment of spacecraft. Star tracker failed and had to make a high-G ballistic re-entry. Recovered October 31, 1967 08:20 GMT.
1967 October 29 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Cosmos 188 launch scrubbed. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soyuz-B ('Baikal') launch was delayed to 30 October due to problems with the celestial navigation system aboard Cosmos 186. Later that day an N1-L3 review is held. The first launch vehicle will be completed in two to three weeks, but the launch complex will not be ready until next January. The first trials of the booster on the pad will begin in February-March 1968, with the first launch in the second half of the year.
1967 October 30 - . 08:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 188 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (P) s/n 5. Mass: 6,530 kg (14,390 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Mnatsakanian.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 3.04 days. Decay Date: 1967-11-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 3020 . COSPAR: 1967-107A. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 180 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Docking target craft for Cosmos 186, which achieved world's first automatic rendezvous on second attempt. Hard docking achieved but electric connections unsuccessful due to misallignment of spacecraft. Ion flow sensor failed and Cosmos 188 had to make a high-G uncontrolled re-entry. When it deviated too far off course, it was destroyed by the on-board self-destruct system,. However officially the Soviet Union reported that it landed succesfully on November 2, 1967 at 09:10 GMT, and that its mission was 'investigation of outer space, development of new systems and elements to be used in the construction of space devices'. Additional Details: here....
1967 October 31 - .
- Cosmos 186 landing. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Rudenko,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Due to failure of a star tracker a guided lifting re-entry of 3-4 G was not accomplished. A ballistic re-entry of 7-8 G however resulted in a successful soft landing in the target zone. Rudenko's recovery crews demonstrated a lack of training. Ustinov and Mishin were anxious to release a proclamation of total mission success, but they needed confirmation that the soft landing rockets had functioned correctly. It was only after 2.5 hours that the recovery teams arrived aboard an Mi-6 helicopter that the correct function of the landing system is verified and the leadership notified.
1967 November 1 - .
- Cosmos 188 self-destructs during re-entry. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin is drunk again at a critical mission phase. Afanasyev, Kerimov, and Tyulin all know about Mishin's drinking problem but do nothing. Meanwhile in orbit Soyuz-B's stellar navigation system has not functioned correctly (it hasn't worked on any Soyuz, Kamanin notes). The decision is made to use the ion orientation system. The TDU braking rocket fires at 10:03 on 2 November. But the spacecraft is not oriented correctly, and the landing will take place 2000 to 3000 km from the recovery area. The APO destruct system determines that the landing point will be 300 to 400 km east of Ulan-Ude, and automatically blows up the capsule during re-entry at an altitude of 60 to 70 km above Irkutsk. This was completely unnecessary, since the capsule would have landed on Soviet territory, or in Mongolian territory close to the border. The orientation problem is found to be due to incorrect functioning of the ion orientation system.
1967 November 4 - .
- Manned Soyuz flight by May 1968? - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Discussion on the Il-18 on the way back to Moscow from Tyuratam. Mishin thinks that a manned flight aboard Soyuz will be possible by April-May of 1968; the others don't think it can happen until the second half of the year..
1967 November 5 - .
- Soyuz capsule recovery issues. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Rudenko. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Kamanin meets with Rudenko. They go over the problems with the training of his recovery crews. They have three helicopters, 10 men, yet nobody could determine if a soft landing had occurred or not..
1967 November 16 - .
- State Commission on Cosmos 186/188. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Problems on the mission included excessive firing of the manoeuvring engine during rendezvous and docking, and failure of the stellar navigation systems. The systems still need work before a man's life can be risked. It is decided to conduct another unmanned dual docking mission in March-April 1968; with a manned flight in May-June 1968. As for the L1, the simulator was still 'raw' and had many problems. Four to six successful unmanned flights are needed to prove the L1 before a manned flight can be made.
1967 November 22 - . 19:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Second stage - 1 x RD-0210 failure, shutoff of stage 4 seconds after ignition. Launcher crashed downrange.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 5S - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 5L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Glushko,
Leonov,
Mishin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1967-11-21 .
The launch takes place at 00:07 local time (22:07 on 22 November Moscow time). Glushko, Chelomei, and Kamanin observe the launch from an observation point in -5 deg C weather. Three to four seconds after second stage ignition, the SAS pulls the spacecraft away from the booster. Telemetry shows that engine number 4 of stage 2 never ignited, and after 3.9 seconds the remaining three engines were shut dwon by the SBN (Booster Safety System) and the SAS abort tower fired. The capsule's radio beacon was detected and the spacecraft was found 80 km southwest of Dzhezkazgan, 285 km down range. The Proton problems are maddening. Over 100 rocket launches have used engines from this factory, with no previous failure. Of ten of the last launches under Mishin's direction (6 Soyuz and 4 L1) only two have went well - an 80% failure rate! Mishin is totally without luck. Kamanin and Leonov take an An-12 to see the L1 at its landing point. Leonov wants to see proof that the cosmonauts would be saved in any conditions. The capsule landed in -17 deg C and 12 m/s winds. The parachute pulled the capsule along the ground for 550 m, and the soft landing rockets fired somewhere above the 1.2 m design height. After safing of the APO self-destruct package, the capsule is lifted to an airfield by a Mi-4. The L1-5S designation seems to indicate this was a test of the podsadka L1. (Mishin Diaries 2-90)
1967 November 29 - .
- Kamanin appeals for 7K-VI program to continue. - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz VI.
Kamanin writes a letter to the Central Committee on the need for the 7K-VI spacecraft for military research. He also complains about his problems in obtaining adequate spacecraft simulators. Later he meets with Grigoriy Nikolayevich Postukov, sculptor of cosmonaut statutes.
1967 December 6 - .
- 7K-VI cancelled. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Mishin,
Pashkov,
Serbin,
Smirnov,
Stroganov,
Ustinov.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz VI.
Kamanin is dumbfounded. The leadership has decided to accept Mishin's recommendations, scrap the 7K-VI project, and replace it with a Soyuz variant! Mishin is an egotist, but he is supported by highly-placed leaders - Ustinov, Smirnov, Pashkov, Serbin, Stroganov, Keldysh, and others. So everyone in the space program has to dance in the service of this 'engineer-performer', who is not a credible chief designer.
1967 December 15 - .
- L3 issues - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Feoktistov. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. There is still no enabling resolution for the L3. Many meetings are held, discussing the L3, L3 trainers, and Feoktistov's assignment as a cosmonaut..
1968 January 30 - .
- Three-hour review of the L1 program at the Institute of Aviation Medicine. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The Volchka L1 trainer, M-220 computer, centrifuge, L1 cabin, and instructor control station are in place. But many critical equipment items have not yet been installed, including essential cabin instruments and flight indicators..
1968 February 6 - .
- L1 commander assignments agreed. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Feoktistov,
Leonov,
Mishin,
Popovich,
Voloshin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
The final medical report rejects Feoktistov's fitness to be a cosmonaut. Mishin accepts the findings of the report, but in classic manner ignores it and advocates Feoktistov be appointed as commander of the active spacecraft in the first Soyuz docking mission after return to flight. Kamanin is livid. Feoktistov has had years of training for EVA, but he has not had one day of training as a spacecraft commander, and now he wants him to command a mission due to launch in only two to three months! However agreement is finally reached on L1 commander assignments: Leonov, Bykovskiy, Popovich, Voloshin. Agreement is not reached on the second (civilian) crew member position for the flights. According to Mishin, the Soyuz and L1 flights planned from March 1 to the end of 1968 will require 16 to 18 crew members total.
1968 February 12 - .
- L1 Expert Commission meeting. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Kamanin states his belief that the L1 will not be ready for manned flight for 2 to 3 years, and will need 8 unmanned flight tests before it can be man-rated. Others disagree, and the final decision is that four unmanned flights without significant failure will be required before the spacecraft is man-rated.
1968 February 17 - .
- Soyuz VI cancellation approved. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Kozlov, Mishin. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz VI. The NTK General Staff approves Mishin's cancellation fo the 7K-VI. Kozlov has agreed only under duress. The military is opposed to the cancellation, but Afanasyev won't listen to them..
1968 February 21 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- L1 Launch Commission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Glushko,
Konopatov,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The booster failure on the previous launch was found to be due to premature fuel injection during engine start, causing initial chamber temperatures to rise 200 degrees above normal. Glushko and Konopatov both guarantee their engines for the next launch. The next L1 flight will use the 'Kruga' landing predictor. This will predict the landing point to within a 150 x 150 km area two to three hours before re-entry. Landing points on the three previous flights would have been 2000 km from Madagascar and India, Novosibirsk, and the North Pole... Mishin plans the next dual Soyuz flight for 5-10 April. Kamanin protests that the parachute and sea trials of the redesigned capsule are not yet complete. Mishin, as usual, dismisses his concerns.
1968 February 29 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- L1 commsision meeting. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
For this L1 launch Chelomei wants to film separation of the first and second stages of the Proton rocket at 126 seconds into the flight - altitude 41 km, distance downrange 47 km. To do this two An-12 and one Tu-124 with long focal-length cameras will orbit 35 to 40 km from base. The discussion turns to how to recover the L1 if it lands in the ice-bound Aral Sea. The circle of possible landing points has a radius of 500 km from a point west of Karaganda. For political reasons it is not possible to deploy recovery forces to areas of Iran and India that are within this circle.
1968 March 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Originally planned N-1 first launch - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. Slipped to May..
1968 March 2 - . 18:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 4 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 6L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.22 days. Decay Date: 1968-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 3134 . COSPAR: 1968-013A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 15,561.71 min.
What at first seemed to be a success, very much needed by the L1 program, ended in failure. The Proton booster lifted off in 18 m/s winds, -3 deg C temperatures, and into very low clouds - it disappeared from view at only 150 m altitude. Aircraft at 9, 10, and 11 km altitude reported the cloud deck topped 8300 m, with 1.5 to 2.0 km visibility. The spacecraft was successfully launched into a 330,000 km apogee orbit 180 degrees away from the moon. On reentry, the guidance system failed, and the planned double skip maneuver to bring the descent module to a landing in the Soviet Union was not possible. Ustinov had ordered the self-destruct package to be armed and the capsule blew up 12 km above the Gulf of Guinea. Kamanin disagreed strongly with this decision; the spacecraft could have still been recovered in the secondary area by Soviet naval vessels after a 20 G reentry. The decsion was made to recover the spacecraft in the future whenever possible.
Officially: Solar Orbit (Heliocentric). Study of remote regions of circumterrestrial space, development of new on-board systems and units of space stations.
1968 March 3 - .
- Zond 4 first midcourse fails. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
At 07:35 the first midcourse manoeuvre for Zond 4, then 225,000 km from earth, was cancelled due to an orientation system problem. The sun tracker worked, but the star tracker could not acquire Sirius. The first and second midcourse manoeuvres are not strictly necessary. However if the third midcourse fails, when the spacecraft is 167,000 km from earth on the return leg, the spacecraft will miss the atmosphere and head back out into space. A meeting is held on cosmonaut training. The simulators are still not adequate. Feoktistov is still demanding that he be trained for the first Soyuz docking mission.
1968 March 5 - .
- Zond 4 midcourse succeeds. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The L1 reaches its apogee. The time comes to attempt the third midcourse manoeuvre. There are three attempts to orient the spacecraft. The first was at the minimum sensitivity setting for the star tracker, the second at the maximum setting, and the third using a high-density filter. Sirius is finally acquired the third time. The spacecraft is oriented and makes a 15 second burn with a 9.129 m/s delta-V (versus 9.202 m/s planned). This is good enough to assure the spacecraft will hit the re-entry corridor without a further correction.
1968 March 6 - .
- Zond 4 on course. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
It is estimated that Zond 4 will fly 45.8 km below the initial re-entry corridor at an altitude of 145 km, after which it will ricochet back out into space and proceed to a final re-entry and landing on Soviet territory. It is calculated it will land on 7 March at 21:56, 13 minutes later than the originally estimated time.
1968 March 7 - .
- Soyuz parachute recertification holding up all manned programs. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Tkachev.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin certified to MAP on 5 March that the Soyuz parachute system development is complete, but Tkachayev has dissented, saying that the system was unreliable and overweight (this from the same chief designer that certified the previous design as having an 0.999 reliability!). The parachute trials will not be finished until May - meaning there will be no manned Soyuz launch in April. This problem is holding up the L1, L3, and Almaz projects as well.
1968 March 7 - .
- Zond 4 self-destructs during re-entry - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The L1's SUS guidance system failed on re-entry. It hit the atmosphere precisely at the calculated time, but wasn't guided to generate lift and fly out of the atmosphere again. A ballistic re-entry would mean no recovery on Soviet soil, so the APO destruct system automatically blew up the capsule at 10 to 15 km altitude, 180-200 km off the African coast at Guinea.
1968 March 12 - .
- Cosmonaut meeting at Yevpatoriya. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Gagarin wants better organisation of the TsPK for the L1 circumlunar manned flights, including: better training in manual navigation in case of failure of automated systems; improved training in survival of 20 G re-entries if the automated SUS capsule guidance system fails. The cosmonauts review material for the Seventh International UFO Conference in Mainz (!).
1968 March 25 - .
- Simulator status - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Feoktistov. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK. Kamanin reviews the unfinished status of Soyuz and L1 simulators. Then there is the Feoktistov issue....
1968 March 26 - .
- A State Commission is held to review L1 and Soyuz status. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Hours are spent arguing over flying Feoktistov as a cosmonaut. Finally the matter is referred to the VPK. Kamanin briefs Ustinov's deputy on his position against Feoktistov. The L1 is reviewed. The star sensor only operated on Zond-4 on the fourth day of flight. However when it worked, it provided a 2 km positional accuracy at re-entry versus the 10 km required. The next L1 is to be launched on 23 April. If that date cannot be met, it will be launched on 25-30 April on a deep-space trajectory (not aimed at the moon).
1968 March 27 - .
- Death of Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin at Novoselovo, Russia. Crash of MiG-15 trainer. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Russian pilot cosmonaut 1960-1968. First person in space. Due to his fame, the Soviet leadership did not want to risk him on another flight, but later relented. Died in MiG trainer crash while requalifying for flight status. 1 spaceflight, 1.8 hours in space. Flew to orbit on Vostok 1 (1961). Gagarin was flying together with instructor pilot Sergin on a flight in a UTI MiG-15 trainer. Gagarin was being requalified as a jet pilot after being denied flight status by the leadership for a long time. At that time the mean flight hours between fatal accidents hours for Soviet jet fighters were: MiG-15, 18,440 hours; MiG-17, 11,460 hours; MiG-19, 4,475 hours; MiG-21, 4,422 hours; Su-7, 2,245 hours; Su-11, 2,100 hours. Gagarin's UTI MiG-15 s/n 612739 was built at the Vodokhod factory in Czechoslovakia and delivered on 19 March 1956. It had a 2100 hour airframe life, and had flown 1113 hours. It had two overhauls to date: one on 13 July 1962, after 13,834 'mil' hours, and the second on 30 March 1967, after 36,986 'mil' hours. It should have had a 500 hour life after the second overhaul, had flown only 62 hours since then, and had 438 hours left.
1968 April 10 - .
- Cosmonauts occupied with Gagarin crash investigation - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin.
Program: Soyuz.
No cosmonauts will be sent to witness the next series of unmanned Soyuz flights beginning on 14 April. All cosmonaut staff efforts are concentrated on the Gagarin crash investigation. Kamanin notes the flight of Apollo 6. According to his information the first manned Apollo flight will take place in May-October 1968, and the first American moon landing by the end of 1969.
1968 April 14 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 212 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (A) s/n 8. Mass: 6,500 kg (14,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Soyuz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Duration: 4.92 days. Decay Date: 1968-04-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 3183 . COSPAR: 1968-029A. Apogee: 200 km (120 mi). Perigee: 180 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.30 min. Cosmos 212 docked with Cosmos 213 in the first completely successful test of the Soyuz 7K-OK attitude control, automatic rendezvous and docking systems. Cosmos 212 was successfully recovered on April 19, 1968 at 08:10 GMT.. Additional Details: here....
1968 April 15 - . 09:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 213 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (P) s/n 7. Mass: 6,500 kg (14,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 5.02 days. Decay Date: 1968-04-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 3193 . COSPAR: 1968-030A. Apogee: 254 km (157 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Cosmos 213 was the target for Cosmos 212 in a successful test of Soyuz 7K-OK rendezvous and docking systems. The Cosmos 213 launch was the most accurate yet. The spacecraft was placed in orbit only 4 km from Cosmos 212, ready for a first-orbit docking. Both spacecraft were recovered, but Cosmos 213 was dragged by heavy wind across the steppes when the parachute lines didn't jettison at touchdown. This failure caused the upcoming Soyuz 2/3 manned docking mission to be scaled back.
Officially: Investigation of outer space, development of new systems and elements to be used in the construction of space devices. Additional Details: here....
1968 April 19 - .
- L1 launch preparations - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Kamanin goes to Baikonur aboard an Il-18 for the L1 launch. This is to be the first flight demonstration of the SUS system that will use the capsule's L/D ratio of 0.3 to make a lifting re-entry. Preparations are on schedule..
1968 April 20 - .
- Cosmos 213 landing/L1 preparations - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK. Unfuelled tests of the Proton rocket on the pad are completed successfully. The K-100 star sensor on the L1 is a special concern..
1968 April 21 - .
- L1 on schedule; N1 in trouble. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
This was a reserve day in the L1 countdown, in case of problems in preparation. However all is on schedule for the launch. The same cannot be said for the N1. There are many delays. Mishin promised the first N1 rollout in the first half of March, but it is still in the assembly building, with no end in sight of preparations. The weather at the cosmodrome is -5 deg at night, clear pleasant days. The Hotel Kosmonavt was finished on 15 April. Although it has all of its furniture, it was not completely painted before the furniture was moved in!
1968 April 22 - .
- The L1 State Commission meets and the launch is set for the next day. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
However the Commission did not agree to disarm the APO destruct system aboard the capsule. They don't want any chance of 'Soviet electronic secrets' falling into the hands of the Americans. Kamanin disagrees - he thinks they should conduct one fully ballistic re-entry and landing of an L1 to see if the landing system would function and the crew would survive. What's the point of deploying recovery ships to the Indian Ocean if they are only going to blow up the capsule anyway if the SUS fails and it reverts to ballistic mode? Mishin's answer: 'I was always against having those forces in the Indian Ocean!' Yet he had demanded those 7 to 9 recovery ships in February!
1968 April 22 - . 23:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Second stage shut-off prematurely due to short-circuit in Zond control system.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 7L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 7L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1968-04-22 .
L1 launch attempt, lift-off at 02:00 local time. The spacecraft was to separate at 589 seconds into the flight. Instead at 260 seconds, a short circuit in the malfunction detection system incorrectly indicated a launch vehicle failure. This in turn triggered the SAS abort system. The SAS shut down the good stage and separated the spacecraft from the booster. The capsule landed safely 520 km downrange from the launch site. This was the third such abort, which if nothing else proved the reliability of the SAS - all of the spacecraft landed safely.
1968 April 23 - .
- L1 launch failure - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The cosmonauts and VVS staff will watch the Proton launch from Area 130. Kamanin observes from Area 81, near the pads. It is a warm, starry night and the booster heads toward space on pillars of fire. Up until T+260 seconds all proceeds normally, then the stage 2 shuts down 79 seconds into its burn. At 02:50 it is reported that the capsule separated successfully from the inert booster and has landed 520 km from the launch pad, 110 km east of Dzhezkazgan. Two Il-14 search aircraft and one Mi-4 helicopter fly over the recovery zone, but no signal is received from the capsule. Mishin immediately blames Chelomei's TsKBEM for the booster failure -- later it is shown that Mishin's L1 spacecraft sent an erroneous abort command to the rocket, which then shut down it engines! The capsule is sighted after dawn and picked up by a Mi-6 helicopter and delivered to Dzhezkazgan airfield at 15:00. It is then taken to Moscow for examination. The SAS abort and capsule landing systems have certainly been proven reliable! They have worked perfectly on the last three launches!
1968 April 29 - .
- Mishin '2+2' scenario for the next manned Soyuz flight. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin calls Kamanin and asks what he would think of a revised scenario for the next manned Soyuz flight. Mishin's '2+2' concept would call for four, instead of five cosmonauts, aboard two Soyuz capsules with transfer of only one cosmonaut by EVA. He gives Kamanin until 6 May to give his opinion on the change of plan. Titov is planning on selling his Volga automobile and buying a Moskovich.
1968 April 30 - .
- Soyuz program review. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Soyuz. Mishin's 'corps de ballet' dance the dance and walk the walk in a Soyuz program review..
1968 May 6 - .
- Review of military spacecraft plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Maksimov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Kamanin meets with Yuryshev, Deputy Chief of NTK/General Staff, and Maksimov, Deputy Chief of TsKIK, to review military spacecraft. Such spacecraft can be placed in two general categories: Category 1 would be manoeuvrable spacecraft that use active gliding to be guided to a landing point. This technology was currently being developed in the Soyuz and L1 projects. Category 2 would be an orbital aircraft which would be launched from a winged, recoverable, aircraft first stage booster. Less work has been accomplished on such spacecraft. The Mikoyan and Tupolev bureaux have been authorised to begin design and development, but this was still in its earliest stages. But Kamanin believes the second approach has the greatest future potential, and should be pursued more vigorously.
1968 May 7 - .
- Soyuz manned flights delayed 2 to 3 more months - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin reviews the ongoing controversy with Mishin over assignment of Feoktistov to spaceflights. He then turns to the trials of the revised parachute system for Soyuz. The new design has been proven in three landings of spacecraft and 23 tests of mock-ups from aircraft. The SAS abort system has not been retested -- Korolev took full responsibility for its design, and the VVS accepted that in the old days. In any case the likelihood of having to use the SAS or the reserve parachute was not great. Yet still Mishin refuses to recommend going ahead with manned flights. 'I will only proceed when the Central Committee orders me!' he has said. Nevertheless he does declare that Soyuz is now ready to resume manned flights, except for the reserve parachute system, which needs two to three months more development. Based on successful completion of these tests, a manned flight will be possible in the first half of August.
1968 May 15 - .
- Soyuz parachute problems will limit crew size. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
One engineer has resigned in the belief that the Gagarin crash was due to a hydraulic accumulator failure. The reason Mishin has been pushing for a reduced Soyuz crew is revealed when the reserve parachute will burst when subjected to forces greater than 1300 kgf/square metre. This implies that the Soyuz SA has to be reduced by 150 to 200 kg mass to allow safe functoning of the reserve parachute in an emergency. A reserve parachute system redesign is not an alternative due to the schedule requirements. Mishin's solution is to fly only two crew in each Soyuz. So he is proposing that the two-Soyuz manned flight carry only two crew in each capsule. No crew transfer will take place, but the BO living module will be depressurised to check its function as an airlock. Kamanin is furious -- this conclusion is reached now, when two years ago crews were standing by for launch on what is now believed to be an unsafe mission! The cosmonauts are also against Mishin's concept - such a flight proves nothing new.
1968 May 20 - .
- Tests to evaluate feasibility of '1+2' Soyuz mission profile. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Khrunov,
Volynov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
Volynov conducts tests in a pressurised suit to see if it is possible to go from the SA capsule to the BO living module in a two-man crew transfer scenario. He shows it is not possible - exit from the SA to the BO is very unsafe, there is a good chance of getting stuck in the hatch. This shows it would be difficult or impossible for the spacecraft commander in the SA to go to the assistance of a single cosmonaut attempting to transfer from one Soyuz to another. Feoktistov proposes another alternative - launch of 3 cosmonauts in one Soyuz, one cosmonaut in another. After docking, a single cosmonaut would transfer from one Soyuz to another, but at least a second cosmonaut would be in the BO to assist him in case of difficulties. Two cosmonauts would return in each Soyuz capsule, meeting the reserve parachute mass limitations. This solution also takes care of a problem with the 1+2 scenario, in that it implied a crew consisting of Khrunov and Yeliseyev, but neither has been trained as a spacecraft commander. A crew could consist of Volynov and one of these, but then the problem is that no spacesuit has been fabricated for Volynov, and it requires two months to make one.
1968 May 21 - .
- L1/Soyuz program review. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Keldysh, Mishin. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK. The next L1 launch is set for 17 July. Mishin wants an L1 crew ready for an around-the-moon flight by June. He also wants to fly a 2+2 Soyuz mission in August. Keldysh insists that the Soyuz be proven in another unmanned flight first..
1968 May 22 - .
- Mishin pushes for '1+2' Soyuz mission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Mishin,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Titov is to tour. He will spend the next two days in Semipalatinsk, then go to Italy in the first week of June. He has been offered command of the second unit at TsPK, but says he doesn't want to be an administrator. He would rather pursue a career as a test pilot, at either OKB MiG or GNIKI VVS. Mishin is now pushing for a 1+2 Soyuz mission in August on safety grounds. He is also still pushing Khrunov as a spacecraft commander, even though Khrunov has no training in manual docking and it would take at least two months to train and qualify him.
1968 May 28 - .
- Tereshkova has a heart-to-heart with Kamanin. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Tereshkova. Program: Soyuz. How is she supposed to have time for space training, her engineering classes at the test pilot academy, flight training, herself, and her daughter -- and still the incessant demands from the state for political and public relations activities?.
1968 May 29 - .
- Further tests to evaluate feasibility of '1+2' Soyuz mission profile. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Mishin,
Ustinov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
Khrunov tries to don the Yastreb space suit unassisted, in another test of the feasibility of a 1+2 Soyuz mission. He simply cannot accomplish the task in the four minute maximum time required. Mishin now has Ustinov interested in his 1+2 mission, with Yeliseyev to make a solo EVA from one Soyuz to another.
1968 May 30 - .
- Soviet of the Chief Designers. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Feoktistov,
Mishin,
Shatalov,
Ustinov,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin still wants to eventually conduct a 2+2 mission, but now wants the flight in August to be a 0+1 test flight. In this he is supported by Keldysh and Ustinov. He wants Feoktistov to be the pilot. Kamanin is adamantly opposed and offers him Beregovoi, Volynov, or Shatalov.
1968 June 3 - .
- Ustinov demands manned Soyuz and L1 flights by October. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Leonov, Ustinov. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK. Meanwhile Saturday evening Leonov had another accident with his Volga - and with a group of Italian visitors in the car..
1968 June 12 - .
- State Commission on Soyuz. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Leonov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin wants one more unpiloted Soyuz launch, resulting in a 0+1 unmanned/manned test flight in September, to be followed by the design 1+3 mission with crew transfer in November/December. The reserve chute failed in tests at an SA re-entry capsule mass of 2800 kg. Therefore, Mishin feels the 0+1 mission would be safe, resulting in a mass for the manned capsule of 2650 kg. But Ustinov insists on the 1+3 mission, meaning an SA mass of 2750 kg. Another consideration is that the capsule may need ballast anyway in order to obtain the correct centre of gravity location for the lifting re-entry manoeuvres. It must be balanced in such a way so that it can re-enter the atmosphere at its maximum 23 degree angle of attack.
1968 June 22 - .
- Soyuz simulator status. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. The state plan required 12 Volga simulators to be built for Soyuz crew training. Four years after the plan was approved, only six have been delivered..
1968 June 26 - .
- November manned circumlunar flight set - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
State commission sets November as date for manned circumlunar flight. The next L1 flight was set for July, with flights to continue at monthly intervals at each translunar launch window. 3 or 4 unmanned flights had to be successful before a manned flight would be attempted.
1968 June 26 - .
- State Commission on L1 failure. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The State Commission determines the cause of the Proton booster shutdown in April was a short in the L1 abort system. This sent an incorrect abort signal to the launch vehicle, triggering it to shut down its engines. The next L1 launch is set for 19 July, followed by one launch per month thereafter. After 3 or 4 successful unmanned circumlunar missions, the spacecraft will be cleared for a manned lunar flyby.
July 1968 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- DIA/CIA warn of impending Zond circumlunar flight - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The information led NASA to decide to send Apollo 8 on a risky lunar orbital mission at the end of December 1968. Interestingly enough the CIA warning to NASA came within days of the L1 State Commission's meeting and decision to press for a November circumlunar flight.
1968 July 3 - .
- VPK confirms Soyuz flight plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Bykovsky,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Leonov,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The VPK confirms the Soyuz flight plan - a 0+1 mission to be followed by a 1+3 mission with crew transfer. Chiefs of the cosmonaut detachments are confirmed and announced. Nikolayev will be Deputy Chief of TsPK; Bykovsky, Commander of the First Detachment of Cosmonauts; Titov, Commander of the Second Detachment, and Popovich, Deputy Commander of the Second Detachment. Kuznetsov, Belyayev, and Leonov are not happy with these appointments. The General Staff also approves creation of a fourth training detachment at TsPK, charged with flight, engineering, and experiment development - requiring an additional 200 staff.
1968 July 10 - .
- L3 recovery controversy. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Mishin,
Ryabikov,
Zakharov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Marshal Zakharov has consulted with Ryabikov at Gosplan on what commitments Grechko has made from Ministry of Defence funds for L3 recovery forces. Gosplan advised him that 800 million roubles and 21,000 staff were committed, but the justification for these amounts were not methodically developed. Mishin is now saying that hundreds, not thousands of cadres will be required, see he can set the return capsule down in within the confines of the cosmodrome.
1968 July 12 - .
- L3 recovery controversy. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
VVS has been charged with arranging for ocean recovery of the L3 capsule in case it splashes down in the Indian Ocean since 1966. TsNII-30 did the research work under project 'Ellips', resulting in the recommendation that the VVS and VMF jointly develop the air and naval forces to recover the capsule at sea, at a cost of 800 million roubles. The Ellips concept requires that the L3 capsule be equipped with radio beacons and dye markers. Despite knowing this for two years, Mishin has done nothing to implement these features into the spacecraft.
1968 July 15 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. Launch Pad: LC81/pad?. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- L1 pad explosion. - .
Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
During launch preparations with the fuelled Proton / L1, there was an explosion, killing three technicians. Their death alone indicates the area around the pad was unsafe at the time. The Block D oxidiser tank of the L1 exploded - the first such failure in 30 uses. The rocket and spacecraft were relatively undamaged. The third stage of the Proton had some external damage due to exposure to the Block D's fuel, but it can be cleaned. The real question is how to remove the L1 spacecraft on the pad. A helicopter could hoist the spacecraft away, but the available Mi-6 or V-10 helos can lift only 8 to 10 tonnes, and the L1 weighs 14 tonnes. A V-10 crew is sent to investigate the possibilities anyway. Some engineers suggest just firing the BPO abort tower and lifting the capsule away from the stack! Emergency political and military meetings are held at the cosmodrome to discuss the impending invasion of Czechoslovakia.
1968 July 21 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Zond 7K-L1 s/n 8L - . Payload: Zond 7K-L1 s/n 8L. Mass: 5,140 kg (11,330 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Decay Date: 1968-07-21 . Block D stage exploded on pad, killing three people. Booster and 7K-L1 spacecraft were still intact however..
1968 July 29 - .
- Reduced L3 recovery forces. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Smirnov,
Vershinin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Vershinin looks bad after his surgery. His loss would be a blow for Kamanin's cause - Vershinin was steadfast against the unobjective positions of Mishin and Smirnov. Vershinin had just sent yet another letter about the procurement of the 16 m centrifuge for the TsPK. This is a six-year long story. The VVS has been trying to procure this essential piece of cosmonaut training equipment since 1962, but it still has not been delivered. Vershinin also has issued a letter on the L3 recovery force issue. He points out that the resolution of the Central Committee ordered the expenditure of 600 million roubles and the commitment of 9,000 men for recovery services. Another 400 million roubles and 12,000 men were earmarked by the Rocket Forces. Despite this huge commitment, Mishin now says he doesn't need any of them, that he can bring his L1 and L3 spacecraft to precision landings within the confines of the cosmodrome, eliminating the need for any Indian Ocean recoveries. This optimism is not accepted, but it is agreed the total requirement can be reduced to 400 million roubles and 7,000 men, through use of lighter recovery ships of the Leninskiy Komsomol class, and the use of three airborne relay stations instead of nine.
1968 August 2 - .
- Reduced L3 recovery forces accepted. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Gagarin, Keldysh, Ryabikov, Vershinin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. Vershinin, Afanasyev, Keldysh, and Ryabikov accept the reduced recovery forces estimate. Meanwhile a letter from the cosmonauts disputes the Gagarin crash investigation finding ('pilot error resulting in an abrupt manoeuvre')..
1968 August 8 - .
- Further Soyuz delays - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The next flight of an unmanned Soyuz has been delayed yet again. It had been set for 27 July, then 10 August, and now 20 August. The problem is qualification of the reserve parachute system. The test at Fedosiya on 3 August was a failure - the SA capsule's parachute hatch didn't jettison, the parachute system couldn't operate, and the capsule was destroyed on impact with the ground. The system needed 3 to 5 final tests for qualification. The first test in the series was successful, but this second test was a disaster. Another setback for Mishin. The same parachute hatch mechanism had never failed before in 200 flights of Vostok, Zenit, and Soyuz spacecraft. Meanwhile the invasion of Czechoslovakia is underway…
1968 August 28 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 238 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 9. Mass: 6,520 kg (14,370 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Soyuz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Duration: 3.96 days. Decay Date: 1968-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3351 . COSPAR: 1968-072A. Apogee: 210 km (130 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Recovered September 1, 1968 9:03 GMT. Final test of redesigned Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft for Soyuz 3 manned mission..
1968 September 12 - .
- L1 Training. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The cosmonauts have been well trained on the L1 spacecraft at TsKBEM, but not on the real thing at the test area at Baikonur. Mishin is opposed to their doing this training at the cosmodrome..
1968 September 13 - .
- L1 recovery plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
200 aircraft and helicopters are ready for the L1 launch, as well as eight ships in the Indian Ocean. The latter are spaced at 300 km intervals in an area 2500 km long x 400 km wide along the re-entry trajectory. There are Ka-25 helicopters aboard only three of the ships. For manned flights, a minimum of nine ships, all equipped with helicopters, plus a long range Tu-95 search aircraft will be required. But this has been recommended 20 times by Kamanin, and rejected 20 times by the Ministry of Defence. Later the L1 State Commission meets in the new three-story building at Area 81. Launch is set for 15 September at 00:42:10.6, which will mean a night landing at 19:00 on 21 September. The capsule has no visual lights or beacons, which will make it very hard to locate. But Mishin is adamant he cannot change the landing time.
1968 September 14 - . 21:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 5 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 9L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.76 days. Decay Date: 1968-09-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 3394 . COSPAR: 1968-076A. Apogee: 385,000 km (239,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 14,722.06 min.
First successful circumlunar flight with recovery. Test flight of manned spacecraft; launched from an earth parking orbit to make a lunar flyby and return to earth. On September 18, 1968, the spacecraft flew around the moon at an altitude of 1950 km. High quality photographs of the earth were taken at a distance of 90,000 km. A biological payload of turtles, wine flies, meal worms, plants, seeds, bacteria, and other living matter was included in the flight. Before re-entry the gyroscopic platform went off line due to ground operator failure. However this time the self destruct command was not given. After a ballistic 20G re-entry the capsule splashed down in the Indian Ocean at 32:63 S, 65:55 E on September 21, 1968 16:08 GMT. Soviet naval vessels were 100 km from the landing location and recovered the spacecraft the next day, shipping it via Bombay back to Soviet Union. Additional Details: here....
1968 September 16 - .
- Zond 5 midcourse aborted - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Beregovoi. Program: Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The first Zond 5 midcourse correction was aborted. The star tracker failed, and the spacecraft wouldn't orient itself properly. Later the reasons for Beregovoi's mistakes in the Soyuz 3 docking are discussed. Kamanin blames them on inadequate simulators..
1968 September 17 - .
- Zond 5 midcourse using earth sensor - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
It is decided to orient Zond 5 using the earth sensor. This is not as accurate as the star tracker, but it is good enough to ensure the spacecraft can be put on a course that will take it back to earth. However it is not accurate enough to allow a a lifting re-entry with a double skip manoeuvre and landing in the Soviet Union. It means the spacecraft must follow a high-G ballistic re-entry and land in the Indian Ocean. Afanasyev is personally supervising the midcourse orientation and engine burn.
1968 September 19 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Bulldozer delays N1 launch by two months - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The Zond 5 situation remains the same. The star trackers quit working, and the use of the back-up systems has not been completely successful. However the spacecraft is on course for a ballistic re-entry. At Area 112 Afanasyev heads the State Commission for the N1-L3 first launch. There are problems with the launch complex. The main electrical cable to the launch complex was accidentally bulldozed. The back-up cables were buried only 30 cm from the main line and both were destroyed. The cables were poorly marked. It will take 50 days to repair the damage. This will delay first launch until the second half of November 1968, and the second launch to February 1969. Most likely the first launch cannot take place until next year.
1968 September 20 - .
- Kamanin hold a cosmonaut meeting. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Tereshkova,
Titov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Tereshkova is having political problems. Titov is to go to Mexico, although he still is making errors of judgement which make it questionable whether he can be trusted on foreign tours. Beregovoi is to complete his cosmonaut examinations on 27 September, and then will be certified for flight.
1968 September 21 - .
- Soyuz parachute failure - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
At the Fedosiya test range a Soyuz parachute test failed when the parachute hatch wouldn't jettison. This was due to an incorrectly inserted safing pin - it was not a spacecraft problem. So the Soyuz was still cleared for manned flight. Aboard Zond 5, the star tracker has completely failed. So the spacecraft will have to make a ballistic re-entry with splashdown in the Indian Ocean planned at 31 deg 58' S, 65 deg 21' E.
1968 September 22 - .
- Zond 5 sucessfully recovered - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
At 17:00 communications with Zond 5 are lost as it re-enters over the South Pole. It has to re-enter at an angle of 5 to 6 degrees to the horizontal. One degree too high, and it will skip off the atmosphere and be lost into space; one degree too low and the G-forces will increase from 10-16 to 30-40 - which are not only enough to kill the crew, but to destroy the spacecraft. The safe entry corridor is only 13 km across and it has to be hit at 11 km/sec. - like hitting a kopek with a rifle at 600 m range. The re-entry schedule:
- 18:37 jettison PAO service module
- 18:53 re-entry begins
- 18:54 nominal time of reaching trajectory's perigee of 33 km
- 18:56 parachute should deploy at 7 km altitude
- 19:08 splashdown
1968 September 23 - .
- L1 lunar crew selections - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Popovich,
Rukavishnikov,
Voronov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Meeting of VVS, Mishin, and other designers at Fedosiya to review trials of the improved Soyuz parachute system. The Soyuz is cleared for manned flights. Mishin tells Leonov he will not support him in his bid to make the first lunar flight. Kamanin tells Leonov that of the three crews - Leonov-Voronov, Bykovsky-Rukavishnikov, Popovich-Makarov - the Bykovsky crew is favoured.
1968 September 27 - .
- Cosmonauts on tour. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Beregovoi, Leonov, Titov. Program: Soyuz. Titov is in Mexico, Leonov is serving on the sculpture commission for Gagarin and space monuments. Beregovoi confides to a film crew that the members of the original cosmonaut group are opposed to his making a spaceflight..
1968 September 28 - .
- Cosmonaut exams are held for Beregovoi, Shatalov, and Volynov. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Bykovsky,
Klimuk,
Kuklin,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Popovich,
Rukavishnikov,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov,
Voloshin,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 3,
Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 5,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The results will establish the order in which they will fly as Soyuz commanders. A 25-person board, consisting of spacecraft designers and cosmonauts, conduct the oral examinations. Each cosmonaut must answer five mandatory essay questions and select two two-part questions. All three are certified for flight and have a complete mastery of the Soyuz systems.
Mishin and Kamanin meet and decide on L1 crews: Leonov-Makarov (with Kuklin as back-up); Bykovsky-Rukavishnikov (Klimuk back-up); and Popovich-Sevastyanov (Voloshin back-up). But that evening Leonov has yet another automobile accident. He hit a bus with his Volga at kilometre 24 near Shchelkovsky. This was his second accident in four months. Kamanin decides to prohibit him from driving automobiles for six months.
1968 October 1 - .
- L1 and Soyuz plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Beregovoi,
Leonov,
Nikolayev.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 3,
Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The L1 cosmonauts are doing training in autonomous navigation, zero-G training, and TBK-60 simulator training. Due to the continuing L1 failures, there would probably be no manned L1 flight until April-May 1969. As for Soyuz, a 0+1 (docking of one unmanned spacecraft and a manned spacecraft with a single cosmonaut aboard) is planned for 25 October, to be followed by a 1+3 mission with a crew transfer by December at the earliest - possibly not until February-March of the following year. Kamanin reassured Beregovoi that he will indeed fly following his excellent exam results -- but Beregovoi still has doubts. Later Kamanin confronts Leonov over his driving. Leonov has had three auto accidents in four months - simply too much. If he is such a bad driver on earth, how will be in space? Kamanin tells him to take two to three days off work and seriously consider his attitude and position. Next there are commissions to attend in charge of selecting monument designs for Gagarin memorials. There are to be obelisks at the Gagarin crash site, at the Vostok 1 landing site, and in Star City. These commissions are taking up a lot of the cosmonauts' time. Kuznetsov meets with Kamanin and tells him that cosmonauts Belyayev and Nikolayev rated Beregovoi poorly in the exam, giving him only a 5 and citing errors in his logic.
1968 October 3 - .
- Zond 5 arrives in Bombay - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The vessel Vasiliy Golovnin docks at Bombay with the L1 capsule..
1968 October 4 - .
- Zond 5 arrives in Moscow - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The L1 capsule is flown by An-12 from Bombay to Moscow..
1968 October 5 - .
- Soyuz 4/5 zero-G training - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Shonin,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Shonin, Khrunov, and Yeliseyev are in zero-G training aboard the Tu-104 aircraft. The cabin is outfitted with two partial Soyuz mock-ups. In space their EVA between two spacecraft is expected to take one hour and forty minutes, but they can only experience 20 to 25 seconds of weightlessness at a time in the aircraft. The 18 staff aboard the Tu-104 have parachutes in case of a serious problem with the aircraft, but it would take 32 seconds for all of them to jump from the three hatches on the aircraft. Meanwhile the pilot cosmonauts are only flying 50 to 60 hours per year, instead of the 150 to 200 hours that Kamanin had requested.
1968 October 9 - .
- Soyuz 3 preparations. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin is at Tyuratam. There is a Soyuz review - the preparation of the spacecraft is on schedule. Mishin is 'sick' (drunk) again and does not attend. Beregovoi weighs in at 80.4 kg and his opponents are using this against him, saying he is too fat for the mission. He had been up to 86 kg, but had already lost weight on Kamanin's recommendation.
1968 October 11 - .
- Soyuz 3 preparations. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At Area 31 one of the Soyuz has thermoregulation system problems and is in repair - it can't be used for flight training. Kamanin notes that Apollo 7 has been launched - the Americans are back in space after almost two years and on the schedule announced a month ago.
1968 October 15 - .
- Soyuz 3 review. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Soyuz 3 has 18 deficiencies remaining of a total of 55 originally identified. 11 have been cleared, the balance will not affect the flight or reduce redundancy in emergencies. It is decided that Beregovoi and his back-ups will not stay at the traditional cosmonaut cottage at Area 2 but rather at the Hotel Kosmonavt at Area 17.
1968 October 20 - .
- Soyuz 2/3 QA coordination issues. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Coordination problems between the ministries in preparation of the Soyuz spacecraft. VVS and MAP have managers assigned for quality control of each system, while MOM (Afanasyev) counterpart staff are disorganised. Yet again conflicts have to be appealed to 'Cardinal' Ustinov.
1968 October 22 - .
- Soyuz 2/3 State Commission. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Barmin, Glushko, Keldysh, Kirillov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 3. Soyuz 2/3 State Commission. All the 'grey eminences' are there - Keldysh, Barmin, Glushko, Kirillov, etc. There are a huge number of physicians - 22 from the VVS, 100 from Minzdrav - all to check the single cosmonaut..
1968 October 23 - .
- Soyuz 2/3 State Commission. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Volynov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 3. State Commission meets again and finds all is ready. Word is received that the Central Committee is opposed to Volynov as back-up..
1968 October 24 - .
- Soyuz 2 roll-out. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Kamanin visits the Korolev and Gagarin cottages. He finds them in bad condition, in need of repair. They should be restored as they were in 1961 and be made into museums. At 16:00 the rocket is rolled out to Area 31. 500 are present at the State Commission meeting.
1968 October 25 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 2 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 11. Mass: 6,450 kg (14,210 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 2.95 days. Decay Date: 1968-10-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 3511 . COSPAR: 1968-093A. Apogee: 229 km (142 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Unmanned docking target for Soyuz 3. Soyuz 2 launched on time at 12:00 local time, in 0 deg C temperatures and 5 m/s winds. Launch was on time 'as in Korolev's time', notes Kamanin. Docking with Soyuz 3 a failure. Recovered October 28, 1968 7:51 GMT, 5 km from its aim point. Maneuver Summary: 177km X 196km orbit to 184km X 230km orbit. Delta V: 12 m/s.
Officially: Complex testing of spaceship systems in conditions of space flight.
1968 October 26 - . 08:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 3 - .
Call Sign: Argon (Argon ). Crew: Beregovoi.
Backup Crew: Shatalov,
Volynov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 10. Mass: 6,575 kg (14,495 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 3.95 days. Decay Date: 1968-10-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 3516 . COSPAR: 1968-094A. Apogee: 205 km (127 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
Second manned Soyuz flight. Rendezvoused with the unmanned Soyuz 2 but failed to dock. Complex testing of spaceship systems; development, in joint flight with space ship Soyuz 2 of processes of space ship manoeuvring and docking in artificial earth satellite orbit; development of elements of celestial navigation; conduct of research under space flight conditions. The failed docking was blamed on manual control of the Soyuz by Beregovoi, who repeatedly put the spacecraft in an orientation that nulled the automatic docking system. Beregovoi used nearly all of his orientation fuel in his first attempt to dock - of 80 kg allocated, only 8 to 10 kg was remaining. Additional Details: here....
1968 October 27 - .
- Kamanin talks to Beregovoi on the 14th orbit of Soyuz 3. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
He can't understand why Beregovoi couldn't dock. Beregovoi seems garbled. The cabin atmosphere is all right. He is ordered to orient the spacecraft to the sun - which he accomplishes readily with minimum propellant expenditure. The Soyuz 2 45K star sensor is not functioning - 'as usual' notes Kamanin.
1968 October 28 - .
- Soyuz 2 lands 45 km from its aim point. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Meanwhile Beregovoi was instructed to conduct experiments with the 45K stellar sensor on Soyuz 3. He would quickly disengage the 45K, then orient the spacecraft to the sun. He would then reengage the sensor and the automatic orientation system. This did two complete turns of the spacecraft searching for the star, but not acquiring it. To Kamanin this shows the uselessness of the system, and the wastage of propellant it causes.
1968 October 30 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 3 - .
Return Crew: Beregovoi.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Telemetry analysis has shown Soyuz 3 used 30 kg of propellant during 20 minutes of manoeuvring in the automatic regime during docking, followed by 40 kg consumed in two minutes of manual manoeuvring. Essentially Beregovoi was trying to dock the spacecraft upside down. This was either due to incorrect configuration of the running lights or cosmonaut error. Soyuz 2 had two continuously illuminated lights on its upper side and two blinking lights on the lower side. Evidently Beregovoi didn't identify these correctly in weightlessness.
In case Beregovoi has to do a ballistic re-entry, Be-2 seaplanes are in the air in case of a splashdown in the Aral Sea. On his 81st revolution, Beregovoi manually oriented the spacecraft for retrofire, then engaged the vertical sensor and ion orientation system. But the spacecraft hit on ion pocket and it took two to three minutes for the automated system to engage. Retrofire started 3 seconds late, coming at 9:45:05 and continuing for 149 seconds, producing a delta V of 95 m/s. The main parachute deployed at 10:12:24 at 7000 m altitude. Beregovoi spent 13 minutes under the main parachute, descending at 4 to 5 m/s. Soyuz 3 landed 10 km from the aimpoint at 07:25 GMT.
1968 October 31 - .
- Soyuz 3 post-flight debriefing - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The post-flight debriefing of Beregovoi reveals that the automated docking sequence from 11,000 to 200 m range from the Soyuz 2 target was normal. At 200 m Beregovoi took over manual control of the spacecraft. At a range of 30 to 40 m he observed the running lights on Soyuz 2 were inverted. He stopped his approach and waited until the spacecraft moved into daylight. By that time the spacecraft were still 30 to 40 m away, but had drifted so that he was 30 degrees off-angle from Soyuz 2. It was in attempting to bring the spacecraft back on axis that he used 30 kg of propellant. He then gave up and hand-flew the spacecraft around Soyuz 2 to take photographs. On the first day of his flight he constantly felt like he was hanging upside-down. This feeling only disappeared on the last day of the flight.
1968 November 9 - .
- Zond 6 State Commission - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The State Commission for the flight of L1 s/n 12 meets at Tyuratam. Launch is set for 10 November. Kamanin notes that the Americans plan to fly Apollo 8 to the moon at great risk in December, but the Russians will not undertake such risk..
1968 November 10 - .
- Soyuz, L1 training - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1, Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5, Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The Soyuz cosmonaut group is in zero-G training at Zhemchug. The L1 group is learning celestial navigation at the State Optics Institute (GOI)..
1968 November 10 - . 19:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 6 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 12L. Mass: 5,375 kg (11,849 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.79 days. Decay Date: 1968-11-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 3535 . COSPAR: 1968-101A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 15,562.22 min.
Test flight of manned circumlunar spacecraft. Successfully launched towards the moon with a scientific payload including cosmic-ray and micrometeoroid detectors, photography equipment, and a biological specimens. A midcourse correction on 12 November resulted in a loop around the moon at an altitude of 2,420 km on 14 November. Zond 6 took spectacular photos of the moon's limb with the earth in the background. Photographs were also taken of the lunar near and far side with panchromatic film from distances of approximately 11,000 km and 3300 km. Each photo was 12.70 by 17.78 cm. Some of the views allowed for stereo pictures. On the return leg a gasket failed, leading to cabin depressurisation, which would have been fatal to a human crew. The 7K-L1 then made the first successful double skip trajectory, dipping into the earth's atmosphere over Antarctica, slowing from 11 km/sec to suborbital velocity, then skipping back out into space before making a final re-entry onto Soviet territory. The landing point was only 16 km from the pad from which it had been launched toward the moon. After the re-entry the main parachute ejected prematurely, ripping the main canopy, leading to the capsule being destroyed on impact with the ground. One negative was recovered from the camera container and a small victory obtained over the Americans. But the criteria for a manned flight had obviously not been met and Mishin's only hope to beet the Americans was a failure or delay in the Apollo 8 flight set for December. The next Zond test was set for January. Additional Details: here....
1968 November 11 - .
- Zond 6 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Two Volga automobiles and two buses take the State Commission from the Hotel Kosmonavt to Area 81. The L1 launch into parking orbit is good (parameters 88.23 minutes period vs 88.3 planned; inclination 51.24 deg vs 51.5 deg planned; perigee 188.5 km vs 192 km planned; apogee 207 km vs 218 km planned). Translunar injection proceeds normally, but afterwards the high gain antenna doesn't deploy. As a result, there is no telemetry from the astro-navigation system. Kamanin rages, 100 million roubles in launch costs, ruined by one defect. The star sensors 100K and 101K will be tested tomorrow. However without course corrections the spacecraft will miss the earth by 1050 km on return. When the midcourse correction is attempted, the 101K sensor fails, but the 100K functions, and acquires Sirius. This is enough to orient the spacecraft, and 40 minutes later an 8.5 second engine burn is made to put the spacecraft on course.
1968 November 13 - .
- Zond 6 midcourse correction. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev,
Mishin,
Tyulin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Tracking of the L1 shows it will hit the earth on return, but without a further midcourse correction the perigee will be 200 km instead of the 45 km required. Therefore another correction will be needed on the way back from the moon. Ustinov calls a meeting and asks 'How do we answer Apollo 8?'. The reply of Mishin and Tyulin is that 'we are not ready to answer Apollo 8. Apollo 8 is a high-risk adventure. The Americans have not accomplished any unmanned lunar flybys to demonstrate that their systems will function correctly; and of only two Saturn V flight tests to date, the second was a failure. We need to make the L1 program public to show the seriousness and completeness of Soviet readiness'. Ustinov orders the following plan be carried out in the next two months: in December, one unmanned L1 flight, and the first launch of the N1 with an L3 mock-up. In January 1969, a lunar flyby with two cosmonauts; a Lunokhod robot rover will be placed on the lunar surface; and a dual Soyuz manned flight with 1+3 crewmembers. Kamanin notes that the problem with the technical approach of Korolev and Mishin is that cosmonauts are seen only as observers and back-ups to automated systems. Therefore the whole manned space program is based on a false assumption. Because of this the Soviets have lost 2-3 years in the space race, which would have been saved if they had followed the Gemini/Apollo 'pilot in the loop' approach. Afterwards Mishin meets with the L1 cosmonaut group. He wants to get rid of the on-board flight plan and reduce the manual for operation of the spacecraft to one page. 'Don't want to bring bureaucracy aboard the spacecraft' he says. This completely absurd idea again demonstrates his belief in total reliance on automated systems.
1968 November 14 - .
- Zond 6 passes behind moon. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Leonov,
Mishin,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The L1 went behind the moon at 05:49:37, and emerges at 06:21:11. At the time of the next orientation session it is 390,000 km from the earth and moving at 0.6 km/s. All orientations have been made on Sirius so far. Two more are needed: one for the midcourse correction, and then the second for the guided re-entry. The 100K sensor has proven itself despite Kamanin's doubts. Mishin's grumbly voice was grating on everyone, and finally he was put to bed. Kamanin despairs that the Soviet space program is dependent on this poorly organised, capricious, shortsighted man. Discussions are held with Moscow. If Apollo 8 succeeds, the next L1 test in January and the manned flight in April are probably not worth the risk. Some of the scientists want to discuss the inclusion of new medical experiments on pending manned spaceflights, but Kamanin is opposed to it. He does not want anything interfering with the primary mission. What to name the manned L1 spacecraft is discussed. Leonov wants to call it Rodina, Sevastyanov Ural, and Kamanin - 'Academician Korolev'.
1968 November 15 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 1M1 mockup erected on pad with L1S payload - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The N1 mockup was again erected on the pad, in order to conduct tests of the L1S payload in advance of the availability of the 3L launch vehicle..
1968 November 15 - .
- Zond 6 hydrogen peroxide temperature falls to dangerous level - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Overnight a serious situation has developed. The hydrogen peroxide temperature aboard the L1 capsule has fallen from +20 deg C to -2 deg C. By the following morning it was down to -5 deg C. At such temperatures it will disassociate into oxygen and water, and the capsule's orientation thrusters will not be able to function for re-entry. A colour television camera was supposed to have been included in the cabin. If it was there it could be turned on and warm the capsule, but Mishin had insisted to the State Commission that it be deleted. The spacecraft could be oriented so that the sun would shine directly over the peroxide tank and warm it, but this might damage the 100K star sensor, which was mounted right next to it. A proposal is made that an attempt is made to orient the spacecraft using the ONA gyroscope package as flywheels, but Mishin and his deputies don't want to try anything. Mishin suddenly says that the next L1 will not be ready until February or later (before the date was January). This was seen by Kamanin as a typical 180-degree turn for him. Mishin looks bad - probably he's been drinking again. Kamanin sees no solution but a complete reorganisation of the space program, moving the manned program to the VVS.
1968 November 16 - .
- Zond 6 depressurises - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Mishin is comatose, pulse 88, blood pressure 160 over 90. The doctors want to put him in the hospital, but he stays. The side of the L1 where the tanks were mounted finally comes into the sun, and the temperature rises to -1 deg C, a safer temperature than before. But now there is a new problem -- the cabin pressure fell from 718 mm at 05:13 to 610 mm by 05:20. By 08:30 it was down to 350 mm - essentially a situation of a depressurised cabin as far as the landing instruments are concerned. By 18:00 the temperature and pressure in the capsule have stabilised and Mishin is in the hospital. Meanwhile Kosygin is visiting the TsPK.
1968 November 17 - .
- Zond 6 midcourse maneuver - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The hydrogen peroxide temperature has risen to +1 deg C, and the cabin pressure is at 380 mm. The eighth stellar orientation and midcourse manoeuvre was made successful - the 100K sensor has rehabilitated itself. The 3.3-second burn moved the perigee by 25 km, and the spacecraft is expected to hit the center of the re-entry corridor - 49 km altitude plus/minus 7 km. But the State Commission has decided to arm the APO destruct system to destroy the spacecraft if it deviates from its ballistic trajectory.
1968 November 18 - .
- Zond 6 re-entry - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
By 20:00 the cabin pressure was down to 180 mm, and then reached 25 mm at re-entry. At 16:00 the spacecraft confirmed that all landing commands had been received successfully. At 16:20 it confirmed correct orientation for re-entry. The tracking vessel Komarov tracked the capsule in its first dip into the atmosphere over the Indian Ocean. The tracking ship crew estimated the capsule would miss the landing point by 1800 km. However Zond 6 successfully completed the double-skip re-entry. It was picked up by PVO radars 300 km from the border of Afghanistan, and tracked to 100 to 150 km north of the cosmodrome. Radio communications and the radar transponder aboard the capsule were inoperative, and the precise landing point could not be determined. The parachute should have deployed at 17:19 and Kiev and Baku received a brief 1 to 2 second radio burst from the capsule, but nothing thereafter. A search begins for the capsule using 50 aircraft and 12 helicopters. Finally at 06:35 the next morning an Mi-4 sees the parachute 38 km southeast of Novokazalinsk, 70 km from Baikonur. The spacecraft is found 3 km away at 12:00.
1968 November 20 - .
- Soviet manned circumlunar flight set for February - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Leonov,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Titov still would prefer to be a test pilot, not a cosmonaut. The Soyuz group is scheduled to complete their training and to depart for the cosmodrome on 20 December for final preparations. Leonov's L1 group is to complete their training on 20 January 1969, then depart to the cosmodrome for a flight to the moon in February.
1968 November 20 - .
- Soyuz spacesuit review - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 3,
Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Yastreb.
Kamanin attends an Yastreb spacesuit review with VVS doctors. The suit removes 200 cal/hour, but when the cosmonaut is exerting himself, he will generate 3 to 4 times more than this. So the cabin is chilled to 18 deg C prior to the EVA, and there will be lots of pauses during preparations to exit the spacecraft. The L1 cosmonaut-engineers at the meeting have little zero-G experience, and need to get a lot more. The new oxygen generating system for the L1 is still not complete. It will be 6 to 8 kg lighter than the old system (using calcium instead of the old material). Mishin insists that the new system should be completed and installed. Ground qualification testing will be completed on 1 January, but the system will not be flight-proven - Kamanin believes it needs test on low earth orbit missions before being adopted for lunar flights. Beregovoi's experience on Soyuz 3 is reviewed. He needed more time to adapt to zero-G before being required to attempt a docking. He had the impression he was upside-down and had intestinal tract problems.
1968 November 23 - .
- Soyuz 4/5 crew training - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. Spacecraft: Yastreb. The Soyuz crews complete training in the TBK-60 vacuum chamber and zero-G flights aboard the Tu-104. These show there exertion level in the Yastreb suit to be 600 to 900 kcal/hr - and the suit is rated to only 1/3 to 1/4 of that amount..
1968 November 28 - .
- Soyuz 4 / 5 spacecraft begin preparation - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Soyuz spacecraft 12 and 13 have begun their 45 day preparation cycle at Baikonur, which implies a 15 January 1969 launch for he Soyuz 4/5 mission. The crews will be ready by 25 December.
Kamanin compares the results of Soyuz capsule re-entries to date:
Soyuz s/n 7 8 9 10 11 Max G's 3.15 3.5 3.5 3.5 3.5 SA Propellant, kg 40.0 40.0 40.0 38.0 38.0 Propellant usage: Used Pre-reentry, kg 8.5 10.0 2.0 3.0 5.3 Used in Re-entry, kg 17.5 29.0 3.7 9.5 12.5 Total 26.0 39.0 5.7 12.5 17.8 Left at chute opening, kg 14.0 0.0 34.3 25.8 20.2 Miss distance, km 157 55 40 15 42
1968 November 29 - .
- No mention of results of planned December 1968 L1 launch in Kamanin's diary... - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Kamanin states he will be travelling to the Far East for a reunion of his World War 2 unit. He will miss the state commission on the L1..
1968 December 17 - .
- The crews take their final examinations to qualify for the Soyuz 4/5 flights. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Kuznetsov,
Shatalov,
Shonin,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft: Yastreb.
All pass. Volynov, Shatalov, and Khrunov do best; Gorbatko and Shonin make mistakes (for example stating that the spacesuit pressure is 35 atmospheres instead of 3.5 atmospheres). Kuznetsov had planned for Gagarin to be cosmonaut commander, and Beregovoi has been poorly prepared for the job. But he still plans to make Beregovoi his deputy in the position. The other cosmonauts bitterly oppose this decision, and spread stories of Beregovoi's incompetence.
1968 December 20 - .
- Volynov crew selection questioned - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Volynov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. The Communist Party Central Committee meets to approve the crews for the upcoming Soyuz 4/5 flights. The committee is unhappy with the selection of Volynov - his mother is a Jew..
1968 December 25 - .
- Launch dates set for Soyuz 4 and 5 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Apollo 8 is on its way back to earth, but re-entry into the earth's atmosphere from lunar distances is risky, as the Soviet experience with the L1 has shown. The State Commission meets at 16:00 and sets the launch dates for Soyuz 4 and 5. Meanwhile Beregovoi and Yurasov are in the Soyuz spacecraft in the assembly building, running communications checks.
1968 December 26 - .
- Heated arguments over technical approach of Soviet space systems - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Mishin,
Mnatsakanian,
Severin,
Shatalov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Flight: Apollo 8.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz 7K-S,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
The training for the Soyuz 4 and 5 flights was completed last night. Today the crews undergo medical tests and start preparation of their flight logs/flight plans. On the return flight to Moscow Shatalov, Beregovoi, Severin, Kamanin, and Mnatsakanian get into a heated argument. The cosmonauts attack Mnatsakanian's Igla automated docking system. It limits docking manoeuvres to periods when the spacecraft are flying over the Soviet Union due to the requirement for ground stations to receive live television. The Americans worked only on the Apollo spacecraft for the last two to three years, while the Soviets have divided their efforts on no less than five spacecraft types: the L1, L3, Soyuz, Soyuz VI, and Almaz. This is all Mishin's fault...
1968 December 27 - .
- Apollo 8 and L1 plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Apollo 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
A State Commission investigating the crash of Zond 6 determined that the coronal discharge effect which caused the parachute to jettison would only occur at the 25 mm capsule pressure. If the capsule had been completely depressurised to a high vacuum, the accident would not have occurred. A discussion was conducted on when to conduct the next L1 test. The next capsule in line was s/n 13 - an unlucky omen. It was even proposed not to fly the capsule with such an unlucky number. That evening, the Soviet engineers could watch live video from the moon from aboard Apollo 8 via Eurovision from Western Europe. They had in any case lost the race to fly a man around the moon. The flight of further L1's, and sending a Soviet man on a lunar flyby, seemed a moot point.
1969 Early - .
- Soyuz VI Flight 1 (cancelled) - . Crew: Kolesnikov, Popovich. Backup Crew: Belousov, Gubarev. Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Flight: Soyuz VI Flight 1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz VI. The planned first flight of the Soyuz VI combat spacecraft was planned for early 1969, beating America's equivalent Manned Orbiting Lab. The project was cancelled in 1968..
1969 January 4 - .
- Soyuz 4/5 preparations - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. Kamanin and 50 VVS officers arrived at Tyuratam aboard an An-24 to supervise the launch of Soyuz 4 and 5..
1969 January 6 - .
- Mishin a no-show. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz, Lunar L3, Lunar L1. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. There is much criticism of Mishin and Keldysh for not attending launches any longer. The opinion is that they are afraid to show their faces..
1969 January 7 - .
- Preparations at Baikonur - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Luna.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The head of the launch commission for Venera-5 and 6 says that will work on the Ye-8 and Ye-8-5 robot moon landers was making progress, it would be fantasy to believe that a moon landing and return to earth could be successfully accomplished in 1969. Venera was 'no answer' to Apollo at all. Meanwhile, he was worried about Soyuz landing in the Aral Sea in the event of problems during re-entry. Kustanin remembers times in the past when supposedly 'waterproof' spacecraft had landed in water. One Soyuz had splashed down in the Aral Sea, and one Zenit spysat in the Volga River. Both sank easily. But the chances of either Soyuz 4 or 5 landing in the Aral Sea were assessed as only 0.003. In any cases 5 helicopters and 3 Be-12 seaplanes were on standby to recover the crew in such an eventuality.
1969 January 8 - .
- Concern over the possibility of Soyuz 4 or 5 landing in the Aral Sea continues. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
An Il-14 is sent on a flight to reconnoitre. It reports 12 to 50 cm ice over the entire surface. Mishin, Chertok, and the rest of he OKB-1 entourage arrive. An argument immediately ensures over provisions and planning for emergency landings. It is decided to make a review of emergency landing and recovery plans as the first agenda item every day of he flights.
1969 January 9 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- State Commission for the first N1 launch - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kurushin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A.
The State Commission for the first N1 launch, headed by Afanasyev, convenes at Area 12 of Baikonur. All of the Chief Designers and top generals of the VVS are in attendance. Many defects are identified in the review, but there seem to be no show-stoppers. Payload integration with the booster is to begin 13 January and launch by 18 February. Then Baikonur commander General Kurushin drops a bombshell - he declares he is not prepared to attempt to launch this 'unready' rocket. Much argument and discussion ensues. Finally Afanasyev asks that the issues raised be reviewed, in preparation for the next commission meeting on 11 January.
1969 January 11 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 state commission meeting. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei. Program: Lunar L3, Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A. The issues raised with the N1 have been cleared up and settled. Afanasyev approves the schedule leading to an 18 February first launch of the N1..
1969 January 12 - .
- Soyuz 4/5 profile still not settled - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At Baikonur, Ustinov and Afanasyev get into an argument with Mishin. They want Soyuz 4 and 5 to accomplish a completely automatic docking, as was done successfully by Cosmos 186/188 and Cosmos 212/213. Mishin categorically rejects this. He wants a manual docking, which was unsuccessful when attempted by Beregovoi on Soyuz 2/3. Meanwhile the Soyuz 4/5 crews hold a news conference.
1969 January 13 - .
- Soyuz 4 launch scrubbed - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Shatalov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The 'unlucky' Shatalov entered the spacecraft at 10:30. But the -24 deg C weather was below the limits of the booster's gyroscopes. The launch was scrubbed. The launch was made successfully the next day. Later in the day Mishin discussed the N1/L3 project with Afanasyev.
1969 January 13 - .
- Soyuz 4/5 profile still not settled - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
In the evening Afanasyev hosts 100 guests - the leadership of the space program - to watch the big Army-Dinamo football game. Space plans are discussed. The State Commission still needs to confirm the crews for Soyuz 4/5. The issue of automatic versus manual rendezvous is again argued. Kamanin believes this reliance on automated systems has cost the Soviet Union the moon race.
1969 January 13 - .
- Soyuz 4 scrub - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The launch of the 13th Soviet cosmonaut into space aboard Soyuz 4 is scrubbed - the first launch scrub in the history of Soviet manned launch attempts. Despite -24 deg C temperatures and 8 to 10 m/s winds, the fuelling of the rocket proceeds successfully. Voice communications are lost with Shatalov whenever the television camera is turned on, but it is decided just to leave the camera off and proceed with the launch. Then at T - 9 minutes a problem is detected with the gyro platform of the rocket. It takes three hours to fix, pushing the launch back to 15:00, meaning the landing will have to be in darkness at the end of the mission. It is decided this is too risky, and the launch is cancelled. As Shatalov exits from the spacecraft, he jokes that he has set a new record: shortest space flight, and first to return to its exact point of lift-off. The engineers are concerned with the internal temperature of the SAS abort system solid rockets if left on the pad for 24 hours in these temperatures. The internal temperature of the fuel cannot go below -2 deg C at night. Any lower, the loss of specific impulse of the fuel would reduce the thrust by more than 5%, the limit established for safe operation.
1969 January 14 - . 07:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 4 - .
Call Sign: Amur (Amur - river). Crew: Shatalov.
Backup Crew: Shonin.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (A) s/n 12. Mass: 6,625 kg (14,605 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 2.97 days. Decay Date: 1969-01-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 3654 . COSPAR: 1969-004A. Apogee: 224 km (139 mi). Perigee: 213 km (132 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Soyuz 4 is launched with Vladimir Shatalov aboard without further problems at 10:30. This time the rockets gyroscopes, the capsule communications, and the television camera all functioned perfectly. Volynov and his crew for Soyuz 5 watched the launch from Area 17. Later Soyuz 4 would dock with Soyuz 5, and following a transfer of two cosmonauts, return with Shatalov, Yevgeni Khrunov and Alexsei Yeliseyev from Soyuz 5. Official purpose: scientific, technical and medico-biological research, checking and testing of onboard systems and design elements of space craft, docking of piloted space craft and construction of an experimental space station, transfer of cosmonauts from one craft to another in orbit. This mission finally successfully completed the simulated lunar orbit docking and crew transfer mission attempted by Soyuz 1 in April 1967. In making the transfer Khrunov and Yeliseyev avoided the most spectacular survivable incident of the space age - the nose-first reentry of Soyuz 5, still attached to its service module.
1969 January 15 - . 07:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 5 - .
Call Sign: Baikal (Baikal - lake in Siberia). Crew: Khrunov,
Volynov,
Yeliseyev.
Backup Crew: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Kubasov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK (P) s/n 13. Mass: 6,585 kg (14,517 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 3.04 days. Decay Date: 1969-01-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 3656 . COSPAR: 1969-005A. Apogee: 212 km (131 mi). Perigee: 196 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
At 3 am an An-12 arrives from Moscow with ten newspapers, and letters for Shatalov, to be delivered by the Soyuz 5 crew to him as the first 'space mail'. At 05:15 the State Commission convened and approved launch at 10:04:30. The countdown proceeds normally; meanwhile communications sessions are held with Shatalov on Soyuz 4. The commission is taken by automobile convoy from Area 2, to Area 17, where the Soyuz 5 crew declares itself ready for flight. At T-25 minutes, with the crew already aboard the spacecraft, a piece of electrical equipment fails and needs to be replaced. Engineer-Captain Viktor Vasilyevich Alyeshin goes to the fuelled booster and replaces it. While doing this he notices that the access hatch has been secured with only three bolts, instead of the four required. Nevertheless the launch proceeds successfully. After Soyuz 5 is in orbit, it and Soyuz 4 begin their mutual series of manoeuvres for rendezvous and docking. Officially the flight conducted scientific, technical and medico-biological research, checking and testing of onboard systems and design elements of space craft, docking of piloted space craft and construction of an experimental space station, transfer of cosmonauts from one craft to another in orbit.
1969 January 16 - .
- 10 Soyuz for military proposed - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The space leadership board planes to depart Tyuratam. During the flight to Moscow, Kamanin discusses with Mishin the possibility of purchase of 10 to 15 Soyuz spacecraft by the Ministry of Defence for military experiments. Mishin is very interested in the possibility.
1969 January 16 - . 12:43 GMT - .
- EVA Soyuz 4/5-1 - .
Crew: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
EVA Duration: 0.0257 days. Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
A day after the launch of Soyuz 5, Soyuz 4 docked with it. The Soyuz 4 active spacecraft was equipped with a long docking probe, designated 'Shtir'. The Soyuz 5 target spacecraft was equipped with the 'Konus' receptacle. The symbology lead Volynov to joke that he 'was being raped' when the hard docking was accomplished. Khrunov and Yeliseyev transferred to and returned in Soyuz 4, the feat they had hoped to accomplish in the cancelled Soyuz 2 flight almost two years earlier. The external crew transfer was also a test of the technique needed for the Soviet lunar landing.
1969 January 17 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 4 - .
Return Crew: Khrunov,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5.
Soyuz 4 landed at 06:51 GMT 48 km south-west of Karaganda, 40 km from the planned point, with the crew of Khrunov, Shatalov and Yeliseyev aboard. Shatalov's performance has been outstanding -- all manoeuvres were made correctly with minimal expenditure of propellant. The soft landing system performed well, in temperatures of -30 deg C and in 60 to 80 cm of snow. The first recovery helicopter reached the capsule only five minutes after touchdown. 25 minutes later the crew is on a helicopter, on their way to the airfield at Karaganda. The crew is given a medical examination at the Hotel Chaika and then taken downstairs for a press conference. At 16:45 they board an An-24, bound for Tyuratam.
1969 January 18 - .
- Volynov's survival celebrated - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Mishin,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
The engineering team at Yevpatoriya celebrated Mishin's birthday and Volynov's survival after his re-entry. These were four stressful days -- aside from the Soyuz missions, Babakin was commanding the Venera 5 and 6 probes to Venus, which had been launched on 5 and 10 January.
1969 January 18 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 5 - .
Return Crew: Volynov.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Brezhnev,
Mishin,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
After Shatalov and Yeliseyev transferred to Soyuz 4, Volynov remained behind to live through the most unbelievable re-entry in the history of spaceflight. The service module of the Soyuz failed to separate after retrofire. Once the Soyuz started reaching the tendrils of the atmosphere, the combined spacecraft sought the most aerodynamically stable position - nose forward, with the heavy descent module with its light metal entry hatch at the front, the less dense service module with its flared base to the back. Luckily the struts between the descent and service modules broke off or burned through before the hatch melted through and the descent module righted itself, with the heat shield to the rear, before being consumed. Due to a failure of the soft-landing rockets the landing was harder than usual and Volynov broke his teeth. The landing came at 7:58 GMT. Additional Details: here....
1969 January 19 - .
- State Commission on Soyuz 4/5 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Yastreb.
At 10:00 a State Commission convenes at Area 17. The mistakes made during the Soyuz 4/5 flight are reviewed. The EVA began with a closed valve on Khrunov's suit. The film camera was not activated, resulting in loss of one of the key propaganda points of the exercise.
1969 January 20 - . 04:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Second stage - One RD-0210 engine fails at T+510 sec, resulting in flight path deviation, automatic shutoff of launch vehicle.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 13L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 13L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1969-01-19 .
Launch failure - but the abort system again functioned perfectly, taking the capsule to a safe landing (in Mongolia!). At 501 seconds into the flight one of the four engines of the second stage shut down, and remained shut down for 25 seconds. The ever-reliable SAS abort system detected the failure, and separated the capsule from the failed booster. Yet again a successful capsule recovery after a booster failure. Additional Details: here....
1969 January 22 - .
- American looks likely to win moon race - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gagarin,
Khrunov,
Korolev,
Mishin,
Shatalov,
Smirnov,
Ustinov,
Volynov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Apollo 8,
Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Kamanin and four cosmonauts return to Moscow from Tyuratam aboard an Il-18. It has been nearly nine years since Gagarin's flight, and now America looks like the winner of the space race, with the successful flight of Apollo 8 around the moon. Kamanin attributes the loss to the mistakes made by Ustinov and Smirnov in the erratic management of the Soviet program, coupled with the insistence of Korolev and Mishin to develop completely automated spacecraft that do not require intervention by the cosmonaut.
1969 January 22 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soyuz 4/5 celebrations - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Lunar L3, Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. TsKBEM closed down for the day, due to celebrations at Kaliningrad and at the Kremlin with the four cosmonauts from the Soyuz 4 /5 mission. Meanwhile, work at Tyuratam preparing the N1 for its first flight continued..
1969 January 23 - .
- Cosmonauts shot at in assassination attempt - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Feoktistov,
Khrunov,
Nikolayev,
Shatalov,
Volynov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4,
Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
The assassination attempt is made on Brezhnev, instead hitting the cosmonaut's car, on the way to the Kremlin. A muted press conference follows. All the cosmonauts are there, except Feoktistov, who is on honeymoon with his second wife, and Nikolyaev, who has the Hong Kong flu.
1969 January 26 - . LV Family: N1.
- MKBS a key justification for continuing with the N1. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Ryazanskiy,
Shcheulov.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS.
In the post-mortems on the N1 after the Apollo 8 mission, MKBS became a key justification for continuing with the N1. MS Ryazanskiy: Our biggest problem - we think only 2 - 3 years ahead. Are we no longer prepared to create a TOS Heavy orbital station? After 7K-VI need to create a large space stations.
VI Shcheulov: Creation of a powerful space station on the basis of N1 would offset, to to some extent, the effect of the United States winning the moon race. MKBS would achieve long-duration through rotation of crews. Modification is necessary in parallel with the existing launch vehicle. We must build two new launch facilities allowing simultaneous launches. (It is necessary to assign the task to develop those launch facilities.) Mishin Diaries 2-159)
1969 January 28 - .
- Soyuz 4/5 crew feted - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Khrunov, Shatalov, Volynov, Yeliseyev. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. The last few days have been occupied with daily press conferences or meetings with the state leadership by the Soyuz 4/5 crews..
1969 January 31 - .
- Kamanin meets with Vershinin. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Leonov,
Mishin,
Vershinin,
Volynov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 4/5,
Soyuz 5.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Spiral OS.
Plans for purchase of ten Soyuz spacecraft for the VVS are discussed. They next turn to Volynov's problems during the Soyuz 5 re-entry. The fault can be attributed entirely to the modular design of the spacecraft, requiring that two modules be jettisoned before re-entry. Vershinin declares that what was needed was a true KLA space flight craft, which would be winged, set toward orbit by aircraft-type booster stages, and could be recovered at a conventional air base borne on wings or rotor blades. Additional Details: here....
1969 February 5 - .
- Cosmonaut centre plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Vershinin.
Program: Soyuz.
Kamanin flies back to Moscow aboard an An-24. Plans for the Cosmonaut Centre are discussed during the flight. It is to consist of 600 officer, 8 generals (vs. 1 currently), 3 directorates (vs. 1 now), and 6 deputy positions (instead of 3). It will become the country's centre for both cosmonaut training and scientific research. Vershinin had spent all day at Chkalovskiy on 3 February. He was unable to get anything going on these plans despite promises to implement them by higher officers.
1969 February 10 - .
- Soyuz plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Beregovoi,
Bykovsky,
Leonov,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Shatalov,
Titov,
Tregub.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8,
Soyuz s/n 15+16,
Soyuz sn 14.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Meeting with TsKBEM Deputy Chief Designer Tregub on manned space flight plans. Soyuz s/n 14 is set for a solo seven day mission in April-May. 15 and 16 with 5 cosmonauts aboard will fly a 7 day mission in August-September, remaining docked for three days. Soyuz s/n 17 through 20 will not fly until after May 1970 - there are no definite plans for them at this time. Additional Details: here....
1969 February 10 - .
- Mishin is considering MKBS weapons aspects - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS.
Mishin is considering MKBS weapons aspects and the use of the transport version of the 7K-VI with the station. Strictly analyze planning for design and development of space weapons systems (separation minima). In achieving mastery of outer space payloads over 100 t are needed, as MKBS should have an orbit above 10,000 km. (Necessary to study optimum orbit). Consider the design of the docking system of the 7K-VI, which provides a transition from one ship to another. (Mishin Diaries 2-194)
1969 February 16 - . LV Family: N1.
- The two-launch scenario with the LKR was still the baseline for the moon landing. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
LK,
LK,
L3M.
Mishin notes: "9. Refine Lunar Expedition using LK, LK-R and E-8". This is the last mention; by mid-1971 a new five-year plan has been approved. Under this the N1-L3 was dropped and OKB-1 was pursuing the N1 with the giant MOK military earth orbit space station and L3M two-launch lunar expedition using new lunar spacecraft (with a podsadka approach to deliver the crew to earth orbit by the new 7K-S!). (Mishin Diaries 2-301)
1969 February 21 - . 09:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: First stage failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 3L launch - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1S s/n 3. Mass: 6,900 kg (15,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Dorofeyev,
Kirillov,
Mishin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A.
Decay Date: 1969-02-21 . Apogee: 30 km (18 mi).
N-1 serial number 3L was the first N-1 launched. The vehicle ran into trouble immediately at lift-off. A fire developed in the tail compartment. The engine monitoring system detected the fire, but then gave an incorrect signal, shutting down all engines at 68.7 seconds into the flight. British intelligence detected the launch attempt, but the CIA's technical means for some reason missed it and they denied for years that it had ever occurred. In retrospect the launch team at Baikonur pointed to a grave mistake - at the christening of the first N1, the champagne bottle broke against the crawler-transporter rather than the hull of the rocket. After the 3L failure everyone knew there was no chance at all of beating the Americans to the moon. Additional Details: here....
1969 March - .
- Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Leonov,
Makarov.
Backup Crew: Kuklin.
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Planned first manned circumnavigation of the moon. Soviet plans to beat America around the moon were upstaged by the sudden decision to fly Apollo 8 into lunar orbit over Christmas 1968. It was decided after the American success to cancel any 'second place' Soviet manned circumlunar flights.
1969 March 17 - .
- Russian military space management changes - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Vershinin. Program: Soyuz. There is a management shuffle in the VVS head shed. Vershinin, a good supporter of Kamanin's attempts to obtain more VVS control of the space programme, is finished. .
1969 March 20 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet of military officers meets to review manned space plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Spiral OS.
A 50 minute presentation is given on space plans. Russia plans to fly no less than six different types of manned spacecraft in 1969-1970 - the Soyuz, L1, L3, Almaz, Soyuz VI, and Spiral. This will result in a decisive answer to the American Apollo programme within two to three years. No N1 launch with the complete L3 lunar landing spacecraft is planned until 1970. Approval is sought for the VVS to buy 10 Soyuz spacecraft for continued manned military flights in low earth orbit. Otherwise between the second half of 1970 and during all of 1971 there will be no spacecraft available for manned flights Additional Details: here....
1969 March 28 - .
- Military Soyuz plan rejected - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Kutakhov,
Zakharov.
Program: Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kutakhov is having trouble selling Kamanin's plans for military spaceflights and the appointment of Beregovoi to the General Staff. Marshal Zakharov has rejected the plan for ten military Soyuz, as he had done with similar earlier plans for Vostok and Voskhod. As far as he is concerned, manned spaceflight has no significant military potential.
1969 April 19 - .
- Military Soyuz meeting - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Kamanin meets with the General Staff, presents the results of the study he has commissioned on the military utility of manned spaceflight, and pleads for support for his proposal to procure ten Soyuz spacecraft..
1969 April 26 - .
- Soyuz program review - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Kolodin,
Kubasov,
Kuklin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Shonin,
Volkov,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 5,
Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt.
The commission considers plans for the rest of the Soyuz production. Spacecraft s/n 14, 15, and 16 are to fly in August 1969, 17 and 18 in November 1969, and 19 and 20 in February-March 1970. Crews selected for the August flights are: for spacecraft 14, Shonin and Kubasov; for 15, Filipchenko, Volkov, and Gorbatko; for 16, Nikolayev and Sevastyanov. Back-ups will be Kuklin, Grechko, and Kolodin. All of the spacecraft will fly 4 to 5 day missions. Spacecraft 15 and 16 will dock and remain together 2 or 3 days to form an 'orbital station'. Experiments planned for the flight are:
- Visual observation of rocket launch plumes using the Svinets device
- Film and photography of the spacecraft 15-16 docking from spacecraft 14
- Demonstration of welding in weightless vacuum conditions using the Vulkan device
- Demonstration of autonomous navigation by the cosmonauts using a sextant
- Medium wave radio communications
- Test of new television sensors for the Soyuz orientation system
Spacecraft 17 through 20 will fly 15 to 16 day missions to demonstrate the new SZhO life support system for the L3, and conduct rendezvous and docking operations using the L3's Kontakt system. Additional Details: here....
1969 May - .
- Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2 (cancelled) - . Crew: Bykovsky, Rukavishnikov. Backup Crew: Klimuk. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Planned second Soviet circumlunar flight. Cancelled after the success of the American Apollo 8..
1969 May 10 - .
- Military space research plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kutakhov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Spiral OS.
Kamanin makes a speech to the VVS Soviet, setting forth again plans for military research in space. His presentation shows how far the USSR is behind the Americans, and the need to regain the lead. He again proposes 10 to 12 military Soyuz flights beginning in the first quarter 1970. This will fill the gap until Soyuz VI and Almaz will begin flying in 1972. Kutakhov is categorically against these Soyuz flights but, under pressure from others, still agrees to form a commission to study the matter. Reference is made to a Ministry of Defence decree of 7 January 1969.
1969 June 1 - .
- Original planned date for first LK test - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Moon. Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: LK. Original planned date for first test of LK in earth orbit..
1969 July - .
- Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3 (cancelled) - . Crew: Popovich, Sevastyanov. Backup Crew: Voloshin. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Makarov. Program: Lunar L1. Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Planned third and final Russian circumlunar flight. Cancelled after the success of the American Apollo 8..
1969 July 3 - . 20:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: First stage failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 5L launch - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1S s/n 5 / Dummy LK. Mass: 6,900 kg (15,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Apollo 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A.
Decay Date: 1969-07-03 .
N-1 serial number 5L began to fail at 0.25 second after liftoff when the oxidizer pump of engine number 8 ingested a slag fragment and exploded. A fire ensued as the vehicle climbed past the top of the tower. Engines were shutdown until the acceleration dropped below 1 G; then the vehicle began to fall back to the pad at a 45 degree angle. The escape tower fired at the top of the brief trajectory, taking the L1S dummy descent module away from the pad. Upon impact of the base of the N1 with the pad, the vehicle exploded, destroying launch pad 110 east, which would take over 18 months to repair. This was the end of a slight Soviet hope of upstaging the US Apollo 11. Additional Details: here....
1969 August 7 - . 23:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 7 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 11. Mass: 5,379 kg (11,858 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-08-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 4062 . COSPAR: 1969-067A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 15,562.22 min.
Circumlunar flight; successfully recovered in USSR August 13, 1969. Only completely successful L1 flight that could have returned cosmonauts alive or uninjured to earth. Official mission was further studies of the moon and circumlunar space, to obtain colour photography of the earth and the moon from varying distances, and to flight test the spacecraft systems. Earth photos were obtained on August 9, 1969. On August 11, 1969, the spacecraft flew past the moon at a distance of 1984.6 km and conducted two picture taking sessions. Successfully accomplished double-dip re-entry and landed 50 km from aim point near Kustani in the USSR.
1969 August 21 - .
- Final crew selections are made for the Soyuz 6, 7, 8 flights. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Khrunov, Kuklin, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov, Shatalov, Yeliseyev. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8. Sevastyanov and Nikolayev did poorly on the final test for the 7/6 crew. Therefore Shatalov and Yeliseyev have been selected. Khrunov has been in an auto accident, and Kuklin didn't pass his centrifuge tests - so they're out as well..
1969 August 26 - .
- Soyuz 6-7-8 are slated to fly in the first half of October. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Borman.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Tests of the spacecraft at Baikonur showed 40 to 60 defects, requiring replacement of 17 to 25 equipment items. This demonstrates the poor quality of final assembly and test at TsKBEM and inadequate measures to protect the spacecraft during storage and transport to the launch site. Soyuz 6 is to launch on 4-6 October, followed by another spacecraft each day thereafter. Nixon has invited two cosmonauts to visit the USA in November -- this is seen by Kamanin as the work of Borman to reciprocate for his visit to the USSR in February.
1969 September 3 - .
- L3 Trainer and Female Cosmonauts - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kuznetsova,
Pashkov,
Ponomaryova,
Smirnov,
Solovyova,
Tereshkova,
Ustinov,
Yerkina.
Program: Lunar L3,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Meeting of Kamanin with S G Donevskiy. The L3 trainer will not be finished until May 1970 - and the current schedule for the first manned L3 launch is December 1970! But in any case Kamanin assesses the latter date as unrealistic -- there is no rocket or spacecraft in being yet. Later in the day Efimov, Moroz, and Kamanin meet with the female cosmonauts - Ponomaryova, Solovyova, Yerkina, and Kuznetsova. They advise them that despite the letter to the Central Committee asking for an all-female Soyuz flight, it has been rejected. Ustinov, Smirnov, and Pashkov are all opposed to the idea, as are MOM, MAP, AN, and VVS. Kamanin believes the whole female cosmonaut concept was a mistake. Flying Tereshkova in the first place started the whole thing, but now there is no follow-up.
1969 September 8 - .
- Kuznetsov is in the hospital for 45 days after a heart attack. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Beregovoi, Kuznetsov, Nikolai F. Program: Soyuz. Beregovoi is in charge of NII TsPK..
1969 September 12 - .
- Shatalov and Yeliseyev are progressing well for their Soyuz 8 flight. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Shatalov,
Tereshkova,
Ustinov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Kamanin advises Nikolayev his chances of being named to fly Soyuz 8 are very low. Tereshkova arrives at Kamanin's office in the evening. She is infuriated that her husband is not to be allowed to fly the mission. She says she will take the matter to Ustinov and Polanskiy. Kamanin tells her that would be a mistake.
1969 September 18 - .
- Approval is given for proceeding with the Soyuz 6-7-8 flights - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Beregovoi,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Nikolayev,
Smirnov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
However the board makes a big fuss over Kamanin having trained only four back-up cosmonauts to support eight prime-crew cosmonauts. A follow-up meeting is held with Smirnov and Afanasyev at 19:15, where Kamanin's training is denounced as a big failure. Nevertheless at 22:00 the word comes from the Kremlin to proceed with the missions. Kamanin points out that simultaneously with this mission he had cosmonauts in training for Soyuz s/n 17, 18, 19, 20 (Kontakt missions) and L1 circumlunar fights. Kuznetsov, Beregovoi, and several other cosmonauts are also enraged with Kamanin for bumping Nikolyaev from the Soyuz 8 crew. Kamanin maintains that in the circumstances he only had enough training resources for 8 prime + 4 back-up crew, especially for a mission scenario that would not be flown again in the future.
1969 September 18 - .
- Soyuz 6/7/8 go-ahead - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Smirnov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Smirnov recommended to the VPK Military-Industrial Commission that the flights go ahead in October. The triple Soyuz flight would make heavy demands on the Soviet tracking system. The problems were worked out in simulations and worldwide exercises conducted from the Baikonur cosmodrome.
1969 September 20 - .
- The success of Zond 7 has emboldened Mishin and Tyulin. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
They want to fly Zond 8 unpiloted in December 1969, to be followed by a two-man L1 lunar flyby in April 1970. This would look bad compared to the Apollo moon landings, but there was no other manned space mission they could offer the leadership in 1970. Of the 15 L1 spacecraft built, only three remain.
1969 September 22 - .
- Kamanin arrives at Tyuratam at 15:00 aboard an An-124 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
A second arrives 50 minutes later. They bring the 49-strong VVS contingent for the Soyuz 6-7-8 state commission. The other members of the commission arrive aboard an Il-18. 2 to 3 weeks earlier an epidemic of dysentery swept the cosmodrome. This was a danger to the space flight crews -- no one showing signs of carrying the disease were allowed near them. They were isolated in special areas and only cleared trainers were allowed access to them during the outbreak. In the evening the American film 'Good Arrangement' is shown, the story of a husband in the role of a nanny for three children.
1969 September 24 - .
- Soyuz 6-7-8 readiness review is made by Ustinov, Kerimov (for Afanasyev), Mishin, and Karas - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Karas,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The members do not believe the three spacecraft and crews are ready for flight. They rate the availability of the actual spacecraft for training before the flight at 20 to 30%, while the trainers are being used at 200% of their rated capacity. The result is the cosmonauts can only train on the technical systems of the actual spacecraft after they have been delivered to the cosmodrome. The situation is even worse with the experimental equipment for the flights, which in some cases they do not see until they are at the cosmodrome. Unwilling to commit themselves, the commission bumps the decision whether to proceed up to the Politburo. Ustinov and Smirnov badly guide the whole space program, in Kamanin's view. The Politburo won't meet until 29 September -- he hopes the Russian bureaucracy can complete all the steps to approve the flights before the scheduled launch day!
1969 September 25 - .
- The Central Committee debates plans for the upcoming visit of two cosmonauts tot he USA. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Beregovoi,
Feoktistov,
Nikolayev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
They rule out 22 October as a start date, in order not to have the embarrassment of them being there during the Apollo 12 mission. They reject Belyayev and Shatalov as candidates for the trip; they want Beregovoi and Belyayev or Beregovoi and Feoktistov. Kamanin opposes Feoktistov, and doesn't' want Beregovoi diverted from his work as cosmonaut deputy-commander, where he feels he is doing well. He has started lots of good new initiatives. Meanwhile Nikolayev continues to make trouble for Kamanin in regard to being bumped from the Soyuz 8 crew.
1969 September 27 - .
- Fuelling begins of Soyuz 6. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 5,
Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
V A Smirnov and other specialists again go over the near-disaster with Soyuz 5. The true cause of the failure of the re-entry capsule to separate has never been established, but the separation systems have been fully reworked (latches, pyrotechnics, etc) and fundamentally improved. The improved system was used on Zond 7, but no flights have yet been flown with the new system on a Soyuz.
A deadly spider is found at the sport hall. Many cosmonauts saw it for the first time, and it led to a discussion of the dangers of Central Asia. - poisonous spiders and scorpions. Kamanin also makes a pilgrimage to Area 2, visiting the Korolev cottage and Gagarin museum.
1969 September 28 - .
- Soyuz 6-7-8 flight preparations - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
It is Sunday, but the cosmonauts are at work, training on the scientific equipment for the flight and preparing for the autonomous navigation experiment. Nikolayev is preparing the work plan for the launch of the first spacecraft. The cosmonauts have been working ten hours per day for weeks now without interruption. The use of a new anti-radiation vitamin preparation the cosmonauts will take during the flights is discussed.
1969 September 29 - .
- Soyuz 7 manual rendezvous proposed - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Shatalov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Meeting with the crew commanders for the upcoming flights. The ship's logs/flight plans are reviewed. The draft flight plans provided by Anokhin at TsKBEM had many errors that had to be corrected. Shatalov proposes a method of making a more fuel-efficient docking on the flight - uncoupling the automatic system and accomplishing not just the final docking manoeuvres but the terminal rendezvous manoeuvres manually. The flight specialists agree to review the proposal.
1969 September 30 - .
- Politburo approves Soyuz 6/7/8 flight. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Kutakhov, Mishin, Smirnov, Ustinov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8. Ustinov, Smirnov, Afanasyev, Mishin, and Kutakhov appear before the Politburo and affirm the readiness of the spacecraft, boosters, and crews of Soyuz 6/7/8 for flight. Approval is given to proceed..
1969 October 1 - .
- Problems with Beregovoi. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Beregovoi. Program: Soyuz. Kamanin notes that Beregovoi is not doing well as chief of the cosmonaut centre. But he still feels no other cosmonaut has any better leadership qualities..
1969 October 2 - .
- Soyuz 6/7/8 State Commission - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8. The State Commission convenes at Tyuratam and affirms everything is ready for the Soyuz 6/7/8 flight..
1969 October 3 - .
- Mishin arrives at Tyuratam. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8. Kamanin notes he now always shows up only after the State Commission has met..
1969 October 5 - .
- Sunday at the cosmodrome - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
It is agreed that future pre-flight reviews of spacecraft operations should not just be limited to standard procedures, but should cover back-up and emergency procedures as well, even though this will take 2 to 3 days longer to prepare. It is Sunday at the cosmodrome. Kamanin gives a speech on the Gagarin launch in 1961. There are chess, tennis, billiards, and ping-pong tournaments.
1969 October 6 - .
- Soyuz 6/7/8 experiment review - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Shatalov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Meeting between the Soyuz 6/7/8 crews and engineers. Shatalov pushes his idea for a manually flown spacecraft rendezvous, provided that Soyuz 7 and 8 visually acquire each other immediately after Soyuz 8 is put into orbit. He believes this would not only save time and fuel, but also provide the chance to develop procedures for interception of non-cooperative enemy satellites. Mishin rejects the idea, seeing a doubling of risk of an unsuccessful flight. The fact is, the Soyuz is only equipped for automatic docking. There are no on-board indicators of range and range-rate to target - necessary inputs for any manual docking. The view through the periscope is the only forward-looking view available to the crew, and it is inadequate for manual docking. Additional Details: here....
1969 October 8 - .
- Soyuz 6/7/8 State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko,
Mishin,
Shatalov,
Volkov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Kamanin takes General Efimov to see the roll-out of the Soyuz 6 booster. Mishin calls during the tour to ask that Volkov be switched with TsKBEM engineer Grechko on the Soyuz 7 crew. Kamanin refuses at this late date, noting in disgust Mishin is always pushing his staff for flight regardless of how it might affect the mission. Efimov is then taken to see the N1 MIK assembly building, the largest building in Europe. They view the construction of the 104-m-long booster's three stages. Next they go out to the pad, surveying the facility from 120 m up in one of the gantries. Kamanin muses that unless the N1 can be made reliable, the Russians will be 7 to 8 years behind the Americans in planetary and lunar exploration. Later the State Commission meets and fixes the launch schedule for the upcoming flights. Mishin does not raise the issue of Grechko flying to the commission. Shatalov is named commander of the entire three-spacecraft group flight.
1969 October 9 - .
- Final preparations - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Beregovoi,
Feoktistov,
Kubasov,
Kurushin,
Shatalov,
Shonin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
The ship's logs/flight plans are reviewed one more time. Tyuratam commander General Kurushin runs through the Svinets ABM experiment again with Shonin and Kubasov - they're ready. The Communist Party has selected Beregovoi and Feoktistov for the trip to the United States in November, ignoring Kamanin's recommendation of Belyayev and Shatalov. Kamanin is not so much against Beregovoi, but he firmly believes that Feoktistov is not worthy of the privilege - he's a degenerate, now on this third marriage..
1969 October 10 - .
- Cosmonaut awards discussed. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Bad weather at the cosmodrome - rain and 12-15 m/s wind. The traditional meeting of the cosmonauts and their support teams takes place at 15:00 at Area 31. Afterwards Kamanin meets with VVS General I M Moroz and Efimov. The future policy is that a cosmonaut will receive the Hero of the Soviet Union award and a military promotion only on their first flight into space. On later flights they will receive a lesser decoration and a cash award. Exceptions would be made for exceptional missions. Mozzhorin disagrees, preferring to keep things as they are.
1969 October 11 - . 11:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 6 - .
Call Sign: Antey (Antaeus - mythological giant). Crew: Kubasov,
Shonin.
Backup Crew: Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 14. Mass: 6,577 kg (14,499 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 4.95 days. Decay Date: 1969-10-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 4122 . COSPAR: 1969-085A. Apogee: 218 km (135 mi). Perigee: 212 km (131 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Tested spacecraft systems and designs, manoeuvring of space craft with respect to each other in orbit, conducted scientific, technical and medico-biological experiments in group flight. Carried Vulkan welding furnace for vacuum welding experiments in depressurized orbital module. Was to have taken spectacular motion pictures of Soyuz 7 - Soyuz 8 docking but failure of rendezvous electronics in all three craft due to new helium pressurization integrity test prior to mission did not permit successful rendezvous and dockings. Additional Details: here....
1969 October 12 - . 10:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 7 - .
Call Sign: Buran (Snowstorm ). Crew: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Volkov.
Backup Crew: Kolodin,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 15. Mass: 6,570 kg (14,480 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kubasov,
Mishin,
Shonin.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 4.94 days. Decay Date: 1969-10-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 4124 . COSPAR: 1969-086A. Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 210 km (130 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Tested spacecraft systems and designs, manoeuvring of space craft with respect to each other in orbit, conducted scientific, technical and medico-biological experiments in group flight. Was to have docked with Soyuz 8 and transferred crew while Soyuz 6 took film from nearby. However failure of rendezvous electronics in all three craft due to a new helium pressurization integrity test prior to the mission did not permit successful rendezvous and dockings. Additional Details: here....
1969 October 13 - . 10:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 8 - .
Call Sign: Granit (Granite ). Crew: Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Backup Crew: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 16. Mass: 6,646 kg (14,651 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Duration: 4.95 days. Decay Date: 1969-10-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 4126 . COSPAR: 1969-087A. Apogee: 227 km (141 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Tested spacecraft systems and designs, manoeuvring of space craft with respect to each other in orbit, conducted scientific, technical and medico-biological experiments in group flight. Was to have docked with Soyuz 7 and transferred crew while Soyuz 6 took film from nearby. However failure of rendezvous electronics in all three craft due to a new helium pressurization integrity test prior to the mission did not permit successful rendezvous and dockings. Recovered October 18, 1969 10:19 GMT. Additional Details: here....
1969 October 14 - .
- Soyuz 7-8 docking problem - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Shatalov,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Orbital manoeuvres for the Soyuz 7-8 docking have proceeded normally. The automated rendezvous system is supposed to kick in when the spacecraft are 250 km apart. The plan is that Soyuz 7 and 8 will dock while Soyuz 6 observes from only 50 m away. However when Soyuz 7 and 8 are only a kilometre apart, the Igla automated docking system fails. The crews could conduct a manual rendezvous, but the this is not allowed by the technical flight controller. Additional Details: here....
1969 October 15 - .
- Second attempt to dock Soyuz 7 & 8 - rendezvous of Soyuz 6 with Soyuz 8 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Kubasov,
Shatalov,
Shonin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Following an orbital correction during the night, Soyuz 7 and 8 are expected to be less than 1 km from each other when communications are regained at 9 am. Instead they are 40 km apart. It will require two more orbits over Soviet territory to refine the tracking of the spacecraft and recalculate the necessary rendezvous manoeuvres. By 12:40 they are 1700 m apart and the crews begin the manual rendezvous manoeuvre. Shatalov fires his engines four times, but in the absence of any indication to the pilot of range to the target, he could not get into a position for a safe docking. He withdraws to a safe distance. Additional Details: here....
1969 October 16 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 6 - further attempts to dock Soyuz 7 and 8 - .
Return Crew: Kubasov,
Shonin.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Kubasov,
Shatalov,
Shonin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Soyuz 6 lands successfully at 09:52 GM, coming to rest in a vertical position. A recovery helicopter lands 10 minutes later, finding the cosmonauts have already emerged from the capsule. After the landing of Soyuz 6 there are two further attempts to dock Soyuz 7 and Soyuz 8, but they fail due to large errors in the ballistic calculations of the manoeuvres necessary to correct their orbits.
1969 October 17 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 7 - .
Return Crew: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Volkov.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Volkov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The landing commission meets at the command post at 08:00. Soyuz 7 is to land on orbit 97, beginning a 95 m/s retrofire impulse at 11:44:11. The main parachute is to deploy at 12:12:34. All is reported normal aboard the spacecraft, except that the Soyuz 7 warning light panel shows 'ASP' - automatic landing sequence. Despite this, Soyuz 7 landed successfully at 09:26 GMT. Additional Details: here....
1969 October 18 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 8 - .
Return Crew: Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Karas,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin's 61st birthday begins with a communications session with Soyuz 8. Yells come from the spacecraft. What's wrong? the ground nervously inquires. They reply they are only celebrating the successful closing of the hatch, and the glowing 'SA hermetic' indication on the panel. This ends fears they had all during the flight of not being able to get the hatch closed with the broken wheel spoke. The 145 second long retrofire begins at 11:29. It looks OK on the telemetry, but Shatalov reports on UHF that the indication aboard the spacecraft was that there was a 4 second underburn. Nevertheless the landing proceeds normally, and there is a loud 'Ura!' at the command point once word of a safe crew recovery is received - the mission is completed. Soyuz 8 landed at 09:10 GMT. At 16:40 the teams head back toward Moscow aboard an Il-18. Kamanin discusses the necessity to complete an extra 8 to 10 Soyuz spacecraft. He is supported by Afanasyev and Kerimov, but Mishin and Karas are opposed now. Kamanin thinks it is insane how Soviet space progress is blocked by these kinds of politics.
1969 October 19 - .
- Post mortem on the Soyuz 6-7-8 mission - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
State commission meets to do a post mortem on the Soyuz 6-7-8 mission. Kamanin gives a 15-minute briefing on the readiness of the crews for flight. He pointed to the need for more information and training on manual flight and navigation of the spacecraft, and more active use of the pilots throughout the mission. Then the commission acts out a few scenes of their meting for the press, television, and a documentary filmmaker. The Soyuz crews are undergoing medical exams at Area 17 at Baikonur.
1969 October 20 - .
- Weight loss of Soyuz 6-7-8 crew - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Kubasov,
Shatalov,
Shonin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
The medical reports show all the cosmonauts lost 1.5 to 3.5 kg during the flight (with Filipchenko having the greatest loss). However Kamanin plays tennis with Gorbatko, Shonin, and Volkov just two days after the flight. They show no apparent ill effects of zero-G.
1969 October 21 - .
- Cosmonaut press conference at Baikonur - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Filipchenko, Gorbatko, Kubasov, Shatalov, Shonin, Volkov, Yeliseyev. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8. The cosmonauts hold a press conference on their flight. They are only allowed to speak one of ten prepared responses to questions, despite Kamanin's objections..
1969 October 22 - .
- Cosmonauts arrive in Moscow - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Kubasov,
Shatalov,
Shonin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
The cosmonauts fly from Baikonur to Moscow, escorted by six MiG-21 fighters to Vnukovo airfield, where they receive honours all around, followed by meetings with reporters. Brezhnev was no there - he was on his way to Baikonur to observe the Tyulpan ICBM exercise.
1969 October 23 - .
- Cosmonauts feted at TsKBEM - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Kubasov,
Mishin,
Shatalov,
Shonin,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Traditional meeting between the cosmonauts and the engineers and workers at TsKBEM. They are quizzed on the flight failures, followed by dinner and toasts. Kamanin tells Afanasyev that instead of messing about with the N1-L3, they should build 8 to 10 more Soyuz and fly, fly, fly -- it is the only way to develop reliable systems. The Ministry of Defence needs a long-range plan of sustained flights of 5 to 6 spacecraft per year. All 300 present applaud the speech, except Mishin, who is against a new series of Soyuz spacecraft.
1969 October 27 - .
- Cosmonauts tours. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Feoktistov,
Khrunov,
Popovich,
Tereshkova,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Kamanin assigns cosmonauts to upcoming foreign propaganda tours. Beregovoi and Feoktistov are to go to the United States, Tereshkova to Hungary, Popovich to France, Khrunov to Odessa. Titov will not be given this privilege because of his numerous automobile accidents, run-ins with the militia, and motorcycle habit.
1969 November - .
- Soyuz n 18 (cancelled) - . Crew: Grechko, Kuklin. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Grechko, Kuklin. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Would have simulated the passive LK lunar lander in an earth-orbit test of the Kontakt docking system..
1969 November - .
- Soyuz n 17 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz n 17.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt.
The Kontakt system designed for the lunar orbit rendezvous and docking of the LOK lunar orbiter and LK lunar lander was to be mounted on two Soyuz spacecraft and tested in earth orbit. These flights were continuously delayed after the success of Apollo 11 and finally cancelled.
1969 November 3 - .
- Press conference preparations - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Keldysh, Mishin. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8. A meeting is held with Mishin and Keldysh to prepare the cosmonauts and other participants for an upcoming press conference. Kamanin notes a huge amount of time is spent in such preparations..
1969 November 5 - .
- Press conference - lunar project raised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Major press conference. Keldysh dodges questions from American reporters on the Soviet lunar landing program. The cosmonauts perform all right, no mistakes. Kamanin views Keldysh as a braking force on the space programme. He attributes the loss of the moon race to bad managers like Keldysh and Mishin.
1969 December 1 - .
- Final L1 State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Semenov,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Yuri Semenov proved his management abilities in the successful unmanned launches and recoveries of Zond 7 and 8 on circumlunar missions. At the final state commission on the L1 program, VPK Deputy Chairman Tyulin said that if had been in charge instead of Mishin, the N1 would have succeeded. Semenov proved himself skilful in coordinating the work of four major, often hostile organizations -- TskBEM, NIIAP, TsKBM, and ZIKh. This would lead to his assignment to head the DOS/Salyut space station programme, and ultimately, head RKK Energia.
1969 December 30 - .
- Soyuz 9 planned - Belyayev seriously ill. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Grechko,
Kolodin,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The leadership suddenly announces that a solo Soyuz mission of 17 to 20 days is to be flown for Lenin's 100th birthday (April 22). This will seize the space endurance record from the Americans and provide biomedical information for the DOS station, to be flown by the end of the year. Nikolayev and Sevastyanov are being pushed for the job. Kamanin objects, he would prefer Kolodin or Grechko, but Mishin won't hear of it. During December Kamanin, the Shatalov Soyuz 7 crew, Sevastyanov, and their wives vacation at Sochi on the Black Sea. Meanwhile Belyayev becomes serious ill. Surgeons operate to remove 2/3 of his stomach, part of his long intestine, and his appendix.
1969 December 31 - .
- 1969 in retrospect. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Keldysh,
Kutakhov,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Tereshkova,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Tereshkova is on a tour of Jordan and Syria. Kamanin muses over the year 1969. He is able to rationalise that it wasn't a bad year -- they flew 9 cosmonauts on five space missions. But of course they lost the moon to the Americans. He blames Mishin, Keldysh, Smirnov, and Ustinov for this. But he also blames the attitude of the Ministry of Defence and VVS. This is indicated by the total indifference to civilian space projects of Grechko and Kutakhov. They don't support the Gagarin Centre, or Kamanin's request for 10 additional Soyuz flights in earth orbit. Kamanin views the L3 spacecraft and mission scenario as unsafe. What is needed is a new spacecraft, launched by two N1 boosters, that will take a crew of 3 to 5 to the moon.
1970 February 2 - .
- Soyuz 9 experiment review - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Nikolayev visits the IMBP to review the modified ECS required for the long-duration Soyuz 9 mission. This will have to function reliably for 20 days. The biomedical experiments and objectives of the mission are also reviewed..
1970 February 7 - .
- Soyuz 10 and 11 crew selections; Soyuz 9 experiment review - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Salyut,
Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11,
Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1.
Kamanin meets with nine generals involved in supervising aspects of the space programme. Only one is from the VVS aviation, the rest have artillery or rocket backgrounds. Naturally they have no bad words for the RSVN or TsUKOS. At the centre, crew selection for the Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11 missions to the DOS space station are underway. A review is conducted of the biomedical and zero-G studies planned for Soyuz 9. This is followed by a meeting with General Komarov and the cosmonauts on plans for the new cosmonaut training building and a nine-story apartment building.
1970 February 14 - .
- Soyuz 9 issues - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Tregub.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin meets with TsKBEM (Tregub, Anokhin) to review issues for the Soyuz 9 mission. These include post-flight care of the cosmonauts, the fact the centrifuge is not available for training, storage of rations and the possibility of spoilage during the long flight.
1970 February 16 - . LV Family: N1.
- Next five year plan emphasized the use of the N1 - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chelomei,
.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Almaz,
Salyut,
LK.
The next five year plan emphasized the use of the N1 for MKBS and robot soil return missions to Mars by the mid-1970's. But an N1M and improved lunar spacecraft would be developed for establishment of a moon base late in the decade. This was all laid out in a review of the proposed five-year plan on 16 February 1970 (Mishin Diaries 2-302):
25. Budget Review - 5 Year Plan (presumed in thousands of rubles)
Experimental design work - 8734
R&D - 680
Projected over 5 yrs
Experimental Base - 3314
N1-L3 - 2665 (Capital investments)
DOS - 170
Almaz - 645
Topaz - 750 (unknown code name).
Apparatus for military use - 825 350
National economy. others - 928 150
Launch Vehicles - 255 116
Launch complexes - 476 91
Skh.A. - 830 293
EYaRD - 380
Launch work - 780 760
N1-L3 71 72 73 74 75 +ú
(11A52) 3 4 4 4 2 17
11A52 for Mars-75 - - - - 2 2
Grand total 19
26. On the draft resolution for the MKBS.
1. Use the same cooperation established in the design and manufacture of DOS.
2. Expand the cooperation of developers in various departments (especially on power, life support systems, equipment for national economic and scientific purposes).
2. Create the necessary experimental and industrial base (with the planned cooperation of developers).
3. Select TsKBEM factory for serial instrument production with MOM.
4. Determine the organization within MOM (former Nikitin) for the development of simulators and control panels.
5. Organize mass production 7K-S at the plant in Omsk (or in the factory "Progress").
6. Hydrogen blocks Sr and S - TSKBEM factory and plant "Progress".
7. Instruct Affiliate TsKBM (T. Bugajski) development of MKA (shuttle) according to TsKBEM's requirements (an interesting allusion to development of the LKS space shuttle by Chelomei's organization).
8. Determine the parent organization for the production of "Almaz" - organization of Chelomei (Reutov).
9. Immediately begin design work on the technical positions for MKBS ... see paragraph 21 (to establish a single NTS Scientific and Technical Council)
1970 February 18 - .
- Kamanin opposes DOS - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Belyayev,
Kozlov,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz,
Salyut,
Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7KT-OK,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
Kamanin recommends the death benefit to be awarded to Belyayev's family. There is to be a one-time payment of 2,000 roubles to his wife; 1,100 roubles to his daughter; 180 roubles/month pension to the wife; 75 roubles/month to the daughter; access to cosmonaut centre sanatoriums; and a seven-room apartment in Moscow.
Kamanin also reviews the government decree on the DOS-7K space station program. The Ministry of Defence is against it - they want to continue with the Almaz and Soyuz VI projects already underway. DOS will bring both of these to a halt. This is a repeat of the situation in 1967. Kozlov was making good progress on the original Soyuz VI, when it was killed by Mishin. Now three years later Mishin's Soyuz VI is put on the back burner. The Soyuz 7K-OK is still the only manned program brought to completion. Kamanin blames all this on Ustinov and Smirnov's stupid political manoeuvring. The DOS decree has not one word on the training of cosmonauts for these space station missions...
1970 February 20 - .
- Soyuz 9 schedule; Soyuz Kontakt flights in limbo - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Serbin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 9,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz Kontakt.
It was originally planned to fly two Soyuz spacecraft in August-September 1970, but at the end of December it was ordered that this be changed to a single 20 day flight in April 1970. Kamanin was given only two days to put together a training programme that had to prepare the cosmonauts for flight by 20 March. The State Commission meets and decides to move the Soyuz 9 flight to May, even though Kamanin says he can support the April schedule. It is the scientific institutes who say they cannot finish development of their experiments - even to meet the May schedule. Kamanin blames such chaos on Smirnov, Serbin, and Ustinov.
1970 February 25 - .
- Soyuz 9 decision preempts Soyuz Kontakt flights - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kerimov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 9,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt.
Meeting with Mishin. It is clear that he wanted to continue with the original plan for a dual Soyuz flight in August. It was Afanasyev and Kerimov who were pushing for a single long-duration flight in May. There is no action by the Ministry of Defence to provide rational decision making in regard to manned spaceflight.
1970 February 26 - .
- Kamanin views DOS, continuation of N1-L3 with dismay - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Salyut,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
The Ministry of Defence and VVS approve the draft DOS resolution. Kamanin has fought against it. He would prefer to develop a single reliable Soyuz spacecraft model by building and flying ten more (there are only four left of the original production lot in assembly). Instead the space leadership keep dreaming up new projects. In Kamanin's view, the DOS and its new Soyuz ferry design join Almaz, Soyuz VI, and the L3 as 'paper spacecraft'. Mishin still thinks he will 'teach the N1 to fly' and complete the L3, but Kamanin thinks the chances of this are nil. There is no coherent plan for Soviet spaceflight.
1970 February 27 - .
- DOS schedules, Soyuz Kontakt flights still in play - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bogomolov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Salyut,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz Kontakt,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
A meeting is held on the DOS project. The Central Committee and Soviet Ministers have directed that two DOS space stations be completed by the end of 1970. TsNIIMASH thinks this is impossible - the task can be accomplished in no less than 18 to 24 months. Mishin insists it can be done in ten months, as directed. Kamanin believes he won't even have it ready by the second half of 1971. It took five to seven years to just bring the Almaz, Soyuz VI, and L1 to flight status. This DOS will stop work on all other projects. Mishin still wants to fly two Soyuz spacecraft to test Bogomolov's Kontakt docking system for the L3.
1970 February 28 - .
- Failure to achieve space objectives in Five-Year Plan - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
Kamanin is asked to assist in preparation of the next five-year plan for spaceflight (1971-1975). He muses that nothing that was to be accomplished in the last five-year plan was achieved, so what is he supposed to put in the new one? 1966-1971 was supposed to have seen Soviet manned flybys and landings on the moon; a cosmonaut contingent increased to 140 and cadres in training for military missions on the Soyuz VI and Almaz. None of this was achieved, and the cosmonaut corps actually only numbers 97.
1970 February-March - .
- Soyuz n 20 (cancelled) - . Crew: Fartushny, Shatalov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Fartushny, Shatalov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. The active spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system..
1970 February-March - .
- Soyuz n 19 (cancelled) - . Crew: Patsayev, Shonin, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Patsayev, Shonin, Yazdovsky. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. The passive spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system. One or two of the crew would have spacewalked to the Soyuz 11 Kontakt and returned in the other spacecraft..
1970 March 18 - .
- Shonin on report - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Shonin,
Tereshkova,
Titov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Nikolayev and crew go to Sochi. Tereshkova is back from sick leave, and she goes there as well. Kamanin meets with Shonin, the topic: many bad reports he has received of Shonin's behaviour since Soyuz 6. He tells him to watch out, or he'll end up on a five-year flight suspension like Titov.
1970 April 9 - .
- State Commission is held to review issues of the Soyuz 9 flight. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
All is ready for a flight in April, but the Communist Party resolution says the flight has to wait for May. The Soyuz ECS is designed to only operate for five days, but will have to operate 3 to 4 times longer for this mission. Various problems are identified and reviewed. Mishin wants to accept a carbon dioxide level in the cabin atmosphere double the percentage considered acceptable earlier. Plans are made for a quick flight of the crew after the long duration mission to Moscow for extensive physical examinations.
1970 April 10 - .
- Documentary film on the Soyuz 6-7-8 missions - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8. Kamanin previews the documentary film 'Launch after Launch' on the Soyuz 6-7-8 missions..
1970 April 25 - . Launch Vehicle: Spiral 50-50.
- Spiral project not raised with General Staff. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dementiev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Spiral 50-50.
Spacecraft: Spiral OS.
Kamanin has been working for seven years on operation and improvement of the TsEZ Central Experimental Facility of he VVS. This includes the Volchok trainer, which simulates launch to orbit; the centrifuge facility; and numerous special test stands. The facility employs 120 engineers and 300 technicians. Later the Spiral project is discussed by the General Staff. It has been two weeks since Kutakhov promised to clarify Minister Dementiev's position on the project, but he never did talk to him. What is Kamanin expected to tell the cosmonauts training for the program? He is also trying to get a flight plan and press kit together in preparation for the Soyuz 9 mission, but there is no Central Committee resolution allowing this work. The KGB and Central Committee want to keep everything secret.
1970 April 27 - .
- Soyuz 9 book. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Titov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Kamanin works at his dacha on his proposed book on Soyuz 9 (to be ghost-written by Mikahil Debrov). Debrov will be in Japan in May, while Kamanin must go to Tyuratam for the Soyuz 9 mission. Titov is trying to get his flight ban lifted..
1970 May 16 - .
- A VVS Military Soviet is held for Soyuz 9. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. The three crews all passed their examinations, physicals, and have been certified as having completed their training..
1970 May 18 - .
- VPK reviews Soyuz 9 readiness. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Serbin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Launch is set for 31 May with an 18 day mission duration. Afterwards Serbin asks why the Soviet Union is not conducting more manned spaceflights. Kamanin tells him, because no more spacecraft have been built. And why no spacecraft, Serbin asks. Kamanin replies that GUKOS, the General Staff, and Mishin were all opposed to production of 10 additional Soyuz ships for military flights.
1970 May 19 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew departs for Baikonur. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Tereshkova.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Kamanin leaves for Tyuratam at 09:00 with 13 others aboard an Il-18 from Chkalov Airfield. The group included the 'space family' - Nikolayev, his wife Tereshkova, and their daughter Aleuka - with extensive photographic and film coverage. After the 10 hour flight, Kamanin goes to the 'Alley of Heroes' at Area 17 of the cosmodrome. Here each crew plants a tree before departing for space. The 11 first trees planted have all grown well, and are now 6 m tall with large crowns. Sevastyanov plants the 22nd tree. After a meeting of the State Commission, everyone watches an Italian movie, 'The Owl Appears at Day' - a story of murder in Sicily, terror against women, and the corruption of the Mafia (apparently a remake of the classic 'M').
1970 May 20 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew preparations at Baikonur - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Soyuz 9 is planned to launch at 24:00. A new feature is that the crews' sleeping hours have been modified to put them in synch with the shifts at ground control over the long mission. The cosmonauts spent all day at Area 17, preparing the flight plan and logs. It is 28 degrees in the shade, and Kamanin plays tennis with the crews in the late afternoon. In the evening the American film 'One Million Years BC' is shown. Kamanin found the struggle between the savages interesting.
1970 May 21 - .
- Dysentery in the Tyuratam garrison threatens cosmonauts. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
The Soyuz 9 crew trains with the bungee arrangements they'll have to exercise with twice a day while in space. They will have to work constantly in order to fight off the effects of sustained zero-gravity. Dysentery has broken out in the Tyuratam garrison. The cosmonauts are given prophylactic measures so that they won't get the bug. A Zenit spy satellite is launched from Area 2. There is some damage to the pad that will require repair, but nothing substantial. The OK is given for Soyuz 9 to launch from the pad. That evening the movie is West German - 'What does a woman do, when her husband disappears?'. At 23:00 the Soyuz 9 crew views the night sky, spotting constellations and guide stars.
1970 May 22 - .
- Delays in Soyuz 9 preparation. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The diet for the long-duration flight is reviewed. The cosmonauts will have four meals a day, totalling 2800 kcal, with 105 g of protein, 102 g fat, 342 g carbohydrates, and 847 g water. Meanwhile problems have been found with Soyuz 9's electrical system - the launch will have to be delayed. Some points in the electrical harnesses, which should have a 38 V capacity, are measuring greater than 60 V. This will have to be fixed, then the spacecraft put through its vacuum chamber test, then fuelling, and finally integration with the booster. Mishin is still not at the cosmodrome - he is managing the launch from Moscow. The result: neither the spacecraft or the booster are ready for an April launch, perhaps not even by the end of May. Of 20 members of the State Commission, only Kamanin and two others are actually at the launch site. This never would have happened in Korolev's time...
1970 May 24 - .
- Cosmonauts recreate. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Kamanin, the cosmonauts, and other VVS officers spend the day at the lake 7 km from the Tyuratam liquid oxygen plant. An asphalt road leads to the recreation area. They play tennis, chess, and billiards. The artificial lake was made by diverting water from the Syr Darya river.
1970 May 25 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew ready for flight. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
They have completed their physical tests and trained with the survival kit. Nikolayev and Sevastyanov were caught smoking just the day before the launch. Kamanin has a serious discussion with them, for this was completely prohibited. Kamanin would replace them with the backup crew, but it is too late for that.
1970 May 26 - .
- Soyuz 9 State Commission. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Fuelling of Soyuz 9 is to begin at 07:00 on 27 May. Launch will be at 24:00 on 2 June..
1970 May 27 - .
- Cosmonauts go fishing. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. A meeting is held at 11:00 at Area 2 in memory of Gagarin. Then the cosmonauts go fishing at the 'Lox Lake' with a television and film crew. Kamanin plays billiards with Mishin..
1970 May 28 - .
- Pace quickens at Baikonur. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. The big shots (Afanasyev and others) are finally showing up, just in order to see the launch. The crew completes preparation of the flight log. At night they do more stellar navigation training, including use of new electronic binoculars..
1970 May 30 - .
- Soyuz 9 final inspection. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The backup crews were to train in the Soyuz 9 spacecraft from 10:00, followed by the prime crew at 12:00, but Mishin didn't allow the backups to start until 11:00. Inspectors have found 15 discrepancies in the spacecraft, 3 to 4 of them serious (including incorrect mounting of the crew head rests, unusable photographic equipment).
1970 May 31 - .
- Go-ahead for Soyuz 9 launch. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Soyuz 9 State Commission meets at Area 31 at 11:00. That evening the spacecraft will be integrated with the booster, with roll-out to the pad scheduled for the following morning at 05:00. At 17:00 the cosmonauts give a formal interview to the Russian 'Parade' magazine. After that they hold a general press conference.
1970 June 1 - . 19:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 9 - . Call Sign: Sokol (Falcon ). Crew: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Backup Crew: Filipchenko, Grechko. Support Crew: Lazarev, Yazdovsky. Payload: Soyuz 7K-OK s/n 17. Mass: 6,590 kg (14,520 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Soyuz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Duration: 17.71 days. Decay Date: 1970-06-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 4407 . COSPAR: 1970-041A. Apogee: 227 km (141 mi). Perigee: 176 km (109 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Manned flight endurance test. Medico-biological, scientific and technical studies and experiments in prolonged orbital flight. Inconclusive results due to slow sun-oriented rotation of spacecraft to conserve fuel producing motion sickness in cosmonauts.. Additional Details: here....
1970 June 2 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 2 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov,
Tereshkova.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At 09:00 the State Commission members and 36 military officers board an aircraft to return to Moscow. Kamanin, the Soyuz 9 back-up crews, Kuznetsov, Shatalov, and 14 other officers board an Il-18 for the flight to mission control at Yevpatoriya. Conversation aboard the flight is about the weather, football - nothing about space. After four hours the plane arrives at Saki. The first communications session with Soyuz 9 is with Issuriysk at 15:40. In a three-minute conversation the crew confirms that all is normal. At 19:00 the first of the daily landing commission meetings takes place. This commission's role is to assess the flight status and to establish contingency plans for the next day in case an emergency return to earth is required.
In the evening Kamanin calls Tereshkova, and promises to tell Nikolayev that she and Aleuka were fine, worried, to kiss him, and the looked forward to meeting him on his return. On 8 June Aleuka will be six years old, and Tereshkova would like to fly to Yevpatoriya to give her a surprise communications session with her father. At 21:25 Kamanin relays the news from his family to Nikolayev during a pass over Yevpatoriya. Kamanin observes that the tracking station is not suited to serve as mission control over a long spaceflight. There is no transport, and no recreational facilities. The only diversions are gymnastics, chess, and billiards. Furthermore there seem to be a lot of unnecessary staff at the command point.
1970 June 3 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 3 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
All is normal aboard Soyuz 9. At 10:00 there is an operational management meeting. There are worries the crew did not engage and disengage the orientation engines at the time scheduled for an engine burn. Kamanin defends the crew -- this was not a mistake, it took the crew 50 minutes to go through the same exercises that took 30 minutes on the ground, and therefore they were delayed in being able to conduct the manoeuvre. There is a television communications session in the evening. The crew looks all right, but Sevastyanov's face is visibly swollen.
1970 June 4 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 4 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Tereshkova,
Tregub.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
There are a total of 500 staff at Yevpatoriya for the mission, including 53 representatives from the VVS, 6 military cosmonauts, and 3 civilian cosmonauts. Mishin returns to Moscow, leaving Tregub in his place. In the afternoon there is a problem with the control of the spacecraft's solar cells. On the 47th orbit Sevastyanov reports that one solar panel is energised, but only generating 26 amps. This could only mean that the automatic control of the solar panels was not working. On the second day the crew had to engage and disengage the solar batteries 12 times manually. After the 15th manual session it became clear that the mission could last only eight days before the batteries would run down. In the orbit of Soyuz 9 in June, the night lasts 40 minutes. On the previous flight, in October, it lasted only 10 minutes and this would not have been a problem. The crew is told to revolve the spacecraft at 0.5 deg/sec around the long axis. By this method the spacecraft remains fully oriented towards the sun, and the batteries don't have to work so long on the night passes. The cosmonauts do not report any unpleasant sensations from the rotation. At the 23:25 communications sessions the cosmonauts report that their appetites are good and they are sleeping well.
1970 June 5 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 5 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Tereshkova.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At 08:40 Kamanin discusses the solar battery problem in a communications section with the cosmonauts. Telemetry shows the system is generating 25.6 to 26.0 V. There will be an emergency situation if the voltage drops to 23 to 24 V - in that case the crew must land within 1.5 orbits of the earth, or two hours. They would likely have to land out of tracking range of Soviet units. The crew gets the spacecraft back into its solar orientation roll on the sixth attempt. At 18:00 clear communications are again obtained with the capsule via Vesna (Khabarovsk and Alma Alta). Nikolayev reports that when oriented to the sun, the system generates 26 V instead of the 31 V it should be generating. A long technical discussion ensues. It is finally decided that the automatic system is actually working correctly, but that Sevastyanov is confusing the ammeter and voltmeter readings (which are displayed on one instrument). Later Kamanin talks to Tereshkova. She will fly via An-24 to Yevpatoriya on 7 June with her daughter.
1970 June 6 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 6 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At an 08:30 communications session Filipchenko reports to the tracking vessel Komarov that all is OK, everything normal, they are eating well. At 22:15 alarming telemetry is received that indicates that the temperatures in the fuel tanks are getting high due to the extended time of continuous exposure to the sun. They drop slightly after two minutes in shadow.
1970 June 7 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 7 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Tereshkova.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Soyuz 9's environmental control system is working well. Tereshkova and her daughter arrive at the command point at 14:40 after landing at the airfield at 12:00. The landing commission meets in the evening to consider contingency landings. It is reported that the crew is medically in better shape on Day 6 than Day 1, according to telemetry. In fact they are doing so well, extension of the flight to 20 days duration is discussed. Between 20:00 and 20:30 Tereshkova and her daughter communicate via radio and television with Nikolayev aboard Soyuz 9.
1970 June 8 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 8 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov, Tereshkova. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. During the day Tereshkova has a meeting with a Young Pioneers Group. In the evening she and Nikolayev enjoy another communications session together..
1970 June 9 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 9 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov, Tereshkova. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Tereshkova and her daughter return to Moscow. The landing commission meets at 20:00. The cosmonauts' activity level seems to be declining - they are drinking little water and their oxygen consumption has declined..
1970 June 10 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 10 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Gorbatko, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. This is the first day 'off' for the Soyuz 9 crew on their long duration flight. No experiments are scheduled and radio communications will be minimised. The crew plays chess via radio with Gorbatko..
1970 June 11 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 11 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Gorbatko,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz,
Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1.
Things are proceeding normally aboard Soyuz 9. Shatalov and Yeliseyev prepare to depart for the Crimea to train for use of the big solar and stellar telescopes planned for the DOS station. The 15-20 day course will be attended by all 12 DOS cosmonauts. The training plan for DOS is discussed, with a May 1971 flight date as the objective. Kamanin discusses smoking with Bykovsky and Gorbatko - they have to stop.
1970 June 12 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 12 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov, Shatalov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Shatalov departs from Yevpatoriya for Leningrad at 14:35 - his father has died..
1970 June 13 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 13 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
The Soyuz 9 crew has completed their 12th day but are beginning to get tired. They are making mistakes (for example putting the television camera on the wrong setting). The landing commission decides to constantly monitor the weather at potential landing sites from 14 June onwards so that a quick landing decision can be made if necessary.
1970 June 14 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 14 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. The crew seems better today. Landing is planned for between June 16 and 19 (on June 16 the crew will beat the US spaceflight endurance record). The crew says everything is excellent..
1970 June 15 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 15 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The first communications session begins alarmingly - contact could not be made with the crew for the first three minutes they were in radio range. But then they came through, and said everything was all right and their condition was excellent. At 12:00 Sevastyanov accidentally engages the ASP automatic landing system. This removes the first lock on the system, which is then armed so that it will be activated by a signal from the barometer at an altitude of 11 km above the earth. It is said not to be dangerous, but Filipchenko made the same mistake on Soyuz 7. Kamanin had asked Mishin to put a lock on the ASP switch to prevent this from happening, but he did nothing. At 12:30 the State Commission arrives. At 17:30 Mishin has his first communications session with the crew. There are problems with the environmental control system - the carbon dioxide level is up to 8.5 mm, and the oxygen level down to 160 mm. The crew is told to turn off ECS cartridge number 2 and use number 3. By 23:00 it is clear that cartridge 2 was working badly - oxygen pressure is up to 170 mm, carbon dioxide down to 4. 5 mm. Nikolayev hints to Mishin that he would like to use the two day reserve of consumables aboard to extend the mission to 20 days. Kamanin is opposed to the idea - this would be a dangerous adventure. The whole point of a reserve is that it is never used except in case of an emergency.
1970 June 16 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 16 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Ryazanskiy,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
All is normal aboard Soyuz 9, except that one of the local telemetry commutators in Ryazanskiy's system has failed. The telemetry data involved is not critical to the flight, and Mishin and Ryazanskiy allow the flight to continue. Mishin is considering extending the flight to 19 or 20 days. To do this the crew will have to stretch their rations. Kamanin finds himself out of the decision loop, 'as usual'. The landing commission wants to complete the flight as scheduled on the 287th orbit.
1970 June 17 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 17 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Today the Soyuz 9 crew set a new space endurance record. Everything is normal aboard the spacecraft, except for the failed telemetry commutator and the engaged ASP switch. What would now be needed, notes Kamanin, are new Soyuz spacecraft to extend the duration in space gradualy to 30, 40, 50, and then 60 days. But there are no new spacecraft - Kamanin's plan for construction of an additional ten Soyuz was blocked. Grechko and others in the leadership want a big greeting ceremony for the crew in Moscow, but Kamanin only wants the crew in the hands of the doctors for the first 10 to 12 days after the flight. At 15:00, Mishin and Kerimov, following their bosses' orders from Moscow, announce that they want to extend the flight to 20 days.
1970 June 18 - .
- Soyuz 9 Day 18 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Bushuyev,
Karas,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Tsybin.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Final Landing Commission meeting is held. The primary landing site is 50 km west of Karaganda. Visibility there is 10 km, winds 6-10 m/s. Mishin wants to land 50 km further wesst, near a city with passenger train service. It is finally agreed to land there, at 71 deg 31' E, but that will mean that an emergency ballistic re-entry (in the event of a guidance system failure) would bring the capsule down in the Aral Sea. That in turn means additional recovery forces, consisting of three amphibious vehicles, three helicopters, five naval cutters, and 15 scuba divers have to be alerted and prepared. The Politburo approves the landing, and the plan to fly the cosmonauts to Chkalovsky Airfield, followed by ten days in the hospital. Mishin and Kerimov discussed having the traditional cosmonaut greeting at Vnukovo Airport, but they'll have to forget such extravaganzas in the years to come, when only long-duration missions are planned. Meanwhile the crew is well, preparing for landing. They secure the BO living module, stow items in the SA re-entry vehicle that are to be returned to earth. There is a communications pass at 08:00 to 08:30. Afanasyev, Karas, Chertok, Bushuyev, Tsybin, and other members of the State Commission now arrive at Yevpatoriya.
1970 June 19 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 9 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Goreglyad,
Leonov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
At 13:00 it was reported that the landing site was ready, 12 to 15 km visibility, 5-7 m/s winds. At 14:00 it is officially ordered that the landing commence. There are 150 technicians in the hall of mission control for the landing. Nikolayev reports the start of the retrofire burn of the TDU. Retrofire and seperation of the spacecraft modules is normal. The PVO radar at Turtsiy picks up the Soyuz at 83 km altitude and follows it down to the point of parachute deployment. Two helicopters sight the parachute and follow the capsule to landing. Within a minute after the capsule has landed General Goreglyad and Colonel Popov are already at the hatch. Following landing Leonov advises that the crew is all right. However the cosmonauts' condition after landing is awful. It is painful and difficult for them to get up. They fall down in their first tortured attempts at walking. They have to be dragged along by the arms. At 16:30 an Il-18 leaves from Saki for Moscow with the cosmonauts aboard. Both of the cosmonauts looked very ill aboard the plane. They had to be supported by Shatalov and Yeliseyev to get down the stairs in Moscow. Nikolayev departs from his prepared speech to the Sate Commission, and says 'Comrade Chairman! The orders for flight aboard the spacecraft Soyuz 9 were fulfilled and we await further orders!' After the report hey are rushed to the doctors.
It is obvious to the Soviets that they were seriously mistaken about the effects of zero-G on human beings (Mishin thought flights of three to four months would be no problem). Kamanin recites again his belief in the need for more long solo Soyuz flights, how the leadership has blocked such flights, and the general lack of support for manned space. He even had to fight to allow the Soyuz 9 crew to go straight to the hospital and their loved ones, rather than attending ceremonies.
1970 June 19 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 9 - . Return Crew: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Soyuz 9 landed at 11:59 GMT..
1970 June 22 - .
- Grechko meets with the cosmonauts. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei, Mishin, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. They push for production of ten additional Soyuz spacecraft, necessary trainers for the L1 and L3, more female-crew flights, and complain of lack of support from GUKOS (who agree with Mishin's approach of total automation of spacecraft)..
1970 June 23 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew still ill. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. The cosmonauts still appear ill, with pulses of 90 to 100 and temperatures of 37.8 deg C. They reported that earth's gravity felt to them like 3 to 4 G's after landing. They are adapting to gravity only very slowly..
1970 June 26 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew improving. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov, Tereshkova. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. The Soyuz 9 crew are still suffering from the effects of their flight, but getting better each day. Tereshkova was taken ill last night..
1970 June 27 - .
- Soviet flights should not exceed 25 days duration. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov, Smirnov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. The crew is recovering slowly. It is recommended to Smirnov that the Soviet Union not plan any spaceflights over 20 to 25 days duration, and that a new series of Soyuz spacecraft be built to extend experience in long-duration flight..
1970 June 29 - .
- Additional Soyuz flights requested. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Kutakhov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK. Kamanin pleads with Kutakhov for construction of at least 3 to 4 new Soyuz spacecraft, and necessary improvements to Star City facilities..
1970 June 30 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew still very weak. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Tereshkova.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Ten days after their 18-day flight, the Soyuz 9 crew can still only work 3 to 4 hours a day. They can only take two short walks daily and tire quickly. Their pulse, temperature, blood pressure fluctuate from day to day, often being in the range of ill people. Meanwhile the head army physician examines Tereshkova, and prescribes a one-week spa cure.
1970 July 3 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew feted at Kremlin. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Nikolayev and Sevastyanov finally attend their post-flight reception at the Kremlin - over 900 people are there to greet them..
1970 July 6 - .
- Soyuz 9 press conference preparations. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Keldysh, Mishin, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Kamanin and the Soyuz 9 cosmonauts meet with Keldysh and Mishin to prepare for a press conference, to be carried live on television..
1970 July 11 - .
- Soyuz 9 cosmonauts meet with Communist Party leaders. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Sevastyanov notes how small the earth appears from space, the same observation made by Gagarin and the American astronauts..
1970 July 14 - .
- Soyuz 9 interview. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. The cosmonauts give an interview with Izvestia..
1970 July 16 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew presses for new Soyuz series. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Karas, Maksimov, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK, Soyuz 7K-S. Sevastyanov and Nikolayev visit GUKOS, and press for construction of a new Soyuz series. Karas and Maksimov say it would interrupt development of the 7K-S. The cosmonauts argue that the Soyuz 7K-OK is now proven, while the 7K-S exists only on paper..
1970 July 28 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew tours Leningrad - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Nikolayev, Sevastyanov. Program: Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 9. Kamanin, Nikolayev, Sevastyanov, and their families take a train to Leningrad. There they do some sightseeing, visit the television tower, and make a local television appearance..
1970 July 30 - .
- Soyuz 9 crew debrefing. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
Nikolayev and Sevastyanov fly to Sochi to write out their post-flight debriefing. Mishin won't accept that there are problems with sustained zero-G flight, since that would wreck the assumptions on which he has based his DOS station plans. Kamanin believes a series of 30, 50, then 50-plus day flights are needed to investigate and prove human adaptation to space.
1970 September 24 - .
- Mishin has new landing scenario for L3 missions. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Mishin's latest plan is land the L3 in the Indian Ocean after return from the moon, but Soyuz is not rated for swells over 3 to 4 balls. Also there is no money for the needed recovery forces. By comparison the Americans have made the sea their home. Their aircraft carriers give them control over 300 times more ocean area than the Soviet Union.
1970 October 14 - .
- Contacts on join USA/USSR docking system. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov.
Program: ASTP.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM.
Communist Party Meeting at the cosmonaut centre. Keldysh calls later. Six specialists are to be sent to the United States to discuss design of a common USA/USSR docking system. Kamanin yet again goes through the correct answers and prepared speeches to be given to the press by Nikolayev and Sevastyanov on their visit to West Germany.
1970 October 16 - .
- Mishin seems to have lost his fight for a water landing on L3 missions. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Mishin,
Shatalov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
All will have to be on dry land. 500 million roubles would have been necessary to fund the sea forces, and the risk to the crews would have been greater. Kamanin sees the whole bogus controversy as a diversionary tactic of Mishin's to take attention away from the fact that the L3 spacecraft is in fact nonexistent - as is its N1 rocket. An additional 300 million roubles are needed to achieve a 'flying' N1. A completely new solution to the lunar landing problem needs to be worked out. Shatalov worked today with Grechko to lay out the program for French President Pompidou's visit to the Baikonur cosmodrome. Pompidou wants to see two live rocket launches, and Shatalov will show him the Soyuz spacecraft.
1970 October 20 - . 19:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 8 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 14. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.17 days. Decay Date: 1970-10-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 4591 . COSPAR: 1970-088A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 15,562.22 min.
Final circumlunar flight; successfully recovered October 26, 1970. The announced objectives were investigations of the moon and circumlunar space and testing of onboard systems. The spacecraft obtained photographs of the earth on October 21 from a distance of 64,480 km. The spacecraft transmitted flight images of the earth for three days. Zond 8 flew past the moon on October 24, 1970, at a distance of 1,110.4 km and obtained both black and white and colour photographs of the lunar surface. Scientific measurements were also obtained during the flight. The spacecraft used a new variant of the double-dip re-entry, coming in over the north pole, bouncing off the atmosphere, being tracked by Soviet radar stations as it soared south over the Soviet Union, then making a final precision re-entry followed by splashdown at the recovery point in the Indian Ocean.
1970 October 23 - .
- Mishin still fighting for an ocean landing for the L3. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. He has recruited some cosmonauts and admirals to fight for the concept..
1970 October 24 - .
- Cosmonauts oppose ocean landing for the L3. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Mishin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. 18 VVS officers and cosmonauts meet to discuss the L3 water landing issue. Kamanin is to draft a letter against the concept to Mishin and Afanaseyev..
1970 October 31 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 10L and 15L - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 10L and 15L. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Despite decision to cancel immediate manned circumlunar flights after Apollo 8, the remaining two L-1 spacecraft were kept in reserve for support of the L3 lunar landing program and possible later manned flights. They were never used..
1970 November 24 - . 05:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511L.
- Cosmos 379 - .
Payload: Lunar Craft T2K no. 1. Mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK.
Duration: 4,683.78 days. Decay Date: 1983-09-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 4760 . COSPAR: 1970-099A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
LK moon lander test using the T2K version. First use of the Soyuz 11A511L booster modified especially for this purpose. The spacecraft made a series of engine burns, simulating the lunar landing profile. After 3.5 days in orbit, the first burn was made in imitation of a descent to the lunar surface after separation of the Block D lunar crasher stage. The orbit changed from 192 km X 233 km to 196 km X 1206 km orbit; delta V: 263 m/s. After 4 days in orbit, a large manoeuvre was made simulating the ascent from the lunar surface. The orbit was changed from 188 km X 1198 km to 177 km X 14,041 km; delta V: 1518 m/s. These main manoeuvres were followed by a series of small adjustments simulating rendezvous and docking with the LOK. The LK tested out without major problems and decayed from orbit on September 21, 1983.
1970 December 13 - .
- Kontakt test flights - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-OK, Soyuz Kontakt. Plans were underway for Kontakt test flights using 7K-OK spacecraft: 7K-OK number 18, 19 with "Kontakt". (Mishin Diaries 2-299).
1971 January 4 - .
- Preparation for Kontakt flights - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Meetings in January 1971 continue the level of coordination in preparation for Kontakt flights (4, 10, 12 January. (Mishin Diaries 2-314))..
1971 February 26 - . 05:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511L.
- Cosmos 398 - .
Payload: Lunar Craft T2K no. 2. Mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK.
Duration: 8,463.78 days. Decay Date: 1995-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 4966 . COSPAR: 1971-016A. Apogee: 1,958 km (1,216 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 106.70 min.
Second space test of the LK moon lander test using the T2K version. Followed the same programme as Cosmos 379.
Maneuver Summary:
189km X 252km orbit to 186km X 1189km orbit. Delta V: 251 m/s
186km X 1189km orbit to 200km X 10905km orbit. Delta V: 1320 m/s
Total Delta V: 2832 m/s.
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1971 April 22 - . 23:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 10 - .
Call Sign: Granit (Granite ). Crew: Rukavishnikov,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Backup Crew: Kolodin,
Kubasov,
Leonov.
Support Crew: Dobrovolsky,
Patsayev,
Volkov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OKS s/n 31. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
Duration: 1.99 days. Decay Date: 1971-04-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 5172 . COSPAR: 1971-034A. Apogee: 258 km (160 mi). Perigee: 209 km (129 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
Intended first space station mission; soft docked with Salyut 1. Launch nearly scrubbed due to poor weather. Soyuz 10 approached to 180 m from Salyut 1 automatically. It was hand docked after faillure of the automatic system, but hard docking could not be achieved because of the angle of approach. Post-flight analysis indicated that the cosmonauts had no instrument to proivde the angle and range rate data necessary for a successful manual docking. Soyuz 10 was connected to the station for 5 hours and 30 minutes. Despite the lack of hard dock, it is said that the crew were unable to enter the station due to a faulty hatch on their own spacecraft. When Shatalov tried to undock from the Salyut, the jammed hatch impeded the docking mechanism, preventing undocking. After several attempts he was unable to undock and land.
1971 April 24 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 10 - .
Return Crew: Rukavishnikov,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chertok,
Mishin,
Rukavishnikov,
Shatalov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
Only a night landing on Soviet territory was possible, which meant the spacecraft could not be oriented for retrofire. The landing commission started planning for an emergency landing in South America, Africa, or Australia. But Shatalov reported the gyroscopes and orientation sensors were functioning well. He proposed that he orient on the dayside, spin up the gyro platform, and let the gyros orient the spacecraft on the nightside for retrofire. The plan is followed and the spacecraft was targeted for a landing area 80-100 km southwest of Karaganda.
PVO radars pick up the capsule as it soars over the Caspian Sea, and a Mi-4 helicopter sights the parachute even before it thumps down, upright, on the steppes. During the landing, the Soyuz air supply became toxic, and Rukavishnikov was overcome and became unconscious. Nevertheless the crew safely landed at 23:40 GMT, 120 km NW of Karaganda. At the cosmodrome, Chertok is assigned to head a special commission to find the cause of the docking failure and correct it before the next mission can be launched. The VVS aircraft leaves at 07:00 for Moscow. Mishin was to accompany the VPK on their aircraft back, but he is drunk and has to go separately at 15:00. The Soyuz 10 crew reaches Chkalovsky Air Base at 14:00 on 26 April and proceed to Star City for further debriefings. Film and photos indicated that the docking system on the Salyut was not damaged, setting the stage for the Soyuz 11 mission.
1971 May 7 - . LV Family: N1.
- MKBS-1 would have a DOS core; MKBS-2 would use the MOK N1-launched core. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Mir.
The planning on MKBS has progressed to the point where there will be an MKBS-1 with a DOS core (AKA DOS-A, later Mir); while MKBS-2 will use the MOK N1-launched core. At the Soviet of the State Chief Designers (17K)- About DOS number 3 and number 4 and DOS-A (MKBS-1)".
1971 May 10 - .
- Cause of Soyuz 10's failure to dock. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chertok.
Program: Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
A sunny day in Moscow. Chertok's investigative commission has found that the likely cause of Soyuz 10's failure to dock was a dented sleeve on the active part of the docking mechanism. In repeated tests the sleeve bent at 130 kg force 60% of the time. The real force of docking was estimated at 160 to 200 kg. Therefore for Soyuz 11 and subsequent models the sleeve will be reinforced by a factor of two. The crew will also be given the capability of steering the docking probe and of operating the orientation engine to improve the chances of docking when difficulties do occur.
1971 June 1 - .
- Soyuz 11 spacecraft closed out. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Dobrovolsky, Kolodin, Leonov, Patsayev, Rukavishnikov, Volkov. Program: Salyut. Flight: Soyuz 11, Soyuz 12 / DOS 1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK. The Soyuz 11 and 12 crews train. The Soyuz-11 spacecraft is closed out, ready for flight..
1971 June 2 - .
- Contingency planning for Soyuz 11. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dobrovolsky,
Kolodin,
Leonov,
Patsayev,
Rukavishnikov,
Volkov.
Program: Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 11,
Soyuz 12 / DOS 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
From 09:00 to 13:00 the Soyuz 11 cosmonauts and engineers discuss the best approaches for docking, contingency plans, and so on. A concrete solution is provided for every possible problem they might encounter aboard the station - bad air, water contaminated, stuck exit hatch, and so on.
1971 June 6 - . 04:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 11 - .
Call Sign: Yantar (Amber ). Crew: Dobrovolsky,
Patsayev,
Volkov.
Backup Crew: Kolodin,
Kubasov,
Leonov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-OKS s/n 32. Mass: 6,790 kg (14,960 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
Duration: 23.77 days. Decay Date: 1971-06-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 5283 . COSPAR: 1971-053A. Apogee: 237 km (147 mi). Perigee: 163 km (101 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
First space station flight, two years before the American Skylab. The Soyuz 11 launch proceeds without any difficulties. The first orbital correction in the set of rendezvous manoeuvres to head for Salyut 1 is made on the fourth revolution. At 15:00 Kamanin and other critical staff board a plane for the mission control centre at Yevpatoriya. The aircraft takes 4 hours 30 minutes to get there.
Equipment aboard Salyut 1 included a telescope, spectrometer, electrophotometer, and television. The crew checked improved on-board spacecraft systems in different conditions of flight and conducted medico-biological research. The main instrument, a large solar telescope, was inoperative because its cover failed to jettison. A small fire and difficult working conditions will lead to a decision to return crew before planned full duration of 30 days.
1971 June 26 - . 23:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: First stage failed.. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 6L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-LOK / LK Mockups. Mass: 9,850 kg (21,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Decay Date: 1971-07-21 . Apogee: 1.00 km (0.60 mi).
Superbooster failure of N1 serial number 6L. This was a substantially improved vehicle, incorporating filters in the propellant lines to prevent any foreign objects from getting into the pumps. The shape of the tail of the booster was modified, and ventilation and refrigeration systems were added to keep the engine compartment cool. It was painted white overall to reduce temperatures while sitting on the pad. After liftoff and ascent, an axial rotation was introduced by gas dynamics interactions of the thirty engines with the air slipstream. The launch vehicle developed a roll beyond the capability of the control system to compensate. and began to break up as it went through Max Q. Control was lost at 50.2 seconds into the flight and it was destroyed by range safety a second later. The engines functioned well and did not shut down up to the point of vehicle destruction. No functional payload was carried. It has been stated that this launch did not have a working launch escape system. Additional Details: here....
1971 June 30 - .
- Landing of Soyuz 11 and death of crew. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dobrovolsky,
Goreglyad,
Patsayev,
Smirnov,
Ustinov,
Volkov.
Program: Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
Kamanin account: The next communications session with Soyuz 11 comes at 00:16. Kamanin reads up to the crew the conditions at the primary and secondary landing zones (10 km visibility, 2-3 m/s wind, 16 deg temperature, 720 mm pressure). The crew is to told to report on HF and UHF using all antennae and to call out parachute opening. They are ordered to wait in the capsule for the recovery crews, not to open the hatch themselves under any circumstances. It should take no more than 20 to 30 minutes until the recovery team can open the hatch from the outside. They are under no circumstances to try to get out of the capsule without the assistance of the doctors. Dobrovolsky confirms: "All received, landing sequence proceeding excellent, all OK, crew is excellent".
Telemetry shows the Soyuz braking engine begins firing at 01:35:24 and makes a nominal 187 second retrofire burn. Ground control waits for verbal confirmation, but there are no voice communications received from the capsule. At 01:47:28 the crew should have reported successful BO and PAO module separations from the capsule, but still nothing heard. It is not clear to ground control at this point - is Soyuz 11 heading for a landing or staying in orbit? From 01:49:37 to 2:04:07 the capsule is in communications range but there is no reply to the ground's calls. It is now obvious that something is wrong aboard Soyuz 11, but it is not clear what.
At 01:54 the VVS command point reports that radar has picked up the spacecraft at 2200 km uprange from the landing zone. It is on course, so the feeling is that the capsule's communications system has simply failed. The parachute deploy signal is received from within the landing zone, but still no transmissions from the crew as on earlier missions. At 02:05 an Il-14 search plane and Mi-8 helicopter spot Soyuz 11 descending under its parachute, within 200 km east of Dzhezkazgan. Soyuz 11 lands at 02:18 Moscow time. Four helicopters land simultaneously as the capsule thumps down on the steppe. The report from the recovery forces to the control centre is only one word: "Wait". There are no further tramsmissions from the recovery forces. It is clear the crew must be dead. Kamanin calls Goreglyad and tells him to set up a State Commission.
Later it is learned that two minutes after landing the hatch was opened by the recovery group and the crew was seen to be without signs of life. At 06:00 by orders of Ustinov and Smirnov the designated members of the State Commission depart from the Crimea for the landing site aboard a Tu-104, then transfer to an An-10. But on arrival they find that Goreglyad has already left for Moscow with the corpses of the crew. At 16:00 the engineers and doctors meet with the State Commission. The spacecraft's cabin, seats, parachute, equipment, and instruments have been examined. They indicate no problems - the spacecraft made a good soft landing. A hard landing was not a factor. All switches on the instrument panel were in their correct positions. A vent in one of two air valves was open 10 mm. There were no other discrepancies, even though the doctors already report that they believe the crew died from decompression of the cabin. At 23:00 the State Commission members leave for Moscow. Additional Details: here....
1971 July 1 - .
- Soyuz 11 capsule evaluated at landing site. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dobrovolsky,
Patsayev,
Volkov.
Program: Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
At 05:00 specialists arrive from Moscow to the Soyuz 11 landing site to test the hermetic seal of the cabin. By 08:00 the pressure tests of the cabin show a slight loss, but it takes 1.5 hours for the cabin to fully depressurise. There are no cracks or holes in the cabin. Therefore the only cause could be the two air valves. The medical experts have already determined that the cosmonauts died from depressurisation of the spacecraft. The crew have haemorrhages in their brains, blood in their lungs, and nitrogen in their blood. The flight recorder shows that four seconds after the depressurisation began Dobrovolsky's breathing rate went to 48/minute (normally 16/minute), asphyxiation began, and 20 to 30 seconds later he was dead. By 19:30 Kamanin is in Moscow, and he sees the bodies laying in state at 21:40. They are cremated at 22:00.
1971 July 7 - .
- Kamanin's last diary entry in service. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev,
Brezhnev,
Bushuyev,
Dobrovolsky,
Khrushchev,
Mishin,
Patsayev,
Serbin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov,
Volkov.
Program: Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK.
Kamanin is furious. Of 25 cosmonauts that have flown, five are buried in the Kremlin Wall, one in Novdevich cemetery, and 19 are still in service. These deaths are due to the incompetent management of Ustinov, Serbin, Smirnov, Mishin, Afanasyev, Bushuyev, and Serbin. Some people are trying to blame Kamanin or the cosmonauts, saying the vent could have been plugged with a finger if the crew was properly trained. Others blame the crew in other ways. But the main problem was already brought up early over and over and over by the VVS and Kutakhov - the crew should never have flown without spacesuits! This has been going on for seven years. Khrushchev, Brezhnev, Ustinov, Smirnov, all wrote of their fear of allowing dangerous spaceflights. But these were the same leaders who supported the categorical rejection of the need for the crew to fly in spacesuits. The need for the suits was rejected first by Korolev, then Mishin. They kept saying that hundreds of manned and unmanned spacecraft had flown without depressurisation ever occurring.
The idea of plugging the vent with a finger is absurd. Had they done so, they would have had only 15 to 17 minutes to work the problem before the onset of G-forces. Imagine the real situation - retrofire was normal - the BO module jettisoned - suddenly the depress light on the caution warning panel is on! Dobrovolsky checks the hatch, but it's not the hatch -- and there are only 25 to 30 seconds until they all become unconscious. Volkov and Patsayev undo their straps and turn on the radio. The whistling of the air can only be heard at the commander's seat - where the vent valve is located. Kamanin discontinues diary entries for two years after this date.
1971 August - .
- Soyuz 12 / DOS 1 (cancelled) - . Crew: Kolodin, Leonov, Rukavishnikov. Backup Crew: Gubarev, Sevastyanov, Voronov. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut. Flight: Soyuz 12 / DOS 1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7KT-OK. If the Soyuz 11 crew had not perished during return to the earth, a second crew would have been sent to the Salyut 1 space station. Further missions to Salyut 1 were cancelled after the disaster..
1971 August 2 - . LV Family: N1.
- Manned military space to have priority in N1 program - . Related Persons: Mishin, Afanasyev, Sergei, . Spacecraft: Soyuz, MKBS, Mir, Soyuz 7K-S. In a follow-up call to Afanasiev, Mishin notes: "On conclusion of the expert committee on the N1-L3 (and Comrade Tsarev VPK): 7KS - MKBS-1 - MKBS-2 - Continue; Enlarge the crew to six people for short stays.".
1971 August 12 - . 05:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511L.
- Cosmos 434 - .
Payload: Lunar Craft T2K no. 3. Mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK.
Duration: 8,296.77 days. Decay Date: 1981-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 5407 . COSPAR: 1971-069A. Apogee: 1,253 km (778 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 99.30 min.
Final LK moon lander test using the T2K version.
Maneuver Summary:
188km X 267km orbit to 190km X 1261km orbit. Delta V: 266 m/s
188km X 1262km orbit to 180km X 11384km orbit. Delta V: 1333 m/s
Total Delta V: 1599 m/s. Ten years later the spacecraft was due to re-enter over Australia soon after the Skylab scare. The Soviet Union told the people of Australia not to worry, it was only an experimental lunar cabin - the first inadvertent admission that their manned lunar project even existed!
1971 September 21 - . LV Family: N1.
- Crew shuttle to be used with MKBS (Soyuz, 7KS, Chelomei spaceplane, or a new high L/D spacecraft) - . Related Persons: Mishin, Chelomei, Bezverby, . Spacecraft: Soyuz, MKBS, Soyuz 7K-S, Mir, LKS. The issues of the crew shuttle to be used with MKBS (evidently choices are the existing Soyuz, 7KS, Chelomei's spaceplane, or the new high L/D spacecraft) Bezverby VK MKBS-1 on N-1 and variants of crew transport spacecraft (Mishin Diaries 2-362).
1971 September 26 - . LV Family: N1.
- MKBS-1 crew vehicle - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Soyuz, MKBS. About MKBS-1 product number 10, 11 - N-1. (Which LV will deliver crew - 7K-T) - Consider options"..
1971 October 1 - .
- Podsadka is considered again: "Think about podsadka approach to providing crew using 7K-S. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Soyuz, MKBS. "Think about podsadka approach to providing crew using 7K-S...MOK (MKBS, transport systems, specialized satellites)". (Mishin Diaries 2-347).
1971 October 10 - . LV Family: N1.
- A detailed list of project phases for the integrated MKBS-Lunar program are laid out. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Mir,
Soyuz 7K-S,
L3M.
Complex number 1
1. Improving N-1 (Increase thrust, increase reliability and survivability, operational testing).
2. Improving upper stages G, D (performance, reliability and survivability, operational testing).
3. Development of DM with operational testing.
4. Development of standardized units of Stage S (Sr, Sr-L3M et al.).
5. Development of block N.
Complex number 2
1. DOS 7KT - series production.
2. MKBS-I
3. 7KS
4. L3M - (SA, LPU, PAO)
5. SA reentry vehicle reusable. (Mishin Diaries 2-348)
1972 January 1 - .
- TsKBEM reorganised - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Dorofeyev,
Mishin,
Semenov,
Shabarov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: LK,
Mars 5NM,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz 7K-S,
Soyuz 7K-T,
Soyuz 7K-TM.
TsKBEM was given a completely new structure as a result of the findings of the expert commissions on the disasters for the previous year, Mishin remained as the Chief Designer for the organisation, but each programme now had its own chief designer:
- N1: Boris Dorofeyev
- 8K98P solid propellant ICBM: Igor Sadovskiy
- N1 payloads: Vladimir Brorov [check]
- Soyuz 7K-TM, or Soyuz M, for Soyuz-Apollo: Konstantin Bushuyev
- Soyuz 7K-T: Yuri Semenov
- Soyuz 7K-S or Soyuz VI: Yevgeni Shabarov
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 18 (cancelled) - . Crew: Filipchenko, Grechko. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Filipchenko, Grechko. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 18 would have been the active spacecraft of the first dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 19 (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Lazarev, Makarov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 19 would have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. Would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 18 . A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 20 (cancelled) - . Crew: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 20 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 21 (cancelled) - . Crew: Dobrovolsky, Sevastyanov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Dobrovolsky, Sevastyanov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 21. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 21 equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. Would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 20 . A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 - .
- Soyuz sn 23 (cancelled) - . Crew: Shcheglov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Shcheglov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 23. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 23 would have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. The spacecraft would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 22. In Kamanin's diary, the name of the second crewmember is illegible..
1972 - .
- Soyuz sn 22 (cancelled) - . Crew: Isakov, Kovalyonok. Backup Crew: Shcheglov. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 22. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 22 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system..
1972 June 16 - .
- Kontakt docking system to be used in MKBS. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chertok.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt,
MKBS.
The reason for continuing with development of the L3 Kontakt docking system even after the L3 was cancelled was that it was to be used in MKBS. The note reads: Chertok - 7K-OK number 18 - rework using the propulsion system from number 36. Work on "Kontakt" to continue, as it can be used in the MKBS).
1972 June 16 - .
- Mishin notes problems with 7KS at Omsk and the rationale for continued testing of Kontak. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chertok.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-S.
"1. Klyucharev VM: Omsk plant (Director Kolupaev) - Delayed production of 7KS living compartments. ZEM - develop work and schedules to recover schedule for completion of 7KS modules. 2. Chertok: 7K-OK number 18 - rework using the proulsion system from number 36. Work on "Kontakt" to continue, as it can be used in the MKBS'.
1972 June 26 - . 14:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 496 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 33L. Mass: 6,675 kg (14,715 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 9.95 days. Decay Date: 1972-07-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 6066 . COSPAR: 1972-045A. Apogee: 253 km (157 mi). Perigee: 176 km (109 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Recovered July 6, 1972 13:54 GMT. Soyuz 7K-T redesign test..
1972 August - .
- Soyuz 12 / DOS 2 (cancelled) - . Crew: Kubasov, Leonov. Backup Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Support Crew: Grechko, Gubarev. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut. Flight: Soyuz 12 / DOS 2. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned first mission to the Salyut DOS 2 space station. Cancelled after it was destroyed during launch..
1972 August 2 - . LV Family: N1.
- The leadership is not returning Mishin's calls - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Mir,
Soyuz 7K-S.
The leadership is not returning Mishin's calls and he considers alternate approaches to accelerate the space program. For study:
1. Increase the payload for the launch vehicle for the 7KST by modernizing Block I by using the 11D58M engine.
2. OB-7KST - New arrangement with the container in front (and for scientific and military research equipment).
3. Work out our technical policy for DOS 7KT in a given situation.
- Spacecraft numbers 34, 33, 35 - maybe defer some of them to DOS-3.
- As was provided for in this case in ZEM plan for 1972
4. Utmost acceleration of 7KS.
5. N1-L3 in this situation - a general solution. All for a successful operation. (But we need to agree with MOM.)
6. Accelerate work on MOK - MKBS 1st step. (Mishin Diaries 2-370)
1972 August 21 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 7L State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kuznetsov,
Lapygin,
Mishin,
Okhapkin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The State Commission was held to verify readiness of N1 7L for launch. Mishin was 'sick' the whole week of the hearings and had to be represented by his deputies. However neither Mishin or his first deputy Okhapkin were available - both were in the hospital. The commission nearly ruled that until Mishin was available, no launch could be approved. However the review continued. Additional Details: here....
1972 October - .
- Soyuz 13 / DOS 2 (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Backup Crew: Grechko, Gubarev. Support Crew: Klimuk, Sevastyanov. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut. Flight: Soyuz 13 / DOS 2. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned second mission to the Salyut DOS 2 space station. Cancelled after it was destroyed during launch..
1972 November 16 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Flight readiness review for the N1. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
There were still three defects in the new digital computer systems and controversy as to whether to fly the fuel cells in the LOK. But without the fuel cells, there could be no translunar mission. The only power available would then be the batteries in the Block G, limiting the flight to low earth orbit. But the launch manager continued to insist there was danger in handling liquid hydrogen. This was simply a bureaucratic hold-up - only 600 kg of LH2 would be flying, which did not represent a real safety issue. Finally a waiver was agreed and the it was decided the LOK would fly with fuel cells.
All else seemed ready to go. The estimated engine reliability was 93%. The turbogenerators had achieved 100% reliability in test stands. There were still dissenting voices on the use of LH2 - the final vote was 7 for flying with it, and 2 against.
1972 November 21 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- State Commission was held to formally approve launch of N1 7L. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
1972 November 23 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Final N1 preparations - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. At 17:00 fuelling of N1 7L began. Lox fuelling was completed at 23:40..
1972 November 23 - . 06:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 7L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-LOK / LK Mockups. Mass: 9,850 kg (21,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Decay Date: 1972-11-23 . Apogee: 40 km (24 mi).
Unmanned test of manned lunar mission launch vehicle serial number 7L. This article incorporated significant changes to the previous model, including roll 'steering' engines to prevent the loss of control that destroyed 6L. The rocket ascended into the sky, and the engines ran 106.93 seconds, only seven seconds before completion of first stage burnout. Programmed shutdown of some engines to prevent overstressing of the structure led to propellant line hammering, rupture of propellant lines, and an explosion of engine number 4. The vehicle disintegrated. Additional Details: here....
1973 Early - .
- Soyuz Kontakt P (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Backup Crew: Fartushny, Klimuk. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz Kontakt P. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The Kontakt-P Soyuz would have been the passive spacecraft, simulating the LK lunar lander..
1973 Early - .
- Soyuz Kontakt A (cancelled) - . Crew: Filipchenko, Gorbatko. Backup Crew: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz Kontakt A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The launches were delayed and then cancelled due to continuing problems with the N1 lunar booster..
1973 June - .
- Soyuz (Almaz) 12 (cancelled) - . Crew: Artyukhin, Popovich. Backup Crew: Volynov, Zholobov. Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Flight: Soyuz (Almaz) 12. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned first crew to the first Almaz space station. Cancelled after the loss of control of Almaz OPS 1 (Salyut 2) in orbit..
1973 June - .
- Soyuz 12 / DOS 3 (cancelled) - . Crew: Kubasov, Leonov. Backup Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Support Crew: Grechko, Gubarev. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut. Flight: Soyuz 12 / DOS 3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned first mission to the Salyut DOS 3 space station (Cosmos 557). Cancelled after it failed in orbit..
1973 June 15 - . 06:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 573 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 35. Mass: 6,675 kg (14,715 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 2.00 days. Decay Date: 1973-06-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 6694 . COSPAR: 1973-041A. Apogee: 308 km (191 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.50 min. Soyuz test flight. Recovered June 17, 1973 6:01 GMT. Soyuz 7K-T redesign test, probably using one of the spacecraft allocated to the failed Salyut 2 or Cosmos 557 stations..
1973 August - .
- Soyuz (Almaz) 13 (cancelled) - . Crew: Demin, Sarafanov. Backup Crew: Rozhdestvensky, Zudov. Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Flight: Soyuz (Almaz) 13. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned second crew to the first Almaz space station. Cancelled after the loss of control of Almaz OPS 1 (Salyut 2) in orbit..
1973 September - .
- Soyuz 13 / DOS 3 (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Backup Crew: Grechko, Gubarev. Support Crew: Klimuk, Sevastyanov. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut. Flight: Soyuz 13 / DOS 3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned second mission to the Salyut DOS 3 space station (Cosmos 557). Cancelled after it failed in orbit..
1973 September 27 - . 12:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 12 - .
Call Sign: Ural (Urals ). Crew: Lazarev,
Makarov.
Backup Crew: Grechko,
Gubarev.
Support Crew: Klimuk,
Sevastyanov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 36. Mass: 6,720 kg (14,810 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 12.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Duration: 1.97 days. Decay Date: 1973-09-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 6836 . COSPAR: 1973-067A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 306 km (190 mi). Inclination: 51.00 deg. Period: 91.00 min.
Experimental flight for the purpose of further development of manned space craft Soyuz 7K-T modifications. After the Soyuz 11 disaster, the Soyuz underwent redesign for increased reliability. Two solo test flights of the new design were planned. Crews for the first flight were those already planned for the deferred follow-on missions to the failed DOS 2 and DOS 3 space stations.
1973 October 5 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, R-7.
- Mishin presents to the Academic Soviet the high-level justification and purpose of MKBS. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Ustinov,
Melnikov.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-S.
Principal basis for the development of the MOK
1. Providing solutions in targeted areas of defense, science and the economy as they may change over 10-20 years. Enabling rapid replacement of legacy systems, devices and components by more sophisticated systems without changing the logic of construction of the MOK as a whole and its constituent satellite systems and basic modules.
2. Solution targets a minimum number of satellite modules using common equipment and apparatus.
3. Complex solution of defense, economic and scientific problems using MKBS - the main base of the MOK, for logistics and maintenance of a long-term operation and cost-effective transport system.
4. The modular structure of the MOK. Wide standardization, harmonization of systems, devices, compartments, aggregates. All elements of these systems, devices, units must be maintainable and interchangeable.
5. Ensuring long-term service life (5-10 years) of the MOK through periodic visits CM astronauts for routine maintenance, based on the MKBS.
6. MOK should provide the most cost-effective creation of rocket-space tools for addressing the full range of targets, most cost-effective organization of logistics, maintenance and management of the complex in comparison with existing systems. The development of the IOC should be considered as the direction of development of rocket and space technology to solve national problems with the least material costs.
7. Stages of creation MOK as the development and creation of the necessary special systems.
And receives the following criticisms:
1. All elements of MKBS (especially spacecraft based on the 7KS) must have the new layout of systems and equipment, providing repair and replacement.
2. GP Melnikov - MKBS is necessary, but give priority to modules SM-1 and SM-2 (these are specialized military free-flyers).
3. You need to rethink the section on handling scientific information.
4. Do we need to upgrade or add all these launch sites (R-7, UR-500 and N-1) for MOK (especially the UR500K launch complex)? VP Barmin offers not to upgrade the old UR-500 launch complexes, and spend those funds on new complexes (in fact these two additional UR-500 complexes would be the only ones built after the N1 / MKBS cancellation).
5. You need a special decision of the Central Committee of the CPSU and special funding for construction.
6. Which launch vehicles to implement the MOK.
ND Ustinov suggests use of the UR-500 with a fluorine-ammonia upper stage to launch the SNTV direct television broadcasting system (Mishin Diaries 3-104)
1973 November 30 - . 05:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 613 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 34L. Mass: 6,675 kg (14,715 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 60.00 days. Decay Date: 1974-01-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 6957 . COSPAR: 1973-096A. Apogee: 276 km (171 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Unmanned Soyuz test flight. Recovered January 29, 1974 5:29 GMT. Soyuz 7K-T duration test..
1973 December 18 - . 11:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 13 - .
Call Sign: Kavkas (Caucasus ). Crew: Klimuk,
Lebedev.
Backup Crew: Vorobyov,
Yazdovsky.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 33A. Mass: 6,560 kg (14,460 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 13.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Duration: 7.87 days. Decay Date: 1973-12-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 6982 . COSPAR: 1973-103A. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
A unique flight of the 7K-T/AF modification of the Soyuz spacecraft. The orbital module was dominated by the large Orion 2 astrophysical camera. The crew conducted astrophysical observations of stars in the ultraviolet range. Additional experiments included spectrozonal photography of specific areas of the earth's surface, and continued testing of space craft's on-board systems.
1974 January 2 - . LV Family: N1, R-7, N11, Molniya 8K78L.
- On the first two days of 1974, Mishin catalogues the issues and notes his supporters. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Ustinov,
Afanasyev, Sergei,
Almaz,
Bezverby,
.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Mir,
Soyuz 7K-S,
LK.
To do:
1. Now, when considering our long-term program and the use of near-earth space (including the Moon) for different purposes, it is necessary to clearly define the sequence of its implementation.
Especially decide - where to start? (Especially in the present situation).
- It is necessary as soon as possible to show the rationality inherent in the program guidelines.
Namely a space-based MOK.
- Optimal location for OAA systems: based on MKBS (DOS) - or visited the MPM for routine maintenance or brought near-MKBS for the same purpose.
- Reusable transport ship based on the 7M, and then a reusable transport system based on the work on the N-1 (but with a new engine system in stage 1).
02.I.1973
- Space problems solved by the OAA.
- A great resource. (even after these events)
Where to start?
? (7KS)
1. DOS 5 (6?) + 7KT + 7KTT + 7KS-OR
7KS-OR (evidently a reconnaissance version of the 7KS) - view as the embodiment of the most efficient use of the developed equipment (Zenit-Yantar)
Negotiations with DI Kozlov (What does he want?)
2. All that in the first only on the basis of the 7M, to create the MTK and MPM (talks with EV Shabarov)
What will branch NII-4 handle?
1. Operative follow-up exploration.
2. Armed struggle in outer space.
(03.I.1974)
3. The defeat of the moving targets.
4. Electronic countermeasures
5. Use of stationary orbit.
6. Use of of sun-synchronous orbits.
Means:
Filial of NII-4 GUKOS support (but only at the lower levels): 1. R-7M; 2. N-1?; 3. N-11
Support in the MO MO for the N-1 - signed by Alekseev and Tolubko.
Navy is indifferent to MOK (they do not understand the prospects)
It is necessary to establish a relationship with the customer. He is interested in this (Attract DI Kozlov!)
(4.I.1974)
- Write a detailed letter on MOK to Afanasyev (copied to the Central Committee) (With a draft work order)
- Draft a memo to the Central Committee for DF Ustinov. (Long-term planning)
- Achieve color television for the Soyuz-M (NN Detinov - CC)
- TsKBEM review of the level of work on special equipment in related organizations.
- Write a memo about the possibilities of "A" in the operational intelligence. (VK Bezverby together with TsNIIMASH).
- Deal with the radio channel on the "Yantar". Orders: VK Bezverby
- The draft memo on the need of long-term integrated planning by the state. TSKBEM work on MOK - 1st to attempt its development. (Mishin Diaries 3-167)
1974 April 3 - . 07:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 638 - .
Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 71-EPSA. Mass: 6,570 kg (14,480 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: ASTP.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM.
Duration: 9.89 days. Decay Date: 1974-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 7234 . COSPAR: 1974-018A. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
Unmanned Soyuz test flight. Recovered April 13, 1974 5:05 GMT. Soyuz ASTP Test.
Maneuver Summary:
190km X 309km orbit to 190km X 266km orbit. Delta V: 12 m/s
190km X 266km orbit to 240km X 300km orbit. Delta V: 23 m/s
240km X 300km orbit to 258km X 274km orbit. Delta V: 12 m/s
Total Delta V: 47 m/s.
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1974 May 27 - . 07:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Cosmos 656 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 61. Mass: 6,675 kg (14,715 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9. Duration: 2.01 days. Decay Date: 1974-05-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 7313 . COSPAR: 1974-036A. Apogee: 364 km (226 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.00 min. Unmanned test flight of the Soyuz 7K-T(A9) Soyuz variant designed for docking with the military Almaz space station. Recovered May 29, 1974 7:50 GMT..
1974 July 3 - . 18:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 14 - .
Call Sign: Berkut (Golden Eagle ). Crew: Artyukhin,
Popovich.
Backup Crew: Demin,
Sarafanov.
Support Crew: Rozhdestvensky,
Volynov,
Zholobov,
Zudov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 62. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 14.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9.
Duration: 15.73 days. Decay Date: 1974-07-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 7361 . COSPAR: 1974-051A. Apogee: 217 km (134 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
On 4 July Soyuz 14 docked with the Salyut 3 space station after 15 revolutions of the earth. The planned experimental program included manned military reconnaissance of the earth's surface, assessing the fundamental value of such observations, and some supplemental medico-biological research. After the crew's return research continued in the development of the on-board systems and the principles of remote control of such a station.
1974 August 6 - . 00:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 670 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-S s/n 1L. Mass: 6,700 kg (14,700 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S. Duration: 2.99 days. Decay Date: 1974-08-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 7405 . COSPAR: 1974-061A. Apogee: 294 km (182 mi). Perigee: 211 km (131 mi). Inclination: 50.60 deg. Period: 89.50 min. Unmanned Soyuz 7K-S test flight. Recovered August 8, 1974 23:59 GMT..
1974 August 12 - . 06:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 672 - .
Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 72-EPSA. Mass: 6,570 kg (14,480 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: ASTP.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM.
Duration: 5.94 days. Decay Date: 1974-08-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 7413 . COSPAR: 1974-064A. Apogee: 226 km (140 mi). Perigee: 222 km (137 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
ASTP precursor. Recovered August 18, 1974 5:02 GMT. Soyuz ASTP test.
Maneuver Summary:
195km X 305km orbit to 195km X 221km orbit. Delta V: 24 m/s
195km X 221km orbit to 223km X 223km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s
231km X 231km orbit to 231km X 231km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
223km X 223km orbit to 231km X 231km orbit. Delta V: 4 m/s
231km X 231km orbit to 227km X 237km orbit. Delta V: 2 m/s
Total Delta V: 39 m/s.
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1974 August 26 - . 19:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 15 - .
Call Sign: Duna (Danube ). Crew: Demin,
Sarafanov.
Backup Crew: Volynov,
Zholobov.
Support Crew: Rozhdestvensky,
Zudov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 63. Mass: 6,760 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9.
Duration: 2.01 days. Decay Date: 1974-08-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 7421 . COSPAR: 1974-067A. Apogee: 236 km (146 mi). Perigee: 173 km (107 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Soyuz 15 was to conduct the second phase of manned operations aboard the Salyut 3 military space station, but the Igla rendezvous system failed and no docking was made. The two day flight could only be characterised as '... research in manoeuvring and docking with the OPS in various modes, and development of methods for evacuation and landing from space complex in new conditions....'
As Chelomei had complained, Soyuz had no reserves or backup systems for repeated manual docking attempts and had to be recovered after a two-day flight. The state commission found that the Igla docking system of the Soyuz needed serious modification. This could not be completed before Salyut 3 decayed. Therefore the planned Soyuz 16 spacecraft became excess to the program (it was later flown as Soyuz 20 to a civilian Salyut station, even though over its two year rated storage life).
Officially: Conduct of joint experiments with the Salyut-3 orbital scientific station.
1974 October - .
- Soyuz 16A (cancelled) - . Crew: Volynov, Zholobov. Backup Crew: Rozhdestvensky, Zudov. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut. Flight: Soyuz 16A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned but cancelled third mission to the Salyut 3 space station..
1974 December 2 - . 09:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 16 - .
Call Sign: Buran (Snowstorm ). Crew: Filipchenko,
Rukavishnikov.
Backup Crew: Andreyev,
Dzhanibekov.
Support Crew: Ivanchenkov,
Romanenko.
Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 73-EPSA. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: ASTP.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM.
Duration: 5.93 days. Decay Date: 1974-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 7561 . COSPAR: 1974-096A. Apogee: 291 km (180 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 89.20 min.
ASTP Manned Test Flight. Check-out of the Soyuz space craft's on-board systems which had been modernized to meet the requirements of the 1975 joint flight in accordance with the programme of the Soviet-United States experiment; conduct of scientific and technical investigations.
1975 January 10 - . 21:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 17 - . Call Sign: Zenit (Zenith ). Crew: Grechko, Gubarev. Backup Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Support Crew: Klimuk, Sevastyanov. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 38. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 17. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 29.56 days. Decay Date: 1975-02-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 7604 . COSPAR: 1975-001A. Apogee: 249 km (154 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 4. Joint experiments with the Salyut scientific orbital station..
1975 April 5 - . 11:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511. FAILURE: During second-third stage separation third stage failed to separate from second stage but still ignited.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Soyuz 18-1 - .
Call Sign: Ural (Urals ). Crew: Lazarev,
Makarov.
Backup Crew: Klimuk,
Sevastyanov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 39. Mass: 6,830 kg (15,050 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 18-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Duration: 0.0149 days. Decay Date: 1975-04-05 . Apogee: 192 km (119 mi).
Carried Oleg Makarov, Vasili Lazarev for rendezvous with Salyut 4; but during second-third stage seperation third stage failed to separate from second stage but still ignited. The crew demanded that the abort procedures be implemented but ground control could not see the launch vehicle gyrations in their telemetry. Soyuz finally was separated from by ground control command at 192 km, and following a 20.6+ G reentry, the capsule landed in the Altai mountains, tumbled down a mountainside, and snagged in some bushes just short of a precipice. The crew was worried that they may have landed in China and would face internment, but after an hour sitting in the cold next to the capsule, they were discovered by locals speaking Russian. Total flight duration was 1574 km and flight time 21 minutes 27 seconds. Lazarev suffered internal injuries from the high-G reentry and tumble down the mountain side and never flew again. Both cosmonauts were denied their 3000 ruble spaceflight bonus pay and had to apeal all the way to Brezhnev before being paid.
1975 May 24 - . 14:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 18 - . Call Sign: Kavkas (Caucasus ). Crew: Klimuk, Sevastyanov. Backup Crew: Kovalyonok, Ponomaryov. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 40. Mass: 6,825 kg (15,046 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 62.97 days. Decay Date: 1975-07-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 7818 . COSPAR: 1975-044A. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 4. Joint experiments with the Salyut scientific orbital station. The crew remained aloft aboard the station during the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project joint flight..
1975 July 15 - . 12:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 19 (ASTP) - .
Call Sign: Soyuz (Union ). Crew: Kubasov,
Leonov.
Backup Crew: Filipchenko,
Rukavishnikov.
Support Crew: Andreyev,
Dzhanibekov,
Ivanchenkov,
Romanenko.
Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 75 (EPSA). Mass: 6,790 kg (14,960 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: ASTP.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Apollo (ASTP),
Soyuz 19 (ASTP).
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM.
Duration: 5.94 days. Decay Date: 1975-07-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 8030 . COSPAR: 1975-065A. Apogee: 220 km (130 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Soyuz 19 initial orbital parameters were 220.8 by 185.07 kilometres, at the desired inclination of 51.80°, while the period of the first orbit was 88.6 minutes. On 17 July the two spacecraft docked. The crew members rotated between the two spacecraft and conducted various mainly ceremonial activities. Leonov was on the American side for 5 hours, 43 minutes, while Kubasov spent 4:57 in the command and docking modules.
After being docked for nearly 44 hours, Apollo and Soyuz parted for the first time and were station-keeping at a range of 50 meters. The Apollo crew placed its craft between Soyuz and the sun so that the diameter of the service module formed a disk which blocked out the sun. After this experiment Apollo moved towards Soyuz for the second docking.
Three hours later Apollo and Soyuz undocked for the second and final time. The spacecraft moved to a 40 m station-keeping distance so that an ultraviolet absorption experiment could be performed. With all the joint flight activities completed, the ships went on their separate ways.
1975 September 29 - . 04:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 772 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-S s/n 2L. Mass: 6,750 kg (14,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S.
Duration: 3.99 days. Decay Date: 1975-10-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 8338 . COSPAR: 1975-093A. Apogee: 245 km (152 mi). Perigee: 154 km (95 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
Unmanned military Soyuz 7K-S test flight. Recovered October 3, 1975 4:10 GMT. Unsuccessful mission. Transmitted only on 166 MHz frequency, at none of the other usual Soyuz wavelengths.
Maneuver Summary:
193 km X 270 km orbit to 195 km X 300 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s
196 km X 300 km orbit to 196 km X 328 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s
Total Delta V: 16 m/s
1975 November 17 - . 14:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 20 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 64. Mass: 6,700 kg (14,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9.
Duration: 90.49 days. Decay Date: 1976-02-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 8430 . COSPAR: 1975-106A. Apogee: 251 km (155 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned long duration test of the Soyuz transport vehicle; docked with Salyut 4. Recovered February 16, 1976 2:24 GMT. Comprehensive checking of improved on-board systems of the space craft under various flight conditions. Carried a biological payload. Living organisms were exposed to three months in space.
1976 February - .
- Development of Mir, Aelita authorised - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Aelita satellite. The Soviet space program was completely reformulated in a resolution of February 1976, which included authorisation to develop the free flyer in conjunction with the DOS-7/DOS-8 space station (which would eventually evolve into Mir)..
1976 July 6 - . 12:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 21 - .
Call Sign: Baikal (Baikal - lake in Siberia). Crew: Volynov,
Zholobov.
Backup Crew: Rozhdestvensky,
Zudov.
Support Crew: Berezovoi,
Glazkov,
Gorbatko,
Lisun.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 41. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 21.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9.
Duration: 49.27 days. Decay Date: 1976-08-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 8934 . COSPAR: 1976-064A. Apogee: 274 km (170 mi). Perigee: 246 km (152 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
Soyuz 21 with Volynov and Zholobov aboard hard-docked with the station on 6 July 1976 after failure of the Igla system at the last stage of rendezvous. Towards the end of the two month mission an early return to earth was requested due to the poor condition of flight engineer Zholobov (who was suffering from space sickness and psychological problems).
1976 September 15 - . 09:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 22 - .
Call Sign: Yastreb (Hawk ). Crew: Aksyonov,
Bykovsky.
Backup Crew: Malyshev,
Strekalov.
Support Crew: Andreyev,
Popov.
Payload: Soyuz ASTP s/n 74 modified with MF6 camera. Mass: 6,510 kg (14,350 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: ASTP.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 22.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-MF6.
Duration: 7.91 days. Decay Date: 1976-09-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 9421 . COSPAR: 1976-093A. Apogee: 296 km (183 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 89.30 min.
Surplus Soyuz ASTP spacecraft modified with a multi-spectral camera manufactured by Carl Zeiss-Jena in place of the universal docking apparatus. Eight days were spent photographing the earth. Tested and perfected scientific-technical methods and devices for studying the geological characteristics of the earth's surface from outer space for economic purposes.
1976 October 14 - . 17:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Soyuz 23 - .
Call Sign: Radon (Radon ). Crew: Rozhdestvensky,
Zudov.
Backup Crew: Glazkov,
Gorbatko.
Support Crew: Berezovoi,
Lisun.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 65. Mass: 6,760 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 23.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9.
Duration: 2.00 days. Decay Date: 1976-10-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 9477 . COSPAR: 1976-100A. Apogee: 269 km (167 mi). Perigee: 239 km (148 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.50 min.
The Soyuz 23 ferry spacecraft suffered a docking system failure. Sensors indicated an incorrect lateral velocity, causing unnecessary firing of the thrusters during rendezvous. The automatic system was turned off, but no fuel remained for a manual docking by the crew.
1976 November 29 - . 16:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 869 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-S s/n 3L. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S.
Duration: 17.77 days. Decay Date: 1976-12-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 9564 . COSPAR: 1976-114A. Apogee: 289 km (179 mi). Perigee: 209 km (129 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
Unmanned military Soyuz 7K-S test flight. Recovered December 17, 1976 10:31 GMT. Transmitted only on 20.008 MHz and 166 MHz frequencies, at none of the other usual Soyuz wavelengths.
Maneuver Summary:
196 km X 290 km orbit to 187 km X 335 km orbit. Delta V: 15 m/s
187 km X 335 km orbit to 259 km X 335 km orbit. Delta V: 21 m/s
259 km X 335 km orbit to 260 km X 345 km orbit. Delta V: 2 m/s
260 km X 345 km orbit to 265 km X 368 km orbit. Delta V: 7 m/s
265 km X 368 km orbit to 267 km X 391 km orbit. Delta V: 6 m/s
267 km X 391 km orbit to 300 km X 310 km orbit. Delta V: 32 m/s
Total Delta V: 83 m/s
1977 February 7 - . 16:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 24 - .
Call Sign: Terek (Terek - river in the Caucasus). Crew: Glazkov,
Gorbatko.
Backup Crew: Berezovoi,
Lisun.
Support Crew: Kozelsky,
Preobrazhensky.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 66. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 24.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9.
Duration: 17.73 days. Decay Date: 1977-02-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 9804 . COSPAR: 1977-008A. Apogee: 264 km (164 mi). Perigee: 226 km (140 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.30 min.
Soyuz 24 docked with Salyut 5 and brought repair equipment and equipment for a change of cabin atmosphere. This special apparatus was designed to allow the entire station to be vented through the EVA airlock. Because of this the planned EVA was cancelled. However analysis after arrival showed no toxins in the air. The crew changed the cabin air anyway, then returned to earth. The mission, although a short 18 days, was characterised as a busy and successful mission, accomplishing nearly as much as the earlier Soyuz 21's 50 day mission.
1977 July - .
- Soyuz 25A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Berezovoi,
Lisun.
Backup Crew: Kozelsky,
Preobrazhensky.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Glushko.
Program: Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 25A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
A Soyuz 25 mission to the Salyut 5 space station with the crew of Berzovoi and Lisun was to have followed Soyuz 24. However during the four months it took to prepare the Soyuz, Salyut 5 consumed higher than expected fuel in maintaining the station's orientation. The flight was cancelled and the spacecraft allocated for Soyuz 25 flew as Soyuz 30 to Glushko's civilian Salyut station.
1977 October 9 - . 02:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 25 - . Call Sign: Foton (Photon). Crew: Kovalyonok, Ryumin. Backup Crew: Ivanchenkov, Romanenko. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 42. Mass: 6,860 kg (15,120 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 25. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 2.03 days. Decay Date: 1977-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 10401 . COSPAR: 1977-099A. Apogee: 240 km (140 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Manned two crew. Unsuccessful mission. Failed to dock with Salyut 6..
1977 November - .
- Soyuz 26A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Dzhanibekov,
Kolodin.
Backup Crew: Lazarev,
Makarov.
Nation: Russia.
Program: Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 26A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Planned mission to Salyut 6 that would make first docking with rear docking port and be the first crew to swap spacecraft and return in the spacecraft that ferried the Soyuz 25 crew. But after Soyuz 25 failed to dock with Salyut 6 and Soyuz 26 as finally flown had quite a different crew and mission profile.
1977 December 10 - . 01:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 26 - . Call Sign: Taimyr (Taimyr - Russian peninsula). Crew: Grechko, Romanenko. Backup Crew: Ivanchenkov, Kovalyonok. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 43. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 26. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 37.42 days. Decay Date: 1978-01-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 10506 . COSPAR: 1977-113A. Apogee: 235 km (146 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Carried Yuri Romanenko, Georgi Grechko to Salyut 6; returned crew of Soyuz 27 to Earth. Conduct of joint experiments with the Salyut-6 scientific station..
1978 January 10 - . 12:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 27 - . Call Sign: Pamir (Pamir mountains). Crew: Dzhanibekov, Makarov. Backup Crew: Ivanchenkov, Kovalyonok. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 44. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 26, Soyuz 27. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 64.95 days. Decay Date: 1978-03-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 10560 . COSPAR: 1978-003A. Apogee: 237 km (147 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Manned two crew. Carried Oleg Makarov, Vladimir Dzhanibekov to Salyut 6; returned crew of Soyuz 26 to Earth. Docked with Salyut 6..
1978 January 20 - . 08:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 1 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 102. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 26.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 18.73 days. Completed Operations Date: 1978-02-08 02:00:20 . Decay Date: 1978-02-08 02:00:20 . USAF Sat Cat: 10603 . COSPAR: 1978-008A. Apogee: 256 km (159 mi). Perigee: 173 km (107 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of fuel, consumable materials and equipment to the Salyut 6 station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 22 Jan 1978 10:12:14 GMT. Undocked on 6 Feb 1978 05:54:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 8 Feb 1978 02:00:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.91 days. Total docked time 14.82 days.
1978 March 2 - . 15:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 28 - .
Call Sign: Zenit (Zenith ). Crew: Gubarev,
Remek.
Backup Crew: Pelczak,
Rukavishnikov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 45. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 26,
Soyuz 28.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Duration: 7.93 days. Decay Date: 1978-03-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 10694 . COSPAR: 1978-023A. Apogee: 246 km (152 mi). Perigee: 192 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Delivery to the Salyut-6 station of the first international 'Intercosmos' team consisting of A.A. Gubarev (USSR) and V. Remek (Czechoslovak Socialist Republic) to carry out scientific research and experiments jointly developed by Soviet a nd Czechoslovak specialists.
1978 April 4 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 1001 - .
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 4L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 10.87 days. Decay Date: 1978-04-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 10783 . COSPAR: 1978-036A. Apogee: 228 km (141 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Manned precursor. Recovered April 15, 1978 12:02 GMT. Unsuccessful mission. Soyuz T test -failure.
Maneuver Summary:
202 km X 231 km orbit to 195 km X 291 km orbit. Delta V: 19 m/s
195 km X 291 km orbit to 306 km X 322 km orbit. Delta V: 40 m/s
306 km X 322 km orbit to 308 km X 318 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
Total Delta V: 60 m/s.
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1978 June 15 - . 20:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 29 - . Call Sign: Foton (Photon). Crew: Ivanchenkov, Kovalyonok. Backup Crew: Lyakhov, Ryumin. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 46. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 29. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 79.64 days. Decay Date: 1978-09-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 10952 . COSPAR: 1978-061A. Apogee: 248 km (154 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Placed on board the Salyut-6 station a crew consisting of V.V. Kovalenko and A.S. Ivanchenkov to conduct scientific and technological investigations and experiments..
1978 June 27 - . 15:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 30 - . Call Sign: Kavkas (Caucasus ). Crew: Hermaszewski, Klimuk. Backup Crew: Jankowski, Kubasov. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T(A9) s/n 67. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 29, Soyuz 30. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T/A9. Duration: 7.92 days. Decay Date: 1978-07-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 10968 . COSPAR: 1978-065A. Apogee: 244 km (151 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Placed on board the Salyut-6 station, under the Intercosmos programme, a second, international, crew consisting of P.I. Klimuk (USSR) and M. Hermaszewski (Poland) to conduct scientific investigations and experiments..
1978 July 7 - . 11:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 2 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 101. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 29.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 27.59 days. Completed Operations Date: 1978-08-04 01:30:51 . Decay Date: 1978-08-04 01:30:51 . USAF Sat Cat: 10979 . COSPAR: 1978-070A. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 248 km (154 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of fuel, consumable materials and equipment to the Salyut 6 station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 9 Jul 1978 12:58:59 GMT. Undocked on 2 Aug 1978 04:57:44 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 4 Aug 1978 01:31:07 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.92 days. Total docked time 23.67 days.
1978 August 7 - . 22:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 3 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 103. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 29.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 15.76 days. Completed Operations Date: 1978-08-24 16:44:38 . Decay Date: 1978-08-24 16:44:38 . USAF Sat Cat: 10999 . COSPAR: 1978-077A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of fuel, consumable materials and equipment to the Salyut 6 station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 9 Aug 1978 23:59:30 GMT. Undocked on 21 Aug 1978 15:42:50 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 23 Aug 1978 16:45:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.10 days. Total docked time 11.66 days.
1978 August 26 - . 14:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 31 - . Call Sign: Yastreb (Hawk ). Crew: Bykovsky, Jaehn. Backup Crew: Gorbatko, Koellner. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 47. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 29, Soyuz 31. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 67.84 days. Decay Date: 1978-11-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 11010 . COSPAR: 1978-081A. Apogee: 243 km (150 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Delivered to the Salyut-6 station the third international 'Intercosmos' crew consisting of V F Bykovsky (USSR) and S Jaehn (German Democratic Republic) to carry out scientific research and experiments..
1978 October 3 - . 23:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 4 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 105. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 29.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 22.72 days. Completed Operations Date: 1978-10-27 16:27:43 . Decay Date: 1978-10-27 16:27:43 . USAF Sat Cat: 11040 . COSPAR: 1978-090A. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of fuel, consumable materials and equipment to the Salyut 6 station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 6 Oct 1978 01:00:15 GMT. Undocked on 24 Oct 1978 13:01:52 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 26 Oct 1978 16:28:13 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.22 days. Total docked time 18.50 days.
1979 January 31 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 1074 - .
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 5L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 60.04 days. Decay Date: 1979-04-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11259 . COSPAR: 1979-008A. Apogee: 238 km (147 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Manned precursor. Recovered April 1, 1979 10:09 GMT. Soyuz T Test.
Maneuver Summary:
197 km X 240 km orbit to 255 km X 297 km orbit. Delta V: 33 m/s
255 km X 297 km orbit to 264 km X 306 km orbit. Delta V: 4 m/s
264 km X 306 km orbit to 309 km X 321 km orbit. Delta V: 17 m/s
309 km X 321 km orbit to 279 km X 357 km orbit. Delta V: 18 m/s
279 km X 357 km orbit to 352 km X 402 km orbit. Delta V: 32 m/s
352 km X 402 km orbit to 363 km X 384 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s
Total Delta V: 112 m/s
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1979 February 16 - .
- Mir and Aelita production go-ahead. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Aelita satellite. Production of the Mir space station and Aelita free-flyer was authorised together..
1979 February 25 - . 11:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 32 - . Call Sign: Proton (Proton ). Crew: Lyakhov, Ryumin. Backup Crew: Lebedev, Popov. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 48. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 32. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 110.18 days. Decay Date: 1979-06-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 11281 . COSPAR: 1979-018A. Apogee: 256 km (159 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Transported a team consisting of V A Lyakhov and V V Ryumin to the Salyut-6 space station to conduct scientific investigations and experiments and repair work. Recovered June 15, 1979 16:18 GMT. Returned unmanned..
1979 March 12 - . 05:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 5 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 104. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 32.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 23.77 days. Completed Operations Date: 1979-04-05 00:09:54 . Decay Date: 1979-04-05 00:09:54 . USAF Sat Cat: 11292 . COSPAR: 1979-022A. Apogee: 256 km (159 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of fuel, consumable materials and equipment to the Salyut 6 station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 14 Mar 1979 07:19:21 GMT. Undocked on 3 Apr 1979 16:10:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 5 Apr 1979 00:10:22 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.40 days. Total docked time 20.37 days.
1979 April 10 - . 17:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 33 - . Call Sign: Saturn (Saturn ). Crew: Ivanov, Georgi, Rukavishnikov. Backup Crew: Aleksandrov, Aleksandr, Romanenko. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 49. Mass: 6,860 kg (15,120 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 32, Soyuz 33. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 1.96 days. Decay Date: 1979-04-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 11324 . COSPAR: 1979-029A. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Manned two crew. Flight under the Intercosmos programme of an international team consisting of N N Rukavishnikov (USSR) and G I Ivanov (Bulgaria). Unsuccessful mission. Failed to rendezvous with Salyut 6..
1979 May 13 - . 04:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 6 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 106. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 32.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 27.61 days. Completed Operations Date: 1979-06-09 18:52:36 . Decay Date: 1979-06-09 18:52:36 . USAF Sat Cat: 11356 . COSPAR: 1979-039A. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of fuel, consumable materials and equipment to the Salyut 6 station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 15 May 1979 06:19:22 GMT. Undocked on 8 Jun 1979 07:59:41 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 9 Jun 1979 18:52:46 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.54 days. Total docked time 24.07 days.
1979 June 6 - . 18:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 34 - .
Call Sign: Proton (Proton ). Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 50. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 32.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Duration: 73.76 days. Decay Date: 1979-08-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 11387 . COSPAR: 1979-049A. Apogee: 254 km (157 mi). Perigee: 192 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Docked with Salyut 6. Launched unmanned to provide return vehicle for Soyuz 32 crew of Lyakhov/Ryumin after Soyuz 33 primary propulsion system failure. Checked the operation of the spacecraft propulsion unit; transportated the crew of the Salyut-6 station back to earth.
1979 June 28 - . 09:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 7 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 107. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 32.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 21.69 days. Completed Operations Date: 1979-07-20 01:57:19 . Decay Date: 1979-07-20 01:57:19 . USAF Sat Cat: 11421 . COSPAR: 1979-059A. Apogee: 251 km (155 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of fuel, consumable materials and equipment to the Salyut 6 station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 30 Jun 1979 11:18:22 GMT. Undocked on 18 Jul 1979 03:49:55 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 20 Jul 1979 01:57:30 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.0 days. Total docked time 17.69 days.
1979 December 16 - . 12:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-1 - .
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 6L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 100.38 days. Decay Date: 1980-03-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 11640 . COSPAR: 1979-103A. Apogee: 252 km (156 mi). Perigee: 213 km (132 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.20 min.
New generation Soyuz capsule; unmanned flight to Salyut 6. Docked with Salyut 6. Recovered March 25, 1980 21:47 GMT. Unmanned test of Soyuz T design.
Officially: Complex experimental testing of new on-board systems and assemblies under various flight conditions and operation in conjunction with the Salyut-6 orbital station.
1980 March 27 - . 18:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 8 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 108. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 29.50 days. Completed Operations Date: 1980-04-26 06:54:00 . Decay Date: 1980-04-26 06:54:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 11743 . COSPAR: 1980-024A. Apogee: 250 km (150 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Unmanned supply vessel for Salyut 6. Delivery of various cargoes to the Salyut-6 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 29 Mar 1980 20:01:00 GMT. Undocked on 25 Apr 1980 08:04:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 26 Apr 1980 06:54:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.0 days. Total docked time 26.50 days.
1980 April 9 - . 13:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 35 - . Call Sign: Dnepr (Dnieper ). Crew: Popov, Ryumin. Backup Crew: Andreyev, Zudov. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 51. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 55.06 days. Decay Date: 1980-06-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 11753 . COSPAR: 1980-027A. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 197 km (122 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Carried crew comprising L I Popov and V V Ryumin to the Salyut-6 station to carry out scientific and technical research and experiments..
1980 April 27 - . 06:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 9 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 109. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 24.76 days. Completed Operations Date: 1980-05-22 00:44:00 . Decay Date: 1980-05-22 00:44:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 11784 . COSPAR: 1980-033A. Apogee: 255 km (158 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned supply vessel for Salyut 6. Delivery of various cargoes to the Salyut-6 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 29 Apr 1980 08:09:19 GMT. Undocked on 20 May 1980 18:51:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 22 May 1980 00:44:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.32 days. Total docked time 21.45 days.
1980 May 26 - . 18:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 36 - . Call Sign: Orion (Orion ). Crew: Farkas, Kubasov. Backup Crew: Dzhanibekov, Magyari. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 52. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35, Soyuz 36. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 65.87 days. Decay Date: 1980-07-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 11811 . COSPAR: 1980-041A. Apogee: 263 km (163 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Transported the fifth international crew under the INTERCOSMOS programme, comprising V N Kubasov (USSR) and B Farkas (Hungary) to the Salyut-6 station to carry out scientific research and experiments..
1980 June 5 - . 14:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-2 - . Call Sign: Yupiter (Jupiter ). Crew: Aksyonov, Malyshev. Backup Crew: Kizim, Makarov. Payload: Soyuz T s/n 7L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35, Soyuz T-2. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 3.93 days. Decay Date: 1980-06-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 11825 . COSPAR: 1980-045A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Test flight of new Soyuz T; docked with Salyut 6. Conducted testing and development of on-board systems in the improved Soyuz T series transport vehicle under piloted conditions..
1980 June 29 - . 04:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 10 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 110. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 19.88 days. Completed Operations Date: 1980-07-19 01:47:18 . Decay Date: 1980-07-19 01:47:18 . USAF Sat Cat: 11867 . COSPAR: 1980-055A. Apogee: 264 km (164 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
Unmanned supply vessel for Salyut 6. Delivery of various cargoes to the Salyut-6 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 1 Jul 1980 05:53:00 GMT. Undocked on 17 Jul 1980 22:21:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 19 Jul 1980 01:47:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.19 days. Total docked time 16.69 days.
1980 July 23 - . 18:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 37 - .
Call Sign: Terek (Terek - river in the Caucasus). Crew: Gorbatko,
Tuan.
Backup Crew: Bykovsky,
Liem.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 53. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35,
Soyuz 37.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Duration: 79.64 days. Decay Date: 1980-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 11905 . COSPAR: 1980-064A. Apogee: 273 km (169 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
Manned two crew. Transported to the Salyut-6 station the sixth international crew under the Intercosmos programme, comprising V V Gorbatko (USSR) and Pham Tuan (Viet Nam), to conduct scientific research and experiments. Returned crew of Soyuz 35 to Earth. Recovered October 11, 1980 9:50 GMT.
1980 September 18 - . 19:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 38 - . Call Sign: Taimyr (Taimyr - Russian peninsula). Crew: Romanenko, Tamayo Mendez. Backup Crew: Khrunov, Lopez Falcon. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 54. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35, Soyuz 38. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 7.86 days. Decay Date: 1980-09-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 11977 . COSPAR: 1980-075A. Apogee: 257 km (159 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Transported to the Salyut-6 station the seventh international crew under the INTERCOSMOS programme, comprising Y V Romanenko (USSR) and A. Tomaio Mendez (Cuba), to conduct scientific research and experiments..
1980 September 28 - . 15:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 11 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 111. Mass: 7,014 kg (15,463 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 35.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 73.95 days. Completed Operations Date: 1980-12-11 14:00:05 . Decay Date: 1980-12-11 14:00:05 . USAF Sat Cat: 11993 . COSPAR: 1980-079A. Apogee: 241 km (149 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Unmanned supply vessel for Salyut 6. Delivery of various cargoes to the Salyut-6 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 30 Sep 1980 17:03:00 GMT. Undocked on 9 Dec 1980 10:23:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 11 Dec 1980 14:00:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.23 days. Total docked time 69.72 days.
1980 November - .
- Soyuz T-3A (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Polyakov, Strekalov. Backup Crew: Isaulov, Potapov, Rukavishnikov. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut 6. Flight: Soyuz T-3A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Planned but cancelled manned flight. Crew dissolved when Lazarev failed physical in early 1981..
1980 November 27 - . 14:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-3 - .
Call Sign: Mayak (Beacon ). Crew: Kizim,
Makarov,
Strekalov.
Backup Crew: Kovalyonok,
Polyakov,
Savinykh.
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 8L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 12.80 days. Decay Date: 1980-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 12077 . COSPAR: 1980-094A. Apogee: 260 km (160 mi). Perigee: 256 km (159 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
Manned three crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Tested the improved transport ship of the 'SOYUZ T' series; transported to the Salyut-6 orbital station a crew consisting of L D Kizim, O G Makarov and G M Strekalov to carry out repair and preventive work and scientific and technical investigation and experiments.
1981 January 24 - . 14:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 12 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 113. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 55.11 days. Completed Operations Date: 1981-03-20 16:58:58 . Decay Date: 1981-03-20 16:58:58 . USAF Sat Cat: 12152 . COSPAR: 1981-007A. Apogee: 308 km (191 mi). Perigee: 247 km (153 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 6. Delivery of various cargoes to the Salyut-6 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 6 on 26 Jan 1981 15:56:00 GMT. Undocked on 19 Mar 1981 18:14:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 20 Mar 1981 16:59:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.02 days. Total docked time 52.10 days.
1981 March 12 - . 19:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-4 - . Call Sign: Foton (Photon ). Crew: Kovalyonok, Savinykh. Backup Crew: Andreyev, Zudov. Payload: Soyuz T s/n 10L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 74.73 days. Decay Date: 1981-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 12334 . COSPAR: 1981-023A. Apogee: 237 km (147 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Transported to the Salyut-6 orbital station cosmonauts V V Kovalenok and V P Savinykh to carry out repairs and preventive maintenance and scientific and technical investigations and experiments..
1981 March 22 - . 14:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 39 - .
Call Sign: Pamir (Pamir mountains). Crew: Dzhanibekov,
Gurragcha.
Backup Crew: Ganzorig,
Lyakhov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 55. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 39,
Soyuz T-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T.
Duration: 7.86 days. Decay Date: 1981-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 12366 . COSPAR: 1981-029A. Apogee: 249 km (154 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Transported to the Salyut-6 orbital station the eighth international crew under the INTERCOSMOS programme, comprising V A Dzhanibekov (USSR) and Z. Gurragchi (Mongolian People's Republic) to conduct scientific investigations and experiments.
1981 May 14 - . 17:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz 40 - . Call Sign: Dnepr (Dnieper ). Crew: Popov, Prunariu. Backup Crew: Dediu, Romanenko. Payload: Soyuz 7K-T s/n 56. Mass: 6,800 kg (14,900 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 6. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz 40, Soyuz T-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Duration: 7.86 days. Decay Date: 1981-05-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 12454 . COSPAR: 1981-042A. Apogee: 270 km (160 mi). Perigee: 192 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 6. Transported to the Salyut-6 orbital station the ninth international crew under the INTERCOSMOS programme, comprising L I Popov (USSR), and D. Prunariu (Romania), to conduct scientific research and experiments..
1982 First half - .
- Soyuz Almaz 4 (cancelled) - . Crew: Laveykin, Malyshev. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Laveykin, Malyshev. Program: Almaz. Flight: Soyuz Almaz 4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T. Planned Soyuz flight to a dock with the Almaz OPS 4 space station. The mission was cancelled together with the Almaz program in 1981..
1982 May 13 - . 09:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-5 - . Call Sign: Elbrus (Elbrus - tallest mountain in Europe). Crew: Berezovoi, Lebedev. Backup Crew: Strekalov, Titov, Vladimir. Payload: Soyuz T s/n 11L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-5. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 106.21 days. Decay Date: 1982-08-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 13173 . COSPAR: 1982-042A. Apogee: 231 km (143 mi). Perigee: 190 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Carried Anatoli Berezovoi, Valentin Lebedev to Salyut 7 to conduct scientific research and experiments; returned crew of Soyuz T-7 to Earth..
1982 May 23 - . 05:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 13 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 114. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 13.75 days. Completed Operations Date: 1982-06-06 00:03:11 . Decay Date: 1982-06-06 00:03:11 . USAF Sat Cat: 13210 . COSPAR: 1982-047A. Apogee: 263 km (163 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 7. Transport of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 25 May 1982 07:56:36 GMT. Undocked on 4 Jun 1982 06:31:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 6 Jun 1982 00:05:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.81 days. Total docked time 9.94 days.
1982 June 24 - . 16:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-6 - .
Call Sign: Pamir (Pamirs ). Crew: Chretien,
Dzhanibekov,
Ivanchenkov.
Backup Crew: Baudry,
Kizim,
Solovyov, Vladimir.
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 9L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-5,
Soyuz T-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 7.91 days. Decay Date: 1982-07-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 13292 . COSPAR: 1982-063A. Apogee: 233 km (144 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Manned three crew. Docked with Salyut 7. Transported to the Salyut-7 orbital station the Soviet-French international crew, comprising V A Dzhanibekov (USSR), A S Ivanchenkov (USSR) and Jean-Loup Chretien (France) to conduct scientific research and experiments.
1982 July 10 - . 09:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 14 - . Payload: Progress s/n 117. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-5. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress. Duration: 33.65 days. Completed Operations Date: 1982-08-13 11:29:16 . Decay Date: 1982-08-13 11:29:16 . USAF Sat Cat: 13361 . COSPAR: 1982-070A. Apogee: 325 km (201 mi). Perigee: 301 km (187 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.70 min. Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 7. Docked with Salyut 7 on 12 Jul 1982 11:41:00 GMT. Undocked on 10 Aug 1982 22:11:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 13 Aug 1982 01:29:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.21 days. Total docked time 29.44 days..
1982 August 19 - . 17:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-7 - . Call Sign: Dnepr (Dnieper ). Crew: Popov, Savitskaya, Serebrov. Backup Crew: Pronina, Romanenko, Savinykh. Payload: Soyuz T s/n 12L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-5, Soyuz T-7. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 113.08 days. Decay Date: 1982-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 13425 . COSPAR: 1982-080A. Apogee: 299 km (185 mi). Perigee: 289 km (179 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.30 min. Docked with Salyut 7. Carried Svetlana Savitskaya, Leonid Popov, Alexander Serebrov to Salyut 7 to conduct scientific and technical research and experiments..
1982 September 18 - . 04:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 15 - . Payload: Progress s/n 112. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-5. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress. Duration: 28.51 days. Completed Operations Date: 1982-10-16 17:08:06 . Decay Date: 1982-10-16 17:08:06 . USAF Sat Cat: 13558 . COSPAR: 1982-094A. Apogee: 241 km (149 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 7. Docked with Salyut 7 on 20 Sep 1982 06:12:00 GMT. Undocked on 14 Oct 1982 13:46:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 16 Oct 1982 17:08:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.19 days. Total docked time 24.32 days..
1982 October 31 - . 11:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 16 - . Payload: Progress s/n 115. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-5. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress. Duration: 44.25 days. Completed Operations Date: 1982-12-14 17:16:24 . Decay Date: 1982-12-14 17:16:24 . USAF Sat Cat: 13638 . COSPAR: 1982-107A. Apogee: 246 km (152 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 7. Docked with Salyut 7 on 2 Nov 1982 13:22:00 GMT. Undocked on 13 Dec 1982 15:32:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 14 Dec 1982 17:17:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.16 days. Total docked time 41.09 days..
1983 April 20 - . 13:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-8 - . Call Sign: Okean (Ocean ). Crew: Serebrov, Strekalov, Titov, Vladimir. Backup Crew: Aleksandrov, Lyakhov, Savinykh. Payload: Soyuz T s/n 13L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-8. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 2.01 days. Decay Date: 1983-04-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 14014 . COSPAR: 1983-035A. Apogee: 213 km (132 mi). Perigee: 196 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Manned three crew. Unsuccessful mission. Failed to rendezvous with Salyut 7. Recovered April 22, 1983 13:29 GMT. Landed 113 km SE Arkalyk..
1983 June 27 - . 09:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-9 - . Call Sign: Proton (Proton ). Crew: Aleksandrov, Lyakhov. Backup Crew: Strekalov, Titov, Vladimir. Payload: Soyuz T s/n 14L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 149.45 days. Decay Date: 1983-11-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 14152 . COSPAR: 1983-062A. Apogee: 228 km (141 mi). Perigee: 197 km (122 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Manned two crew. Docked with Salyut 7. Transported to the Salyut-7 orbital station a crew consisting of V A Lyakhov, commander of the spacecraft, and A P Aleksandrov, flight engineer, to conduct scientific and technical research and experiments..
1983 August 17 - . 12:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 17 - . Payload: Progress s/n 119. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress. Duration: 31.48 days. Completed Operations Date: 1983-09-17 23:42:37 . Decay Date: 1983-09-17 23:42:37 . USAF Sat Cat: 14283 . COSPAR: 1983-085A. Apogee: 242 km (150 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Unmanned supply vessel to Salyut 7. Docked with Salyut 7 on 19 Aug 1983 13:47:00 GMT. Undocked on 17 Sep 1983 11:44:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 17 Sep 1983 23:43:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.57 days. Total docked time 28.91 days..
1983 September 26 - . 19:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U. FAILURE: Launch vehicle blew up on pad.. Failed Stage: 0.
- Soyuz T-10-1 - . Call Sign: Okean (Ocean). Crew: Strekalov, Titov, Vladimir. Backup Crew: Kizim, Solovyov, Vladimir. Payload: Soyuz 7K-ST s/n 16L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10-1, Soyuz T-9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 0.0001 days. Decay Date: 1983-09-27 . Apogee: 2.00 km (1.20 mi). Aborted September 27, 1983 19:38 GMT. Unsuccessful mission. Launch vehicle blew up on pad at Tyuratam; crew saved by abort system..
1983 October 20 - . 09:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 18 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 118. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 26.76 days. Completed Operations Date: 1983-11-16 04:17:55 . Decay Date: 1983-11-16 04:17:55 . USAF Sat Cat: 14422 . COSPAR: 1983-106A. Apogee: 242 km (150 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Transport of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 22 Oct 1983 11:34:00 GMT. Boosted Salyut to 326 X 356 orbit on 4 Nov 1983. Undocked on 13 Nov 1983 03:08:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 16 Nov 1983 04:18:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 5.11 days. Total docked time 21.65 days.
1984 February 8 - . 12:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-10 - .
Call Sign: Mayak (Beacon ). Crew: Atkov,
Kizim,
Solovyov, Vladimir.
Backup Crew: Polyakov,
Savinykh,
Vasyutin.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-ST s/n 15L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 62.95 days. Decay Date: 1984-04-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 14701 . COSPAR: 1984-014A. Apogee: 219 km (136 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Manned three crew. Docked with Salyut 7. Transported a crew consisting of ship's commander L D Kizim, flight engineer V A Solovyov and cosmonaut-research O Y Atkov to the SALYUT-7 orbital station to conduct scientific and technical studies and experiments.
1984 February 21 - . 06:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 19 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 120. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 40.48 days. Completed Operations Date: 1984-04-01 18:17:55 . Decay Date: 1984-04-01 18:17:55 . USAF Sat Cat: 14757 . COSPAR: 1984-018A. Apogee: 245 km (152 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Transport of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 23 Feb 1984 08:21:00 GMT. Undocked on 31 Mar 1984 09:40:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 1 Apr 1984 18:18:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.43 days. Total docked time 37.05 days.
1984 April 3 - . 13:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Soyuz T-11 - .
Call Sign: Yupiter (Jupiter ). Crew: Malyshev,
Sharma,
Strekalov.
Backup Crew: Berezovoi,
Grechko,
Malhotra.
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 17L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10,
Soyuz T-11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 181.91 days. Decay Date: 1984-10-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 14872 . COSPAR: 1984-032A. Apogee: 224 km (139 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Manned three crew. Docked with Salyut 7.Transported a Soviet-Indian international crew comprising ship's commander Y V Malyshev, flight engineer G M Strekalov (USSR) and cosmonaut-researcher R Sharma (India) to the SALYUT-7 orbital station to conduct scientific and technical studies and experiments.
1984 April 15 - . 08:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 20 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 121. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 21.68 days. Completed Operations Date: 1984-05-07 00:32:58 . Decay Date: 1984-05-07 00:32:58 . USAF Sat Cat: 14932 . COSPAR: 1984-038A. Apogee: 260 km (160 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
Transport of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. First launch of Progress by Soyuz-U2 launch vehicle. Docked with Salyut 7 on 17 Apr 1984 09:22:00 GMT. Undocked on 6 May 1984 17:46:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 7 May 1984 00:32:51 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.33 days. Total docked time 19.35 days.
1984 May 7 - . 22:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 21 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 116. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 18.68 days. Completed Operations Date: 1984-05-27 15:00:15 . Decay Date: 1984-05-27 15:00:15 . USAF Sat Cat: 14961 . COSPAR: 1984-042A. Apogee: 246 km (152 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Transport of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 10 May 1984 00:10:00 GMT. Undocked on 26 May 1984 09:41:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 26 May 1984 15:00:30 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.28 days. Total docked time 16.40 days.
1984 May 28 - . 14:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 22 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 122. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 48.19 days. Completed Operations Date: 1984-07-15 18:52:08 . Decay Date: 1984-07-15 18:52:08 . USAF Sat Cat: 14996 . COSPAR: 1984-051A. Apogee: 244 km (151 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Transport of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 30 May 1984 15:47:00 GMT. Undocked on 15 Jul 1984 13:36:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 15 Jul 1984 18:52:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.28 days. Total docked time 45.91 days.
1984 July 17 - . 17:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz T-12 - . Call Sign: Pamir (Pamir mountains). Crew: Dzhanibekov, Savitskaya, Volk. Backup Crew: Ivanova, Savinykh, Vasyutin. Payload: Soyuz T s/n 18L. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10, Soyuz T-12. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Duration: 11.80 days. Decay Date: 1984-07-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 15119 . COSPAR: 1984-073A. Apogee: 218 km (135 mi). Perigee: 192 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Docked with Salyut 7. Transported a crew comprising ship's commander V A Dzhanibekov, flight engineer S E Savitskaya and cosmonaut-research I P Volk to the Salyut-7 orbital station to conduct scientific and technical studies and experiments..
1984 August 14 - . 06:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 23 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 124. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 13.79 days. Completed Operations Date: 1984-08-28 01:27:45 . Decay Date: 1984-08-28 01:27:45 . USAF Sat Cat: 15193 . COSPAR: 1984-086A. Apogee: 250 km (150 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Transport of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 16 Aug 1984 08:11:00 GMT. Undocked on 26 Aug 1984 16:13:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 28 Aug 1984 01:28:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.46 days. Total docked time 10.33 days.
1985 March - .
- Soyuz T-13A (cancelled) - . Crew: Savinykh, Vasyutin, Volkov, Aleksandr. Backup Crew: Aleksandrov, Saley, Viktorenko. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut 7. Flight: Soyuz T-13A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. A mission was planned from 1982 to operate the military experiments aboard TKS-3 after it had docked with Salyut 7. Salyut 7 problems resulted in a complete breakdown of the TKS-3 plans and the crew was split-up and launched on two seperate flights..
1985 June 6 - . 06:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz T-13 - .
Call Sign: Pamir (Pamir mountains). Crew: Dzhanibekov,
Savinykh.
Backup Crew: Aleksandrov,
Popov.
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 19L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-13 EO-4-a,
Soyuz T-13 EO-4-b.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 112.13 days. Decay Date: 1985-09-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 15804 . COSPAR: 1985-043A. Apogee: 222 km (137 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Docked with Salyut 7. Delivered to the Salyut-7 orbital station a crew consisting of flight commander V A Dzhanibekov and flight engineer V P Savinykh to carry out emergency repairs to inert Salyut 7 station and to conduct scientific and technical research and experiments.
1985 June 21 - . 00:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress 24 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 125. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-13 EO-4-a,
Soyuz T-13 EO-4-b.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 24.91 days. Completed Operations Date: 1985-07-15 22:33:50 . Decay Date: 1985-07-15 22:33:50 . USAF Sat Cat: 15838 . COSPAR: 1985-051A. Apogee: 251 km (155 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Delivery to the Salyut-7 orbital station of a mixed cargo with a total mass of 2,000 kg. Docked with Salyut 7 on 23 Jun 1985 02:54:00 GMT. Undocked on 15 Jul 1985 12:28:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 15 Jul 1985 22:33:31 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.51 days. Total docked time 22.40 days.
1985 July 19 - . 13:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Cosmos 1669 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 126. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-13 EO-4-a,
Soyuz T-13 EO-4-b.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 41.51 days. Completed Operations Date: 1985-08-30 01:19:52 . Decay Date: 1985-08-30 01:19:52 . USAF Sat Cat: 15918 . COSPAR: 1985-062A. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Progress vehicle, given Cosmos designation instead of Progress because control lost early in mission but regained later. Resupplied Salyut 7. On departure briefly undocked and redocked to verify reliability of docking system. Transported of various cargoes to the Salyut-7 orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 21 Jul 1985 15:05:00 GMT. Undocked on 28 Aug 1985 21:50:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 30 Aug 1985 01:20:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.23 days. Total docked time 38.28 days.
1985 September 17 - . 12:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz T-14 - .
Call Sign: Cheget (Tcheget - mountain in the Caucasus). Crew: Grechko,
Vasyutin,
Volkov, Aleksandr.
Backup Crew: Saley,
Strekalov,
Viktorenko.
Payload: Soyuz T s/n 20L. Mass: 6,850 kg (15,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-13 EO-4-a,
Soyuz T-13 EO-4-b,
Soyuz T-14 EO-4-c,
Soyuz T-14 Salyut 7 EP-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 64.91 days. Decay Date: 1985-11-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 16051 . COSPAR: 1985-081A. Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 196 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Docked with Salyut 7. Transported a crew comprising ship's commander V V Vasyutin, flight engineer G M Grechko and cosmonaut-researcher A A Volkov to the Salyut-7 orbital station to conduct scientific and technical studies and experiments. Grechko returned in Soyuz T-13 on 25 September 1985 - emergency return.
1986 Early - .
- Soyuz T-15A (cancelled) - . Crew: Levchenko, Manarov, Volynov. Backup Crew: Berezovoi, Shchukin, Solovyov. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut 7. Flight: Soyuz T-15A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Final expedition to Salyut 7 station was cancelled when control was lost..
1986 March 13 - . 12:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz T-15 - .
Call Sign: Mayak (Beacon ). Crew: Kizim,
Solovyov, Vladimir.
Backup Crew: Aleksandrov,
Viktorenko.
Payload: Soyuz T 11F732 s/n 21L. Mass: 7,020 kg (15,470 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Duration: 125.00 days. Decay Date: 1986-07-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 16643 . COSPAR: 1986-022A. Apogee: 366 km (227 mi). Perigee: 331 km (205 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
Mir Main Expedition EO-01. Epic repair mission. The crew, consisting of ship's commander L D Kizim and flight engineer V A Solovyov first docked with the Mir orbital station to conduct scientific and technical studies and experiments. Mir then maneuvered 17 April to match Salyut 7's orbit at 4000 km separation, then again on 4 May to catch up. After six weeks aboard Mir, Soyuz T-15 undocked on 5 May, then rendezvoused and manually docked with the inoperative Salyut 7 station. This was the only flight in history by a single spacecraft between two space stations. The Salyut-7 station was found to be ice bound and without electrical power. The crew repaired the station, regaining power, heat, and environmental control. The also removed experimental results left behind by last crew. Soyuz T-15 undocked Salyut 7 on 25 June, and redocked with Mir on 26 June, delivering 400 kg of scientific material from Salyut 7, including a multichannel spectrometer. Following further work aboard Mir, the crew landed on July 16, 1986 at 12:34 GMT. No crew ever revisited Salyut 7; it made an uncontrolled reentry over Argentina.
1986 March 19 - . 10:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 25 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 134. Mass: 7,270 kg (16,020 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 32.61 days. Completed Operations Date: 1986-04-21 00:48:05 . Decay Date: 1986-04-21 00:48:05 . USAF Sat Cat: 16645 . COSPAR: 1986-023A. Apogee: 251 km (155 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned supply vessel transporting sundry cargoes to the Mir orbital station. Docked with Mir on 21 Mar 1986 11:16:02 GMT. Undocked on 20 Apr 1986 19:24:08 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 21 Apr 1986 00:48:30 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.27 days. Total docked time 30.34 days.
1986 April 23 - . 19:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 26 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 136. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 60.83 days. Completed Operations Date: 1986-06-23 15:40:56 . Decay Date: 1986-06-23 15:40:56 . USAF Sat Cat: 16687 . COSPAR: 1986-032A. Apogee: 257 km (159 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Mir. Rendezvoused with Mir on 25 April, but problem with Mir's radio communication system delays docking until the next day. Docked with Mir on 26 Apr 1986 21:26:06 GMT. Undocked on 22 Jun 1986 18:25:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 23 Jun 1986 15:41:01 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.96 days. Total docked time 56.87 days.
1986 May 21 - . 08:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-1 - .
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 51. Mass: 7,070 kg (15,580 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 8.93 days. Decay Date: 1986-05-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 16722 . COSPAR: 1986-035A. Apogee: 225 km (139 mi). Perigee: 192 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Test of new Soyuz vehicle. Recovered May 30, 1986 6:49 GMT. Unmanned test of Soyuz TM. Docked with Mir May 23 1987. Undocked 29 May.
Officially: Comprehensive experimental testing of spacecraft in independent flight and jointly with the Mir orbital station.
1986 June - .
- Soyuz T-15B (cancelled) - . Crew: Aleksandrov, Saley, Viktorenko. Backup Crew: Moskalenko, Serebrov, Solovyov. Nation: Russia. Program: Salyut 7. Flight: Soyuz T-15B. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz T. Planned second crew to opeate TKS-3 military experiments aboard Salyut 7 before control of the station was lost. Salyut 7 and Cosmos 1686 burned up in the atmosphere together in a fiery show over Argentina on February 7, 1991..
1986 September - .
- Soyuz T-15C (cancelled) - .
Crew: Dobrokvashina,
Ivanova,
Savitskaya.
Backup Crew: Aleksandrov,
Solovyov,
Viktorenko.
Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: Salyut 7.
Flight: Soyuz T-15C.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz T.
Cancelled all-female flight to be launched on International Woman's Day, to have docked with Mir or Salyut 7. Breakdown of Salyut 7, exhaustion of stock of Soyuz T spacecraft, and official resistance led to cancellation of the mission. Officially cancelled due to birth of Savitskaya's baby. No female cosmonauts would be in training again until a decade later.
1987 January 16 - . 06:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 27 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 135. Mass: 7,230 kg (15,930 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2,
Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 40.42 days. Completed Operations Date: 1987-02-26 07:04:37 . Decay Date: 1987-02-26 07:04:37 . USAF Sat Cat: 17299 . COSPAR: 1987-005A. Apogee: 263 km (163 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Mir; raised Mir's orbit. Transported sundry cargoes to the Mir orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 18 Jan 1987 07:26:50 GMT. Undocked on 23 Feb 1987 11:29:01 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 25 Feb 1987 16:05:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.25 days. Total docked time 36.17 days.
1987 February 5 - . 21:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-2 - . Call Sign: Taimyr (Taimyr - Russian peninsula). Crew: Laveykin, Romanenko. Backup Crew: Serebrov, Titov, Vladimir. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 52. Mass: 7,100 kg (15,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2, Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 174.14 days. Decay Date: 1987-07-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 17482 . COSPAR: 1987-013A. Apogee: 365 km (226 mi). Perigee: 341 km (211 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Mir Expedition EO-02. Docked with Mir 7 February 1987. Carried Yuri Romanenko, Aleksander Laveykin to Mir; returned Laveykin, crew of Soyuz TM-3 to Earth..
1987 March 3 - . 11:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 28 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 137. Mass: 7,246 kg (15,974 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2,
Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 24.69 days. Completed Operations Date: 1987-03-28 03:48:55 . Decay Date: 1987-03-28 03:48:55 . USAF Sat Cat: 17564 . COSPAR: 1987-023A. Apogee: 254 km (157 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Mir. Orbit of station at time of rendezvous was 344 X 369 km, 51. 62 deg. Docked with Mir on 5 Mar 1987 12:42:36 GMT. Undocked on 26 Mar 1987 05:06:48 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 28 Mar 1987 03:49:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.01 days. Total docked time 20.68 days.
1987 April 21 - . 15:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 29 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 127. Mass: 7,100 kg (15,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2,
Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 19.72 days. Completed Operations Date: 1987-05-11 08:27:43 . Decay Date: 1987-05-11 08:27:43 . USAF Sat Cat: 17878 . COSPAR: 1987-034A. Apogee: 237 km (147 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Mir. Deorbited May 11, 1987. Docked with Mir at 343 X 363 1705 23 April at rear port of Kvant. Undocked May 11 03:10. Deorbited28 May 02:59 .
Officially: Transporting sundry cargoes to the Mir orbital station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 23 Apr 1987 17:04:51 GMT. Undocked on 11 May 1987 03:10:01 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 11 May 1987 08:28:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.30 days. Total docked time 17.42 days.
1987 May 19 - . 04:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 30 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 128. Mass: 7,249 kg (15,981 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2,
Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 61.07 days. Completed Operations Date: 1987-07-19 05:41:50 . Decay Date: 1987-07-19 05:41:50 . USAF Sat Cat: 17999 . COSPAR: 1987-044A. Apogee: 365 km (226 mi). Perigee: 341 km (211 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
Unmanned supply vessel to Mir. Rendezvoused with Mir/Kvant in its orbit of 343 X 366 km, 51. 6 deg. Docked with the station on 21 May 1987 05:50:38 GMT. Undocked on 19 Jul 1987 00:19:51 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 19 Jul 1987 05:42:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.30 days. Total docked time 58.77 days.
1987 July 22 - . 01:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-3 - .
Call Sign: Vityaz (Knight ). Crew: Aleksandrov,
Faris,
Viktorenko.
Backup Crew: Habib,
Savinykh,
Solovyov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 53. Mass: 7,100 kg (15,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2,
Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1,
Soyuz TM-3,
Soyuz TM-3 Mir EP-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 160.30 days. Decay Date: 1987-12-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 18222 . COSPAR: 1987-063A. Apogee: 353 km (219 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.00 min.
Manned three crew. Transported to the Mir orbital space station a Soviet-Syrian crew comprising cosmonauts A S Viktorenko, A P Aleksandrov and M A Faris to conduct joint research and experiments with cosmonauts Y Romanenko and A Laveykin. Maneuvered from initial 231 X 217 km orbit to Mir's 311 X 359 km orbit. Docked with rear Mir port at 3:30 GMT 24 July. Undocked with rear port 30 July and docked to forward port.
1987 August 3 - . 20:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 31 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 138. Mass: 7,212 kg (15,899 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1,
Soyuz TM-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 50.18 days. Completed Operations Date: 1987-09-24 01:01:49 . Decay Date: 1987-09-24 01:01:49 . USAF Sat Cat: 18283 . COSPAR: 1987-066A. Apogee: 250 km (150 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Rendezvous transfer orbits 187 X 250 km, 51. 64 deg; 266 X 314 km; 309 X 360 km. Docked with Mir on 5 Aug 1987 22:27:35 GMT. Refueled Mir propellants tanks on 15/16 Sept. Undocked on 21 Sep 1987 23:57:41 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 23 Sep 1987 01:02:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.12 days. Total docked time 47.06 days.
1987 September 23 - . 23:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 32 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 139. Mass: 7,035 kg (15,509 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1,
Soyuz TM-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 55.98 days. Completed Operations Date: 1987-11-19 23:19:51 . Decay Date: 1987-11-19 23:19:51 . USAF Sat Cat: 18376 . COSPAR: 1987-082A. Apogee: 355 km (220 mi). Perigee: 295 km (183 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.00 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Delivered 850 kg propellants, 315 kg food, 2,000 kg total. Docked with Mir on 26 Sep 1987 01:08:15 GMT. Undocked on 10 Nov 1987 04:09:10 GMT. Redocked from 2,500 m on 10 Nov 1987 05:47 GMT. Undocked again 17 Nov 1998 19:25 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 19 Nov 1987 00:58:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.17 days. Total docked time 52.82 days.
1987 November 20 - . 23:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 33 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 140. Mass: 6,895 kg (15,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1,
Soyuz TM-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 28.58 days. Completed Operations Date: 1987-12-20 13:36:48 . Decay Date: 1987-12-20 13:36:48 . USAF Sat Cat: 18568 . COSPAR: 1987-094A. Apogee: 343 km (213 mi). Perigee: 326 km (202 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Space station orbit at rendezvous was 326 km x 343 km. Docked on 23 Nov 1987 01:39:13 GMT. Undocked on 19 Dec 1987 08:15:46 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 19 Dec 1987 13:37:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.30 days. Total docked time 26.28 days.
1987 December 21 - . 11:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-4 - . Call Sign: Okean (Ocean ). Crew: Levchenko, Manarov, Titov, Vladimir. Backup Crew: Kaleri, Shchukin, Volkov, Aleksandr. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 54. Mass: 7,070 kg (15,580 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1, Soyuz TM-3, Soyuz TM-4, Soyuz TM-4 LII-1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 178.95 days. Decay Date: 1988-06-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 18699 . COSPAR: 1987-104A. Apogee: 357 km (221 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Mir Expedition EO-03. Carried Musa Manarov, Anatoly Levchenko, Vladimir Titov to Mir; returned crew of Soyuz TM-5 to Earth. Orbits 168 x 243 km, 255 x 296 km, 333 x 359 km. Docked with Mir 12:51 GMT 23 December. 30 December moved to forward port..
1988 January 20 - . 22:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 34 - . Payload: Progress s/n 142. Mass: 7,078 kg (15,604 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress. Duration: 43.36 days. Completed Operations Date: 1988-03-05 07:29:36 . Decay Date: 1988-03-05 07:29:36 . USAF Sat Cat: 18795 . COSPAR: 1988-003A. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 329 km (204 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked on 23 Jan 1988 00:09:09 GMT. Undocked on 4 Mar 1988 03:40:09 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 4 Mar 1988 07:29:30 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.21 days. Total docked time 41.15 days..
1988 March 23 - . 21:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 35 - . Payload: Progress s/n 143. Mass: 7,037 kg (15,513 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress. Duration: 42.41 days. Completed Operations Date: 1988-05-06 06:56:07 . Decay Date: 1988-05-06 06:56:07 . USAF Sat Cat: 18992 . COSPAR: 1988-024A. Apogee: 262 km (162 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked on 25 Mar 1988 22:21:35 GMT. Undocked on 5 May 1988 01:36:03 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 5 May 1988 06:56:19 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.28 days. Total docked time 40.14 days..
1988 May 13 - . 00:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 36 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 144. Mass: 7,077 kg (15,602 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 23.87 days. Completed Operations Date: 1988-06-05 21:18:15 . Decay Date: 1988-06-05 21:18:15 . USAF Sat Cat: 19117 . COSPAR: 1988-038A. Apogee: 246 km (152 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Rendezvous transfer orbits 185x246 km, 51. 66 deg; 223x334 km; 331x357 km. Docked with Mir on 15 May 1988 02:13:26 GMT. Undocked on 5 Jun 1988 11:11:55 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 5 Jun 1988 21:18:40 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.49 days. Total docked time 21.37 days.
1988 June 7 - . 14:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-5 - .
Call Sign: Rodnik (Spring - water spring). Crew: Aleksandrov, Aleksandr,
Savinykh,
Solovyov.
Backup Crew: Lyakhov,
Serebrov,
Stoyanov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 55. Mass: 7,000 kg (15,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4,
Soyuz TM-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 91.45 days. Decay Date: 1988-09-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 19204 . COSPAR: 1988-048A. Apogee: 216 km (134 mi). Perigee: 196 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Transported to the Mir orbital station a Soviet/Bulgarian crew comprising cosmonauts A Y Solovyev, V P Savinykh and A P Aleksandrov (Bulgaria) to conduct joint research and experiments with cosmonauts V G Titov and M K Manarov. Interim orbit 343 x 282 km. Maneuvered to Mir's 355 x 349 km orbit. Docked 15:57 GMT 9 June to Mir's aft port. Moved to forward port 18 June.
1988 July 18 - . 21:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 37 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 145. Mass: 7,065 kg (15,575 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 24.69 days. Completed Operations Date: 1988-08-13 13:45:31 . Decay Date: 1988-08-13 13:45:31 . USAF Sat Cat: 19322 . COSPAR: 1988-061A. Apogee: 256 km (159 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Rendezvous transfer orbits 187x256 km, 51. 62 deg; 235 x 319 km; 343 x 347 km. Docked with Mir on 20 Jul 1988 22:33:40 GMT. Refuelling operations on 7,8, and 9 August 1998. Undocked on 12 Aug 1988 08:31:54 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 12 Aug 1988 13:45:40 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.27 days. Total docked time 22.42 days.
1988 August 29 - . 04:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-6 - .
Call Sign: Proton (Proton ). Crew: Lyakhov,
Mohmand,
Polyakov.
Backup Crew: Arzamazov,
Berezovoi,
Masum.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 56. Mass: 7,070 kg (15,580 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4,
Soyuz TM-6,
Soyuz TM-6 Mir LD-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 114.23 days. Decay Date: 1988-12-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 19443 . COSPAR: 1988-075A. Apogee: 228 km (141 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Transported to the Mir orbital station a Soviet-Afghan crew comprising the cosmonauts V A Lyakhov, V V Polyakov and A A Momand (Afghanistan) to conduct joint research and experiments with the cosmonauts V G Titov and M K Manarov. Returned Manarov, Titov (Soyuz TM-4), Chretien (Soyuz TM-7) to Earth. Initial orbit 195 X 228 km at 51. 57 deg. Maneuvered to a 235 x 259 km orbit, then docked with Mir at 05:41 GMT on 31 August at its 339 x 366 km orbit. Moved from aft to forward port 8 Sept 88.
1988 September 9 - . 23:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 38 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 146. Mass: 7,027 kg (15,491 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4,
Soyuz TM-6 Mir LD-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 74.81 days. Completed Operations Date: 1988-11-24 19:07:18 . Decay Date: 1988-11-24 19:07:18 . USAF Sat Cat: 19486 . COSPAR: 1988-083A. Apogee: 248 km (154 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. During launch first test of Buran ejection seat was made during ascent to orbit. The K-36M.11F35 seat was installed in an 'experimental droppable compartment' installed in place of the Launch Escape Tower engine on top of the shroud. Rendezvous orbits 186 X 246 km, 51. 63 deg; 234 X 332 km, 337 X 363 km. Docked with Mir on 12 Sep 1988 01:22:28 GMT. Delivered 2,000 kg supplies including 300 kg of food. Refuelled Mir. Undocked on 23 Nov 1988 12:12:46 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 23 Nov 1988 19:06:58 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.36 days. Total docked time 72.45 days.
1988 November 26 - . 15:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-7 - .
Call Sign: Donbass (Donbass - River Don basin). Crew: Chretien,
Krikalyov,
Volkov, Aleksandr.
Backup Crew: Serebrov,
Tognini,
Viktorenko.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 57. Mass: 7,000 kg (15,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-4,
Soyuz TM-6 Mir LD-2,
Soyuz TM-7,
Soyuz TM-7 Aragatz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 151.47 days. Decay Date: 1989-04-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 19660 . COSPAR: 1988-104A. Apogee: 235 km (146 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Mir Expedition EO-04. Carried Alexander Volkov, Sergei Krikalev, Jean-Loup Chretien to Mir; returned Volkov, Krikalev to Earth. Initial Orbit: 194 X 235 km. Thereafter maneuvered to rendezvous orbit 256 X 291 km before docking with Mir in 337 X 369 km at 17:16 GMT 28 November.
1988 December 25 - . 04:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 39 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 147. Mass: 7,015 kg (15,465 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-6 Mir LD-2,
Soyuz TM-7.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 44.40 days. Completed Operations Date: 1989-02-07 13:49:23 . Decay Date: 1989-02-07 13:49:23 . USAF Sat Cat: 19728 . COSPAR: 1988-114A. Apogee: 238 km (147 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Made second test of Buran ejection seat during ascent to orbit. The K-36M.11F35 seat was installed in an 'experimental droppable compartment' installed in place of the Launch Escape Tower engine on top of the shroud. Rendezvous orbits 187 X 237 km, 51.63 deg; 236 X 338 km; 325 X 353 km at Mir. Delivered 1,300 kg cargo. Docked with Mir on 27 Dec 1988 05:35:10 GMT. Undocked on 7 Feb 1989 06:45:34 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 7 Feb 1989 13:49:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.35 days. Total docked time 42.05 days.
1989 February 10 - . 08:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. Launch Pad: LC1 or LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 40 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 148. Mass: 7,022 kg (15,480 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-6 Mir LD-2,
Soyuz TM-7.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 22.71 days. Completed Operations Date: 1989-03-05 01:59:08 . Decay Date: 1989-03-05 01:59:08 . USAF Sat Cat: 19783 . COSPAR: 1989-008A. Apogee: 244 km (151 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Conducted third test of Buran ejection seat during ascent to orbit. The K-36M.11F35 seat was installed in an 'experimental droppable compartment' installed in place of the Launch Escape Tower engine on top of the shroud. Docked with Mir on 12 Feb 1989 10:29:38 GMT. Undocked on 3 Mar 1989 01:45:52 GMT. Unfurled experimental space mirror petal structure on undocking. Destroyed in reentry on 5 Mar 1989 01:59:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.08 days. Total docked time 18.64 days.
1989 March 16 - . 18:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. Launch Pad: LC1 or LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 41 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 149. Mass: 6,995 kg (15,421 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-6 Mir LD-2,
Soyuz TM-7.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 39.72 days. Completed Operations Date: 1989-04-25 12:11:45 . Decay Date: 1989-04-25 12:11:45 . USAF Sat Cat: 19895 . COSPAR: 1989-023A. Apogee: 243 km (150 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Conducted fourth test of Buran ejection seat during ascent to orbit. The K-36M.11F35 seat was installed in an 'experimental droppable compartment' installed in place of the Launch Escape Tower engine on top of the shroud. Delivered Bulgarian Spektr 256 spectrometer, power supplies for failed equipment. Docked with Mir on 18 Mar 1989 20:50:46 GMT. Between April 9 and 17 boosted Mir into a 373 X 416 km storage orbit after the decision was made to delay remanning the station. However these maneuvers resulted in the spacecraft running out of fuel. Undocked on 21 Apr 1989 01:46:15 GMT. Destroyed in uncontrolled decay of orbit on 25 Apr 1989 12:12:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 6.52 days. Total docked time 33.21 days.
1989 April - .
- Soyuz TM-8A (cancelled) - . Crew: Afanasyev, Sevastyanov, Stankevicius. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sevastyanov, Stankevicius. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-8A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Planned flight to ensure continuous occupation cancelled due to budget cutbacks and delay in launching Kvant 2 and Kristall modules..
1989 August 23 - . 03:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-1 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 201. Mass: 7,270 kg (16,020 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 100.34 days. Completed Operations Date: 1989-12-01 11:21:28 . Decay Date: 1989-12-01 11:21:28 . USAF Sat Cat: 20191 . COSPAR: 1989-066A. Apogee: 217 km (134 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Unmanned supply vehicle to Mir; first flight of new vehicle design. Tested on-board systems under different conditions and delivered expendable materials and sundry cargo to the Mir manned space station. Docked with Mir on 25 Aug 1989 05:19:02 GMT. Undocked on 1 Dec 1989 09:02:23 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 1 Dec 1989 11:21:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.19 days. Total docked time 98.16 days.
1989 September 5 - . 21:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-8 - .
Call Sign: Vityaz (Knight ). Crew: Serebrov,
Viktorenko.
Backup Crew: Balandin,
Solovyov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 58. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 166.29 days. Decay Date: 1990-02-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 20218 . COSPAR: 1989-071A. Apogee: 392 km (243 mi). Perigee: 390 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Manned two crew. Mir Expedition EO-05. Docked with Mir 8 September. Transported to the Mir orbital station a team consisting of A S Viktorenko, commander of the spacecraft, and A A Serebrov, on-board engineer, to carry out scientific and technological research and experiments. Flight cost 80 million rubles. Expected return 25 million rubles net profit.
1989 December 20 - . 03:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-2 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 202. Mass: 7,300 kg (16,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 51.18 days. Completed Operations Date: 1990-02-09 07:56:10 . Decay Date: 1990-02-09 07:56:10 . USAF Sat Cat: 20373 . COSPAR: 1989-099A. Apogee: 392 km (243 mi). Perigee: 390 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir; carried US microgravity payload. Delivered various cargoes to the Mir orbital station, including scientific apparatus produced in the United States of America and intended, pursuant to a commercial agreement, for the conduct of experiments on space biotechnology. Docked with Mir on 22 Dec 1989 05:41:21 GMT. Undocked on 9 Feb 1990 02:33:07 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 9 Feb 1990 07:56:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.31 days. Total docked time 48.87 days.
1990 February 11 - . 06:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-9 - .
Call Sign: Rodnik (Spring - water spring). Crew: Balandin,
Solovyov.
Backup Crew: Manakov,
Strekalov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 60. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-8,
Soyuz TM-9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 179.05 days. Decay Date: 1990-08-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 20494 . COSPAR: 1990-014A. Apogee: 387 km (240 mi). Perigee: 373 km (231 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
Manned two crew. Mir Expedition EO-06. Docked with Mir. Transported to the Mir orbital station a crew comprising the cosmonauts A Y Solovyov and A N Balandin to conduct an extensive programme of geophysical and astrophysical research, experiments on biology and biotechnology and work on space materials science.
1990 February 28 - . 23:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-3 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 203. Mass: 7,249 kg (15,981 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-9. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 58.07 days. Completed Operations Date: 1990-04-29 00:52:03 . Decay Date: 1990-04-29 00:52:03 . USAF Sat Cat: 20513 . COSPAR: 1990-020A. Apogee: 218 km (135 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 3 Mar 1990 01:04:32 GMT. Undocked on 27 Apr 1990 20:24:43 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 28 Apr 1990 00:52:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.26 days. Total docked time 55.81 days..
1990 May 5 - . 20:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress 42 - .
Payload: Progress s/n 150. Mass: 7,011 kg (15,456 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress.
Duration: 21.66 days. Completed Operations Date: 1990-05-28 12:27:29 . Decay Date: 1990-05-28 12:27:29 . USAF Sat Cat: 20602 . COSPAR: 1990-041A. Apogee: 243 km (150 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir; last of original design Progress spacecraft. Conducted fifth and final test of Buran ejection seat during ascent to orbit. The K-36M.11F35 seat was installed in an 'experimental droppable compartment' installed in place of the Launch Escape Tower engine on top of the shroud. Docked with Mir on 7 May 1990 22:45:03 GMT. Undocked on 27 May 1990 07:08:58 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 27 May 1990 12:27:30 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.31 days. Total docked time 19.35 days.
1990 August 1 - . 09:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-10 - .
Call Sign: Vulkan (Volcano ). Crew: Manakov,
Strekalov.
Backup Crew: Afanasyev,
Manarov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 61A. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-10,
Soyuz TM-9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 130.86 days. Decay Date: 1990-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 20722 . COSPAR: 1990-067A. Apogee: 219 km (136 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Manned two crew. Docked with Mir. Mir Expedition EO-07. Transported to the Mir manned orbital station the crew consisting of the cosmonauts G M Manakov and G M Strekalov for the purpose of carrying out a programme of geophysical and astrophysical research, biological and biotechnological experiments, and work on space-materials science.
1990 August 15 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-4 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 204. Mass: 7,294 kg (16,080 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 36.32 days. Completed Operations Date: 1990-09-20 11:43:08 . Decay Date: 1990-09-20 11:43:08 . USAF Sat Cat: 20752 . COSPAR: 1990-072A. Apogee: 219 km (136 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Delivered cables for rewiring operations and equipment for Soyuz TM-11 Japanese journalist flight. Docked with Mir on 17 Aug 1990 05:26:13 GMT. Undocked on 17 Sep 1990 12:42:43 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 20 Sep 1990 11:42:49 GMT. Total free-flight time 5.02 days. Total docked time 31.30 days.
1990 September 27 - . 10:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-5 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 206. Mass: 7,320 kg (16,130 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 62.02 days. Completed Operations Date: 1990-11-28 10:59:23 . Decay Date: 1990-11-28 10:59:23 . USAF Sat Cat: 20824 . COSPAR: 1990-085A. Apogee: 229 km (142 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Included first Progress recoverable capsule for return of 150 kg of payload to earth. Docked with Mir on 29 Sep 1990 12:26:50 GMT. Undocked on 28 Nov 1990 06:15:46 GMT. After deorbit burn, capsule separated for reentry with an expected landing in Kazakhstan at 28 Nov 1990 11:04:05 GMT. However the recoverable capsule's beacon signal was never received after reentry. All experimental data and materials in capsule lost. Total free-flight time 2.28 days. Total docked time 59.74 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-10. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Decay Date: 1990-11-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 20824 . COSPAR: 1990-085xx. Apogee: 406 km (252 mi). Perigee: 361 km (224 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
1990 December 2 - . 08:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-11 - .
Call Sign: Derbent (Derbent - Russian city). Crew: Afanasyev,
Akiyama,
Manarov.
Backup Crew: Artsebarsky,
Kikuchi,
Krikalyov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 61. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-10,
Soyuz TM-11,
Soyuz TM-11 Kosmoreporter.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 175.08 days. Decay Date: 1991-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 20981 . COSPAR: 1990-107A. Apogee: 400 km (240 mi). Perigee: 367 km (228 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
Docked with Mir. Mir Expedition EO-08. Transported to the Mir manned orbital station the international crew consisting of the cosmonauts V M Afanasyev, M Kh Manarov, and T Akiyami (Japan) for the purpose of carrying out joint work with the cosmonauts G M Manakov and G M Strekalov. Launched jointly with the private Japanese company TBS. The Japanese television network ended up paying $ 28 million for the first commercial flight to Mir to put Akiyama, the first journalist in space aboard Soyuz TM-11. Akiyama made daily television broadcasts.
1991 January 14 - . 14:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-6 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 205. Mass: 7,125 kg (15,707 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 60.14 days. Completed Operations Date: 1991-03-15 18:06:59 . Decay Date: 1991-03-15 18:06:59 . USAF Sat Cat: 21053 . COSPAR: 1991-002A. Apogee: 205 km (127 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Delivered new life support equipment to replace life-expired equipment aboard. Docked with Mir on 16 Jan 1991 16:35:25 GMT. Undocked on 15 Mar 1991 12:46:41 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 15 Mar 1991 18:07:26 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.30 days. Total docked time 57.84 days.
1991 March 19 - . 13:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-7 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 208. Mass: 7,307 kg (16,109 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 49.18 days. Completed Operations Date: 1991-05-07 17:21:50 . Decay Date: 1991-05-07 17:21:50 . USAF Sat Cat: 21188 . COSPAR: 1991-020A. Apogee: 213 km (132 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Attempted to dock with Mir on 21 March 1998 14:28 GMT, but missed the station by 500 m. Docking attempted again on 23 March but at 50 meters the docking was aborted; the Progress missed hitting the station by five meters. Thereafter it was placed in a station-keeping co-orbit with Mir while the problem was diagnosed. Finally docked with Mir on 28 Mar 1991 12:02:28 GMT. On 12 and 14 Apr 1998 two burns of the engine of Progress M-7 raised the station's orbit from a 360 x 377 km orbit to a 370 x 382 km orbit. Undocked on 6 May 1991 22:59:36 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 7 May 1991 17:20:05 GMT. Total free-flight time 9.72 days. Total docked time 39.46 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-11. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1991-020xx.
1991 May 18 - . 12:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-12 - .
Call Sign: Ozon (Ozone ). Crew: Artsebarsky,
Krikalyov,
Sharman.
Backup Crew: Kaleri,
Mace, Timothy,
Volkov, Aleksandr.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 62. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-11,
Soyuz TM-12,
Soyuz TM-12 Juno,
Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 144.64 days. Decay Date: 1991-10-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 21311 . COSPAR: 1991-034A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 389 km (241 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Docked with Mir. Mir Expedition EO-09. Carried Anatoli Artsebarski, Sergei Krikalev, Helen Sharman to Mir; returned Artsebarski, crew of Soyuz TM 8 to Earth. Second commercial flight with paying British passenger. Sponsoring British consortium was not quite able to come up with money, however. Flight continued at Soviet expense with very limited UK experiments.
1991 May 30 - . 08:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-8 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 207. Mass: 7,296 kg (16,084 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-12, Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 77.95 days. Completed Operations Date: 1991-08-16 07:02:29 . Decay Date: 1991-08-16 07:02:29 . USAF Sat Cat: 21395 . COSPAR: 1991-038A. Apogee: 396 km (246 mi). Perigee: 390 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 1 Jun 1991 09:44:37 GMT. Undocked on 15 Aug 1991 22:16:59 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 16 Aug 1991 06:56:32 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.43 days. Total docked time 75.52 days..
1991 August - .
- Soyuz TM-13A (cancelled) - . Crew: Kaleri, Viehboeck, Volkov, Aleksandr. Backup Crew: Avdeyev, Lothaller, Viktorenko. Nation: Russia. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-13A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Soyuz TM-13 and TM-14 crews were reshuffled extensively due to commercial considerations and necessity of flying a Kazakh cosmonaut. This was the original crew assignment. Kaleri and Avdeyev were replaced by Kazakh researchers in the final crew..
1991 August 20 - . 22:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-9 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 210. Mass: 7,311 kg (16,117 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-12,
Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 40.39 days. Completed Operations Date: 1991-10-01 08:24:38 . Decay Date: 1991-10-01 08:24:38 . USAF Sat Cat: 21662 . COSPAR: 1991-057A. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir; carried reentry capsule for return of 150 kg of experiment results. Docked with Mir on 23 Aug 1991 00:54:17 GMT. Undocked on 30 Sep 1991 01:53:00 GMT. 350 kg return capsule detached from the Propess' orbital module at an altitude of 110 to 130 km. The capsule underwent a ballistic descent to 15 km, followed by a parachute descent from there to surface. The capsule's beacon began transmitting at 4.5 km. Landed in Kazakhstan on 30 Sep 1991 08:16:24 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.35 days. Total docked time 38.04 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-12, Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1991-057xx.
1991 October 2 - . 05:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-13 - .
Call Sign: Donbass (Donbass - River Don basin). Crew: Aubakirov,
Viehboeck,
Volkov, Aleksandr.
Backup Crew: Lothaller,
Musabayev,
Viktorenko.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 63. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-12,
Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3,
Soyuz TM-13,
Soyuz TM-13 Austromir.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 175.12 days. Decay Date: 1992-03-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 21735 . COSPAR: 1991-069A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Manned three crew. Docked with Mir. Mir Expedition EO-10. Transported to the Mir manned orbital station an international crew comprising the cosmonauts A Volkov (USSR), T Aubakirov (USSR) and F. Viehbock (Austria), to conduct joint scientific and technical research with the cosmonauts A. Artsebarsky and S Krikalev. Austria paid $ 7 million for mission. Kazakh cosmonaut added at last minute.
1991 October 17 - . 00:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-10 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 211. Mass: 7,306 kg (16,106 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3,
Soyuz TM-13.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 95.50 days. Completed Operations Date: 1992-01-20 12:03:05 . Decay Date: 1992-01-20 12:03:05 . USAF Sat Cat: 21746 . COSPAR: 1991-073A. Apogee: 217 km (134 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. First attempted to dock with Mir on 19 October 1991. The docking was automatically aborted at a distance of 150 m from the station. Successfully docked with the forward port of Mir on on 21 Oct 1991 03:40:50 GMT. Unloading began next day. Undocked on 20 Jan 1992 07:13:44 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 20 Jan 1992 12:03:30 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.35 days. Total docked time 91.15 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3, Soyuz TM-13. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Decay Date: 1992-01-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 21746 . COSPAR: 1991-073xx. Apogee: 378 km (234 mi). Perigee: 376 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.10 min.
1991 End - .
- Soyuz TM-14A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Aubakirov,
Avdeyev,
Viktorenko.
Backup Crew: Musabayev,
Poleshchuk,
Solovyov.
Nation: Russia.
Program: Mir.
Flight: Soyuz TM-14A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Soyuz TM-13 and TM-14 crews were reshuffled extensively due to commercial seat bookings by Austria and Germany and the necessity of flying a Kazakh-born cosmonaut as part of the Baikonur rental agreement. This was the original crew assignment. The Kazakh researchers were moved to the earlier Soyuz TM-13 flight.
1991 December - .
- Soyuz Buran Support (cancelled) - . Crew: Bachurin, Ivanchenkov. Backup Crew: Balandin, Borodai. Nation: Russia. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz Buran Support. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Planned Soyuz flight to Mir. Main purpose was to provide spaceflight experience to Bachurin and Borodai, who had been selected as back-up crew of the first manned Buran flight. Cancelled in cut-backs after fall of the Soviet Union..
1991 End - .
- Soyuz TM-14B (cancelled) - .
Crew: Aleksandrov,
Aubakirov,
Korzun.
Backup Crew: Laveykin,
Musabayev,
Tsibliyev.
Nation: Russia.
Program: Mir.
Flight: Soyuz TM-14B.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Soyuz TM-13 and TM-14 crews were reshuffled extensively due to commercial seat bookings by Austria and Germany and the necessity of flying a Kazakh-born cosmonaut as part of the Baikonur rental agreement. This was the second crew assignment. The Kazakh researchers were moved to the earlier Soyuz TM-13 flight and paying German researchers took their place in the final crew.
1992 January 25 - . 07:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-11 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 212. Mass: 7,320 kg (16,130 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3, Soyuz TM-13. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 48.33 days. Completed Operations Date: 1992-03-13 13:13:31 . Decay Date: 1992-03-13 13:13:31 . USAF Sat Cat: 21851 . COSPAR: 1992-004A. Apogee: 227 km (141 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 27 Jan 1992 09:30:43 GMT. Undocked on 13 Mar 1992 08:43:40 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 13 Mar 1992 15:47:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.36 days. Total docked time 45.97 days..
1992 March 17 - . 10:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-14 - . Call Sign: Vityaz (Knight ). Crew: Flade, Kaleri, Viktorenko. Backup Crew: Avdeyev, Ewald, Solovyov. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 64. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3, Soyuz TM-13, Soyuz TM-14, Soyuz TM-14 Mir 92. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 145.59 days. Decay Date: 1992-08-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 21908 . COSPAR: 1992-014A. Apogee: 394 km (244 mi). Perigee: 373 km (231 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min. Mir Expedition EO-11. Joint flight with Germany. Docked at the Kvant rear port at 12:33 GMT on March 19..
1992 April 19 - . 21:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-12 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 213. Mass: 7,320 kg (16,130 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-14. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 69.11 days. Decay Date: 1992-06-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 21946 . COSPAR: 1992-022A. Apogee: 394 km (244 mi). Perigee: 373 km (231 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 21 Apr 1992 23:21:59 GMT. Undocked on 27 Jun 1992 21:34:44 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 28 Jun 1992 00:02:51 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.18 days. Total docked time 66.93 days..
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-14. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1992-022xx.
1992 June 30 - . 16:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-13 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 214. Mass: 7,320 kg (16,130 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-14.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 23.64 days. Completed Operations Date: 1992-07-24 08:08:22 . Decay Date: 1992-07-24 08:08:22 . USAF Sat Cat: 22004 . COSPAR: 1992-035A. Apogee: 226 km (140 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. An initial docking attempt on 2 Jul 1992 was a failure. Docked with Mir on 4 Jul 1992 16:55:13 GMT. Undocked on 24 Jul 1992 04:14:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 24 Jul 1992 08:03:35 GMT. Total free-flight time 4.17 days. Total docked time 19.47 days. It was docked to Mir for only a few weeks, since on 26 Jul the Soyuz TM-15 was to be launched with a replacement crew and would need to use the same docking port.
1992 July 27 - . 06:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-15 - .
Call Sign: Rodnik (Spring - water spring). Crew: Avdeyev,
Solovyov,
Tognini.
Backup Crew: Haignere,
Manakov,
Poleshchuk.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 65. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-14,
Soyuz TM-15,
Soyuz TM-15 Antares.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 188.90 days. Decay Date: 1993-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22054 . COSPAR: 1992-046A. Apogee: 216 km (134 mi). Perigee: 196 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Mir Expedition EO-12. Russian astronauts Solovyov and Avdeev and French astronaut Tognini were inserted into an initial 190 x 200 km orbit inclined 51.6 deg. Later on July 27 they maneuvered to a 223 x 343 km orbit, and on July 28 docked with Mir in its 405 x 410 km orbit.
1992 August 15 - . 22:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-14 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 209. Mass: 7,176 kg (15,820 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 67.04 days. Completed Operations Date: 1992-10-22 23:12:40 . Decay Date: 1992-10-22 23:12:40 . USAF Sat Cat: 22090 . COSPAR: 1992-055A. Apogee: 221 km (137 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Progress M-38 was specially modified to carry the first VDU (Vynosnaya Dvigatel'naya Ustanovka, External Engine Unit) propulsion unit. The VDU was mounted externally on a special structure between the cargo module and the service module, replacing the OKD fuel section present on normal Progress vehicles. The crew spacewalked to extract the VDU from Progress and place it on the end of the Sofora boom extending from the Kvant module. The VDU was used to provide attitude control capability for the Mir station. Docked with Mir on 18 Aug 1992 00:20:48 GMT. Undocked on 21 Oct 1992 16:46:01 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 21 Oct 1992 23:12:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.35 days. Total docked time 64.68 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-15. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1992-055xx.
1992 October 27 - . 17:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-15 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 215. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 102.56 days. Completed Operations Date: 1993-02-07 06:54:51 . Decay Date: 1993-02-07 06:54:51 . USAF Sat Cat: 22203 . COSPAR: 1992-071A. Apogee: 205 km (127 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 29 Oct 1992 19:05:51 GMT. Undocked on 4 Feb 1993 00:44:53 GMT. After completion of the Znamya and autonomous operation experiments, destroyed in reentry on 7 Feb 1993 06:43:20 GMT. Total free-flight time 5.32 days. Total docked time 97.24 days.
1993 January 24 - . 05:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-16 - .
Call Sign: Vulkan (Volcano ). Crew: Manakov,
Poleshchuk.
Backup Crew: Serebrov,
Tsibliyev.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 101. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-15,
Soyuz TM-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 179.03 days. Decay Date: 1993-07-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 22319 . COSPAR: 1993-005A. Apogee: 394 km (244 mi). Perigee: 393 km (244 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Manned two crew. Mir Expedition EO-13. Transported to the Mir manned orbital station a crew of the thirteenth main expedition comprising the cosmonauts G M Manakov and A F Poleschuk.The Soyuz carried the APAS androgynous docking system instead of the usual probe system.
1993 February 21 - . 18:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-16 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 216. Mass: 7,338 kg (16,177 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 33.65 days. Completed Operations Date: 1993-03-27 10:05:12 . Decay Date: 1993-03-27 10:05:12 . USAF Sat Cat: 22530 . COSPAR: 1993-012A. Apogee: 234 km (145 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 23 Feb 1993 20:17:57 GMT. Undocked on 26 Mar 1993 06:50:00 GMT. Redocked with Mir on 1993-03-26 07:06:03 GMT. Final undocking on 1993-03-27 04:21:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 27 Mar 1993 10:25:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.33 days. Total docked time 31.32 days.
1993 March 31 - . 03:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-17 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 217. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 337.00 days. Completed Operations Date: 1994-03-03 03:29:47 . Decay Date: 1994-03-03 03:29:47 . USAF Sat Cat: 22588 . COSPAR: 1993-019A. Apogee: 365 km (226 mi). Perigee: 362 km (224 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Conducted docked and undocked longevity spacecraft longevity tests. Docked with Mir on 1 Apr 1993 05:16:18 GMT. Undocked on 11 Aug 1993 15:36:42 GMT. Destroyed in reentry over the South Atlantic on 3 Mar 1994 03:28:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 204.56 days. Total docked time 132.43 days.
1993 May 22 - . 06:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-18 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 218. Mass: 7,348 kg (16,199 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 43.44 days. Completed Operations Date: 1993-07-04 17:14:25 . Decay Date: 1993-07-04 17:14:25 . USAF Sat Cat: 22666 . COSPAR: 1993-034A. Apogee: 240 km (140 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Last launch using Soyuz-U2 launch vehicle. Docked with Mir's front port on 24 May 1993 08:24:44 GMT. In addition to other supplies, carried repair equipment for a spacewalk device damaged a month before. Undocked on 3 Jul 1993 15:58:16 GMT, with Soyuz TM-17 docking at the same port only minutes later at 17:45 GMT. Meanwhile, Progress M-17 remained docked to the Kvant rear port on a longevity test. Progress M-18 was destroyed in reentry on 4 Jul 1993 17:13:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 3.12 days. Total docked time 40.31 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-16. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1993-034xx.
1993 July 1 - . 14:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-17 - .
Call Sign: Sirius (Sirius ). Crew: Haignere,
Serebrov,
Tsibliyev.
Backup Crew: Afanasyev,
Andre-Deshays,
Usachyov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 66. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-16,
Soyuz TM-17,
Soyuz TM-17 Altair.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 196.74 days. Decay Date: 1994-02-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 22704 . COSPAR: 1993-043A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 388 km (241 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Mir Expedition EO-14. Carried Vasili Tsibliyev, Alexander Serebrov, Jean-Pierre Haignere to Mir; returned Serebrov, Tsibliyev to Earth. Progress M-18 undocked from Mir's front port at around 17:25 GMT on July 3, and Soyuz TM-17 docked at the same port only 20 minutes later at 17:45 GMT.
1993 August 10 - . 22:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-19 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 219. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-17. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 69.08 days. Completed Operations Date: 1993-10-20 00:17:41 . Decay Date: 1993-10-20 00:17:41 . USAF Sat Cat: 22745 . COSPAR: 1993-052A. Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 179 km (111 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir at the Kvant rear port on 13 Aug 1993 00:00:06 GMT. Undocked on 13 Oct 1993 17:59:06 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 19 Oct 1993 00:22:14 GMT. Total free-flight time 7.33 days. Total docked time 61.75 days..
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-17. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1993-052xx.
1993 October 11 - . 21:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-20 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 220. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-17.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 40.48 days. Decay Date: 1993-11-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 22867 . COSPAR: 1993-064A. Apogee: 226 km (140 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir, carried a Raduga reentry capsule for return of experimental materials to earth. Docked with Mir on 13 Oct 1993 23:24:46 GMT. Undocked on 21 Nov 1993 02:38:43 GMT. Capsule landed in Kazakhstan on 21 Nov 1993 09:06:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.35 days. Total docked time 38.13 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-17. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1993-064xx.
1994 January 8 - . 10:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-18 - . Call Sign: Derbent (Derbent - Russian city). Crew: Afanasyev, Polyakov, Usachyov. Backup Crew: Arzamazov, Malenchenko, Strekalov. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 67. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-17, Soyuz TM-18, Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 182.02 days. Decay Date: 1994-07-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22957 . COSPAR: 1994-001A. Apogee: 335 km (208 mi). Perigee: 244 km (151 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.10 min. Mir Expedition EO-15. Docked at the Kvant module on January 10 at 11:15 GMT. Transported to the Mir orbital station of a crew comprising the cosmonauts V M Afanasev, Y V Usachev, and V V Polyakov for the fifteenth main expedition..
1994 January 28 - . 02:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-21 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 221. Mass: 7,130 kg (15,710 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18, Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 54.13 days. Completed Operations Date: 1994-03-21 05:24:50 . Decay Date: 1994-03-21 05:24:50 . USAF Sat Cat: 22975 . COSPAR: 1994-005A. Apogee: 236 km (146 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 30 Jan 1994 03:56:13 GMT. Undocked on 23 Mar 1994 01:20:29 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 23 Mar 1994 05:13:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.23 days. Total docked time 51.89 days..
1994 March 22 - . 04:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-22 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 222. Mass: 7,103 kg (15,659 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18,
Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 61.99 days. Completed Operations Date: 1994-05-23 04:48:12 . Decay Date: 1994-05-23 04:48:12 . USAF Sat Cat: 23035 . COSPAR: 1994-019A. Apogee: 335 km (208 mi). Perigee: 260 km (160 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Launched into an initial 192 x 238 x 51.6 km orbit. Docked with Mir on 24 Mar 1994 06:39:37 GMT. Fired its engine around 15 May to raise the orbit of the Mir station from 381 x 400 km to 398 x 399 km. Undocked on 23 May 1994 00:58:38 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 23 May 1994 04:40:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.23 days. Total docked time 59.76 days.
1994 May 22 - . 04:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Progress M-23 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 223. Mass: 7,117 kg (15,690 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18,
Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 41.44 days. Decay Date: 1994-07-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 23114 . COSPAR: 1994-031A. Apogee: 399 km (247 mi). Perigee: 397 km (246 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.52 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir, with Raduga return capsule. Docked with Mir on 24 May 1994 06:18:35 GMT. Undocked on 2 Jul 1994 08:46:49 GMT. The braking engine was ignited at 14:44 GMT, and the Raduga VBK reentry capsule was ejected at 14:55:45 GMT. The Progress burnt up in the atmosphere at 14:57 GMT. The Raduga deployed its parachute after reentry and landed on 2 Jul 1994 15:09:00 GMT at 51 deg 41 min N, 59 deg 21 min E, in the Orenburg region. Total free-flight time 2.34 days. Total docked time 39.10 days.
- VBK Raduga - . Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-18, Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. COSPAR: 1994-031xx.
1994 July 1 - . 12:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-19 - . Call Sign: Agat (Agate ). Crew: Malenchenko, Musabayev. Backup Crew: Dezhurov, Strekalov. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 68. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18, Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4, Soyuz TM-19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 125.95 days. Decay Date: 1994-11-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 23139 . COSPAR: 1994-036A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 396 km (246 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.49 min. Mir Expedition EO-16. Soyuz TM-19 docked at the rear port of the Kvant module (vacated by Progress M-23 on July 2) at 13:55:01 GMT on July 3..
1994 August 25 - . 14:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-24 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 224. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4,
Soyuz TM-19.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 40.35 days. Completed Operations Date: 1994-10-04 22:41:48 . Decay Date: 1994-10-04 22:41:48 . USAF Sat Cat: 23215 . COSPAR: 1994-052A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 394 km (244 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.47 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Failed to dock with Mir on 27 Aug 1994. A second automatic docking attempt on 30 Aug 1994 also failed and the Progress collided with the Kvant module. A third and final attempt, manually controlled by Mir commander Yuriy Malenchenko, was successful on 2 Sep 1994 13:30:28 GMT. The Mir commander and flight engineer, Yuriy Malenchenko and Talgat Musabaev, made a spacewalk on 9 Sep 1994 to inspect the damage to the Kvant module made when the Progress collided with Kvant. Undocked on 4 Oct 1994 18:55:52 GMT, leaving the rear docking port free for Soyuz TM-20. Destroyed in reentry over the Pacific at 38.4 deg S, 137.4 deg W,on 4 Oct 1994 22:43:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 8.12 days. Total docked time 32.23 days.
1994 October 3 - . 22:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-20 - .
Call Sign: Vityaz (Knight ). Crew: Kondakova,
Merbold,
Viktorenko.
Backup Crew: Budarin,
Reiter,
Solovyov.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 69. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4,
Soyuz TM-19,
Soyuz TM-20,
Soyuz TM-20 Euromir 94.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 169.22 days. Decay Date: 1995-03-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 23288 . COSPAR: 1994-063A. Apogee: 395 km (245 mi). Perigee: 392 km (243 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.43 min.
Mir Expedition EO-17. Docked at the Mir forward port at 00:28 on 1994 October 6. The Mir crew of Viktorenko, Kondakova and Polyakov boarded Soyuz TM-20 on January 11, and undocked from Mir's front port at 09:00 GMT. The spacecraft withdrew to about two hundred metres from Mir and then redocked in a test of the automatic Kurs system, which had failed in Progress M-24's attempted docking. Redocking came at 09:25 GMT.
1994 November 11 - . 07:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-25 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 225. Mass: 7,125 kg (15,707 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4, Soyuz TM-20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 97.39 days. Decay Date: 1995-02-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 23348 . COSPAR: 1994-075A. Apogee: 394 km (244 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.41 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 13 Nov 1994 09:04:29 GMT. Undocked on 16 Feb 1995 13:03:00 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 16 Feb 1995 16:45:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.23 days. Total docked time 95.17 days..
1995 February 15 - . 16:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-26 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 226. Mass: 7,139 kg (15,738 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4, Soyuz TM-20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 27.56 days. Completed Operations Date: 1995-03-15 06:14:32 . Decay Date: 1995-03-15 06:14:32 . USAF Sat Cat: 23477 . COSPAR: 1995-005A. Apogee: 396 km (246 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 17 Feb 1995 18:21:34 GMT. Undocked on 15 Mar 1995 02:26:38 GMT. Destroyed in reentry over the Pacific Ocean on 15 Mar 1995 06:15:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.22 days. Total docked time 25.34 days..
1995 March 14 - . 06:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-21 - .
Call Sign: Uragan (Hurricane ). Crew: Dezhurov,
Strekalov,
Thagard.
Backup Crew: Avdeyev,
Dunbar,
Gidzenko.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 70. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4,
Soyuz TM-20,
Soyuz TM-21.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 181.03 days. Decay Date: 1995-09-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23519 . COSPAR: 1995-010A. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 392 km (243 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Mir Expedition EO-18. Soyuz TM-21 carried the EO-18 Mir crew and American Norman Thagard. Thagard was the first American to be launched in a Soyuz. Soyuz docked with Mir at 07:45:26 GMT on March 16 . On July 4 Soyuz TM-21 undocked and backed off to a distance of 100 m from Mir. The US space shuttle Atlantis, with the EO-18 crew aboard, then undocked and began a flyaround at a distance of 210 m, while the EO-19 crew aboard Soyuz took pictures before redocking with the station. Soyuz TM-21 again undocked with the EO-19 crew on September 11 from the Kvant rear port on Mir and landed at 50 deg 41'N 68 deg 15'E, 108 km northeast of Arkalyk in Kazakhstan, at 06:52:40 GMT .
1995 April 9 - . 19:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-27 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 227. Mass: 7,170 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-21.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 43.33 days. Completed Operations Date: 1995-05-23 03:27:40 . Decay Date: 1995-05-23 03:27:40 . USAF Sat Cat: 23555 . COSPAR: 1995-020A. Apogee: 399 km (247 mi). Perigee: 396 km (246 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir; carried GFZ-1 German sub-satellite to Mir. Docked with Mir on 11 Apr 1995 21:00:44 GMT. Undocked on 22 May 1995 23:42:37 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 23 May 1995 03:27:52 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.22 days. Total docked time 41.11 days.
1995 July 20 - . 03:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-28 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 228. Mass: 7,125 kg (15,707 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-71 Mir EO-19.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 46.25 days. Completed Operations Date: 1995-09-04 08:58:14 . Decay Date: 1995-09-04 08:58:14 . USAF Sat Cat: 23617 . COSPAR: 1995-036A. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 393 km (244 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir's front port on 22 Jul 1995 04:39:37 GMT. Undocked on 4 Sep 1995 05:09:53 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 4 Sep 1995 08:58:55 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.22 days. Total docked time 44.02 days. Two Icons of Saint Anastasia were taken into space aboard the craft and transferred to the Mir station where they remained for about seven months. They were returned to earth, apparently aboard Soyuz TM-22, and later shown in diffent shrines around the world.
1995 September 3 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U2.
- Soyuz TM-22 - .
Call Sign: Uran (Uranus ). Crew: Avdeyev,
Gidzenko,
Reiter.
Backup Crew: Duque,
Kaleri,
Korzun.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 71. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-22,
STS-71 Mir EO-19.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 179.07 days. Decay Date: 1996-02-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23665 . COSPAR: 1995-047A. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Mir Expedition EO-20. Crew commander was Yuriy Pavlovich Gidzenko of the Russian Air Force. Flight engineer was Sergey Vasilyevich Avdeev of RKK Energiya, and cosmonaut-researcher was Thomas Reiter of the European Space Agency. Soyuz TM-22 docked with Mir's front (-X) port at 10:29:54 GMT on September 5 and the hatch was opened at 11:01:23.
1995 October 8 - . 18:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-29 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 229. Mass: 7,122 kg (15,701 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-22.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 71.89 days. Completed Operations Date: 1995-12-19 16:15:20 . Decay Date: 1995-12-19 16:15:20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23678 . COSPAR: 1995-053A. Apogee: 400 km (240 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Launched into an initial 194 x 242 km x 51.7 deg orbit. Docked with Mir's rear of the Kvant module port on 10 Oct 1995 20:32:40 GMT (Soyuz TM-22 was docked to the front port). Undocked on 19 Dec 1995 09:15:05 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 19 Dec 1995 16:15:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.36 days. Total docked time 69.53 days.
1995 December 18 - . 14:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-30 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 230. Mass: 7,068 kg (15,582 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-22. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 65.85 days. Decay Date: 1996-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 23744 . COSPAR: 1995-070A. Apogee: 409 km (254 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.60 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 20 Dec 1995 16:10:15 GMT. Undocked on 22 Feb 1996 07:30:02 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 22 Feb 1996 11:02:36 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.22 days. Total docked time 63.64 days..
1996 February 21 - . 12:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-23 - . Call Sign: Skif (Roman-age tribe). Crew: Onufrienko, Usachyov. Backup Crew: Lazutkin, Tsibliyev. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 72. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-22, Soyuz TM-23. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 193.80 days. Decay Date: 1996-09-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 23798 . COSPAR: 1996-011A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 375 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.20 min. Mir Expedition EO-21. Soyuz TM-23 docked with Mir at 14:20:35 on February 23..
1996 May 5 - . 07:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-31 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 231. Mass: 7,140 kg (15,740 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-23,
STS-76 Mir NASA-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 88.56 days. Completed Operations Date: 1996-08-01 20:32:45 . Decay Date: 1996-08-01 20:32:45 . USAF Sat Cat: 23860 . COSPAR: 1996-028A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 376 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Delivered 1,140 kg of fuel and 1,700 kg of cargo to the Mir complex. Docked with Mir on 7 May 1996 08:54:19 GMT. Undocked on 1 Aug 1996 16:44:54 GMT. Destroyed in reentry over the Pacific on 1 Aug 1996 20:33:03 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.23 days. Total docked time 86.33 days.
1996 July 31 - . 20:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-32 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 232. Mass: 7,130 kg (15,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-23,
STS-76 Mir NASA-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 96.11 days. Completed Operations Date: 1996-11-04 22:47:04 . Decay Date: 1996-11-04 22:47:04 . USAF Sat Cat: 24071 . COSPAR: 1996-043A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 371 km (230 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. This was the first successful launch of a Soyuz-U after two failures. Docked with Mir at the forward docking port on 2 Aug 1996 22:03:40 GMT. Undocked on 18 Aug 1996 09:33:45 GMT in order to free up the docking port. By 29 August 1994 Mir was in a 375 x 390 km x 51.6 deg orbit; the Progress M-32 cargo ship, flying separately, was in a 375 x 392 km x 51.6 deg orbit. Redocked with Mir on 3 Sep 1996 09:35:00 GMT at the rear port of the Kvant module. Finally undocked from Mir on 20 Nov 1996 19:51:20 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 20 Nov 1996 22:42:25 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.20 days. Total docked time 93.91 days.
1996 August 17 - . 13:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-24 - .
Call Sign: Fregat (Frigate ). Crew: Andre-Deshays,
Kaleri,
Korzun.
Backup Crew: Eyharts,
Lazutkin,
Tsibliyev.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 73. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-23,
Soyuz TM-24,
Soyuz TM-24 Cassiopee,
STS-76 Mir NASA-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 196.73 days. Decay Date: 1997-03-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 24280 . COSPAR: 1996-047A. Apogee: 394 km (244 mi). Perigee: 378 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
Mir Expedition EO-22. Valeriy Korzun and Aleksandr Kaleri of the Russian Space Agency (RKA) Claudie Andre-Deshays of the French space agency CNES. This launch was the first of the Soyuz-U booster with a crew aboard following two launch failures of on unmanned flights. Soyuz docked with Mir's front port at 14:50:21 GMT on August 19; Mir was in a 375 x 390 km x 51.6 deg orbit.
On Feb 7 at 16:28:01 GMT the EO-22 crew and American astronaut Linenger undocked the Soyuz TM-24 ferry from the front docking port, flew it around to the far side of the complex and redocked at the rear Kvant port at 16:51:27 GMT. This cleared the forward port for the arrival of the EO-23 crew, who brought with them German astronaut Reinhold Ewald on Feb 12.
1996 November 19 - . 23:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-33 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 233. Mass: 7,190 kg (15,850 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-24,
STS-79 Mir NASA-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 112.17 days. Completed Operations Date: 1997-03-12 03:22:59 . Decay Date: 1997-03-12 03:22:59 . USAF Sat Cat: 24663 . COSPAR: 1996-066A. Apogee: 387 km (240 mi). Perigee: 361 km (224 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.00 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 22 Nov 1996 01:01:30 GMT. Undocked on 6 Feb 1997 12:13:53 GMT. Thereafter in independent orbital flight in a 377 x 395 km x 51.65 deg orbit. Failed to redock with Mir on 4 Mar 1996. Destroyed in reentry on 12 Mar 1997 03:23:37 GMT. Total free-flight time 35.70 days. Total docked time 76.47 days.
1997 February 10 - . 14:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-25 - . Call Sign: Sirius (Sirius ). Crew: Ewald, Lazutkin, Tsibliyev. Backup Crew: Dezhurov, Padalka, Schlegel. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 74. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-24, Soyuz TM-25, Soyuz TM-25 Mir 97, STS-81 Mir NASA-3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 184.92 days. Decay Date: 1997-08-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 24717 . COSPAR: 1997-003A. Apogee: 392 km (243 mi). Perigee: 385 km (239 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.30 min. Mir Expedition EO-23. Soyuz TM-25 docked with Mir at the forward port on February 12 at 15:51:13 GMT..
1997 April 6 - . 16:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-34 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 234. Mass: 7,156 kg (15,776 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-25,
STS-81 Mir NASA-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 86.60 days. Completed Operations Date: 1997-07-02 06:31:45 . Decay Date: 1997-07-02 06:31:45 . USAF Sat Cat: 24757 . COSPAR: 1997-014A. Apogee: 393 km (244 mi). Perigee: 375 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. It carried supplies for the Mir station and repair equipment for Mir's oxygen generators, replacement oxygen-generating 'candles' and a pair of new spacesuits. Docked with Mir at the rear Kvant module port on 8 Apr 1997 17:30:03 GMT. The Mir complex raised its orbit by 5 km on 15 Apr 1997 at 12:00 GMT, using Progress M-34's engine. Undocked on 24 Jun 1997 10:22:50 GMT. It was then used to perform a redocking test using newly developed remote-control procedures which were to replace the automatic system that Russia could no longer afford to buy from Ukraine. At 25 Jun 1997 09:18 GMT Mir commander Tsibliev was remotely commanding the approach of Progress to the Kvant module. This involved guiding the Progress via a television monitor. The Progress was difficult to see against the cloudy earth background at the time of the attempted docking. It went off course and collided with a solar array on the Spektr module and then the module itself. A large hole was made in a solar panel, one of the radiators was buckled, a hole was punched into Spektr's hull, and the module began to depressurize. This was not a slow leak - the crew heard a hissing sound and felt their ears pop. They disconnected the power cables leading from Mir to the main station and closed the hatch on the core module transfer section that led to Spektr. The Spektr module became fully depressurized, remaining docked to Mir with its docking hatch open. The loss of electrical connection between Spektr's solar panels and the main station cut the available power supply to the station, crippling its operations until later repairs reconnected the electrical lines. Tsibliev was also the pilot on a previous orbital collision, when he banged Soyuz TM-17 into Mir in Jan 1994. After the return of the crew to earth he was found to be to blame for the incident, although the fines assessed were later dismissed. The Progress M-34 cargo ship was backed to a safe distance from the station and was destroyed in reentry on 2 Jul 1997 06:31:50 GMT. Total free-flight time 9.90 days. Total docked time 76.70 days.
1997 July 5 - . 04:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-35 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 235. Mass: 7,150 kg (15,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-25,
STS-84 Mir NASA-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 82.50 days. Decay Date: 1997-10-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 24851 . COSPAR: 1997-033A. Apogee: 391 km (242 mi). Perigee: 383 km (237 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 7 Jul 1997 05:59:24 GMT. Undocked on 6 Aug 1997 11:46:45 GMT. Redocked with Mir on 18 Aug 1997 12:52:48 GMT. Final undocking on 7 Oct 1997 12:03:49 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 7 Oct 1997 17:23:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.30 days. Total docked time 80.21 days.
1997 August 5 - . 15:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-26 - . Call Sign: Rodnik. Crew: Solovyov, Vinogradov. Backup Crew: Avdeyev, Padalka. Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 75. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-25, Soyuz TM-26, STS-84 Mir NASA-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TM. Duration: 197.73 days. Decay Date: 1998-02-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 24886 . COSPAR: 1997-038A. Apogee: 385 km (239 mi). Perigee: 378 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.20 min. Mir Expedition EO-24. The Soyuz docked manually at 17:02 GMT August 7. Over the next six months the crew undertook seven internal and external spacewalks to repair the crippled space station..
1997 October 5 - . 15:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-36 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 237. Mass: 7,195 kg (15,862 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-26, STS-84 Mir NASA-4, STS-86, STS-86 Mir NASA-5. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 74.92 days. Decay Date: 1997-12-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 25002 . COSPAR: 1997-058A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 378 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.20 min. Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir on 8 Oct 1997 17:07:09 GMT. Undocked on 17 Dec 1997 06:01:53 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 19 Dec 1997 13:20:01 GMT. Total free-flight time 5.39 days. Total docked time 69.54 days..
1997 December 20 - . 08:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-37 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 236. Mass: 7,040 kg (15,520 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-26,
STS-86 Mir NASA-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 61.69 days. Decay Date: 1998-03-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 25102 . COSPAR: 1997-081A. Apogee: 403 km (250 mi). Perigee: 363 km (225 mi). Inclination: 51.80 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
Unmanned resupply vessel to Mir. Docked with Mir at the rear Kvant port on 22 Dec 1997 10:22:20 GMT. Undocked on 30 Jan 1998 12:00:00 GMT. Redocked with Mir on 23 Feb 1998 09:42:28 GMT. Final undocking 15 Mar 1998 19:16:01 GMT. Destroyed in reentry on 15 Mar 1998 23:04:00 GMT. Total free-flight time 2.23 days. Total docked time 59.47 days.
1998 January 29 - . 16:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-27 - .
Call Sign: Kristall. Crew: Budarin,
Eyharts,
Musabayev.
Backup Crew: Afanasyev,
Haignere,
Treshchev.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 76. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-26,
Soyuz TM-27,
Soyuz TM-27 Mir Pegase,
STS-86 Mir NASA-5,
STS-89,
STS-89 Mir NASA-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 207.53 days. Decay Date: 1998-08-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 25146 . COSPAR: 1998-004A. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 363 km (225 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
Soyuz TM-27 carried the Mir EO-25 crew and French astronaut Leopold Eyharts. NASA and the Russian Space Agency had hoped Soyuz TM-27 could dock with Mir while Endeavour was still there, resulting in an on-board crew of 13, a record which would have stood for years or decades. But the French vetoed this, saying the commotion and time wasted would ruin Eyharts Pegase experimental programme. Soyuz TM-27 docked at the Kvant module port at 17:54 GMT on January 31, 1998, less than five hours before Endeavour landed in Florida.
Solovyov handed over command of Mir to EO-25 commander Musabayev, and the Mir EO-24 crew and Eyharts undocked from the forward port of Mir at 05:52 GMT on February 19 aboard the Soyuz TM-26 for their return home. On February 20, the EO-25 crew and Andy Thomas of the NASA-7 mission boarded Soyuz TM-27 and undocked from the Kvant port at 08:48 GMT. They redocked with the forward port on Mir at 09:32 GMT. This freed up the Kvant port for a test redocking of the Progress M-37 cargo ship, parked in a following orbit with Mir during the crew transfer.
1998 March 14 - . 22:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-38 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 240. Mass: 7,007 kg (15,447 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-27,
STS-89 Mir NASA-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 61.05 days. Decay Date: 1998-05-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 25256 . COSPAR: 1998-015A. Apogee: 379 km (235 mi). Perigee: 372 km (231 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.10 min.
Progress M-38 was specially modified to carry the second VDU (Vynosnaya Dvigatel'naya Ustanovka, External Engine Unit) propulsion unit. The VDU was mounted externally on a special structure between the cargo module and the service module, replacing the OKD fuel section present on normal Progress vehicles. The crew spacewalks to extract the VDU from Progress and place it on the end of the Sofora boom extending from the Kvant module. The VDU was used to provide attitude control capability for the station. By 03:20 GMT on March 15 1998 Progress M-38 had successfully completed its first two orbital manoeuvres. It replaced Progress M-37 at the docking port on the Kvant module, with a successful docking on March 16 1998 at 22:45 GMT. Undocked May 15 at 1844 UTC, freeing up the docking port on the Kvant module for Progress M-39. Deorbited over Pacific May 15, 1998.
1998 May 14 - . 22:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-39 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 238. Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-27, STS-89 Mir NASA-6. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 167.08 days. Decay Date: 1998-10-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 25340 . COSPAR: 1998-031A. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 360 km (220 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.90 min. Docked with Mir at the Kvant port at 23:51 GMT on May 16 1998, bringing supplies and scientific experiments to the station. Undocked 09:28 GMT on August 12 1998 in order to clear the port for Soyuz TM-28. Deorbited over Pacific Ocean on October 29, 1998..
1998 August 13 - . 09:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-28 - .
Call Sign: Altair. Crew: Avdeyev,
Baturin,
Padalka.
Backup Crew: Kaleri,
Zalyotin.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 77. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-27,
Soyuz TM-28,
Soyuz TM-28 Mir EO-26/-27,
Soyuz TM-28 Mir EP-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 198.69 days. Decay Date: 1999-02-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 25429 . COSPAR: 1998-047A. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 363 km (225 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
Soyuz TM-28 docked at 10:56 GMT on August 15 with the rear (Kvant) port of the Mir space station, which had been vacated at 09:28 GMT on August 12 by Progress M-39. The EO-25 crew, Musabayev and Budarin, landed with Baturin on Aug 25, leaving the EO-26 crew of Padalka and Avdeyev on the station. As only one final Soyuz mission to Mir was planned, with two of the seats on that Soyuz pre-sold to Slovak and French experimenters, the return crew of Soyuz TM-28 was subject to constant replanning and revision. On February 8, 1999, at 11:23 GMT Padalka and Avdeyev undocked from Mir's -X port in Soyuz TM-28, and redocked at the +X Kvant port at 11:39 GMT, freeing up the front port for the Soyuz TM-29 docking. Finally on February 27, 1999 EO-26 commander Padalka and Slovak cosmonaut Bella undocked Soyuz TM-28 from the Kvant rear docking port at 22:52 GMT, landing in Kazakhstan on February 28 at 02:14 GMT. Avdeyev remained on Mir with the EO-27 crew delivered on Soyuz TM-29, heading for a manned space flight time record.
1998 October 25 - . 04:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-40 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 239. Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-28,
Soyuz TM-28 Mir EO-26/-27.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 103.25 days. Decay Date: 1999-02-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 25512 . COSPAR: 1998-062A. Apogee: 360 km (220 mi). Perigee: 349 km (216 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.63 min.
Docked with the rear (+X, Kvant) docking port of the Mir station on October 27. Delivered fuel, dry cargo, and the Znamya-2.5 solar illumination experiment. This was a follow-on to the earlier Znamya-2 experiment on Progress M-15 in 1992. The 25 m diameter Znamya reflector, which would unfold from the nose of the Progress, was to reflect sunlight over a 6 km area onto selected cities. Znamya-2.5 was developed by the Space Regatta Consortium, led by RKK Energia. Energia had long studied such space mirrors as a means of providing lighting to Siberian towns. The project was opposed by environmentalists and astronomers, who feared light pollution. Progress M-40 undocked on February 4, 1999 at 09:59 GMT, but the attempted deployment of the Znamya-2.5 reflector was thwarted when it snagged on a rendezvous system antenna. After two more failed attempts to deploy the antenna the experiment was abandoned. Progress M-40 fired its engines at 10:16 GMT on February 5, braked out of orbit, and burned up over the Pacific Ocean.
1999 February 20 - . 04:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-29 - .
Call Sign: Derbent. Crew: Afanasyev,
Bella,
Haignere.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 78. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev,
Bella,
Haignere.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-28,
Soyuz TM-28 Mir EO-26/-27,
Soyuz TM-29,
Soyuz TM-29 Mir Stefanik.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 188.85 days. Decay Date: 1999-08-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 25632 . COSPAR: 1999-007A. Apogee: 357 km (221 mi). Perigee: 341 km (211 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.52 min.
Soyuz TM-29 docked with Mir on February 22 at 05:36 GMT. Since two crew seats had been sold (to Slovakia and France), Afansyev was the only Russian cosmonaut aboard. This meant that Russian engineer Avdeyev already aboard Mir would have to accept a double-length assignment. After the February 27 departure of EO-26 crew commander Padalka and Slovak cosmonaut Bella aboard Soyuz TM-28, the new EO-27 Mir crew consisted of Afanasyev as Commander, Avdeyev as Engineer and French cosmonaut Haignere. Follwoing an extended mission and three space walks, the last operational crew aboard Mir prepared to return. The station was powered down and prepared for free drift mode.
1999 April 2 - . 11:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-41 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 241. Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-28 Mir EO-26/-27,
Soyuz TM-29.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 105.99 days. Decay Date: 1999-07-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 25664 . COSPAR: 1999-015A. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.51 min.
Resupply craft docked uneventfully with the Mir complex two days later. It also delivered the Sputnik-99 amateur radio satellite, launched into orbit by hand by the cosmonauts during an EVA on April 16. Still hopeful of finding a backer to pay to keep Mir in space, Progress M-41 began a series of engine burns in late April to raise the orbit of the station. It finally undocked from Mir at 11:20 GMT on July 17 and was deorbited over the Pacific later the same day.
1999 July 16 - . 16:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-42 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 242. Mass: 7,450 kg (16,420 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-28 Mir EO-26/-27,
Soyuz TM-29.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 200.57 days. Decay Date: 2000-02-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 25858 . COSPAR: 1999-038A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 340 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.42 min.
Delivered supplies to the crew of the Mir complex. Docked with the Kvant port at 17:53 GMT on July 18. Remained docked to the station after the departure of the last operational crew in September 1999. Undocked on February 2. 2000, to clear the port for Progress M1, at 0311:52 GMT. Deorbited over the Pacific later the same day at 0610:40 UTC with an 8 minute burn.
2000 February 1 - . 06:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-1 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 250. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 85.53 days. Decay Date: 2000-04-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 26067 . COSPAR: 2000-005A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 342 km (212 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.44 min.
Progress M1 was a modification of the Progress M for the International Space Station. The first such spacecraft was diverted to raise the orbit of Mir. It docked with the unoccupied Mir space station on February 3 at 0802:20 GMT. Burns of its motor to raise Mir's orbit began on February 5 and continued through February 9. Progress M1-1 undocked at 16:33 GMT on April 26 to clear the docking port for Progress M1-2. It was deorbited over the Pacific at 19:27 GMT the same day.
2000 April 4 - . 05:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-30 - .
Call Sign: Yenisey. Crew: Kaleri,
Zalyotin.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 204. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kaleri,
Zalyotin.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-30.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 72.82 days. Decay Date: 2000-06-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 26116 . COSPAR: 2000-018A. Apogee: 384 km (238 mi). Perigee: 358 km (222 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.97 min.
Soyuz TM-30 docked with Mir's forward (-X) port on April 6 at 0631 GMT. Zalyotin and Kaleri reactivated the uninhabited station. Unloading Progress M1-1 and M1-2, they resupplied the station. The Progress spacecraft were also used to raise the station's orbit to 360 x 378 km x 51.6 deg. The orbital plane of Mir was then around 120 degrees away from that of ISS (making transport between the stations impossible, as desired by NASA).
2000 April 25 - . 20:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-2 - . Payload: Progress M1 s/n 252. Mass: 7,280 kg (16,040 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-30. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M1. Duration: 173.00 days. Decay Date: 2000-10-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 26301 . COSPAR: 2000-021A. Apogee: 380 km (230 mi). Perigee: 363 km (225 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.98 min. Progress M1-2 docked with the rear Kvant port of Mir at 2128 GMT on April 27. Mir's orbit was raised on April 29 in the first of a series of three burns by Progress M1-2. It later undocked and was deorbited over the Pacific on 15 October..
2000 August 6 - . 18:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-3 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 251. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-106.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 86.53 days. Decay Date: 2000-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 26461 . COSPAR: 2000-044A. Apogee: 362 km (224 mi). Perigee: 347 km (215 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 91.63 min.
Progress M1-3 automatically docked with the International Space Station on August 8 at 20:13 GMT at the rear Zvezda port. The supply ship began refuelling of the station a few days later. It remained attached for offloading of its dry cargo by the STS-106 crew. It later separated from Zvezda's rear port at 0405 GMT November 1 and was deorbited over the Pacific at 0705 GMT.
2000 October 16 - . 21:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-43 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 243. Mass: 6,860 kg (15,120 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 101.00 days. Decay Date: 2001-01-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 26570 . COSPAR: 2000-064A. Apogee: 228 km (141 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.64 min.
Mir Servicing flight. Launch delayed from October 15. Progress docked with Mir, primarily to raise its orbit and preserve the option of a MirCorp-financed flight in 2001. However the funding never came through and the decision was taken to deorbit Mir. Progress M-43 undocked at 0519 GMT on January 25 from the +X Kvant port to clear it for Progress M1-5 (which would deorbit the Mir station). On January 29 Progress M-43 was in a 271 x 280 km x 51.6 deg orbit.
2000 October 31 - . 07:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-31 - .
Call Sign: Uran. Crew: Gidzenko,
Krikalyov,
Shepherd.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 205. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gidzenko,
Krikalyov,
Shepherd.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-31.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 186.91 days. Decay Date: 2001-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 26603 . COSPAR: 2000-070A. Apogee: 385 km (239 mi). Perigee: 378 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 92.18 min.
Soyuz TM-31 delivered the Expedition One crew to the International Space Station with Gidzenko as the Soyuz crew commander with the call-sign 'Uran'. The spacecraft docked at Zvezda's rear port at 0921 GMT on November 2. The hatch to Zvezda was opened at 1023 GMT. Once aboard ISS, Shepherd became the ISS Commander, with 'Station Alpha' as the ISS callsign. Soyuz TM-31, with Shepherd, Gidzenko and Krikalyov aboard, undocked from the -Y port on Zvezda on February 24, 2001 at 1006 GMT and redocked with the -Z port on Zarya at 1037 GMT. This freed the Zvezda port for a Progress resupply ship. After the departure of the Progress, Soyuz TM-31 undocked from the Zarya nadir port April 18 2001 at 1240 GMT and redocked with the Zvezda aft port at 1301 GMT, leaving clearance for the Raffaello MPLM module to be berthed at the Unity nadir during the STS-100 mission.
2000 November 16 - . 00:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-4 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 253. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-31.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 84.58 days. Decay Date: 2001-02-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 26615 . COSPAR: 2000-073A. Apogee: 363 km (225 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.70 min.
Progress M1-4 was an unmanned resupply craft that rendezvoused with the International Space Station on November 18. After problems with the automatic system, ISS Expedition 1 crew member Gidzenko took over manual control with the remote TORU system at 0302 GMT. The first docking attempt was aborted when M1-4 was only 5 m from the station at 0309 GMT. On the second attempt docking was successfully achieved at 0348 GMT at Zarya's nadir port. The problem on the first attempt was icing of the TORU system TV camera on the Progress when the spacecraft was in shadow. Progress M1-4 undocked from ISS at 1623 GMT on December 1. Following the mission of STS-97 Progress M1-4 redocked to Zarya's nadir port on December 26 at 1054 GMT. The redocking tested a fix to the software that caused problems in the vehicle's first docking attempt on November 18. Yuri Gidzenko completed the docking manually using the remote control TORU system. Progress M1-4 undocked from Zarya's nadir port for the last time at 1126 GMT on February 8. It was deorbited over the Pacific and reentered at 1350 GMT the same day.
2001 January 24 - . 04:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-5 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 254. Mass: 7,300 kg (16,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 58.00 days. Decay Date: 2001-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 26688 . COSPAR: 2001-003A. Apogee: 215 km (133 mi). Perigee: 151 km (93 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.20 min.
Mir Deorbiting mission. Launch delayed from January 16 and 18. The Mir station had a power failure on January 18, delaying the launch of the Progress cargo ship that was to deorbit it for a few days. Nick-named "Hearse", it was to deliver the 130 tonne Mir station to its cremation over the southern Pacific. Six cosmonauts were on "Hot-Standby" to reach Mir in the event the automatic docking failed. Progress M1-5 carried 2677 kg of fuel. A special three-day fuel-economy approach was be used to keep as much fuel as possibile for the deorbit. Progress M1-5 docked with the +X Kvant port at 0533 GMT on January 27. It later undocked and was deorbited over the Pacific together with Mir on 23 March.
2001 February 26 - . 08:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-44 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 244. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-31.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 49.22 days. Decay Date: 2001-04-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 26713 . COSPAR: 2001-008A. Apogee: 393 km (244 mi). Perigee: 376 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
ISS Servicing flight. Launch delayed from February10/20. Progress M-44 was a Russian, automatic cargo carrier that carried 2.5 tonnes of food, water, fuel, oxygen, and equipment to the International Space Station. In preparation for the docking, the ISS crew repositioned the Soyuz TM-31 escape craft from its port on Zvezda to a port on the Zarya module. Progress M-44 docked with the -Y port on Zvezda at 09:47 UT on 28 February. It undocked from Zvezda's aft port on April 16 at 0848 GMT and was deorbited at 1323 GMT over the Pacific Ocean.
2001 April 28 - . 07:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-32 - .
Call Sign: Kristall. Crew: Baturin,
Musabayev,
Tito.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 206. Mass: 6,750 kg (14,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Baturin,
Musabayev,
Tito.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-32 ISS EP-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 185.89 days. Decay Date: 2001-10-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 26749 . COSPAR: 2001-017A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 385 km (239 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Soyuz TM-32 was designated ISS flight 2S by NASA and EP-1 (Visiting Crew 1) by RKK Energia. Soyuz TM-32 was a fresh lifeboat for the station; the Soyuz TM-31 crew themselves would return in Soyuz TM-31, which was at the end of its rated in-space storage tie. Dennis Tito's inclusion in the crew created controversy between NASA and the Russians since he was the first space tourist to fly to ISS. He had originally paid to fly to the Mir station but funds ran out to keep that station in orbit. Soyuz TM-32 docked with the -Z port on Zarya at 0758 GMT on April 30 after Endeavour had departed.. The crew transferred their customized reentry seat liners to Soyuz TM-31, at which point TM-32 became the Station's rescue vehicle. After a six day stay, the Soyuz TM-32 crew returned to earth aboard Soyuz TM-31. The Expedition 3 crew entered Soyuz TM-32) on October 19, 2001 and undocked from the nadir port of Zarya at 1048 GMT, flying it out and then sideways a few meters before approaching the station again to dock with the Pirs nadir port at 1104 GMT. This freed up Zarya for the arrival of a new Soyuz. The docking port at the aft end of Zvezda was occupied by the Progress M-45 cargo ship.
2001 May 20 - . 22:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Progress M1-6 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 255. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-102 ISS EO-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 93.44 days. Decay Date: 2001-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 26773 . COSPAR: 2001-021A. Apogee: 402 km (249 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
ISS Servicing flight. Launch delayed from april 12. This Progress resupply mission to the ISS was launched by the first Soyuz-FG rocket - a modified Soyuz-U with 5 percent improved perfomance using new fuel utilisation systems. Progress M1-6 after launch was also designated as ISS supply mission 4P. It carried 2.5 tonnes of food, fuel, water, life-support material, and equipment, including spare computer equipment for the ISS Destiny module. Nearly one tonne of the fuel was for raising the altitude of the ISS. Progress M1-6 docked with Zvezda's aft (-Y) port at 0024 GMT on May 23. It undocked at 0601 GMT on August 22 and deorbited at around 0900 GMT the same day.
2001 August 21 - . 09:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-45 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 245. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-105 ISS EO-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 93.50 days. Decay Date: 2001-11-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 26890 . COSPAR: 2001-036A. Apogee: 389 km (241 mi). Perigee: 376 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
ISS Servicing Mission. Launch delayed from July 4 and 24. Progress M-45, 7K-TGM No. 245 (of the older generation series of Progress) docked with the ISS at 0951 GMT on August 23 at the aft Zvezda port vacated by Progress M6-1 a day earlier. It and delivered 2.5 tonnes of fuel, water, oxygen, equipment and spare parts. Progress M-45 undocked on November 22 and was deorbited over the Pacific later the same day.
2001 September 14 - . 23:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-SO1 - .
Payload: Progress M-SO1 s/n 301. Mass: 6,900 kg (15,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-105 ISS EO-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M-SO.
Duration: 12.00 days. Decay Date: 2001-09-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 26908 . COSPAR: 2001-041A. Apogee: 335 km (208 mi). Perigee: 329 km (204 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Progress M-SO1 was the designation given to the service module section of a Progress M; the 3900 kg Pirs docking and airlock module for the ISS replaced the standard cargo and fuel sections. It also carried an astronaut chair, a space suit, a small crane, and some equipment for the Zvezda module of the ISS. Progress-M No. 301 was launched into an initial 180 km circular orbit. By September 16 it had maneuvered into a 238 x 264 km orbit; by 0038 GMT on September 17, a 385 x 395 km x 51.6 deg orbit upon rendezvous with the ISS. The Progress began a fly around of the station and lined up with the nadir port on Zvezda. Docking of Pirs with Zvezda came at 0105 GMT on September 17. The Progress M-SO1 later undocked from the Pirs nadir port to leave it free for future dockings. Pirs gave extra clearance from the Station for ships docking underneath Zvezda, and was also used as an airlock for spacewalks using the Russian Orlan EVA suits. Progress M-SO1 service module undocked from the Pirs module at 1536 GMT on September 26 and was deorbited over the Pacific at 2330 GMT the same day.
2001 October 21 - . 08:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-33 - .
Call Sign: Derbent. Crew: Afanasyev,
Andre-Deshays,
Kozeyev.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 207. Mass: 6,750 kg (14,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev,
Andre-Deshays,
Kozeyev.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-33 ISS EP-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 195.79 days. Decay Date: 2002-05-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 26955 . COSPAR: 2001-048A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 386 km (239 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Soyuz TM-33, an ISS lifeboat, carried two Russian and one French cosmonaut to the International Space Station (ISS). It docked with the ISS at 10:00 UT on 23 October. This new crew spent eight days on the ISS, and returned on the older Soyuz TM-32 at 03:59 UT on 31 October. The new Soyuz was to remain docked as a lifeboat craft for the long-term ISS crew of three (two Russian and one American) astronauts. On May 5, 2002, after a week aboard the station, the visting Soyuz TM-34 crew moved to the old Soyuz TM-33, docked at the Pirs port. They undocked at 0031:08 UTC on May 5, leaving the EO-4 crew of Onufrienko, Walz and Bursch with the new Soyuz TM-34 as their rescue vehicle. Soyuz TM-33 made its deorbit burn at 0257 UTC and landed successfully at 0352 UTC 25 km SE of Arkalyk.
2001 November 26 - . 18:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Progress M1-7 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 256. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-105 ISS EO-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 113.29 days. Decay Date: 2002-03-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 26983 . COSPAR: 2001-051A. Apogee: 392 km (243 mi). Perigee: 384 km (238 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
ISS Servicing flight. Launch delayed from November 14. The Progress M1-7 Russian automatic cargo carrier soft docked with the International Space Station Zvezda module at 1943 GMT on Nov 28. The docking probe retracted, but the eight peripheral latches would not engage. It turned out that a rubber seal had been left on the docking ring by Progress M-45. Cosmonauts from aboard the station cleared the debris in a spacewalk on December 3. As they watched from a few meters away Progress M1-7 was commanded to a hard dock with the station. NASA referred to this flight as `Progress 6'. It delivered 2.5 tonnes of food, fuel and equipment to the station, as well as a microsatellite named Kolibri. The Expedition 4 crew finished loading trash into Progress M1-7 on 19 March 2002, and it undocked from Zvezda's aft port at 1743 UTC. The Kolibri-2000 microsatellite was ejected from the Progress cargo compartment at 2228 UTC; Progress fired its engines to deorbit over the Pacific at about 0127 UTC on Mar 20.
2002 March 21 - . 20:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-8 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 257. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-108 ISS EO-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 95.67 days. Decay Date: 2002-06-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 27395 . COSPAR: 2002-013A. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 379 km (235 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
ISS Servicing mission. Launch delayed from February 15 and 28. The Progress M1-8 resupply spacecraft was flown on ISS mission 7P. It docked with the Zvezda module on the Station at 2058 UTC on March 24. Progress M1-8 undocked from the Zvezda module at 0826 UTC on June 25. The deorbit burn was at 1135 UTC, lowering its orbit from 379 x 398 km x 51.6 deg to 50 x 398 km. The spacecraft reentered over the Pacific at 1213 UTC with debris impact near 46 S 144 W.
2002 April 25 - . 06:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Soyuz TM-34 - .
Call Sign: Uran. Crew: Gidzenko,
Shuttleworth,
Vittori.
Payload: Soyuz TM s/n 208. Mass: 6,750 kg (14,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Gidzenko,
Shuttleworth,
Vittori.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TM-34 ISS EP-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TM.
Duration: 198.73 days. Decay Date: 2002-11-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 27416 . COSPAR: 2002-020A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 387 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Launch delayed from April 10, 22 and 17. Soyuz TM-34 was launched on ISS Mission 4S with Commander Yuri Gidzenko of Rosaviakosmos, Flight Engineer is Roberto Vittori of ESA, and Tourist Mark Shuttleworth, a South African citizen. At 1210 UTC Soyuz TM-34 was in a 242 x 269 km x 51.6 deg orbit. The flight was also referred to as ISS Mission 4S, the EP-3 visiting crew flight, and even as 'Soyuz 4' by NASA. Soyuz TM-34 docked with the nadir port on the Zarya module at 0755 UTC on April 27. The 4S flight docked at the Zarya nadir port on April 27. and the crew would return to Earth in the old TM-33 vehicle, leaving TM-34 as the active ISS rescue vehicle.
2002 June 26 - . 05:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-46 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 246. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-111 ISS EO-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 110.00 days. Decay Date: 2002-10-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 27454 . COSPAR: 2002-033A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 387 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Launch delayed from May 21, then moved forward from July 14. Progress M-46 was launched on ISS mission 8P and docked with the Zvezda module at 0623 UTC on June 29 after carrying out tests of the Kurs rendezvous system on June 28. Seperated from ISS and commanded to destructive re-entry on 14 October 2002.
2002 September 25 - . 16:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Progress M1-9 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 258. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-111 ISS EO-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 129.00 days. Decay Date: 2003-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 27531 . COSPAR: 2002-045A. Apogee: 324 km (201 mi). Perigee: 282 km (175 mi). Inclination: 51.63 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Launch delayed from July 22, September 10 and 20. Progress-M1 9, known to NASA as Progress 9P, was a Russian automatic cargo transportation craft that was to deliver food, fuel, and supplies to the International Space Station (ISS). It docked with the Zvezda module of the ISS on September 29 at 1700 UTC. Prior to the docking, the port was vacated by the earlier Progress-M 46. Undocked from the station on 1 February 2003 and commanded to destructive re-entry in the atmosphere.
2002 October 30 - . 03:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-1 - .
Call Sign: Yenisey. Crew: De Winne,
Lonchakov,
Zalyotin.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 211. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: De Winne,
Lonchakov,
Zalyotin.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-1 ISS EP-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 185.96 days. Decay Date: 2003-05-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 27552 . COSPAR: 2002-050A. Apogee: 295 km (183 mi). Perigee: 278 km (172 mi). Inclination: 51.62 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
Launch delayed from October 22, 28 pending investigation of causes of failure of another Soyuz booster on 15 October. Soyuz-TMA 1 was a Russian automatic passenger craft. It carried the EP-4 visiting crew of three astronauts (two Russians and one Belgian) to automatically dock with the International Space Station (ISS). This was the first flight of the new Soyuz-TMA model. It was to remain parked at the ISS as the escape craft, relieving the Soyuz TM-34. The crew conducted several microgravity experiments on the ISS during their 10-day stay before returning in Soyuz TM-34.
2003 February 2 - . 12:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-47 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 247. Mass: 7,290 kg (16,070 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: STS-113 ISS EO-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 206.00 days. Decay Date: 2003-08-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 27681 . COSPAR: 2003-006A. Apogee: 247 km (154 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 88.77 min.
Launch delayed from original schedule of January 30, and was made just one day after the Columbia disaster resulted in a suspension of shuttle flights. Docked successfully with the ISS on 14:49 GMT on 4 February 2003. Undocked from Zvezda on August 27 and deorbited later the same day.
2003 April 18 - .
- Soyuz TMA-2A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Duque,
Kotov,
Padalka.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Duque,
Kotov,
Padalka.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Soyuz TMA-2 was originally to switch lifeboats on the International Space Station. The crew would have returned to earth in the Soyuz TMA-1 already docked to the station. After the loss of Columbia, and the grounding of the remaining shuttles, it was decided instead that the EO-6 crew (Bowersox, Budarin, and Pettit) aboard the station would return in Soyuz TMA-1. Soyuz TMA-2 would be instead flown by a two-man skeleton crew (Malenchenko and Lu) to keep the station alive until shuttle flights could resume.
2003 April 26 - . 03:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-2 - . Call Sign: Agat. Crew: Lu, Malenchenko. Backup Crew: Foale, Kaleri. Return Crew: Duque, Lu, Malenchenko. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 212. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-2. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 184.95 days. Decay Date: 2003-10-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 27781 . COSPAR: 2003-016A. Apogee: 394 km (244 mi). Perigee: 386 km (239 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min. Two-man Russian/American crew to provide minimal manning of space station while shuttle is grounded. Replaced three-man crew aboard ISS since before STS-107 disaster..
2003 June 8 - . 10:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-10 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 259. Mass: 7,270 kg (16,020 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 117.06 days. Decay Date: 2003-10-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 27823 . COSPAR: 2003-025A. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 247 km (153 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
Resupply of International Space Station. Additional water carried to meet needs of skeleton crew. Successfully docked with the nadir port on Pirs at 1115 GMT on June 11. It undocked from the station on September 4 to clear the port for Soyuz TMA-3 but then unusually spent a month on an autonomous earth observation mission. The deorbit engine ignited at 11:26 GMT on October 3 from a 247 x 340 km x 51.6 deg orbit, reducing the perigee to 69 km. Progress M1-10 reentered the atmosphere over the Pacific at 11:58 GMT and broke up around 12:05 GMT.
2003 August 29 - . 01:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-48 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 248. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 152.00 days. Decay Date: 2004-01-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 27873 . COSPAR: 2003-039A. Apogee: 383 km (237 mi). Perigee: 376 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.10 min.
Delayed from July 30, moved up from September 18 and August 30. Docked with the Zvezda module of the ISS on August 31. Undocked from the station at 08:36 GMT on 28 January 2004 after being filled with trash and unneeded equipment. Deorbited and reentered over the Pacific at 13:46 GMT.
2003 October 18 - . 05:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-3 - .
Call Sign: Ingul. Crew: Duque,
Foale,
Kaleri.
Return Crew: Foale,
Kaleri,
Kuipers.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 213. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Duque,
Foale,
Kaleri,
Kuipers.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-2,
Soyuz TMA-3,
Soyuz TMA-3 Cervantes.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 194.77 days. Decay Date: 2004-04-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 28052 . COSPAR: 2003-047A. Apogee: 384 km (238 mi). Perigee: 376 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
The spacecraft carried the Expedition 8 crew of Mike Foale and Aleksandr Kaleri and the EP-5 (Cervantes) mission crewmember Pedro Duque. During the flight to the station spacecraft Commander was Aleksandr Kaleri . Soyuz TMA-3 docked with the Pirs module at 07:16 GMT on October 20. Once the EO-7 crew aboard the ISS was relieved, the roles switched, with Foale becoming the ISS Commander. Duque carried out out 24 experiments in the fields of life and physical sciences, Earth observation, education and technology. The experiments were sponsored by the European Space Agency and Spain. After ten days in space, Duque returned to earth with the EO-7 crew of Malenchenko and Lu aboard Soyuz TMA-2.
2003 November 12 - .
- Soyuz TMA-3A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Dezhurov,
Kuipers,
Skripochka.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dezhurov,
Kuipers,
Skripochka.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-3A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Soyuz TMA-3 was originally to switch lifeboats on the International Space Station. The crew would have returned to earth in the Soyuz TMA-2 already docked to the station. After the Columbia disaster, the remaining shuttles were grounded. The Soyuz was then the only means of keeping the station manned. It was therefore decided that Soyuz TMA-3 would fly with the skeleton crew of Foale and Kaleri.
2004 January 29 - . 11:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M1-11 - .
Payload: Progress M1 s/n 260. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M1.
Duration: 116.00 days. Decay Date: 2004-06-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 28142 . COSPAR: 2004-002A. Apogee: 263 km (163 mi). Perigee: 192 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 88.73 min.
ISS resupply, to dock at the Zvezda module of the station 13:15 GMT on 31 January. Launch delayed from November 20, 2003. Payload delivered amounted to 2345 kg and included a new flex hose for the Destiny module's leaky window, replacement parts for the Russian Elektron oxygen-generating unit, a spare Elektron, new Russian Solid Fuel Oxygen Generator candles, batteries for the Zarya and Zvezda modules, gas analyser equipment, updated fire suppression and detection equipment, a new Russian Orlan spacesuit, film, cameras, data cassettes and the Matreshka experiment package for installation on Zvezda's exterior during a spacewalk.
A few days prior to its departure from the ISS, ground controllers fired the Progress M1-11's engines for 11 minutes, boosting the Station's altitude by 3.7 km and adjusting its inclination by one one-hundredth of a degree. Progress M1-11 undocked from the Station at 11:19 GMT on 24 May 2005, clearing the way for the arrival of Progress M-49. It was thereafter commanded to a destructive re-entry over the Pacific Ocean.
2004 April 19 - . 03:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-4 - .
Call Sign: Altair. Crew: Fincke,
Kuipers,
Padalka.
Return Crew: Fincke,
Padalka,
Shargin.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 214. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Fincke,
Kuipers,
Padalka,
Shargin.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-3,
Soyuz TMA-4,
Soyuz TMA-4 Delta.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 187.89 days. Decay Date: 2004-10-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 28228 . COSPAR: 2004-013A. Apogee: 367 km (228 mi). Perigee: 359 km (223 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
Soyuz TMA-4 was ISS transport mission ISS 8S and delivered the EO-9 caretaker crew of Gennadiy Padalka and Michael Fincke, together with the ESA/Netherlands Delta mission crewmember Andre Kuipers, to the Space Station. Soyuz TMA-4 docked with the nadir port on Zarya at 05:01 GMT on April 21 and the hatches to the ISS were opened at 06:30 GMT. Another gyro on the station had shut down prior to the docking and possibly would require a maintenance spacewalk to replace its failed electronics.
After Soyuz TMA-5 docked with the ISS on October 16, the EO-9 crew handed activities over to the EO-10 crew.
May 2004 - .
- Soyuz TMA-4A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Musabayev,
Schlegel.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Musabayev,
Schlegel.
Agency: RAKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-4A.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Soyuz TMA-4 was originally to switch lifeboats on the International Space Station. The crew would have returned to earth in the Soyuz TMA-3 already docked to the station. After the Columbia disaster, the remaining shuttles were grounded. The Soyuz was then the only means of keeping the station manned. It was therefore decided that Soyuz TMA-4 would fly with the skeleton crew of McArthur and Tokarev.
2004 May 25 - . 12:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-49 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 249. Mass: 7,283 kg (16,056 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 66.00 days. Decay Date: 2004-07-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 28261 . COSPAR: 2004-019A. Apogee: 367 km (228 mi). Perigee: 359 km (223 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
Docked at the aft port of the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station on 27 May at 13:55 GMT. Delivered two and a half tons of food, water, fuel, spare parts and supplies. Progress M-49 undocked from the Zvezda module on 30 July 2004 at 7:05 GMT, after having been filled with a tonne of trash. Fincke filmed its departure, and Station exterior cameras captured rare footage of the Progress' fiery re-entry into Earth's atmosphere after it was deorbited.
2004 August 11 - . 05:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-50 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 250. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-4. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 133.73 days. Decay Date: 2004-12-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 28399 . COSPAR: 2004-032A. Apogee: 365 km (226 mi). Perigee: 358 km (222 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min. Delayed from July 22 and 28. Docked with the International Space Station at 05:01 GMT on August 14. Undocked from the Zvezda module of the ISS on December 22 at 19:34 GMT and was deorbited over the Pacific at 22:32 GMT..
2004 October 14 - . 03:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-5 - .
Call Sign: Tien Shan. Crew: Chiao,
Shargin,
Sharipov.
Return Crew: Chiao,
Sharipov,
Vittori.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 215. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chiao,
Shargin,
Sharipov,
Vittori.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 192.79 days. Decay Date: 2005-04-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 28444 . COSPAR: 2004-040A. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 353 km (219 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.70 min.
Soyuz TMA-5 docked with the Pirs module on October 16 at 0416 GMT. Aboard the spacecraft were the EO-10 crew of Sharipov and Chiao, and guest cosmonaut Shargin. After a week at the station, the EO-9 crew of Padalka and Fincke, together with Shargin, entered Soyuz TMA-4 at 18:14 GMT on October 23 and returned to earth. Chiao and Sharipov continued as the ISS skeleton station crew.
2004 December 23 - . 22:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-51 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 251. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 76.00 days. Decay Date: 2005-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 28503 . COSPAR: 2004-051A. Apogee: 355 km (220 mi). Perigee: 316 km (196 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Launch delayed from November 24, December 22 . Progress M-51 docked with the Zvezda module of the International Space Station on December 25 at 23:58 GMT, bringing critical food supplies to the EO-10 crew. Press hype during the delays prior to the launch had portrayed the situation as one where failure of the Progress to dock would have required the crew to either return to earth or starve.
Undocked from at 16:06 GMT on February 27, 2005, in order to clear the port for Progress M-52, which would launch the next day. Progress M-51 lowered its perigee at around 18:30 GMT and remained in orbit for several days. FInally an engine firing was commanded, bringing it down in a destructive re-entry over the Pacific Ocean on March 9.
2005 February 28 - . 19:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-52 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 252. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Kozlov bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-5. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 107.20 days. Decay Date: 2005-06-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 28624 . COSPAR: 2005-007A. Apogee: 360 km (220 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Docked with the Zvezda module of the International Space Station at 20:10 GMT on March 2. Undocked at 20:16 GMT on 15 June. Retrofire at 23:16 GMT lowered its perigee to 62 km, and resulting in a destructive re-entry over the Pacific at 23:57 GMT..
2005 April 15 - . 00:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-6 - .
Call Sign: Basalt. Crew: Krikalyov,
Phillips,
Vittori.
Return Crew: Krikalyov,
Olsen,
Phillips.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 216. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Krikalyov,
Olsen,
Phillips,
Vittori.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-5,
Soyuz TMA-6,
Soyuz TMA-6 Eneide.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 179.02 days. Decay Date: 2005-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 28640 . COSPAR: 2005-013A. Apogee: 360 km (220 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
The Soyuz TMA-6 docked with International Space Station's Pirs module at 02:20 GMT on April 17. Commander of the long-duration EO-11 crew was Russian cosmonaut Sergey Krikalyov. Flight engineer and science officer was American astronaut John Phillips. Italian Roberto Vittori accompanied the EO-10 crew aboard Soyuz TMA-6 to the station on the European Space Agency EP-8 Eneide mission.
2005 June 16 - . 23:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-53 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 353. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 82.62 days. Decay Date: 2005-09-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 28700 . COSPAR: 2005-021A. Apogee: 353 km (219 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
Delayed from June 10. Space station resupply mission. After a communications failure, ISS Commander Krikalyov took manual remote control used the TORU system to guide Progress M-53 to a docking at the ISS Zvezda module at 00:42 GMT on 19 June. Undocked at 10:26 GMT on 7 September into a 350 km x 351 km orbit. Progress M-53 began retrofire at 13:26 GMT the same day, lowering its perigee to 56 km and thereby ensuring a destructive re-entry into the Pacific Ocean.
2005 September 8 - . 13:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-54 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 354. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Kozlov bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-6. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 176.00 days. Decay Date: 2006-03-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 28866 . COSPAR: 2005-035A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 347 km (215 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Delayed from August 24. Resupply spacecraft which docked with the ISS Zvezda module at 14:42 GMT on 10 September. Undocked from the Zvezda module on March 3 2006 at 10:06 GMT and fired its engines to reenter over the Pacific at 13:05 GMT..
2005 October 1 - . 03:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-7 - .
Call Sign: Rassvet. Crew: McArthur,
Olsen,
Tokarev.
Return Crew: McArthur,
Pontes,
Tokarev.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 217. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: McArthur,
Olsen,
Pontes,
Tokarev.
Agency: NASA,
RAKA,
Shanghai Astronautics Bureau.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-6,
Soyuz TMA-7,
Soyuz TMA-8 ISS EP-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 189.83 days. Decay Date: 2006-04-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 28877 . COSPAR: 2005-039A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 347 km (215 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
Launch delayed from September 27. Soyuz TMA-7 docked with the International Space Station at 05:27 GMT on 3 October, bringing the long duration EO-12 crew of (McArthur, Commander; Tokarev, Flight Engineer) and space tourist Olsen. McArthur, Tokarev and Pontes (brought to the station aboard Soyuz TMA-8) transferred to TMA-7 on April 8, 2006, closing the hatches at 17:15 GMT and undocking from Zvezda at 20:28 GMT, leaving Vinogradov and Williams from Soyuz TMA-8 as the Expedition 13 in charge of the station. Soyuz TMA-7 fired its engines at 22:58 GMT for the deorbit burn and landed in Kazakhstan at 23:48 GMT.
2005 December 21 - . 18:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-55 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 355. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-7. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 179.96 days. Decay Date: 2006-06-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 28906 . COSPAR: 2005-047A. Apogee: 349 km (216 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. The resupply spacecraft docked with the ISS Pirs module at 19:46 GMT on 23 December. It undocked at 14:06 GMT on June 19, 2006; fired its engines at 17:06 GMT to lower its orbit into the atmosphere; and burned up over the Pacific Ocean at 17:41 GMT..
2006 March 30 - . 02:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-8 - .
Call Sign: Carat. Crew: Pontes,
Vinogradov,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Return Crew: Ansari,
Vinogradov,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 218. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Ansari,
Pontes,
Vinogradov,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Agency: NASA,
RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-7,
Soyuz TMA-8,
Soyuz TMA-8 ISS EP-10.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 182.95 days. Decay Date: 2006-09-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 28996 . COSPAR: 2006-009A. Apogee: 349 km (216 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Soyuz TMA-8 docked with the Zarya nadir port of the ISS at 04:19 GMT on April 1. It undocked from Zarya on 28 September at 21:53 GMT, with the return crew of Vinogradov, Williams and space tourist Ansari aboard. It landed in Kazakhstan at 01:13 GMT on 29 September.
2006 April 24 - . 16:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-56 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 356. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-8. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 157.35 days. Decay Date: 2006-09-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 29057 . COSPAR: 2006-013A. Apogee: 349 km (216 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Progress M-56 docked at the Zvezda port of the International Space Station on 26 April at 17:41 GMT. It undocked at 00:28 GMT on 29 September and was then commanded to a destructive reentry over the south Pacific Ocean..
2006 June 24 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-57 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 357. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-8. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 207.00 days. Decay Date: 2007-01-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 29245 . COSPAR: 2006-025A. Apogee: 349 km (216 mi). Perigee: 335 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min. The Progress flew International Space Station resupply mission 22P (NASA called the flight Progress 22). It docked at the ISS Pirs port at 16:25 GMT on June 26..
2006 September 18 - . 04:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-9 - .
Call Sign: Vostok. Crew: Ansari,
Lopez-Alegria,
Tyurin.
Return Crew: Lopez-Alegria,
Simonyi,
Tyurin.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 219. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Ansari,
Lopez-Alegria,
Simonyi,
Tyurin.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-8,
Soyuz TMA-9.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 215.35 days. Decay Date: 2007-04-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 29400 . COSPAR: 2006-040A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 330 km (200 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
Carried the Expedition 14 crew and space tourist Anousheh Ansari to the International Space Station. Ansari replaced tourist Daisuke Enomoto, who was removed from flight status by the Russians just 28 days before the flight. Docked at the Zvezda port of the station at 05:21 GMT on September 20. On 21 April 2007, Lopez-Alegria, Tyurin and space tourist Charles Simonyi (who was taken to the station aboard Soyuz TMA-10) boarded Soyuz TMA-9, separated from the ISS, conducted retrofire, and landed in Kazakhstan at 12:31 GMT.
2006 October 23 - . 13:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-58 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 358. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-8.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 155.38 days. Decay Date: 2007-03-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 29503 . COSPAR: 2006-045A. Apogee: 351 km (218 mi). Perigee: 321 km (199 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
The Progress docked with the Zvezda module of the ISS at 14:29 GMT on October 26. There were indications that the Kurs rendezvous antenna on the forward docking ring had not retracted correctly, but this proved not to be the case. Hard dock was commanded at 18:06 GMT. Progress M-58 undocked from the Zvezda module on 27 March 2007 at 18:11 GMT and was deorbited at 22:44 GMT.
2007 January 18 - . 02:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-59 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 359. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Lopez-Alegria, Tyurin, Williams. Agency: RAKA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-9, STS-117 ISS EO-15. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 195.00 days. Decay Date: 2007-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 29714 . COSPAR: 2007-002A. Apogee: 351 km (218 mi). Perigee: 321 km (199 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min. Progress docked to the Pirs port of the ISS at 01:59 GMT on 20 January. The cargo craft brought up 780 kg of propellant for the Russian thrusters, 50 kg of oxygen and 1500 kg of spare parts, experiment hardware and life support components..
2007 April 7 - . 17:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-10 - .
Call Sign: Pulsar. Crew: Kotov,
Simonyi,
Yurchikhin.
Return Crew: Kotov,
Muszaphar,
Yurchikhin.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 220 / ISS-14S. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kotov,
Muszaphar,
Simonyi,
Yurchikhin.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-10,
Soyuz TMA-10 ISS EP-12.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 196.71 days. Decay Date: 2007-10-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 31100 . COSPAR: 2007-008A. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 330 km (200 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Carried the Expedition 15 crew and space tourist Charles Simonyi to the International Space Station. Soyuz TMA-10 docked at the Zarya port of the International Space Station at 19:10 GMT on 9 April. It undocked from Zarya at 19:20 GMT on Sep 27 September and docked at the Zvezda port at 19:47 GMT to clear Zarya for Soyuz TMA-10.
The EO-15 crew and EP-13 space tourist Shukor (brought to the station by Soyuz TMA-11) boarded Soyuz TM-10 and undocked from the Zvezda port at 07:14 GMT on 21 October. The re-entry burn began at 09:47 and was normal. But afterwards, due to failure of an explosive bolt, the Soyuz service module remained connected to the re-entry capsule. The Soyuz tumbled, then began re-entry with the forward hatch taking the re-entry heating, until the connecting strut burned through. The Soyuz the righted itself with the heat shield taking the heating, but defaulted to an 8.6 G ballistic re-entry, landing 340 km short of the aim point at 10:36 GMT. Improved procedures after the ballistic re-entry of Soyuz TMA-1 meant a helicopter recovery crew reached the capsule only 20 minutes after thumpdown. However the true nature of the failure was concealed from the world until the same thing happened on Soyuz TMA-11.
2007 May 12 - . 03:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-60 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 360. Mass: 7,280 kg (16,040 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kotov,
Williams,
Yurchikhin.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-10,
STS-117 ISS EO-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 136.65 days. Decay Date: 2007-09-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 31393 . COSPAR: 2007-017A. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 330 km (200 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Space station resupply spacecraft which docked with the Zvezda port of the International Space Station at 05:10 GMT on 15 May. It undocked on 19 September was conducted plasma depletion experiments before being deorbited over the Pacific at 19:01 GMT on 25 September..
2007 August 2 - . 17:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-61 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 361. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-10,
STS-117 ISS EO-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 173.00 days. Decay Date: 2008-01-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 32001 . COSPAR: 2007-033A. Apogee: 346 km (214 mi). Perigee: 334 km (207 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
International space station resupply; docked with the Pirs module at 18:40 GMT on 5 August. Undocked at 03:59 GMT on 22 December to clear port for Progress M-62 launched the next day. Deorbited over the Pacific on 22 January 2008 after a month of free flight carrying out the Plazma-Progress experiment.
2007 October 10 - . 13:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-11 - .
Call Sign: Agat. Crew: Malenchenko,
Muszaphar,
Whitson.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 221 / ISS 15S. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Malenchenko,
Muszaphar,
Whitson.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-11,
Soyuz TMA-11 ISS EP-13.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 191.80 days. Decay Date: 2008-04-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 32256 . COSPAR: 2007-045A. Apogee: 344 km (213 mi). Perigee: 340 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Soyuz TMA-11 delivered the EO-16 crew of Whitson and Malenchenko and EP-13 space tourist Shukor to the International Space Station. The Soyuz docked at the Zarya module at 14:50 GMT on 12 October. Whitson was EO-16 commander, with third astronaut Clay Anderson remaining aboard the station after the EO-15 crew and Shukor returned to earth on Soyuz TMA-10.
Malenchenko and Whitson, together with visiting Korean astronaut Yi, who had been delivered to the ISS by Soyuz TMA-12, undocked from the station aboard Soyuz TMA-11 at 05:06 GMT on 19 April 2008. Following the deorbit burn at 07:40 GMT the aft service module of the Soyuz failed to separate and the spacecraft began re-entry in a reversed position, with the forward hatch taking the initial re-entry heating. As was the case with Soyuz 5 in 1970, the connections with the service module finally melted away, and the freed capsule righted itself aerodynamically with the heat shield taking the brunt of the re-entry heating. However the crew experienced a rough ride, a ballistic re-entry of over 8 G's force, smoke in the cabin, a failure of the soft landing system, and a very hard landing. They landed 470 km short of the target point at 50 deg 31" N, 61 deg 7" E at 08:29 GMT. A small grass fire was started at the landing point and the injured crew had to be helped from the capsule by passers-by. Malenchenko and Whitson suffered no permanent injury, but Yi was hit by Whitson's personal effects bag on impact and required physical therapy for neck and spine injuries.
2007 December 23 - . 07:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-62 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 362. Mass: 7,130 kg (15,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-11,
STS-120 ISS EO-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 54.11 days. Decay Date: 2008-02-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 32391 . COSPAR: 2007-064B. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 333 km (206 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
Resupply spacecraft that docked with the Pirs port of the International Space Station at 08:14 GMT on 26 December. Undocked on 4 February 2008 at 10:32 GMT and then carried out Earth observations for ten days before being deorbited on 15 February at 09:44 GMT.
2008 February 5 - . 13:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-63 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 363. Mass: 7,130 kg (15,710 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-11, STS-120 ISS EO-16. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 61.96 days. Decay Date: 2008-04-07 12:00:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 32484 . COSPAR: 2008-004A. Apogee: 339 km (210 mi). Perigee: 338 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min. Docked with the ISS at the Pirs module on 7 February at 14:38 GMT. Undocked on 7 April at 08:49 GMT and was deorbited over the Pacific later the same day..
2008 April 8 - . 11:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-12 - .
Call Sign: Eridanus. Crew: Kononenko,
Volkov, Sergey,
Yi Soyeon.
Return Crew: Garriott, Richard,
Kononenko,
Volkov, Sergey.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 222. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Garriott, Richard,
Kononenko,
Volkov, Sergey,
Yi Soyeon.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-12,
STS-123 ISS EO-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 198.54 days. Decay Date: 2008-04-19 08:29:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 32756 . COSPAR: 2008-015A. Apogee: 343 km (213 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
Launched the EO-17 long-duration crew to replace the EO-16 crew. The commander was the son of cosmonaut Aleksandr Volkov. Also aboard was Oleg Kononenko (no relation to the 1970's Buran pilot of the same name) and Korean astronaut Yi Soyeon. Soyuz TMA-12 docked at the Pirs module of the International Space Station on 2008 Apr 10 at 12:57 GMT on 10 April. Volkov and Kononenko stayed aboard as the EO-17 long duration crew. Yi returned to earth with the EO-16 crew aboard Soyuz TMA-11. Soyuz TMA-12 undocked on 24 October at 00:16 GMT with the EO-17 crew of Kononenko and Volkov, plus space tourist Richard Garriott, aboard. They landed safely at 03:37 GMT.
2008 May 14 - . 20:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-64 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 364. Mass: 7,056 kg (15,555 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-12,
STS-123 ISS EO-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 137.02 days. Decay Date: 2008-09-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 32847 . COSPAR: 2008-023A. Apogee: 343 km (213 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
Unmanned space station resupply mission. Docked with the International Space Station at the Zarya port on 16 May. Undocked on 1 September at 19:47 GMT. It then flew for a week in independent orbit, carrying out the Plazma-Progress experiment. On 8 September at 20:47 GMT it was deorbited to destruction over the Pacific Ocean.
2008 September 10 - . 19:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-65 - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 365. Mass: 7,100 kg (15,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-12,
STS-124 ISS EO-17.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 88.00 days. Decay Date: 2008-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 33340 . COSPAR: 2008-043A. Apogee: 357 km (221 mi). Perigee: 348 km (216 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
Docking with the ISS at the Zvezda module was delayed due to NASA Houston operations being curtailed during Hurricane Ike. The resupply spacecraft finally docked at 18:43 GMT on 27 September. It undocked at 16:20 GMT on 14 November, but then flew independently in orbit until 7 December in order to conduct continue ionospheric experiments.
2008 October 12 - . 07:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-13 - . Call Sign: Titan. Crew: Fincke, Garriott, Richard, Lonchakov. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 223. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Fincke, Garriott, Richard, Lonchakov. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-13. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 178.01 days. Decay Date: 2009-04-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 33399 . COSPAR: 2008-050A. Apogee: 362 km (224 mi). Perigee: 352 km (218 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.70 min. Docked at the Zarya port of the ISS on 14 October at 08:26 GMT..
2008 November 26 - . 12:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-01M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 401. Mass: 7,290 kg (16,070 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-13, STS-126 ISS EO-18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 74.00 days. Decay Date: 2009-02-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 33443 . COSPAR: 2008-060A. Apogee: 362 km (224 mi). Perigee: 352 km (218 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.70 min. ISS resupply spacecraft, a modernized version of Progress with a digital control system, docked at the Pirs port of the station on 30 November..
2009 February 10 - . 05:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-66 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 366. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-13, STS-126 ISS EO-18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 97.00 days. Decay Date: 2009-05-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 33593 . COSPAR: 2009-006A. Apogee: 357 km (221 mi). Perigee: 342 km (212 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. ISS resupply. Docked with the ISS at 07:18 GMT on 13 February. Undocked at 15:18 on 6 May and destroyed over the Pacific on 18 May..
2009 March 26 - . 11:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-14 - . Call Sign: Altair. Crew: Barratt, Padalka, Simonyi. Backup Crew: Dyson, Surayev, Walker. Return Crew: Barratt, Laliberte, Padalka. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 224. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-14. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 198.66 days. Decay Date: 2009-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 34669 . COSPAR: 2009-015A. Apogee: 354 km (219 mi). Perigee: 344 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Delivered EO-19 crew and space tourist Simonyi to ISS; returned EO-19 crew and space tourist Laliberte to earth on 11 October 2009 at 04:32 GMT..
2009 May 7 - . 18:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-02M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 402. Mass: 7,120 kg (15,690 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-14.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 67.00 days. Decay Date: 2009-07-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 34905 . COSPAR: 2009-024A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
ISS logistics flight. Docked with the Pirs module of the ISS on 12 May at 19:24. Undocked with ISS on 30 June, conducted scientific experiments, then made a second rendezvous with the ISS at the Zvezda module to test docking systems for the upcoming Mini-Research Module 2. Backed away after getting within 10 m of the station. Retrofire on 13 July followed by burn up over the Pacific at 16:28 GMT.
2009 May 27 - . 10:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-15 - . Call Sign: Parus. Crew: De Winne, Romanenko, Roman, Thirsk. Backup Crew: Hadfield, Kondratiyev, Kuipers. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 225. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-15. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 187.86 days. Decay Date: 2009-12-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 35010 . COSPAR: 2009-030A. Apogee: 354 km (219 mi). Perigee: 344 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Delivered EO-20 crew to the ISS. Returned to earth 1 December 2009..
2009 July 24 - . 10:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-67 - . Payload: Progress M s/n 367. Mass: 7,285 kg (16,060 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-14, Soyuz TMA-15. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 65.00 days. Decay Date: 2009-09-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 35641 . COSPAR: 2009-040A. Apogee: 354 km (219 mi). Perigee: 344 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Docked at the Zvezda port of the International Space Station at 11:12 GMT on 29 July. Undocked and was deorbited over the Pacific Ocean on 27 September at 09:33 GMT..
2009 September 30 - . 07:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-16 - . Call Sign: Bort. Crew: Laliberte, Surayev, Williams, Jeffrey. Backup Crew: Barrett, Skvortsov, Walker, Shannon. Return Crew: Surayev, Williams. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 226. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-16. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 169.17 days. Decay Date: 2010-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 35940 . COSPAR: 2009-053A. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 342 km (212 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Docked with the International Space Station at 08:35 GMT on 2 October. Carried the EO-21 crew of Suraev and Williams, and space tourist Guy Laliberte due to the station. Surayev and Williams landed aboard Soyuz TMA-16 in Kazakhstan on 18 March 2010..
2009 October 15 - . 01:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-03M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 403. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-15, Soyuz TMA-16. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 194.00 days. Decay Date: 2010-05-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 35948 . COSPAR: 2009-056A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 314 km (195 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min. Docked at the Pirs module of the International Space Station at 01:41 GMT on 18 October..
2009 November 10 - . 14:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Poisk - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 302 / 240GK s/n 2L. Mass: 3,670 kg (8,090 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M-SO.
USAF Sat Cat: 36086 . COSPAR: 2009-060A. Perigee: 11 km (6 mi).
Docking/research module for the ISS, consisting of a pressurized Small Research Module and a Progress M service module. Docked at the zenith port of the Zvezda module of the ISS at 15:41 GMT on 12 November. On 8 December at 00:16 GMT the service module separated from Small Research Module, leaving the docking port clear for future spacecraft visiting the ISS. At 04:48 GMT the service module retrofired into a descructive reentry over the Pacific at 05:27 GMT.
2009 December 20 - . 21:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-17 - . Call Sign: Pulsar. Crew: Creamer, Kotov, Noguchi. Backup Crew: Furukawa, Shkaplerov, Wheelock. Payload: Soyuz 7K-STMA s/n 227 / ISS-21S. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-17. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 163.23 days. Decay Date: 2010-06-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 36129 . COSPAR: 2009-074A. Apogee: 351 km (218 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Docked with Zarya port of ISS at 22:48 GMT on 22 December. Undocked at 0:04 GMT on 2 June 2010 and landed in Kazakhstan at 03:25 GMT..
2010 February 3 - . 03:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-04M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 404 / ISS-36P. Mass: 7,400 kg (16,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-16, Soyuz TMA-17. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 148.42 days. Decay Date: 2010-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 36361 . COSPAR: 2010-003A. Apogee: 353 km (219 mi). Perigee: 346 km (214 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Undocked from the Zvezda module of the ISS on 10 May 2010. Conducted free-flight experiments until deorbited at 13:54 GMT on 1 July..
2010 April 2 - . 04:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-18 - .
Call Sign: Cliff. Crew: Caldwell,
Korniyenko,
Skvortsov, Aleksandr.
Backup Crew: Borisenko, Andrei,
Kelly, Scott,
Samokutyayev.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-STMA s/n 228. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-18.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 176.05 days. Decay Date: 2010-04-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 36505 . COSPAR: 2010-011A. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
ISS EO-23. The crew first attempted to depart the ISS on 24 September. However the latches between the Soyuz and the station failed to release. Return to earth the next day was successful, with undocking at 02:03 GMT; deorbit burn at 04:31 GMT; and landing in Kazakhstan at 05:23 GMT.
2010 April 28 - . 17:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-05M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 405 / ISS-37P. Mass: 7,400 kg (16,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-17, Soyuz TMA-18, Soyuz TMA-18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 201.00 days. Decay Date: 2010-11-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 36521 . COSPAR: 2010-018A. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Undocked from the Pirs module of the ISS on 25 October 2010 at 14:22 GMT and was deorbited over the Pacific on 15 November 2010 after three weeks of independent flight..
2010 June 15 - . 21:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-19 - .
Call Sign: Olympus. Crew: Walker, Shannon,
Wheelock,
Yurchikhin.
Backup Crew: Coleman, Catherine,
Kondratiyev,
Nespoli.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-STMA s/n 229. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-19.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 163.30 days. Decay Date: 2010-11-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 36603 . COSPAR: 2010-029A. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
ISS EO-24 crew. The return to earth was reported advanced four days to avoid coinciding with an OSCE conference in Kazakhstan. The crew undocked from the Rassvet module of the ISS at 01:23 GMT on 26 November 2010. There was a leak in the descent module, but ground controllers concluded the return to earth could be conducted safely. The Soyuz made its deorbit burn at 03:55 GMT and landed safely in Kazakhstan at 04:46 GMT.
2010 June 30 - . 15:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-06M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 406 / ISS-38P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-18,
Soyuz TMA-19.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 67.86 days. Decay Date: 2010-07-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 36748 . COSPAR: 2010-033A. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
First docking attempt with the ISS on 2 July aborted due to radio interference. Successfully docked with the ISS at the Zvezda module on 4 July at 16:17 GMT. Undocked from the Zvezda module of the ISS at 11:21 GMT on 31 August 2010. Conducted experiments in free flight until deorbited at 12:13 GMT on 6 September.
2010 September 10 - . 10:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-07M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 407 / ISS-39P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-18, Soyuz TMA-19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 163.00 days. Decay Date: 2011-02-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 37156 . COSPAR: 2010-044A. Apogee: 355 km (220 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Docked at the Zvezda module of the ISS at 11:58 GMT on 12 September 2010. Undocked from Zvezda on 20 February 2011 at 13:12 GMT and deorbited over the Pacific at 16:12 GMT..
2010 October 7 - . 23:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-01M - . Call Sign: Ingul. Crew: Kaleri, Kelly, Scott, Skripochka. Backup Crew: Garan, Kononenko, Volkov, Sergey. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 701. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-01M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 159.78 days. Decay Date: 2011-03-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 37183 . COSPAR: 2010-052A. Apogee: 355 km (220 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min. ISS EO-25 crew. The Soyuz docked at the Poisk module of the ISS at 00:01 GMT on 10 October. The crew entered the spacecraft and undocked at 04:27 GMT on 16 March 2011. Following retrofire and re-entry they landed safely in Kazakhstan at 07:53 GMT..
2010 October 27 - . 15:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-08M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 408 / ISS-40P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-01M, Soyuz TMA-19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 88.59 days. Decay Date: 2011-01-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 37196 . COSPAR: 2010-055A. Apogee: 355 km (220 mi). Perigee: 352 km (218 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Undocked from the Pirs module of the ISS at 00:42 GMT on 24 January 2011 and deorbited over the Pacific at 05:16 GMT the same day..
2010 December 15 - . 19:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-20 - .
Call Sign: Varyag. Crew: Coleman, Catherine,
Kondratiyev,
Nespoli.
Backup Crew: Fossum,
Furukawa,
Ivanishin.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-STMA s/n 230. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-20.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 159.30 days. Decay Date: 2011-05-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 37254 . COSPAR: 2010-067A. Apogee: 355 km (220 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
ISS EO-26 crew. Docked at the Rassvet module of the ISS at 20:11 GMT on 17 December. The crew boarded Soyuz TMA-20 and undocked at 21:35 GMT on 23 May 2011. They pulled back 200 m from the station, then took comprehensive photography of the station until 22:17 as it rotated before them. After departure from the visinity of the station, the Soyuz fired its engines at 01:36 GMT on 24 May to start the descent into the atmosphere. The orbital module and service modules separated from the descent module at 02:01 GMT. The crew landed safely in Kazakhstan at 02:27 GMT.
2011 January 28 - . 01:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-09M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 409 / ISS-41P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-01M, Soyuz TMA-20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 88.00 days. Decay Date: 2011-04-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 37359 . COSPAR: 2011-004A. Apogee: 345 km (214 mi). Perigee: 270 km (160 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.70 min. Undocked from the Pirs module of the ISS on 22 April at 11:41 GMT and deorbited over the Pacific on 26 April..
2011 April 4 - . 22:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-21 - .
Call Sign: Tarkhany /
Gagarin. Crew: Borisenko,
Garan,
Samokutyayev.
Backup Crew: Burbank,
Ivanishin,
Shkaplerov.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-STMA s/n 231. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-21.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 164.24 days. Decay Date: 2011-09-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 37382 . COSPAR: 2011-012A. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 343 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
ISS EO-27 crew. The Soyuz docked at the Poisk module of the ISS at 23:09 GMT on 6 April, and undocked at 00:38 GMT on 16 September 2011, eight days later than planned due to the Progress M-11M launch failure. A dropout of communications after the reentry burn caused concern, but the crew landed safely in Kazakhstan at 03:59 GMT.
2011 April 27 - . 13:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-10M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 410 / ISS-42P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-20, Soyuz TMA-21. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 185.00 days. Decay Date: 2011-10-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 37396 . COSPAR: 2011-017A. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 343 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Docked with the ISS Pirs module at 14:28 GMT on 29 April. Undocked at 09:04 GMT on 29 October. Following retrofire at 12:10 GMT it was destroyed on reentry over the Pacific at 12:48 GMT..
2011 June 7 - . 20:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-02M - . Call Sign: Eridanus. Crew: Fossum, Furukawa, Volkov, Sergey. Backup Crew: Kononenko, Kuipers, Pettit. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 702. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-02M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 167.26 days. Decay Date: 2011-11-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 37633 . COSPAR: 2011-023A. Apogee: 403 km (250 mi). Perigee: 374 km (232 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min. Carried the EO-28 crew to the station. Docked with the ISS at the Rassvet on 9 June at 21:18 GMT. Undocked from the same port on 21 November at 23:00 GMT, followed by landing of the crew in Kazakhstan at 02:26 GMT on 22 November..
2011 June 21 - . 14:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-11M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 411 / ISS-43P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-02M,
Soyuz TMA-21.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 71.79 days. Decay Date: 2011-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 37679 . COSPAR: 2011-027A. Apogee: 383 km (237 mi). Perigee: 343 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
ISS resupply. Also carried the 40 kg Chibis satellite. Docked with the Zvezda module of the ISS on 23 June at 16:37 GMT. Undocked from Zvezda at 09:38 GMT on 23 August. After several maneuvers to carry out the Radar-4 experiment, deorbited over the Pacific at 09:34 GMT on 1 September.
2011 August 24 - . 13:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB. FAILURE: Five minutes and 25 seconds into flight, during the burn of the booster's third stage, the engine's gas generator failed and the engine shut down. The upper stage and spacecraft crashed in the Gorno-Altai region.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Progress M-12M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 412 / ISS-44P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-02M,
Soyuz TMA-21.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
ISS resupply mission. The Progress M failed to reach orbit. Five minutes and 25 seconds into flight, during the burn of the booster's third stage, the engine's gas generator failed and the engine shut down. The upper stage and spacecraft crashed in the Gorno-Altai region of Russia. First ever failure of a Progress spacecraft to dock with a space station in its 135-mission history. The six crew aboard the ISS had sufficient supplies, but the mishap delayed the launch of the Expedition 29 replacement crew until the cause of the failure was understood and the Soyuz launch vehicle cleared again for manned launches. The return to Earth of the first half of the Expedition 28 crew has also delayed to mid-September, meaning the station would be reduced to a three-person crew for a time.
2011 October 30 - . 10:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-13M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 413 / ISS-45P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-02M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 87.00 days. Decay Date: 2012-01-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 37857 . COSPAR: 2011-062A. Apogee: 403 km (250 mi). Perigee: 374 km (232 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
Space station resupply. Docked with the Pirs module of the ISS on 2 November. This restored resupply of the station after the Progress M-12M launch failure and two intermediate successful flights of the Soyuz booster. Also carried the Chibis-M subsatellite.
2011 November 14 - . 04:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-22 - .
Call Sign: Astraeus. Crew: Burbank,
Ivanishin,
Shkaplerov.
Backup Crew: Acaba,
Padalka,
Revin.
Payload: Soyuz 7K-STMA s/n 232. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-22.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 165.31 days. Decay Date: 2012-04-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 37877 . COSPAR: 2011-067A. Apogee: 410 km (250 mi). Perigee: 376 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Launch delayed two months to verify booster after launch failure of Progress M-12M in August 2011. After successful launch of Progress M-13M on 30 October, Soyuz TMA-22 was cleared for launch. Delivered the EO-29 crew to the ISS, docking at the Poisk module of the station at 05:24 GMT on 16 November. Undocked on 27 April 2012 at 08:15 GMT and landed in Kazakhstan at 11:45 GMT.
2011 December 21 - . 13:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-03M - . Call Sign: Antares. Crew: Kononenko, Kuipers, Pettit. Backup Crew: Hoshide, Malenchenko, Williams. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 703. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-03M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 192.79 days. Decay Date: 2012-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 38036 . COSPAR: 2011-078A. Apogee: 405 km (251 mi). Perigee: 375 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min. Docked at the Rassvet module of the ISS at 15:19 GMT on 23 December. Undocked from the ISS on 1 July 2012 at 04:47 GMT and landed in Kazakhstan at 08:14 GMT..
2012 January 25 - . 23:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-14M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 414 / ISS-46P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 94.00 days. Decay Date: 2012-04-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 38073 . COSPAR: 2012-004A. Apogee: 405 km (251 mi). Perigee: 375 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min. Docked with the International Space Station at the Pirs module on 28 January at 00:09 GMT. Undocked on 19 April 11:04 GMT to begin nine days of autonomous Radar-Progress ionospheric experiments. Deorbited over the Pacific Ocean on 28 April..
2012 April 20 - . 12:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-15M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 415 / ISS-47P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 122.00 days. Decay Date: 2012-08-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 38222 . COSPAR: 2012-015A. Apogee: 406 km (252 mi). Perigee: 392 km (243 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Docked at the Pirs module of the International Space Station on 22 April at 14:39 GMT. Undocked and after three weeks of independent flight involving Radar-Progress experiments using thruster burns to study the ionosphere, was deorbited over the Pacific on 20 August.
2012 May 15 - . 03:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-04M - .
Call Sign: Altair. Crew: Acaba,
Padalka,
Revin.
Backup Crew: Ford, Kevin,
Novitskiy,
Tarelkin.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 705. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-04M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 124.99 days. Decay Date: 2012-09-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 38291 . COSPAR: 2012-022A. Apogee: 406 km (252 mi). Perigee: 392 km (243 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Docked at the station's Poisk module on 17 May at 04:36 GMT. On 16 September at 23:09 GMT undocked from the station to return the crew to earth. Soyuz TMA-04M flew for 2 hr 47 min in a 403 km x 426 km orbit, then fired its engines for the deorbit burn at 01:56 GMT on 17 September to enter a 13 kmx 425 km reentry orbit. The crew landed safely in Kazakhstan at 02:23 GMT.
2012 July 15 - . 02:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-05M - . Call Sign: Agate. Crew: Hoshide, Malenchenko, Williams. Backup Crew: Hadfield, Marshburn, Romanenko, Roman. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 706. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-05M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 126.97 days. Decay Date: 2012-11-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 38671 . COSPAR: 2012-037A. Apogee: 428 km (265 mi). Perigee: 403 km (250 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.90 min. Docked with the ISS at 04:51 GMT on 17 July. Undocked at 22:26 GMT on 18 November; landed in Kazakhstan at 01:53 GMT on 29 November..
2012 August 1 - . 19:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-16M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 416 / ISS-48P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 192.00 days. Decay Date: 2013-02-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 38738 . COSPAR: 2012-042A. Apogee: 428 km (265 mi). Perigee: 403 km (250 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.90 min. Undocked from the Pirs module at 13:16 GMT on 9 February. Deorbited over the Pacific Ocean at 16:19 GMT with debris impact at 17:05 GMT..
2012 October 23 - . 10:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-06M - . Call Sign: Kazbek. Crew: Ford, Kevin, Novitskiy, Tarelkin. Backup Crew: Cassidy, Misurkin, Vinogradov. Payload: ISS-32S. Soyuz TMA s/n 707. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-06M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 143.68 days. Decay Date: 2013-03-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 38871 . COSPAR: 2012-058A. Apogee: 422 km (262 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.80 min. Docked with the Poisk module of the ISS at 12:29 GMT on 25 October. Undocked at 23:43 GMT on 15 March 2013. Retrofire at 02:13 GMT the next day,followed by landing in Kazakhstan at about 03:06 GMT on 16 March..
2012 October 31 - . 07:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U-PVB.
- Progress M-17M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 417 / ISS-49P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 172.00 days. Decay Date: 2013-04-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 38975 . COSPAR: 2012-060A. Apogee: 422 km (262 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.80 min.
Docked with the Zvezda module of the ISS after a quick-rendezvous 5 hour 52 min flight. Undocked from Zvezda at 12:02 GMT on 15 April for independent flight to conduct Radar-Progress ionospheric tests. Retrofire on 21 April on 14:07 GMT lasted 173 seconds, producing a delta-V of 90 m/s. Impacted in the Pacific at 15:02 GMT.
2012 December 19 - . 12:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-07M - . Call Sign: Parus. Crew: Hadfield, Marshburn, Romanenko, Roman. Backup Crew: Nyberg, Parmitano, Yurchikhin. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 704A. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-07M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 145.60 days. Decay Date: 2013-05-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 39032 . COSPAR: 2012-074A. Apogee: 421 km (261 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.80 min. Docked with the Rassvet module of the ISS at 14:09 GMT on 21 December. Undocked at 23:08 GMT on 13 May 2013. Retrofire at 01:37 GMT on 14 May was followed by landing in Kazakhstan at 02:31 GMT..
2013 February 11 - . 14:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-18M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 418 / ISS-50P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 165.00 days. Decay Date: 2013-07-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 39082 . COSPAR: 2013-007A. Apogee: 421 km (261 mi). Perigee: 409 km (254 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.88 min. Docked with the Pirs module of the ISS at 20:34 GMT on launch day. Undocked from the Pirs module at 20:53 GMT on July 25 and was deorbited over the South Pacific three hours later, with debris ocean impact around 00:42 GMT July 26..
2013 March 28 - . 20:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-08M - .
Call Sign: Karat. Crew: Cassidy,
Misurkin,
Vinogradov.
Backup Crew: Hopkins,
Kotov,
Ryazansky.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 708. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-08M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 166.26 days. Decay Date: 2013-09-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 39125 . COSPAR: 2013-013A. Apogee: 421 km (261 mi). Perigee: 409 km (254 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.88 min.
Docked with the Poisk module of the ISS at 02:28 GMT on 29 March. Soyuz TMA-08M undocked from the ISS and made its deorbit burn at 02:05 GMT. The BO and PAO modules were jettisoned at 02:32 GMT and the SA descent module containing Vinogradov, Misurkin and Cassidy touched down safely in Kazakhstan at 02:58 GMT after 166.3 days in space.
2013 April 24 - . 10:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-19M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 419 / ISS-51P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 56.00 days. Decay Date: 2013-06-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 39148 . COSPAR: 2013-017A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 360 km (220 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.34 min.
Although one of the spacecraft's rendezvous antennae did not deploy, it docked successfully with the aft port of the ISS Zvezda module at 12:25 GMT on 26 April. Undocked from the Zvezda module at 13:58 GMT on 11 June to clear the port for the ATV resupply vehicle. Maneuvered to a 416 km x 456 km orbit for Radar-Progress ionospheric experiments.
2013 May 28 - . 20:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-09M - .
Call Sign: Olympus. Crew: Nyberg,
Parmitano,
Yurchikhin.
Backup Crew: Mastracchio,
Tyurin,
Wakata.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 709. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-09M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 166.26 days. Decay Date: 2013-11-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 39170 . COSPAR: 2013-025A. Apogee: 421 km (261 mi). Perigee: 409 km (254 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.88 min.
Docked with the Rassvet module of the ISS at 02:10 GMT on 29 May after a 5 hour 39 minute flight. On 1 November 2013 Yurchikin, Nyberg and Parmitano, undocked from the Rassvet module at 08:33 GMT and flew around the station at a distance of 200 m to redock at 08:54 GMT with the Zvezda aft port freed up by ATV-4. Undocked from the Zvezda module on 10 November at 23:26 GMT and landed in Kazakhstan at 02:49 GMT on 11 November.
2013 July 27 - . 20:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-20M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 420 / ISS-52P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 199.00 days. Decay Date: 2014-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 39219 . COSPAR: 2013-039A. Apogee: 414 km (257 mi). Perigee: 361 km (224 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
Docked with the Pirs module of the ISS 5 hr 41 min after launch. Payload delivered to the station included a 1U cubesat, Chasqui 1 from Peru's Universidad Nacional de Ingenieria. Undocked from the Pirs module of the ISS at 16:21 GMT on 3 February 2014. Deorbited on February 11 following a week of independent operations, with impact in the South Pacifc at 15:55 GMT.
2013 September 25 - . 20:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-10M - . Call Sign: Pulsar. Crew: Hopkins, Kotov, Ryazansky. Backup Crew: Artemyev, Skvortsov, Swanson. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 710. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-10M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 166.27 days. Decay Date: 2014-03-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 39263 . COSPAR: 2013-054A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 411 km (255 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.82 min. Docked with the Poisk module of the ISS 5 hours 46 minutes after launch. Undocked from the Poisk module of the ISS at 00:02 GMT on 11 March, landing in Kazakhstan at 03:24 GMT..
2013 November 7 - . 04:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-11M - . Call Sign: Vostok. Crew: Mastracchio, Tyurin, Wakata. Backup Crew: Gerst, Surayev, Wiseman. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 711. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-11M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 187.91 days. Decay Date: 2014-05-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 39373 . COSPAR: 2013-061A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 415 km (257 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.90 min. Docked with the Rassvet module of the ISS at 10:27 GMT the day of launch. Undocked from the Rassvet module at 22:36 GMT on May 13 and made the deorbit burn at 01:05 GMT May 14. Landing in Kazakhstan came at 01:58:30 GMT on May 14..
2013 November 25 - . 20:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-21M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 421 / ISS-53P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 196.00 days. Decay Date: 2014-06-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 39456 . COSPAR: 2013-069A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 412 km (256 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.87 min.
It made a 1.5 km flyby of ISS at 21:50 GMT on November 27 to test the new Kurs-NA rendezvous system, and then a re-rendezvous on November 29. A glitch forced a switch to manual TORU control for the last 60 m to docking with the Zvezda module at 22:30 GMT. Undocked from Zvezda on June 9 at 13:30 GMT and was deorbited the same day, with debris falling in the South Pacific around 17:23 GMT.
2014 February 5 - . 16:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-22M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 422 / ISS-54P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 72.00 days. Decay Date: 2014-04-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 39506 . COSPAR: 2014-005A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 361 km (224 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.34 min.
ISS mission 54P; docked at the Pirs module of the ISS at 22:22 GMT the same day as launch. Undocked from the Pirs module at 13:58 GMT April 7; it remained in a 360 x 417 km orbit for Radar-Progress ionospheric studies until April 18, when it was deorbited over the Pacific.
2014 March 25 - . 21:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-12M - .
Call Sign: Cliff. Crew: Artemyev,
Skvortsov,
Swanson.
Backup Crew: Samokutyayev,
Serova,
Wilmore.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 712. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-12M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 169.21 days. Decay Date: 2014-09-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 39622 . COSPAR: 2014-013A. Apogee: 417 km (259 mi). Perigee: 412 km (256 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.85 min.
The third planned rendezvous burn at 23:48 GMT was cancelled due to a software problem, leaving the spacecraft in a 297 x 333 km x 51.7 deg orbit. Rendezvous with the ISS was rescheduled to 27 March. It maneuvered to a 414 x 425 km orbit on 26 March. Docking with the ISS at the Poisk module was at 23:53 GMT on 27 March. On September 10 at 23:01 GMT Skvortsov, Artemev and Swanson undocked from the Poisk module in Soyuz TMA-12M. The deorbit burn at 01:30 GMT September 11 was followed by module separation at 01:58, atmosphere entry at 02:01, and landing in Kazakhstan at 02:23.
2014 April 9 - . 15:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-23M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 427 / ISS-55P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Duration: 113.00 days. Decay Date: 2014-07-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 39648 . COSPAR: 2014-018A. Apogee: 417 km (259 mi). Perigee: 412 km (256 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.85 min.
Docked with the Pirs module of the ISS at 21:14 GMT the same day as launch. Undocked from at 21:44 GMT on July 21 and then carried out 10 days of independent operations as part of the Radar-Progress experiment program. Deorbited on July 31 with impact at 22:43 GMT in the South Pacific.
2014 May 28 - . 19:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-13M - . Call Sign: Cepheus. Crew: Gerst, Surayev, Wiseman. Backup Crew: Cristoforetti, Shkaplerov, Virts. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 713. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-13M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 165.33 days. Decay Date: 2014-11-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 39775 . COSPAR: 2014-031A. Apogee: 417 km (259 mi). Perigee: 412 km (256 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.85 min. Docked with the Rassvet module of the ISS at 01:44 GMT May 29. Undocked from Rassvet at 00:31 GMT on November 10. The deorbit burn at 03:05 GMT reduced velocity by 128 m/s, dipping perigee into the atmosphere. Landed in Kazakhstan at 03:58 GMT..
2014 July 23 - . 21:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-24M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 423 / ISS-56P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 120.00 days. Decay Date: 2014-11-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 40097 . COSPAR: 2014-042A. Apogee: 419 km (260 mi). Perigee: 413 km (256 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.89 min. Docked with the Pirs module of the ISS at 03:31 GMT on July 24. Undocked from Pirs at 05:38 GMT on October 27..
2014 September 25 - . 20:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-14M - .
Call Sign: Tarkhany. Crew: Samokutyayev,
Serova,
Wilmore.
Backup Crew: Kelly, Scott,
Korniyenko,
Padalka.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 714. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-14M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 167.24 days. Decay Date: 2015-03-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 40246 . COSPAR: 2014-057A. Apogee: 408 km (253 mi). Perigee: 396 km (246 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.60 min.
Expedition 42 crew transported to the ISS (Samokutyaev, Wilmore and Serova). The port solar array failed to deploy after Soyuz separated from the launch vehicle third stage, but this did not impact the rendezvous. Soyuz TMA-14M docked with the Poisk module of the ISS at 02:11 GMT on September 26. Serova was the fourth Russian woman in space but the first since 1997. On March 11 2015 at 22:44 GMT Soyuz TMA-14M undocked from the Poisk module with the same crew aboard. It performed its deorbit burn at 01:16 GMT March 12 and landed in Kazakhstan at around 02:08 GMT.
2014 October 29 - . 07:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-2-1a.
- Progress M-25M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 424 / ISS-57P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 179.00 days. Decay Date: 2015-04-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 40292 . COSPAR: 2014-067A. Apogee: 403 km (250 mi). Perigee: 396 km (246 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.56 min. Docked with the ISS Pirs module at 13:08 GMT 29 October. Undocked from the Pirs module at 06:41 GMT on April 25 and was deorbited on April 26, with debris falling in the South Pacific at 13:00 GMT..
2014 November 23 - . 21:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-15M - .
Call Sign: Astraeus. Crew: Cristoforetti,
Shkaplerov,
Virts.
Backup Crew: Yui,
Kononenko,
Lindgren.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 715. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-15M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 199.70 days. Decay Date: 2015-06-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 40312 . COSPAR: 2014-074A. Apogee: 404 km (251 mi). Perigee: 399 km (247 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.59 min.
Docked at the Rassvet module of the ISS at 02:49 GMT on 24 November 2014 with the crew of Shkaplerov, Virts, and Cristoforetti. Return was delayed over a month before the booster for the Soyuz TMA-16M crew could be cleared for flight following the third-stage explosion of the booster for Progress TMA-11M. Undocked on 11 June 2015 with the same crew at 10:20 GMT and then landed at 13:43 in Kazakhstan.
2015 February 17 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-26M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 426 / ISS-58P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Decay Date: 2015-08-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 40392 . COSPAR: 2015-008A. Apogee: 237 km (147 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
Docked with the ISS Zvezda module at 16:57 GMT the same day as launched. Progress M-26M's engines were used to move the ISS out of the path of some space debris on 23 April and (following a malfunction on May 16) made an ISS orbit reboost on 18 May 18. Progress M-26M undocked 14 August at 10:19 GMT; was deorbited at 13:28 GMT; and impacted the Pacific around 141:7 GMT.
2015 March 27 - . 19:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-16M - .
Call Sign: Altair. Crew: Kelly, Scott,
Korniyenko,
Padalka.
Backup Crew: Ovchinin,
Volkov, Sergey,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Return Crew: Aimbetov,
Mogensen,
Padalka.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 716. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-16M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 168.21 days. Decay Date: 2015-04-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 40540 . COSPAR: 2015-016A. Apogee: 213 km (132 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
Docked with the Poisk module of the ISS at 5 hours 50 minutes after launch. Padalka was the commander, and Kelly and Kornienko were part of a long-duration crew that would spend nearly a year aboard the space station. On 28 August Padalka, Kelly and Kornienko flew Soyuz TMA-16M from the Poisk to Zvezda docking ports. Undocking from Poisk was at 07:12 GMT and docking with Zvezda was at 07:30 GMT. This freed the Poisk port for the TMA-18M arrival, and freed Zvezda for a refuelling spacecraft once TMA-16M returned to Earth. ISS EO- 44 concluded when Soyuz TMA-16M undocked from the Zvezda aft port at 21:29 GMT on 11 September, carrying Expedition 44 commander Padalka and EP-18 visiting crew members Mogensen and Aimbetov. Soyuz TMA-16M landed in Kazakhstan at 00:51:36 GMT on 12 September.
2015 April 28 - . 07:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-2-1a. FAILURE: The third stage did not shut down correctly and damaged the spacecraft during separation.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Progress M-27M - . Payload: Progress M s/n 425 / ISS-59P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress M. Duration: 10.00 days. Decay Date: 2015-05-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 40619 . COSPAR: 2015-024A. Apogee: 258 km (160 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Limited telemetry was obtained from the Progress, but Russian mission control was unable to control the damaged, spinning spacecraft. The Progress reentered over the South Pacific off the southwest coast of Chile at 02:20 GMT on May 8..
2015 July 3 - . 14:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-28M - .
Payload: Progress M s/n 428 / ISS-60P. Mass: 7,250 kg (15,980 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Decay Date: 2015-12-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 40713 . COSPAR: 2015-031A. Apogee: 290 km (180 mi). Perigee: 262 km (162 mi). Inclination: 51.63 deg. Period: 90.03 min.
Carried critical supplies to the ISS after consecutive failures of all three primary resupply spacecraft to reach orbit… a prior Progress, a Cygnus, and a Dragon. Docking was at the Pirs module of the ISS on 5 July at 07:11 GMT. This launch used the older Soyuz-U rocket instead of the newer Soyuz-2-1a which ran into problems on the Progress M-27M launch. Undocked from Pirs at 0735 UTC Dec 19 and was deorbited over the South Pacific, with debris impact at 1128 UTC.
2015 July 22 - . 21:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-17M - . Call Sign: Antares. Crew: Kononenko, Yui, Lindgren. Backup Crew: Kopra, Malenchenko, Peake. Return Crew: Kononenko, Yui, Lindgren. Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 717. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-17M. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA. Duration: 112.67 days. Decay Date: 2015-11-12 13:12:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 40744 . COSPAR: 2015-035A. Apogee: 406 km (252 mi). Perigee: 398 km (247 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.60 min. One solar panel of the Soyuz failed to deploy after launch. Docked with the Rassvet module of the ISS at 02:45 GMT on 22 July..
2015 September 2 - . 04:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-18M - .
Call Sign: Eridanus. Crew: Aimbetov,
Mogensen,
Volkov, Sergey.
Backup Crew: Skripochka,
Pesquet,
Prokopyev.
Return Crew: Volkov, Sergey,
Kelly, Scott,
Korniyenko.
Payload: Soyuz TMA s/n 718. Mass: 7,200 kg (15,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-18M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 181.99 days. Decay Date: 2016-03-02 04:25:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 40885 . COSPAR: 2015-043A. Apogee: 406 km (252 mi). Perigee: 398 km (247 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.60 min.
Docked with ISS at the Poisk port at 07:39 GMT on 4 September. On Mar 2 at 0102 UTC Volkov, Kornienko and Kelly, aboard Soyuz TMA-18M, undocked from the Poisk module, concluding Expedition 46. Tim Kopra then became commander of Expedition 47, with flight engineers Yuriy Malenchenko and Tim Peake. Soyuz TMA-18M made the deorbit burn at 0332 UTC and landed in Kazakhstan at 0426 UTC. Soyuz commander Volkov had spent six months in space, while Kornienko and Kelly completed 340d 8h 21min in space, or about 0.93 years.
2015 October 1 - . 16:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress M-29M - .
Mass: 7,283 kg (16,056 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress M.
Decay Date: 2016-04-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 40944 . COSPAR: 2015-055A. Apogee: 406 km (252 mi). Perigee: 398 km (247 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.60 min.
Docked with the ISS Zvezda module at 22:52 GMT on 1 October. The spacecraft delivered a variety of supplies and maintenance equipment to the station. Progress M-29M undocked from the Zvezda module on Mar 30 at 1415 UTC and performed attitude control experiments in a 373 x 401 km orbit. Progress M-29M was deorbited on Apr 8, reentered around 1416 UTC over the S Pacific.
2015 December 15 - . 11:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-19M - .
Call Sign: Agat. Crew: Malenchenko,
Kopra,
Peake.
Backup Crew: Ivanishin,
Onishi,
Rubins.
Return Crew: Malenchenko,
Kopra,
Peake.
Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-19M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 185.92 days. Decay Date: 2016-06-18 09:15:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 41124 . COSPAR: 2015-076A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 404 km (251 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
Docked with ISS. On Jun 18 Expedition 47 crew members Yuriy Malenchenko, Tim Kopra and Tim Peake transferred from the Rassvet module to Soyuz TMA-19, closing hatches at 0235 UTC and undocking at 0552 UTC. Soyuz TMA-19M made its deorbit burn at 0822 UTC and reentered for a safe landing in Kazakhstan at 0915 UTC.
2015 December 21 - . 08:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-2-1A.
- Progress MS-01 - .
Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress MS.
Decay Date: 2016-07-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 41177 . COSPAR: 2015-080A. Apogee: 279 km (173 mi). Perigee: 270 km (160 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
First Progress-MS cargo ship. Progress-MS was similar to previous Progress ships but with improved onboard systems. It docked with the Pirs module at 1027 UTC Dec 23. Progress MS-01 undocked from the Pirs module at 0536 UTC on Jul 1, backed off to 180m, and redocked at 0605 UTC under TORU remote control. During redocking there was an incorrect thruster firing that made the vehicle swing visibly from side to side. The problem was reportedly under investigation but did not affect Progress MS-01's final undocking, which happened at 0348 UTC Jul 3. Progress MS-01 was deorbited and destroyed over the South Pacifc at 0750 UTC Jul 3.
2016 March 18 - . 21:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz TMA-20M - .
Call Sign: Kazbek. Crew: Ovchinin,
Skripochka,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Backup Crew: Ryzhikov,
Borisenko,
Kimbrough.
Return Crew: Ovchinin,
Skripochka,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz TMA-20M.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz TMA.
Duration: 172.16 days. Decay Date: 2016-09-07 01:13:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 41391 . COSPAR: 2016-018A. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
Soyuz TMA-20M was launched carrying Alexey Ovchinin, Oleg Skripochka and Jeff Williams. This was the last of the 11F732A47 Soyuz TMA-M series, which were replaced by the improved Soyuz-MS variant. On Sep 6 at 2151 UTC Soyuz TMA-20M undocked from the Poisk module with Ovchinin, Skripochka and Williams. The spacecraft laded in Kazakhstan at 0113 UTC on Sep 7.
2016 March 31 - . 16:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-2-1A.
- Progress MS-02 - . Nation: Russia. Agency: RKA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Progress MS. Decay Date: 2016-10-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 41436 . COSPAR: 2016-022A. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 261 km (162 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Docked with Zvezda on Apr 2 at 1758 UTC..
2016 July 7 - . 01:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-01 - .
Call Sign: Irkut. Crew: Ivanishin,
Onishi,
Rubins.
Backup Crew: Novitskiy,
Pesquet,
Whitson.
Return Crew: Ivanishin,
Onishi,
Rubins.
Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-01.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz MS.
Duration: 115.10 days. Decay Date: 2016-10-30 03:58:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 41639 . COSPAR: 2016-044A. Apogee: 239 km (148 mi). Perigee: 181 km (112 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg.
Launched on into a 181 x 239 km orbit; docked with the ISS Rassvet module at 0406 UTC Jul 9. The Soyuz MS was a new variant of the ferry ship with upgraded onboard systems. Crew was Anatoliy Ivanishin (Roscosmos), Takuya Onishi (JAXA) and Kate Rubins (NASA). On Oct 30 at 0035 UTC Ivanishin, Onishi and Rubins undocked from Rassvet in Soyuz MS-01; they landed in Kazakhstan at 0358 UTC.
2016 July 16 - . 21:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress MS-03 - .
Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress MS.
Decay Date: 2017-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 41670 . COSPAR: 2016-045A. Apogee: 225 km (139 mi). Perigee: 182 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
Progress MS-03 cargo ship docked with the Pirs module at 0020 UTC Jul 19. It carried 2405 kg of cargo (including 705 kg of ISS propellant) as well as 880 kg of its own onboard propellant. Undocked at 1425 UTC and was deorbited at 1734 UTC with impact in the South Pacific at 1824 UTC.
2016 October 19 - . 08:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-02 - .
Call Sign: Favor. Crew: Ryzhikov,
Borisenko,
Kimbrough.
Backup Crew: Misurkin,
Tikhonov,
Vande Hei.
Return Crew: Ryzhikov,
Borisenko,
Kimbrough.
Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-02.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz MS.
Duration: 173.14 days. Decay Date: 2017-04-10 11:20:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 41820 . COSPAR: 2016-063A. Apogee: 306 km (190 mi). Perigee: 289 km (179 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
Soyuz MS-02 with astronauts Sergey Ryzhikov, Andrey Borisenko and Shane Kimbrough. They docked with the Poisk module at 0952 UTC Oct 21. On Apr 10, Soyuz MS-02 undocked from Poisk at 0757 UTC and landed in Kazakhstan at 1120 UTC, returing Ryzhikov, Borisenko and Kimbrough to Earth. Peggy Whitson became ISS commander of Expedition 51.
2016 November 17 - . 20:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-03 - . Call Sign: Kazbek. Crew: Novitskiy, Pesquet, Whitson. Backup Crew: Yurchikhin, Fischer, Nespoli. Return Crew: Novitskiy, Pesquet. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-03. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. Decay Date: 2017-06-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 41864 . COSPAR: 2016-070A. Apogee: 228 km (141 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Soyuz MS-03 was launched with the crew of Oleg Novitskiy (Roskosmos), Thomas Pesquet (ESA) and Peggy Whitson (NASA). The Soyuz docked with the ISS Rassvet module at 2158 UTC Nov 19..
2016 December 1 - . 14:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U. FAILURE: Third stage continued burning after payload separation.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Progress MS-04 - .
Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress MS.
COSPAR: 2016-0F02. Apogee: 190 km (110 mi). Perigee: -4,000 km (-4,000 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
The launch vehicle failed during third stage burn and its debris fell in the Tuva Republic. Lost with the rest of the cargo was the first Orlan-MKS spacesuit. Reports suggested the Progress separated from the rocket third stage prematurely and the accelerating stage then crashed into the Progress.
2017 February 22 - . 05:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-U.
- Progress MS-05 - .
Nation: Russia.
Agency: RKA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Progress MS.
Decay Date: 2017-07-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 42056 . COSPAR: 2017-010A. Apogee: 210 km (130 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
See Progress-MS 05. Launched of the final Soyuz-U-PVB rocket. Among other cargo the Progress cargo craft carried a new Orlan-MKS spacesuit. The ship docked with the Pirs module at 0830 UTC Feb 24.
2017 April 20 - . 07:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-04 - .
Call Sign: Olympus. Crew: Yurchikhin,
Fischer.
Backup Crew: Ryazansky,
Bresnik.
Return Crew: Yurchikhin,
Fischer,
Whitson.
Nation: Russia.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-04.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz MS.
Decay Date: 2017-09-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 42682 . COSPAR: 2017-020A. Apogee: 409 km (254 mi). Perigee: 399 km (247 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.66 min.
See Soyuz-MS 04. Soyuz MS-04 docked with the ISS Poisk module 6hr 4min after launch. Soyuz commander was Fyodor Yurchikin and flight engineer was Jack Fischer. This was the first two-person Soyuz mission in 14 years (Soyuz TMA-2 in Apr 2003), as Russia scaled back its ISS crew pending completion of the delayed Nauka module.
2017 July 28 - . 15:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-05 - . Call Sign: Borei. Crew: Ryazansky, Bresnik, Nespoli. Backup Crew: Misurkin, Vande Hai, Kanai. Return Crew: Ryazansky, Bresnik, Nespoli. Payload: Soyuz 11F732A48 No. 736. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-05. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. USAF Sat Cat: 42898 . COSPAR: 2017-043A. Apogee: 407 km (252 mi). Perigee: 403 km (250 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.66 min. See Soyuz-MS 05. ..
2017 September 12 - . 21:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-06 - . Call Sign: Altair. Crew: Misurkin, Vande Hai, Acaba. Backup Crew: Shkaplerov, Tingle, Walker, Shannon. Return Crew: Misurkin, Vande Hai, Acaba. Payload: Soyuz 11F732A48 No. 734. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-06. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. USAF Sat Cat: 42937 . COSPAR: 2017-054A. Apogee: 407 km (252 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.65 min. See Soyuz-MS 06. ..
2017 December 17 - . 07:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-07 - . Call Sign: Astraeus. Crew: Shkaplerov, Tingle, Kanai. Backup Crew: Prokopyev, Gerst, Epps. Return Crew: Shkaplerov, Tingle, Kanai. Payload: Soyuz 11F732A48 No. 737. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-07. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. USAF Sat Cat: 43063 . COSPAR: 2017-081A. Apogee: 407 km (252 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.66 min. See Soyuz-MS 07. ..
2018 March 21 - . 17:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-08 - . Call Sign: Hawaii. Crew: Artemyev, Feustel, Arnold. Backup Crew: Ovchinin, Hague. Return Crew: Artemyev, Feustel, Arnold. Payload: Soyuz 11F732A48 No. 738. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-08. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. USAF Sat Cat: 43238 . COSPAR: 2018-026A. Apogee: 408 km (253 mi). Perigee: 403 km (250 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.68 min. See Soyuz-MS 08. ..
2018 June 6 - . 11:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-09 - . Call Sign: Altai. Crew: Prokopyev, Gerst, Aunon. Backup Crew: Kononenko, Saint-Jacques, McClain. Return Crew: Prokopyev, Gerst, Aunon. Payload: Soyuz 11F732A48 No. 739. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-09. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. USAF Sat Cat: 43493 . COSPAR: 2018-051A. Apogee: 408 km (253 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.66 min. See Soyuz-MS 09. ..
2018 October 11 - . 08:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-10 - . Call Sign: Burlak. Crew: Kononenko, Saint-Jacques, McClain. Backup Crew: Skvortsov, Parmitano, Morgan, Andrew. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-10. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. COSPAR: 2018-F01. See Soyuz-MS 10. ..
2018 December 3 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Soyuz MS-11 - . Call Sign: Antares. Crew: Ovchinin, Hague. Backup Crew: Kononenko, Saint-Jacques. Return Crew: Ovchinin, Hague. Nation: Russia. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz MS-11. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz MS. USAF Sat Cat: 43756 . COSPAR: 2018-098A. Apogee: 411 km (255 mi). Perigee: 404 km (251 mi). Inclination: 51.64 deg. Period: 92.71 min. See Soyuz-MS 11. ..
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use

