Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Proton
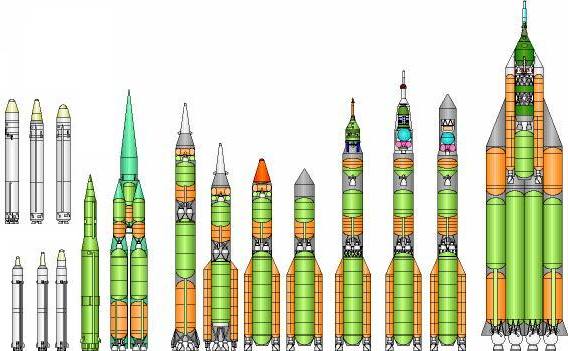
Universal Rockets
Chelomei's Universal Rocket Family. From left to right: UR-100 (three variants) and UR-100N (three variants). UR-200. Original UR-500 configuration, composed of clustered UR-200's. Conventional UR-500 monoblock configuration. Selected UR-500 polyblock configuration. UR-500 two-stage configuration - ICBM version and as flown. UR-500K configuration with LK-1; with Block D upper stage and L1; with Block D upper stage for satellite launch. UR-700.
Credit: © Mark Wade
Status: Active. First Launch: 2014-12-27. Last Launch: 2014-12-27. Number: 1 .
Development of the Proton began in 1962 as a two-stage vehicle that could be used to launch large military payloads or act as a ballistic missile with a 100 megaton nuclear warhead. The ICBM was cancelled in 1965, but development of a three-stage version for the crash program to send a Soviet man around the moon began in 1964. The hurried development caused severe reliability problems in early production. But these were eventually solved, and from the 1970's the Proton was used to launch all Russian space stations, medium- and geosynchronous orbit satellites, and lunar and planetary probes.
The Proton had its origin in the early 1960's, at a time when all Soviet rockets required military justification to be developed. At this time the military-political leadership formulated a requirement for a heavy rocket that could be used to launch large military payloads into space as well as act as a ballistic missile for nuclear warheads up to 100 MT in yield.
There were competitors for the original military Global Rocket 2 (GR-2) requirement.
The OKB-1 of S P Korolev had begun design of the enormous N1 lunar rocket, and had already put the Soviet Union first in ballistic missiles and space through use of its R-7 ICBM. Korolev was working on the successor R-9 ICBM, and the NII variant of the N1 (using the top two stages) could meet the GR-2 requirement.
M K Yangel's KB Yuzhnoye proposed creation of two related launch vehicles to fulfill the military requirement - the R-46 heavy ICBM and the R-56 launch vehicle. These would cover the entire range of military requirements. Yangel's OKB had already supplied the military with the great majority of its operational strategic rockets - the R-12 and R-14 IRBM's and the R-16 ICBM.
OKB-52, under V N Chelomei, proposed to create a related family of rockets, each designed from the beginning for dual use as ballistic missiles and space launchers - the medium UR-200, the heavy UR-500 and the huge UR-700 for lunar requirements.
By 16 March and 1 August 1961 the Central Committee and Politburo had approved development of the UR-200 (8K81) universal rocket. The UR-200 draft project was completed in July 1962.
The GR-2 project required that the factory-completed modules of the rocket be transported by rail to the launch complex, quickly assembled at the site, followed by automatic erection and launch. Approval to proceed with the UR-500 8K82 was provided in the Central Committee decree of 24 April 1962. However Chelomei had begun studies on the design considerably earlier, in the second half of 1961.
At first the launch vehicle was simply to consist of 4 two-stage UR-200 rockets lashed together, the first and second stages working in parallel in clusters. A third stage would be modified from the UR-200 second stage. (Yangel proposed a similar solution, his R-56 rockets being composed of R-46's clustered together). However study of this configuration, which included manufacturing of a dynamic test article (now in the TsNIIMASH museum), indicated that the payload capacity could not meet the military's requirements.
The selected solution was to develop a conventional tandem three-stage vehicle. The upper two stages would be modified versions of the UR-200 first and second stages. However the first stage would have to be a new design. There were two logical solutions, both of which were implemented by the Americans in their rockets of the same class: to take a two stage rocket and attach large solid fuel boosters in parallel to the central body, as was done in the Titan 3C design; or to build a new powerful first stage, as was done on the Saturn I rocket. Chelomei additionally had to consider what would be needed for his UR-700 lunar launch vehicle. His solution was to build a core module of the largest possible rail-transportable diameter (4.15 m). This could consist of an oxidizer tank, or a fuel tank with the engine installation. The design had to meet requirements from two sides. On the one hand, the maximum length and diameter of the modules was dictated by the size of rail wagons and platforms, and existing rail tunnels, waterways, and turntables. On the other hand, the size of the rocket stage, and its corresponding volume and mass, were driven by the UR-500 launch mass and characteristics of the future UR-700.
Two variants of the first stage were considered: polyblock and monoblock. The monoblock approach was that the first stage be assembled from two separate modules with the same diameter: an upper oxidizer module and a lower fuel and engine block. In assembly trials of this design it proved difficult, because of the height of the first stage, to obtain access to the upper stages and payload atop the rocket. The payload advantage of this design was relatively small compared to the alternative. This variant was studied by Chelomei's Filial Number 1, Chief Designer V N Bugayskiy, under the lead engineer M S Mishetyan.
The second (polyblock) variant consisted of a center large diameter oxidizer tank surrounded by several smaller diameter fuel tanks. This version could be assembled in a special rig with the lateral blocks being sequentially mounted on the center. This had the advantage of easier installation of the upper stages and payload due to the smaller length of the first stage. This variant was studied in Filial 1 under the lead engineer E. T. Radchenko. In January 1962 this design was chosen as most advantageous, following studies that indicated improved wind loads and bending moment characteristics compared to the monoblock design. The polyblock design received patent number 36616 in 26 July 1966. Named on the patent were V N Chelomei, V N Bugayckiy, V A Birodov, G D Dermichev, N I Yegorov, V K Karrask, Yu P Kolesnikov, Ya B Nodelman, and E T Radchenko.
Another key issue was the selection of the engine for the first stage. In order that the rocket could meet the quick response requirements of the military, it was decided that it would use storable liquid fuels. These would allow the fuelled rocket to be held in readiness for quick launch over a wide range of temperature conditions and eliminate the need for thermostatically controlled storage of the rocket. Nitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) and unsymmetrical di-methyl hydrazine (UDMH) had already been selected as the propellants for the UR-200 and therefore for the corresponding upper stages of the UR-500. However the largest rocket engine developed for the UR-200 was the 50 metric ton thrust 8D45 engine of S A Kosberg's KBKhA design bureau. By the beginning of work on the UR-500 more than 700 trials of this engine had been undertaken, including 225 resource trials. The advantage of using this engine was that it could contribute to the desired short length of the first stage. However the drawback was that to achieve the required first stage thrust, 15 to 16 engines would have to be clustered, which, from the point of view of V N Chelomei, was much too many.
In November 1961 OKB-52 began to collaborate with V P Glushko's OKB-456 in developing a more appropriate engine. Glushko had completed a storable liquid engine design of 150 metric tons for use in Korolev's N1. However Korolev refused to accept this design, due to his refusal to use toxic propellants in his rockets and his belief that such propellants could never deliver the required specific impulse. Korolev insisted on development of an oxygen-kerosene engine; Glushko categorically refused to do so. As a result, the two leading Soviet rocket designers irrevocably split. Korolev had to turn for development of his N1 engines to the aviation engine OKB of N D Kuznetsov.
Since Chelomei agreed with Glushko on the selection of propellants, Glushko's N1 engine instead went into the first stage of the UR-500. In May 1962 advanced project UR-500 was published. The initial design featured four fixed Glushko engines mounted below the core, with four gimbaled Kosberg engines on the lateral tanks. The second stage of the UR-500 was a larger-diameter variant of the first stage of the UR-200, with the engines gimbaled for directional control. The third stage used the UR-200's fixed engine with a four-nozzle steering engine. In order to meet the constant diameter requirement the third stage used toroidal propellant tanks.
Development of the engines and further elaboration of the study led to modifications to the original design of the first stage. Glushko conducted tests of the new engine from 1961 to 1963, followed by tests of the clustered engine assembly from June 1963 to January 1965. Through use of a regenerative fuel pump cycle Glushko was able to improve the thrust of the engine by 12.5%. It was therefore decided to use only the large Glushko engine in the first stage. The first layout had one engine at the base of the core and 4 to 8 fuel tanks with peripheral engines. Now the center engine was abandoned and the 'clean' oxidizer tank core was surrounded by six fuel tank/engine assemblies. This had the advantage of reducing the length of the stage while increasing the dry weight fraction.
The 29 April 1962 decree ordered development of this powerful new rocket to be completed within three years. This was a difficult task, considering the factory and launch facilities that would have to be built to allow testing of the rocket to begin. Head of the original UR-500 development team was P A Ivensen. In 1962 this role was taken by Yu N Trufanov. At the project stage the technical parameters of the rocket were developed by D A Polukhin (subsequently chief of the team), V K Karrask, G D Dermichev, V A Virodov, E T Radchenko, E S Kulaga, N N Mirkin, Yu P Kolosnov, V F Gusev, and A T Tarasov.
The launch complex at Tyuratam was designed and built by GSKB Spetsmash in accordance with a decree of 26 May 1962. There were two pads, located 600 m apart and shielded against rocket explosions so that on-pad failure of a vehicle would not destroy the complex.
As payloads for the UR-500, Chelomei considered a broad spectrum of space craft, destined to solve defense, scientific investigation, and national economic tasks. These were to be called raketoplans - piloted spacecraft for solving military tasks in space. For example, orbital raketoplans were intended to fulfill intelligence, satellite inspection, and destruction tasks. For these purposes the raketoplan was to be equipped with an orbital maneuvering engine, targeting systems, rendezvous systems, and space-to-space weapons. Later raketoplans would be used for scientific tasks, including flight to the moon and return to earth, and economic exploitation of near-earth space. Due to their high lift to drag ratios, raketoplans could, after completing their tasks in space, make a guided descent into the earth's atmosphere with a landing on Soviet territory.
The draft project UR-500 was completed in 1963. The fundamental technological problems of the project had been solved by the end of 1964. In the early fall of that year, Khrushchev and the political leadership of the country visited Baikonur. Chelomei with great pride guided Khrushchev around a dummy UR-500 installed in its launch gantry at the new launch complex, presented the heavy transporters for the launch vehicle and showed a scale model of the launch silo planned for the combat version. Khrushchev's comment was 'what should we build - communism or silos for the UR-500?' It was clear that Khrushchev was not very supportive of the military version of the UR-500…
Soon thereafter Khrushchev was ousted from power and the new leadership, under Brezhnev, was adverse to all projects Khrushchev had supported. This included Chelomei and his OKB-52. An expert commission under M V Keldysh was directed to examine all of Chelomei's projects and make recommendations as to which should be cancelled. Keldysh found that Yangel's R-36 universal rocket was superior to Chelomei's UR-200. The UR-200 was accordingly cancelled. The UR-500 was to continue, not as a huge ICBM but only in the space launcher role. The raketoplan was stopped, but work on the high-priority LK-1manned lunar flyby program continued.
In the spring of 1965, when Chelomei's activities were still under investigation, the Khrunichev factory completed construction of the first UR-500. In place of the third stage, an automated space physics laboratory 'Proton', for measurement of high energy particles, was built. The Proton satellites used the structural shell of the rocket's third stage.
All of the components were shipped by rail to Tyuratam for launch from the new rocket complex on the left ('Chelomeevskoy') arm of the range. The rocket was assembled in the Proton MIK assembly building at site 92 at Baikonur. The special transporter-installer took the rocket by rail from the MIK to launch site number 81, and the rockets was raised from the horizontal to the vertical position and installed on the launch table. Unlike the R-7 'Semyorka', the '500 was not suspended above the flame pit but fastened by its tail directly on the launch table. The UR-500 had a very cleanly designed compound umbilical cable which connected all services to a single coupling in the base of the core oxidizer tank. This umbilical remained connected until the rocket reached a height of 100 to 150 mm, then automatically detached and was retracted into a protective cover on the launch pad. Doors also closed on the launch vehicle, making a hermetic seal.
The first launch was not without problems. A leak in the oxidizer pipeline resulted in nitrogen tetroxide spilling on electrical wires. The question was: proceed with the launch or abort? Chelomei decided to go ahead, and on 16 July 1965 the first UR-500 successfully launched the Proton 1 satellite. In the first hours after launch specialists from OKB-52 could only receive signals in the first hours that indicated the satellite was 'alive'. However it later functioned normally and provided physics data for 45 days.
Aside from its index 8K82 and 'company' designation UR-500, at the first launch the rocket was called 'Gerkules' (other sources say 'Atlantis'), as indicated by the large symbol on the second stage skin. This name was however was not taken up. In the open press it was known only by the name of its first payload, 'Proton'.
Flight trials of the two-stage variant of the rocket went through 6 July 1966. In four launches three heavy Proton satellites reached orbit. The third launch failed when the second stage cut off, and the rocket crashed in the Akmolinsk region. The payload capacity of the Proton was given in the press as 12.2 metric tons; however this included the empty mass of the last stage. The payload of the two-stage version was really only 8.4 metric tons, only 24% more than Korolev's Soyuz rocket based on the R-7, even though the UR-500 was 75% larger. These deficiencies would be rectified in the three-stage version, fully developed in accordance with the decree of 3 August 1964.
More at: Proton.
| Initial UR-500 While Chelomei's OKB was still preparing the UR-200 draft project, it was proposed to use this as the basis for the UR-500 heavy universal rocket, with five times the payload capacity. These initial 1961 studies consisted of 4 two-stage UR-200 rockets lashed together, the first and second stages working in parallel in clusters. A third stage would be modified from the UR-200 second stage. However analysis indicated that the payload capacity could not meet the military's requirements. |
| Monoblock UR-500 During UR-500 design studies, two variants of the first stage were considered: polyblock and monoblock. The monoblock approach was that the first stage be assembled from two separate modules with the same diameter: an upper oxidizer module and a lower fuel and engine block. In assembly trials of this design it proved difficult, because of the height of the first stage, to obtain access to the upper stages and payload atop the rocket. Although there was a payload advantage compared to the more compact polyblock design, this was relatively small and outweighed by the operational difficulties. |
| Polyblock UR-500 UR-500 design studies considered two variants of the first stage: polyblock and monoblock. The polyblock variant consisted of a center large diameter oxidizer tank surrounded by several smaller diameter fuel tanks. This version could be assembled in a special rig with the lateral blocks being sequentially mounted on the center. In January 1962 this design was chosen as most advantageous, following studies that indicated improved wind loads and bending moment characteristics compared to the monoblock design. The developed version of the design would become known as the Proton. |
| Proton/Briz K/M Earlier 8K82K model Proton, but Briz M storable propellant upper stage replaced the Block D cryogenic stage. |
| Proton-K Development of a three-stage version of the UR-500 was authorized in the decree of 3 August 1964. Decrees of 12 October and 11 November 1964 authorized development of the Almaz manned military space station and the manned circumlunar spacecraft LK-1 as payloads for the UR-500K. Remarkably, due to continuing failures, the 8K82K did not satisfactorily complete its state trials until its 61st launch (Salyut 6 / serial number 29501 / 29 September 1977). Thereafter it reached a level of launch reliability comparable to that of other world launch vehicles. |
| Proton-K Blok-DM1 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-K Blok-DM2 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-K Blok-DM3 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-K Blok-DM4 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-K/17S40 Version of Proton using Block DM-5 / 17S40 fourth stage. This stage has a new payload adapter for use with heavier payloads launched into sub-synchronous orbits. Used for launch of Arkon reconnaissance satellite. |
| Proton-K/17S40 DM2 Version of the 17S40 with payload adapter for deployment of multiple LM 700 (Iridium) spacecraft into medium earth orbit. |
| Proton-K/D This four stage version of the Proton was originally designed to send manned circumlunar spacecraft into translunar trajectory. Guidance to the Block D stage must be supplied by spacecraft. The design was proposed on 8 September 1965 by Korolev as an alternate to Chelomei's LK-1 circumlunar mission. It combined the Proton 8K82K booster for the LK-1 with the N1 lunar Block D stage to boost a stripped-down Soyuz 7K-L1 spacecraft around the moon. The Korolev design was selected, and first flight came on 10 March 1967. The crash lunar program led to a poor launch record. Following a protracted ten year test period, the booster finally reached a level of launch reliability comparable to that of other world launch vehicles. |
| Proton-K/D-1 This derivative of the original four stage Block D / 11S824 version of the Proton was used from 1978 to launch Lavochkin OKB planetary probes (Mars, Venera) and high earth orbit astronomical observatories (Astron, Granat). Guidance to the Block D-1 stage must be supplied by spacecraft. Equipped with N2O4/UDMH verniers for precise placement of payloads in high orbits or planetary trajectories. |
| Proton-K/D-2 This four stage version of the Proton was a modification of the original Block D / 11S824M for launch of late 1980's Lavochkin OKB probes on missions to Mars. Guidance to the Block D-2 stage must be supplied by spacecraft. |
| Proton-K/DM The original four stage Proton / Block D configuration was used until 1976, at which time it was replaced by a modernized version equipped with N2O4/UDMH verniers for precise placement of payloads in geosynchronous orbit and its own self-contained guidance unit. This was accepted into military service in 1978 with the first Raduga launch. The stage was first developed for launch of geosynchronous military communications and early warning satellites (Raduga, Ekran, Gorizont, Potok, SPRN). Its later versions continue in use for launch of MEO and geosynchronous communication satellites, and was Russia's most successful commercial launcher. |
| Proton-K/DM-2 This improved four stage version uses the Block DM-2 / 11S861 fourth stage, which has its own guidance unit. This reduces payload but does not require the spacecraft's guidance system to provide steering commands to booster. Replaced the original Block DM / 11S86 version from 1982 to 1995. Used for launch of Glonass navigation satellites into medium earth orbit; and launch of Luch, Ekran-M, Potok, Raduga, Gorizont, Raduga-1, Elektro, and Gals communications satellites into geosynchronous orbit. Commercial version with Saab payload adapter-separation system for Western payloads was dubbed 'Block DM1'. |
| Proton-K/DM-2 DM1 Version of the 11S861 with adapter for Lockheed Martin AS 4000 bus spacecraft. |
| Proton-K/DM-2M This four stage version uses the Block DM-2M / 11S861-01 upper stage, which has its own self-contained guidance unit. This reduces payload but does not require the spacecraft's guidance system to provide steering commands to booster. Used for launches of Russian geosynchronous satellites from 1994 on. |
| Proton-K/DM-2M DM3 Version of the 11S861-01 with Saab payload adapter-separation system for insertion of Hughes HS-601 bus spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit. |
| Proton-K/DM-2M DM4 Version of the 11S861-01 with Saab payload adapter-separation system for insertion of FS-1300 bus spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit. |
| Proton-M Briz-M 2 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M Briz-M P1 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M Briz-M P1M1 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M Briz-M P1M2 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M Briz-M P2 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M Briz-M P2M Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M Briz-M P3 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M Briz-M P4 Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Proton-M/Briz-M Improved Proton orbital launch vehicle. Improvements in lower stages to reduce structural mass, increase thrust, and fully utilize propellants (reducing release of toxic chemicals in stage impact areas). Briz M storable propellant upper stage replaces Block D cryogenic stage. |
| Proton-M/DM-2 Improved Proton-M, mated to the older 11S861 upper stage rather than the Briz-M for certain payloads. |
| Proton-M/DM-3 Improved Proton-M, mated to the older DM-3 upper stage rather than the Briz-M for certain payloads. |
| UR-500 The original UR-500 two stage configuration was designed as a monster ICBM. It was flown four times from 1965, but never deployed as an operational missile. The design was succeeded by three and four stage versions for launching of large payloads into space. |
| UR-500MK In 1975 Chelomei proposed this version of the Proton powered by LOx/kerosene NK-33 engines developed for the cancelled N1 moon booster. This would give the Soviet Union an equivalent to the all-new Zenit-2 booster being developed by Glushko, but at a fraction of the time and expense through the use of existing components. The proposal had no chance politically, and was never seriously considered. |
| UR-530 1976 design for an upgraded Proton, replacing the first stage with a cluster of six modular stages derived from the UR-100N first stage. Detail design to the draft project stage was undertaken in 1976-1977 but the much larger and more expensive Energia/Buran system was selected for development instead. |
Family: orbital launch vehicle, Soviet Space Stations, Space station, Space station orbit. People: Chelomei. Country: Russia. Engines: RD-0225. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000, Ekspress-2000, LK-1, TGR, Almaz APOS, Molniya-1, N-4, Soyuz 7K-L1, Orlan, N-6, Luna Ye-8, Mars M-69, Luna Ye-8-5, Soyuz 7K-L1E, Salyut 1, Mars M-71, Luna Ye-8-LS, DLB Beacon Lander, Almaz OPS-2, Almaz OPS, Salyut 4, Mars M-73, Raduga, Luna Ye-8-5M, Venera 4V-1, Prognoz SPRN, Mir-2, Ekran, TKS VA, OPS + TKS, KSI, TKS, Salyut 6, Gorizont, Mars 5M, USB, 37K-Mir, Iskra, Salyut 7, Potok, Glonass, LKS, Astron, Venera 4V-2, Tselina-2, Vega 5VK, Luch, AS 4000, Vega 5VS, Mir, Almaz-T, Ekran-M, Kvant, Eurostar 2000, Fobos 1F, KS space station, Etalon, FS-1300, Raduga-1, Kvant-2, Granat, HS 601, Kristall, Tellura, Mak, Spektr - Original, Almaz-1B, Gals, Ekspress, Elektro, Spektr, Almaz-2, Priroda, Spacebus 3000, AS 2100, Mars M1, LM 700, Arkon-1, Kupon, Star bus, ISS Zarya, Yamal, LMI, HS 702, ISS Commercial Enterprise Module, ISS Zvezda, Integral, Cubesat, Spacebus 4000, Eurostar 3000, DS2000, Yakhta, Garpun. Propellants: N2O4/UDMH. Launch Sites: Baikonur, Baikonur LC200/39. Agency: RVSN, Chelomei bureau, MOM, SES. Bibliography: 107, 111, 112, 118, 120, 150, 151, 154, 163, 181, 191, 193, 195, 2, 219, 23, 273, 274, 276, 279, 296, 299, 367, 376, 42, 428, 439, 443, 445, 474, 475, 476, 552, 554, 6, 67, 72, 76.
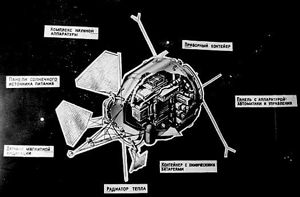 | N-4 Spacecraft Cutaway view of N-4 spacecraft. This heavy high-energy physics station was launched on the first four test launches of the Proton launch vehicle. Credit: Chelomei School, Leninsk |
 | UR-100 and UR-500 UR-100 and UR-500 Dynamic test models Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | UR-500DH2 Memorial Museum of Cosmonautics, June 1994 Credit: © Dietrich Haeseler |
 | Proton UR-500 Proton two stage configuration as flown in the first four launches. This version had a shorter second stage than the UR-500K that followed and only 40% of the payload. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Proton UR-500 Model of the Proton UR-500 two stage configuration as first flown. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Proton UR-500 The very first Proton UR-500 is enclosed by its launch gantry. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Proton 8K82K Proton 8K82K launch vehicle in its original form, with Chelomei's manned LK-1 circumlunar spacecraft as the payload. Credit: © Mark Wade |
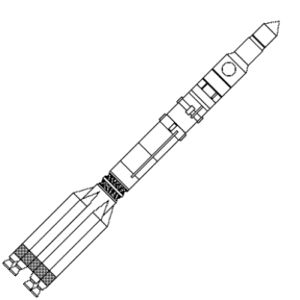 | Proton K LV Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Proton 8K82K Proton 8K82K launch vehicle with Kristall space station payload Credit: Lockheed Martin |
 | UR-200 and UR-500 Dynamic test models of UR-200 ICBM and early Proton concept 'collection of UR-200's' Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Proton 8K82K/DM Proton 8K82K / Block DM launch vehicle Credit: Lockheed Martin |
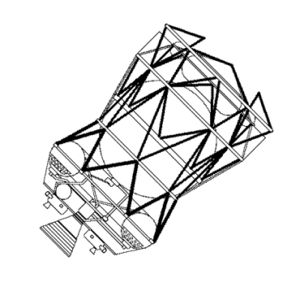 | Block D Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Proton liftoff Credit: Lockheed Martin |
 | UR-500 / L1 Rollout Credit: RKK Energia |
 | Proton w/ LK Proton 8K82K Block D launch vehicle with Soyuz 7K-L1 manned circumlunar spacecraft. |
 | Proton 8K82K / 11S82 Proton 8K82K / 11S824M with Vega payload - COSPAR 1984-128 |
 | Proton 8K82K / 11S82 Proton 8K82K / 11S824F with Phobos payload - COSPAR 1988-058 |
 | Proton sunrise Credit: Lockheed Martin |
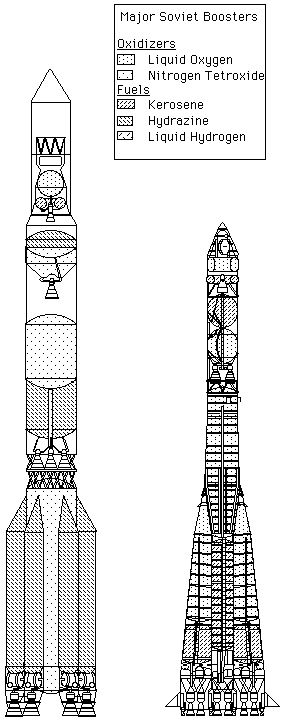 | R-7 vs Proton R-7 / Proton LVs Cutaway Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Protpyld Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Proton launch Credit: Lockheed-Martin |
 | Proton Iridium Proton Iridium payload preparation in former Buran payload facility. Credit: © Mark Wade |
1961 During the Year - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Initial UR-500.
- Initial UR-500 studies for the GR-2 requirement - . Nation: Russia. The initial design consisted simply of 4 two-stage UR-200 rockets lashed together, the first and second stages working in parallel in clusters. A third stage would be modified from the UR-200 second stage..
1961 August 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Chelomei begins UR-500 Proton design studies. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau.
Program: GR-2.
At first the launch vehicle was simply to consist of 4 two-stage UR-200 rockets lashed together, the first and second stages working in parallel in clusters. A third stage would be modified from the UR-200 second stage. However study of this configuration, which included manufacturing of a dynamic test article, indicated that the payload capacity could not meet the military's requirements.
1961 November - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Preliminary design work by Chelomei on UR-500 (Proton) rocket. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Glushko,
Korolev.
OKB-52 began to collaborate with V P Glushko's OKB-456 in developing an appropriate engine. Glushko had completed a storable liquid engine design of 150 tonnes for use in Korolev's N1. However Korolev refused to accept this design, due to his refusal to use toxic propellants in his rockets and his belief that such propellants could never deliver the required specific impulse.
1961 November 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Development of RD-253 engine begun. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Glushko,
Korolev.
Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau.
Program: GR-2.
OKB-52 began to collaborate with V P Glushko's OKB-456 in developing a high thrust storable propellant engine for the UR-500 Proton launch vehicle. Glushko had completed a storable liquid engine design of 150 tonnes for use in Korolev's N1. However Korolev refused to accept this design, due to his categorical refusal to use toxic propellants in his rockets and his belief that such propellants could never deliver the required specific impulse. Korolev insisted on development of an oxygen-kerosene engine; Glushko categorically refused to do so. As a result, the two leading Soviet rocket designers irrevocably split. Korolev had to turn for development of his N1 engines to the aviation engine design OKB of N D Kuznetsov.
1962 January - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Proton design selected - . Nation: Russia. This 'polyblock' design was chosen for the Proton launch vehicle, following studies that indicated improved wind loads and bending moment characteristics compared to the monoblock design..
1962 January 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Proton configuration selected. - . Nation: Russia. Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau. Program: GR-2. The 'polyblock' design was chosen as most advantageous, following studies that indicated improved wind loads and bending moment characteristics compared to the conventional 'monoblock' design..
1962 April 24 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Approval to proceed with the UR-500 (8K82) was provided in a Central Committee decree - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: LK-1.
Council of Soviet Ministers (SM) Decree 'On start of work on the UR-500 missile and carrier-rocket' was issued. The rocket was to be built initially for the GR-2 requirement - a heavy rocket that could be used to launch large military payloads into space as well as act as a ballistic missile for multiple nuclear warheads up to 100 MT in yield. The decree ordered development of this powerful new rocket to be completed within three years. This was a difficult task, considering the factory and launch facilities that would have to be built to allow testing of the rocket to begin. The draft project UR-500 was completed in 1963.
1962 May - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Advanced project for the Proton UR-500 completed - .
Nation: Russia.
The initial design featured four ungimballed Glushko engines mounted below the core, with four steerable Kosberg engines on the lateral tanks. The second stage of the UR-500 was a larger-diameter variant of the first stage of the UR-200, with the engines gimballed for directional control. The third stage used the UR-200's fixed engine with a four-nozzled steering engine. In order to meet the constant diameter requirement the third stage used toroidal propellant tanks.
1962 May 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- UR-500 advanced project published. - . Nation: Russia. Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau. Program: GR-2.
1963 June - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Tests of clustered Proton engines begun - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Glushko.
Glushko conducted tests of the new engine from 1961 to 1963, followed by tests of the clustered engine assembly from June 1963 to January 1965. Through use of a regenerative fuel pump cycle Glushko was able to improve the thrust of the engine by 12.5%. It was therefore decided to use only the large Glushko engine in the first stage. The first layout had one engine at the base of the core and 4 to 8 fuel tanks with peripheral engines. Now the centre engine was abandoned and the 'clean' oxidiser tank core was surrounded by six fuel tank/engine assemblies. This had the advantage of reducing the length of the stage while increasing the dry weight fraction.
1963 June 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- First tests of RD-253 engine cluster for Proton. - . Nation: Russia. Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau. Program: GR-2. Ground tests of the clustered engine assembly ran from June 1963 to January 1965..
1964 August 15 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Chief Designers review of Voskhod at OKB-1 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Khrushchev, Sergei.
Program: Voskhod.
Flight: Voskhod 1.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Voskhod.
All concerned designers, bureaux, and institutes certify the reliability of the systems of the spacecraft and launch vehicle. The second phase of trials of the soft landing system have been successful. Of 10 drops, 9 landed with vertical velocity under 7.5 m/s, and of those, 6 landed with a speed of only 0.0 to 1.5 m/s. There are still concerns about how the system will function in soft soils or adverse weather conditions. Nevertheless the decision is taken to ship the spacecraft to the cosmodrome for final preparations between 18 and 25 August. It is likely that the manned flight cannot occur until the end of September. Later in the day Kamanin is visited by Sergei Nikitovich Khrushchev and other experts from Chelomei's design bureau. They brief Kamanin on plans for a manned circumnavigation of the moon using their spacecraft launched by their UR-500 booster by the end of 1967.
1964 October 12 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Almaz project starts - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Spacecraft: Almaz APOS,
Soyuz R.
The day before the overthrow of his patron, Chelomei obtained permission to begin development of a larger military space station, the Almaz. This 20 tonne station would take three cosmonauts to orbit in a single launch of his UR-500K Proton rocket. Therefore there were now two competing projects for the same mission - Almaz and Soyuz-R. First flight of the Almaz, with a one year operational period, was set for 1968.
1964 November 11 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Development of the manned circumlunar spacecraft LK-1 authorised - . Nation: Russia.
1965 July 16 - . 11:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: UR-500.
- Proton 1 - .
Payload: N-4 s/n 1. Mass: 8,300 kg (18,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Proton.
Class: Astronomy.
Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: N-4 .
Decay Date: 1965-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 1466 . COSPAR: 1965-054A. Apogee: 578 km (359 mi). Perigee: 181 km (112 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
The first launch of the Proton launch vehicle was not without problems. A leak in the oxidiser pipeline resulted in nitrogen tetroxide spilling on electrical wires. The question was: proceed with the launch or abort? Chelomei decided to go ahead, and on 16 July 1965 the first UR-500 successfully launched the Proton 1 satellite. In the first hours after launch specialists from OKB-52 could only receive signals in the first hours that indicated the satellite was 'alive'. However it later functioned normally and provided physics data on ultra-high-energy cosmic particles for 45 days.
At the first launch the rocket was called 'Gerkules' (other sources say 'Atlantis'), as indicated by the large symbol on the second stage skin. This name was however was not taken up.
1965 September 8 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Development of four stage version of the Proton proposed. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei, Korolev. The design was proposed by Korolev as an alternate to Chelomei's LK-1 circumlunar mission. It combined the Proton 8K82K booster for the LK-1 with the N1 lunar Block D stage to boost a stripped-down Soyuz 7K-L1 spacecraft around the moon..
1965 September 15 - . LV Family: , Proton, .
- Korolev conceived of podsadka over a month before before the UR-500K-L1 was authorized. - .
Related Persons: Korolev,
Mishin.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
Korolev conceived of podsadka over a month before before the UR-500K-L1 was authorized.Initial calculations by OKB-1 showed that the developmental L1 would have a dry mass of 4641 kg, or 4847 kg after delivery of cosmonauts via podsadka. On the other hand, Kolyako in Division 2 estimated the translunar payload of the Block D as ~ 5000 kg in the single launch scenario, or ~ 5300 kg in the podsadka scenario.
1965 October 25 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- L1 manned circumlunar mission taken from Chelomei, given to Korolev. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On the Concentration of Forces of Industrial Design Organisations for the Creation of Rocket-Space Complex Means for Circling the Moon--work on the UR-500K-L1 program' was issued. As a result of a presentation to the Military Industrial Commission, Afanasyev backed Korolev in wresting control of the manned circumlunar project from Chelomei. The Chelomei LK-1 circumlunar spacecraft was cancelled. In its place, Korolev would use a derivative of the Soyuz 7K-OK, the 7K-L1, launched by Chelomei's UR-500K, but with a Block D translunar injection stage from the N1. He envisioned launch of the unmanned 7K-L1 into low earth orbit, followed by launch and docking of a 7K-OK with the 7K-L1. The crew would then transfer to the L1, which would then be boosted toward the moon. This was the original reason for the development of the 7K-OK.
1965 November 2 - . 12:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: UR-500.
- Proton 2 - . Payload: N-4 s/n 2. Mass: 8,300 kg (18,200 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Proton. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: N-4 . Decay Date: 1966-02-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 1701 . COSPAR: 1965-087A. Apogee: 608 km (377 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 92.50 min. High energy physics laboratory. Investigation of ultra-high-energy cosmic particles. .
1965 November 13 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Industrial orders to cancel LK-1 spacecraft and implement L1. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: LK-1, Soyuz 7K-L1. Ministry of General Machine Building (MOM) Decree 'On work on the UR-500K-L1 program' was issued..
1966 March 24 - . 21:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: UR-500. FAILURE: Second stage malfunction.. Failed Stage: 2.
- N-4 s/n 3 - . Payload: N-4. Mass: 8,300 kg (18,200 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Proton. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: N-4. Decay Date: 1966-03-24 .
1966 April 10 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmonaut training for lunar flights announced - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Leonov. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Leonov announces that cosmonauts are in training for lunar missions..
1966 April 27 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Soyuz L1 full scale development, LK-1 cancellation approved. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: LK-1, Soyuz 7K-L1. Decree 10 'On approving the work plan to build the p8loted spacecraft 7K-L1 -- approving the plan for for the UR-500K-L1 and terminating the UR-500K-LK-1' was issued..
1966 July 6 - . 12:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: UR-500.
- Proton 3 - . Payload: N-4 s/n 4. Mass: 8,300 kg (18,200 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Proton. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: N-4 . Decay Date: 1966-09-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 2290 . COSPAR: 1966-060A. Apogee: 594 km (369 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 92.30 min. Space station 'Proton 3'. Investigation of ultra high energy cosmic particles .
1966 September 2 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Lunar flight cosmonauts assignments. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Artyukhin,
Beregovoi,
Bykovsky,
Dobrovolsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Khrunov,
Klimuk,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Kubasov,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Rukavishnikov,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov,
Volkov,
Voloshin,
Volynov,
Voronov,
Yeliseyev,
Zholobov.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
In the period 1966 to 1968 there were five simultaneous Soviet manned space projects (Soyuz 7K-OK orbital; Soyuz 7K-L1 circumlunar; Soyuz VI military; L3 manned lunar landing; Almaz space station). Cosmonaut assignments were in constant flux, resulting in many claims in later years that 'I was being trained for the first moon flight'. Additional Details: here....
1966 October 4 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Dummy Proton/Block D mounted on pad. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
A dummy 8K82K/Block D rocket was mounted at the launch site. The dummy was loaded with imitation propellants (kerosene as fuel and water/ethyl alcohol as oxidiser). The nitrogen tetroxide oxidiser had to be kept above -11 degrees C, and it was originally planned for a thermostatically-controlled electrical heating of the tank walls to achieve this. It was ultimately decided that the risk of explosion of such a system was too great, and the system was abandoned.
1966 November 21 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- First Proton/Soyuz L1 begins assembly. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The first flight rocket (serial number 22701) began assembly on 21 November 1966, with mechanical assembly completed by 29 November. Electrical connections and tests were completed by 4 December 1966. Due to New Year's holidays work did not resume until 28 January 1967. By 28 February the fully assembled booster / spacecraft unit was completed in the MIK, including the 7K-L1P boilerplate spacecraft.
1966 December 2 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, .
- The 2-launch N1 scenario was discussed in an interdepartmental technical review with MV Keldysh. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Bushuyev,
Keldysh,
.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
LK,
Luna Ye-8.
At this point the Ye-8 would be delivered to the moon by a UR-500K launch vehicle. The basic constraint was the 5300 kg payload capability of the Block D to translunar injection. This meant tradeoffs in the accuracy of the Ye-8's initial landing versus its lifetime on the surface waiting for arrival of the LK. It was agreed that a working group would meet the next day to develop final specifications Ye-8 and a more detailed outline of the N1-L3 expedition using Ye-8. (start-up sequence, the time, the connections between LK, LOK and Ye-8, the means for determining the location). KD Bushuyev was to study the backup LK concept. (Mishin Diaries 1-235)
1966 December 24 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- First session of State Commission for the L1 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Chelomei,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Tyulin chairs the meeting. Mishin, Chelomei and Barmin brief the status of the spacecraft, booster, and launch site. There is much to be done in order to fly cosmonauts around the moon by 7 November 1967 - the 50th anniversary of the October Revolution. The first manned flight around the moon is planned for 26 June 1967. To achieve this, four flights of the L1 without a crew have to be completed first. The UR-500K booster should be capable of launching the L1 on a direct flight around the Moon and back to the earth. But since the UR-500K has not yet flown, and its 19-tonne low earth payload has not bee verified, Mishin plans to follow the podsadka scenario. The UR-500K will place in low earth orbit an L1 without a crew, and then a Soyuz booster will place a manned Soyuz 7K-OK Soyuz in orbit. The Soyuz crew will rendezvous and dock with the L1, and the crew for the circumlunar mission will spacewalk through open space from the 7K-OK into the L1. The spacecraft will then separate. The 7K-OK returns to earth, while the L1 is boosted on a circumlunar trajectory. After 4 to 6 launches of the UR-500K to verify its reliability and payload margins, it should be possible to make the direct flight to the moon on subsequent versions. For the time being it is necessary to develop both versions in parallel.
1967 January - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- First L-1 Zond spacecraft mated to Proton - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1P #1. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Fit tests at Tyuratam. Not launched (Interavia SD)..
1967 February 4 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- UR-500K/L1 manned circumlunar design authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 115-46 'On the Progress of the Work on the Development of the UR500K-L1 --confirmation of schedule for piloted lunar missions' was issued..
1967 March 10 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Cosmos 146 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1P s/n 2P. Mass: 5,017 kg (11,060 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Duration: 7.90 days. Decay Date: 1967-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 2705 . COSPAR: 1967-021A. Apogee: 312 km (193 mi). Perigee: 178 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 89.30 min.
Protoype Soyuz 7K-L1P launched by Proton into planned highly elliptical earth orbit. The first flight four-stage Proton rocket began assembly on 21 November 1966, with mechanical assembly completed by 29 November. Electrical connections and tests were completed by 4 December 1966. Due to New Year's holidays work did not resume until 28 January 1967. By 28 February the fully assembled booster / spacecraft unit was completed in the MIK, including the 7K-L1P boilerplate spacecraft. The launch tower was added on 2 March 1967 and the system was declared ready for launch. A serious potential problem during preparations was the discovery that fuel gases could lead to pump cavitation at the turbine exits. Tests on the ground showed that the problem was not the fuel itself, but in the monitoring equipment. The launch vehicle and Block D stage functioned correctly and put the spacecraft into a translunar trajectory. The spacecraft was not aimed at the moon, did not have a heat shield for reentry, and no recovery was planned or attempted. A successful launch that created false confidence just before the string of failures that would follow.
1967 April 8 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D ullage rocket failure; no restart.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 154 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1P s/n 3P. Mass: 5,020 kg (11,060 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Mishin,
Tsybin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Duration: 1.98 days. Decay Date: 1967-04-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 2745 . COSPAR: 1967-032A. Apogee: 203 km (126 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
Protoype Soyuz 7K-L1 manned circumlunar spacecraft. There are high winds for the L1 launch, 15-17 m/s. The official limit is 20 m/s, but Chelomei wants to scrub the launch if winds go over 15 m/s. Nevertheless the launch proceeds in 17-18 m/s winds and the L1 reached earth orbit. However the Block D translunar injection stage failed to fire (ullage rockets, which had to fire to settle propellants in tanks before main engine fired, were jettisoned prematurely). The failure is blamed on Mishin and has Tsybin seething in anger. Mishin is disorganised and has made many mistakes. Spacecraft burned up two days later when orbit decayed. Later in the day comes the news the RTS has to be replaced on one of the Soyuz 1/2 spacecraft. This will have a 3 to 4 day schedule impact, and push the launch back to 15-20 April. The crews arrive the same day for the upcoming Soyuz launch.
1967 May 5 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, N11.
- Recommendation that podsadka be dropped and L1 direct flight become the baseline. - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soviet of Chief Designers met with the Civil Chief Designer UR500K-L1 and recommended that podsadka be dropped and direct flight become the baseline. This was evidently to make possible the objective of a Soviet man around the moon before 4 October 1967. The reasons given were:
a) The successful flights of the UR-500K and Block D on the L1 2P and 3P and the further 4 separate UR-500 launches provided confidence in the launch vehicle's reliability.
b) The main delays with L1 development will be in relation to development by BTsVM of the Argon-11 digital computer for its control system.
c) The failure of 7K-OK number 4 (Soyuz 1) indicated a delay in development of docking in earth orbit.
It was recommended that the 7K-L1 launch sequence be revised to two missions per month as follows:
- 4L - "Zond" unmanned 17 - 29 June 1966
- 5L - unmanned, circumlunar, 27 June - 5 July
- 6L - "Zond", unmanned, 12 - 17 July
- 7L - unmanned, circumlunar, 25 July - 3 August
Followed by manned launches according to astronomical constraints (which would mean 23 August, 21 September, 19 October). (Mishin Diaries 2-22)
1967 September 27 - . 22:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: First stage -1 RD-253 failed, resulting at T+67 sec in deviation from flight path.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 4L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 4L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Mishin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1967-09-28 .
First attempted circumlunar flight. The UR-500K failed, crashing 50 to 60 km from the launch pad. The L1 radio beacon was detected 65 km north of the Baikonur aerodrome by an Il-14 search aircraft. An Mi-6 helicopter recovered the capsule and had it back to the cosmodrome by 13:30. Mishin's record: of seven launches of the Soyuz and L1, only one has been successful. Film of the launch shows that one engine of the first stage failed. Mishin still wants to launch the next L1 by 28 October. The other chief designers oppose the move. Barmin says at least five months are needed to diagnose the cause of the failures and makes fixes to ensure they don't happen again. Nevertheless the leadership sides with Mishin, and Barmin is ordered to prepare the left Proton pad for a launch within 30 to 40 days.
1967 October 7 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Soviet of Chief Designers - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Dementiev,
Glushko,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
In Moscow, Mishin heads a meeting of all the Chief Designers (including Chelomei, Mishin, and Glushko). Glushko says that the last UR-500K failure was due to errors made during manufacture of an engine in 1965 at Factory 19 at Perm. Ustinov notes that the failure has cost the state 100 million roubles and has delayed the program two to three months. He brutally attacks Dementiev, Minister of Aviation Industry, for the poor work of his factories on the space program. Another issue is continued delays in the Salyut computer for the L1. Ustinov orders an alternate technical solution to be developed in parallel with the digital computer development. The next Soyuz flight is set for the end of December, the next L1 attempt for 21-22 November.
1967 November 17 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- UR-500 launch vehicle version for military payloads authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 1070-363 'On approval of work on the UR-500 launch vehicle' was issued..
1967 November 21 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cause of Proton failure in last launch. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Glushko. Program: Lunar L1. Glushko at Baikonur. He reports the Perm factory is under close supervision - the engine that failed on the last launch was found to have resin in the main fuel line..
1967 November 22 - . 19:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Second stage - 1 x RD-0210 failure, shutoff of stage 4 seconds after ignition. Launcher crashed downrange.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 5S - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 5L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Glushko,
Leonov,
Mishin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1967-11-21 .
The launch takes place at 00:07 local time (22:07 on 22 November Moscow time). Glushko, Chelomei, and Kamanin observe the launch from an observation point in -5 deg C weather. Three to four seconds after second stage ignition, the SAS pulls the spacecraft away from the booster. Telemetry shows that engine number 4 of stage 2 never ignited, and after 3.9 seconds the remaining three engines were shut dwon by the SBN (Booster Safety System) and the SAS abort tower fired. The capsule's radio beacon was detected and the spacecraft was found 80 km southwest of Dzhezkazgan, 285 km down range. The Proton problems are maddening. Over 100 rocket launches have used engines from this factory, with no previous failure. Of ten of the last launches under Mishin's direction (6 Soyuz and 4 L1) only two have went well - an 80% failure rate! Mishin is totally without luck. Kamanin and Leonov take an An-12 to see the L1 at its landing point. Leonov wants to see proof that the cosmonauts would be saved in any conditions. The capsule landed in -17 deg C and 12 m/s winds. The parachute pulled the capsule along the ground for 550 m, and the soft landing rockets fired somewhere above the 1.2 m design height. After safing of the APO self-destruct package, the capsule is lifted to an airfield by a Mi-4. The L1-5S designation seems to indicate this was a test of the podsadka L1. (Mishin Diaries 2-90)
1968 February 7 - . LV Family: , Proton, .
- Status of development of the LK-R. - . Related Persons: Mishin, Bushuyev, Keldysh, . Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, LK. At the expert commission on the UR-500K-L1 (Tyulin, Stroganov, Keldysh, Kashtanov and others), Bushuyev provided the status of development of the LK-R. (Mishin Diaries 2-120).
1968 February 21 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- L1 Launch Commission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Glushko,
Konopatov,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The booster failure on the previous launch was found to be due to premature fuel injection during engine start, causing initial chamber temperatures to rise 200 degrees above normal. Glushko and Konopatov both guarantee their engines for the next launch. The next L1 flight will use the 'Kruga' landing predictor. This will predict the landing point to within a 150 x 150 km area two to three hours before re-entry. Landing points on the three previous flights would have been 2000 km from Madagascar and India, Novosibirsk, and the North Pole... Mishin plans the next dual Soyuz flight for 5-10 April. Kamanin protests that the parachute and sea trials of the redesigned capsule are not yet complete. Mishin, as usual, dismisses his concerns.
1968 February 29 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- L1 commsision meeting. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
For this L1 launch Chelomei wants to film separation of the first and second stages of the Proton rocket at 126 seconds into the flight - altitude 41 km, distance downrange 47 km. To do this two An-12 and one Tu-124 with long focal-length cameras will orbit 35 to 40 km from base. The discussion turns to how to recover the L1 if it lands in the ice-bound Aral Sea. The circle of possible landing points has a radius of 500 km from a point west of Karaganda. For political reasons it is not possible to deploy recovery forces to areas of Iran and India that are within this circle.
1968 March 2 - . 18:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 4 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 6L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.22 days. Decay Date: 1968-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 3134 . COSPAR: 1968-013A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 15,561.71 min.
What at first seemed to be a success, very much needed by the L1 program, ended in failure. The Proton booster lifted off in 18 m/s winds, -3 deg C temperatures, and into very low clouds - it disappeared from view at only 150 m altitude. Aircraft at 9, 10, and 11 km altitude reported the cloud deck topped 8300 m, with 1.5 to 2.0 km visibility. The spacecraft was successfully launched into a 330,000 km apogee orbit 180 degrees away from the moon. On reentry, the guidance system failed, and the planned double skip maneuver to bring the descent module to a landing in the Soviet Union was not possible. Ustinov had ordered the self-destruct package to be armed and the capsule blew up 12 km above the Gulf of Guinea. Kamanin disagreed strongly with this decision; the spacecraft could have still been recovered in the secondary area by Soviet naval vessels after a 20 G reentry. The decsion was made to recover the spacecraft in the future whenever possible.
Officially: Solar Orbit (Heliocentric). Study of remote regions of circumterrestrial space, development of new on-board systems and units of space stations.
1968 April 22 - . 23:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Second stage shut-off prematurely due to short-circuit in Zond control system.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 7L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 7L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1968-04-22 .
L1 launch attempt, lift-off at 02:00 local time. The spacecraft was to separate at 589 seconds into the flight. Instead at 260 seconds, a short circuit in the malfunction detection system incorrectly indicated a launch vehicle failure. This in turn triggered the SAS abort system. The SAS shut down the good stage and separated the spacecraft from the booster. The capsule landed safely 520 km downrange from the launch site. This was the third such abort, which if nothing else proved the reliability of the SAS - all of the spacecraft landed safely.
July 1968 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- DIA/CIA warn of impending Zond circumlunar flight - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The information led NASA to decide to send Apollo 8 on a risky lunar orbital mission at the end of December 1968. Interestingly enough the CIA warning to NASA came within days of the L1 State Commission's meeting and decision to press for a November circumlunar flight.
1968 July 15 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. Launch Pad: LC81/pad?. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- L1 pad explosion. - .
Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
During launch preparations with the fuelled Proton / L1, there was an explosion, killing three technicians. Their death alone indicates the area around the pad was unsafe at the time. The Block D oxidiser tank of the L1 exploded - the first such failure in 30 uses. The rocket and spacecraft were relatively undamaged. The third stage of the Proton had some external damage due to exposure to the Block D's fuel, but it can be cleaned. The real question is how to remove the L1 spacecraft on the pad. A helicopter could hoist the spacecraft away, but the available Mi-6 or V-10 helos can lift only 8 to 10 tonnes, and the L1 weighs 14 tonnes. A V-10 crew is sent to investigate the possibilities anyway. Some engineers suggest just firing the BPO abort tower and lifting the capsule away from the stack! Emergency political and military meetings are held at the cosmodrome to discuss the impending invasion of Czechoslovakia.
1968 July 21 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Zond 7K-L1 s/n 8L - . Payload: Zond 7K-L1 s/n 8L. Mass: 5,140 kg (11,330 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Decay Date: 1968-07-21 . Block D stage exploded on pad, killing three people. Booster and 7K-L1 spacecraft were still intact however..
1968 September 14 - . 21:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 5 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 9L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.76 days. Decay Date: 1968-09-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 3394 . COSPAR: 1968-076A. Apogee: 385,000 km (239,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 14,722.06 min.
First successful circumlunar flight with recovery. Test flight of manned spacecraft; launched from an earth parking orbit to make a lunar flyby and return to earth. On September 18, 1968, the spacecraft flew around the moon at an altitude of 1950 km. High quality photographs of the earth were taken at a distance of 90,000 km. A biological payload of turtles, wine flies, meal worms, plants, seeds, bacteria, and other living matter was included in the flight. Before re-entry the gyroscopic platform went off line due to ground operator failure. However this time the self destruct command was not given. After a ballistic 20G re-entry the capsule splashed down in the Indian Ocean at 32:63 S, 65:55 E on September 21, 1968 16:08 GMT. Soviet naval vessels were 100 km from the landing location and recovered the spacecraft the next day, shipping it via Bombay back to Soviet Union. Additional Details: here....
1968 November 10 - . 19:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 6 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 12L. Mass: 5,375 kg (11,849 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.79 days. Decay Date: 1968-11-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 3535 . COSPAR: 1968-101A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 15,562.22 min.
Test flight of manned circumlunar spacecraft. Successfully launched towards the moon with a scientific payload including cosmic-ray and micrometeoroid detectors, photography equipment, and a biological specimens. A midcourse correction on 12 November resulted in a loop around the moon at an altitude of 2,420 km on 14 November. Zond 6 took spectacular photos of the moon's limb with the earth in the background. Photographs were also taken of the lunar near and far side with panchromatic film from distances of approximately 11,000 km and 3300 km. Each photo was 12.70 by 17.78 cm. Some of the views allowed for stereo pictures. On the return leg a gasket failed, leading to cabin depressurisation, which would have been fatal to a human crew. The 7K-L1 then made the first successful double skip trajectory, dipping into the earth's atmosphere over Antarctica, slowing from 11 km/sec to suborbital velocity, then skipping back out into space before making a final re-entry onto Soviet territory. The landing point was only 16 km from the pad from which it had been launched toward the moon. After the re-entry the main parachute ejected prematurely, ripping the main canopy, leading to the capsule being destroyed on impact with the ground. One negative was recovered from the camera container and a small victory obtained over the Americans. But the criteria for a manned flight had obviously not been met and Mishin's only hope to beet the Americans was a failure or delay in the Apollo 8 flight set for December. The next Zond test was set for January. Additional Details: here....
1968 November 16 - . 11:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Proton 4 - . Payload: N-6 s/n 1. Mass: 16,000 kg (35,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Proton. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: N-6 . Decay Date: 1969-07-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 3544 . COSPAR: 1968-103A. Apogee: 477 km (296 mi). Perigee: 248 km (154 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min. First launch of the Proton three-stage variant. The satellite studied the nature of high and ultra-high energy cosmic rays and their interaction with atomic nuclei. Scientific payload 12,500 kg; operated for 100 days in orbit. .
1969 January 20 - . 04:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Second stage - One RD-0210 engine fails at T+510 sec, resulting in flight path deviation, automatic shutoff of launch vehicle.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 13L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 13L. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
Decay Date: 1969-01-19 .
Launch failure - but the abort system again functioned perfectly, taking the capsule to a safe landing (in Mongolia!). At 501 seconds into the flight one of the four engines of the second stage shut down, and remained shut down for 25 seconds. The ever-reliable SAS abort system detected the failure, and separated the capsule from the failed booster. Yet again a successful capsule recovery after a booster failure. Additional Details: here....
1969 January 25 - . LV Family: N1, Proton.
- N1-L3 launch schemes - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-L1S,
Soyuz 7K-L3S,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
LK,
Luna Ye-8.
Mishin meeting with his guidance expert, NA Pilyugin, to consider the possibility of 2 launch schemes: with Ye-8 and without Ye-8 OV. All possibilities to improve the accuracy of the landing without the Ye-8 were to be examined. The first N1 missions would rehearse the two-launch scenario, with the Ye-8 being launched by a UR-500K and an L3S (orbital version of the L1S) standing in for the LOK (no LK being available yet).
1969 February 4 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- UR-500K failure state commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Konopatov.
Program: Luna.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
At Area 81 a State Commission is held on failures of the UR-500K booster. A D Konopatov describes the analysis of the stage 2 and 3 failures on the 20 January launch attempt. The number 4 engine of stage 2 shut down 25 seconds into its burn due to high temperatures detected in the turbopump. The same thing occurred on the third stage. The couldn't pin down the source of the problem. Engines of this type had worked correctly 700 times on earlier flights. Despite the cause of the failure not being identified, approval is given at 14:30 for the launch of the Ye-8 to proceed. Babakin confirms the spacecraft is ready.
1969 February 19 - . 06:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: First-stage engine failure caused the rocket to crash 15 km from the pad.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Ye-8 s/n 201 + Lunokhod s/n 201 - first stage malfunction - .
Payload: Ye-8 s/n 201 / 8EL No. 201. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
Decay Date: 1969-02-19 .
Attempted launch of a Ye-8 with a Lunokhod lunar rover. Evidently coordinate in some way with the N1 launch two days later. A first-stage booster engine failure causes the rocket to crash 15 km from the pad after a lift-off at 09:48 local time. Kamanin meanwhile has the Hong Kong flu.
1969 March 27 - . 10:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: T+51s payload shroud failed. Second stage continued but third stage failed to ignite.. Failed Stage: S.
- M-69 s/n 521 - . Payload: M-69 s/n 521. Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Mars. Class: Mars. Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV. Spacecraft: Mars M-69. Decay Date: 1969-03-27 . Mars probe intended to enter Martian orbit and comprehensively photograph Mars, together with a landing probe..
1969 April 2 - . 10:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: First stage - 1 x RD-253 fire beginning at T+ 0.02 sec, rocket crashed near pad.. Failed Stage: 1.
- M-69 s/n 522 - .
Payload: M-69 s/n 522. Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-69.
Decay Date: 1969-04-02 .
Mars probe intended to enter Martian orbit and comprehensively photograph Mars, together with a landing probe. Further Mars launches during the 1969 launch window were cancelled when this attempt resulted in a major accident, which almost wiped out all of the leaders of the space industry. The Proton rocket lifted off, but one engine failed. The vehicle flew at an altitude of 50 m horizontally, finally exploding only a short distance from the launch pad, spraying the whole complex with poisonous propellants that were quickly spread by the wind. Everyone took off in their autos to escape, but which direction to go? Finally it was decided that the launch point was the safest, but this proved to be even more dangerous - the second stage was still intact and liable to explode. The contamination was so bad that there was no way to clean up - the only possibility was just to wait for rain to wash it away. This didn't happen until the Mars launch window was closed, so the first such probe was not put into space until 1971. This accident also severely damaged plans to divert attention from America's Apollo programme during the rest of 1969. 10-12 UR-500K launches had been intended to land on the moon lunar soil return and rover robots to supplement the N1 launches.
1969 June 14 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D upper stage did not fire and payload did not attain earth orbit,. Failed Stage: U.
- Ye-8-5 s/n 402 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 402. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1,
Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1969-06-04 .
Another attempt to launch a Ye-8-5 to return lunar soil to the earth, 'scooping', the Americans' impending Apollo 11 mission. Yet another UR-500K launch failure. This time the UR-500K booster functioned perfectly, but the Block D upper stage did not fire, and the payload did not even attain earth orbit. Every UR-500K launch is costing the Soviet state 100 million roubles. This failure pretty much ended the chances for the Russians to trump the American moon landing. Tass yesterday began running stories to prepare the masses for the upcoming Apollo 11 triumph. The party line is that the Soviet Union is not about to risks the lives of its cosmonauts on flights to the moon, when automated probes can safely retrieve soil from the moon for study on earth. Additional Details: here....
1969 July 13 - . 02:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 15 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 401. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1969-07-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 4036 . COSPAR: 1969-058A. Apogee: 870 km (540 mi). Perigee: 240 km (140 mi). Inclination: 126.00 deg. Period: 160.00 min.
Unmanned soil return mission launched coincident with Apollo 11 mission in last ditch attempt to return lunar soil to earth before United States. After completing 86 communications sessions and 52 orbits of the Moon at various inclinations and altitudes, crashed on the moon on 20 July in an attempted landing. Altitude data used in programming inaccurate or guidance system unable to cope with effect of lunar mascons.
Officially: Testing of on-board systems of the automatic station and further scientific investigation of the moon and circumlunar space. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1969 August 1 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- The DOS Conspiracy begins - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Almaz,
Salyut.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
With the collapse of the work on the N1, the whole reason for Mishin's design bureau's existence simply vanished in the air. A new high-priority project was needed. Korolev had begun development of a Multi-Module Space Base (MKBS) before 1966. However MKBS was to be launched by the N1; as long as this was not available, there would be no MKBS. Almaz on the other hand did not require a new launch vehicle, although the UR-500 was in a period of intense 'baby sickness'. So while TsKBEM was in a period of analysis and instability, Chelomei's Reutov and Fili facilities were building space stations for the Ministry of Defence.
On one of these August 1969 days, three of Chelomei's TsKBM engineers came to the office of Mishin's deputy, Chertok, with a plan to get a space station orbited before the American Skylab. They wanted a collaboration between the two competing design bureaux. Their plan was to take an Almaz spaceframe, install Soyuz systems, add a new docking tunnel with a hatch to reach the interior, and presto - a space station was finished. Tentative discussions with potential allies within Chelomei's design bureau found support there as well. The DOS 'long-duration orbiting station' was the result of this 'conspiracy'.
1969 August 7 - . 23:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 7 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 11. Mass: 5,379 kg (11,858 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.00 days. Decay Date: 1969-08-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 4062 . COSPAR: 1969-067A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 15,562.22 min.
Circumlunar flight; successfully recovered in USSR August 13, 1969. Only completely successful L1 flight that could have returned cosmonauts alive or uninjured to earth. Official mission was further studies of the moon and circumlunar space, to obtain colour photography of the earth and the moon from varying distances, and to flight test the spacecraft systems. Earth photos were obtained on August 9, 1969. On August 11, 1969, the spacecraft flew past the moon at a distance of 1984.6 km and conducted two picture taking sessions. Successfully accomplished double-dip re-entry and landed 50 km from aim point near Kustani in the USSR.
1969 September 23 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Two Volga buses transport the cosmonauts and VVS specialists to Area 31. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Chelomei,
Mishin.
Program: Luna.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
To ensure the buses do not exceed 60 km/hour checkpoints are manned along the roads. The readiness review is conducted form 10:00 to 13:00. The crews, and spacecraft are ready. Mishin is away 'sick' again. General Pushkin and Beregovoi are at Area 81 to view the Ye-8-5 launch. Kamanin likes Chelomei's UR-500K rocket. He blames its series of failures on its engines and Block D upper stage, not on the fundamental booster design. If it had been more successful, the Russians would have beaten the Americans in a lunar flyby. The launch proceeds as planned at 15:00, but the Block D fails to restart in parking orbit, and is given the cover name 'Cosmos 300'.
1969 September 23 - . 14:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D lost LOX due to valve defect.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 300 - . Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 403. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1969-09-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 4104 . COSPAR: 1969-080A. Apogee: 189 km (117 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 88.20 min. Robotic lunar soil return mission. Failed to leave low earth orbit due to Block D stage failure..
1969 September 24 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Ye-8-5 failure analysis - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Savin,
Smirnov,
Tyulin.
Program: Luna.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
The cause of the Ye-8-5 failure is found to be a valve that was stuck open after the first stage burn, resulting in the oxidiser boiling away in the vacuum of space. Tyulin inquires about the possibility of commanding the Ye-8-5 to conduct a series of manoeuvres and testing re-entry of the soil return capsule in the earth's atmosphere. An interesting concept, but the engineers have not planned for such an eventuality.
NII-2 MO, represented by Lt General Korolev and Chief Designer Savin present plans for their Svinets experiment. It will observe ICBM rocket plumes from space in order to aid design of anti-ballistic missile systems. They had asked Smirnov to conduct a solid propellant rocket launch in order to test the device properly, but he could only schedule a liquid propellant rocket launch. Kamanin had wanted this experiment to be conducted aboard Voskhod 3, but Smirnov has cancelled that mission as well - delaying Soviet ABM development, in Kamanin's view.
1969 October 22 - . 14:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D control system failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 305 - . Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 404. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1969-10-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 4150 . COSPAR: 1969-092A. Apogee: 208 km (129 mi). Perigee: 182 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.40 deg. Period: 88.40 min. Robotic lunar soil return mission. Failed to leave low earth orbit due to Block D stage failure..
1969 November 28 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: First stage malfunction.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Soyuz 7K-L1E s/n 1 - first stage malfunction - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1E s/n 1. Mass: 10,380 kg (22,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Block D.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1E.
Decay Date: 1969-11-16 .
Attempted test flight of Block D upper stage in N1 lunar crasher configuration. Payload was a modified Soyuz 7K-L1 circumlunar spacecraft, which provided guidance to the Block D and was equipped with television cameras that viewed the behavior of the Block D stage propellants under zero-G conditions. Mission flown successfully over a year later as Cosmos 382.
1969 December 1 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- First flight Almaz station close to completion - . Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz. Spacecraft: Almaz OPS. Ten stations 'in advanced stage of completion' by end of year..
1970 February 1 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Space station programs rationalised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Mishin.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-S,
Soyuz OB-VI.
Brezhnev orders a cooperative crash program to build a civilian space station to beat Skylab into orbit. The civilian station (later named Salyut) will use the Almaz spaceframe fitted out with Soyuz functional equipment. Mishin's OIS military station was cancelled and Chelomei's Almaz would continue, but as second priority to the civilian station. The Soyuz 7K-S station ferry, the 7K-ST, would be revised to be a more conservative modification of the Soyuz 7K-OK. The OIS cosmonaut group was incorporated into the Almaz group.
1970 February 6 - . 04:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. Launch Pad: LC81/23?. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Failure of vehicle on launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Ye-8-5 s/n 405 - failure of vehicle on launch - . Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 405. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1970-02-06 . Robotic lunar soil return mission..
1970 June 16 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Development of TKS ferry for Almaz authorised. Soyuz 7K-TK cancelled - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TK,
TKS.
Decree 437-160 'On creation of the TKS and termination of the 7K-TK' was issued. In 1969 Chelomei proposed replacement of the 11F72 Soyuz 7K-TK with his own transport-supply spacecraft 11F72 (transportnovo korablya snabzheniya - TKS). This would consist of the same 11F74 VA landing capsule used on the Almaz station, together with a new 11F77 functional-cargo block (funktsionalno-gruzovovo blok, FGB). This would transport three crew and sufficient supplies for 90 day operation of the Almaz.
1970 August 18 - . 03:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- 82-EV test - . Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Apogee: 200 km (120 mi). Heavily instrumented suborbital flight to provide data to root out causes of continuing launch vehicle failures. Heavy mass model of an unspecified spacecraft used to simulate payload...
1970 September 12 - . 13:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 16 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 406. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1970-09-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 4527 . COSPAR: 1970-072A. Apogee: 110 km (60 mi). Perigee: 110 km (60 mi). Inclination: 70.00 deg. Period: 119.00 min.
Lunar Sample Return. Landed on Moon 20 September 1970 at 05:18:00 GMT, Latitude 0.68 S, Longitude 56.30 E - Mare Fecunditatis. Luna 16 was launched toward the Moon from a preliminary earth orbit and entered a lunar orbit on September 17, 1970. On September 20, the spacecraft soft landed on the lunar surface as planned. The spacecraft was equipped with an extendable arm with a drilling rig for the collection of a lunar soil sample. After 26 hours and 25 minutes on the lunar surface, the ascent stage, with a hermetically sealed soil sample container, left the lunar surface carrying 100 grams of collected material. It landed in the Soviet Union on September 24, 1970. The lower stage of Luna 16 remained on the lunar surface and continued transmission of lunar temperature and radiation data. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1970 October 20 - . 19:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Zond 8 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 14. Mass: 5,390 kg (11,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1 .
Duration: 5.17 days. Decay Date: 1970-10-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 4591 . COSPAR: 1970-088A. Apogee: 400,000 km (240,000 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 15,562.22 min.
Final circumlunar flight; successfully recovered October 26, 1970. The announced objectives were investigations of the moon and circumlunar space and testing of onboard systems. The spacecraft obtained photographs of the earth on October 21 from a distance of 64,480 km. The spacecraft transmitted flight images of the earth for three days. Zond 8 flew past the moon on October 24, 1970, at a distance of 1,110.4 km and obtained both black and white and colour photographs of the lunar surface. Scientific measurements were also obtained during the flight. The spacecraft used a new variant of the double-dip re-entry, coming in over the north pole, bouncing off the atmosphere, being tracked by Soviet radar stations as it soared south over the Soviet Union, then making a final precision re-entry followed by splashdown at the recovery point in the Indian Ocean.
1970 October 31 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 10L and 15L - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1 s/n 10L and 15L. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. Despite decision to cancel immediate manned circumlunar flights after Apollo 8, the remaining two L-1 spacecraft were kept in reserve for support of the L3 lunar landing program and possible later manned flights. They were never used..
1970 November 10 - . 14:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 17 - .
Payload: Ye-8 s/n 203. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Ye-8.
Decay Date: 1970-11-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 4691 . COSPAR: 1970-095A. Apogee: 85 km (52 mi). Perigee: 85 km (52 mi). Inclination: 141.00 deg. Period: 116.00 min.
Luna 17 was launched from an earth parking orbit towards the Moon and entered lunar orbit on November 15, 1970. Luna 17 landed on Moon 17 November 1970 at 03:47:00 GMT, Latitude 38.28 N, Longitude 325.00 E - Mare Imbrium (Sea of Rains). The payload, the Lunokhod 1 unmanned rover, rolled down a ramp from the landing stage and began exploring the surface. Lunokhod was intended to operate through three lunar days but actually operated for eleven lunar days (earth months). The operations of Lunokhod officially ceased on October 4, 1971, the anniversary of Sputnik 1. By then it had traveled 10,540 m and had transmitted more than 20,000 TV pictures and more than 200 TV panoramas. It had also conducted more than 500 lunar soil tests. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1970 December 2 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Cosmos 382 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1E s/n 2K. Mass: 10,380 kg (22,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Block D.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1E.
Duration: 8,549.30 days. USAF Sat Cat: 4786 . COSPAR: 1970-103A. Apogee: 5,269 km (3,273 mi). Perigee: 2,384 km (1,481 mi). Inclination: 55.90 deg. Period: 171.00 min.
Test of Block D upper stage in its N1 lunar crasher configuration in earth orbit. The three maneuvers simulated the lunar orbit insertion burn; the lunar orbit circularization burn; and the descent burn to bring the LK lunar lander just over the surface. Payload was a modified Soyuz 7K-L1 circumlunar spacecraft, which provided guidance to the Block D and was equipped with television cameras that viewed the behavior of the Block D stage propellants under zero-G conditions.
Maneuver Summary:
190km X 300km orbit to 303km X 5038km orbit. Delta V: 982 m/s
318km X 5040km orbit to 1616km X 5071km orbit. Delta V: 285 m/s
1616km X 5071km orbit to 2577km X 5082km orbit. Delta V: 1311 m/s
Total Delta V: 2578 m/s.
1971 April 19 - . 01:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Salyut 1 - .
Payload: Zarya s/n 121. Mass: 18,500 kg (40,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11,
Soyuz 12 / DOS 1.
Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1.
Duration: 179.93 days. Decay Date: 1971-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 5160 . COSPAR: 1971-032A. Apogee: 214 km (132 mi). Perigee: 180 km (110 mi). Inclination: 51.40 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
First manned space station. Salyut 1 included a number of military experiments, including the OD-4 optical visual ranger, the Orion ultraviolet instrument for characterising rocket plumes, and the highly classified Svinets radiometer. Primary objectives included photography of the earth, spectrographs of the earth's horizon, experiments with intense gamma rays, and studying manual methods for station orientation.
At 05:20 the State Commission and their guests arrive at the Area 95 observation point to view the launch. The booster takes off on schedule at 06:40 in light rain and 60 km/hr wind. The tracking station reports good orbital insertion, separation from the third stage, and antennae and solar panel deployment. But the cover of the scientific equipment bay does not separate. This will mean that many experiments cannot be accomplished. It is decided to launch the crew to the station anyway, since the station is otherwise functioning normally. The cosmonauts go to the baths in the evening. Additional Details: here....
1971 May 10 - . 16:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: No Block D ignition due wrong timer setting.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 419 - .
Payload: M-71 s/n 170. Mass: 4,650 kg (10,250 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-71.
Decay Date: 1971-05-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 5221 . COSPAR: 1971-042A. Apogee: 187 km (116 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 87.70 min.
Mars probe intended to enter Martian orbit and comprehensively photograph Mars. Rocket block failed to reignite in Earth Orbit. It is widely believed this spacecraft was launched with the primary purpose of overtaking Mariner 8, which had been launched (unsuccessfully, as it turned out) two days earlier, and becoming the first Mars orbiter. The Proton booster successfully put the spacecraft into low (174 km x 159 km) Earth parking orbit with an inclination of 51.4 degrees, but the Block D stage 4 failed to function due to a bad ignition timer setting (the timer, which was supposed to start ignition 1.5 hours after orbit was erroneously set for 1.5 years.) The orbit decayed and the spacecraft re-entered Earth's atmosphere 2 days later on 12 May 1971. The mission was designated Cosmos 419.
1971 May 19 - . 16:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Mars 2 - .
Payload: M-71 s/n 171. Mass: 4,650 kg (10,250 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-71.
USAF Sat Cat: 5234 . COSPAR: 1971-045A. Apogee: 25,000 km (15,000 mi). Perigee: 1,380 km (850 mi). Inclination: 48.90 deg. Period: 1,080.00 min.
Mars probe intended to conduct of a series of scientific investigations of the planet Mars and the space around it. Parameters are for Mars orbit. Mid-course corrections were made on 17 June and 20 November. Mars 2 released the descent module (1971-045D) 4.5 hours before reaching Mars on 27 November 1971. The descent system malfunctioned and the lander crashed at 45 deg S, 302 deg W, delivering the Soviet Union coat of arms to the surface. Meanwhile, the orbiter engine performed a burn to put the spacecraft into a 1380 x 24,940 km, 18 hour orbit about Mars with an inclination of 48.9 degrees. Scientific instruments were generally turned on for about 30 minutes near periapsis. Data was sent back for many months. It was announced that Mars 2 and 3 had completed their missions by 22 August 1972. On-orbit dry mass: 2265 kg. Had the lander survived, data would have been relayed to the earth via the orbiter.
1971 May 28 - . 15:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Mars 3 - .
Payload: M-71 s/n 172. Mass: 4,643 kg (10,236 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-71.
USAF Sat Cat: 5252 . COSPAR: 1971-049A. Apogee: 214,500 km (133,200 mi). Perigee: 1,528 km (949 mi). Inclination: 60.00 deg. Period: 18,243.00 min.
Mars probe intended to conduct of a series of scientific investigations of the planet Mars and the space around it. Parameters are for Mars orbit. The Mars 3 orbiter also carried a French-built experiment which was not carried on Mars 2. Called Spectrum 1, the instrument measured solar radiation at metric wavelengths in conjunction with Earth-based receivers to study the cause of solar outbursts. The Spectrum 1 antenna was mounted on one of the solar panels. A mid-course correction was made on 8 June. The descent module (COSPAR 1971-049F) was released at 09:14 GMT on 2 December 1971 about 4.5 hours before reaching Mars. Through aerodynamic braking, parachutes, and retro-rockets, the lander achieved a soft landing at 45 S, 158 W and began operations. However, after 20 sec the instruments stopped working for unknown reasons. Meanwhile, the orbiter engine performed a burn to put the spacecraft into a long 11-day period orbit about Mars with an inclination thought to be similar to that of Mars 2 (48.9 degrees). Data was sent back for many months. It was announced that Mars 2 and 3 had completed their missions by 22 August 1972.
1971 September 2 - . 13:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 18 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 407. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1971-09-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 5448 . COSPAR: 1971-073A. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). Perigee: 100 km (60 mi). Inclination: 35.00 deg. Period: 119.00 min.
Attempted lunar soil return mission; crashed while attempting to soft land at Latitude 3.57 N, Longitude 50.50 E - Mare Fecunditatis. Luna 18 used a new method of navigation in lunar orbit and for landing. The spacecraft's designer, Babakhin, had died at age 56 only the month before. Luna 18 successfully reached earth parking orbit before being put on a translunar trajectory. On September 7, 1971, it entered lunar orbit. The spacecraft completed 85 communications sessions and 54 lunar orbits before it was sent towards the lunar surface by use of braking rockets. It impacted the Moon on September 11, 1971, in a rugged mountainous terrain. Signals ceased at the moment of impact. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1971 September 28 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 19 - .
Payload: Ye-8-LS s/n 202. Mass: 5,810 kg (12,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-LS.
USAF Sat Cat: 5488 . COSPAR: 1971-082A. Apogee: 140 km (80 mi). Perigee: 140 km (80 mi). Inclination: 40.60 deg. Period: 121.75 min.
Heavy lunar Orbiter; conducted lunar surface mapping. Luna 19 entered an intermediate earth parking orbit and was then put on a translunar trajectory by the Proton Block D stage. It entered lunar orbit on October 3, 1971. Luna 19 extended the systematic study of lunar gravitational fields and location of mascons (mass concentrations). It also studied the lunar radiation environment, the gamma-active lunar surface, and the solar wind. Photographic coverage via a television system was also obtained. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1972 February 14 - . 03:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 20 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 408. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1972-02-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 5835 . COSPAR: 1972-007A. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). Perigee: 100 km (60 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 118.00 min.
Soft landed on Moon; returned soil samples to Earth. Landed on Moon 21 February 1972 at 19:19:00 GMT, Latitude 3.57 N, Longitude 56.50 E - Mare Fecunditatis. Luna 20 was placed in an intermediate earth parking orbit and from this orbit was sent towards the Moon. It entered lunar orbit on February 18, 1972. On 21 February 1972, Luna 20 soft landed on the Moon in a mountainous area known as the Apollonius highlands, 120 km from where Luna 18 had crashed. While on the lunar surface, the panoramic television system was operated. Lunar samples were obtained by means of an extendable drilling apparatus. The ascent stage of Luna 20 was launched from the lunar surface on 22 February 1972 carrying 30 grams of collected lunar samples in a sealed capsule. It landed in the Soviet Union on 25 February 1972. The lunar samples were recovered the following day.
1972 June 15 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Almaz / TKS project rescheduled. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: Almaz OPS, Almaz OPS-2, TKS. Ministry of General Machine Building (MOM) Decree 'On schedule of work for the Almaz and TKS programs' was issued..
1972 July 29 - . 03:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K. FAILURE: Second stage malfunction at T+ 162 sec.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Zarya s/n 122 - . Payload: Zarya s/n 122. Mass: 18,000 kg (39,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz. Spacecraft: Salyut 1. Decay Date: 1972-07-29 . Second Salyut space station (DOS 2), failed to reach orbit..
1972 October 18 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- UR-500K failure investigation. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei. Afanasyev was back at the cosmodrome for investigation of the latest UR-500K failure..
1972 December 31 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Brezhnev selects Almaz for next space station - . Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz. Spacecraft: Almaz OPS. Brezhnev personally selects Almaz for next space station launch. Following two successive failures of DOS-7K station (Salyut 1 and the July 29, 1972 launch failure), Brezhnev personally selects Almaz for next launch (Salyut 2)..
1973 January 8 - . 06:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 21 - .
Payload: Ye-8 s/n 204. Mass: 5,567 kg (12,273 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
Decay Date: 1973-01-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 6333 . COSPAR: 1973-001A. Apogee: 110 km (60 mi). Perigee: 90 km (55 mi). Inclination: 60.00 deg. Period: 118.00 min.
The Proton / Block D launcher put the spacecraft into Earth parking orbit followed by translunar injection. On 12 January 1973, Luna 21 braked into a 90 x 100 km orbit about the Moon. On 13 and 14 January, the perilune was lowered to 16 km altitude. On 15 January after 40 orbits, the braking rocket was fired at 16 km altitude, and the craft went into free fall. At an altitude of 750 meters the main thrusters began firing, slowing the fall until a height of 22 meters was reached. At this point the main thrusters shut down and the secondary thrusters ignited, slowing the fall until the lander was 1.5 meters above the surface, where the engine was cut off. Landing occurred at 23:35 GMT in LeMonnier crater at 25.85 degrees N, 30.45 degrees E. The lander carried a bas relief of Lenin and the Soviet coat-of-arms. After landing, Lunokhod 2 took TV images of the surrounding area, then rolled down a ramp to the surface at 01:14 GMT on 16 January and took pictures of the Luna 21 lander and landing site. It stopped and charged batteries until 18 January, took more images of the lander and landing site, and then set out over the Moon. The rover would run during the lunar day, stopping occasionally to recharge its batteries via the solar panels. At night the rover would hibernate until the next sunrise, heated by the radioactive source. Lunokhod 2 operated for about 4 months, covered 37 km of terrain including hilly upland areas and rilles, and sent back 86 panoramic images and over 80,000 TV pictures. Many mechanical tests of the surface, laser ranging measurements, and other experiments were completed during this time. On June 4 it was announced that the program was completed, leading to speculation that the vehicle probably failed in mid-May or could not be revived after the lunar night of May-June. The Lunokhod was not left in a position such that the laser retroreflector could be used, indicating that the failure may have happened suddenly.
1973 April 3 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Salyut 2 - .
Payload: Almaz s/n 101-01. Mass: 18,500 kg (40,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS.
Duration: 54.62 days. Decay Date: 1973-05-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 6398 . COSPAR: 1973-017A. Apogee: 248 km (154 mi). Perigee: 216 km (134 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
The first flight of the Almaz manned military space station. In January 1973 the first Almaz OPS was delivered to Baikonur. Launch and initial orbital checkout went according to plan. But before a crew could be launched the station depressurized. It was concluded that a short in electrical equipment started a fire in pressure vessel, leading to rupture of hull and depressurization. An alternate theory was that debris from an explosion of the third stage of Proton penetrated the hull. Control was lost on April 25, 1973, and the OPS cased operations on 29 April. Decayed May 28, 1973. Initial crew was to have been Popovich and Artyukhin.
Officially: Testing of improved design, on-board systems and equipment; conduct of scientific and technical research and experiments. Additional Details: here....
1973 May 11 - . 00:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 557 - . Payload: Zarya s/n 123. Mass: 19,400 kg (42,700 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz. Spacecraft: Salyut 4. Duration: 10.98 days. Decay Date: 1973-05-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 6498 . COSPAR: 1973-026A. Apogee: 225 km (139 mi). Perigee: 206 km (128 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Salyut failure. Unsuccessful mission. Salyut out of control. Decayed May 22, 1973. Was to have been manned by initial crew of Leonov and Kubasov. Last chance to upstage Skylab, launched three days later..
1973 July 21 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Mars 4 - .
Payload: M-73 s/n 52S. Mass: 4,650 kg (10,250 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-73.
USAF Sat Cat: 6742 . COSPAR: 1973-047A.
Failed; did not enter Martian orbit as planned; intended to be a Mars orbiter mission. Mars 4 reached Mars on 10 February 1974. Due to use of helium in preflight tests of the computer chips, which resulted in degradation of the chips during the voyage to Mars, the retro-rockets never fired to slow the craft into Mars orbit. Mars 4 flew by the planet at a range of 2,200 km. It returned one swath of pictures and some radio occultation data. Final heliocentric orbit 1.02 x 1.63 AU, 2.2 degree inclination, 556 day period.
1973 July 25 - . 18:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Mars 5 - .
Payload: M-73 s/n 53S. Mass: 4,650 kg (10,250 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-73.
USAF Sat Cat: 6754 . COSPAR: 1973-049A.
Mars probe intended to enter Martian orbit and comprehensively photograph Mars. Parameters are for Mars orbit. Mars 5 reached Mars on 12 February 1974 and was inserted into a 1760 km x 32,586 km orbit. Due to computer chip failures the orbiter operated only a few days and returned atmospheric data and images of a small portion of the Martian southern hemisphere.
1973 August 5 - . 17:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Mars 6 - .
Payload: M-73 s/n 50P. Mass: 4,650 kg (10,250 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-73.
USAF Sat Cat: 6768 . COSPAR: 1973-052A.
Mars probe intended to make a soft landing on Mars. Total fueled launch mass of the lander and orbital bus was 3260 kg. It reached Mars on 12 March 1974, separated from the bus, and entered the atmosphere, where a parachute opened, slowing the descent. As the probe descended through the atmosphere it transmitted data for 150 seconds, representing the first data returned from the atmosphere of Mars. Unfortunately, the data were largely unreadable due to a flaw in a computer chip which led to degradation of the system during its journey to Mars. When the retro-rockets fired for landing, contact was lost with the craft. Mars 6 landed at about 24 degrees south, 25 degrees west in the Margaritifer Sinus region of Mars. Bus ended up in a final heliocentric orbit 1.01 x 1.67 AU, 2.2 degree inclination, 567 day period.
1973 August 9 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Mars 7 - .
Payload: M-73 s/n 51P. Mass: 4,650 kg (10,250 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M-73.
USAF Sat Cat: 6776 . COSPAR: 1973-053A.
Mars probe intended to make a soft landing on Mars. Mars 7 reached Mars on 9 March 1974. Due to a problem in the operation of one of the onboard systems (attitude control or retro-rockets) the landing probe separated prematurely and missed the planet by 1,300 km. The early separation was probably due to a computer chip error which resulted in degradation of the systems during the trip to Mars. Ended up in a final heliocentric orbit 1.01 x 1.69 AU, 2.2 degree inclination, 574 day period.
1973 October 5 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, R-7.
- Mishin presents to the Academic Soviet the high-level justification and purpose of MKBS. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Ustinov,
Melnikov.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-S.
Principal basis for the development of the MOK
1. Providing solutions in targeted areas of defense, science and the economy as they may change over 10-20 years. Enabling rapid replacement of legacy systems, devices and components by more sophisticated systems without changing the logic of construction of the MOK as a whole and its constituent satellite systems and basic modules.
2. Solution targets a minimum number of satellite modules using common equipment and apparatus.
3. Complex solution of defense, economic and scientific problems using MKBS - the main base of the MOK, for logistics and maintenance of a long-term operation and cost-effective transport system.
4. The modular structure of the MOK. Wide standardization, harmonization of systems, devices, compartments, aggregates. All elements of these systems, devices, units must be maintainable and interchangeable.
5. Ensuring long-term service life (5-10 years) of the MOK through periodic visits CM astronauts for routine maintenance, based on the MKBS.
6. MOK should provide the most cost-effective creation of rocket-space tools for addressing the full range of targets, most cost-effective organization of logistics, maintenance and management of the complex in comparison with existing systems. The development of the IOC should be considered as the direction of development of rocket and space technology to solve national problems with the least material costs.
7. Stages of creation MOK as the development and creation of the necessary special systems.
And receives the following criticisms:
1. All elements of MKBS (especially spacecraft based on the 7KS) must have the new layout of systems and equipment, providing repair and replacement.
2. GP Melnikov - MKBS is necessary, but give priority to modules SM-1 and SM-2 (these are specialized military free-flyers).
3. You need to rethink the section on handling scientific information.
4. Do we need to upgrade or add all these launch sites (R-7, UR-500 and N-1) for MOK (especially the UR500K launch complex)? VP Barmin offers not to upgrade the old UR-500 launch complexes, and spend those funds on new complexes (in fact these two additional UR-500 complexes would be the only ones built after the N1 / MKBS cancellation).
5. You need a special decision of the Central Committee of the CPSU and special funding for construction.
6. Which launch vehicles to implement the MOK.
ND Ustinov suggests use of the UR-500 with a fluorine-ammonia upper stage to launch the SNTV direct television broadcasting system (Mishin Diaries 3-104)
1973 December 11 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, N11.
- Mishin lays out his planned program in desperate notes. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Afanasyev, Sergei,
Bezverby,
.
Spacecraft: ,
MKBS.
Review materials sent from Moscow.
1. Long-term program TSKBEM (projected) (See. Ref. 4/4748 dated 10 October 1973 from MOM).
MKBS-1 on UR-500K (this would later be Mir)-
Number 1 - 1977
Number 2 - 1978 - 79
MKBS on N-1 - Number 1 - 1983
Number 2 - 1988
N-11 (this refers to the use of the N-11 to replace the UR-500K for boosting modules to MKBS-1/Mir)
1 - 1978
2 - 1979
MKTS on the basis of the first-stage N1 - 1985 with the augmented engine - 1988-90 (this is a reference to the aerospike / air-augmented N1 with the spaceplane second stage, as revealed to USAF agent Peter X in that year!)
Performance in accordance with the "additional materials to the plan for experimental work in 1976-1990. See ref. 10414 dated 6.XII.1973.
2. TSKBEM work plan for 1974.
- Clarify:
a) The number for transport spacecraft to object "A", S.A. (Afanasiev?)
b) The number of DM (ZEM cannot produce the quantity.)
- No specification from TSNIIMMASH for the heavy launch vehicle (not to mention its scientific and technical justification).
3. Thematic plan for experimental work for TsKBEM in 1974.
4. NIR
All these materials require serious revision. (Focused, real and concrete, etc.) -Need to reduce the subject areas, the scope of work and remove excessive detail.
Call Bezverby VK - For papers on MOK.
Received in response via telegram a runaround (old papers are in the materials of the Academic Council). And I need - new papers. (I do not have - or have not yet found - my copies of these papers)
1974 March 26 - . 13:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Cosmos 637 - .
Payload: Gran dummy s/n 21D. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga.
Completed Operations Date: 1974-03-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 7229 . COSPAR: 1974-017A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,493 km (22,054 mi). Inclination: 14.30 deg. Period: 1,428.80 min.
Test of Block D stage in geosynchronous satellite delivery role. Placed dummy Raduga satellite in geosynchronous orbit. As of 4 September 2001 located at 44.61 deg E drifting at 1.835 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 119.66E drifting at 1.819E degrees per day.
1974 May 29 - . 08:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 22 - .
Payload: Ye-8-LS s/n 206. Mass: 5,835 kg (12,863 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-LS.
Decay Date: 1975-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 7315 . COSPAR: 1974-037A. Apogee: 220 km (130 mi). Perigee: 220 km (130 mi). Inclination: 19.60 deg. Period: 130.00 min.
Heavy lunar orbiter. Scientific investigation of the moon and circumlunar space from the orbit of an artificial satellite of the Moon, which was begun by the Luna 19 automatic station. The spacecraft carried imaging cameras and also had the objectives of studying the Moon's magnetic field, surface gamma ray emissions and composition of lunar surface rocks, and the gravitational field, as well as micrometeoroids and cosmic rays. Luna 22 braked into a circular lunar orbit on 2 June 1974. The spacecraft made many orbit adjustments over its 18 month lifetime in order to optimise the operation of various experiments, lowering the perilune to as low as 25 km. Manoeuvring fuel was exhausted on 2 September and the mission was ended in early November. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1974 June 24 - . 22:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Salyut 3 - .
Payload: Almaz s/n 101-02. Mass: 18,500 kg (40,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS.
Duration: 90.00 days. Decay Date: 1975-01-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 7342 . COSPAR: 1974-046A. Apogee: 253 km (157 mi). Perigee: 213 km (132 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
First successful Almaz military manned space station flight. Tested a wide array of reconnaissance sensors. Following the successful Soyuz 14 and unsuccessful Soyuz 15 missions, on 23 September 1974 the station ejected a film return capsule. The KSI capsule suffered damage during re-entry but all the film was recoverable. On 24 January 1975 trials of the on-board 23 mm Nudelmann aircraft cannon (other sources say it was a Nudelmann NR-30 30 mm gun) were conducted. The next day the station was commanded to retrofire to a destructive re-entry over the Pacific Ocean. Although only one of three planned crews managed to board the station, that crew did complete the first completely successful Soviet space station flight. Additional Details: here....
1974 July 29 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Molniya 1-S - .
Payload: Molniya 1 s/n 38. Mass: 800 kg (1,760 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Molniya.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-2.
Spacecraft: Molniya-1.
Completed Operations Date: 1974-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 7392 . COSPAR: 1974-060A. Apogee: 35,848 km (22,274 mi). Perigee: 35,738 km (22,206 mi). Inclination: 14.80 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min.
Evidently a unique experimental satellite. Arrangements for experimental television broadcasts and establishment of long-range radio-communications. As of 29 August 2001 located at 104.72 deg E drifting at 0.115 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 41.05E drifting at 0.029W degrees per day.
1974 October 28 - . 14:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 23 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5M s/n 410. Mass: 5,300 kg (11,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1974-11-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 7491 . COSPAR: 1974-084A. Apogee: 105 km (65 mi). Perigee: 17 km (10 mi).
Failed lunar soil return mission. After successfully entering earth orbit, flying to the moon, entering lunar orbit, and descending toward the surface, the spacecraft was damaged during landing in Mare Crisium (Sea of Crises). The sample collecting apparatus could not operate and no samples were returned. The lander continued transmissions for three days after landing. In 1976, Luna 24 landed several hundred meters away and successfully returned samples. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1974 December 26 - . 04:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Salyut 4 - .
Payload: Zarya s/n 124. Mass: 18,500 kg (40,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Salyut 4.
Duration: 768.82 days. Decay Date: 1977-02-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 7591 . COSPAR: 1974-104A. Apogee: 251 km (155 mi). Perigee: 212 km (131 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
Deorbited February 2, 1977.
Maneuver Summary:
211km X 250km orbit to 215km X 286km orbit. Delta V: 11 m/s
211km X 284km orbit to 276km X 344km orbit. Delta V: 35 m/s
277km X 342km orbit to 338km X 351km orbit. Delta V: 19 m/s
330km X 340km orbit to 337km X 350km orbit. Delta V: 4 m/s
337km X 349km orbit to 339km X 351km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
332km X 348km orbit to 348km X 355km orbit. Delta V: 6 m/s
347km X 354km orbit to 343km X 351km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
335km X 344km orbit to 335km X 360km orbit. Delta V: 4 m/s
335km X 360km orbit to 342km X 361km orbit. Delta V: 2 m/s
330km X 351km orbit to 344km X 353km orbit. Delta V: 4 m/s
186km X 187km orbit to 90km X 186km orbit. Delta V: 28 m/s
Total Delta V: 87/115 m/s.
Officially: Further testing of station design, on-board systems and equipment; conduct of scientific and technical research and experiments in outer space. Further testing of station design, on-board systems and equipment; conduct of scientific and technical researc h and experiments in outer space.
1975 April 29 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: UR-500MK.
- UR-500MK designed - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Glushko.
In response to the Ministry of Defence's guidelines for third generation launch vehicles, the Ministry of General Machine Building issued instructions for Chelomei to study boosters meeting the military's requirements. These included Lox/Kerosene propellants in place of the toxic N2O4/UDMH favoured previously. Chelomei's competitor in the design, Glushko, was then head of NPO Energia which included Glushko's former OKB-456 engine design bureau. Therefore Chelomei was forced to propose using Kuznetsov Lox/Kerosene engines from the cancelled N1 moon program. The use of existing Proton tankage tooling for the stages and the Kuznetsov engines would allow a high-performance vehicle to be developed at minimum cost. However Chelomei was out of favour, Kuznetsov was discredited after the N1 fiasco, and Glushko was ascendant. The proposal stood no chance. Glushko's Zenit launch vehicle became the accepted solution.
1975 June 8 - . 02:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Venera 9 - .
Payload: 4V-1 s/n 660. Mass: 4,936 kg (10,882 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 7915 . COSPAR: 1975-050A. Apogee: 112,200 km (69,700 mi). Perigee: 1,510 km (930 mi). Inclination: 34.15 deg. Period: 2,898.00 min.
Combined Venus orbiter/lander mission. After separation of the lander, the orbiter spacecraft entered Venus orbit and acted as a communications relay for the lander and explored cloud layers and atmospheric parameters. On October 20, 1975, the Descent Craft was separated from the Orbiter, and landing was made with the sun near zenith at 05:13 GMT on October 22. The Descent Craft included a system of circulating fluid to distribute the heat load. This system, plus precooling prior to entry, permitted operation of the spacecraft for 53 min after landing. The landing was about 2,200 km from the Venera 10 landing site. Preliminary results indicated: (A) clouds 30-40 km thick with bases at 30-35 km altitude, (B) atmospheric constituents including HCl, HF, Br, and I, (C) surface pressure about 90 (earth) atmospheres, (D) surface temperature 485 deg C, (E) light levels comparable to those at earth midlatitudes on a cloudy summer day, and (F) successful TV photography showing shadows, no apparent dust in the air, and a variety of 30-40 cm rocks which were not eroded. Venera 9 and 10 were the first probes to send back black and white pictures from the Venusian surface. They were supposed to make 360 degree panoramic shots, but on both landers one of two camera covers failed to come off, restricting their field of view to 180 degrees. Parameters are for Venus orbit.
1975 June 14 - . 03:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Venera 10 - .
Payload: 4V-1 s/n 661. Mass: 5,033 kg (11,095 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 7947 . COSPAR: 1975-054A. Apogee: 113,900 km (70,700 mi). Perigee: 1,620 km (1,000 mi). Inclination: 29.50 deg. Period: 2,963.00 min.
The orbiter spacecraft entered Venus orbit and was separated from the lander on October 23, 1975. The lander touched down with the sun near zenith, at 05:17 GMT, on October 25. A system of circulating fluid was used to distribute the heat load. This system, plus precooling prior to entry, permitted operation of the spacecraft for 65 min after landing. During descent, heat dissipation and deceleration were accomplished sequentially by protective hemispheric shells, three parachutes, a disk-shaped drag brake, and a compressible, metal, doughnut-shaped, landing cushion. The landing was about 2,200 km distant from Venera 9. Preliminary results provided: (A) profile of altitude (km)/pressure (earth atmospheres) / temperature (deg C) of 42/3.3/158, 15/37/363, and 0/92/465, (B) successful TV photography showing large pancake rocks with lava or other weathered rocks in between, and (C) surface wind speed of 3.5 m/s. Venera 9 and 10 were the first probes to send back black and white pictures from the Venusian surface. They were supposed to make 360 degree panoramic shots, but on both landers one of two camera covers failed to come off, restricting their field of view to 180 degrees.
1975 October 8 - . 00:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Cosmos 775 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 1. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1975-10-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 8357 . COSPAR: 1975-097A. Apogee: 35,853 km (22,277 mi). Perigee: 35,749 km (22,213 mi). Inclination: 14.90 deg. Period: 1,436.80 min.
First launch of a prototype for a new geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Exploded in orbit. The next launch did not come until nine years later, so this may have been a version of the Oko elliptical orbit early warning satellite. As of 29 August 2001 located at 113.71 deg E drifting at 0.044 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 54.82E drifting at 0.255W degrees per day.
1975 October 16 - . 04:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1. FAILURE: Block D stage failed.. Failed Stage: U.
- Ye-8-5M s/n 412 - Block D stage failed. - . Payload: Ye-8-5M s/n 412. Mass: 5,300 kg (11,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1975-10-16 . Attempted robotic lunar soil return mission. Block D stage failed..
1975 December 22 - . 13:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 1 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 11L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1978-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 8513 . COSPAR: 1975-123A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,758 km (22,218 mi). Inclination: 13.30 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
Statsionar-1. Provision of uninterrupted round-the-clock telephone and telegraph radio-communications system in the USSR, transmission of USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network and international cooperation. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 85 deg E in 1975-1978? As of 27 August 2001 located at 70.55 deg E drifting at 0.084 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 85.79E drifting at 0.009E degrees per day.
1976 June 22 - . 18:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Salyut 5 - .
Payload: Almaz s/n 103-01. Mass: 19,000 kg (41,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS.
Duration: 411.24 days. Decay Date: 1977-08-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 8911 . COSPAR: 1976-057A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 215 km (133 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Second successful flight of the Almaz manned military space station. It had taken only 60 days and 1450 man-hours to prepare Almaz 0101-2 for flight, using the services of 368 officers and 337 non-commissioned officers. The tracking ships Academician Sergei Korolev and Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin were stationed in the Atlantic and Caribean to provide communications when out of tracking range of the USSR. Salyut 5 operated for 409 days, during which the crews of Soyuz 22 and 24 visited the station. Soyuz 23 was to have docked but its long-distance rendezvous system failed. Soyuz 25 was planned, but the mission would have been incomplete due to low orientation fuel on Salyut 5, so it was cancelled.
During the flight of Salyut 5 a 'parallel crew' was aboard a duplicate station on the ground. They conducted the same operations in support of over 300 astrophysical, geophysical, technological, and medical/biological experiments. Astrophysics studies included an infrared telescope-spectrometer in the 2-15 micrometer range which also obtained solar spectra. Earth resources studies were conducted as well as Kristall, Potok, Diffuziya, Sfera, and Reatsiya technology experiments. Presumably Salyut 5 was equipped with a SAR side-looking radar for reconnaissance of land and sea targets even through cloud cover.
The film capsule was ejected 22 February 1977 (and sold at Sotheby's, New York, on December 11, 1993!). The station was deorbited on 8 August 1977. In addition to the human crew two Russian tortoises (Testudo horsfieldi) and Zebrafish (Danio rerio) were flown.
The results of the Salyut 3 and 5 flights showed that manned reconnaissance was not worth the expense. There was minimal time to operate the equipment after the crew took the necessary time for maintenance of station housekeeping and environmental control systems. The experiments themselves showed good results and especially the value of reconnaissance of the same location in many different spectral bands and parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Additional Details: here....
1976 August 9 - . 15:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Luna 24 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5M s/n 413. Mass: 5,306 kg (11,697 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1976-08-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 9272 . COSPAR: 1976-081A. Apogee: 115 km (71 mi). Perigee: 115 km (71 mi). Inclination: 120.00 deg. Period: 119.00 min.
Lunar Sample Return. Landed on Moon 18 Aug 1976 at 02:00:00 GMT, Latitude 12.25 N, Longitude 62.20 E - Mare Crisium (Sea of Crisis). The last of the Luna series of spacecraft, Luna 24 was the third Soviet mission to retrieve lunar ground samples (the first two were returned by Luna 16 and 20). The mission successfully returned 170 grams of lunar samples to the Earth on 22 August 1976.
1976 September 11 - . 18:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 2 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 12L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1980-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 9416 . COSPAR: 1976-092A. Apogee: 35,866 km (22,286 mi). Perigee: 35,704 km (22,185 mi). Inclination: 13.10 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Statsionar 1. Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 86 deg E in 1976-1980? As of 28 August 2001 located at 67.16 deg E drifting at 0.070 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 72.27E drifting at 0.098W degrees per day.
1976 October 26 - . 14:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 1 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 11L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1978-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 9503 . COSPAR: 1976-107A. Apogee: 36,080 km (22,410 mi). Perigee: 35,516 km (22,068 mi). Inclination: 13.00 deg. Period: 1,436.70 min.
Statsionar T. Transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to the network of public receiving units located in population centres in Siberia and the Far North. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 99 deg E in 1976-1978 As of 29 August 2001 located at 68.75 deg E drifting at 0.171 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 73.60E drifting at 0.187W degrees per day.
1976 December 15 - . 01:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 881 - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 009P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA .
Duration: 0.0600 days. Decay Date: 1976-12-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 9606 . COSPAR: 1976-121A. Apogee: 241 km (149 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Launch of mission LVI-1 came at 04:00 on 15 December. At 176 seconds the ADU escape tower separated from the LVI. Once the final stage had shut down in orbit, by command from the launch vehicle sequencer, the VA 009A (also given as 009P) and its TDU separated from the LVI. Two seconds later VA 009 (or 009L) was ejected. Fifteen minutes after launch all systems of the both VA capsules were in operation. The guidance system detected the direction of flight and oriented each spacecraft for retro-fire, and the pair began the return to earth after less than one revolution. At an external atmospheric pressure of 165 mm (10 km altitude) the NO section jettisoned, the three-cupola drogue parachute ejected, and the antennae and altimeter were deployed. The Komara landing radio beacon (installed on the landing section of the parachute) was activated when the spacecraft was 1.0 to 1.5 m above the ground - which occurred at the same moment on both 009 and 009A. The Kaktus special system tripped the soft landing PRSP (parachute landing propulsion system). The soft landing was accomplished with higher accuracy than Soyuz, both capsules being recovered at 44 deg N, 73 deg E, on December 15, 1976 3:00 GMT. The flights were officially given the designations Cosmos 881 (VA 009A) and Cosmos 882 (VA 009). US intelligence believed them to be tests of recoverable manned spaceplane prototypes.
- Cosmos 882 - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 009L. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1976-12-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 9607 . COSPAR: 1976-121B. Apogee: 213 km (132 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Test of TKS-VA capsule. Two satellites launched by a single rocket..
1977 July 17 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 929 - .
Payload: TKS s/n 16101. Mass: 19,000 kg (41,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: TKS .
Duration: 199.62 days. Decay Date: 1978-02-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 10146 . COSPAR: 1977-066A. Apogee: 260 km (160 mi). Perigee: 226 km (140 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
First test of TKS manned shuttle. Maneuvered extensively. TKS-VA capsule returned to earth August 16, 1977. Deorbited February 2, 1978.
Maneuver Summary:
214 km X 261 km orbit to 215 km X 279 km orbit. Delta V: 5 m/s
207 km X 261 km orbit to 208 km X 264 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
208 km X 260 km orbit to 209 km X 267 km orbit. Delta V: 2 m/s
192 km X 222 km orbit to 219 km X 232 km orbit. Delta V: 9 m/s
219 km X 232 km orbit to 303 km X 327 km orbit. Delta V: 51 m/s
303 km X 327 km orbit to 312 km X 318 km orbit. Delta V: 4 m/s
312 km X 319 km orbit to 314 km X 325 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
284 km X 294 km orbit to 290 km X 301 km orbit. Delta V: 3 m/s
288 km X 300 km orbit to 286 km X 305 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
285 km X 303 km orbit to 439 km X 447 km orbit. Delta V: 84 m/s
437 km X 448 km orbit to 335 km X 437 km orbit. Delta V: 31 m/s
335 km X 437 km orbit to 337 km X 438 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
337 km X 438 km orbit to 90 km X 337 km orbit. Delta V: 100 m/s
Total Delta V: 193/293 m/s
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1977 July 23 - . 21:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 3 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 13L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1980-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 10159 . COSPAR: 1977-071A. Apogee: 35,853 km (22,277 mi). Perigee: 35,763 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 12.70 deg. Period: 1,437.20 min.
Statsionar-2. Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 35 deg E in 1977-1980 As of 30 August 2001 located at 44.45 deg E drifting at 0.191 deg W per day. As of 2007 Feb 27 located at 49.63E drifting at 0.221E degrees per day.
1977 August 4 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K. FAILURE: First stage engine steering unit failure at T+40.1 seconds. Failed Stage: 1.
- TKS VA s/n 009L/P - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 009L/P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1977-08-04 . Spacecraft lost in booster explosion..
- TKS VA s/n 009P/P - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 009P/P. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Almaz.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA.
A repeat test of the VA capsules from LVI-1 of a month earlier were atop the Proton (VA's 009P and 009L). However the booster failed at 49 seconds after launch. The SAS launch escape system pulled the top capsule (009P) away from the exploding Proton rocket and it was successfully recovered. The lower capsule was lost with the booster.
1977 September 20 - . 17:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 2 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 12L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1978-06-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 10365 . COSPAR: 1977-092A. Apogee: 35,938 km (22,330 mi). Perigee: 35,663 km (22,159 mi). Inclination: 12.70 deg. Period: 1,436.80 min.
Statsionar T. Transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to the network of public receiving units located in population centres in Siberia and the Far North. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 99 deg E in 1977-1978 As of 5 September 2001 located at 65.77 deg E drifting at 0.168 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 79.61E drifting at 0.200W degrees per day.
1977 September 29 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Proton 8K82K launch vehicle completes its state trials tests and is accepted into service. - .
Nation: Russia.
Remarkably, due to continuing failures, the 8K82K did not satisfactorily complete its state trials until its 61st launch (Salyut 6 / serial number 29501 / 29 September 1977). Thereafter it reached a level of launch reliability comparable to that of other world launch vehicles.
1977 September 29 - . 06:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Salyut 6 - .
Payload: Zarya s/n 125 s/n 5L. Mass: 19,824 kg (43,704 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 6.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Salyut 6.
Duration: 1,763.71 days. Decay Date: 1982-07-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 10382 . COSPAR: 1977-097A. Apogee: 237 km (147 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Conduct of scientific and technical research and experiments; further testing of station design, on-board system and equipment. Soyuz 25 docking unsuccessful. EVA 20 Dec 1977 to examine forward docking port (no damage). EVA 29 July 1978 to retrieve externally mounted experiments (micrometeorites, biopolymers, radiation plates, materials tests). Soyuz 33 failure to dock due to propulsion failure April 1979. Soyuz 34 launched unmanned to provide replacement vehicle June 1979. EVA August 15 to dislodge 10 m diameter KRT-10 radio telescope from aft docking collar. Repair mission Soyuz T-3 December 1980 (temperature control hydraulics). Repair mission Soyuz T-4 March 1981 (stuck solar array). Salyut ejected a module on May 31 (perhaps retained Soyuz Orbital Module). Kosmos 1267 docks 19 June 1981. Commanded to reentry using Kosmos 1267 propulsion system over Pacific July 29 1982. Additional Details: here....
1978 March 30 - . 00:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. Launch Pad: LC81/24?. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 997 - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 102L. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Cosmos 997.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA .
Decay Date: 1978-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 10770 . COSPAR: 1978-032A. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Given the on-pad explosion of the LVI-2 launch attempt, plans to crew the upper VA re-entry capsule in the next test was abandoned. LVI-3 (VA's 102P and 102L / Cosmos 997 and Cosmos 998) was launched unmanned four months behind the original schedule. Both capsules were recovered after one orbit. One source indicates that one of the capsules was 009P, on its third launch and second flight to orbit. This was said to have demonstrated the multiple re-entry capability of the heat shield and the first planned reuse of a spacecraft (Gemini 2 was refurbished and reflown as MOL-1 in the 1960's, but was not designed for that purpose).
- Cosmos 998 - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 102P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1978-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 10771 . COSPAR: 1978-032B. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Dual reentry test of two TKS-VA capsules. Recovered March 30, 1978 after one orbit..
1978 May 27 - . 01:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM. FAILURE: Stage 1 - vehicle failed at launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Ekran s/n 13L - . Payload: Ekran s/n 13L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Ekran. Failed launch of communications satellite..
1978 July 18 - . 21:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 4 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 14L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1981-03-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 10987 . COSPAR: 1978-073A. Apogee: 35,854 km (22,278 mi). Perigee: 35,757 km (22,218 mi). Inclination: 12.30 deg. Period: 1,437.10 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 35 deg E in 1978-1981 As of 1 September 2001 located at 42.47 deg E drifting at 0.129 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 108.35E drifting at 0.106E degrees per day.
1978 August 17 - . 20:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM. FAILURE: Stage 1 - vehicle failed at launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Ekran s/n 15L - . Payload: Ekran s/n 15L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Ekran.
1978 September 9 - . 03:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Venera 11 - .
Payload: 4V-1 s/n 360. Mass: 4,715 kg (10,394 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 11020 . COSPAR: 1978-084A.
Venera 11 was part of a two-spacecraft mission to study Venus and the interplanetary medium. Each of the two spacecraft, Venera 11 and Venera 12, consisted of a flight platform and a lander probe. Identical instruments were carried on both spacecraft. Venera 11 was launched into a 177 x 205 km, 51.5 degree inclination earth orbit from which it was propelled into a 3.5 month Venus transfer orbit. After ejection of the lander probe, the flight platform continued on past Venus in a heliocentric orbit. Near encounter with Venus occurred on December 25, 1978, at approximately 34,000 km altitude. The flight platform acted as a data relay for the descent craft for 95 minutes until it flew out of range and returned its own measurements on interplanetary space. The Venera 11 descent craft separated from its flight platform on December 23, 1978 and entered the Venus atmosphere two days later at 11.2 km/sec. During the descent, it employed aerodynamic braking followed by parachute braking and ending with atmospheric braking. It made a soft landing on the surface at 06:24 Moscow time on 25 December after a descent time of approximately 1 hour. The touchdown speed was 7-8 m/s.
Both Venera 11 and 12 landers failed to return colour television views of the surface and perform soil analysis experiments. All of the camera protective covers failed to eject after landing (the cause was not established) The soil drilling experiment was apparently damaged by a leak in the soil collection device, the interior of which was exposed to the high Venusian atmospheric pressure. The leak had probably formed during the descent phase because the lander was less aerodynamically stable than had been thought.
Two further experiments on the lander failed as well. Results reported included evidence of lightning and thunder, a high Ar36/Ar40 ratio, and the discovery of carbon monoxide at low altitudes.
1978 September 14 - . 02:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Venera 12 - .
Payload: 4V-1 s/n 361. Mass: 4,715 kg (10,394 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 11025 . COSPAR: 1978-086A.
Venera 12 was part of a two-spacecraft mission to study Venus and the interplanetary medium. Each of the two spacecraft, Venera 11 and Venera 12, consisted of a flight platform and a lander probe. Identical instruments were carried on both spacecraft. Venera 12 was launched into a 177 x 205 km, 51.5 degree inclination Earth orbit from which it was propelled into a 3.5 month Venus transfer orbit which involved two mid-course corrections, on 21 September and 14 December. After ejection of the lander probe on 19 December, two days before encounter, the flight platform continued on past Venus in a heliocentric orbit. Near encounter with Venus occurred on December 21, 1978, at approximately 34,000 km altitude. The flight platform acted as a data relay for the descent craft for 110 minutes until it flew out of range and returned to its own measurements on interplanetary space. The Venera 12 descent craft entered the Venus atmosphere at 11.2 km/sec two days after separation from the flight bus. During the descent, it employed aerodynamic braking followed by parachute braking and ending with atmospheric braking. It made a soft landing on the surface at 06:30 Moscow time on 21 December after a descent time of approximately 1 hour. The touchdown speed was 7-8 m/s.
Both Venera 11 and 12 landers failed to return colour television views of the surface and perform soil analysis experiments. All of the camera protective covers failed to eject after landing (the cause was not established) The soil drilling experiment was apparently damaged by a leak in the soil collection device, the interior of which was exposed to the high Venusian atmospheric pressure. The leak had probably formed during the descent phase because the lander was less aerodynamically stable than had been thought. Therefore the landing gear of the following two landers (Venera-13/14) were equipped with tooth-shaped stabilisers.
Results reported included evidence of lightning and thunder, a high Ar36/Ar40 ratio, and the discovery of carbon monoxide at low altitudes.
The Venera-12 flyby bus continued in solar orbit and successfully used its Soviet-French ultraviolet spectrometer to study Comet Bradfield on 13 February 1980 (one year and two months after its Venus encounter). At that time the spacecraft was 190,373,790 km from Earth.
1978 October 17 - . 16:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM. FAILURE: Second stage explosion.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Ekran s/n 14L - . Payload: Ekran s/n 14L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Ekran.
1978 December 19 - . 12:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM. FAILURE: Block DM malfunction, wrong orbit.. Failed Stage: U.
- Gorizont 1 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 11L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1980-01-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 11158 . COSPAR: 1978-118A. Apogee: 49,371 km (30,677 mi). Perigee: 22,193 km (13,790 mi). Inclination: 22.40 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
Did not achieve geostationary orbit due to malfunction of Block D. Operation of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 53 deg E in 1979-1980 As of 29 August 2001 located at 75.87 deg E drifting at 0.132 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 57.49E drifting at 0.119E degrees per day.
1979 February 21 - . 07:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 3 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 16L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1981-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11273 . COSPAR: 1979-015A. Apogee: 35,919 km (22,318 mi). Perigee: 35,623 km (22,135 mi). Inclination: 14.60 deg. Period: 1,435.30 min.
Transmission of color and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 99 deg E in 1979-1981 As of 3 September 2001 located at 51.81 deg E drifting at 0.088 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 98.64E drifting at 0.060E degrees per day.
1979 April 20 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K. FAILURE: Engines ignited but immediately shut down on launch pad. Booster could be reused with new payload.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Payload: TKS VA s/n 008. Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA . Decay Date: 1979-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 11362 . Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
1979 April 25 - . 03:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 5 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 15L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1982-05-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 11343 . COSPAR: 1979-035A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 11.90 deg. Period: 1,436.50 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1979-1982 As of 29 August 2001 located at 84.16 deg E drifting at 0.043 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 65.45E drifting at 0.034E degrees per day.
1979 May 22 - . 23:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 1100 - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 102P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Cosmos 1100.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA .
Duration: 0.0600 days. Decay Date: 1979-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 11362 . COSPAR: 1979-042A. Apogee: 222 km (137 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
The Proton launch vehicle that shut down on the original LVI-4 launch attempt was undamaged, and just a month later, with a switch of payload, LVI-4 was orbited as Cosmos 1100 and 1101. The pair launched were the 102P/102L twins from LVI-3. One capsule failed when the automatic system suffered an electrical distribution failure and it did not land correctly, spending two orbits in space, while the other landed as planned after one orbit. The launch again successfully demonstrated the reusability of the VA capsule. Plans to launch the upper capsule manned were scrubbed due to the inability to get two consecutive failure-free launches of the Proton/TKS-VA.
- Cosmos 1101 - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 102L. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1979-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 11363 . COSPAR: 1979-042B. Apogee: 222 km (137 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Test of TKS-VA manned capsule. Two satellites launched by a single rocket..
1979 July 5 - . 23:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 2 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 12L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1983-12-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 11440 . COSPAR: 1979-062A. Apogee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 11.50 deg. Period: 1,435.80 min.
Stationed at 14 deg W. Statsionar 4. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1979-1981; 90 deg E in 1981-1983 As of 26 August 2001 located at 59.72 deg E drifting at 0.012 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 84.05E drifting at 0.107W degrees per day.
1979 October 3 - . 17:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 4 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 17L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1981-03-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11561 . COSPAR: 1979-087A. Apogee: 35,827 km (22,261 mi). Perigee: 35,725 km (22,198 mi). Inclination: 14.50 deg. Period: 1,435.60 min.
Transmission of color and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1979-1981 As of 4 September 2001 located at 52.52 deg E drifting at 0.007 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 4 located at 96.71E drifting at 0.048W degrees per day.
1979 December 28 - . 11:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 3 - . Payload: Gorizont s/n 13L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Gorizont . Completed Operations Date: 1989-12-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 11648 . COSPAR: 1979-105A. Apogee: 35,831 km (22,264 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 11.00 deg. Period: 1,437.10 min. Stationed at 53 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 53 deg E in 1980-1984; 40 deg E in 1984-1989 As of 30 August 2001 located at 47.84 deg E drifting at 0.163 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 109.81E drifting at 0.002E degrees per day..
1980 February 20 - . 08:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 6 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 16L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1986-03-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11708 . COSPAR: 1980-016A. Apogee: 35,816 km (22,254 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 11.40 deg. Period: 1,436.70 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg E in 1980-1982; 45 deg E in 1982-1986 As of 1 September 2001 located at 41.36 deg E drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Feb 27 located at 101.46E drifting at 0.146E degrees per day.
1980 June 14 - . 00:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 4 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 15L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1988-10-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 11841 . COSPAR: 1980-049A. Apogee: 36,269 km (22,536 mi). Perigee: 36,239 km (22,517 mi). Inclination: 14.30 deg. Period: 1,460.10 min.
Stationed at 14 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1980-1984; 11 deg W in 1984-1985; 14 deg W in 1985; 11 deg W in 1985-1988 As of 3 September 2001 located at 106.01 deg W drifting at 5.930 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 145.19W drifting at 5.924W degrees per day.
1980 July 14 - . 22:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 5 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 19L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1980-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11890 . COSPAR: 1980-060A. Apogee: 35,834 km (22,266 mi). Perigee: 35,737 km (22,205 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Transmission of color and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1980 Last known longitude (14 March 1994) 95.12 deg E drifting at 0.122 deg W per day.
1980 October 5 - . 17:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 7 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 17L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1986-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 12003 . COSPAR: 1980-081A. Apogee: 35,805 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,755 km (22,217 mi). Inclination: 14.00 deg. Period: 1,435.80 min.
Radio, telegraph, TV. Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1980-1981; 25 deg W in 1982-1986 As of 30 August 2001 located at 103.91 deg W drifting at 0.397 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 3 located at 30.06W drifting at 0.092W degrees per day.
1980 December 26 - . 11:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 6 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 20L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1981-12-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 12120 . COSPAR: 1980-104A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 14.00 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min.
Transmission of color and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1981 As of 3 September 2001 located at 96.55 deg E drifting at 0.071 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 2 located at 55.67E drifting at 0.097E degrees per day.
1981 March 18 - . 04:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 8 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 18L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1981-04-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 12351 . COSPAR: 1981-027A. Apogee: 36,115 km (22,440 mi). Perigee: 35,411 km (22,003 mi). Inclination: 10.80 deg. Period: 1,434.90 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. As of 3 September 2001 located at 8.37 deg E drifting at 0.322 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 69.95E drifting at 0.520E degrees per day.
1981 April 25 - . 02:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 1267 - .
Payload: TKS s/n 16301. Mass: 19,000 kg (41,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: TKS .
Duration: 459.91 days. Decay Date: 1982-07-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 12419 . COSPAR: 1981-039A. Apogee: 259 km (160 mi). Perigee: 192 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
TKS space station ferry. Flown unmanned to the Salyut 6 space station after the Almaz military station program was cancelled. Capsule recovered 24 May 1981. Docked with Salyut 6 on June 19 at 10:52 AM MT after 57 days autonomous flight. Deorbited and destroyed with Salyut July 29, 1982. Additional Details: here....
1981 June 25 - . 23:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 7 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 21L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1982-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 12564 . COSPAR: 1981-061A. Apogee: 35,819 km (22,256 mi). Perigee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 10.50 deg. Period: 1,437.00 min.
Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1981-1982 As of 1 September 2001 located at 78.87 deg E drifting at 0.201 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 66.59E drifting at 0.197W degrees per day.
1981 July 30 - . 21:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 9 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 19L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1986-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 12618 . COSPAR: 1981-069A. Apogee: 35,828 km (22,262 mi). Perigee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Inclination: 13.80 deg. Period: 1,437.20 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg E in 1981-1986 As of 30 August 2001 located at 112.14 deg E drifting at 0.090 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 76.83E drifting at 0.307W degrees per day.
1981 October 9 - . 16:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 10 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 20L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1987-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 12897 . COSPAR: 1981-102A. Apogee: 35,820 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 13.70 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1981-1987 As of 5 September 2001 located at 76.66 deg E drifting at 0.069 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 65.57E drifting at 0.042W degrees per day.
1981 October 30 - . 06:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Venera 13 - .
Payload: 4V-1 s/n 760. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 12927 . COSPAR: 1981-106A.
Venera 13 and 14 were identical spacecraft built to take advantage of the 1981 Venus launch opportunity and launched 5 days apart. After launch and a four month cruise to Venus, the descent vehicle separated and plunged into the Venus atmosphere on 1 March 1982. As it flew by Venus the bus acted as a data relay for the brief life of the descent vehicle, and then continued on into a heliocentric orbit. After the descent vehicle braked to subsonic speed a parachute was deployed. At an altitude of 47 km the parachute was released and simple airbraking was used the rest of the way to the surface. Venera 13 landed about 950 km northeast of Venera 14 at 7 deg 30 min S, 303 E, just east of the eastern extension of an elevated region known as Phoebe Regio. The area was composed of bedrock outcrops surrounded by dark, fine-grained soil. After landing an imaging panorama was started and a mechanical drilling arm reached to the surface and obtained a sample, which was deposited in a hermetically sealed chamber, maintained at 30 degrees C and a pressure of about .05 atmospheres. The composition of the sample, as determined by the X-ray flourescence spectrometer, put it in the class of weakly differentiated melanocratic alkaline gabbroids. The lander survived for 127 minutes (the planned design life was 32 minutes) in an environment with a temperature of 457 degrees C and a pressure of 84 Earth atmospheres. The bus carried instruments built by Austrian and French specialists, as well as Soviet scientific equipment.
1981 November 4 - . 05:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Venera 14 - .
Payload: 4V-1 s/n 761. Mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 12938 . COSPAR: 1981-110A.
Venera 13 and 14 were identical spacecraft built to take advantage of the 1981 Venus launch opportunity and launched 5 days apart. After launch and a four month cruise to Venus, the descent vehicle separated and plunged into the Venus atmosphere on 5 March 1982. As it flew by Venus the bus acted as a data relay for the brief life of the descent vehicle, and then continued on into a heliocentric orbit. The parachute of the descent vehicle opened after the lander reached subsonic speed. At an altitude of about 50 km the parachute was released and simple airbraking was used the rest of the way to the surface. Venera 14 landed about 950 km southwest of Venera 13 near the eastern flank of Phoebe Regio at 13 deg 15 min S by 310 E on a basaltic plain. After landing an imaging panorama was started It has been reported that the surface analysis arm accidentally landed on one of the ejected camera covers and therefore didn't send back any data on the Venusian soil. This is visible in photographs sent back. On the other hand, the official account very specifically states that the mechanical drilling arm obtained a sample, which was deposited in a hermetically sealed chamber, maintained at 30 degrees C and a pressure of about .05 atmospheres. The composition of the sample was determined by the X-ray flourescence spectrometer, showing it to be similar to oceanic tholeiitic basalts. The lander survived for 57 minutes (the planned design life was 32 minutes) in an environment with a temperature of 465 degrees C and a pressure of 94 Earth atmospheres.
1982 February 5 - . 09:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 8 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 22L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1984-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 13056 . COSPAR: 1982-009A. Apogee: 36,010 km (22,370 mi). Perigee: 35,756 km (22,217 mi). Inclination: 10.00 deg. Period: 1,441.00 min.
Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1982-1983 As of 28 August 2001 located at 30.39 deg W drifting at 1.165 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 85.74E drifting at 1.235W degrees per day.
1982 March 15 - . 04:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 5 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 14L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1989-11-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 13092 . COSPAR: 1982-020A. Apogee: 36,427 km (22,634 mi). Perigee: 36,139 km (22,455 mi). Inclination: 9.70 deg. Period: 1,461.50 min.
Stationed at 53 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 53 deg E in 1982-1986; 96 deg E in 1986-1989 As of 28 August 2001 located at 156.27 deg E drifting at 6.267 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 91.82E drifting at 6.281W degrees per day.
1982 April 19 - . 19:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Salyut 7 - .
Payload: Zarya s/n 125-2. Mass: 18,900 kg (41,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Salyut 7.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Salyut 7.
Duration: 3,215.34 days. Decay Date: 1991-02-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 13138 . COSPAR: 1982-033A. Apogee: 284 km (176 mi). Perigee: 279 km (173 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
Second Soviet replenishable long-duration 'civilian' space station. Objectives: Continuation of scientific research on board manned space complexes in the interests of science and the Soviet national economy; testing of advanced systems and apparatus for orbital stations. Continuation of the scientific research in progress on board manned space complexes in the interests of science and the national economy; testing of advanced systems and apparatus for orbital stations. Although of the same design as Salyut 6, technical breakdowns throughout its life made Salyut 7 a much less productive station. Replaced finally by Mir. Two different TKS resupply craft, originally designed for the Almaz military station, docked with Salyut 7 to provide a larger complex. With the cancellation of Almaz, a large proportion of the experiments carried out on board had military objectives. As of January 1990 out of fuel, unable to manoeuvre, uncontrolled re-entry expected in three to four years. Re-entered in 1991 with 70 kg fuel remaining over Argentina. Controllers attempted to control impact point (set for Atlantic Ocean) by setting Salyut 7/Kosmos 1686 assembly into a tumble. This however failed and Salyut 7 re-entered February 7, 1991 04:00 GMT. Many fragments fell on the town of Capitan Bermudez, 25 km from Rosario and 400 km from Buenos Aires, Argentina. At 1 am local time the sky was lit up with hundreds of incandescent meteors travelling from Southwest to Northeast. At dawn the inhabitants discovered numerous metal fragments, which seemed to have fallen in distinct groups at various locations in the city. Luckily no one was hurt in the metallic shower. Additional Details: here....
- Iskra 2 - . Payload: RK-02. Mass: 28 kg (61 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Communications. Type: Amateur radio communications satellite. Spacecraft: Iskra. Decay Date: 1982-07-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 13176 . COSPAR: 1982-033C. Apogee: 345 km (214 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Deployed from Salyut 7 5/17/82. Launched from Salyut 7. Experiments in amateur radio communications. Launched into orbit from aboard the Salyut-7 orbital scientific station. .
1982 May 17 - . 23:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Cosmos 1366 - .
Payload: Potok no. 1 s/n 11L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 1987-10-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 13177 . COSPAR: 1982-044A. Apogee: 35,805 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 13.70 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Stationed at 80 deg E. Investigation of outer space; experiments in relaying telegraph and telephone information in the centimetre wavelength range. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1982-1987 As of 4 September 2001 located at 81.31 deg E drifting at 0.033 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 68.65E drifting at 0.023E degrees per day.
1982 July 22 - . 22:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM. FAILURE: Stage 1 - vehicle failed at launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Ekran s/n 23L - . Payload: Ekran s/n 23L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Ekran.
1982 September 16 - . 18:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 9 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 24L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1983-12-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 13554 . COSPAR: 1982-093A. Apogee: 35,877 km (22,292 mi). Perigee: 35,704 km (22,185 mi). Inclination: 13.10 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1982-1983 As of 3 September 2001 located at 99.83 deg E drifting at 0.132 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 45.75E drifting at 0.063E degrees per day.
1982 October 12 - . 14:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1413 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 11L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 13603 . COSPAR: 1982-100A. Apogee: 19,076 km (11,853 mi). Perigee: 19,062 km (11,844 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 673.30 min. Glonass test flight. Testing of the components and equipment of the space navigation system established in order to locate the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and its merchant and fishing vessels. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket. .
- Cosmos 1415 - . Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 13607 . COSPAR: 1982-100E. Apogee: 19,100 km (11,800 mi). Perigee: 19,100 km (11,800 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 673.00 min. Glonass test flight. Testing of the components and equipment of the space navigation system established in order to locate the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and its merchant and fishing vessels. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket..
- Cosmos 1414 - . Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 13606 . COSPAR: 1982-100D. Apogee: 19,230 km (11,940 mi). Perigee: 19,028 km (11,823 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass test flight. Testing of the components and equipment of the space navigation system established in order to locate the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and its merchant and fishing vessels. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket..
1982 October 20 - . 16:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 6 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 16L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1989-03-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 13624 . COSPAR: 1982-103A. Apogee: 35,814 km (22,253 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 12.80 deg. Period: 1,436.60 min.
Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg E in 1982-1984; 140 deg E in 1984-1988; 170 deg W in 1988-1989 As of 31 August 2001 located at 45.17 deg W drifting at 0.179 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 146.19W drifting at 0.287W degrees per day.
1982 November 18 - . 11:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Iskra 3 - . Payload: RK-03. Mass: 28 kg (61 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Salyut 7. Class: Communications. Type: Amateur radio communications satellite. Flight: Soyuz T-5. Spacecraft: Iskra. Decay Date: 1982-12-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 13663 . COSPAR: 1982-033AD. Apogee: 356 km (221 mi). Perigee: 349 km (216 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Launched from Salyut 7 airlock. Conduct of experiments in the field of amateur radiocommunications. .
1982 November 26 - . 14:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 11 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 21L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1989-01-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 13669 . COSPAR: 1982-113A. Apogee: 36,702 km (22,805 mi). Perigee: 36,341 km (22,581 mi). Inclination: 12.80 deg. Period: 1,473.80 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg E in 1982-1989 As of 3 September 2001 located at 70.20 deg W drifting at 9.239 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 51.72E drifting at 9.241W degrees per day.
1982 December 24 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM. FAILURE: Stage 1 - vehicle failed at launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Raduga s/n 22L - . Payload: Raduga s/n 22L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Raduga. Decay Date: 1982-12-24 .
1983 March 2 - . 09:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 1443 - .
Payload: TKS-M s/n 16401L. Mass: 20,000 kg (44,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: TKS .
Duration: 200.62 days. Decay Date: 1983-09-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 13868 . COSPAR: 1983-013A. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
TKS manned ferry spacecraft from the cancelled Almaz OPS-4 mission. Flown unmanned to the Salyut 7 space station. Docked with Salyut 7 on 4 March 1983. Separated from Salyut 7 on 14 August. The VA re-entry capsule separated and the space station deorbited itself on September 19, 1983 at 0:28 GMT. The VA capsule continued in space for four more days, demonstrating autonomous flight, before successfully re-entering on 23 August 1983. Returned 350 kg of material from the station. Additional Details: here....
1983 March 12 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 10 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 18L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1984-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 13878 . COSPAR: 1983-016A. Apogee: 37,453 km (23,272 mi). Perigee: 37,194 km (23,111 mi). Inclination: 14.30 deg. Period: 1,515.30 min.
Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1983-1984 As of 5 September 2001 located at 6.05 deg E drifting at 18.878 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 154.32W drifting at 18.879W degrees per day.
1983 March 23 - . 12:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Astron - . Payload: Astron 1 s/n 602L. Mass: 3,250 kg (7,160 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV. Spacecraft: Astron. USAF Sat Cat: 13901 . COSPAR: 1983-020A. Apogee: 175,948 km (109,328 mi). Perigee: 28,386 km (17,638 mi). Inclination: 34.70 deg. Period: 5,931.70 min. Astrophysics. Electrophysical research of galactic and extragalactic sources of ultraviolet ray and X-ray emission. The scientific apparatus was built jointly by scientists and specialists from the USSR and France. .
1983 April 8 - . 04:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 12 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 23L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1985-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 13974 . COSPAR: 1983-028A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 8.40 deg. Period: 1,435.80 min.
Provision of uninterrupted round the clock telephone and telegraph radiocommunication in the USSR and simultaneous transmission of colour and black-and-white USSR central television programmes to stations in the Orbita network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1983-1984 As of 4 September 2001 located at 65.56 deg E drifting at 0.028 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 82.54E drifting at 0.059W degrees per day.
1983 June 2 - . 02:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Venera 15 - .
Payload: 4V-2 s/n 860. Mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-2.
USAF Sat Cat: 14104 . COSPAR: 1983-053A. Apogee: 65,000 km (40,000 mi). Perigee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Inclination: 87.50 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
Venera 15 was part of a two spacecraft mission (along with Venera 16) designed to use side-looking radar mappers to study the surface properties of Venus. The two spacecraft were inserted into Venus orbit a day apart with their orbital planes shifted by an angle of approximately 4 degrees relative to one another. This made it possible to reimage an area if necessary. Each spacecraft was in a nearly polar orbit with a periapsis at 62 N latitude. Together, the two spacecraft imaged the area from the north pole down to about 30 degrees N latitude over the 8 months of mapping operations. Data is for Venus orbit.
1983 June 7 - . 02:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Venera 16 - .
Payload: 4V-2 s/n 861. Mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV.
Spacecraft: Venera 4V-2.
USAF Sat Cat: 14107 . COSPAR: 1983-054A.
Venus radar mapper; entered Venus orbit 10/14/83. Venera 16 was part of a two spacecraft mission (along with Venera 15) designed to use side-looking radar mappers to study the surface properties of Venus. The two spacecraft were inserted into Venus orbit a day apart with their orbital planes shifted by an angle of approximately 4 degrees relative to one another. This made it possible to reimage an area if necessary. Each spacecraft was in a nearly polar orbit with a periapsis at 62 N latitude. Together, the two spacecraft imaged the area from the north pole down to about 30 degrees N latitude over the 8 months of mapping operations.
1983 June 30 - . 23:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 7 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 17L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1989-06-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 14160 . COSPAR: 1983-066A. Apogee: 36,374 km (22,601 mi). Perigee: 36,296 km (22,553 mi). Inclination: 12.30 deg. Period: 1,464.20 min.
Stationed at 14 deg W. Radio telephone and telegraph communications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1983-1986; 16 deg W in 1986-1987; 11 deg W in 1987-1989 As of 3 September 2001 located at 105.97 deg E drifting at 6.939 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 169.25W drifting at 6.932W degrees per day.
1983 August 10 - . 18:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1490 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 12L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass .
USAF Sat Cat: 14258 . COSPAR: 1983-084A. Apogee: 19,160 km (11,900 mi). Perigee: 19,100 km (11,800 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
Glonass test flight. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet navy and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket.
- Cosmos 1492 - .
Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
USAF Sat Cat: 14260 . COSPAR: 1983-084C. Apogee: 19,159 km (11,904 mi). Perigee: 19,156 km (11,902 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 676.80 min.
Glonass test flight. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet navy and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket.
- Cosmos 1491 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 13L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
USAF Sat Cat: 14259 . COSPAR: 1983-084B. Apogee: 19,028 km (11,823 mi). Perigee: 18,863 km (11,720 mi). Inclination: 65.80 deg. Period: 668.40 min.
Glonass test flight. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet navy and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket.
1983 August 25 - . 20:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 13 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 24L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1987-10-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 14307 . COSPAR: 1983-088A. Apogee: 36,447 km (22,647 mi). Perigee: 36,323 km (22,570 mi). Inclination: 8.00 deg. Period: 1,466.80 min.
Operation of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 45 deg E in 1983-1987 As of 28 August 2001 located at 174.92 deg W drifting at 7.555 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 42.12E drifting at 7.563W degrees per day.
1983 September 29 - . 17:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 11 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 25L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1984-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 14377 . COSPAR: 1983-100A. Apogee: 35,815 km (22,254 mi). Perigee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Inclination: 8.60 deg. Period: 1,436.90 min.
Launch date suspect Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1983-1984 As of 28 August 2001 located at 73.31 deg E drifting at 0.215 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 73.35E drifting at 0.222W degrees per day.
1983 November 30 - . 13:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 8 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 18L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1988-11-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 14532 . COSPAR: 1983-118A. Apogee: 36,462 km (22,656 mi). Perigee: 36,254 km (22,527 mi). Inclination: 7.40 deg. Period: 1,465.40 min.
Stationed at 90 deg E. Radio telephone and telegraph communications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg E in 1983-1987; 140 deg E in 1987-1988 As of 2 September 2001 located at 3.86 deg W drifting at 7.211 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 143.68W drifting at 7.218W degrees per day.
1983 December 29 - . 00:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1519 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 14L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 14590 . COSPAR: 1983-127A. Apogee: 19,150 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,108 km (11,873 mi). Inclination: 66.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet navy and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket. .
- Cosmos 1521 - . Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 14592 . COSPAR: 1983-127C. Apogee: 19,149 km (11,898 mi). Perigee: 18,992 km (11,801 mi). Inclination: 66.50 deg. Period: 673.40 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet navy and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket..
- Cosmos 1520 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 15L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 14591 . COSPAR: 1983-127B. Apogee: 19,185 km (11,920 mi). Perigee: 19,075 km (11,852 mi). Inclination: 65.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet navy and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single carrier rocket..
1984 February 15 - . 08:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 14 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 25L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1987-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 14725 . COSPAR: 1984-016A. Apogee: 35,817 km (22,255 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 11.80 deg. Period: 1,436.50 min.
Stationed at 84 deg. E. Radio telephone and telegraph communications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1984-1987 As of 29 August 2001 located at 83.95 deg E drifting at 0.059 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 64.01E drifting at 0.027E degrees per day.
1984 March 2 - . 03:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Cosmos 1540 - .
Payload: Potok no. 2 s/n 12L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 1988-02-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 14783 . COSPAR: 1984-022A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,761 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 8.10 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Stationed at 79 deg E. Investigation of outer space; experiments in relaying telegraph and telephone information in the centimetre wavelength range. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1984-1988 As of 28 August 2001 located at 75.35 deg E drifting at 0.041 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 69.92E drifting at 0.020W degrees per day.
1984 March 16 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 12 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 26L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1986-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 14821 . COSPAR: 1984-028A. Apogee: 37,048 km (23,020 mi). Perigee: 36,973 km (22,973 mi). Inclination: 9.10 deg. Period: 1,499.10 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1984-1986 As of 4 September 2001 located at 148.57 deg W drifting at 15.168 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 82.29W drifting at 15.169W degrees per day.
1984 March 29 - . 05:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Cosmos 1546 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 2. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1986-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 14867 . COSPAR: 1984-031A. Apogee: 35,856 km (22,279 mi). Perigee: 35,709 km (22,188 mi). Inclination: 11.70 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Stationed at 24 deg W in 1984-1985; 80 deg E in 1986 As of 5 September 2001 located at 72.67 deg E drifting at 0.068 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 2 located at 81.39E drifting at 0.003E degrees per day.
1984 April 22 - . 04:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 9 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 19L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1987-04-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 14940 . COSPAR: 1984-041A. Apogee: 35,805 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,740 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 11.50 deg. Period: 1,435.40 min.
Stationed at 53 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 53 deg E in 1984-1987 As of 3 September 2001 located at 55.62 deg E drifting at 0.094 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 2 located at 96.90E drifting at 0.028E degrees per day.
1984 May 19 - . 15:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1554 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 16L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 14977 . COSPAR: 1984-047A. Apogee: 19,159 km (11,904 mi). Perigee: 19,101 km (11,868 mi). Inclination: 65.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1555 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 17L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 14978 . COSPAR: 1984-047B. Apogee: 19,158 km (11,904 mi). Perigee: 19,100 km (11,800 mi). Inclination: 66.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1556 - . Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 14979 . COSPAR: 1984-047C. Apogee: 19,161 km (11,906 mi). Perigee: 19,129 km (11,886 mi). Inclination: 65.50 deg. Period: 676.30 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1984 June 22 - . 00:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 15 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 27L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1988-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 15057 . COSPAR: 1984-063A. Apogee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Perigee: 35,750 km (22,210 mi). Inclination: 7.20 deg. Period: 1,435.10 min.
Stationed at 128 deg. E. Radio telephone and telegraph communications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 128 deg E in 1984-1988 As of 4 September 2001 located at 29.81 deg E drifting at 0.199 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 18.52E drifting at 0.067E degrees per day.
1984 August 1 - . 21:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 10 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 20L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1990-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 15144 . COSPAR: 1984-078A. Apogee: 35,810 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Inclination: 6.80 deg. Period: 1,436.90 min.
Stationed at 80 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1984-1989; 170 deg W in 1989-1990 As of 5 September 2001 located at 157.76 deg W drifting at 0.193 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 46.55W drifting at 0.187W degrees per day.
1984 August 24 - . 19:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 13 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 27L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1987-04-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 15219 . COSPAR: 1984-090A. Apogee: 37,087 km (23,044 mi). Perigee: 36,957 km (22,963 mi). Inclination: 8.20 deg. Period: 1,499.70 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1984-1987 As of 2 September 2001 located at 163.33 deg W drifting at 15.302 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 35.81W drifting at 15.302W degrees per day.
1984 September 4 - . 15:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1593 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 18L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 15259 . COSPAR: 1984-095A. Apogee: 19,170 km (11,910 mi). Perigee: 19,090 km (11,860 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1595 - . Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 15261 . COSPAR: 1984-095C. Apogee: 19,178 km (11,916 mi). Perigee: 19,079 km (11,855 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1594 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 19L. Mass: 1,250 kg (2,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 15260 . COSPAR: 1984-095B. Apogee: 19,188 km (11,922 mi). Perigee: 19,145 km (11,896 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 677.20 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1984 September 28 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1603 - . Payload: Tselina-2 no. 1. Mass: 6,000 kg (13,200 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Tselina. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Tselina-2. USAF Sat Cat: 15333 . COSPAR: 1984-106A. Apogee: 863 km (536 mi). Perigee: 832 km (516 mi). Inclination: 71.00 deg. Period: 101.90 min. First launch of new Tselina-2 ELINT satellite. .
1984 December 15 - . 09:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Vega 1 - .
Payload: 5VK s/n 901. Mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV.
Spacecraft: Vega 5VK.
USAF Sat Cat: 15432 . COSPAR: 1984-125A.
Investigations of the planet Venus and Halley's Comet. The APV-V plasma antenna did not deploy until the first mid-course correction burn. Deployed lander and balloon at Venus on June 19 1985. Rendezvoused with comet Halley on March 6, 1986. Fitted with scientific apparatus and equipment built in the USSR, Austria, Bulgaria, Hungary, German Democratic Republic, Poland, France, Federal Republic of Germany and C zechoslovakia.
1984 December 21 - . 09:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Vega 2 - .
Payload: 5VK s/n 902. Mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Venera.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV.
Spacecraft: Vega 5VK.
USAF Sat Cat: 15449 . COSPAR: 1984-128A.
Investigations of the planet Venus and Halley's Comet. The APV-V plasma antenna did not deploy until the first mid-course correction burn. Deployed lander and balloon at Venus on June 14, 1985. The surface experiments of the lander failed to send back data because they were inadvertently switched on at an altitude of 20 km. Apparently high winds activated a G-force sensor that was to automatically switch on the surface package after the jolt of touchdown. The bus continued in heliocentric orbit and rendezvoused with comet Halley on March 9, 1986. The images of the comet were nearly lost when a television sensor failed shortly before the flyby. A back-up sensor was activated just in time. Fitted with scientific apparatus and equipment built in the USSR, Austria, Bulgaria, Hungary, German Democratic Republic, Poland, France, Federal Republic of Germany and C zechoslovakia.
1985 January 18 - . 10:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 11 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 21L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1991-09-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 15484 . COSPAR: 1985-007A. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 11.00 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
Stationed at 140 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 140 deg E in 1985-1987; 53 deg E in 1987-1989; 11 deg W in 1989-1991 As of 5 September 2001 located at 22.94 deg W drifting at 0.085 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 14.60W drifting at 0.040W degrees per day.
1985 February 21 - . 07:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Cosmos 1629 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 3. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1986-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 15574 . COSPAR: 1985-016A. Apogee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Perigee: 35,738 km (22,206 mi). Inclination: 6.50 deg. Period: 1,434.50 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg E in 1985; 24 deg W in 1985-1986 As of 5 September 2001 located at 151.95 deg W drifting at 0.251 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 3 located at 24.42W drifting at 0.038E degrees per day.
1985 March 22 - . 05:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 14 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 28L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1987-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 15626 . COSPAR: 1985-024A. Apogee: 37,457 km (23,274 mi). Perigee: 37,333 km (23,197 mi). Inclination: 12.70 deg. Period: 1,519.00 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1985-1987 As of 5 September 2001 located at 178.66 deg E drifting at 19.729 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 122.42E drifting at 19.716W degrees per day.
1985 May 17 - . 22:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1650 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 20L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 15697 . COSPAR: 1985-037A. Apogee: 19,177 km (11,916 mi). Perigee: 19,081 km (11,856 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1652 - . Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 15699 . COSPAR: 1985-037C. Apogee: 19,155 km (11,902 mi). Perigee: 19,110 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.90 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1651 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 21L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 15698 . COSPAR: 1985-037B. Apogee: 19,143 km (11,894 mi). Perigee: 19,111 km (11,875 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.60 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1985 May 30 - . 14:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1656 - . Payload: Tselina-2 no. 2. Mass: 6,000 kg (13,200 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Tselina. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Tselina-2. USAF Sat Cat: 15755 . COSPAR: 1985-042A. Apogee: 852 km (529 mi). Perigee: 802 km (498 mi). Inclination: 71.10 deg. Period: 101.40 min.
1985 August 8 - . 21:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 16 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 26L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1988-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 15946 . COSPAR: 1985-070A. Apogee: 35,818 km (22,256 mi). Perigee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Inclination: 10.80 deg. Period: 1,436.90 min.
Stationed at 45 deg. E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 45 deg E in 1985-1987; 170 deg W in 1987-1988 As of 1 September 2001 located at 34.20 deg W drifting at 0.087 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 161.95W drifting at 0.182W degrees per day.
1985 September 27 - . 08:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 1686 - .
Payload: TKS-M s/n 16501. Mass: 20,000 kg (44,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Soyuz T-13 EO-4-a,
Soyuz T-14 EO-4-c.
Spacecraft: TKS .
Duration: 1,958.80 days. Decay Date: 1991-02-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 16095 . COSPAR: 1985-086A. Apogee: 284 km (176 mi). Perigee: 280 km (170 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
Modification of cancelled TKS manned ferry; docked with Salyut 7. All landing systems were removed from the VA re-entry capsule and replaced with military optical sensor experiments (infrared telescope and Ozon spectrometer). Burned up in the atmosphere and together with the Salyut 7 station over Argentina on February 7, 1991 04:00 GMT. Re-entered with unused 3 m diameter recoverable capsule of 2-3,000 kg mass, solid rocket motors, and cesium sensors.
Maneuver Summary:
172 km X 302 km orbit to 284 km X 319 km orbit. Delta V: 36 m/s
281 km X 315 km orbit to 290 km X 336 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s
290 km X 336 km orbit to 335 km X 352 km orbit. Delta V: 16 m/s
Maneuvers after docking with Salyut 7:
336 km X 353 km orbit to 338 km X 358 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
338 km X 358 km orbit to 358 km X 359 km orbit. Delta V: 5 m/s
331 km X 333 km orbit to 333 km X 385 km orbit. Delta V: 14 m/s
333 km X 385 km orbit to 332 km X 468 km orbit. Delta V: 23 m/s
332 km X 468 km orbit to 466 km X 468 km orbit. Delta V: 37 m/s
466 km X 468 km orbit to 470 km X 475 km orbit. Delta V: 2 m/s
470 km X 475 km orbit to 475 km X 475 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
Total Delta V: 143 m/s
Officially: Testing the equipment, assemblies and design components of a satellite in various modes of flight, including joint flight with the Salyut-7 station.
1985 October 25 - . 15:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1700 - .
Payload: Luch s/n 11L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Luch .
Completed Operations Date: 1986-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 16199 . COSPAR: 1985-102A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 5.90 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Stationed at 95 deg E. Experimental retransmission of telephone and telegraph data in the centimetre band. First launch in Altair/SR system for communication with Mir space station and other orbital spacecraft. First tests with Mir were conducted on 29 March 1986 using Mir's large aft antenna communicating with Cosmos 1700 stationed in geosynchronous orbit at 95 degrees East. In September 1986 Cosmos 1700 ceased operating and drifted off its geosynchronous orbit position. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 95 deg E in 1985-1986 As of 4 September 2001 located at 85.03 deg E drifting at 0.142 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 76.37E drifting at 0.157E degrees per day.
1985 November 15 - . 14:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 17 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 28L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1992-12-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 16250 . COSPAR: 1985-107A. Apogee: 35,873 km (22,290 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 5.80 deg. Period: 1,438.00 min.
Stationed at 49 deg. E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg E in 1985-1988; 69 deg E in 1988-1990; 85 deg E in 1990-1991; 49 deg E in 1991-1992 As of 5 September 2001 located at 174.18 deg W drifting at 0.357 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 98.19E drifting at 0.512W degrees per day.
1985 December 24 - . 21:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1710 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 22L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 16396 . COSPAR: 1985-118A. Apogee: 19,146 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,112 km (11,875 mi). Inclination: 66.30 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1712 - . Payload: Glonass Dummy. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 16398 . COSPAR: 1985-118C. Apogee: 19,154 km (11,901 mi). Perigee: 19,135 km (11,889 mi). Inclination: 65.20 deg. Period: 676.30 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1711 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 23L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 16397 . COSPAR: 1985-118B. Apogee: 19,150 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,108 km (11,873 mi). Inclination: 66.30 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1986 January 17 - . 10:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 18 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 29L. Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1991-12-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 16497 . COSPAR: 1986-007A. Apogee: 36,493 km (22,675 mi). Perigee: 35,909 km (22,312 mi). Inclination: 5.80 deg. Period: 1,457.30 min.
Stationed at 335 deg. E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 25 deg W in 1986-1989; 170 deg W in 1989-1991 As of 28 August 2001 located at 163.25 deg W drifting at 5.255 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 22.49E drifting at 5.257W degrees per day.
1986 February 19 - . 21:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Mir - .
Payload: Mir s/n 127-01. Mass: 20,100 kg (44,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: Mir .
Decay Date: 2001-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 16609 . COSPAR: 1986-017A. Apogee: 395 km (245 mi). Perigee: 387 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
The core module of Russia's new space station was placed in an initial orbit of 172 x 301 km. It was established in its operational orbit on 6 March. It passed just 10 km from Salyut 7 on 8 March. First use of the geosynchronous Luch relay sattelite for communications with the station was on 29 March. Equipment launched with the core module included:
- Splav-2 crystal growth facility
- Zona zone melt facility
- Kashtan electrophoresis unit
- Bulgarian Rozhen photometer
- Spektr-256 and MKS-M spectrometers
- Pion-M multipurpose physics unit (41 kg)
- Biryuza semiconductor materials unit
- -Ruchei electrophoresis installation
- Yantar metal coating equipment
- Mariye magnetic spectrometer
- Korund furnace (136 kg)
Total costs of Mir from February 1986 through return of Soyuz TM-9 in April 1989 were given as 1.471 billion rubles. This sum ncluded Mir, Kvant, all Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, and 2 new modules. As of April 1989 50% of the scientific equipment was inoperable and the interior was cramped due to lack of extension modules. Electric power supply problems were first reported in April 1989 (batteries would not hold charge from panels). Mass 27,300 kg as of January 1990. Complex mass with Kvant-2 65,790 kg; with Kristall, Soyuz TM, and Progress M, 89,990 kg. Additional Details: here....
1986 April 4 - . 03:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Cosmos 1738 - .
Payload: Potok no. 3 s/n 13L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 1989-04-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 16667 . COSPAR: 1986-027A. Apogee: 35,847 km (22,274 mi). Perigee: 35,712 km (22,190 mi). Inclination: 5.60 deg. Period: 1,435.70 min.
Stationed at 13.5 deg W. Continuation of the investigation of outer space; experimental retransmission of telephone and telegraph data in the centimetre band. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1986-1989 As of 3 September 2001 located at 0.26 deg W drifting at 0.077 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 55.28W drifting at 0.287W degrees per day.
1986 May 24 - . 01:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 15 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 30L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1988-01-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 16729 . COSPAR: 1986-038A. Apogee: 36,905 km (22,931 mi). Perigee: 36,824 km (22,881 mi). Inclination: 11.60 deg. Period: 1,491.50 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1986-1988 As of 5 September 2001 located at 80.69 deg W drifting at 13.420 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 63.41W drifting at 13.419W degrees per day.
1986 June 10 - . 00:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 12 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 24L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1991-01-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 16769 . COSPAR: 1986-044A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,763 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 10.10 deg. Period: 1,435.70 min.
Stationed at 345 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1986-1989; 40 deg E in 1989-1990 As of 28 August 2001 located at 84.75 deg E drifting at 0.265 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 45.79E drifting at 0.142E degrees per day.
1986 September 16 - . 11:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1778 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 24L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 16961 . COSPAR: 1986-071A. Apogee: 19,138 km (11,891 mi). Perigee: 19,121 km (11,881 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1779 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 25L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 16962 . COSPAR: 1986-071B. Apogee: 19,133 km (11,888 mi). Perigee: 19,125 km (11,883 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1780 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 26L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 16963 . COSPAR: 1986-071C. Apogee: 19,147 km (11,897 mi). Perigee: 19,112 km (11,875 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1986 October 25 - . 15:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 19 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 30L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1993-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 17046 . COSPAR: 1986-082A. Apogee: 36,353 km (22,588 mi). Perigee: 36,252 km (22,525 mi). Inclination: 5.10 deg. Period: 1,462.60 min.
Stationed at 36 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 45 deg E in 1986-1991; 34 deg E in 1991-1993. Raduga 19 performed an end-of-life maneuver in September, 1993. As of 28 August 2001 located at 160.57 deg E drifting at 6.520 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 57.63W drifting at 6.529W degrees per day.
1986 November 18 - . 14:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 13 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 22L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1991-04-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 17083 . COSPAR: 1986-090A. Apogee: 36,863 km (22,905 mi). Perigee: 36,759 km (22,840 mi). Inclination: 10.30 deg. Period: 1,488.80 min.
Stationed at 90 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg E in 1986-1991 As of 5 September 2001 located at 132.70 deg W drifting at 12.791 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 94.81E drifting at 12.778W degrees per day.
1986 November 29 - . 08:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K. FAILURE: Second stage explosion.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Almaz-T s/n 303 Failure - . Payload: Almaz-K s/n 303. Mass: 18,550 kg (40,890 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Almaz. Class: Surveillance. Type: Civilian Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz. Spacecraft: Almaz-T. Decay Date: 1986-12-29 . In the second half of 1986 the first Almaz-T s/n 303 was readied for launch. General V V Favorskiy ordered it to be completed and launched with a full-up lab module in place of trials equipment. Unfortunately did not reach orbit..
1987 January 30 - . 09:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: Block DM-2 ignition failure, remained in LEO.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 1817 - . Payload: Ekran-M s/n 11L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Ekran-M . Decay Date: 1987-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 17365 . COSPAR: 1987-010A. Apogee: 208 km (129 mi). Perigee: 173 km (107 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.30 min. Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Launch vehicle failure; left in unusable orbit. Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space. .
1987 March 19 - . 03:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Raduga 20 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 31L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1991-12-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 17611 . COSPAR: 1987-028A. Apogee: 37,159 km (23,089 mi). Perigee: 36,922 km (22,942 mi). Inclination: 5.10 deg. Period: 1,500.60 min.
Stationed at 85 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1987-1991 As of 30 August 2001 located at 6.40 deg W drifting at 15.515 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 6.61W drifting at 15.520W degrees per day.
1987 March 31 - . 00:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Kvant 1 - .
Payload: 37KE s/n 010 / 77KE s/n 16601. Mass: 20,000 kg (44,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Flight: Soyuz TM-2,
Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1.
Spacecraft Bus: 37K.
Spacecraft: Kvant.
Duration: 2,586.99 days. Decay Date: 2001-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 17845 . COSPAR: 1987-030A. Apogee: 393 km (244 mi). Perigee: 385 km (239 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
MIR module; high energy observatory. Docked with Mir. Rendezvous with Mir 5 April; soft dock 9 April; EVA on 11 April to remove fabric strip from docking apparatus and hard dock; jettisoned service module on 12 April at 22:18
Maneuver Summary:
168 km X 278 km orbit to 172 km X 300 km orbit. Delta V: 7 m/s
169 km X 296 km orbit to 172 km X 314 km orbit. Delta V: 5 m/s
170 km X 313 km orbit to 297 km X 345 km orbit. Delta V: 46 m/s
298 km X 344 km orbit to 345 km X 364 km orbit. Delta V: 18 m/s
Service Module only, after undocking with Mir:
345 km X 364 km orbit to 341 km X 363 km orbit. Delta V: 1 m/s
340 km X 361 km orbit to 383 km X 406 km orbit. Delta V: 24 m/s
Total Delta V: 101 m/s
Officially: Extra-atmospheric astronomic research and resolution of a number of problems with scientific and economic applications.
- FSB - . Payload: FSB No. 16601. Mass: 18,500 kg (40,700 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-2, Soyuz TM-2 Mir LD-1. Spacecraft Bus: 37K. Spacecraft: Kvant. Decay Date: 1988-08-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 17851 . COSPAR: 1987-030C. Apogee: 404 km (251 mi). Perigee: 380 km (230 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
1987 April 24 - . 12:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: Block DM-2 failure, remained in LEO.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 1838 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 30L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . Decay Date: 1991-05-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 17902 . COSPAR: 1987-036A. Apogee: 10,401 km (6,462 mi). Perigee: 140 km (80 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 208.50 min. Glonass; upper stage failure; unusable orbit. Fourth stage failure .
- Cosmos 1839 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 31L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. Decay Date: 1991-05-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 17903 . COSPAR: 1987-036B. Apogee: 9,694 km (6,023 mi). Perigee: 137 km (85 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 199.10 min. Glonass; upper stage failure; unusable orbit. Fourth stage failure.
- Cosmos 1840 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 32L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. Decay Date: 1991-09-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 17904 . COSPAR: 1987-036C. Apogee: 4,362 km (2,710 mi). Perigee: 125 km (77 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 132.80 min. Glonass; upper stage failure; unusable orbit. Fourth stage failure.
1987 May 11 - . 14:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 14 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 23L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1992-06-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 17969 . COSPAR: 1987-040A. Apogee: 36,658 km (22,778 mi). Perigee: 36,416 km (22,627 mi). Inclination: 6.60 deg. Period: 1,474.60 min.
Stationed at 140 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 140 deg E in 1987-1989; 103 deg E in 1989-1992 As of 28 August 2001 located at 132.07 deg W drifting at 9.420 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 61.02W drifting at 9.418W degrees per day.
1987 July 25 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 1870 - .
Payload: Almaz-K s/n 304. Mass: 18,550 kg (40,890 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Civilian Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz-T.
Duration: 734.00 days. Decay Date: 1989-07-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 18225 . COSPAR: 1987-064A. Apogee: 278 km (172 mi). Perigee: 263 km (163 mi). Inclination: 71.90 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
First flight of Almaz radars imaging satellite taken out of mothballs after death of Ustinov. At the beginning of 1987 it was decided not to man the Almaz-T, instead operate it in a fully automatic mode. Thus the final Almaz cosmonaut training group was disbanded. Cosmos 1870 conducted remote sensing of the earth's surface, oceans and seas in the interests of various branches of science and the economy. Its side-looking radar had a 20-25 m ground resolution and functioned throughout its two year service life.
1987 September 3 - . 19:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 16 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 29L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran.
Completed Operations Date: 1989-10-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 18328 . COSPAR: 1987-073A. Apogee: 36,895 km (22,925 mi). Perigee: 36,871 km (22,910 mi). Inclination: 5.10 deg. Period: 1,492.50 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1987-1989 As of 31 August 2001 located at 146.34 deg W drifting at 13.641 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 69.25E drifting at 13.645W degrees per day.
1987 September 16 - . 02:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1883 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 33L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 18355 . COSPAR: 1987-079A. Apogee: 19,141 km (11,893 mi). Perigee: 19,119 km (11,879 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1884 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 34L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 18356 . COSPAR: 1987-079B. Apogee: 19,157 km (11,903 mi). Perigee: 19,101 km (11,868 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1885 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 35L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 18357 . COSPAR: 1987-079C. Apogee: 19,156 km (11,902 mi). Perigee: 19,101 km (11,868 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1987 October 1 - . 17:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1888 - .
Payload: Potok no. 4 s/n 15L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 1994-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 18384 . COSPAR: 1987-084A. Apogee: 35,804 km (22,247 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 4.00 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Stationed at 80 deg E; later moved to 13.5 deg W. Communications experiments. Investigation of outer space; relaying of telephone and telegraph information. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1987-1990; 14 deg W in 1990-1994 As of 3 September 2001 located at 1.75 deg E drifting at 0.093 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 68.17W drifting at 0.344W degrees per day.
1987 October 28 - . 15:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1894 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 4. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1991-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 18443 . COSPAR: 1987-091A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 4.10 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1987-1991 As of 5 September 2001 located at 165.32 deg W drifting at 0.190 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 85.03W drifting at 0.375E degrees per day.
1987 November 26 - . 13:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1897 - .
Payload: Luch s/n 12L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Luch .
Completed Operations Date: 1992-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 18575 . COSPAR: 1987-096A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,763 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 3.80 deg. Period: 1,435.60 min.
Stationed at 95 deg E. Relaying of telephone and telegraph information. Second launch in Altair/SR system for communication with Mir space station and other orbital spacecraft. In late July 1988 Cosmos 1897 was moved from its station at 95 degrees East to 12 degrees East to support the Buran shuttle test flight of November 14, 1988. During February 1987 the satellite was moved back to its original position at 95 degrees East. The satellite drifted to 90 degrees East by March 1991. By late April it was maneuvered it back to 95 degrees East, but by the end of 1991 it had drifted to 77 degrees East and was considered inoperative. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 95 deg E in 1987-1988; 12 deg E in 1988-1989; 95 deg E in 1989-1992 As of 5 September 2001 located at 62.12 deg E drifting at 0.168 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 94.48E drifting at 0.087E degrees per day.
1987 December 10 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 21 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 32L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1997-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 18631 . COSPAR: 1987-100A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Inclination: 3.90 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min.
Stationed at 128 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 128 deg E in 1987-1991; 170 deg W in 1991-1997 As of 3 September 2001 located at 140.92 deg W drifting at 0.213 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 154.31W drifting at 0.091W degrees per day.
1987 December 27 - . 11:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Ekran 17 - .
Payload: Ekran-M s/n 13L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran-M .
Completed Operations Date: 1993-01-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 18715 . COSPAR: 1987-109A. Apogee: 37,239 km (23,139 mi). Perigee: 36,890 km (22,920 mi). Inclination: 3.60 deg. Period: 1,501.90 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmitting USSR Central Television programmes to a network of communal receivers. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1988-1992 As of 5 September 2001 located at 125.85 deg W drifting at 15.807 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 124.58E drifting at 15.805W degrees per day.
1988 January 18 - . 09:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: Third stage malfunction.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Gorizont s/n 25L - . Payload: Gorizont s/n 25L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Gorizont.
1988 February 17 - . 00:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: Block DM-2 failure, remained in LEO.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 1917 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 38L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass .
Decay Date: 1988-02-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 18857 . COSPAR: 1988-009A. Apogee: 152 km (94 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 87.30 min.
Triple Glonass launch; three satellites (Cosmos 1917, 1918, 1919) failed to separate. A Proton carrier rocket was put into staging orbit to test components, also apparatus for a space navigation system. The satellites were not put into their designed orbit owing to a malfunction in the separation assembly controls.
- Cosmos 1919 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 36L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
Decay Date: 1988-02-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 18857 . COSPAR: 1988-009C. Apogee: 194 km (120 mi). Perigee: 166 km (103 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 87.90 min.
Triple Glonass launch; three satellites (Cosmos 1917, 1918, 1919) failed to separate. A Proton carrier rocket was put into staging orbit to test components, also apparatus for a space navigation system. The satellites were not put into their designed orbit owing to a malfunction in the separation assembly controls.
- Cosmos 1919 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 36L. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. COSPAR: 1988-009xx.
- Cosmos 1918 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 37L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
Decay Date: 1988-02-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 18857 . COSPAR: 1988-009B. Apogee: 194 km (120 mi). Perigee: 166 km (103 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 87.90 min.
Triple Glonass launch; three satellites (Cosmos 1917, 1918, 1919) failed to separate. A Proton carrier rocket was put into staging orbit to test components, also apparatus for a space navigation system. The satellites were not put into their designed orbit owing to a malfunction in the separation assembly controls.
- Cosmos 1918 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 37L. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. COSPAR: 1988-009xx.
1988 March 31 - . 04:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 15 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 26L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1992-09-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 19017 . COSPAR: 1988-028A. Apogee: 36,630 km (22,760 mi). Perigee: 36,343 km (22,582 mi). Inclination: 3.70 deg. Period: 1,472.00 min.
Stationed at 346 deg E. Radio telephone and telegraph communications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1988-1991; 11 deg W in 1991-1992 As of 31 August 2001 located at 29.28 deg W drifting at 8.804 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 152.02W drifting at 8.807W degrees per day.
1988 April 26 - . 03:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1940 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 5. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1988-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 19073 . COSPAR: 1988-034A. Apogee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Perigee: 35,590 km (22,110 mi). Inclination: 9.00 deg. Period: 1,430.50 min.
Given on Western lists as a geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. However not listed as such in Russian lists, and officially ...'conducted atmospheric, ocean studies. Investigation of the seas and oceans and the processes occurring in the earth's atmosphere'. So may have carried test instruments for second generation SPRN or had other purposes. Stationed initially at 12 deg E; Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1988 As of 1 September 2001 located at 49.66 deg W drifting at 1.409 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 70.52W drifting at 1.424E degrees per day.
1988 May 6 - . 02:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Ekran 18 - .
Payload: Ekran s/n 31L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran .
Completed Operations Date: 1990-12-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 19090 . COSPAR: 1988-036A. Apogee: 37,337 km (23,200 mi). Perigee: 37,236 km (23,137 mi). Inclination: 4.50 deg. Period: 1,513.40 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1988-1990 As of 2 September 2001 located at 7.21 deg E drifting at 18.450 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 80.93W drifting at 18.443W degrees per day.
1988 May 21 - . 17:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1946 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 39L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 19163 . COSPAR: 1988-043A. Apogee: 19,149 km (11,898 mi). Perigee: 19,109 km (11,873 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and systems for a space-based navigation system being constructed to track Soviet civil aircraft and naval and fishing vessels. .
- Cosmos 1947 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 40L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 19164 . COSPAR: 1988-043B. Apogee: 19,141 km (11,893 mi). Perigee: 19,117 km (11,878 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and systems for a space-based navigation system being constructed to track Soviet civil aircraft and naval and fishing vessels..
- Cosmos 1948 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 41L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 19165 . COSPAR: 1988-043C. Apogee: 19,133 km (11,888 mi). Perigee: 19,127 km (11,884 mi). Inclination: 66.10 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and systems for a space-based navigation system being constructed to track Soviet civil aircraft and naval and fishing vessels..
1988 July 7 - . 17:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-2.
- Phobos 1 - .
Payload: 1F s/n 101. Mass: 6,220 kg (13,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV.
Spacecraft: Fobos 1F.
USAF Sat Cat: 19281 . COSPAR: 1988-058A. Apogee: 130,504 km (81,091 mi). Perigee: 2,628 km (1,632 mi). Inclination: 50.80 deg. Period: 3,267.73 min.
Second of two missions to Mars' moon Phobos; carried 2 landers; planned to enter Mars orbit. Phobos 1 operated nominally until an expected communications session on 2 September 1988 failed to occur. The failure of controllers to regain contact with the spacecraft was traced to an error in the software uploaded on 29/30 August which had deactivated the attitude thrusters. This resulted in a loss of lock on the Sun, resulting in the spacecraft orienting the solar arrays away from the Sun, thus depleting the batteries. Left in solar Orbit (Heliocentric).
- 1F DPS - . Payload: Dolgozhivushchaya PS. Mass: 6,220 kg (13,710 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mars. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV. Spacecraft: Fobos 1F. COSPAR: 1988-058xx.
1988 July 12 - . 17:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-2.
- Phobos 2 - .
Payload: 1F s/n 102. Mass: 6,220 kg (13,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV.
Spacecraft: Fobos 1F.
USAF Sat Cat: 19287 . COSPAR: 1988-059A. Apogee: 79,750 km (49,550 mi). Perigee: 850 km (520 mi). Inclination: 1.00 deg. Period: 4,590.00 min.
First of two Mars missions to Mars' moon Phobos; carried two landers; entered Mars orbit 1/29/89; failed 3/27/89; extremely limited science data. Phobos 2 operated nominally throughout its cruise and Mars orbital insertion phases, gathering data on the Sun, interplanetary medium, Mars, and Phobos. Shortly before the final phase of the mission, during which the spacecraft was to approach within 50 m of Phobos' surface and release two landers, one a mobile 'hopper', the other a stationary platform, contact with Phobos 2 was lost. The mission ended when the spacecraft signal failed to be successfully reacquired on 27 March 1989. The cause of the failure was determined to be a malfunction of the on-board computer.
- 1F PPS - . Payload: Prigayushchaya PS. Mass: 6,220 kg (13,710 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mars. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV. Spacecraft: Fobos 1F. COSPAR: 1988-059xx.
- 1F DPS - . Payload: Dolgozhivushchaya PS. Mass: 6,220 kg (13,710 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: Mars. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV. Spacecraft: Fobos 1F. COSPAR: 1988-059xx.
1988 August 1 - . 21:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1961 - .
Payload: Potok no. 5 s/n 16L. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-12-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 19344 . COSPAR: 1988-066A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 8.60 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Stationed at 13.5 deg W; later moved to 80 deg E. Investigation of outer space and relay of telegraph and telephone messages. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1988-1992; 80 deg E in 1992-1993. In September, 1993, Cosmos 1961 began drifting off station after a mission of five years had apparently been terminated. As of 4 September 2001 located at 80.01 deg E drifting at 0.015 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 74.58E drifting at 0.039E degrees per day.
1988 August 18 - . 19:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 16 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 28L. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1992-01-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 19397 . COSPAR: 1988-071A. Apogee: 35,919 km (22,318 mi). Perigee: 35,816 km (22,254 mi). Inclination: 3.20 deg. Period: 1,440.30 min.
Stationed at 80 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1988-1992 As of 28 August 2001 located at 176.78 deg W drifting at 1.036 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 169.61W drifting at 1.046W degrees per day.
1988 September 16 - . 02:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1970 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 42L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 19501 . COSPAR: 1988-085A. Apogee: 19,150 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,110 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1971 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 44L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 19502 . COSPAR: 1988-085B. Apogee: 19,157 km (11,903 mi). Perigee: 19,101 km (11,868 mi). Inclination: 65.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1972 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 43L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 19503 . COSPAR: 1988-085C. Apogee: 19,136 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,123 km (11,882 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1988 October 20 - . 15:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 22 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 34L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1998-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 19596 . COSPAR: 1988-095A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 2.90 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min.
Stationed at 35 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 34 deg E in 1988-1992; 12 deg E in 1992-1998 As of 3 September 2001 located at 8.88 deg E drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 67.55E drifting at 0.412W degrees per day.
1988 December 10 - . 11:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Ekran 19 - .
Payload: Ekran-M s/n 12L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran-M .
Completed Operations Date: 1997-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 19683 . COSPAR: 1988-108A. Apogee: 36,980 km (22,970 mi). Perigee: 36,684 km (22,794 mi). Inclination: 8.80 deg. Period: 1,489.90 min.
Stationed at 99 deg E. Transmission of Central Television programmes to a network of receivers for collective use. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1988-1996 As of 28 August 2001 located at 156.78 deg W drifting at 13.031 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 173.37E drifting at 13.036W degrees per day.
1989 January 10 - . 02:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 1987 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 27L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 19749 . COSPAR: 1989-001A. Apogee: 19,141 km (11,893 mi). Perigee: 19,119 km (11,879 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 1988 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 45L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 19750 . COSPAR: 1989-001B. Apogee: 19,147 km (11,897 mi). Perigee: 19,111 km (11,875 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 1989 - . Payload: Etalon PKA s/n 1L. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Earth. Type: Geodetic satellite. Spacecraft: Etalon. USAF Sat Cat: 19751 . COSPAR: 1989-001C. Apogee: 19,152 km (11,900 mi). Perigee: 19,097 km (11,866 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.50 min. Etalon series. Acquisition of data to enhance accuracy in identifying and forecasting movements of space apparatus, and for geophysical and geodetic research. .
1989 January 26 - . 09:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 17 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 29L. Mass: 2,120 kg (4,670 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1997-02-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 19765 . COSPAR: 1989-004A. Apogee: 36,224 km (22,508 mi). Perigee: 36,034 km (22,390 mi). Inclination: 8.40 deg. Period: 1,453.60 min.
Stationed at 53 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. The Rimsat network was initiated when Gorizont 17 was leased to the corporation and transferred from 53 degrees E (where it was then a backup to Gorizont 27) to 134 degrees E during late-June and July, 1993. At the close of 1994, Gorizont 17 was still on station but nearing the end of its operational life after six years. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 53 deg E in 1989-1993; 134 deg E in 1993-1995; 34 deg E in 1995-1997 As of 30 August 2001 located at 22.84 deg W drifting at 4.340 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 147.41W drifting at 4.350W degrees per day.
1989 April 14 - . 04:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 23 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 33L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1996-04-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 19928 . COSPAR: 1989-030A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 2.60 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Stationed at 336 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 25 deg W in 1989-1995; 44 deg E in 1995-1996 As of 4 September 2001 located at 53.34 deg E drifting at 0.294 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 28.48E drifting at 0.016E degrees per day.
1989 May 31 - . 08:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2022 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 28L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 20024 . COSPAR: 1989-039A. Apogee: 19,141 km (11,893 mi). Perigee: 19,119 km (11,879 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 2024 - . Payload: Etalon PKA s/n 2L. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Earth. Type: Geodetic satellite. Spacecraft: Etalon. USAF Sat Cat: 20026 . COSPAR: 1989-039C. Apogee: 19,146 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,095 km (11,865 mi). Inclination: 65.50 deg. Period: 675.40 min. Etalon series. Acquisition of data to enhance accuracy in identifying and forecasting movements of space apparatus, and for geophysical and geodetic research. .
- Cosmos 2023 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 29L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 20025 . COSPAR: 1989-039B. Apogee: 19,169 km (11,911 mi). Perigee: 19,091 km (11,862 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1989 June 21 - . 23:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 1-1 - .
Payload: Raduga-1 s/n 11. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga-1.
Completed Operations Date: 1996-12-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 20083 . COSPAR: 1989-048A. Apogee: 36,313 km (22,563 mi). Perigee: 36,147 km (22,460 mi). Inclination: 8.10 deg. Period: 1,458.80 min.
Stationed at 49 deg E; first launch of alternate Raduga design. Maintenance of telephone and telegraph radio communications. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 49 deg E in 1989-1992; 70 deg E in 1992-1996 As of 2 September 2001 located at 18.58 deg E drifting at 5.633 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 167.42W drifting at 5.632W degrees per day.
1989 July 5 - . 22:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 18 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 27L. Mass: 2,120 kg (4,670 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1996-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20107 . COSPAR: 1989-052A. Apogee: 36,165 km (22,471 mi). Perigee: 35,902 km (22,308 mi). Inclination: 8.00 deg. Period: 1,448.70 min.
Stationed at 140 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 140 deg E in 1989-1996 As of 5 September 2001 located at 100.49 deg E drifting at 3.169 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 90.76W drifting at 3.156W degrees per day.
1989 September 28 - . 17:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 19 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 31L. Mass: 2,120 kg (4,670 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1998-05-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 20263 . COSPAR: 1989-081A. Apogee: 35,827 km (22,261 mi). Perigee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Inclination: 7.90 deg. Period: 1,437.30 min.
Stationed at 97.5 deg E. Operation of the long-range telephone and telegraph radio-communications system and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 97 deg E in 1989-1996; 34 deg E in 1996-1998 As of 4 September 2001 located at 105.39 deg E drifting at 0.168 deg E per day. As of 2007 Feb 28 located at 84.84E drifting at 0.295W degrees per day.
1989 November 26 - . 13:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Kvant 2 - .
Payload: 77KSD s/n 17101. Mass: 19,565 kg (43,133 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Flight: Soyuz TM-8.
Spacecraft Bus: Mir.
Spacecraft: Kvant-2.
Duration: 1,615.45 days. Decay Date: 2001-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 20335 . COSPAR: 1989-093A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 388 km (241 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Mir expansion module. Scheduled docking 2 December delayed due to failure of solar panel to extend and failure of automatic rendezvous system. Faults corrected by ground control and docked with Mir December 6, 1989 at 12:21 GMT. Transferred to lateral port December 8.
Officially: Delivery to the Mir orbital station of additional equipment and apparatus for the purpose of expanding the research and experiments conducted in the interests of science and the national economy.
1989 December 1 - . 20:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Granat - . Payload: Granat 1AS s/n 1. Mass: 3,200 kg (7,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: 4MV. Spacecraft: Granat. Decay Date: 1999-05-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 20352 . COSPAR: 1989-096A. Apogee: 149,862 km (93,119 mi). Perigee: 53,697 km (33,365 mi). Inclination: 86.60 deg. Period: 5,899.90 min. X-, gamma-ray observatory; Danish, French, Bulgarian payloads. Granat orbital observatory. Conduct of studies of X-ray and soft gamma ray radiation sources in space by the USSR jointly with France, Denmark and Bulgaria. .
1989 December 15 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 24 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 36L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1994-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20367 . COSPAR: 1989-098A. Apogee: 35,813 km (22,253 mi). Perigee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Inclination: 7.90 deg. Period: 1,436.90 min.
Stationed at 45 deg E. Radio telephone and telegraph communications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 45 deg E in 1990-1994. Replaced by Raduga 31. As of 3 September 2001 located at 103.47 deg E drifting at 0.067 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 47.08E drifting at 0.104W degrees per day.
1989 December 27 - . 11:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2054 - .
Payload: Luch s/n 14L. Mass: 2,150 kg (4,730 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Luch .
Completed Operations Date: 1997-03-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20391 . COSPAR: 1989-101A. Apogee: 35,822 km (22,258 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 7.70 deg. Period: 1,436.80 min.
Stationed at 346 deg E. Relaying of telegraph and telephone information. The third Altair/SR geosynchronous satellite for communication with Mir space station and other orbital spacecraft. Combined with Cosmos 1897, it permitted Mir to maintain contact with Mission Control in Moscow 70% of the time. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 16 deg W in 1990-1997 As of 30 August 2001 located at 21.03 deg W drifting at 0.023 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 68.57W drifting at 0.338W degrees per day.
1990 February 15 - . 07:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 25 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 35L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1997-12-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20499 . COSPAR: 1990-016A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 1.70 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Stationed at 70 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and television broadcasting. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 70 deg E in 1990-1995; 170 deg W in 1995-1997 As of 5 September 2001 located at 171.03 deg W drifting at 0.038 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 31.27W drifting at 0.005W degrees per day.
1990 May 19 - . 08:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2079 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 46L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 20619 . COSPAR: 1990-045A. Apogee: 19,195 km (11,927 mi). Perigee: 19,062 km (11,844 mi). Inclination: 65.30 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and vessels in its merchant marine and fishing fleet. .
- Cosmos 2080 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 51L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 20620 . COSPAR: 1990-045B. Apogee: 19,145 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,113 km (11,876 mi). Inclination: 65.30 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and vessels in its merchant marine and fishing fleet..
- Cosmos 2081 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 52L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 20621 . COSPAR: 1990-045C. Apogee: 19,164 km (11,907 mi). Perigee: 19,094 km (11,864 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and vessels in its merchant marine and fishing fleet..
1990 May 31 - . 10:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Kristall - .
Payload: 77KST s/n 17201. Mass: 19,640 kg (43,290 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Flight: Soyuz TM-9.
Spacecraft Bus: Mir.
Spacecraft: Kristall.
Decay Date: 2001-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 20635 . COSPAR: 1990-048A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 388 km (241 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Mir module; materials processing laboratory. Docked with Mir. Kristall: Mass: 19,500 kg. Mass on docking 17,200 kg. Length: 11. 9 m or 13. 73 m?. Solar array span 36 m. Diameter: 4. 35 m. Payload: 7,000 kg. Two compartments. Instrument-Payload Compartment contains food containers, and industrial processing units Krater 3, Optizon 1, Zona 02, and Zona 03. 0. 8 m hatch leads to Junction-Docking compartment. This contains spherical universal docker with two APAS-89 androgynous docking units. These will be used to dock with Buran shuttle and 1,000 kg X-ray telescope to be delivered by Buran in 1991. Third opening houses earth observation cameras.
Launch originally planned for 30 March 1990. Delayed to April 18, then further delayed due to computer chip problems.
Launched 31 May 1990 12:33 GMT. Docking scheduled June 6 at 12:36 but delayed due to problem with one of Kristall's orientation engines. Docking successful 10 June at 12:47. On June 11 moved to side port. Work within module began 15 June.
Spektr: Late 1991 launch. Remote sensing work. Occupies port opposite Kvant 2. Before this occurs Kristall solar arrays will be relocated to Kvant.
Officially: Specialized module. Experimental-industrial production of semi-conducting materials; refinement of biologically active substances for the production of new medicinal preparations. Cultivation of crystals of different albumine compositions and hybridizatio n of cells. Conduct of astrophysical and technical experiments.
1990 June 20 - . 23:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM.
- Gorizont 20 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 30L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1999-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20659 . COSPAR: 1990-054A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 1.50 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Stationed at 90 deg E. Provision of telephone and telegraph communications and transmission of television programmes, continuation of work in the context of the 'Intercosmos' programme for the development of new frequency ranges and the creation of long-range systems of space c ommunications jointly with the Byelorussian SSR, GDR, Hungary and Czechoslovakia. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg E in 1990; 14 deg W in 1990-1995; 26 deg E in 1995-1998; 96 deg E in 1998-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 77.53 deg E drifting at 0.186 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 83.10E drifting at 0.160E degrees per day.
1990 July 18 - . 21:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2085 - .
Payload: Potok no. 6 s/n 17L. Mass: 2,150 kg (4,730 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20693 . COSPAR: 1990-061A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 1.50 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Stationed at 80 deg E. Relaying of telegraph and telephone information. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1990-1994 As of 29 August 2001 located at 71.92 deg E drifting at 0.041 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 79.57E drifting at 0.022W degrees per day.
1990 August 9 - . 20:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: Third stage failure.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Ekran-M s/n 14L - . Payload: Ekran-M s/n 14L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Ekran-M.
1990 November 3 - . 14:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 21 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 32L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 20923 . COSPAR: 1990-094A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 1.30 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Stationed at 90 deg E. Operation of the long-range telephone and telegraph radio-communications system and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg E in 1990-1993. Gorizont 28 replaced Gorizont 21 at 90 degrees E in 1993. This allowed Gorizont 21 to be repositioned from mid-November to late-December for the inauguration of a new station at 145 degrees E. 145 deg E in 1993-1999 As of 2 September 2001 located at 4.18 deg E drifting at 0.139 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 5.59E drifting at 0.135E degrees per day.
1990 November 23 - . 13:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 22 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 33L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 20953 . COSPAR: 1990-102A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 1.20 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Stationed at 40 deg E. Operation of the long-range telephone and telegraph radio-communications system and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 40 deg E in 1990-1996; 140 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 31 August 2001 located at 45.22 deg E drifting at 0.368 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 85.49E drifting at 0.416E degrees per day.
1990 December 8 - . 02:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2109 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 47L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 21006 . COSPAR: 1990-110A. Apogee: 19,271 km (11,974 mi). Perigee: 18,988 km (11,798 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket. .
- Cosmos 2110 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 48L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 21007 . COSPAR: 1990-110B. Apogee: 19,215 km (11,939 mi). Perigee: 19,045 km (11,833 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
- Cosmos 2111 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 49L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 21008 . COSPAR: 1990-110C. Apogee: 19,148 km (11,897 mi). Perigee: 19,110 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing components and apparatus from the space navigation system being set up to determine the position of Soviet civil aircraft and vessels in the Soviet merchant marine and fishing fleet. Three satellites launched by a single rocket..
1990 December 20 - . 11:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 26 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 37L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1993-10-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 21016 . COSPAR: 1990-112A. Apogee: 35,823 km (22,259 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 7.00 deg. Period: 1,436.80 min.
Stationed at 85 deg E. Radio telephone and telegraph communications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1991-1993. Raduga 26 then began a series of small maneuvers coincident with the launch of Raduga 30, and was placed in a graveyard orbit. As of 1 September 2001 located at 93.34 deg E drifting at 0.101 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 52.76E drifting at 0.024W degrees per day.
1990 December 27 - . 11:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 1-2 - .
Payload: Raduga-1 s/n 12. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga-1.
Completed Operations Date: 1996-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 21038 . COSPAR: 1990-116A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 1.00 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Stationed at 49 deg E; second launch of alternate Raduga design. Further expansion of the long-range telephone and telegraph radio-communications system in the territory of the USSR. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 49 deg E in 1991-1996 As of 27 August 2001 located at 93.45 deg E drifting at 0.139 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 51.16E drifting at 0.090W degrees per day.
1991 February 14 - . 08:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2133 - .
Payload: SPRN Generation 2 No. 1. Mass: 2,150 kg (4,730 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 21111 . COSPAR: 1991-010A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.50 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. First launch of improved second generation version. Declared purpose: 'Investigation of outer space and of processes occurring in the Earth's atmosphere'. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1991; 24 deg W in 1992-1993; 80 deg E in 1993-1995 As of 2 September 2001 located at 80.48 deg E drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 74.02E drifting at 0.040E degrees per day.
1991 February 28 - . 05:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 27 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 38L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1998-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 21132 . COSPAR: 1991-014A. Apogee: 35,809 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 7.30 deg. Period: 1,436.50 min.
Provision of telephone and telegraph radiocommunications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 128 deg E in 1991-1998 As of 29 August 2001 located at 109.47 deg E drifting at 0.276 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 119.06E drifting at 0.198W degrees per day.
1991 March 31 - . 15:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/40. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Almaz 1 - .
Payload: Almaz-K s/n 305. Mass: 18,550 kg (40,890 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Civilian Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz-T.
Decay Date: 1992-10-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 21213 . COSPAR: 1991-024A. Apogee: 351 km (218 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 72.70 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Second flight of Almaz radar imaging satellite. Surveyed the territory of the Soviet Union and of other countries for purposes of geology, cartography, oceanology, ecology and agriculture, and studied the ice situation at high latitudes. Launched eight months after its target date into an initial operational orbit of approximately 270 km with an inclination of 72.7 degrees, slightly higher than the 71.9 degrees inclination of Cosmos 1870. Unfortunately, the failure of one of the SAR antennas to deploy fully rendered that side inoperable. Returned images of 10 to 15 meter resolution through 17 October 1992. Its radiometer provided images of 10 to 30 km radiometer resolution over a 600 km swath. Its engines completed 760,000 firings during its 18 month service life.
1991 April 4 - . 10:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2139 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 50L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 21216 . COSPAR: 1991-025A. Apogee: 19,160 km (11,900 mi). Perigee: 19,098 km (11,866 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and vessels in its merchant marine and fishing fleet. .
- Cosmos 2140 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 53L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 21217 . COSPAR: 1991-025B. Apogee: 19,161 km (11,906 mi). Perigee: 19,097 km (11,866 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and vessels in its merchant marine and fishing fleet..
- Cosmos 2141 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 54L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 21218 . COSPAR: 1991-025C. Apogee: 19,146 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,113 km (11,876 mi). Inclination: 64.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of the Soviet Union's civil aircraft and vessels in its merchant marine and fishing fleet..
1991 June 17 - . 21:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Mak 1 - . Payload: Mak. Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Mir. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Flight: Soyuz TM-12, Soyuz TM-12 Mir LD-3. Spacecraft: Mak. Decay Date: 1991-10-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 21425 . COSPAR: 1986-017DV. Apogee: 389 km (241 mi). Perigee: 377 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min. Deployed from MIR 6/17/91. Launched from Mir airlock. Investigation of features at the Earth's atmosphere. Launched with the Mir orbital station. .
1991 July 1 - . 21:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 23 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 34L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1992-06-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 21533 . COSPAR: 1991-046A. Apogee: 36,188 km (22,486 mi). Perigee: 36,158 km (22,467 mi). Inclination: 6.80 deg. Period: 1,455.90 min.
Stationed at 103 deg E. Maintenance of telephone and telegraph radio communications and transmission of television broadcasts. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 103 deg E in 1991-1992 As of 5 September 2001 located at 159.68 deg E drifting at 4.917 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 0.82W drifting at 4.909W degrees per day.
1991 September 13 - . 17:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2155 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 6. Mass: 2,150 kg (4,730 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1992-06-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 21702 . COSPAR: 1991-064A. Apogee: 35,825 km (22,260 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.40 deg. Period: 1,437.00 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Declared purpose: 'Relaying of telegraph and telephone information'. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1991-1992 As of 3 September 2001 located at 160.51 deg W drifting at 0.257 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 94.69E drifting at 0.424W degrees per day.
1991 October 23 - . 15:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 24 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 35L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
Completed Operations Date: 1998-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 21759 . COSPAR: 1991-074A. Apogee: 36,394 km (22,614 mi). Perigee: 36,220 km (22,500 mi). Inclination: 6.50 deg. Period: 1,462.80 min.
Stationed at 80 deg E. Maintenance of telephone and telegraph radio communications and transmission of television broadcasts. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1991-1998 As of 28 August 2001 located at 158.79 deg E drifting at 6.583 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 172.52W drifting at 6.586W degrees per day.
1991 November 22 - . 13:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2172 - .
Payload: Potok no. 7 s/n 18L. Mass: 2,150 kg (4,730 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 21789 . COSPAR: 1991-079A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.30 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Stationed at 13 deg W. Relaying of telegraph and telephone information. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 14 deg W in 1991-1995 As of 1 September 2001 located at 7.91 deg W drifting at 0.026 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 39.91W drifting at 0.204W degrees per day.
1991 December 19 - . 11:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 28 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 39L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
USAF Sat Cat: 21821 . COSPAR: 1991-087A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 6.40 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min.
Telephone and telegraph communications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg E in 1992-1999; 45 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 61.74 deg E drifting at 0.302 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 115.81E drifting at 0.085E degrees per day.
1992 January 29 - . 22:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2177 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 68L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 21853 . COSPAR: 1992-005A. Apogee: 19,146 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,112 km (11,875 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigational satellite. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet. .
- Cosmos 2178 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 69L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 21854 . COSPAR: 1992-005B. Apogee: 19,171 km (11,912 mi). Perigee: 19,087 km (11,860 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigational satellite. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet..
- Cosmos 2179 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 71L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 21855 . COSPAR: 1992-005C. Apogee: 19,140 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,120 km (11,880 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigational satellite. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet..
1992 April 2 - . 01:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 25 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 36L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 21922 . COSPAR: 1992-017A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Stationed at 103 deg E. Transmission of Russian radio and television programmes in Siberia and the solution of communications problems in Russia's eastern regions. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 103 deg E in 1992-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 140.44 deg E drifting at 0.018 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 44.59W drifting at 1.512W degrees per day.
1992 July 14 - . 22:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 26 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 37L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 22041 . COSPAR: 1992-043A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.50 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Stationed at 349 deg E. Development of the communications and television broadcasting system. Launched in the interests of the Ministry of Communications of the Russian Federation. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 11 deg W in 1992-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 13.53 deg W drifting at 0.004 deg E per day. As of 2007 Feb 21 located at 16.60E drifting at 0.001E degrees per day.
1992 July 30 - . 01:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2204 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 56L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass .
USAF Sat Cat: 22056 . COSPAR: 1992-047A. Apogee: 19,148 km (11,897 mi). Perigee: 19,110 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet. Constellation 3. Put into service on 30 July 1992 and taken out of service on 4 August 1997.
- Cosmos 2206 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 74L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 22058 . COSPAR: 1992-047C. Apogee: 19,154 km (11,901 mi). Perigee: 19,106 km (11,871 mi). Inclination: 63.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet..
- Cosmos 2205 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 72L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 22057 . COSPAR: 1992-047B. Apogee: 19,142 km (11,894 mi). Perigee: 19,118 km (11,879 mi). Inclination: 63.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass. Testing of components and apparatus of the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet..
1992 September 10 - . 18:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2209 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 7. Mass: 2,200 kg (4,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1996-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22112 . COSPAR: 1992-059A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.40 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Stationed at 24 deg W. Declared purpose:'Investigation of outer space and of processes occurring in the Earth's atmosphere'. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1992-1996 As of 5 September 2001 located at 68.52 deg W drifting at 0.336 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 171.17W drifting at 0.109E degrees per day.
1992 October 30 - . 14:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Ekran 20 - .
Payload: Ekran-M s/n 15L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran-M .
USAF Sat Cat: 22210 . COSPAR: 1992-074A. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.70 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Transmission of television programmes to a network of multiple user receiving stations. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg E in 1992-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 79.69 deg E drifting at 0.201 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 78.67E drifting at 0.192E degrees per day.
1992 November 27 - . 13:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 27 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 38L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 22245 . COSPAR: 1992-082A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.60 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Stationed at 53 deg E. Development of the communications and television broadcasting system. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 53 deg E in 1992-1996; 96 deg E in 1996-1998; 50 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 26.46 deg E drifting at 0.193 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 26.21E drifting at 0.345W degrees per day.
1992 December 17 - . 12:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2224 - .
Payload: SPRN Generation 2 No. 2. Mass: 2,200 kg (4,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1999-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22269 . COSPAR: 1992-088A. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,757 km (22,218 mi). Inclination: 4.80 deg. Period: 1,435.80 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Stationed at 12 deg E. Declared purpose: 'Investigation of outer space and of processes occurring in the Earth's atmosphere. Prognoz series'. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 12 deg E in 1993; 24 deg W in 1994; 12 deg E in 1994-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 53.14 deg E drifting at 0.397 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 142.40E drifting at 0.029E degrees per day.
1993 February 17 - . 20:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2234 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 73L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 22512 . COSPAR: 1993-010A. Apogee: 19,152 km (11,900 mi). Perigee: 19,106 km (11,871 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation spacecraft. Work on the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet. .
- Cosmos 2235 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 59L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
USAF Sat Cat: 22513 . COSPAR: 1993-010B. Apogee: 19,144 km (11,895 mi). Perigee: 19,115 km (11,877 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
Glonass navigation spacecraft. Work on the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet. Constellation 1. Put into service on 25 August 1993 and taken out of service on 4 August 1997.
- Cosmos 2236 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 57L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
USAF Sat Cat: 22514 . COSPAR: 1993-010C. Apogee: 19,156 km (11,902 mi). Perigee: 19,104 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 66.00 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
Glonass navigation spacecraft. Work on the Glonass global space navigation system being set up to determine the position of civil aircraft and vessels of the merchant marine and fishing fleet. Constellation 1. Put into service on 14 March 1993 and taken out of service on 23 August 1997.
1993 March 25 - . 02:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 29 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 42L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
USAF Sat Cat: 22557 . COSPAR: 1993-013A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 1.00 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Telephone and telegraph communications and transmission of television programmes. Raduga 29 joined Raduga 22. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 12 deg E in 1993-1999. As of 3 September 2001 located at 11.13 deg E drifting at 0.020 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 2 located at 61.26E drifting at 0.381E degrees per day.
1993 May 27 - . 01:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: Second stage did not reach planned velocity. Cause determined to be propellant contamination.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Gorizont s/n 39L - . Payload: Gorizont s/n 39L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Gorizont.
1993 September 30 - . 17:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 30 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 41L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
USAF Sat Cat: 22836 . COSPAR: 1993-062A. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,762 km (22,221 mi). Inclination: 5.10 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Stationed at 83 deg E, replacing Raduga-26. Operation of telephone and telegraph radio communications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg E in 1993-1999 As of 6 September 2001 located at 86.23 deg E drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. Raduga 30 followed on 30 September 1993 and was transferred to 85 degrees E. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 74.18E drifting at 0.046E degrees per day.
1993 October 28 - . 15:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 28 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 40L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 22880 . COSPAR: 1993-069A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 5.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Gorizont 28 replaced Gorizont 21 at 90 degrees E. This allowed Gorizont 21 to be repositioned from mid-November to late-December for the inauguration of a new station at 145 degrees E. As of 6 September 2001 located at 96.68 deg E drifting at 0.011 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 116.96E drifting at 0.001E degrees per day.
1993 November 18 - . 13:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 29 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 41L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 22907 . COSPAR: 1993-072A. Apogee: 35,835 km (22,266 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 5.00 deg. Period: 1,437.70 min.
Gorizont 29 (18 November 1993) and 30 (20 May 1994) were launched for Rimsat, Ltd., to provide communications services in the Pacific region under an agreement signed in 1992 between Rimsat and the Applied Mechanics NPO. Gorizont 29 was located at 130 degrees E in accordance with a lease arrangement with Rimsat Corporation (using slots allocated to Tonga by the International Telecommunications Union). Intended for use under commercial conditions. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 130 deg E in 1993-1997; 161 deg E in 1997-1998; 130 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 130.39 deg E drifting at 0.011 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 168.05E drifting at 0.374W degrees per day.
1994 January 20 - . 09:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Gals - .
Payload: Gals s/n 11L. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Gals.
USAF Sat Cat: 22963 . COSPAR: 1994-002A. Apogee: 36,121 km (22,444 mi). Perigee: 36,121 km (22,444 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,453.00 min.
Direct broadcasting satellite (new generation of satellites) intended for development of the Russian television system and international cooperation. Also tested SPT-100 plasma engine. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 71 deg E in 1994-1996; 36 deg E in 1996-1999; 42 deg E in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 37.30 deg E drifting at 0.121 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 67.44E drifting at 0.298E degrees per day.
1994 February 5 - . 08:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 1-3 - .
Payload: Raduga-1. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 22981 . COSPAR: 1994-008A. Apogee: 36,513 km (22,688 mi). Perigee: 36,513 km (22,688 mi). Inclination: 1.40 deg. Period: 1,473.00 min.
Joined Raduga 1-2 at 48 deg E; third launch of alternate Raduga design. Extension of the telephone and telegraph radio communications system on the territory of the Russian Federation. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 49 deg E in 1994-1999 As of 1 September 2001 located at 49.75 deg E drifting at 0.057 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 100.54E drifting at 0.021W degrees per day.
1994 February 18 - . 07:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 31 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 40L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
Completed Operations Date: 1995-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 23010 . COSPAR: 1994-012A. Apogee: 36,483 km (22,669 mi). Perigee: 36,483 km (22,669 mi). Inclination: 1.50 deg. Period: 1,472.00 min.
Stationed at 44 deg E; replaced Raduga 24. Operation of telephone and telegraph radio communications and transmission of television programmes. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 45 deg E in 1994-1995 As of 29 August 2001 located at 65.21 deg E drifting at 0.236 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 81.01E drifting at 0.234E degrees per day.
1994 April 11 - . 07:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2275 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 58L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 23043 . COSPAR: 1994-021A. Apogee: 19,143 km (11,894 mi). Perigee: 19,117 km (11,878 mi). Inclination: 63.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigational satellite. .
- Cosmos 2276 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 60L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23044 . COSPAR: 1994-021B. Apogee: 19,216 km (11,940 mi). Perigee: 19,044 km (11,833 mi). Inclination: 64.30 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigational satellite..
- Cosmos 2277 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 61L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23045 . COSPAR: 1994-021C. Apogee: 19,157 km (11,903 mi). Perigee: 19,103 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 64.30 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigational satellite..
1994 May 20 - . 02:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 30 - .
Payload: Gorizont s/n 42L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont .
USAF Sat Cat: 23108 . COSPAR: 1994-030A. Apogee: 35,833 km (22,265 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 4.80 deg. Period: 1,437.60 min.
Stationed at 142.5 deg E as 'Rimsat-2' - leased to Rimsat Corporation, using an orbital slot allocated to Tonga. Communications satellite intended for use under commercial conditions. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 142 deg E in 1994-1997; 122 deg E in 1997-1999; 142 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 142.86 deg E drifting at 0.016 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 173.22W drifting at 0.132W degrees per day.
1994 July 6 - . 23:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2282 - .
Payload: SPRN Generation 2 No. 3. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 23168 . COSPAR: 1994-038A. Apogee: 35,817 km (22,255 mi). Perigee: 35,754 km (22,216 mi). Inclination: 1.86 deg. Period: 1,436.06 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1994-1995 As of 5 September 2001 located at 170.85 deg W drifting at 0.127 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 58.90W drifting at 0.281E degrees per day.
1994 August 11 - . 15:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2287 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 67L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 23203 . COSPAR: 1994-050A. Apogee: 19,142 km (11,894 mi). Perigee: 19,118 km (11,879 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite. .
- Cosmos 2288 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 70L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23204 . COSPAR: 1994-050B. Apogee: 19,168 km (11,910 mi). Perigee: 19,091 km (11,862 mi). Inclination: 64.81 deg. Period: 675.73 min. Glonass navigation satellite..
- Cosmos 2289 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 75L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23205 . COSPAR: 1994-050C. Apogee: 19,133 km (11,888 mi). Perigee: 19,126 km (11,884 mi). Inclination: 64.81 deg. Period: 675.73 min. Glonass navigation satellite..
1994 September 21 - . 17:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2291 - .
Payload: Potok no. 8 s/n 19L. Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
USAF Sat Cat: 23267 . COSPAR: 1994-060A. Apogee: 35,829 km (22,263 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 4.50 deg. Period: 1,436.90 min.
Cosmos 2291 quickly moved to 80 degrees E, joining Cosmos 2085 as a replacement for Cosmos1961. Thus, at the end of 1994 the Potok constellation had been restored to its normal 4·sateellite complement: Cosmos 2085 and 2291 at 80 degrees E and Cosmos 1888 and 2172 at 13.5 degrees W. Cosmos 2291 continued at 80 deg E in 1994-1995; then it was moved to 14 deg W in 1995-1999 As of 6 September 2001 located at 62.64 deg W drifting at 0.324 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 112.35W drifting at 0.417W degrees per day.
1994 October 13 - . 16:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress - .
Payload: Ekspress s/n 11L. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Gals.
USAF Sat Cat: 23319 . COSPAR: 1994-067A. Apogee: 35,935 km (22,328 mi). Perigee: 35,887 km (22,299 mi). Inclination: 1.70 deg. Period: 1,442.40 min.
First launch of new Ekspress communications satellite. Replaces Gorizont series. Ekspress 1 reached its checkout location of 70 degrees E at the end of October 1994 and was moved to its operational position at 14 degrees W shortly after the start of 1995. Stationed at 14.00W in 1995-2001. As of 2007 March 10 located at 95.05E drifting at 1.636W degrees per day.
1994 October 31 - . 14:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Elektro 1 - .
Payload: Elektro s/n 1L. Mass: 2,850 kg (6,280 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Elektro .
Completed Operations Date: 1998-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 23327 . COSPAR: 1994-069A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 4.70 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Stationed at 76.61 deg E. Elektro 1 was finally launched on 31 October 1994, 15 years after its original public schedule. Malfunction of the local vertical sensor and the attitude control system delayed the positioning of the spacecraft at its intended location of 76 degrees E, but by early December Elektro 1 was on station. However problems with the local vertical sensor continued to plague the spacecraft, and useful images were not available. Stayed in geosynchronous orbit at 76 deg E in 1995-1998 before being shut down. As of 4 September 2001 located at 71.89 deg E drifting at 0.069 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 67.89E drifting at 0.000W degrees per day.
1994 November 20 - . 00:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2294 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 62L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 23396 . COSPAR: 1994-076A. Apogee: 19,203 km (11,932 mi). Perigee: 19,057 km (11,841 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite. .
- Cosmos 2296 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 64L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23398 . COSPAR: 1994-076C. Apogee: 19,138 km (11,891 mi). Perigee: 19,122 km (11,881 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite..
- Cosmos 2295 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 63L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23397 . COSPAR: 1994-076B. Apogee: 19,155 km (11,902 mi). Perigee: 19,105 km (11,871 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite..
1994 December 16 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Luch - .
Payload: Luch s/n 13L. Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Luch .
Completed Operations Date: 1998-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 23426 . COSPAR: 1994-082A. Apogee: 35,815 km (22,254 mi). Perigee: 35,757 km (22,218 mi). Inclination: 2.48 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min.
Stationed at 95 deg E. Relaying of telegraph and telephone information. Improved Altair/SR geosynchronous satellite for communication with Mir space station and other orbital spacecraft. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 95 deg E in 1994-1997; 16 deg W in 1997-1998 As of 4 September 2001 located at 143.35 deg W drifting at 0.319 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 64.95W drifting at 0.320E degrees per day.
1994 December 28 - . 11:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 32 - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 43L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga .
USAF Sat Cat: 23448 . COSPAR: 1994-087A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 1.41 deg. Period: 1,436.22 min.
Raduga 32 joined Raduga 25 and Raduga 1-1 at 70 degrees E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 70 deg E in 1995-1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 80.00 deg E drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 73.08E drifting at 0.033E degrees per day.
1995 March 7 - . 09:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2307 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 65L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 23511 . COSPAR: 1995-009A. Apogee: 19,149 km (11,898 mi). Perigee: 19,110 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite. .
- Cosmos 2309 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 77L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23513 . COSPAR: 1995-009C. Apogee: 19,165 km (11,908 mi). Perigee: 19,094 km (11,864 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 675.90 min. Glonass navigation satellite. Plane 2. Put into service 6 April 1995..
- Cosmos 2308 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 66L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23512 . COSPAR: 1995-009B. Apogee: 19,145 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,115 km (11,877 mi). Inclination: 63.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite..
1995 May 20 - . 03:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Spektr - .
Payload: 77KSO s/n 17301. Mass: 19,640 kg (43,290 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Flight: Soyuz TM-21.
Spacecraft Bus: Mir.
Spacecraft: Spektr.
Decay Date: 2001-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 23579 . COSPAR: 1995-024A. Apogee: 335 km (208 mi). Perigee: 221 km (137 mi). Inclination: 51.68 deg. Period: 89.78 min. MIR experiment module. Docked to Mir Jun 1
Officially: Docked to Mir Jun 1 .
1995 July 24 - . 15:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2316 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 80L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 23620 . COSPAR: 1995-037A. Apogee: 19,167 km (11,909 mi). Perigee: 19,093 km (11,863 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation spacecraft. Constellation 2. Put into service 26 August 1995. .
- Cosmos 2317 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 81L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23621 . COSPAR: 1995-037B. Apogee: 19,171 km (11,912 mi). Perigee: 19,089 km (11,861 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation spacecraft. Constellation 2. Put into service 25 August 1995..
- Cosmos 2318 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 85L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23622 . COSPAR: 1995-037C. Apogee: 19,206 km (11,934 mi). Perigee: 19,054 km (11,839 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation spacecraft. Constellation 2. Put into service 22 August 1995..
1995 August 30 - . 19:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2319 - .
Payload: Potok no. 9 s/n 20L. Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
USAF Sat Cat: 23653 . COSPAR: 1995-045A. Apogee: 35,837 km (22,268 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 3.80 deg. Period: 1,437.10 min.
Stationed at 80 deg E. Relaying of telegraph and telephone information. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1995-1999 As of 31 August 2001 located at 16.12 deg W drifting at 0.037 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 5 located at 17.95W drifting at 0.052W degrees per day.
1995 October 11 - . 16:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Luch 1 - .
Payload: Luch. Mass: 2,400 kg (5,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Luch.
Completed Operations Date: 1999-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 23680 . COSPAR: 1995-054A. Apogee: 35,817 km (22,255 mi). Perigee: 35,754 km (22,216 mi). Inclination: 2.60 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Stationed at 77 deg E. Relaying of telegraph and telephone information. Improved Altair/SR geosynchronous satellite for communication with Mir space station and other orbital spacecraft. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 77 deg E in 1995-1999 As of 2 September 2001 located at 75.63 deg E drifting at 0.029 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 77.39E drifting at 0.002E degrees per day.
1995 November 17 - . 14:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gals-2 - .
Payload: Gals s/n 12L. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Gals.
USAF Sat Cat: 23717 . COSPAR: 1995-063A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Three transponders for direct broadcast television. Stationed at 70 deg E. Used SPT-100 plasma engine. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 71 deg E in 1995-1996; 36 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 36.88 deg E drifting at 0.031 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 62.06E drifting at 1.427W degrees per day.
1995 December 14 - . 06:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2323 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 76L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass . USAF Sat Cat: 23734 . COSPAR: 1995-068A. Apogee: 19,165 km (11,908 mi). Perigee: 19,095 km (11,865 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite. Constellation 2. Put into service 18 January 1996. .
- Cosmos 2324 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 78L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23735 . COSPAR: 1995-068B. Apogee: 19,142 km (11,894 mi). Perigee: 19,133 km (11,888 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite. Constellation 2. Still in reserve as of August 1997..
- Cosmos 2325 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 82L. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 23736 . COSPAR: 1995-068C. Apogee: 19,147 km (11,897 mi). Perigee: 19,112 km (11,875 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Glonass navigation satellite. Constellation 2. Put into service 18 January 1996..
1996 January 25 - . 09:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 31 - . Payload: Gorizont s/n 43L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Gorizont . USAF Sat Cat: 23775 . COSPAR: 1996-005A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.90 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min. Stationed at 39.8E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 40 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 40.11 deg E drifting at 0.042 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 74.36E drifting at 1.416W degrees per day..
1996 February 19 - . 08:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: No second Block DM-2 ignition (blocked LOX valve). Block DM-2 propellant automatically jettisoned.. Failed Stage: U.
- Raduga s/n 44L - . Payload: Raduga s/n 44L. Mass: 1,965 kg (4,332 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Raduga. Decay Date: 2004-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 23794 . COSPAR: 1996-010A. Apogee: 36,582 km (22,730 mi). Perigee: 259 km (160 mi). Inclination: 47.20 deg. Period: 646.10 min. Secret military name for Raduga program is Gran'..
1996 April 8 - . 23:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Astra 1F - . Mass: 3,010 kg (6,630 lb). Nation: Europe. Agency: SES. Program: Astra. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 23842 . COSPAR: 1996-021A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Geostationary at 19.3E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 19 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 19.16 deg E drifting at 0.002 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 19.18E drifting at 0.016W degrees per day..
1996 April 23 - . 11:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Priroda - . Payload: 77KSI s/n 17401. Mass: 19,000 kg (41,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RAKA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Flight: Soyuz TM-23, STS-76 Mir NASA-1. Spacecraft Bus: Mir. Spacecraft: Priroda. Decay Date: 2001-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 23848 . COSPAR: 1996-023A. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 220 km (130 mi). Inclination: 51.67 deg. Period: 89.89 min. LEO. Remote sensing module for Mir space station Docked with Mir Apr 26. .
1996 May 25 - . 02:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Gorizont 32 - . Payload: Gorizont s/n 44L. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Gorizont . USAF Sat Cat: 23880 . COSPAR: 1996-034A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 3.30 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min. Stationed at 53.2E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 53 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 53.25 deg E drifting at 0.005 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 14.58W drifting at 0.023W degrees per day..
1996 September 6 - . 17:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Inmarsat 3 F2 - . Mass: 1,021 kg (2,250 lb). Nation: International. Agency: INMARSAT. Manufacturer: Lockheed. Program: Inmarsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 24307 . COSPAR: 1996-053A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,766 km (22,223 mi). Inclination: 2.50 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Geostationary at 15.5W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 15 deg W in 1996-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 15.48 deg W drifting at 0.005 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 7 located at 15.47W drifting at 0.007W degrees per day..
1996 September 26 - . 17:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress No. 12 - . Payload: Ekspress s/n 12L. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: AO Infor. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. USAF Sat Cat: 24435 . COSPAR: 1996-058A. Apogee: 35,809 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 3.50 deg. Period: 1,436.50 min. Stationed at 80.0 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 103.84 deg E drifting at 0.012 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 82.98E drifting at 0.225W degrees per day..
1996 November 16 - . 20:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-2. FAILURE: No second Block D-2 ignition.. Failed Stage: U.
- Mars-96 (Mars 8) - .
Payload: M1 s/n 520. Mass: 6,180 kg (13,620 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: VKS.
Program: Mars.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV.
Spacecraft: Mars M1.
Decay Date: 1996-11-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 24656 . COSPAR: 1996-064A. Apogee: 340 km (210 mi). Perigee: 110 km (60 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
The Mars 96 spacecraft was launched into Earth orbit, but failed to achieve insertion into Mars cruise trajectory and re-entered the Earth's atmosphere at about 00:45 to 01:30 GMT on 17 November 1996 and crashed within a presumed 320 km by 80 km area which includes parts of the Pacific Ocean, Chile, and Bolivia. The Russian Mars 96 mission was designed to send an orbiter, two small autonomous stations, and two surface penetrators to Mars.
- Penetrator 1 - . Payload: PN s/n 520/4. Mass: 6,180 kg (13,620 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mars. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV. Spacecraft: Mars M1. COSPAR: 1996-064xx.
- MAS 2 - . Payload: MAS s/n 520/2. Mass: 6,180 kg (13,620 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mars. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV. Spacecraft: Mars M1. COSPAR: 1996-064xx.
- Penetrator 2 - . Payload: PN s/n 520/5. Mass: 6,180 kg (13,620 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mars. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV. Spacecraft: Mars M1. COSPAR: 1996-064xx.
- MAS 1 - . Payload: MAS s/n 520/1. Mass: 6,180 kg (13,620 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Program: Mars. Spacecraft Bus: 5MV. Spacecraft: Mars M1. COSPAR: 1996-064xx.
1997 May 24 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Telstar 5 - . Mass: 3,700 kg (8,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Skynet Palo Alto. Program: Telstar series. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 24812 . COSPAR: 1997-026A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Geosynchronous. Stationed over 97.0W Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 97 deg W in 1997-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 96.99 deg W drifting at 0.006 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 97.04W drifting at 0.005W degrees per day..
1997 June 6 - . 16:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/17S40.
- Cosmos 2344 - . Payload: Arkon-1 s/n 1. Mass: 6,000 kg (13,200 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Manufacturer: Lavochkin bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Arkon-1. USAF Sat Cat: 24827 . COSPAR: 1997-028A. Apogee: 2,739 km (1,701 mi). Perigee: 1,502 km (933 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 130.00 min. First launch in a new series of electro-optical military reconnaisance satellites. .
1997 June 18 - . 14:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/17S40.
- Iridium 14 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV014. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 24836 . COSPAR: 1997-030A. Apogee: 778 km (483 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.39 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 5. Ascending node 294.2 degrees. Not in service..
- Iridium 10 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV010. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-10-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 24839 . COSPAR: 1997-030D. Apogee: 780 km (480 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 5. Ascending node 294 degrees..
- Iridium 13 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV013. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-04-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 24840 . COSPAR: 1997-030E. Apogee: 780 km (480 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 5. Ascending node 294.2 degrees..
- Iridium 16 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV016. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 24841 . COSPAR: 1997-030F. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 5. Ascending node 294.2 degrees..
- Iridium 11 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV011. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 24842 . COSPAR: 1997-030G. Apogee: 774 km (480 mi). Perigee: 749 km (465 mi). Inclination: 86.44 deg. Period: 100.07 min. Plane 5. Ascending node 294.6 degrees. Not in service..
- Iridium 9 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV009. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2003-03-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 24838 . COSPAR: 1997-030C. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 775 km (481 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 5. Ascending node 294.2 degrees..
- Iridium 12 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV012. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-09-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 24837 . COSPAR: 1997-030B. Apogee: 780 km (480 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 5. Ascending node 294.2 degrees..
1997 August 14 - . 20:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2345 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 8. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MO.
Manufacturer: Lavochkin bureau.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
Completed Operations Date: 1999-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 24894 . COSPAR: 1997-041A. Apogee: 36,504 km (22,682 mi). Perigee: 35,134 km (21,831 mi). Inclination: 2.60 deg. Period: 1,437.80 min.
Geosynchronous ballistic missile early warning satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 23 deg W in 1997-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 142.44 deg E drifting at 0.028 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 66.03W drifting at 0.329E degrees per day.
1997 August 28 - . 00:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Panamsat 5 - .
Payload: PAS 5 / HS 601HP. Mass: 3,600 kg (7,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Panamsat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Panamsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 24916 . COSPAR: 1997-046A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 58.0W. Used HS-601 XIPS ion engine for station keeping. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 58 deg W in 1997-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 156.02 deg W drifting at 1.125 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 26.11E drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
1997 September 14 - . 01:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/17S40.
- Iridium 29 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV029. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 24944 . COSPAR: 1997-051A. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 3. Ascending node 230.9 degrees..
- Iridium 27 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV027. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2002-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 24947 . COSPAR: 1997-051D. Apogee: 553 km (343 mi). Perigee: 542 km (336 mi). Inclination: 86.65 deg. Period: 95.61 min. Plane 3. Ascending node 223.2 degrees. Failed in low orbit..
- Iridium 33 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV033. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 24946 . COSPAR: 1997-051C. Apogee: 778 km (483 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 3. Ascending node 230.9 degrees. Active when it collided with Cosmos 2251 at 16:56 GMT on 10 February 2009, destroying both satellites and creating a debris cloud im MEO..
- Iridium 32 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV032. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 24945 . COSPAR: 1997-051B. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 3. Ascending node 230.9 degrees..
- Iridium 30 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV030. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2017-09-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 24949 . COSPAR: 1997-051F. Apogee: 780 km (480 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 3. Ascending node 230.8 degrees..
- Iridium 31 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV031. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-12-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 24950 . COSPAR: 1997-051G. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 3. Ascending node 230.9 degrees..
- Iridium 28 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV028. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 24948 . COSPAR: 1997-051E. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 3. Ascending node 230.9 degrees..
1997 November 12 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Kupon - .
Payload: Kupon K95K. Nation: Russia.
Agency: TsBank.
Manufacturer: Lavochkin bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: Kupon.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-03-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 25045 . COSPAR: 1997-070A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,435.50 min.
Geosynchronous. Kupon is the first communications satellite for the Russian banking system, and the first commercial communications satellite sold by the Lavochkin, who have in the past been more commonly associated with planetary probes and early warning satellites. Kupon, owned by the Russian Federation Central Bank (and possibly Global Information Systems of Moscow), relays financial data for the Bankir network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 55 deg E in 1997-1998 As of 1 September 2001 located at 86.25 deg E drifting at 0.142 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 78.29E drifting at 0.156E degrees per day.
1997 December 2 - . 23:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Astra 1G - . Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 3,379 kg (7,449 lb). Nation: Europe. Agency: SES. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: Astra. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 25071 . COSPAR: 1997-076A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Geosynchronous. Stationed over 23.9E Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 19 deg E in 1998-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 19.18 deg E drifting at 0.002 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 19.17E drifting at 0.012W degrees per day..
1997 December 24 - . 23:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M. FAILURE: DM-3 Stage failed, leaving spacecraft in geosynchronous transfer orbit.. Failed Stage: U.
- Asiasat 3 - .
Payload: HGS-1 / HS 601HP. Mass: 3,400 kg (7,400 lb). Nation: China.
Agency: Asiasat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Asiasat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25126 . COSPAR: 1997-086A. Apogee: 35,964 km (22,346 mi). Perigee: 35,612 km (22,128 mi). Inclination: 5.50 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
The spacecraft was left in a high inclination useless orbit by a failure of the DM-3 stage and became an insurance writeoff. Two trips around the Moon to remove the inclination under its new owner (Hughes) saw it back into very limited service (as HGS-1) by August 1998 over the Indian Ocean and available for sale at bargain rates. Operated in geosynchronous orbit at 150-154 deg W in 1998; 60 deg W in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 59.68 deg W drifting at 0.024 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 169.58W drifting at 0.011W degrees per day.
1998 April 7 - . 02:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/17S40.
- Iridium 62 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV062. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-11-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 25285 . COSPAR: 1998-021A. Apogee: 778 km (483 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 1. Ascending node 167.9 degrees..
- Iridium 68 - .
Payload: Iridium s/n SV068. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Iridium.
Manufacturer: Lockheed,
Motorola.
Program: Iridium.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700.
Decay Date: 2018-06-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 25291 . COSPAR: 1998-021G. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min.
The Proton launch vehicle placed the Iridium cluster and the Block DM2 stage into low parking orbit. The DM2 fired twice to enter the deployment orbit and dispensed the seven satellites, which used their own propulsion units to reach operational altitude. The DM2 stage then fired again to deorbit itself, to avoid creating space debris. SV068 placed in Plane 1. Ascending node 167.8 degrees.
- Iridium 63 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV063. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 25286 . COSPAR: 1998-021B. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 1. Ascending node 167.8 degrees..
- Iridium 64 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV064. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. USAF Sat Cat: 25287 . COSPAR: 1998-021C. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 1. Ascending node 167.6 degrees..
- Iridium 65 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV065. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-07-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 25288 . COSPAR: 1998-021D. Apogee: 778 km (483 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 1. Ascending node 167.9 degrees..
- Iridium 66 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV066. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-08-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 25289 . COSPAR: 1998-021E. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 1. Ascending node 167.8 degrees..
- Iridium 67 - . Payload: Iridium s/n SV067. Mass: 689 kg (1,518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Iridium. Manufacturer: Lockheed, Motorola. Program: Iridium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: LM 700. Decay Date: 2018-07-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 25290 . COSPAR: 1998-021F. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 86.40 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Plane 1. Ascending node 167.8 degrees..
1998 April 29 - . 04:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2350 - . Payload: SPRN Generation 2 No. 4. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Manufacturer: Lavochkin bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN. Completed Operations Date: 1998-07-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 25315 . COSPAR: 1998-025A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Inclination: 2.10 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min. Geostationary at 73.0 degrees E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 1998 As of 3 September 2001 located at 72.67 deg E drifting at 0.041 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 70.07E drifting at 0.036W degrees per day..
1998 May 7 - . 23:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Echostar 4 - .
Payload: A2100AX. Mass: 3,478 kg (7,667 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Echostar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 25331 . COSPAR: 1998-028A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geostationary at 148.0 degrees W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 128 deg W in 1998; 148 deg W in 1998-1999; 110 deg W in 1999; 119 deg W in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 118.91 deg W drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 77.02W drifting at 0.001W degrees per day.
1998 August 30 - . 00:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Astra 2A - .
Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 3,626 kg (7,993 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: SES.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Astra.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25462 . COSPAR: 1998-050A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,766 km (22,223 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
The first burn of the Proton's Block DM3 put the spacecraft into a 220 x 36,007 km x 51.6 deg transfer orbit. Astra 2A satellite was a Hughes HS-601, owned by Societe Europeene de Satellites, based in Luxembourg. Luxembourg has not registered any of the Astra satellites with the United Nations, in violation of treaty requirements. Geostationary at 28.3 degrees E. Used HS-601 XIPS ion engine for station keeping. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 28 deg E in 1998-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 28.21 deg E drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 28.20E drifting at 0.028W degrees per day.
1998 November 4 - . 05:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Panamsat 8 - .
Payload: PAS 8. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Panamsat.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Panamsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 25522 . COSPAR: 1998-065A. Apogee: 35,810 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,763 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
The Proton launch vehicles Block DM3 fourth stage put the Panamsat PAS 8 into a 6784 km x 35941 km x 17.3 degree transfer orbit. PAS 8 had 24 C-band and 24 Ku-band transponders and was to be located over the Pacific after its R-4D apogee engine manoeuvred the orbit to geostationary altitude and inclination. Geostationary at 166.1 degrees E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 166 deg E in 1998-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 166.05 deg E drifting at 0.003 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 165.96E drifting at 0.002E degrees per day.
1998 November 20 - . 06:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Zarya - .
Payload: FGB 77KM s/n 175-01. Mass: 20,000 kg (44,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: ISS.
Spacecraft: ISS Zarya.
USAF Sat Cat: 25544 . COSPAR: 1998-067A. Apogee: 403 km (250 mi). Perigee: 374 km (232 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
This was the first launch in the assembly of the International Space Station. The Zarya FGB was funded by NASA and built by Khrunichev in Moscow under subcontract from Boeing for NASA. Its design from the TKS military station resupply spacecraft of the 1970's and the later 77KS Mir modules. Zarya included a multiple docking adapter, a pressurised cabin section, and a propulsion/instrument section with a rear docking port. Initial orbit was 176 lm x 343 km x 51.6 degrees. By November 25 it had manoeuvred to a 383 km x 396 km x 51.7 degree orbit, awaiting the launch of Shuttle mission STS-88 which docked the Unity node to it.
1998 December 30 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2362 - . Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Manufacturer: AKO Polyot. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 25593 . COSPAR: 1998-077A. Apogee: 19,177 km (11,916 mi). Perigee: 19,082 km (11,856 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2363 - . Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Manufacturer: AKO Polyot. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 25594 . COSPAR: 1998-077B. Apogee: 19,163 km (11,907 mi). Perigee: 19,097 km (11,866 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2364 - . Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Manufacturer: AKO Polyot. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 25595 . COSPAR: 1998-077C. Apogee: 19,135 km (11,889 mi). Perigee: 19,125 km (11,883 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
1999 February 15 - . 05:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Telstar 6 - .
Mass: 3,700 kg (8,100 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Skynet Palo Alto.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Telstar series.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 25626 . COSPAR: 1999-005A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Loral Skynet's Telstar 6 had a mixed C and Ku band communications payload. The Block DM3 upper stage released Telstar 6 in a 6638 km x 35,756 km x 17.4 degree geosynchronous transfer orbit. After the first burn of its on-board R-4D engine on February 18, Telstar 6 was in a 15,037 km x 35,800 km x 7.9 deg transfer orbit heading for its final geosynchronous slot at 93 deg W Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 93 deg W in 1999. As of 2 September 2001 located at 93.01 deg W drifting at 0.004 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 93.03W drifting at 0.007W degrees per day.
1999 February 28 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga-1 - .
Payload: Raduga-1 s/n 14. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MO.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 25642 . COSPAR: 1999-010A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 10.90 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min.
Geosynchronous communications satellite, stationed at 35 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 34.80 deg E drifting at 0.013 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 107.14E drifting at 0.165W degrees per day.
1999 March 21 - . 00:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Asiasat 3S - .
Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 3,463 kg (7,634 lb). Nation: China.
Agency: Asiasat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Asiasat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25657 . COSPAR: 1999-013A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
A replacement for Asiasat 3, placed in the wrong orbit by a Proton launch in 1997, Asiasat 3S carried C and Ku band transponders. The Blok DM3 upper stage placed it a 9,677 km x 35,967 km x 13.1 deg geosynchronous transfer orbit. Asiasat's on-board R4D apogee engine was to be used to raise perigee to geostationary altitude. Mass in transfer orbit was 3,463 kg, down to 2,500 kg after insertion in geostationary orbit. Operated in geosynchronous orbit at 105 deg E from 1999. As of 4 September 2001 located at 105.52 deg E drifting at 0.008 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 105.46E drifting at 0.017W degrees per day.
1999 May 20 - . 22:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Nimiq 1 - .
Payload: A2100AX. Mass: 3,600 kg (7,900 lb). Nation: Canada.
Agency: Telesat.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Anik.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 25740 . COSPAR: 1999-027A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Telesat Canada's Nimiq television broadcasting satellite was placed into a 7050 km x 35790 km x 15.9 degree transfer orbit. The Nimiq was to use its liquid apogee engine (Royal Ordnance Leros 1) to reach geosynchronous orbit. Telesat Canada also operated the Anik Canadian domestic communications satellites, the first of which was launched in 1972. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 91 deg W in 1999. As of 4 September 2001 located at 91.11 deg W drifting at 0.002 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 91.18W drifting at 0.012W degrees per day.
1999 June 18 - . 01:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Astra 1H - .
Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 3,700 kg (8,100 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: SES.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Astra.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25785 . COSPAR: 1999-033A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous communications satellite. Stationed at 19 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 19 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 19.12 deg E drifting at 0.002 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 19.23E drifting at 0.019W degrees per day.
1999 July 5 - . 13:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton/Briz K/M. FAILURE: Second stage explosion.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Raduga - .
Payload: Raduga s/n 45L. Mass: 1,954 kg (4,307 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga.
Apogee: 30 km (18 mi).
Carried a Russian Defence Ministry communications satellite. First attempted flight of the Khrunichev Briz-M upper stage in place of the usual Block DM. After the second stage explosion the remainder of the vehicle survived for 45 seconds before breaking up. Debris landed near Karaganda. As a result of this accident the Kazakh government suspended launches from Baikonur pending Russian agreement to pay back part of rent owed.
1999 September 6 - . 16:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Yamal 101 - .
Mass: 1,360 kg (2,990 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: AO Gazco.
Manufacturer: Korolev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: USP (Victoria).
Spacecraft: Yamal.
USAF Sat Cat: 25896 . COSPAR: 1999-047A. Apogee: 36,298 km (22,554 mi). Perigee: 35,503 km (22,060 mi). Inclination: 2.40 deg. Period: 1,441.90 min.
The first two Yamal communications satellites were placed into a 197 km x 36,311 km x 49.3 degree transfer orbit The DM-2M fourth stage made two successful burns, placing the satellites in circular 36,000 km geosynchronous orbits. Yamal 101 reportedly ran into problems after it was deployed. RKK Energia built the new Yamal satellites for AO Gazcom of Moscow, a joint venture of RKKE and RAO Gazprom, the Russian natural gas monopoly. The two satellites will support internal communications for RAO Gazprom. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 89 deg E in 1999. As of 30 August 2001 located at 112.86 deg E drifting at 1.484 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 42.96E drifting at 1.484W degrees per day.
- Yamal 102 - . Mass: 1,360 kg (2,990 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: AO Gazco. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: USP (Victoria). Spacecraft: Yamal. Completed Operations Date: 1999-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 25897 . COSPAR: 1999-047B. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Geosynchronous communications satellite. Stationed at 90 deg E. As of 5 September 2001 located at 89.85 deg E drifting at 0.005 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 89.78E drifting at 0.010W degrees per day..
1999 September 26 - . 22:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- LMI-1 - .
Nation: Russia.
Agency: Lockheed.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: AS 2100.
Spacecraft: LMI.
USAF Sat Cat: 25924 . COSPAR: 1999-053A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous communications satellite. Stationed at 75 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 75 deg E in 1999. As of 2 September 2001 located at 74.98 deg E drifting at 0.005 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 75.00E drifting at 0.004W degrees per day.
1999 October 27 - . 16:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2. FAILURE: Failed early in second-stage burn.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Ekspress-A1 - . Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Svyaz. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. Communications satellite; failed to reach orbit..
2000 February 12 - . 09:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Garuda 1 - .
Payload: ACES / A2100AXX. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: Indonesia.
Agency: ACES.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 26089 . COSPAR: 2000-011A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 1.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous communications satellite for the ACES consortium (PSN of Indonesia, PLDT of the Phillipines, Lockheed Martin, and Jasmine of Thailand). The satellite had two large 12-m diameter L-band antennae for cellular telephone relay. Stationed at 123 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 123 deg E in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 122.97 deg E drifting at 0.023 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 123.10E drifting at 0.005W degrees per day.
2000 March 12 - . 04:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress 6A - .
Payload: Ekspress A No. 2. Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: Intersputnik.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Gals.
USAF Sat Cat: 26098 . COSPAR: 2000-013A. Apogee: 35,838 km (22,268 mi). Perigee: 35,736 km (22,205 mi). Inclination: 5.30 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
GO Kosmicheskaya Svyaz geosynchronous communications satellite, to be assigned to the Ekspress 6A slot at 80E. Replaced the first Ekspress A, lost in a launch failure in 1999. Russian satellite bus with a ommunications payload from Alcatel France. Stationed at 80 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 80.02 deg E drifting at 0.008 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 102.77E drifting at 0.018W degrees per day.
2000 April 17 - . 21:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Sesat - .
Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: Eutelsat.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Gals.
Spacecraft: Ekspress.
USAF Sat Cat: 26243 . COSPAR: 2000-019A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Sesat (Siberia-Europe Satellite) used an MSS-2500-GSO (Gals/Ekspress) satellite bus built by NPO PM of Krasnoyarsk, with an Alcatel Espace France payload of 18 Ku-band transponders. The satellite had 8 Fakel SPD-100 plasma thrusters for stationkeeping. Eutelsat operated their Hot Bird fleet of European television broadcast satellites since the 1980's, but the venture into broadcasting to Siberia represented a new step for them. Stationed at 36 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 39 deg E in 2000. As of 4 September 2001 located at 35.97 deg E drifting at 0.005 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 35.92E drifting at 0.004E degrees per day.
2000 June 6 - . 02:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton/Briz K/M.
- Gorizont - .
Payload: Gorizont 45. Mass: 2,125 kg (4,684 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: Svyaz.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Gorizont.
Completed Operations Date: 2000-06-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 26372 . COSPAR: 2000-029A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.30 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Communications satellite. First successful Proton/Briz-M launch. The Proton placed the Briz-M/Gorizont payload stack into a suborbital trajectory. The stage then performed four maneuvers to put the satellite into geosynchronous orbit:
- Burn 1 placed the stack into a 200 km, 51.6 deg parking orbit probably inclined at around 51.6
- Burn 2 raised apogee to 6000 km and changed inclination slightly
- Burn 3, at second perigee, four hours after launch put the stack in a 369 x 34,988 km x 48.8 deg transfer orbit. The Briz-M then jettisoned its empty toroidal supplementary fuel tank.
- Burn 4, ten hours after launch, placed Gorizont No. 45L in near-geostationary orbit.
Gorizont No. 45L was expected to be the final launch of that model of television broadcasting satellite. It carried 6 C-band transponders, one L-band, and one Ku-band transponder. The newer Ekspress satellites are replacing the system. Stationed at 145 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 145 deg E in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 145.25 deg E drifting at 0.002 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 144.69E drifting at 0.019W degrees per day.
2000 June 24 - . 00:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress A No. 3 - .
Payload: Ekspress A3 / Ekspress 3A. Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: Intersputnik.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Gals.
USAF Sat Cat: 26378 . COSPAR: 2000-031A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from June 23. Geosynchronous communications satellite. Stationed at 11 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 11 deg W in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 10.99 deg W drifting at 0.005 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 11.00W drifting at 0.005E degrees per day.
2000 June 30 - . 22:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Sirius 1 - .
Payload: CD Radio 1. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Sirius.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Sirius.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 26390 . COSPAR: 2000-035A. Apogee: 47,107 km (29,270 mi). Perigee: 24,465 km (15,201 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Digital Audio Radio Satellite, used for transmission of S-band radio broadcasts direct to receivers in cars in the United States. Sirius 1 was inserted into an initial 6,166 x 47110 km x 63.4 deg transfer orbit by the Proton-K's Blok DM3 upper stage. The satellite's R4D liquid apogee engine made several burns to raise the orbit to 24,388 x 47,097 km x 63.3 deg by July 8. This elliptical, inclined 24 hour orbit had a 24 hour period, designed to keep the satellite between longitude 60W and 140W, with apogee over the northern hemisphere. Stationed at 66 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 66 deg W in 2000. As of 6 September 2001 located at 65.59 deg W drifting at 0.015 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 65.37W drifting at 0.004E degrees per day.
2000 July 4 - . 23:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2371 - .
Payload: Geyzer. Mass: 2,400 kg (5,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MO.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Potok.
Completed Operations Date: 2000-07-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 26394 . COSPAR: 2000-036A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 8.60 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Second flight using RD-0210 Phase 2 engines. Geizer military communications satellite. The Blok DM upper stage inserted the Geizer into geosynchronous orbit at 06:20 GMT on July 5. Stationed at 80 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 80 deg E in 2000. As of 6 September 2001 located at 79.81 deg E drifting at 0.014 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 79.73E drifting at 0.022W degrees per day.
2000 July 12 - . 04:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Zvezda - .
Mass: 20,295 kg (44,742 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RAKA.
Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau,
Korolev bureau.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: ISS.
Spacecraft: ISS Zvezda.
USAF Sat Cat: 26400 . COSPAR: 2000-037A. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 179 km (111 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
Years behind schedule, the Zvezda living module of the International Space Station, built and financed by Russia, finally reached orbit. Zvezda's initial orbit was 179 x 332 km x 51.6 deg. On July 14 the orbit was raised to 288 x 357 km. ISS was then in a 365 x 372 km orbit. After matching orbits with the ISS, Zvezda then became the passive docking target for the Russian-built, US-financed Zarya module already attached to the station. The Zarya/Unity stack docked with the Zvezda module at 00:45 GMT on July 26, forming the basic core of the International Space Station. A flood of NASA missions would follow to bring the station into operation.
2000 August 28 - . 20:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga-1 - .
Mass: 2,400 kg (5,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MO.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 26477 . COSPAR: 2000-049A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
Raduga-1 military communications satellite initially named Cosmos 2372 by the RVSN press service. Stationed at 50 deg E. As of 5 September 2001 located at 49.25 deg E drifting at 0.048 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 45.70E drifting at 0.012W degrees per day.
2000 September 5 - . 09:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Sirius 2 - .
Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Sirius.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Sirius.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 26483 . COSPAR: 2000-051A. Apogee: 47,090 km (29,260 mi). Perigee: 24,480 km (15,210 mi). Inclination: 63.90 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Sirius Radio's Sirius 2 was launched into a 144 x 168 km x 64.8 deg parking orbit. The Blok DM3 stage then made two burns to deliver Sirius 2 to an elliptical 6192 x 47057 km x 63.4 deg orbit. The was to provide digital radio broadcasts to mobile users in North America. Stationed at 64 deg W. As of 31 August 2001 located at 64.56 deg W drifting at 0.003 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 67.77W drifting at 0.049E degrees per day.
2000 October 1 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- GE-1A - .
Payload: A2100AX. Mass: 3,593 kg (7,921 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: GE Americom.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 26554 . COSPAR: 2000-059A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Ku-band communications satellite to provide broadcast services for eastern Asia. Stationed at 108 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 108 deg E in 2000. As of 4 September 2001 located at 108.22 deg E drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 108.21E drifting at 0.011W degrees per day.
2000 October 13 - . 14:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2374 - .
Payload: Glonass s/n 83. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MO.
Manufacturer: AKO Polyot.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
USAF Sat Cat: 26564 . COSPAR: 2000-063A. Apogee: 19,136 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,124 km (11,883 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
Three navigation satellites for the GLONASS system were launched by a single Proton-K/Blok DM-2 upper stage into an initial 160 km x 64.8 deg parking orbit. The Blok DM-2 made two burns to maneuver into a 19120 x 19120 km x 64.8 deg orbit and deployed the three satellites about four hours after launch.
- Cosmos 2376 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 88. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Manufacturer: AKO Polyot. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 26566 . COSPAR: 2000-063C. Apogee: 19,278 km (11,978 mi). Perigee: 18,982 km (11,794 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2375 - . Payload: Glonass s/n 87. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Manufacturer: AKO Polyot. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 26565 . COSPAR: 2000-063B. Apogee: 19,136 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,124 km (11,883 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
2000 October 21 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- GE 6 - .
Payload: A2100AX. Mass: 3,909 kg (8,617 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: GE Americom.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 26580 . COSPAR: 2000-067A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications satellite. Stationed at 72 deg W. The GE 6 was a Lockheed Martin A2100 series satellite with a mass of 3552 kg at launch and 1900 kg dry. It was to provide broadcast and data services in North America. The DM3 upper stage made two burns and placed the GE 6 in a 5850 x 35726 km x 18.7 deg intermediate transfer orbit at 0441 UTC on October 22. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 72 deg W in 2000. As of 3 September 2001 located at 72.01 deg W drifting at 0.008 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 72.00W drifting at 0.005W degrees per day.
2000 November 30 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Sirius CD Radio 3 - .
Payload: CD Radio 3. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Sirius.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Sirius.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 26626 . COSPAR: 2000-077A. Apogee: 47,084 km (29,256 mi). Perigee: 24,485 km (15,214 mi). Inclination: 64.20 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Direct Radio Broadcasting satellite. Launch delayed from early October due to delays in delivery of engines. Stationed at 66 deg W. The third Sirius digital radio broadcast satellite was a Loral FS-1300 series vehicle and was placed in an initial elliptical 63 degree orbit by the Proton upper stage. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 66 deg W in 2000. As of 30 August 2001 located at 64.69 deg W drifting at 0.027 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 65.64W drifting at 0.010E degrees per day.
2001 April 7 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekran-M No. 18 - .
Payload: Ekran-M s/n 18L. Mass: 1,970 kg (4,340 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: GPKS.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Ekran-M.
USAF Sat Cat: 26736 . COSPAR: 2001-014A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 1.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Direct Broadcasting satellite. Maiden flight of new version of Proton. Launch delayed from August 2000, March 16 and April 6. Ekran-M No. 18 was a UHF television broadcasting satellite which was to be stationed at 99 deg E to provided television service to the Russian Far East. The satellite had a launch mass of around 2100 kg and was to replace the recently failed Ekran-M 15 that had been operating since October 1992 at the 105 deg-E longitude orbital slot.
The improved 3-stage Proton launch vehicle, with a new digital flight control system and enhanced first stage engines, delivered its payload section to a suborbital trajectory at 0356 GMT. The Briz-M upper stage then fired to enter a 200 km parking orbit. It appears that only two more burns were used to reach geostationary orbit: one at around 0440 GMT to enter a 200 x 35800 km GTO, after which the Briz-M toroidal drop tank was jettisoned, and one at around 1000 GMT, to circularize the orbit at geostationary altitude. Briz-M reportedly separated from its payload at 1031 GMT. Ekran was expected to reach its 99 deg E final location on around April 24. As of 5 September 2001 located at 99.27 deg E drifting at 0.009 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 99.30E drifting at 0.005W degrees per day.
2001 May 15 - . 01:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- PAS 10 - .
Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 3,712 kg (8,183 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Panamsat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Panamsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 26766 . COSPAR: 2001-019A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from April 4. PAS 10 (PanAmSat 10) was an American geosynchronous communications spacecraft. The 3.7 tonne (with fuel) satellite carried 48 transponders (24 in C-band and 24 in Ku-band) to provide direct-to-home video channels to Europe, Middle-East, and South Africa after parking over 68.5 deg-E longitude. PAS 10 replaced PAS 4. As of 5 September 2001 located at 68.50 deg E drifting at 0.001 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 68.45E drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
2001 June 16 - . 01:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Astra 2C - .
Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 3,728 kg (8,218 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: SES.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Astra.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 26853 . COSPAR: 2001-025A. Apogee: 35,805 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,768 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from June 11. Astra 2C was a European (SES - Societe Europeene des Satellites, Luxembourg) geosynchronous communications Boeing 601HP spacecraft. The 3.7 tonne (including 1.2 tonne of fuel), 8 kW satellite was the fifth in the Astra series. It carried 32 Ku-band transponders to provide voice, video, and data links to Western Europe through a pair of 3 m diameter dishes, after parking over 28.2 deg-E longitude. As of 5 September 2001 located at 19.13 deg E drifting at 0.005 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 19.23E drifting at 0.024W degrees per day.
2001 August 24 - . 20:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2379 - .
Payload: SPRN No. 9. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: VKS.
Manufacturer: Lavochkin bureau.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN.
USAF Sat Cat: 26892 . COSPAR: 2001-037A. Apogee: 35,810 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,768 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 1.60 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Launch delayed from August 23. Early-warning geosynchronous satellite. The Proton upper stage entered a geostationary transfer orbit after its first burn at 2152 GMT. A second burn was at 0310 GMT put the payload into its operational orbit. It was to provide early warning of missiles launched from the United States with the help of a heat-sensing array of detectors. According to the Moscow Kommersant newspaper, these early warning geosynchronous satellites belong to the US-KMO group, also known as Prognoz fleet, while the highly elliptical complement belongs to the US-KS group, also known as Oko fleet, both supplemented by about eight ground-based radars. As of 6 September 2001 located at 80.17 deg E drifting at 0.031 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 23.84W drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
2001 October 6 - . 16:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga-1 - .
Payload: Globus 2 / Raduga 1-6. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: VKS.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3.
Spacecraft: Raduga-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 26936 . COSPAR: 2001-045A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,770 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 0.90 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
The Blok-DM2 upper stage put the Russian geosynchronous military communications satellite into a geosynchronous transfer orbit at 1755 GMT. A second burn at 2318 GMT to circularized the orbit at geostationary altitude. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 106.48E drifting at 9.104W degrees per day.
2001 December 1 - . 18:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2380 - . Payload: Glonass 790. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 26987 . COSPAR: 2001-053A. Apogee: 19,146 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,114 km (11,876 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Three navigation satellites of the GLONASS system were launched to replenish the constellation. This was the second end-of-year replenishment launch since 2000..
- Cosmos 2382 - . Payload: Glonass-M 711. Mass: 1,480 kg (3,260 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 26989 . COSPAR: 2001-053C. Apogee: 19,156 km (11,902 mi). Perigee: 19,104 km (11,870 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. First launch of the Uragan-M improved model GLONASS satellite..
- Cosmos 2381 - . Payload: Glonass 789. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 26988 . COSPAR: 2001-053B. Apogee: 19,185 km (11,920 mi). Perigee: 19,074 km (11,852 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
2002 March 30 - . 17:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Intelsat 903 - .
Mass: 4,726 kg (10,419 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 27403 . COSPAR: 2002-016A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications satellite. Moved from Proton M to Proton K booster. Launch delayed from November 26, 2001, and March 4, 2002. The three stage Proton booster put the DM3 upper stage and payload on a suborbital trajectory. The first DM3 burn reached a circular 160 km orbit at 1742 UTC. The second burn at 1838 UTC raised apogee to about 35800 km, and a third burn near apogee at 2339 UTC raised perigee to about 3500 km and lowered inclination to 25 deg. Blok DM3 separated from the Intelsat 903 payload at 0008 UTC on March 31. By April 5, Intelsat 903 was in a 31653 x 35817 km x 0.7 deg near-synchronous orbit. Intelsat 903 had a launch mass of 4726 kg and a dry mass around 2350 kg, and carried C and Ku band antennas. It was built by SS/Loral using a derivative of the FS-1300 platform. As of 2007 Mar 5 located at 34.50W drifting at 0.011W degrees per day.
2002 May 7 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- DirecTV-5 - .
Payload: Tempo 1. Mass: 3,640 kg (8,020 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DirecTV.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: DirecTV.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 27426 . COSPAR: 2002-023A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Direct Broadcasting satellite. Launch delayed from October 2000, February, May 21 and October19, 2001, as the user and launch provider moved the payload from Proton to Atlas 2AS and then back again to Proton. The DM3 upper stage made two burns to put the DirecTV satellite in a 6568 x 35809 km x 17.7 deg transfer orbit. The Loral FS-1300 class satellite used its R-4D apogee engine to reach geostationary orbit at 129 W by May 19. The DirecTV satellite broadcasting company was a subsidiary of GM/Hughes. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 110.11W drifting at 0.004W degrees per day.
2002 June 10 - . 01:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress A1R - .
Payload: Ekspress A No. 4. Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: Svyaz.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Gals.
USAF Sat Cat: 27441 . COSPAR: 2002-029A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Launch delayed from May 2002. The Ekspress A1R Russian domestic communications satellite was built by NPO PM and Alcatel for Kosmicheskiya Svyaz, the Russian satcom operator. The Proton's parking orbit was off-nominal but the 11S861-01 Blok DM-2M upper stage corrected for this and delivered the payload to the correct orbit. Parking orbit was about 180 x 185 km x 51.6 deg; transfer orbit after the first DM-2M burn was 328 x 36133 km x 47.4 deg; orbit at spacecraft separation was 36102 x 36171 km x 0.2 deg. Two SOZ ullage motors were left in the transfer orbit. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 14.07W drifting at 0.008W degrees per day.
2002 July 25 - . 15:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/17S40.
- Cosmos 2392 - .
Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Arkon-1.
USAF Sat Cat: 27470 . COSPAR: 2002-037A. Apogee: 1,774 km (1,102 mi). Perigee: 1,506 km (935 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 119.10 min.
This was the second launch of the Arkon-1 electro-optical reconnaissance. The 17S40 Blok DM5 upper stage and satellite were placed by the Proton into a parking orbit. The DM then made two burns to place the satellite in its 1500 x 1836 km x 64.4 deg operational orbit.
2002 August 22 - . 05:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Echostar 8 - .
Mass: 4,660 kg (10,270 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Echostar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 27501 . COSPAR: 2002-039A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from June 16 and 22, July 18, August 2 and 20 due to payload problems. Echostar 8 was an American geostationary communication spacecraft. The 4.7-ton satellite was to provide digital TV broadcast to North America through its 16 spot beams and 41 transponders in the Ku-band after parking over 110° W longitude. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 110.01W drifting at 0.003W degrees per day.
2002 October 17 - . 04:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/17S40.
- Integral - . Mass: 4,100 kg (9,000 lb). Nation: Europe. Class: Astronomy. Type: Gamma ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: Integral. USAF Sat Cat: 27540 . COSPAR: 2002-048A. Apogee: 153,435 km (95,339 mi). Perigee: 9,283 km (5,768 mi). Inclination: 53.40 deg. Period: 4,310.60 min. INTEGRAL (INTErnational Gamma Ray Astrophysics Laboratory) was a European (ESA) astrophysics satellite. The orbit had a very high apogee to escape magnetospheric radiation..
2002 November 25 - . 23:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M. FAILURE: The Block DM upper stage failed to ignite for its second burn, leaving the satellite in parking orbit.. Failed Stage: U.
- Astra 1K - .
Payload: Spacebus 3000B3S. Mass: 5,250 kg (11,570 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: SES.
Manufacturer: Cannes.
Program: Astra.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000.
Decay Date: 2002-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 27557 . COSPAR: 2002-053A. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 244 km (151 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 90.10 min.
Delayed from December 2001 and July 15, August 16 and 25. Astra 1K was to be a European (Luxembourg-based) geostationary communications spacecraft. The 5.0-ton, 13-kW spacecraft was the most massive of civilian communications spacecraft ever launched. Its 52 Ku-band and two Ka-band transponders could cover 1,100 channels and were to replace three earlier Astra satellites. However the DM-3 upper stage, after operating successfully to place itself and the satellite in parking orbit, failed to ignite for transfer orbit injection, leaving the spacecraft stranded in parking orbit. In an effort to prevent imminent re-entry, the spacecraft was raised to a circular orbit at an altitude of 290 km. Three options were considered: force re-entry over the Pacific Ocean; retrieval by a US shuttle; or use of all the fuel aboard the satellite to attempt to move it to a geostationary orbit at 19.2° E longitude. The decision was taken in December to deorbit the spacecraft, resulting in a huge insurance loss and bringing into question both continued use of the Block D series of upper stages and the 'bigger is better' comsat philosophy.
2002 December 25 - . 10:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Cosmos 2394 - . Payload: Glonass. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 27617 . COSPAR: 2002-060A. Apogee: 19,136 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,124 km (11,883 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Three navigation satellites of the GLONASS system were launched to replenish the constellation. This was the third end-of-year replenishment launch since 2000..
- Cosmos 2395 - . Payload: Glonass. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 27618 . COSPAR: 2002-060B. Apogee: 19,335 km (12,014 mi). Perigee: 19,130 km (11,880 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 679.80 min.
- Cosmos 2396 - . Payload: Glonass-M. Mass: 1,480 kg (3,260 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 27619 . COSPAR: 2002-060C. Apogee: 19,135 km (11,889 mi). Perigee: 18,915 km (11,753 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 671.60 min.
2002 December 29 - . 23:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Nimiq 2 - . Payload: A2100AX. Mass: 3,600 kg (7,900 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: Telesat. Manufacturer: Lockheed. Program: Anik. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100. USAF Sat Cat: 27632 . COSPAR: 2002-062A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min. Payload moved from Atlas 5. Direct broadcast satellite. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 82.05W drifting at 0.004W degrees per day..
2003 April 24 - . 04:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2397 - . Payload: US-KMO (Prognoz 2). Mass: 2,155 kg (4,750 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VKS. Manufacturer: Lavochkin bureau. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN. USAF Sat Cat: 27775 . COSPAR: 2003-015A. Apogee: 35,928 km (22,324 mi). Perigee: 35,886 km (22,298 mi). Inclination: 2.20 deg. Period: 1,442.30 min. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 60.65W drifting at 0.723E degrees per day..
2003 June 6 - . 22:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton/Briz K/M.
- AMC-9 - .
Payload: Spacebus 3000B3. Mass: 4,100 kg (9,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SES Americom.
Manufacturer: Cannes.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 27820 . COSPAR: 2003-024A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from December 2002, then to February 10, 2003, then to February 28, March 15, April 28 and May 19. Finally moved forward from June 12 and 7. Upper stage changed from DM3 after several failures. The fifth burn of the Briz-M upper stage placed the spacecraft in a geostationary transfer orbit of 6,445 km x 35,674 km x 17.2 deg. The satellite used its own engine to place itself in geosynchronous orbit at apogee. Alcatel Spacebus 3000B3 with C and Ku band communications for North America from a geotationary position of 72 deg W. Americom at the time of launch had become a subsidiary of Societe Europeene des Satellites (SES), Luxembourg, which operated the European Astra satellie constellation. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 83.02W drifting at 0.008W degrees per day.
2003 November 24 - . 06:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Yamal-200 KA-1 - . Mass: 1,360 kg (2,990 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Gazprom. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: USP (Victoria). Spacecraft: Yamal. USAF Sat Cat: 28094 . COSPAR: 2003-053B. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Two geosynchronous communications satellites launched for Gazprom. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 49.00E drifting at 0.012E degrees per day..
- Yamal-200 KA-2 - . Mass: 1,320 kg (2,910 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Gazprom. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: USP (Victoria). Spacecraft: Yamal. Decay Date: 2004-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 28089 . COSPAR: 2003-053A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0300 deg. Period: 1,436.13 min. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 90.00E drifting at 0.016W degrees per day..
2003 December 10 - . 17:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton/Briz K/M.
- Cosmos 2402 - . Payload: Glonass 794. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28112 . COSPAR: 2003-056A. Apogee: 19,314 km (12,001 mi). Perigee: 19,018 km (11,817 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 677.20 min. Three navigation satellites of the GLONASS system were launched to replenish the constellation. This was the fourth end-of-year replenishment launch since 2000..
- Cosmos 2403 - . Payload: Glonass 795. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28113 . COSPAR: 2003-056B. Apogee: 19,102 km (11,869 mi). Perigee: 18,963 km (11,783 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 671.90 min.
- Cosmos 2404 - . Payload: Glonass-M 701. Mass: 1,480 kg (3,260 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28114 . COSPAR: 2003-056C. Apogee: 19,104 km (11,870 mi). Perigee: 18,961 km (11,781 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 671.90 min. Improved version of the Glonass satellite..
2003 December 28 - . 23:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress AM-22 - . Mass: 2,542 kg (5,604 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. USAF Sat Cat: 28134 . COSPAR: 2003-060A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min. The Ekspress AM-22 communications satellite was built by NPO PM and Alcatel Space for GPKS, the Russian Space Communications Company. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 52.99E drifting at 0.005W degrees per day..
2004 March 15 - . 23:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- W3A - .
Payload: Eurostar 3000S. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: Eutelsat.
Manufacturer: EADS Astrium.
Program: Eutelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 28187 . COSPAR: 2004-008A. Apogee: 35,811 km (22,251 mi). Perigee: 35,761 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Moved from Ariane 5. The satellite was to provide a full range of telecommunications applications including digital DVB broadcasting, multimedia, broadband access and pay-per-use bandwidth for corporate networks over a large zone covering Europe and Africa, for a minimum of 12 years. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 6.95E drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
2004 March 27 - . 03:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga-1 - . Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Raduga-1. USAF Sat Cat: 28194 . COSPAR: 2004-010A. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,768 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 1.30 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Military communications satellite. Parked in geostationary orbit at 85.0 deg E, after being placed in unusual subsynchronous drift orbit. Original name Cosmos 2406. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 85.19E drifting at 0.029W degrees per day..
2004 April 26 - . 20:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress AM-11 - . Mass: 2,542 kg (5,604 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Svyaz. Manufacturer: Cannes, Reshetnev bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. USAF Sat Cat: 28234 . COSPAR: 2004-015A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Delayed from April 10. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 79.96W drifting at 3.741W degrees per day..
2004 June 16 - . 22:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Intelsat 10-02 - . Payload: Eurostar 3000H. Mass: 5,575 kg (12,290 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Intelsat. Manufacturer: EADS Astrium. Program: Intelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 28358 . COSPAR: 2004-022A. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Heaviest single payload to geosynchronous transfer orbit to that date. Delayed from late 2003, June 10 and 15, 2004. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 0.99W drifting at 0.002W degrees per day..
2004 August 4 - . 22:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Amazonas - . Payload: Eurostar 3000S. Mass: 4,545 kg (10,020 lb). Nation: Spain. Agency: Hispasat. Manufacturer: EADS Astrium. Program: Hispasat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 28393 . COSPAR: 2004-031A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Delayed from June, July 25. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 61.03W drifting at 0.005W degrees per day..
2004 October 14 - . 21:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- AMC- 15 - .
Payload: A2100AXS. Mass: 4,021 kg (8,864 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SES Americom.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 28446 . COSPAR: 2004-041A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications satellite for SES Americom, equipped with Ku-band and Ka-band transponders. The Briz-M upper stage made three burns, then released the satellite on October 15 at 03:58 GMT into a 7132 x 35780 km x 18.6 deg orbit. AMC-15's on-board engine would be used to maneuver the spacecraft into its final geostationary orbit. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 105.02W drifting at 0.003W degrees per day.
2004 October 29 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress AM-1 - .
Mass: 2,542 kg (5,604 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: ILS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4.
Spacecraft: Gals.
USAF Sat Cat: 28463 . COSPAR: 2004-043A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Russian Satellite Communications Company spacecraft, to be stationed at 40 deg E, providing 28 C, Ku, and L band transponders for a wide range of communications and data services. The Ekspress-AM uses an improved Ekspress-M or 727M bus, first used on the Sesat satellite, while the earlier models used the KAUR-4 MSO-2500 bus. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 39.98E drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
2004 December 26 - . 13:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2411 - . Payload: Glonass 796. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28508 . COSPAR: 2004-053A. Apogee: 19,149 km (11,898 mi). Perigee: 19,141 km (11,893 mi). Inclination: 64.85 deg. Period: 676.05 min. Three Russian navigation satellites orbited in a single launch. Two of the satellites (s/n 796 and 797) were standard Uragan satellites, while s/n 712 had an uprated Glonass-M payload. This was the fifth end-of-year replenishment launch since 2000..
- Cosmos 2412 - . Payload: Glonass 797. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28509 . COSPAR: 2004-053B. Apogee: 19,148 km (11,897 mi). Perigee: 19,143 km (11,894 mi). Inclination: 64.85 deg. Period: 676.05 min.
- Cosmos 2413 - . Payload: Glonass-M 712. Mass: 1,480 kg (3,260 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28510 . COSPAR: 2004-053C. Apogee: 19,148 km (11,897 mi). Perigee: 19,142 km (11,894 mi). Inclination: 64.85 deg. Period: 676.05 min.
2005 February 3 - . 02:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- AMC-12 - . Payload: Spacebus 4000C3. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SES Americom. Manufacturer: Cannes. Program: Americom. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 28526 . COSPAR: 2005-003A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Americom 12 satellite, also known as Worldsat 2. The first Alcatel Spacebus 4000 satellite to be launched..
2005 March 29 - . 22:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Ekspress AM-2 - . Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Svyaz. Manufacturer: Cannes, Reshetnev bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. USAF Sat Cat: 28629 . COSPAR: 2005-010A. Apogee: 35,893 km (22,302 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,438.50 min. Delayed from December 2004, then moved up from March 31, 2005. Communications payload of C, Ku and L band transponders. It was to be stationed at 80 deg E. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 80.01E drifting at 0.008W degrees per day..
2005 May 22 - . 17:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- DirecTV-8 - .
Mass: 3,711 kg (8,181 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DirecTV.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: DirecTV.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 28659 . COSPAR: 2005-019A. Apogee: 35,842 km (22,271 mi). Perigee: 35,711 km (22,189 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,435.60 min.
Provided United States direct-television broadcast coverage from the 101 degrees West longitude orbital slot. The satellite carried 16 high-power transponders for high-quality national digital video services. Purchased in October 2003 together with DirecTV-9S for a total price of $220 million for both. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 100.77W drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
2005 June 24 - . 19:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Ekspress AM-3 - . Payload: Ekspress AM. Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Svyaz. Manufacturer: Cannes, Reshetnev bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. USAF Sat Cat: 28707 . COSPAR: 2005-023A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Delayed from April 2005. Satellite built by NPO PM with Alcatel C-, Ku- and L-band transponders.Stationed over 80 deg E longitude. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 139.98E drifting at 0.015W degrees per day..
2005 September 8 - . 19:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Anik F1-R - . Payload: Eurostar 3000S. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: Telesat. Manufacturer: EADS Astrium. Program: Anik. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 28868 . COSPAR: 2005-036A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Moved up from October, delayed from August 9, moved up from September 15 . Telesat Canada communications satellite operating in C- and Ku-band. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 107.32W drifting at 0.005W degrees per day..
2005 December 25 - . 05:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2417 - .
Payload: Glonass 798. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: KNITs.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
USAF Sat Cat: 28915 . COSPAR: 2005-050A. Apogee: 19,171 km (11,912 mi). Perigee: 19,089 km (11,861 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
The Block D upper stage delivered three GLONASS navigation satellites into their planned orbits at 08:39 GMT. These satellites were placed in GLONASS orbit plane 3. The satellites had an extended seven-year service life compared to earlier models. This was the sixth end-of-year replenishment launch since 2000. When operational they brought the total of operational GLONASS SVs in orbit to 16. The launch was part of a Russian government-funded program to replenish and expand the Glonass constellation to at least 18 operating satellites satellites by 2007 (compared to 14 satellites at the end of 2005). In 2006 launch of a new Glonass satellite design with a ten-year service was planned.
- Cosmos 2418 - . Payload: Glonass-M s/n 713. Mass: 1,480 kg (3,260 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28916 . COSPAR: 2005-050B. Apogee: 19,172 km (11,912 mi). Perigee: 19,087 km (11,860 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2419 - . Payload: Glonass-M s/n 714. Mass: 1,480 kg (3,260 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 28917 . COSPAR: 2005-050C. Apogee: 19,165 km (11,908 mi). Perigee: 19,094 km (11,864 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
2005 December 29 - . 02:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- AMC-23 - .
Payload: Spacebus 4000C3 / AMC-13, GE-3i, WorldSat 3. Mass: 4,981 kg (10,981 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SES Americom.
Manufacturer: Alenia.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000.
USAF Sat Cat: 28924 . COSPAR: 2005-052A. Apogee: 35,801 km (22,245 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Delayed from November, December 1 and 6. AMC-23 was to provide Ku-band multimedia and telecommunications services to Pacific rim countries over a planned 16 year life. A C-band payload was partly leased to the Japanese JSAT system. The Briz-M upper stage separated from the three-stage Proton launch vehicle at suborbital velocity, then conducted five engine burns before delivering the satellite to a 6193 km x 35,615 km x 18.5 deg geosynchronous transfer orbit at 11:48 GMT. The satellite would use its own Astrium S400 apogee engine to circularize the orbit at geostationary altitude. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 171.97E drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
2006 February 28 - . 20:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M. FAILURE: Briz-M stage shut down 27.5 minutes into a planned 31-minute burn and could not be restarted. The failure left the satellite in a useless orbit from which it quickly decayed... Failed Stage: U.
- Arabsat 4 - . Payload: Eurostar 2000+. Mass: 3,341 kg (7,365 lb). Nation: Arab States. Agency: Arabsat. Manufacturer: EADS Astrium. Program: Arabsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 2000. Decay Date: 2006-03-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 28943 . COSPAR: 2006-006A. Apogee: 14,684 km (9,124 mi). Perigee: 497 km (308 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 273.80 min. The satellite seperated from the stage but the mission could not be rescued. It was ordered to fire its apogee engine around 00:20 GMT on March 24 to lower its perigee into the atmosphere. It reportedly burned up over the South Pacific at 02:07 GMT..
2006 June 17 - . 22:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Kazsat 1 - . Mass: 1,380 kg (3,040 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KazSat. Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Yakhta. USAF Sat Cat: 29230 . COSPAR: 2006-022A. Apogee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Perigee: 35,381 km (21,984 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,425.60 min. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 103.02E drifting at 0.000W degrees per day..
2006 August 4 - . 21:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Hot Bird 8 - . Mass: 4,875 kg (10,747 lb). Nation: Europe. Agency: Eutelsat. Manufacturer: EADS Astrium. Program: Eutelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 29270 . COSPAR: 2006-032A. Apogee: 35,817 km (22,255 mi). Perigee: 35,755 km (22,217 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ku-band communications direct broadcast satellite to supplement Eutelsat constellation of Hot Birds. As of 2007 Mar 4 located at 13.03E drifting at 0.010E degrees per day..
2006 November 8 - . 20:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Badr 4 ARABSAT 4B - . Payload: Eurostar 2000+. Mass: 3,280 kg (7,230 lb). Nation: Arab States. Agency: Arabsat. Manufacturer: EADS Astrium. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 2000. USAF Sat Cat: 29526 . COSPAR: 2006-051A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Dry mass 1487 kg. The satellite provided Ku-band communications services for Arab League countries. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 26.06E drifting at 0.011E degrees per day..
2006 December 11 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Measat 3 - .
Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 4,900 kg (10,800 lb). Nation: Malaysia.
Agency: Binarian.
Program: Measat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 29648 . COSPAR: 2006-056A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Malaysian communications satellite, to be stationed at 91.5° East together with Measat 1, covering South Asia, Malaysia and Indonesia, and supplementing Measats 1 and 2 launched ten years earlier. The Proton booster released the satellite in a 416 x 35807 x 49.1 deg geosynchronous transfer orbit. The Boeing 601HP 3 axis stabilized spacecraft, had a design lifetime of 15 years. C-band 24 active transponders using 65-watt TWTAs; Ku-band 24 active transponders using 120-watt TWTAs . End of life power of 9.8 kW provided by two solar wings, each with 4 panels of triple-junction gallium arsenide solar cells. A 445N liquid apogee motor circularised the spacecraft in geosynchronous orbit, and 12 x 10 N bipropellant thrusters provided stabilization and stationkeeping. Length in orbit with solar panels deployed 26.2 m; width, with antennas deployed, 7.7 m; stowed diameter 3.8 m. Mass in geostationary orbit after apogee motor maneuver at beginning of life 3220 kg. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 91.49E drifting at 0.012W degrees per day.
2006 December 24 - . 20:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2424 - .
Payload: Glonass-M s/n 715. Mass: 2,480 kg (5,460 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: KNITs.
Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
USAF Sat Cat: 29672 . COSPAR: 2006-062C. Apogee: 19,176 km (11,915 mi). Perigee: 19,083 km (11,857 mi). Inclination: 65.20 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
Three Glonass satellites are lofted in a single launch in support of restoring the Glonass navigation satellite constellation to full military and commercial functionality. They were placed in Glonass orbit plane 2, beginning its population. At the time of launch the constellation consisted of 11 operational spacecraft, and five more on-orbit spares. A fully operational constellation would consist of 24 satellites - eight in each of three orbital planes. Only two planes were populated by 2006 - the full complement of 24 satellites was not to be reached until 2009. This was the first launch to repopulate plane 2; planes 1 and 3 had satellites operational.
- Cosmos 2425 - . Payload: Glonass-M s/n 716. Mass: 2,480 kg (5,460 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 29670 . COSPAR: 2006-062A. Apogee: 19,187 km (11,922 mi). Perigee: 19,073 km (11,851 mi). Inclination: 65.20 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2426 - . Payload: Glonass-M s/n 717. Mass: 2,480 kg (5,460 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 29671 . COSPAR: 2006-062B. Apogee: 19,183 km (11,919 mi). Perigee: 19,077 km (11,853 mi). Inclination: 65.20 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
2007 April 9 - . 22:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Anik F3 - . Payload: Eurostar 3000S. Mass: 4,634 kg (10,216 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: Telesat. Manufacturer: Friedrichshafen. Program: Anik. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 31102 . COSPAR: 2007-009A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min. Communications satellite with C, Ku and Ka band transponders..
2007 July 7 - . 01:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- DirecTV-10 - .
Mass: 5,893 kg (12,991 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DirecTV.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: DirecTV.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 31862 . COSPAR: 2007-032A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
First launch of a pair of satellites, DirecTV 10 and 11, that will beam HDTV programs to 500 local markets from the company's primary orbital slot at 101 degrees west longitude. Acquisition and launch cost of $300 million per satellite; one ground spare also built.
2007 September 5 - . 22:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M. FAILURE: Second stage engine failure soon after ignition.. Failed Stage: 2.
- JCSAT 11 - . Payload: A2100AXS. Mass: 4,007 kg (8,833 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Manufacturer: Lockheed. Program: JCSAT. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
2007 October 26 - . 07:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2431 - . Payload: Glonass-M s/n 718. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 32275 . COSPAR: 2007-052A. Apogee: 19,130 km (11,880 mi). Perigee: 19,128 km (11,885 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Three Uragan-M satellites were launched to replenish the Glonass navigation system, placed in GLONASS orbit plane 3. Cosmos 2431 set to operational on 4 December; plane/slot 3/17, frequency channel -1.
- Cosmos 2432 - . Payload: Glonass-M s/n 719. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 32276 . COSPAR: 2007-052B. Apogee: 19,135 km (11,889 mi). Perigee: 19,121 km (11,881 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Set to operational; plane/slot 3/20, frequency channel 2 on 27 November..
- Cosmos 2433 - . Payload: Glonass-M s/n 720. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: KNITs. Manufacturer: Reshetnev bureau. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 32277 . COSPAR: 2007-052C. Apogee: 19,135 km (11,889 mi). Perigee: 19,121 km (11,881 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Set to operational; plane/slot 3/19, frequency channel 3 on 25 November..
2007 November 17 - . 22:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Sirius 4 - .
Payload: A2100AX. Mass: 4,600 kg (10,100 lb). Nation: Sweden.
Agency: ILS.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Sirius.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 32299 . COSPAR: 2007-057A. Apogee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,641 km (22,146 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,432.20 min.
Sirius 4 carried Ku-band and Ka-band communications payloads for Nordic, Baltic and East European communications. Three upper-stage burns placed Sirius 4 into a 6916 km x 35478 km x 17.4 deg geostationary transfer orbit. A series of maneuvers by the satellite using its own Leros engine maneuvered the satellite into geosynchronous orbit, stationed at 5 deg East.
2007 December 9 - . 00:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Cosmos 2434 - . Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Raduga-1. USAF Sat Cat: 32373 . COSPAR: 2007-058A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Raduga-1 / Globus communications satellite..
2007 December 25 - . 19:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2435 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 21. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 32394 . COSPAR: 2007-065B. Apogee: 19,179 km (11,917 mi). Perigee: 19,081 km (11,856 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2436 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 22. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 32395 . COSPAR: 2007-065C. Apogee: 19,150 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,100 km (11,800 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2437 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 23. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 32393 . COSPAR: 2007-065A. Apogee: 19,137 km (11,891 mi). Perigee: 19,123 km (11,882 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Three GLONASS-M satellites lofted in a single launch - inserted in GLONASS orbit plane 2. This was the second launch to populate this plane..
2008 January 28 - . 00:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekspress AM-33 - . Mass: 2,579 kg (5,685 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Svyaz. Manufacturer: Cannes, Reshetnev bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. USAF Sat Cat: 32478 . COSPAR: 2008-003A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0300 deg. Period: 1,436.12 min. Stationed at 96.5 degrees east longitude to provide Internet, video, radio, and data services for at a planned 12 year life. The satellite also was earmarked to provide mobile communications for the Russian president and other top government officials..
2008 February 11 - . 11:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Thor 5 - . Mass: 1,940 kg (4,270 lb). Nation: Norway. Agency: ILS. Program: Thor Comsat. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Star bus. USAF Sat Cat: 32487 . COSPAR: 2008-006A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ku-band light geostationary satellite operated by Telenor Satellite Broadcasting..
2008 March 14 - . 23:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M. FAILURE: Premature shutdown of Briz upper stage due to escape of turbine gases through a thin-walled tube.. Failed Stage: U.
- AMC-14 - .
Payload: A2100AXS. Mass: 4,140 kg (9,120 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SES Americom.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 32708 . COSPAR: 2008-011A. Apogee: 35,979 km (22,356 mi). Perigee: 35,592 km (22,115 mi). Inclination: 14.47 deg. Period: 1,436.03 min.
The Briz M stage failed during its second burn, shutting down by 2 minutes 13 seconds early, leaving the satellite in a 770 km x 26447 km x 49.2 deg orbit. The spacecraft separated and raised this to 772 km x 35576 km x 49.0 deg, but operational geostationary orbit could not be attained and the satellite was a writeoff. AMC 14 had a total mass at launch of 4140 kg of which 2130 kg was propellant. The final orbit attained was an inclined orbit at geostationary altitude.
2008 June 26 - . 23:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2440 - . Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN. USAF Sat Cat: 33108 . COSPAR: 2008-033A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 2.10 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
2008 August 18 - . 22:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Inmarsat-4 F3 - . Payload: Eurostar 3000GM. Mass: 4,960 kg (10,930 lb). Nation: International. Agency: Inmarsat. Program: Inmarsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 33278 . COSPAR: 2008-039A. Apogee: 36,027 km (22,386 mi). Perigee: 36,009 km (22,374 mi). Inclination: 3.10 deg. Period: 1,447.90 min. Maritime communications satellite with a solar panel span of 45 m, and a 10-m diameter L-band mobile communications antenna..
2008 September 19 - . 21:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Nimiq 4 - . Payload: Eurostar 3000S. Mass: 4,800 kg (10,500 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: ILS. Program: Anik. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 33373 . COSPAR: 2008-044A. Apogee: 35,749 km (22,213 mi). Perigee: 35,653 km (22,153 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,431.70 min. Geostationary television broadcasting satellite launched for Telesat..
2008 September 25 - . 08:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2442 - . Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 33378 . COSPAR: 2008-046A. Apogee: 19,144 km (11,895 mi). Perigee: 19,089 km (11,861 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.20 min. Continued replenishment of Glonass navigation satellite constellation..
- Cosmos 2443 - . Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 33379 . COSPAR: 2008-046B. Apogee: 19,142 km (11,894 mi). Perigee: 19,136 km (11,890 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 676.10 min.
- Cosmos 2444 - . Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 33380 . COSPAR: 2008-046C. Apogee: 19,145 km (11,896 mi). Perigee: 19,132 km (11,888 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 676.10 min.
2008 November 5 - . 20:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Astra 1M - .
Mass: 5,344 kg (11,781 lb). Nation: Luxembourg.
Agency: ILS.
Program: Astra.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 33436 . COSPAR: 2008-057A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,770 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
ASTRA 1M was positioned at Astra's prime 19.2 deg E position, providing pan-European coverage for Direct-to-Home services. Its entry into service would have allowed Astra to redeploy other satellites to its orbital position of 23.5° east. Total power consumption: 9.3 kW BOL, 8.3 kW EOL; Transponder capacity: 36/32 at 26 and 33 MHz; TWTA output power: 150 W; Channel capacity in10.7 - 12.75 GHz: 72 channels (bands D, B, E and F) .
2008 December 10 - . 13:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ciel-2 - . Payload: Spacebus 4000C4. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: ILS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 33453 . COSPAR: 2008-063A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Communications satellite owned by Ciel Satellite Group, Ottawa and controlled from Saskatoon, Canada. Ciel was at the time using Echostar V (redesignated Ciel-1)..
2008 December 25 - . 10:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2447 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 727. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 33466 . COSPAR: 2008-067A. Apogee: 19,139 km (11,892 mi). Perigee: 19,121 km (11,881 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Three Glonass satellites launched as part of a continuing effort to reconstitute the full Russian navigation satellite constellation..
- Cosmos 2449 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 729. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 33467 . COSPAR: 2008-067B. Apogee: 19,138 km (11,891 mi). Perigee: 19,117 km (11,878 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.60 min.
- Cosmos 2448 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 728. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 33468 . COSPAR: 2008-067C. Apogee: 19,143 km (11,894 mi). Perigee: 19,117 km (11,878 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
2009 February 11 - . 00:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekspress AM-44 - . Mass: 3,672 kg (8,095 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-4. Spacecraft: Gals. USAF Sat Cat: 33595 . COSPAR: 2009-007A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
- Express MD1 - . Mass: 1,140 kg (2,510 lb). Nation: Russia. Manufacturer: Chelomei bureau. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Yakhta. USAF Sat Cat: 33596 . COSPAR: 2009-007B. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. C and L-band transponders..
2009 February 28 - . 04:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Raduga 1-8 - . Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Raduga-1. USAF Sat Cat: 34264 . COSPAR: 2009-010A. Apogee: 35,943 km (22,333 mi). Perigee: 35,635 km (22,142 mi). Inclination: 1.20 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
2009 April 3 - . 16:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Eutelsat W2A - . Payload: Spacebus 4000C4. Mass: 5,900 kg (13,000 lb). Nation: Europe. Agency: ILS. Program: Eutelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 34710 . COSPAR: 2009-016A. Apogee: 35,808 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,765 km (22,223 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ku, S and C-band communications payload; stationed at 1.7 deg East..
2009 May 16 - . 00:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Protostar 2 / SES 7 - . Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Nation: Bermuda. Agency: ILS. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 34941 . COSPAR: 2009-027A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. S band transponder known as Indostar 2, launched to replace Indostar 1 (Cakrawarta) in providing communications services to Indonesia. Sold in 2009 to SES when Protostar was wound up and renamed SES 7..
2009 June 30 - . 19:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Sirius FM-5 - . Mass: 5,976 kg (13,174 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Program: Sirius. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 35493 . COSPAR: 2009-034A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Direct radio broadcast satellite for North America. 2900 kg dry mass..
2009 August 11 - . 19:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Asiasat 5 - . Mass: 3,760 kg (8,280 lb). Nation: China. Agency: ILS. Program: Asiasat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 35696 . COSPAR: 2009-042A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Provided C-band and Ku-band communications services..
2009 September 17 - . 19:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Nimiq-5 - . Mass: 4,745 kg (10,460 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: ILS. Program: Anik. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 35873 . COSPAR: 2009-050A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
2009 November 24 - . 14:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Eutelsat W7 - . Payload: Spacebus 4000C4. Mass: 5,627 kg (12,405 lb). Nation: Europe. Agency: ILS. Program: Eutelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 36101 . COSPAR: 2009-065A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Communications satellite, replacing SESAT-1 in broadcasting and data services to Russia and Africa..
2009 December 14 - . 10:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2456 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 730. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 36111 . COSPAR: 2009-070A. Apogee: 19,132 km (11,888 mi). Perigee: 19,129 km (11,886 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.80 min. Annual replenishment of GLONASS satellite constellation..
- Cosmos 2457 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 733. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 36112 . COSPAR: 2009-070B. Apogee: 19,133 km (11,888 mi). Perigee: 19,128 km (11,885 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.80 min.
- Cosmos 2458 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 734. Mass: 1,370 kg (3,020 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 36113 . COSPAR: 2009-070C. Apogee: 19,128 km (11,885 mi). Perigee: 18,991 km (11,800 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 672.90 min.
2009 December 29 - . 00:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- DirecTV-12 - . Mass: 5,900 kg (13,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Program: DirecTV. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 36131 . COSPAR: 2009-075A. Apogee: 37,150 km (23,080 mi). Perigee: 34,409 km (21,380 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,435.70 min. Direct television broadcast to United States..
2010 January 28 - . 00:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Raduga-1M - . Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Raduga-1. Decay Date: 2014-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 36358 . COSPAR: 2010-002A. Apogee: 35,591 km (22,115 mi). Perigee: 35,567 km (22,100 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,425.50 min. Second new-generation Globus-M military communications satellite..
2010 February 12 - . 00:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Intelsat 16 - . Payload: Intelsat IS-16 Star-2.4. Mass: 2,060 kg (4,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Program: Intelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Star bus. USAF Sat Cat: 36397 . COSPAR: 2010-006A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ku-band satellite providing backup for Sky Latin America service..
2010 March 1 - . 21:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2459 - . Payload: Uragan-M 24. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 36400 . COSPAR: 2010-007A. Apogee: 19,217 km (11,940 mi). Perigee: 19,043 km (11,832 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2461 - . Payload: Uragan-M 26. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 36401 . COSPAR: 2010-007B. Apogee: 19,137 km (11,891 mi). Perigee: 19,123 km (11,882 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2460 - . Payload: Uragan-M 25. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 36402 . COSPAR: 2010-007C. Apogee: 19,136 km (11,890 mi). Perigee: 19,124 km (11,883 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
2010 March 20 - . 18:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Echostar 14 - . Mass: 6,380 kg (14,060 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Program: Echostar. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 36499 . COSPAR: 2010-010A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
2010 April 24 - . 11:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- SES 1 - . Payload: Star-2.4. Mass: 2,560 kg (5,640 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Star bus. USAF Sat Cat: 36516 . COSPAR: 2010-016A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Communications satellite. Replaced AMC-2 and AMC-4 with Ku and C band services to the United States from 101 deg W..
2010 June 3 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Arabsat 5B - . Mass: 5,420 kg (11,940 lb). Nation: Arab States. Agency: ILS. Program: Arabsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 36592 . COSPAR: 2010-025A. Apogee: 35,804 km (22,247 mi). Perigee: 35,767 km (22,224 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Direct-to-home broadcast satellite, stationed at 26 deg E..
2010 July 10 - . 18:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Echostar 15 - . Mass: 5,520 kg (12,160 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Program: Echostar. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 36792 . COSPAR: 2010-034A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Supported Dish direct-to-home broadcast network to North America..
2010 September 2 - . 00:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2466 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 738. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 37137 . COSPAR: 2010-041A. Apogee: 19,184 km (11,920 mi). Perigee: 19,076 km (11,853 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2465 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 737. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 37138 . COSPAR: 2010-041B. Apogee: 19,221 km (11,943 mi). Perigee: 19,038 km (11,829 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2464 - . Payload: Uragan-M s/n 736. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 37139 . COSPAR: 2010-041C. Apogee: 19,181 km (11,918 mi). Perigee: 19,078 km (11,854 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Replenishment of Glonass navigation satellite constellation..
2010 October 14 - . 18:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- XM-5 - . Payload: Sirius XM-5. Mass: 5,983 kg (13,190 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Sirius. Program: XM. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 37185 . COSPAR: 2010-053A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Fifth direct-broadcast digital radio satellite in the Sirius constellation..
2010 November 14 - . 17:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Skyterra 1 - . Payload: BSS-GEM. Mass: 5,400 kg (11,900 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 37218 . COSPAR: 2010-061A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 6.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. GeoMobile class satellite with a 22-meter L-band reflector..
2010 December 6 - . 10:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-3. FAILURE: Block DM-3 upper stage was loaded with 1500 kg excess liquid oxygen in error. This caused a 100 m/s shortfall in the third stage burn into parking orbit. The upper stages and payload reentered over the Pacific.. Failed Stage: U.
- Glonass-M - . Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. The launch was to have allowed the Glonass communications network to receive full operational status after a multi-year replenishment effort. The failure led to several high-level sackings..
- Glonass-M - . Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
- Glonass-M - . Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
2010 December 26 - . 21:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ka Sat - . Payload: KA-SAT . Mass: 6,150 kg (13,550 lb). Nation: Europe. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 37258 . COSPAR: 2010-069A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ka band communications with 80 spot beams; 6150 kg loaded / 3200 kg unfuelled..
2011 May 20 - . 19:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Telstar 14R - . Mass: 4,970 kg (10,950 lb). Nation: USA. Program: Telstar series. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 37602 . COSPAR: 2011-021A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ku-band direct-broadcast satellite providing satellite television to Brazil. Failed to fully deploy one of its solar arrays..
2011 July 15 - . 23:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- SES 3 - . Payload: Orbital Star-2.4E. Mass: 3,112 kg (6,860 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Star bus. USAF Sat Cat: 37748 . COSPAR: 2011-035A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. C/Ku band communications payload..
- Kazsat 2 - . Mass: 1,330 kg (2,930 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Yakhta. USAF Sat Cat: 37749 . COSPAR: 2011-035B. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ku-band communications payload. Operator Kazakhstan National Center for Space Communications..
2011 August 17 - . 21:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M. FAILURE: Cause was a timing error in the inertial platform, leading to incorrect orientiation of the stage during the later burns.. Failed Stage: U.
- Ekspress AM-4 - .
Mass: 5,775 kg (12,731 lb). Nation: Russia.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000.
Decay Date: 2012-03-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 37798 . COSPAR: 2011-045A. Apogee: 20,389 km (12,669 mi). Perigee: 674 km (418 mi). Inclination: 51.10 deg. Period: 364.70 min.
Communications satellite delivered to an incorrect orbit when the Briz-M upper stage malfunctioned. The first two Briz-M burns, to a 173 km x 173 km, and then to a 270 km x 4998 km orbit, were successful. The third burn, at 00:52 GMT on 18 August, seemed to have gone wrong, with early separation of the wrap-around DTB propellant tank. A fourth burn left the payload stranded in a 694 km x 20242 km orbit. Cause was a timing error in the inertial platform, leading to incorrect orientiation of the stage during the later burns.
2011 September 20 - . 22:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Cosmos 2473 - . Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Garpun. USAF Sat Cat: 37806 . COSPAR: 2011-048A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. First launch of the Garpun military communications and data relay satellite, built by Reshetnev..
2011 September 29 - . 18:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Quetzsat 1 - . Mass: 5,514 kg (12,156 lb). Nation: Mexico. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 37826 . COSPAR: 2011-054A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ku-band communications satellite to be leased to Echostar..
2011 October 19 - . 18:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Viasat 1 - . Mass: 6,740 kg (14,850 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 37843 . COSPAR: 2011-059A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Ka-band broadband data satellite for North American service. Coverage included 9 Canadian spot beams owned by Telesat and 63 US beams owned by ViaSat..
2011 November 4 - . 12:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Cosmos 2476 - . Payload: Uragan s/n 743. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 37867 . COSPAR: 2011-064A. Apogee: 19,173 km (11,913 mi). Perigee: 19,087 km (11,860 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min. Replenishment of Glonass navigation satellite constellation..
- Cosmos 2477 - . Payload: Uragan s/n 744. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 37868 . COSPAR: 2011-064B. Apogee: 19,168 km (11,910 mi). Perigee: 19,092 km (11,863 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 675.70 min.
- Cosmos 2475 - . Payload: Uragan s/n 745. Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. USAF Sat Cat: 37869 . COSPAR: 2011-064C. Apogee: 19,175 km (11,914 mi). Perigee: 19,021 km (11,819 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 674.50 min.
2011 November 25 - . 19:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- AsiaSat 7 - . Mass: 3,750 kg (8,260 lb). Nation: China. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 37934 . COSPAR: 2011-069B. Apogee: 34,313 km (21,321 mi). Perigee: 11,873 km (7,377 mi). Inclination: 0.30 deg. Period: 839.20 min. Communications satellite for Asiasat of Hong Kong..
2011 December 11 - . 11:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Amos 5 - . Payload: Ekspress-1000N. Mass: 1,600 kg (3,500 lb). Nation: Israel. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 37950 . COSPAR: 2011-074A. Apogee: 36,056 km (22,404 mi). Perigee: 35,690 km (22,170 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,440.50 min. Communications satellite operated by IAI Spacecom..
- Luch 5A - . Payload: Ekspress-1000A. Mass: 1,148 kg (2,530 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 37951 . COSPAR: 2011-074B. Apogee: 36,012 km (22,376 mi). Perigee: 35,672 km (22,165 mi). Inclination: 4.90 deg. Period: 1,438.90 min. Tracking and data relay satellite..
2012 February 14 - . 19:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- SES-4 - . Mass: 6,180 kg (13,620 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 38087 . COSPAR: 2012-007A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. SES World Skies communications satellite to replace NSS 7 at 22 deg West..
2012 March 25 - . 12:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Intelsat IS-22 - .
Payload: BSS-702MP. Mass: 6,200 kg (13,600 lb). Nation: Luxembourg.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 38098 . COSPAR: 2012-011A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
The satellite hosted an Intelsat C- and Ku-band commercial communications payload and a UHF communications payload for the Australian Defense Forces. First Proton launch to use a supersynchronous orbit to maximize use of booster propellant and conserve spacecraft fuel.
2012 March 30 - . 05:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2.
- Cosmos 2479 - . Payload: US-KMO 71Kh6. Mass: 2,600 kg (5,700 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: Prognoz SPRN. USAF Sat Cat: 38101 . COSPAR: 2012-012A. Apogee: 35,883 km (22,296 mi). Perigee: 35,692 km (22,177 mi). Inclination: 2.10 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min. Early warning satellite stationed in geosynchronous orbit at 80.1 deg E..
2012 April 23 - . 22:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Yahsat-1B - . Mass: 6,100 kg (13,400 lb). Nation: UAE. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 38245 . COSPAR: 2012-016A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Communications satellite for Al Yah Satellite Communications of Abu Dhabi..
2012 May 17 - . 19:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Nimiq 6 - . Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: Canada. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 38342 . COSPAR: 2012-026A. Apogee: 35,429 km (22,014 mi). Perigee: 35,379 km (21,983 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,416.60 min. Canadian television broadcast satellite with 24 Ku-band transponders..
2012 July 9 - . 18:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- SES 5 - . Payload: SES-5. Mass: 6,008 kg (13,245 lb). Nation: Europe. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 38652 . COSPAR: 2012-036A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Payload of two Ku-band beams, serving Scandinavia and the Baltic, and sub-Saharan Africa. Total of 36 Ku-band transponders..
2012 August 6 - . 19:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Telkom 3 - . Payload: Ekspress-1000N. Mass: 1,600 kg (3,500 lb). Nation: Indonesia. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 38744 . COSPAR: 2012-044A. Apogee: 4,922 km (3,058 mi). Perigee: 264 km (164 mi). Inclination: 49.90 deg. Period: 140.90 min. Failed mission. The Briz-M s/n 99532 upper stage exploded on 16 October, presumably when residual fuel and oxidizer came into contact, and generated a huge amount of orbital debris..
- Ekspress MD2 - . Mass: 1,140 kg (2,510 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Yakhta. USAF Sat Cat: 38745 . COSPAR: 2012-044B. Apogee: 4,983 km (3,096 mi). Perigee: 264 km (164 mi). Inclination: 49.90 deg. Period: 141.70 min. Failed mission. The Briz-M s/n 99532 upper stage exploded on 16 October, presumably when residual fuel and oxidizer came into contact, and generated a huge amount of orbital debris..
2012 October 14 - . 08:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Intelsat IS-23 - .
Mass: 2,730 kg (6,010 lb). Nation: USA.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Star bus.
USAF Sat Cat: 38867 . COSPAR: 2012-057A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications satellite to provide Ku and C band communications services for the Americas, Europe and Africa from 53 deg W. First Star-2 class satellite to be directly inserted into geosynchronous orbit by its launch vehicle rather than using spacecraft liquid apogee motor burns from a transfer orbit.
2012 November 2 - . 00:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Yamal-300K - . Payload: Ekspress-1000NTA. Mass: 1,870 kg (4,120 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 38978 . COSPAR: 2012-061B. Apogee: 35,810 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 0.58 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min. Gazprom Space Systems communications satellite using an Ekspress-1000HTA bus with a C and Ku band payload, stationed at 90.8 deg E..
- Luch-5B - . Payload: Ekspress-1000AM. Mass: 1,350 kg (2,970 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 38977 . COSPAR: 2012-061A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.0500 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Launched to provide communications support to the International Space Station. Used an Ekspress-1000A bus and was the the second of a pair of Russian data relay satellites for the ISS..
2012 November 20 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Echostar 16 - .
Mass: 6,650 kg (14,660 lb). Nation: USA.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 39008 . COSPAR: 2012-065A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.0200 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min.
Geosynchronous direct broadcast satellite leased to DISH Network for use in direct-to-Home services in the United States. Payload 32 Ku-band high-power transponders, stationed at 61.5 deg W. Carried a Ku-band television payload, had a dry mass of 3520 kg plus 3130 kg of propellant.
2012 December 8 - . 13:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Yamal 402 - . Payload: Spacebus 4000C3. Mass: 5,250 kg (11,570 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 39022 . COSPAR: 2012-070A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Left in a lower than planned transfer orbit of 3038 km x 35680 km x 26.1 deg when the final Briz-M burn ended prematurely on 8 December. The satellite used its on-board fuel to reach geosynhronous orbit, reaching its station at 53 deg E on 17 December..
2013 March 26 - . 19:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Satmex 8 - . Payload: EUTE 117 WEST A. Mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Nation: Mexico. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 39122 . COSPAR: 2013-012A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0200 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min. Communications satellite for Satelites Mexicanos..
2013 April 15 - . 18:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Anik G-1 - . Mass: 4,905 kg (10,813 lb). Nation: Canada. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 39127 . COSPAR: 2013-014A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min. Carried Ku, C and X-band communications payloads for Telesat..
2013 May 14 - . 16:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Eutelsat 3D - . Payload: Spacebus 4000C3. Mass: 5,370 kg (11,830 lb). Nation: Europe. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 39163 . COSPAR: 2013-022A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min. Ku-band and Ka-band transponders. Stationed at 3 deg E until replaced by Eutelsat 3B; then to move to 7 deg E..
2013 June 3 - . 09:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/3. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- SES-6 - . Mass: 6,140 kg (13,530 lb). Nation: Europe. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 39172 . COSPAR: 2013-026A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0900 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Civilian communications..
2013 July 2 - . 02:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-3. FAILURE: Proton unstable in pitch; by T+17 s arced over towards ground; nose disintegrated at T+24s; booster crashed into ground at T+32s, less 2 km downrange.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Glonass-M No. 48 - . Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass. Uragan-M (Glonass-M) navigation satellite constellation replenishment launch; previous attempt with Proton in 2010 also failed..
- Glonass-M No. 49 - . Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
- Glonass-M No. 50 - . Mass: 1,415 kg (3,119 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Glonass.
2013 September 29 - . 21:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Astra 2E - . Mass: 6,020 kg (13,270 lb). Nation: SES. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 39285 . COSPAR: 2013-056A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0500 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min. Eurostar E3000 satellite carrying Ka-band and Ku-band transponders..
2013 October 25 - . 18:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Sirius FM6 - . Mass: 6,003 kg (13,234 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 39360 . COSPAR: 2013-058A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0300 deg. Period: 1,436.07 min. Provided satellite digital radio services for Sirius XM..
2013 November 11 - . 23:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Raduga-1M - . Payload: Raduga 1M-3. Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: KAUR-3. Spacecraft: Raduga-1. USAF Sat Cat: 39375 . COSPAR: 2013-062A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 0.0300 deg. Period: 1,436.07 min. Globus-1M military communications satellite..
2013 December 8 - . 12:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Inmarsat 5 F1 - . Payload: BSS-702HP. Mass: 6,090 kg (13,420 lb). Nation: International. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 39476 . COSPAR: 2013-073A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.08 min. First Inmarsat 5 satellite, carrying the Ka-band Global Xpress communications payload.
2013 December 26 - . 10:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekspress AM-5 - .
Mass: 3,600 kg (7,900 lb). Nation: Russia.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-2000.
USAF Sat Cat: 39487 . COSPAR: 2013-077A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min.
AM-5 used a Reshetnev Ekspress-2000 bus with C, Ku, Ka and L-band communications payloads developed in collaboration with the Canadian company MDA. The Briz-M made four burns to deliver Ekspress AM-5 to a sub-geostationary orbit of around 33,800 x 37,800 km x 0.18 deg. It used its on-board electric propulsion system (ion drive) to complete the trek to GEO.
2014 February 14 - . 21:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Turksat-4A - . Mass: 4,850 kg (10,690 lb). Nation: Turkey. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: DS2000. USAF Sat Cat: 39522 . COSPAR: 2014-007A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.0600 deg. Period: 1,436.12 min. Positioned at 42 deg E, provided Ku-band direct TV broadcasting channels and C- and Ka-band communications channels..
2014 March 15 - . 23:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekspress-AT1 - . Payload: Ekspress-1000NTA. Mass: 1,672 kg (3,686 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 39612 . COSPAR: 2014-010A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.0300 deg. Period: 1,436.08 min. Two satellites built by ISS Reshetnev of Krasnoyarsk for Kosmicheskaya Svyaz (Russan Satellite Communications Co.) in one launch. The satellite carried Ku-band communications payloads and was stationed over 56 deg E..
- Ekspress-AT2 - . Payload: Ekspress-1000K. Mass: 1,326 kg (2,923 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 39613 . COSPAR: 2014-010B. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. The satellite carried Ku-band communications payloads and was stationed over 140 deg E..
2014 April 28 - . 04:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Luch-5V - .
Payload: Ekspress-1000A. Mass: 1,148 kg (2,530 lb). Nation: Russia.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000.
USAF Sat Cat: 39727 . COSPAR: 2014-023A. Apogee: 35,804 km (22,247 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 4.70 deg. Period: 1,436.17 min.
Follow-on relay satellites, replacing the Luch (Altair) and Luch-2 (Gelios) satellites. Data relay channels pass on communications between other orbiting satellites to the ground. Also can receive COSPAS/SARSAT ground-based distress signals and relay them to ground stations, and collect and retransmit Planet-S System hydrometeorological data.
- Kazsat-3 - . Payload: Ekspress-1000NTA. Mass: 1,600 kg (3,500 lb). Nation: Kazakhstan. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 39728 . COSPAR: 2014-023B. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Positioned at 58.5 deg E; designed for 15 years lifetime. Carried 28 active Ku-band transponders covering Kazakhstan.
2014 May 15 - . 21:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M. FAILURE: Failed to reach orbit; third stage failure; reentered over China.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Ekpress AM-4R - .
Mass: 5,775 kg (12,731 lb). Nation: Russia.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000.
Launch vehicle suffered a third stage failure and the stage and payload reentered over China. Debris was found north of Harbin, in Heilongjiang province. The communications satellite payload, Ekspress AM-4R, had been built to replace a satellite lost in an earlier Proton failure; it used an Astrium Eurostar 3000 bus and was intended for the Russian domestic operator Kosmicheskaya Svyaz.
2014 September 27 - . 20:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Luch - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Data relay satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 40258 . COSPAR: 2014-058A. Apogee: 35,859 km (22,281 mi). Perigee: 35,826 km (22,261 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,438.96 min. Experimental or first of a new series of military communications and ELINT satellites. Variously reported to provide secure datalink services with reconnaisance satellites; and to have the Olimp-K SIGINT payload; to have a laser communications device..
2014 October 21 - . 15:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekspress AM-6 - .
Payload: EXPRESS AM-6. Mass: 3,358 kg (7,403 lb). Nation: Russia.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-2000.
USAF Sat Cat: 40277 . COSPAR: 2014-064A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.0200 deg. Period: 1,436.08 min.
The final Briz-M burn was incomplete, leaving the communications satellite in an orbit with a 1373 min period - significantly below the planned orbit. Ekspress AM-6 had to reach its geosynchronous destination using extra xenon propellant from its own electric propulsion system at the cost of operational lifetime. Ekspress AM-6 orbit is 1373.2 min, 31307 x 37784 km x 0.7 deg; the Briz-M's auxiliary SOZ thrusters disposed of the stage into a 1512.4 min, 34984 x 39549 km x 1.0 deg orbit. Stationed in geosynchronous orbit at 140 deg east.
2014 December 15 - . 00:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Yamal 401 - . Payload: Spacebus-4000C3. Mass: 4,900 kg (10,800 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 4000. USAF Sat Cat: 40345 . COSPAR: 2014-082A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.0600 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min. Communications satellite for the Russian corporation Gazprom Space Systems. Stationed in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg east..
2014 December 27 - . 21:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Astra 2G - . Mass: 6,002 kg (13,232 lb). Nation: SES. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 40364 . COSPAR: 2014-089A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Carried Ku and Ka-band telecom payloads for European and West African service. Stationed in geosynchronous orbit at 21 deg east..
2015 February 1 - . 12:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Inmarsat 5 F2 - . Payload: Boeing 702HP. Mass: 6,070 kg (13,380 lb). Nation: International. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 40384 . COSPAR: 2015-005A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.0200 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Second satellite in the Inmarsat 5 series; launched into a supersynchronous geotransfer orbit. The satellite provided additional Ka-band mobile broadband capacity for Inmarsat Global..
2015 March 18 - . 22:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekspress AM-7 - . Payload: EXPRESS AM-7. Mass: 5,700 kg (12,500 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 40505 . COSPAR: 2015-012A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Communications satellite for Russia's Kosmicheskaya Svyaz. Five transponders were leased to Eutelsat and marketed under the name Eutelsat 53A..
2015 May 16 - . 05:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M. FAILURE: Malfunction of the third stage vernier engine 8 minutes into flight led to a premature shutdown and impact of stage 3, Briz-M and payload in the Chita region between Lake Baikal and the Chinese border.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Mexsat-1 - . Payload: Boeing 702-GEM. Mass: 5,325 kg (11,739 lb). Nation: Mexico. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. Apogee: 160 km (90 mi). Perigee: -2,000 km (-2,000 mi). Inclination: 50.50 deg. Satellite for the Mexican Communications Ministry, providing secure military communications and enhanced civilian services..
2015 August 28 - . 11:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: Baikonur LC200. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Inmarsat 5 F3 - . Payload: Boeing 702HP. Mass: 6,100 kg (13,400 lb). Nation: International. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 40882 . COSPAR: 2015-042A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0500 deg. Period: 1,436.05 min. First Proton flight since the launch failure in May. Communications satellite providing roadband mobile communications services with 89 Ka-band transponders..
2015 September 14 - . 19:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/DM-3.
- Ekspress AM-8 - . Payload: EXPRESS AM-8. Mass: 2,100 kg (4,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Ekspress-1000. USAF Sat Cat: 40895 . COSPAR: 2015-048A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Communications satellite with a Thales Alenia Ka/C/L-band payload. By 5 October it was in a 35,784 km x 35,788 km x 0.0 deg orbit stationary over 80.2 deg E..
2015 October 16 - . 20:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Turksat 4B - . Mass: 4,924 kg (10,855 lb). Nation: Turkey. Manufacturer: Mitsubishi. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: DS2000. USAF Sat Cat: 40984 . COSPAR: 2015-060A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Second Turksat-4 satellite for Turk Telecom with C, Ku and Ka-band communications payloads.Located at 50 E..
2015 December 13 - . 00:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Cosmos 2513 - . Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Garpun. USAF Sat Cat: 41121 . COSPAR: 2015-075A. Apogee: 35,657 km (22,156 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 48.60 deg. Second Garpun (`Harpoon') military communications satellite..
2015 December 24 - . 21:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Ekspress-AMU1 - . Nation: Russia. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000. USAF Sat Cat: 41191 . COSPAR: 2015-082A. Apogee: 35,760 km (22,220 mi). Perigee: 4,323 km (2,686 mi). Inclination: 22.40 deg. Ekspress-AMU1, built by Astrium using the Eurostar 3000 bus, has 61 Ku-band transponders and 10 Ka transponders. The multi-beam Ka antennas use a new feed array developed by Airbus Defense and Space..
2016 January 29 - . 22:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Eutelsat 9B - .
Nation: Russia.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 41310 . COSPAR: 2016-005A. Apogee: 35,663 km (22,159 mi). Perigee: 4,374 km (2,717 mi). Inclination: 12.10 deg.
The European communications operator Eutelsat will use the satellite's 66 Ku-band transponders to increase performance at the 9 degrees East location. The satellite also carried a European Space Agency laser communications package, EDRS-A, as part of the European Data Relay System. EDRS will relay data from low-orbiting satellites, converting an optical communications signal from the satellite to a Ka-band radio downlink.
2016 March 14 - . 09:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- ExoMars TGO - .
Nation: Russia.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft: ExoMars.
USAF Sat Cat: 41388 . COSPAR: 2016-017A. Apogee: -71,368 km (-71,368 mi). Perigee: 750 km (460 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg.
first ESA ExoMars mission. The main spacecraft on this mission was the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO), which entered Mars orbit to study its atmosphere. Attached to it was the Schiaparelli EDM lander. The TGO carried a color and stereo camera, IR and UV spectrometers, a neutron detector, and a communications relay package to support future surface missions. The combined spacecraft had a mass of 4332 kg. TGO was built by Thales/Cannes (formerly GTC/Sud Aviation) and EDM by Thales/Torino (formerly Fiat). Proton-M No. 93560 put the stack into a suborbital trajectory. The Briz-M upper stage, S/N 99560, separated at 0941 UTC and fired for 6 minutes to enter a 185 x 185 km x 51.5 deg parking orbit at 0947 UTC. After completing one orbit, a second burn at 1110 UTC raised the orbit to 250 x 5800 km. At the next perigee, at 1324 UTC, the orbit was raised to 696 x 21086 km and the Briz-M additional propellant tank was jettisoned. On completing this orbit, the fourth burn began at 1948 UTC to propel the vehicle to escape velocity. ExoMars TGO/EDM separated from the Briz-M at 2013 UTC in a hyperbolic Earth escape orbit (C3 = 13.78 km**2/s**2). The ExoMars spacecraft entered the Martian gravitational Hill sphere at 0110 UTC Oct 16, and at 1442 UTC Oct 16 split into the separate TGO (Trace Gas Orbiter) and EDM (Entry-Descent-Landing Demonstrator Module) vehicles. TGO made an insertion burn on Oct 19 from 1304 to 1523 UTC, entering a 4-day-period, 346 x 95228 km x 9.7 orbit deg around Mars.
ExoMars-2016 mass breakdown as follows:
Schiaparelli EDM Surface Platform 280 kg SP hydrazine 46 kg Front Shield 200 kg? Back Cover 54 kg? Parachute system 20 kg? ------------------------------------- EDM total 600 kg TGO spacecraft 1365 kg (including 41 kg separation assembly) TGO propellant 2367 kg ------------------------------------- ExoMars-2016 launch total 4332 kg
- Schiaparelli - .
Nation: Russia.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft: Schiaparelli.
COSPAR: 2016-017. Apogee: -71,368 km (-71,368 mi). Perigee: 750 km (460 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg.
The Schiaparelli EDM was the EDL Demonstrator Module, where EDL was "Entry, Descent and Landing". EDM consisted of an aeroshell containing the EDM Surface Platform (ESP, a triply-nested three-letter-acronym proving that ESA can compete with NASA in the TLA race). EDM attempted o land on the surface as a technology demonstration, and carried a small meteorology payload. The EDM separated from TGO three days before Mars arrival and entered the Martian atmosphere on a hyperbolic trajectory towards a landing site at 6.1W 1.9S in Meridiani Planum. After entry a parachute slowed the vehicle, the back cover and forward shield were jettisoned, and thrusters slowed the ESP further. The ESP underside consisted of a crushable structure to absorb impact with the surface. In the event, Schiaparelli approached on a 62 x -13982 km x 8.2 deg hyperbola and entered the Martian atmosphere at 1442 UTC at a speed of 5.86 km/s and an angle of -11.9 degrees. During descent, data was relayed to Mars orbiting spacecraft for later retransmission as well as sent on a live link picked up by the GMRT radio telescope near Pune, India.Schiaparelli survived the entry and deployed its parachute 4 minutes later at an altitude of 11 km. The heatshield was jettisoned 30 seconds later, and at 1447 UTC the parachute and attached backshell were separated at an altitude of 1.3 km over the Meridiani Planum landing site at 6.11W 2.07S. It appeared that the parachute / backshell separated 15 seconds earlier than expected. The thrusters fired for only 3 seconds, and the lander transitioned to landing mode while still well above the surface. A free fall of 19 seconds ensued, followed by a high speed (hundreds of km/hr) impact. At this point communications from the lander ceased. MRO imaged the EDM lander's impact scar at 6.11W 2.07S. The parachute was 0.16 km E 0.91km S of the lander.
2016 June 9 - . 07:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Intelsat IS-31 - .
Nation: Russia.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 41581 . COSPAR: 2016-035A. Apogee: 65,039 km (40,413 mi). Perigee: 3,362 km (2,089 mi). Inclination: 29.50 deg.
Satellite with the DirecTV Latin America 2 (DLA-2) Ku-band payload was launched into a supersynchronous transfer orbit. The Proton second stage suffered an early shutdown of one of its 4 engines, leaving the vehicle 28m/s slow at stage 3 separation. Fortunately the Briz-M stage was able to correct the problem by adjusting its burn times and delivered the satellite to the correct orbit.
2017 June 8 - . 03:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Echostar 21 - . Payload: Terrestar 2. Nation: USA. USAF Sat Cat: 42749 . COSPAR: 2017-032A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 6.46 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min. See EchoStar 21. ..
2017 August 16 - . 22:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Cosmos 2520 - . Payload: Blagovest No. 11L. Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: Ekspress-2000. USAF Sat Cat: 42907 . COSPAR: 2017-046A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0300 deg. Period: 1,436.04 min. See Kosmos 2520 (Blagovest 11L). ..
2017 September 11 - . 19:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Amazonas 5 - . Nation: Spain. USAF Sat Cat: 42934 . COSPAR: 2017-053A. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,768 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min. See Amazonas 5. ..
2017 September 28 - . 18:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Asiasat 9 - . Nation: China. USAF Sat Cat: 42942 . COSPAR: 2017-057A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. See AsiaSat 9. ..
2018 April 18 - . 22:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Cosmos 2526 - . Payload: Blagovest No. 12L. Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: Ekspress-2000. USAF Sat Cat: 43432 . COSPAR: 2018-037A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.0300 deg. Period: 1,436.06 min. See Kosmos 2526 (Blagovest 12L). ..
2018 December 21 - . 00:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Cosmos 2533 - .
Nation: Russia.
Type: Comms 1. Spacecraft: Ekspress-2000.
USAF Sat Cat: 43867 . COSPAR: 2018-107A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.0800 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
See Kosmos 2533 (Blagovest 13L). Blagovest military communications satellite. Some reports suggested a problem with the final Briz-M burn, but on December 29 it was shown by US tracking in a 35421 x 35802 km x 0.2 deg orbit drifting over 77E.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use