
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
TKS VA
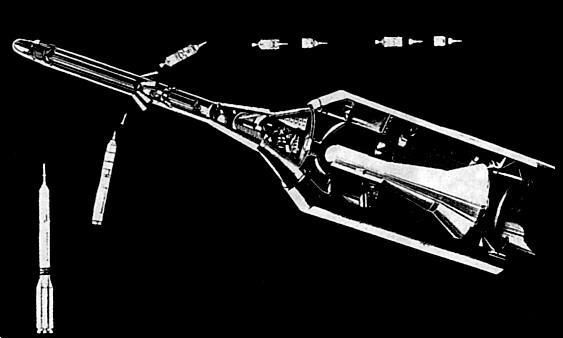
TKS VA Test
Configuration of the 82LB72 LVI dual-VA capsule test configuration. Externally the test configuration was identical with an all-up TKS ferry. The second VA, housed within the fairing, had no launch escape system and could not be rescued in the case of a launch vehicle failure.
AKA: 11F74;Vozvrashchaemiy apparat. Status: Operational 1976. First Launch: 1976-12-15. Last Launch: 1979-05-22. Number: 8 . Payload: 1,880 kg (4,140 lb). Gross mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Height: 3.64 m (11.94 ft). Diameter: 2.79 m (9.15 ft).
It was derived from earlier capsule designs for the Chelomei ballistic Raketoplan and LK-1 manned circumlunar spacecraft of the 1960's. Although extensively flight tested, it never flew with a crew aboard.
The TKS VA BSO test configuration of the TKS VA was used to prove the recovery systems. Two TKS capsules were orbited in a single launch. The upper spacecraft consisted of the TKS SA capsule, the TKS BSO module on its nose for orbital maneuvering and retrofire, and the SAS launch escape tower. The lower spacecraft consisted of only the TKS and BSO and was lost in the event of a launch vehicle failure.
The VA was capable of 31 hours of autonomous flight after separation from the FGB. The crew of three were provided with seats with customized form-fitting liners facing a control panel similar to that used in Soyuz T. Access to the FGB on the pad was through a square hatch in the side of the capsule. This could also be used to conduct EVA's in orbit, with the VA acting as an air lock for the FGB. Access to the FGB was via a hatch in the heat shield below the middle seat.
With the crew, 50 kg of payload could be returned. Without the crew 500 kg of payload could be returned. Total internal volume was 8.37 m3. Retrofire was initiated by the BSO block on the nose of the VA. The VA capsule had a hypersonic lift to drag ratio of 0.25. This allowed the BSU-V manned capsule guidance system to maneuver the spacecraft to its landing point using the optimum path for minimal heating and G-forces.
The reusable heat shield material developed for the VA was far superior to that used on the Soyuz capsule and was used as well on Chelomei's K-1 and LKS manned spacecraft designs. Once the capsule was subsonic a drogue parachute deployed for seven seconds, followed by the main chute with 1770 square meters of area. The capsule made a soft landing using a retrorocket in the parachute lines. This was triggered by the Probki radioactive sensor system within the Kaktus gamma ray altimeter, which set off the DU braking unit for a soft landing of the capsule.
Crew Size: 3. Habitable Volume: 4.56 m3. Crew: 255 kg (562 lb). Miscellaneous Contingency: 50 kg (110 lb).
More at: TKS VA.
Family: Manned spacecraft module. Country: Russia. Spacecraft: TKS. Launch Vehicles: Proton, Proton-K. Launch Sites: Baikonur, Baikonur LC81/24. Bibliography: 2, 274, 279, 439, 6, 67, 13283.
 | TKS capsule TKS capsule at Khrunichev factory. Credit: Khrunichev |
1976 December 15 - . 01:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 881 - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 009P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA .
Duration: 0.0600 days. Decay Date: 1976-12-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 9606 . COSPAR: 1976-121A. Apogee: 241 km (149 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Launch of mission LVI-1 came at 04:00 on 15 December. At 176 seconds the ADU escape tower separated from the LVI. Once the final stage had shut down in orbit, by command from the launch vehicle sequencer, the VA 009A (also given as 009P) and its TDU separated from the LVI. Two seconds later VA 009 (or 009L) was ejected. Fifteen minutes after launch all systems of the both VA capsules were in operation. The guidance system detected the direction of flight and oriented each spacecraft for retro-fire, and the pair began the return to earth after less than one revolution. At an external atmospheric pressure of 165 mm (10 km altitude) the NO section jettisoned, the three-cupola drogue parachute ejected, and the antennae and altimeter were deployed. The Komara landing radio beacon (installed on the landing section of the parachute) was activated when the spacecraft was 1.0 to 1.5 m above the ground - which occurred at the same moment on both 009 and 009A. The Kaktus special system tripped the soft landing PRSP (parachute landing propulsion system). The soft landing was accomplished with higher accuracy than Soyuz, both capsules being recovered at 44 deg N, 73 deg E, on December 15, 1976 3:00 GMT. The flights were officially given the designations Cosmos 881 (VA 009A) and Cosmos 882 (VA 009). US intelligence believed them to be tests of recoverable manned spaceplane prototypes.
- Cosmos 882 - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 009L. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1976-12-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 9607 . COSPAR: 1976-121B. Apogee: 213 km (132 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Test of TKS-VA capsule. Two satellites launched by a single rocket..
1977 August 4 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K. FAILURE: First stage engine steering unit failure at T+40.1 seconds. Failed Stage: 1.
- TKS VA s/n 009L/P - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 009L/P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1977-08-04 . Spacecraft lost in booster explosion..
- TKS VA s/n 009P/P - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 009P/P. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Almaz.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA.
A repeat test of the VA capsules from LVI-1 of a month earlier were atop the Proton (VA's 009P and 009L). However the booster failed at 49 seconds after launch. The SAS launch escape system pulled the top capsule (009P) away from the exploding Proton rocket and it was successfully recovered. The lower capsule was lost with the booster.
1978 March 30 - . 00:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. Launch Pad: LC81/24?. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 997 - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 102L. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Cosmos 997.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA .
Decay Date: 1978-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 10770 . COSPAR: 1978-032A. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Given the on-pad explosion of the LVI-2 launch attempt, plans to crew the upper VA re-entry capsule in the next test was abandoned. LVI-3 (VA's 102P and 102L / Cosmos 997 and Cosmos 998) was launched unmanned four months behind the original schedule. Both capsules were recovered after one orbit. One source indicates that one of the capsules was 009P, on its third launch and second flight to orbit. This was said to have demonstrated the multiple re-entry capability of the heat shield and the first planned reuse of a spacecraft (Gemini 2 was refurbished and reflown as MOL-1 in the 1960's, but was not designed for that purpose).
- Cosmos 998 - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 102P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1978-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 10771 . COSPAR: 1978-032B. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Dual reentry test of two TKS-VA capsules. Recovered March 30, 1978 after one orbit..
1979 April 20 - .
- TKS VA s/n 103 - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 103. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA .
1979 April 20 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24.
- TKS VA s/n 008 - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 008. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: TKS VA s/n 008.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA .
On 20 April 1979 LVI-4 VA (VA s/n 103 and s/n 008) was awaiting launch. The booster ignited, but then shut down on the pad. This triggered the launch escape system, which pulled the top capsule away from the booster. The parachute system failed and the capsule crashed to the ground. The lower capsule remained in the rocket. The top capsule was to have been manned, but the inability to demonstrate two consecutive failure-free launches of the Proton/TKS-VA combination made that (luckily) impossible.
1979 April 20 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K. FAILURE: Engines ignited but immediately shut down on launch pad. Booster could be reused with new payload.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Payload: TKS VA s/n 008. Nation: Russia. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA . Decay Date: 1979-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 11362 . Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
1979 May 22 - . 23:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Cosmos 1100 - .
Payload: TKS VA s/n 102P. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Almaz.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Cosmos 1100.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: TKS VA .
Duration: 0.0600 days. Decay Date: 1979-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 11362 . COSPAR: 1979-042A. Apogee: 222 km (137 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
The Proton launch vehicle that shut down on the original LVI-4 launch attempt was undamaged, and just a month later, with a switch of payload, LVI-4 was orbited as Cosmos 1100 and 1101. The pair launched were the 102P/102L twins from LVI-3. One capsule failed when the automatic system suffered an electrical distribution failure and it did not land correctly, spending two orbits in space, while the other landed as planned after one orbit. The launch again successfully demonstrated the reusability of the VA capsule. Plans to launch the upper capsule manned were scrubbed due to the inability to get two consecutive failure-free launches of the Proton/TKS-VA.
- Cosmos 1101 - . Payload: TKS VA s/n 102L. Mass: 4,250 kg (9,360 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Almaz. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: TKS VA. Decay Date: 1979-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 11363 . COSPAR: 1979-042B. Apogee: 222 km (137 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Test of TKS-VA manned capsule. Two satellites launched by a single rocket..
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use



