
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Almaz-1B
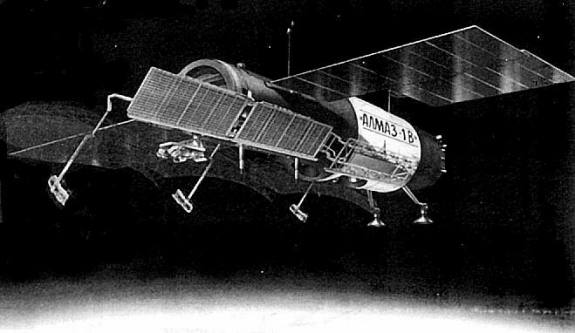
Almaz-1V
Almaz-1V unmanned earth resources satellite. Development was authorised in 1986 but the project was abandoned after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Credit: Khrunichev
AKA: Almaz-1V. Status: Study 1993. Thrust: 7.84 kN (1,763 lbf). Gross mass: 18,550 kg (40,890 lb). Specific impulse: 291 s.
Civilian derivative of the Almaz-1V military radarsat, developed for international earth resources missions, including a 3 band sounder with 5 to 7 m resolution and a high-resolution scanning infrared system.
Work began on a successor to the Almaz reconnaissance platform in 1973. This Almaz-1V was to have a 5 to 7 m resolution radar ground mapping system, coupled with a 2.5 to 4 m optical camera. It was designed to be man-tended by the TKS logistics spacecraft. 100 engineers applied for training on the system, but the medical commission cleared only six for cosmonaut training.
However the Soviet military showed no interest in use of the Almaz-T by the mid-1980's. The Ministry of Defense was satisfied with the performance of its new electro-optical satellites. Finally the Academy of Sciences agreed to take the project over. A VPK decree of 12 April 1986 required Almaz 1B to be developed for international earth resources missions, including a 3 band sounder with 5 to 7 m resolution and a high-resolution scanning infrared system. The existing military Almaz-T's would be flown as prototypes of this design.
The first Almaz-1B was to have been launched in 1993 on a two year mission. Almaz-1B would have carried three synthetic aperture radars: SAR-10 (9.6 cm wavelength, 5-40 m resolution, 25-300 km swath); SAR-70 (70 cm wavelength, 15-60 m resolution, 100-150 km swath), and a 3.6 cm wavelength SAR with 5-7 m resolution. Multi-spectral scanners, including MSU-E and MSU-SK, would also carried as well as a Balkan-2 lidar. However a lack of funding postponed the flight of Almaz-1B to late 1997 before it faded from sight.
Family: Civilian radarsat, Surveillance, Surveillance orbit. Country: Russia. Engines: RD-0225. Launch Vehicles: Proton, Proton-K. Propellants: N2O4/UDMH. Agency: AN, Reshetnev bureau. Bibliography: 119, 385, 443, 445.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use