Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
LK-1
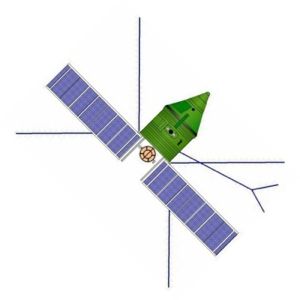 Chelomei LK-1 Chelomei LK-1 manned circumlunar spacecraft Credit: © Mark Wade |
Status: Cancelled 1965. Gross mass: 17,000 kg (37,000 lb). Unfuelled mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Height: 5.20 m (17.00 ft). Span: 7.27 m (23.85 ft).
In October 1965 Korolev managed to get the project cancelled and started development of his Soyuz 7K-L1/Block D spacecraft in place of the LK-1.
Design was said to have been ordered informally by Khrushchev on 13 May 1961 in response to the American Apollo program. In fact the LK-1 had its basis in a family of manned and unmanned vehicles that reached the draft project stage in the 1961-1963 period under the generic names of kosmoplans and raketoplans.
Authorization to proceed with development of the three-stage UR-500K launch vehicle and the LK-1 itself was finally included in the omnibus 3 August 1964 lunar project decree. By that time design had been completed. 12 were to be built in 1965 to 1966 with first flight in 1967.
At launch the spacecraft consisted of the following modules:
- ADU Emergency Engine Unit. This solid fuel escape tower would pull the VA capsule away from the launch vehicle in case of a failure during the launch phase. It separated after first stage booster burnout.
- VA Re-entry Capsule, which could accommodate one or two cosmonauts. The capsule had the same conical shape as the US Apollo capsule, but was much smaller (2.8 m diameter vs. 3.9 m for Apollo). It had a modest hypersonic lift to drag ratio, which would allow it to fly a lifting re-entry culminating to a landing on Soviet territory.
- PAB Equipment-Rocket System Block. This was analogous to the Apollo's service module. It included the electrical power and communications systems, and a small rocket system for midcourse maneuvers on the lunar flyby trajectory. Solar panels and a parabolic antenna deployed from the base of the PAB after separation of the translunar injection stage.
- RB Translunar Injection Stage. At the appropriate moment in the parking orbit, this would be fired to place the spacecraft on a loop around the moon. It would separate after burnout.
The capsule of the LK-1 was developed further. It was proposed to be used on Chelomei's LK-700 lunar lander and TKS space station resupply ship. The TKS flew in the 1970's, but never in a manned flight.
Crew Size: 1. Spacecraft delta v: 3,300 m/s (10,800 ft/sec). Electric System: 2.00 average kW.
Family: Lunar Flyby, Manned Circumlunar, Moon. Country: Russia. Engines: R6-117. Spacecraft: LK-1 VA, LK-1 PAO. Launch Vehicles: Proton, Proton-K. Propellants: N2O4/UDMH. Agency: Chelomei bureau. Bibliography: 154, 191, 196, 288, 367, 376, 474, 72, 73, 75.
 | Lk1Npom |
1961 May 13 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet response to Apollo program - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Spacecraft: Elektron-A,
Elektron-B,
Kosmoplan,
LK-1,
Raketoplan.
Soviet Decree 'On the Revision of Plans for Space Objects for Accomplishing Goals of Defence Designations--heavy boosters, course of work on Elektron, and suspension of work of work on the Kosmoplan and Raketoplan with continuation of new Raketoplan work' was issued. The decree set the end of 1965 as the date for the first launch of the N1. It also authorised Chelomei to stop work on Kosmoplan interplanetary probes and instead concentrate on a specific Raketoplan design - the LK-1 manned lunar flyby spacecraft.
1961 June 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Moon program go-ahead in response to U.S. start - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev,
Yangel.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V.
Chelomei is informally asked by Khruschev to begin design of a booster and spacecraft for a manned circumlunar mission (UR-500 Proton and LK-1). There is no authorization for a lunar landing program, although Korolev, Yangel, and Chelomei all begin booster designs.
1962 April 24 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Approval to proceed with the UR-500 (8K82) was provided in a Central Committee decree - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: LK-1.
Council of Soviet Ministers (SM) Decree 'On start of work on the UR-500 missile and carrier-rocket' was issued. The rocket was to be built initially for the GR-2 requirement - a heavy rocket that could be used to launch large military payloads into space as well as act as a ballistic missile for multiple nuclear warheads up to 100 MT in yield. The decree ordered development of this powerful new rocket to be completed within three years. This was a difficult task, considering the factory and launch facilities that would have to be built to allow testing of the rocket to begin. The draft project UR-500 was completed in 1963.
1964 May 22 - .
- Kosmoplan and Raketoplan canceled, except for LK-1 manned circumlunar spacecraft. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: Kosmoplan, LK-1, Raketoplan. Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On termination of work on the Kosmoplan and Raketoplan at OKB-52 and approval for the LK-1' was issued..
1964 July 19 - .
- Korolev obtains preliminary approval for a single-launch, lunar orbit rendezvous, manned landing. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Chelomei,
Feoktistov,
Glushko,
Korolev,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Yangel.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: L3-1963,
LK,
LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Work on the original N1-L3 had begun in 1963. This had been preceded by two years of working on a draft project for the LK lunar lander and its propulsion system. But there was no money for full scale development -- no code name from Gosplan against which to charge such work. It was annoying that Chelomei, Glushko, and Yangel were wasting resources on alternate designs at the same time. Additional Details: here....
1964 July 27 - .
- Space simulator plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz A,
TMK-1,
TMK-E.
A two-day conference is held at IAKM to review requirements for trainers and task simulators over the next 6 to 7 years. The plan includes basic instructional versions of planned spacecraft, trainers for flying around the moon, and a mock-up of the TMK Heavy Interplanetary Spacecraft. These will require a new facility of to 7,000 square metres. Trainers and strands at TsPK will be housed in building D, a hangar-type facility. The TBK-60 thermal/barometric chamber will be housed in a single hangar. To fully specify TsPK trainers and stands for the lunar mission, trainers for space navigation, and military combat spacecraft will not be completed until 1965.
1964 August 1 - .
- Full scale development of Soviet manned lunar flyby and landing projects authorised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-1,
Luna Ye-8,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz A.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 655-268 'On Work on the Exploration of the Moon and Mastery of Space--piloted LK-1 circumlunar and L3 lunar landing projects and the Ye-6M lunar lander' was issued. Chelomei was to develop the three-stage UR-500K booster and LK-1 spacecraft for the manned lunar flyby. Korolev was to develop the totally different N1 booster and L3 spacecraft complex for the manned lunar landing. First launch of the N1 was to be by the first quarter 1966, with manned lunar landings in 1967 to 1968. Reprioritization led to work being stopped on Korolev's Zvezda 6-man orbiting weapons platform by mid-1965, after a huge mockup had been built.
Korolev felt that if he had the full support of the Communist Party, the military, and industry he could achieve this goal, and this decree ordered such support. The USSR would be first on the moon. But in truth the draft project behind the decree had not solved all of the technical problems, or provided a solution on how to achieve the required payload on either the booster or spacecraft side. New technology features required for success of the scheme included an advanced guidance system in the N1 third stage equipment bay, the enormous fuel tanks in the N1 first stage, and the Lox/LH2 fuel cells needed for the LOK lunar orbiter. But the real technical problem with the N1-L3 design was the total lack of any weight growth reserve. Even thought the systems had not even been developed yet, engineers were fighting over tens of grams in their weight allocations, let alone the kilograms normally at issue.
Development of Korolev's Soyuz A-B-V, a competing circumlunar project, was evidently still authorised, although it duplicated Chelomei's LK-1.
1964 August 15 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K.
- Chief Designers review of Voskhod at OKB-1 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Khrushchev, Sergei.
Program: Voskhod.
Flight: Voskhod 1.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Voskhod.
All concerned designers, bureaux, and institutes certify the reliability of the systems of the spacecraft and launch vehicle. The second phase of trials of the soft landing system have been successful. Of 10 drops, 9 landed with vertical velocity under 7.5 m/s, and of those, 6 landed with a speed of only 0.0 to 1.5 m/s. There are still concerns about how the system will function in soft soils or adverse weather conditions. Nevertheless the decision is taken to ship the spacecraft to the cosmodrome for final preparations between 18 and 25 August. It is likely that the manned flight cannot occur until the end of September. Later in the day Kamanin is visited by Sergei Nikitovich Khrushchev and other experts from Chelomei's design bureau. They brief Kamanin on plans for a manned circumnavigation of the moon using their spacecraft launched by their UR-500 booster by the end of 1967.
1964 September 14 - .
- Voskhod abort system - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Komarov,
Korolev,
Krylov,
Lazarev,
Volynov,
Yegorov.
Program: Voskhod,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Voskhod 1.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Voskhod.
Kamanin reviews the Voskhod abort system with Korolev. Up to T+27 seconds, there is no possibility of saving the crew in the event of a booster failure; from T+27 seconds to T+44 seconds, escape would be difficult, but is possible; and from T+44 seconds to T+501 seconds abort should be possible, with the capsule landing on Soviet territory. Afterwards, Korolev speaks with Kamanin secretly and privately. Korolev reveals that he has discussed a greater VVS role in space with Marshal Krylov, but that Krylov is adamantly opposed to the VVS assuming such a mission. Korolev is seeking a resolution from the Communist Party that will authorise him to develop a manned lunar flyby and landing system using his N1 booster. He believes that Chelomei's UR-500 booster will not have sufficient payload to mount a manned flyby - a docking in low earth orbit will be required. But Chelomei has rejected the use of docking, and is even designing his UR-700 to allow a lunar landing without the use of docking.
Finally Korolev gets to the purpose of the secret meeting. He wants Feoktistov to be aboard Voskhod 1, despite the opinion of Kamanin and the physicians. Kamanin reiterates that the most qualified crew would be Komarov, Volynov, and Lazarev; and if he gives in on Feoktistov, then Komarov, Feoktistov, Lazarev. But Korolev is opposed to Lazarev, and insists that the crew should be Komarov, Feoktistov, and Yegorov. From Kamanin's point of view this is flying a space mission with two invalids aboard. Lazarev is a qualified and fit flight surgeon, a qualified pilot as well as a physician with 15 years of research experience in aviation medicine. Korolev is adamant that the two passengers should be civilian, not military. No agreement is possible.
1964 October 13 - .
- Khrushchev ousted from power. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei, Khrushchev. Spacecraft: IS-A, Kosmoplan, LK-1, OGCh, US-A, US-P. Brezhnev faction assumes control of Politubro. Brezhnev was adverse to all projects Khrushchev had supported. These included those of Chelomei and his OKB-52..
1964 October 28 - .
- Lunar project orders issued to industry. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1, Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, LK-1, Luna Ye-8, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Military-Industrial Commission (VPK) Decree 'On assignment of lunar programs to OKB-52 and OKB-1' was issued..
November 1964 - .
- No direction on space from new Soviet leadership. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Korolev,
Okhapkin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Voskhod,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Voskhod.
After the triumph of the Voskhod-1 flight, Korolev gathers a group of his closest associates in his small office - Chertok, Bushuyev, Okhapkin, and Turkov. Firm plans do not exist yet for further manned spaceflights. Following the traditional Kremlin celebrations after the return of the Voskhod 1 crew, he has heard no more from the new political management. Khrushchev's old enthusiasm for space does not exist in the new leadership. Korolev is angry. "The Americans have unified their forces into a single thrust, and make no secret of their plans to dominate outer space. But we keep our plans secret even to ourselves. No one has agreed on our future space plans - the opinion of OKB-1 differs from that of the Minister of Defense, which differs from that of the VVS, which differs from that of the VPK. Some want us to build more Vostoks, others more Voskhods, while within this bureau our priority is to get on with the Soyuz. Brezhnev's only concern is to launch something soon, to show that space affairs will go better under his rule than Khruschev's." Korolev however does not think the new leadership will support continuation of Chelomei's parallel lunar project. Okhapkin speaks up. "Do not underestimate Chelomei. He is of the same design school as Tupolev and Myasishchev. If we give him the will and the means, his products will equal those of the Americans. Now is the right moment to combine forces with Chelomei".
1965 February 2 - .
- Cosmonaut organisation - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Malinovskiy,
Nikolayev.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz PPK,
Soyuz R,
Soyuz V.
Kamanin will organise the cosmonauts into two groups: the first group will be commanded by Nikolayev, and the latest group by Beregovoi. They will be assigned to support and train seven missions: military space (reconnaissance, interceptor, and combat spacecraft); space navigation; life support and rescue systems; communications and telemetry systems; scientific orbital stations; lunar fly-by; and lunar landing expeditions. All of this may be for nought, since Marshall Malinovskiy has said that heavy launch vehicles and lunar flights have no military utility and should be funded and handled by the Academy of Science.
1965 June 26 - .
- Poor progress on space trainers - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dementiev,
Smirnov,
Titov.
Program: Voskhod,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 4,
Voskhod 5,
Voskhod 6.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz A,
Spiral OS,
TMK-1,
TMK-E.
Titov and Kamanin visit LII to review the status of simulator construction. The engineers haven't had any time to even consider trainers for winged spacecraft. The Soyuz trainer will only be completed by July 1966, and the trainer for the new Voskhod configuration is still on paper only. Simulators for manned lunar or planetary flights have not even been discussed yet. It is clear that Kamanin is going to have to go up the chain of command to Dementiev and Smirnov to get resources allocated for the work to be accelerated.
1965 August 16 - .
- Chelomei's lunar spacecraft attacked - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: LK-1.
Korolev discusses Chelomei's manned lunar flyby spacecraft with Kamanin. The Party ordered Chelomei to have 12 manned circumlunar spacecraft completed during 1966 and the first quarter of 1967. Chelomei has worked on the he project for many years, but his bureau has not yet decided on a single firm design for the spacecraft, let alone start construction.
1965 August 18 - .
- Soyuz development program reoriented; Soyuz 7K-OK earth orbit version to be built in lieu of Soyuz A. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4,
Soyuz s/n 3/4.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V.
Military-Industrial Commission (VPK) Decree 180 'On the Order of Work on the Soyuz Complex--approval of the schedule of work for Soyuz spacecraft' was issued. It set the following schedule for the new Soyuz 7K-OK version: two spacecraft to be completed in fourth quarter 1965, two in first quarter 1966, and three in second quarter 1966. Air-drop and sea trails of the 7K-OK spacecraft are to be completed in the third and fourth quarters 1965, and first automated docking of two unmanned Soyuz spacecraft in space in the first quarter of 1966. Korolev insists the automated docking system will be completely reliable, but Kamanin wishes that the potential of the cosmonauts to accomplish a manual rendezvous and docking had been considered in the design. With this decree the mission of the first Soyuz missions has been changed from a docking with unmanned Soyuz B and V tanker spacecraft, to docking of two Soyuz A-type spacecraft. It is also evident that although nothing is official, Korolev is confident he has killed off Chelomei's LK-1 circumlunar spacecraft, and that a Soyuz variant will be launched in its place.
1965 September 1 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1 1964.
- Voskhod/Soyuz crewing plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Artyukhin,
Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Katys,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Korolev,
Matinchenko,
Nikolayev,
Ponomaryova,
Solovyova,
Volynov.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 5.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Voskhod.
Kamanin meets with Korolev at 15:00 to discuss crew plans. As Soyuz pilot candidates, Kamanin proposes Gagarin, Nikolayev, Bykovsky, Komarov, Kolodin, Artyukhin, and Matinchenko. Korolev counters by proposing supplemental training of a supplemental group of engineer-cosmonauts from the ranks of OKB-1. He calls Anokhin, his lead test pilot, informs Korolev that there are 100 engineers working at the bureau that are potential cosmonauts candidates, of which perhaps 25 would complete the selection process. Kamanin agrees to assist OKB-1 in flight training of these engineer-cosmonauts. Kamanin again proposes Volynov and Katys as prime crew for the Voskhod 3 12-15 day flight. Korolev reveals that, even though Kamanin will have the crew ready by October, the spacecraft for the flight may not yet even be ready by November - Kamanin thinks January 1966 is more realistic. The discussion turns to the female EVA flight - Ponomaryova as pilot, Solovyova as spacewalker. It is decided that a group of 6 to 8 cosmonauts will begin dedicated training in September for lunar flyby and landing missions. Korolev advises Kamanin that metal fabrication of the N1 superbooster first article will be completed by the end of 1965. The booster will have a payload to low earth orbit of 90 tonnes, and later versions with uprated engines will reach 130 tonnes payload. Korolev foresees the payload for the first N1 tests being a handful of Soyuz spacecraft.
1965 October 25 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- L1 manned circumlunar mission taken from Chelomei, given to Korolev. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On the Concentration of Forces of Industrial Design Organisations for the Creation of Rocket-Space Complex Means for Circling the Moon--work on the UR-500K-L1 program' was issued. As a result of a presentation to the Military Industrial Commission, Afanasyev backed Korolev in wresting control of the manned circumlunar project from Chelomei. The Chelomei LK-1 circumlunar spacecraft was cancelled. In its place, Korolev would use a derivative of the Soyuz 7K-OK, the 7K-L1, launched by Chelomei's UR-500K, but with a Block D translunar injection stage from the N1. He envisioned launch of the unmanned 7K-L1 into low earth orbit, followed by launch and docking of a 7K-OK with the 7K-L1. The crew would then transfer to the L1, which would then be boosted toward the moon. This was the original reason for the development of the 7K-OK.
1965 November 13 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Industrial orders to cancel LK-1 spacecraft and implement L1. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: LK-1, Soyuz 7K-L1. Ministry of General Machine Building (MOM) Decree 'On work on the UR-500K-L1 program' was issued..
1966 April 27 - . Launch Vehicle: Proton.
- Soyuz L1 full scale development, LK-1 cancellation approved. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: LK-1, Soyuz 7K-L1. Decree 10 'On approving the work plan to build the p8loted spacecraft 7K-L1 -- approving the plan for for the UR-500K-L1 and terminating the UR-500K-LK-1' was issued..
1966 December 28 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-700.
- Almaz and LK-700 development status - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Almaz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK-1,
LK-700,
Raketoplan.
Kamanin accompanies 17 generals and other officers of the VVS in a tour of Chelomei's OKB-52. Chelomei spends five hours personally acquainting the visitors with his bureau's space technology capabilities. It was the first in-depth meeting Kamanin and Vershinin have had with Chelomei, despite meeting with him occasionally since 1961. They have mainly interacted with Korolev and now Mishin. Additional Details: here....
1967 December 8 - .
- TsKBEM confirms Mishin's decision to cancel Soyuz VI - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Chelomei,
Feoktistov,
Gaidukov,
Karas,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Okhapkin,
Shcheulov.
Program: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-S,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
Mishin is away on 'cure' for his drinking problem. A 'Podlipki Soviet' is held at TsKBEM. The issue is cancellation of Kozlov's 7K-VI military Soyuz. Bushuyev, Chertok, Okhapkin, Feoktistov are in favour of cancelling it. Opposed are Karas, Shcheulov, Kostonin, Gaidukov, and the various military representatives at the meeting. It was now six years since OKB-1 was required to put a military manned spacecraft into space - and, factually speaking, nothing has been done. Military experiments proposed for each manned flight by OKB-1 to date had been rejected on various grounds - no weight, no space aboard the spacecraft. Good progress has been made with Kozlov's VI and Chelomei's Almaz - now they've managed to kill the VI, and Mishin and Kerimov are constantly denigrating Almaz (saying it is too heavy, and unsuited for the purpose). The whole thing is a replay of the LK-1 situation. In 1963, a resolution was issued to send a Soviet man around the moon. Instead, after two years of development, Korolev managed to get Chelomei's LK-1 lunar spacecraft cancelled, and started all over with his own L1. Additional Details: here....
1968 December 30 - .
- How to beat the Americans to the lunar landing - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Chelomei,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Okhapkin,
Pilyugin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Luna.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Luna Ye-8-5,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
Meeting of the VPK Military-Industrial Commission to discuss how to beat the Americans to the lunar landing Ustinov called the meeting to order. Mishin was 'sick' again -- Okhapkin represented TsKBEM and gave a summary of the programme to that date:
- The project had only been authorised on 3 August 1964. It consisted of two parts, circumlunar flights using Chelomei's UR-500K booster and LK-1 spacecraft, and a lunar landing using Korolev's N1 booster and L3 spacecraft.
- On 25 October 1965 the programme was redirected. Military support was ordered and the decision was made to cancel Chelomei's LK-1 spacecraft and instead use the L1 version of Korolev's Soyuz for the circumlunar flights. This was ordered by the resolution 'On organisation of construction units for support of rocket-space systems for the lunar flyby'. That resolution ordered a manned L1 flight by the end of 1967 or early 1968.
- The program actually took three years to implement rather than the two planned. Nine launches of he L1 had been made since March 1967, but it had not been possible to man-rate the UR-500K/L1 booster/spacecraft combination due to failures in both the launch vehicle and spacecraft. Flight trials of the N1 booster had not even begun yet.
Keldysh proposed that further work on the L1 be abandoned, and Proton boosters instead be used to launch the Ye-8-5 lunar soil return robot spacecraft being developed by Babakin. Babakin had been accelerating this programme since the beginning of 1968 with the support of Keldysh, even though it would only return around 100 g of lunar soil, versus the tens of kilograms the Apollo manned flights would return. However it now offered an interesting possibility - he proposed obtaining lunar soil and returning it to earth before an American manned landing. The government's organs of mass communication would say that the Soviet Union's lunar program only consisted of robot probes, emphasising that his was much safer and that Russia would never risk it's citizen's lives for mere political sensation. Additional Details: here....
1970 October 28 - .
- Chelomei's 'war' with Korolev and Mishin - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Chelomei,
Mishin,
Serbin,
Smirnov.
Program: Almaz,
Salyut,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK-1,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
Kamanin meets with Chelomei. Chelomei discusses his 'war' with Korolev and Mishin. Korolev interfered with, and then finally took the manned lunar flyby project from Chelomei. Now Mishin is doing the same thing with Almaz. Chelomei had already invested five years in development of Almaz, and was on the way to producing a good space station. Then Mishin pushes him out of the way and seizes his production line to build the DOS-7K. DOS#1 is actually Almaz#5, nothing more than a bad copy of Chelomei's station. Serbin and Smirnov do not trust Mishin, which is why they have only authorised him to build four DOS stations. Serbin, Smirnov, and Afanasyev have visited Chelomei, and told him to accelerate work on the Almaz, using three shifts 24 hours a day.
Kamanin notes the second hijacking in Turkey of a Soviet airliner in the last two weeks.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use