
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Luna Ye-8
 Lunokhod 1 / Ye-8-LS Mature First Generation Soviet Space Systems Credit: © Mark Wade |
AKA: 8EK;Lunokhod;Ye-8. Status: Operational 1969. First Launch: 1969-02-19. Last Launch: 1973-01-08. Number: 2 . Gross mass: 5,590 kg (12,320 lb).
Lunokhod's original primary mission was survey of sites for manned lunar landings and bases. The best landing area having been located, Lunokhod would then provide a radio homing beacon for precision landing of the LK manned spacecraft that would follow. In the event of a rescue mission, the single cosmonaut could walk from the primary and back-up LK lunar landers through use of extra life support supplies aboard the Lunokhod.
After the success of the Apollo 11 and the loss of the moon race, Lunokhod was instead used to explore the lunar surface by robot. This supported the legend that the Soviet Union would not risk cosmonauts in space and had never sought to send a man to the moon.
The design had its origins in Korolev's L2 project of 1963. This evolved within OKB-1 to the globular Ye-8 lunar rover design of 1965 before further development of unmanned planetary spacecraft was passed to the Lavochkin bureau. There the design was refined and modified for a single launch by a Proton launch vehicle. By the time the spacecraft flew, America had won the manned moon race and mission objectives were to collect images of the lunar surface, examine ambient light levels to determine the feasibility of astronomical observations from the Moon, perform laser ranging experiments from Earth, observe solar X-rays, measure local magnetic fields, and study mechanical properties of the lunar surface material.
The lander had dual ramps by which the Lunokhod descended to the lunar surface. The lander and rover together weighed 1814 kg on the lunar surface.
The Lunokhod itself consisted of a tub-like compartment with a large convex lid on eight wheels. It stood 135 cm high, 170 cm long and 160 cm wide, with a mass of 840 kg. The 8 wheels each had an independent suspension, motor and brake. The rover had two speeds, ~1 km/hr and ~2 km/hr. Lunokhod was equipped with four TV cameras, three of them panoramic cameras. The fourth was mounted high on the rover for navigation, and could return high resolution images at different rates (3.2, 5.7, 10.9 or 21.1 seconds per frame). These images were used by a five-man team of controllers on Earth who sent driving commands to the rover in real time. Communications were through a cone-shaped omni-antenna and a highly directional helical antenna. Power was supplied by a solar panel on the inside of a round hinged lid which covered the instrument bay. A Polonium-210 isotopic heat source was used to keep the rover warm during the lunar nights. Scientific instruments included a soil mechanics tester, solar X-ray experiment, an astrophotometer to measure visible and UV light levels, a magnetometer deployed in front of the rover on the end of a 2.5 m boom, a radiometer, a photodetector (Rubin-1) for laser detection experiments, and a French-supplied laser corner-reflector. Lunokhod was designed to operate through three lunar days (three earth months) but greatly exceeded this in operation.
More at: Luna Ye-8.
| L2-1963 Russian lunar rover. Study 1963. The L2 was a project to land a remote-controlled self-propelled rover on the surface of the moon. It was described in a 23 September 1963 letter setting out the space exploration plan for 1965 to 1975. |
| Luna Ye-8-5 Russian lunar lander. Unmanned lunar soil sample return mission. Lunar lander and sample return satellite, Russia. Launched 1969 - 1972. |
| Luna Ye-8-LS Russian lunar orbiter. Lunar surface mapping. Lunar lander, Russia. Launched 1971 - 1974. |
| DLB Beacon Lander Russian lunar logistics spacecraft. Study 1971. In most Soviet manned lunar landing scenarios, versions of the Ye-8 unmanned landers would precede manned landings on the moon. |
| Luna Ye-8-5M Russian lunar lander. 4 launches, 1974.10.28 (Luna 23) to 1976.08.09 (Luna 24 Return Vehicle). Lunar sample return. Conduct of further scientific investigation of the moon and circumlunar space. |
Family: Moon. Country: Russia. Engines: KTDU-417. Launch Vehicles: Proton, Proton-K/D, N1, N1 1969. Projects: Luna. Launch Sites: Baikonur, Baikonur LC81/23, Baikonur LC81/24. Agency: MOM, Lavochkin bureau. Bibliography: 16, 2, 274, 296, 367, 376, 474, 6, 67, 70, 75, 12778.
 | Lunokhod lander Credit: NASA |
 | Lunokhod The Lunokhod unmanned lunar surface rover. Credit: Lavochkin |
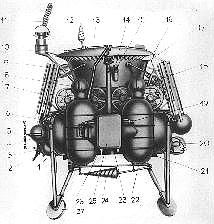 | Lunokhod bus Lunokhod bus / Ye-8-LS Credit: NASA |
 | Lunokhod 1 / Ye-8-LS Mature First Generation Soviet Space Systems Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Luna Ye-8 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Luna 17 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1964 August 1 - .
- Full scale development of Soviet manned lunar flyby and landing projects authorised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-1,
Luna Ye-8,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz A.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 655-268 'On Work on the Exploration of the Moon and Mastery of Space--piloted LK-1 circumlunar and L3 lunar landing projects and the Ye-6M lunar lander' was issued. Chelomei was to develop the three-stage UR-500K booster and LK-1 spacecraft for the manned lunar flyby. Korolev was to develop the totally different N1 booster and L3 spacecraft complex for the manned lunar landing. First launch of the N1 was to be by the first quarter 1966, with manned lunar landings in 1967 to 1968. Reprioritization led to work being stopped on Korolev's Zvezda 6-man orbiting weapons platform by mid-1965, after a huge mockup had been built.
Korolev felt that if he had the full support of the Communist Party, the military, and industry he could achieve this goal, and this decree ordered such support. The USSR would be first on the moon. But in truth the draft project behind the decree had not solved all of the technical problems, or provided a solution on how to achieve the required payload on either the booster or spacecraft side. New technology features required for success of the scheme included an advanced guidance system in the N1 third stage equipment bay, the enormous fuel tanks in the N1 first stage, and the Lox/LH2 fuel cells needed for the LOK lunar orbiter. But the real technical problem with the N1-L3 design was the total lack of any weight growth reserve. Even thought the systems had not even been developed yet, engineers were fighting over tens of grams in their weight allocations, let alone the kilograms normally at issue.
Development of Korolev's Soyuz A-B-V, a competing circumlunar project, was evidently still authorised, although it duplicated Chelomei's LK-1.
1964 October 28 - .
- Lunar project orders issued to industry. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1, Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, LK-1, Luna Ye-8, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Military-Industrial Commission (VPK) Decree 'On assignment of lunar programs to OKB-52 and OKB-1' was issued..
1965 March 2 - .
- Babakin takes over Lavochkin OKB - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Chelomei,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: Luna E-6,
Luna Ye-8.
Former Lavochkin bureau, part of Chelomei, regained status of a separate design bureau with former Korolev deputy GN Babakin as its head. By the end of 1965 all materials on the E-6, Ye-8, and planetary probes were passed by Korolev to the Lavochkin Bureau, who took over responsibility for all future lunar and planetary unmanned probes.
1966 December 2 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, .
- The 2-launch N1 scenario was discussed in an interdepartmental technical review with MV Keldysh. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Bushuyev,
Keldysh,
.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
LK,
Luna Ye-8.
At this point the Ye-8 would be delivered to the moon by a UR-500K launch vehicle. The basic constraint was the 5300 kg payload capability of the Block D to translunar injection. This meant tradeoffs in the accuracy of the Ye-8's initial landing versus its lifetime on the surface waiting for arrival of the LK. It was agreed that a working group would meet the next day to develop final specifications Ye-8 and a more detailed outline of the N1-L3 expedition using Ye-8. (start-up sequence, the time, the connections between LK, LOK and Ye-8, the means for determining the location). KD Bushuyev was to study the backup LK concept. (Mishin Diaries 1-235)
1967 April 1 - .
- Ye-8 proposed with a life support system to allow a lunar cosmonaut to wait on the moon for a rescue expedition - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Babakin,
.
Spacecraft: ,
LK,
LKR,
Luna Ye-8.
Ye-8 proposed with a life support system to allow a lunar cosmonaut to remain on the moon until a rescue expedition could be launched with an LKR. As an alternative to a 2-launch scenario, the possibility was raised of the Ye-8 being equipped with a life support system to allow the cosmonaut to remain on the moon until a rescue expedition could be launched with an LKR. But Ye-8 chief designer Babakin said at that time that this was not feasible (Mishin Diaries 2-60; 2-62).
1967 August 29 - .
- Ye-8 as safety station was still being pursued. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: , Luna Ye-8. Mishin complained the detailed specifications for the Ye-8 life support system with interface documents on connections to the cosmonaut's space suit were still not available. (Mishin Diaries 2-149).
1967 October 14 - .
- L2 communications issues worked out. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: , Soyuz 7K-LOK, LK, Luna Ye-8. Detailed issues of communicating simultaneously at lunar distances with the Ye-8, LK, and LOK from both the Crimea and Cuban tracking stations were being worked out. (Mishin Diaries 2-84).
1967 November 25 - .
- Lunar Soviet - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: , Soyuz 7K-LOK, LK, Luna Ye-8. Lunar Soviet: the issues of communicating simultaneously at lunar distances with the Ye-8, LK, and LOK were considered in relation to Soviet tracking ships. (Mishin Diaries 2-90).
1968 February 3 - .
- Ye-8-5 robot lunar soil return plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Luna,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
VVS Party Conference. It is clear to Kamanin that there is no support from the Air Force for manned spaceflight. Kamanin only heard yesterday that Babakin is working on an automatic soil sample return spacecraft. He will need a minimum of two to three years to complete it. Kamanin complained that it would interfere with plans for the L1 program. An uninterrupted series of flights will be needed to complete the L1 spacecraft qualification, and the Ye-8, using the same booster, could be an interference in achieving that goal.
1968 February 27 - .
- Soviet on plan through 1975 for automated probes to the moon and planets. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Keldysh,
Tereshkova.
Spacecraft: DLB Lunar Base,
Luna Ye-8,
Luna Ye-8-5.
Keldysh heads a Soviet on plans through 1975 for automated probes and space research of the moon and planets. Barmin attends, his interest being the relation of this work to his lunar base. Kamanin finds the plan not well thought out... Tereshkova sees Kamanin and tells him she cannot handle the stress of both political demands on her time and cosmonaut training. She wants Kamanin's assistance to get her out of political tasks.
1968 March 20 - .
- Lunar spacesuit review. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Severin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Krechet,
LK,
Luna Ye-8,
Orlan.
Meeting with Gay Ilyich Severin. Two spacesuits are being developed for the L3 program: the Krechet-94 and Orlan. Both have been in development for two years. The Krechet-94 will allow six hours of lunar surface activity, the Orlan, 2.5 hours. Both weigh about 90 kg. There are consumables for a total of 52 hours of life support in the LK and the LT Lunar Cart. Kamanin feels the suits are too heavy, due to Mishin's demand for a 5 km range from the LK over a three day traverse with the LT. Severin could have instead developed the spacesuit used by Leonov to have a four hour autonomous operation, but Mishin insisted on doubling of the capacity.
1968 June 17 - .
- Discussion on homing the LK and LK-R on the Ye-8. - . Related Persons: Mishin, Bushuyev, Bezverby, . Spacecraft: LK, Luna Ye-8. Mishin's notes indicate continued discussion within OKB-1 with VK Bezverby and KD Bushuyev on homing the LK and LK-R on the Ye-8 (precision landing, coordination of interfaces). (Mishin Diaries 2-139).
1968 August 23 - . LV Family: N1.
- N1-L3 expedition using the Ye-8 - . Related Persons: Mishin, Ustinov, Babakin, . Spacecraft: , Luna Ye-8. At a meeting with DF Ustinov, head of the Military Industrial Commission, the N1-L3 expedition using the Ye-8 was pitched by Babakin. (Mishin Diaries 2-149).
1968 December 25 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- L3 lunar lander behind schedule - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Keldysh,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Apollo,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
The L3 spacecraft still does not even exist in mock-up form. All of the leadership are responsible for this farce - Malinovskiy, Smirnov, Ustinov, Brezhnev. There is no single manager of the space program. The VPK and Central Committee operate on rumours. The Interagency Soviet headed by Keldysh was supposed to coordinate space activities, but in fact has not functioned in the last four to five years. There is no single military space organisation in the Ministry of Defence. Piloted flight tests are being run by former artillery officers in the RSVN. Various organizations of MAP and VVS coordinate ground and flight tests poorly. These are the reasons for the failure of the Soviet Union in space. Today in the Central Committee Ustinov asked - 'how to answer Apollo 8?' Ustinov relies on Keldysh, Keldysh supports Mishin, and Mishin is unfit for his duties. But Mishin is not even there! The program they come up with: In January 1969, 2 Venera probes will be launched, two manned Soyuz missions, and L1 s/n 13 will be sent around the moon. In February the first N1 will be launched. By the end of March the first Ye-8 robot will land on the moon and return lunar soil to the earth. This meeting is followed by a session of the VPK at 16:00. The crews are named for the Soyuz 4 and 5 flights.
1969 January 8 - .
- Plan for Soviet lunar and planetary launches to answer America's Apollo program during 1969 approved. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Babakin. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8, Luna Ye-8-5, Mars M-69, Soyuz 7K-L1, Venera 2V (V-69). Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 19-10 'On Work on Research of the Moon, Venus and Mars by Automatic Stations--work on automated lunar and interplanetary spacecraft' was issued.. Additional Details: here....
1969 January 24 - .
- Mishin's lunar plans - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1E, LK, LKR, , Luna Ye-8. Mishin notes that: 1. T1K, T2K, L1E are essential. 2. One more time reviewed the scheme for a lunar expedition of LK + LK-R + Ye-8. (Mishin Diaries 2-158).
1969 January 25 - . LV Family: N1, Proton.
- N1-L3 launch schemes - .
Related Persons: Mishin.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-L1S,
Soyuz 7K-L3S,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
LK,
Luna Ye-8.
Mishin meeting with his guidance expert, NA Pilyugin, to consider the possibility of 2 launch schemes: with Ye-8 and without Ye-8 OV. All possibilities to improve the accuracy of the landing without the Ye-8 were to be examined. The first N1 missions would rehearse the two-launch scenario, with the Ye-8 being launched by a UR-500K and an L3S (orbital version of the L1S) standing in for the LOK (no LK being available yet).
1969 January 25 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Apollo vs Ye-8-5 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Luna,
Apollo.
Flight: Apollo 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
America is preparing Apollo 9 for flight, and Kamanin muses that the Soviet reply will be the N1 and Ye-8-5, neither of which is proven or reliable. The Soviet Union would have a better chance of sending a manned L1 on a flight around the moon during the first quarter of 1969. Meanwhile Mishin's bureau has a new L3M lunar lander on the drawing boards. This will land 4 to 5 men on the moon, but require two N1 or seven UR-500K launches to assemble in orbit.
1969 January 30 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1/Ye-8-5 launch preparations - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin, Tyulin. Program: Lunar L3, Luna. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8. Mishin agrees with Tyulin that he will fly to Tyuratam on 3 February to supervise launch of the Ye-8 on 18 February and the first N1 on 21 February. .
1969 February 3 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1/Ye-8 preparations - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Luna.
Spacecraft: LK,
Luna Ye-8.
Kamanin arrives at Tyuratam at 15:30 aboard an An-24. The State Commission for the first Ye-8 robot lunar rover mission is chaired by Tyulin at Area 31. The spacecraft will make a soft landing on the moon, deploy a mobile lunar rover that can traverse slopes up to 30 degrees. The rover will find a position that is clear of obstacles for the first Soviet manned lunar landing. It will then park there, and provide a landing beacon for the LK manned lander. The spacecraft will have a mass of 1700 kg in lunar orbit. Launch is set for 19-20 February.
1969 February 4 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- UR-500K failure state commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Konopatov.
Program: Luna.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
At Area 81 a State Commission is held on failures of the UR-500K booster. A D Konopatov describes the analysis of the stage 2 and 3 failures on the 20 January launch attempt. The number 4 engine of stage 2 shut down 25 seconds into its burn due to high temperatures detected in the turbopump. The same thing occurred on the third stage. The couldn't pin down the source of the problem. Engines of this type had worked correctly 700 times on earlier flights. Despite the cause of the failure not being identified, approval is given at 14:30 for the launch of the Ye-8 to proceed. Babakin confirms the spacecraft is ready.
1969 February 11 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Military space objectives - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Luna.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
The Ye-8 and N1 are on schedule for their respective launches. Kamanin discusses the cosmonaut training curriculum with Kerimov. No one has ever defined what it is cosmonauts are actually supposed to do in space. No one really knows what their purpose is --- not Keldysh, not Mishin, not Smirnov, not Ustinov. Kerimov agrees to put together a state commission to define the role of man in space and draw up plans for future space missions.
1969 February 19 - . 06:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: First-stage engine failure caused the rocket to crash 15 km from the pad.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Ye-8 s/n 201 + Lunokhod s/n 201 - first stage malfunction - .
Payload: Ye-8 s/n 201 / 8EL No. 201. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
Decay Date: 1969-02-19 .
Attempted launch of a Ye-8 with a Lunokhod lunar rover. Evidently coordinate in some way with the N1 launch two days later. A first-stage booster engine failure causes the rocket to crash 15 km from the pad after a lift-off at 09:48 local time. Kamanin meanwhile has the Hong Kong flu.
1969 May 16 - .
- Myth 'we were never in the moon race' disseminated by the Soviet Union - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Keldysh.
Program: Luna,
Apollo,
Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Apollo 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Keldysh first revealed the new 'party line' at a press conference on the semi-successful Venera 5 landing on Venus. When asked about Soviet lunar plans, he revealed that Russia would only use robot probes, that it wouldn't risk men's lives in such an endeavour. At the same time Babakin was hard at work finishing the first Ye-8-5 robot lunar soil return spacecraft, to be launched before Apollo 11.
1969 June 10 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Revised Soviet lunar plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Luna.
Spacecraft: LK,
Luna Ye-8,
Luna Ye-8-5,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The VPK Military-Industrial Commission issues a decree on the schedule for the rest of 1969. There are to be five launches of Ye-8-5 lunar soil return robots, on 14 June, 13 and 28 July, 25 August, and 25 September. There are to be two launches of Ye-8 Lunokhod robot rovers on 22 October and 21 November. Further manned L1 flights are cancelled. There are no plans made for the L3 since the N1 is not ready.
1969 June 14 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D upper stage did not fire and payload did not attain earth orbit,. Failed Stage: U.
- Ye-8-5 s/n 402 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 402. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L1,
Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1969-06-04 .
Another attempt to launch a Ye-8-5 to return lunar soil to the earth, 'scooping', the Americans' impending Apollo 11 mission. Yet another UR-500K launch failure. This time the UR-500K booster functioned perfectly, but the Block D upper stage did not fire, and the payload did not even attain earth orbit. Every UR-500K launch is costing the Soviet state 100 million roubles. This failure pretty much ended the chances for the Russians to trump the American moon landing. Tass yesterday began running stories to prepare the masses for the upcoming Apollo 11 triumph. The party line is that the Soviet Union is not about to risks the lives of its cosmonauts on flights to the moon, when automated probes can safely retrieve soil from the moon for study on earth. Additional Details: here....
1969 July 13 - . 02:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 15 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 401. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1969-07-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 4036 . COSPAR: 1969-058A. Apogee: 870 km (540 mi). Perigee: 240 km (140 mi). Inclination: 126.00 deg. Period: 160.00 min.
Unmanned soil return mission launched coincident with Apollo 11 mission in last ditch attempt to return lunar soil to earth before United States. After completing 86 communications sessions and 52 orbits of the Moon at various inclinations and altitudes, crashed on the moon on 20 July in an attempted landing. Altitude data used in programming inaccurate or guidance system unable to cope with effect of lunar mascons.
Officially: Testing of on-board systems of the automatic station and further scientific investigation of the moon and circumlunar space. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1969 September 5 - .
- State Commission meets on the Luna 15 failure investigation - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Luna.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
It is felt the problems are understood and go-ahead is given for the next lunar soil return robot launch attempt on 23 September. Kamanin considers this very unlikely to be successful -- all of the plans for automated spacecraft and their booster rockets have not been realised to date.
1969 September 23 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Two Volga buses transport the cosmonauts and VVS specialists to Area 31. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Chelomei,
Mishin.
Program: Luna.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
To ensure the buses do not exceed 60 km/hour checkpoints are manned along the roads. The readiness review is conducted form 10:00 to 13:00. The crews, and spacecraft are ready. Mishin is away 'sick' again. General Pushkin and Beregovoi are at Area 81 to view the Ye-8-5 launch. Kamanin likes Chelomei's UR-500K rocket. He blames its series of failures on its engines and Block D upper stage, not on the fundamental booster design. If it had been more successful, the Russians would have beaten the Americans in a lunar flyby. The launch proceeds as planned at 15:00, but the Block D fails to restart in parking orbit, and is given the cover name 'Cosmos 300'.
1969 September 23 - . 14:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D lost LOX due to valve defect.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 300 - . Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 403. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1969-09-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 4104 . COSPAR: 1969-080A. Apogee: 189 km (117 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 88.20 min. Robotic lunar soil return mission. Failed to leave low earth orbit due to Block D stage failure..
1969 September 24 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Ye-8-5 failure analysis - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Savin,
Smirnov,
Tyulin.
Program: Luna.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
The cause of the Ye-8-5 failure is found to be a valve that was stuck open after the first stage burn, resulting in the oxidiser boiling away in the vacuum of space. Tyulin inquires about the possibility of commanding the Ye-8-5 to conduct a series of manoeuvres and testing re-entry of the soil return capsule in the earth's atmosphere. An interesting concept, but the engineers have not planned for such an eventuality.
NII-2 MO, represented by Lt General Korolev and Chief Designer Savin present plans for their Svinets experiment. It will observe ICBM rocket plumes from space in order to aid design of anti-ballistic missile systems. They had asked Smirnov to conduct a solid propellant rocket launch in order to test the device properly, but he could only schedule a liquid propellant rocket launch. Kamanin had wanted this experiment to be conducted aboard Voskhod 3, but Smirnov has cancelled that mission as well - delaying Soviet ABM development, in Kamanin's view.
1969 October 22 - . 14:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Block D control system failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Cosmos 305 - . Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 404. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1969-10-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 4150 . COSPAR: 1969-092A. Apogee: 208 km (129 mi). Perigee: 182 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.40 deg. Period: 88.40 min. Robotic lunar soil return mission. Failed to leave low earth orbit due to Block D stage failure..
1970 February 6 - . 04:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. Launch Pad: LC81/23?. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: Failure of vehicle on launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Ye-8-5 s/n 405 - failure of vehicle on launch - . Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 405. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1970-02-06 . Robotic lunar soil return mission..
1970 September 12 - . 13:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 16 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 406. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1970-09-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 4527 . COSPAR: 1970-072A. Apogee: 110 km (60 mi). Perigee: 110 km (60 mi). Inclination: 70.00 deg. Period: 119.00 min.
Lunar Sample Return. Landed on Moon 20 September 1970 at 05:18:00 GMT, Latitude 0.68 S, Longitude 56.30 E - Mare Fecunditatis. Luna 16 was launched toward the Moon from a preliminary earth orbit and entered a lunar orbit on September 17, 1970. On September 20, the spacecraft soft landed on the lunar surface as planned. The spacecraft was equipped with an extendable arm with a drilling rig for the collection of a lunar soil sample. After 26 hours and 25 minutes on the lunar surface, the ascent stage, with a hermetically sealed soil sample container, left the lunar surface carrying 100 grams of collected material. It landed in the Soviet Union on September 24, 1970. The lower stage of Luna 16 remained on the lunar surface and continued transmission of lunar temperature and radiation data. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1970 September 18 - .
- Luna 16 - . Nation: Russia. Program: Luna. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Luna 16 is underway. This is the latest attempt to obtain lunar soil Five previous launches failed, four due to UR-500K booster failures. Luna 15 almost made it but crashed on the moon..
1970 September 20 - .
- Luna 16 lands on moon. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Luna.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Luna 16 first placed itself into a 106 x 15 km lunar orbit, inclination 71 degrees. After the trajectory was measured and calculations made on earth, it was instructed to make its Phase 1 descent using a timed burn. Phase 2 began at 600 m altitude. From this point the new-design braking rocket was controlled automatically according to height and velocity as measured by radar. At 220 m altitude the main engine shut down, and small braking rockets fired. These were shut down just 2 m above the surface. At 08:18 Luna 16 successfully made a soft landing on the moon. Getting there required 68 communications sessions over nine days of flight. At 10:00 the drill obtains the soil sample and inserts it into the return capsule.
1970 September 21 - .
- Luna 16 ascent stage heads for earth. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Luna.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
At 10:43 the Luna 16 ascent stage fires, thrusting the return capsule with the lunar soil toward the earth. It will land somewhere on Soviet territory within a 1500 km radius of Dzhezkazgan. The 25 cm diameter capsule is equipped with a 10 square meter parachute. It was thought that it would take 10 to 15 launches to perfect this system, but instead it has succeeded on the sixth attempt.
1970 September 24 - .
- Luna 16 returns lunar soil to earth. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Luna. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Luna 16 lands only 30 km from its aim point, 80 km southeast of Dzhezkazgan. There was ideal weather in the recovery area, the radio beacon worked well, and a helicopter picked up the capsule only a few minutes after landing..
1970 November 18 - .
- Luna 17 lands on moon. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei. Program: Luna. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8. Luna 17 / Lunokhod have landed on the Sea of Storms on the moon. Chelomei is assisting Kamanin in securing funds for the water basin for zero-G training, further simulators, etc..
1970 November 23 - .
- First lunar rover. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Luna. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8. Lunokhod 1 is ready to go on its first lunar drive..
1970 November 25 - .
- NASA Administrator discussed significance of Russian unmanned lunar probes to Apollo. - .
Nation: USA.
Program: Apollo.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
George M. Low, Acting NASA Administrator, discussed the significance of unmanned lunar probes Luna XVI and XVII launched by the U.S.S.R. September 12 and November 10. Luna XVI had brought lunar samples back to earth and Luna XVII had landed an unmanned Lunokhod roving vehicle on the moon's surface. Low stated in a letter to Chairman Clinton P. Anderson of the Senate Committee on Aeronautical and Space Sciences that while the two launches were impressive their contributions to science and technology were relatively minor. Low suggested that the main lesson to be learned from the two launches specifically and the U.S. and U.S.S.R. space programs in general was that while the Soviet launch rate was increasing that of the United States was decreasing. These trends in the two countries' space programs should be a cause of concern if the United States was interested in maintaining a position of leadership in space.
1971 September 2 - . 13:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 18 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 407. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1971-09-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 5448 . COSPAR: 1971-073A. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). Perigee: 100 km (60 mi). Inclination: 35.00 deg. Period: 119.00 min.
Attempted lunar soil return mission; crashed while attempting to soft land at Latitude 3.57 N, Longitude 50.50 E - Mare Fecunditatis. Luna 18 used a new method of navigation in lunar orbit and for landing. The spacecraft's designer, Babakhin, had died at age 56 only the month before. Luna 18 successfully reached earth parking orbit before being put on a translunar trajectory. On September 7, 1971, it entered lunar orbit. The spacecraft completed 85 communications sessions and 54 lunar orbits before it was sent towards the lunar surface by use of braking rockets. It impacted the Moon on September 11, 1971, in a rugged mountainous terrain. Signals ceased at the moment of impact. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1971 September 28 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 19 - .
Payload: Ye-8-LS s/n 202. Mass: 5,810 kg (12,800 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-LS.
USAF Sat Cat: 5488 . COSPAR: 1971-082A. Apogee: 140 km (80 mi). Perigee: 140 km (80 mi). Inclination: 40.60 deg. Period: 121.75 min.
Heavy lunar Orbiter; conducted lunar surface mapping. Luna 19 entered an intermediate earth parking orbit and was then put on a translunar trajectory by the Proton Block D stage. It entered lunar orbit on October 3, 1971. Luna 19 extended the systematic study of lunar gravitational fields and location of mascons (mass concentrations). It also studied the lunar radiation environment, the gamma-active lunar surface, and the solar wind. Photographic coverage via a television system was also obtained. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1972 February 14 - . 03:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 20 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5 s/n 408. Mass: 5,600 kg (12,300 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1972-02-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 5835 . COSPAR: 1972-007A. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). Perigee: 100 km (60 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 118.00 min.
Soft landed on Moon; returned soil samples to Earth. Landed on Moon 21 February 1972 at 19:19:00 GMT, Latitude 3.57 N, Longitude 56.50 E - Mare Fecunditatis. Luna 20 was placed in an intermediate earth parking orbit and from this orbit was sent towards the Moon. It entered lunar orbit on February 18, 1972. On 21 February 1972, Luna 20 soft landed on the Moon in a mountainous area known as the Apollonius highlands, 120 km from where Luna 18 had crashed. While on the lunar surface, the panoramic television system was operated. Lunar samples were obtained by means of an extendable drilling apparatus. The ascent stage of Luna 20 was launched from the lunar surface on 22 February 1972 carrying 30 grams of collected lunar samples in a sealed capsule. It landed in the Soviet Union on 25 February 1972. The lunar samples were recovered the following day.
1973 January 8 - . 06:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 21 - .
Payload: Ye-8 s/n 204. Mass: 5,567 kg (12,273 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
Decay Date: 1973-01-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 6333 . COSPAR: 1973-001A. Apogee: 110 km (60 mi). Perigee: 90 km (55 mi). Inclination: 60.00 deg. Period: 118.00 min.
The Proton / Block D launcher put the spacecraft into Earth parking orbit followed by translunar injection. On 12 January 1973, Luna 21 braked into a 90 x 100 km orbit about the Moon. On 13 and 14 January, the perilune was lowered to 16 km altitude. On 15 January after 40 orbits, the braking rocket was fired at 16 km altitude, and the craft went into free fall. At an altitude of 750 meters the main thrusters began firing, slowing the fall until a height of 22 meters was reached. At this point the main thrusters shut down and the secondary thrusters ignited, slowing the fall until the lander was 1.5 meters above the surface, where the engine was cut off. Landing occurred at 23:35 GMT in LeMonnier crater at 25.85 degrees N, 30.45 degrees E. The lander carried a bas relief of Lenin and the Soviet coat-of-arms. After landing, Lunokhod 2 took TV images of the surrounding area, then rolled down a ramp to the surface at 01:14 GMT on 16 January and took pictures of the Luna 21 lander and landing site. It stopped and charged batteries until 18 January, took more images of the lander and landing site, and then set out over the Moon. The rover would run during the lunar day, stopping occasionally to recharge its batteries via the solar panels. At night the rover would hibernate until the next sunrise, heated by the radioactive source. Lunokhod 2 operated for about 4 months, covered 37 km of terrain including hilly upland areas and rilles, and sent back 86 panoramic images and over 80,000 TV pictures. Many mechanical tests of the surface, laser ranging measurements, and other experiments were completed during this time. On June 4 it was announced that the program was completed, leading to speculation that the vehicle probably failed in mid-May or could not be revived after the lunar night of May-June. The Lunokhod was not left in a position such that the laser retroreflector could be used, indicating that the failure may have happened suddenly.
1974 May 29 - . 08:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 22 - .
Payload: Ye-8-LS s/n 206. Mass: 5,835 kg (12,863 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-LS.
Decay Date: 1975-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 7315 . COSPAR: 1974-037A. Apogee: 220 km (130 mi). Perigee: 220 km (130 mi). Inclination: 19.60 deg. Period: 130.00 min.
Heavy lunar orbiter. Scientific investigation of the moon and circumlunar space from the orbit of an artificial satellite of the Moon, which was begun by the Luna 19 automatic station. The spacecraft carried imaging cameras and also had the objectives of studying the Moon's magnetic field, surface gamma ray emissions and composition of lunar surface rocks, and the gravitational field, as well as micrometeoroids and cosmic rays. Luna 22 braked into a circular lunar orbit on 2 June 1974. The spacecraft made many orbit adjustments over its 18 month lifetime in order to optimise the operation of various experiments, lowering the perilune to as low as 25 km. Manoeuvring fuel was exhausted on 2 September and the mission was ended in early November. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1974 October 28 - . 14:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/24. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Luna 23 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5M s/n 410. Mass: 5,300 kg (11,600 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1974-11-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 7491 . COSPAR: 1974-084A. Apogee: 105 km (65 mi). Perigee: 17 km (10 mi).
Failed lunar soil return mission. After successfully entering earth orbit, flying to the moon, entering lunar orbit, and descending toward the surface, the spacecraft was damaged during landing in Mare Crisium (Sea of Crises). The sample collecting apparatus could not operate and no samples were returned. The lander continued transmissions for three days after landing. In 1976, Luna 24 landed several hundred meters away and successfully returned samples. Parameters are for lunar orbit.
1975 October 16 - . 04:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1. FAILURE: Block D stage failed.. Failed Stage: U.
- Ye-8-5M s/n 412 - Block D stage failed. - . Payload: Ye-8-5M s/n 412. Mass: 5,300 kg (11,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5. Decay Date: 1975-10-16 . Attempted robotic lunar soil return mission. Block D stage failed..
1976 August 9 - . 15:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D-1.
- Luna 24 - .
Payload: Ye-8-5M s/n 413. Mass: 5,306 kg (11,697 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Luna.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Decay Date: 1976-08-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 9272 . COSPAR: 1976-081A. Apogee: 115 km (71 mi). Perigee: 115 km (71 mi). Inclination: 120.00 deg. Period: 119.00 min.
Lunar Sample Return. Landed on Moon 18 Aug 1976 at 02:00:00 GMT, Latitude 12.25 N, Longitude 62.20 E - Mare Crisium (Sea of Crisis). The last of the Luna series of spacecraft, Luna 24 was the third Soviet mission to retrieve lunar ground samples (the first two were returned by Luna 16 and 20). The mission successfully returned 170 grams of lunar samples to the Earth on 22 August 1976.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use