Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
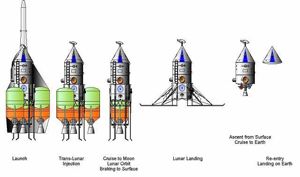
Lunar L3
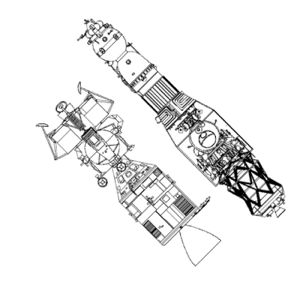 Apollo vs N1-L3 Apollo CSM / LM vs L3 Lunar Complex Credit: © Mark Wade |
| Soviet Lunar Landing The Russians were never able to have enough success with the N1 booster to have a serious schedule for the first Soviet lunar landing. In January 1969, before the first N1 launch, it was not expected that a Soviet landing would take place until 1972 at the earliest. |
| Soyuz n 17 Cancelled 16 day mission with Soyuz n 17 to conduct rendezvous and docking operations and demonstrate life support system for the LK manned lunar lander. |
| Soyuz n 18 Cancelled 16 day mission with Soyuz n 18 to conduct rendezvous and docking operations and demonstrate life support system for the LOK manned lunar orbiter. |
| L3-1 Planned first Soviet manned lunar landing, slated by end 1969 before N1 flight tests began in early 1969. Crew possibly Leonov and Makarov. |
| Soyuz n 19 The active spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system. These would have been 15 to 16 day missions to demonstrate both the new SZhO life support system for the L3, to conduct rendezvous and docking operations using the L3's Kontakt system, and to conduct EVA transfer of one cosmonaut. |
| Soyuz n 20 Passive spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system. One or two of the crew would have spacewalked to the Soyuz 11 Kontakt and returned in the other spacecraft. |
| L3-2 Planned first Soviet manned lunar landing, slated for 1970 before N1 flight tests began in early 1969. Crew possibly Bykovsky and Rukavishnikov. |
| L3-3 Planned first Soviet manned lunar landing, slated for 1970 before N1 flight tests began in early 1969. Crew possibly Popovich and Sevastyanov. |
| Soyuz sn 18 Soyuz s/n 18 would have been the active spacecraft of the first dual-spacecraft test of the Kontakt docking system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place. |
| Soyuz sn 19 Soyuz s/n 19 was to have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. It would have been the docking target for Soyuz s/n 18. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place. |
| Soyuz sn 20 Soyuz s/n 20 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place. |
| Soyuz sn 21 Soyuz s/n 21 equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. Would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 20 . A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place. |
| Soyuz sn 22 Soyuz s/n 22 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place. |
| Soyuz sn 23 Soyuz s/n 23 would have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. The spacecraft would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 22. |
| Soyuz Kontakt A Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The Kontakt-A Soyuz would have been the active spacecraft, simulating the LOK lunar orbiter. |
| Soyuz Kontakt P Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The Kontakt-P Soyuz would have been the passive spacecraft, simulating the LK lunar lander. |
People: Mishin, Afanasyev, Sergei, Kirillov, Dorofeyev. Country: Russia. Spacecraft: Luna E-6LS, Soyuz 7K-L1A, Soyuz 7K-L1E, LK, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Flights: Apollo 11, Soyuz n 17, Soyuz n 18, Soyuz n 19, Soyuz n 20, Soyuz sn 18, Soyuz sn 19, Soyuz sn 20, Soyuz sn 21, Soyuz sn 22, Soyuz sn 23, Soviet Lunar Landing, Soyuz Kontakt A, Soyuz Kontakt P. Launch Vehicles: Molniya 8K78M, Proton-K/D, Soyuz 11A511L, N1 1969. Launch Sites: Baikonur. Agency: RVSN, MOM.
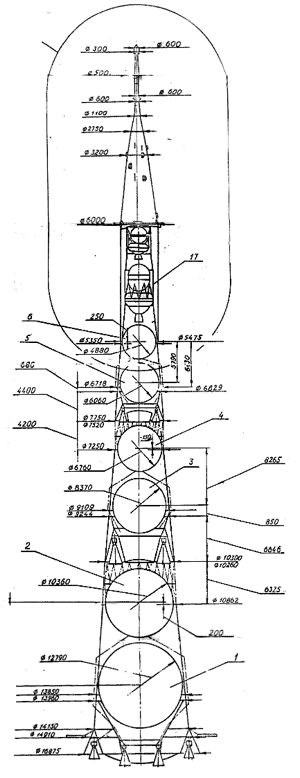 | N1 Cutaway Dimensioned Russian cutaway drawing of N1 launch vehicle. |
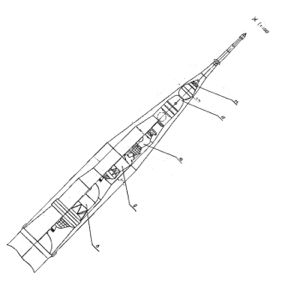 | L3 Cutaway Dimensioned Russian cutaway drawing of L3 manned lunar landing complex. |
 | LOK Orbital Module LOK Orbital Module, view down from top of spacecraft toward Soyuz descent module. Credit: © Mark Wade |
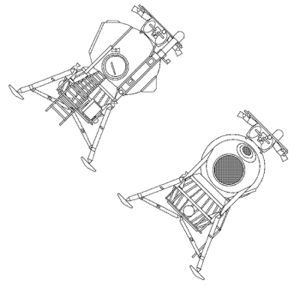 | LK Two View Two view layout drawing of LK lunar lander. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Early LK Test Model Dynamic Test Model of Early LK Concept. Credit: © Mark Wade |
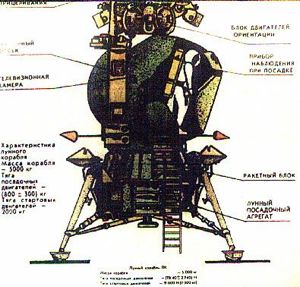 | LK drawing at Kaluga Cutaway drawing of LK lunar lander, showing position of cosmonaut in cabin. Credit: e |
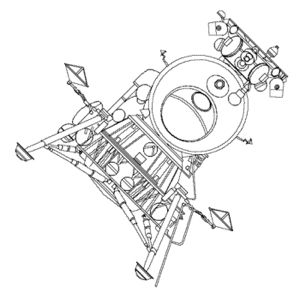 | LK Detail forward view drawing of the LK lunar lander. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | LOK Block I forward View of the dome covering the pressurized instrument compartment of the LOK. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | LK ladder base Detail of the base of the ladder, showing the battery racks below the ladder. Note the shape of the foot pad. Credit: © Mark Wade |
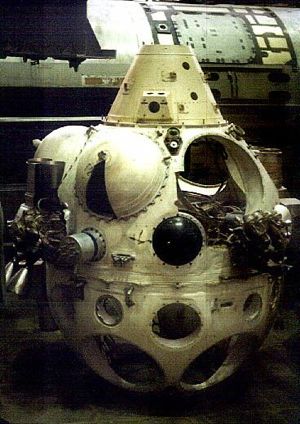
 | LK Overall view of the LK preserved at the Orevo Museum of the Bauman Moscow State Technical University. Credit: © Mark Wade |
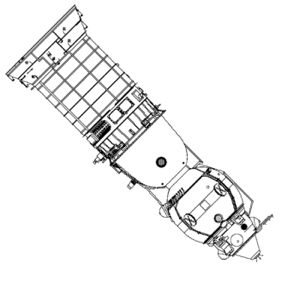 | Soyuz LOK Soyuz LOK lunar orbiter. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | LOK Orbital Module LOK Orbital Module. Note the far greater amount of external cabling and connecting plates than in the standard Soyuz. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | S5.51 LOK engine The complex plumbing fed numerous smaller attitude control thrusters at the base of the LOK. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | LOK Orbital Module LOK Orbital Module interior Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | LOK Lunar Orbiter The Soyuz 7K-LOK lunar orbiter spacecraft to be used in the L3 lunar landing project complex. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Chelomei LK-700 Chelomei LK-700 manned direct lunar landing spacecraft - cruise and landed configurations Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Soyuz 7K-LOK Soyuz 7K-LOK manned lunar orbit spacecraft. Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Krechet Spacesuit Front view of the Krechet lunar space suit Credit: Andy Salmon |
1959 December 31 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Nuclear propulsion work abandoned. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Korolev. Program: Lunar L3. Korolev abandons work on nuclear-powered rockets. Future launch vehicles to be based on conventional lox/keroesene propellants..
1962 During the Year - . Launch Vehicle: UR-700.
- Development of RD-270 engine begun - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Yangel.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: LK-700.
The RD-270 engine was proposed for Chelomei's UR-700 and Yangel R-56 lunar landing launchers in competition to Korolev N1. The RD-270 was in the same class as the F-1 engine developed for America's Saturn V launch vehicle, but burned storable but toxic propellants.
1962 August 1 - .
- Russian methods for sending a man to the moon - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
A recent Russian article discussed various methods which the Soviet Union had been studying for sending a man to the moon during the decade. The earth orbital rendezvous method was reported the most reliable, but consideration also had been given to the direct ascent method, using the "Mastodon" rocket.
1963 March 21 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
1963 September 1 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
1964 February 12 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1 1962.
- Kremlin meeting on lunar landing plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: L3-1963.
VVS officers meet with O G Ivanovskiy for two hours. The Communist Party plans a lunar expedition in the 1968-1970 period. For this the N1 booster will be used, which has a low earth orbit payload of 72 tonnes. The minimum spacecraft to take a crew to the lunar surface and back will have a minimum payload of 200 tonnes; therefore three N1 launches will be required to launch components, which will have to be assembled in orbit. However all of these plans are only on paper, and Kamanin does not see any way the Soviet Union can beat the Americans to the moon, who are already flying Apollo hardware for that mission.
1964 February 18 - .
- Lunar trainers - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Tereshkova.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4.
Spacecraft: L3-1963,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V.
Concepts for trainers for lunar landings and fly-bys are discussed. The five flown cosmonauts sit for entrance examinations to the Zhukovskiy Institute. Kamanin is irritated that of the five, only Bykovsky seems really bright and alert. Tereshkova is still studying for the examination.
1964 July 19 - .
- Korolev obtains preliminary approval for a single-launch, lunar orbit rendezvous, manned landing. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Chelomei,
Feoktistov,
Glushko,
Korolev,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Yangel.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: L3-1963,
LK,
LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Work on the original N1-L3 had begun in 1963. This had been preceded by two years of working on a draft project for the LK lunar lander and its propulsion system. But there was no money for full scale development -- no code name from Gosplan against which to charge such work. It was annoying that Chelomei, Glushko, and Yangel were wasting resources on alternate designs at the same time. Additional Details: here....
1964 July 21 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Korolev's single-launch lunar scheme reviewed by the Chief Designers - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Glushko, Isayev, Keldysh, Khrushchev, Korolev, Kuznetsov, Pilyugin, Smirnov. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, Soyuz 7K-LOK. How to achieve the additional N1 payload was a key point of discussion.. Additional Details: here....
1964 August 1 - .
- Full scale development of Soviet manned lunar flyby and landing projects authorised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz A-1,
Soyuz A-2,
Soyuz A-3,
Soyuz A-4.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-1,
Luna Ye-8,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz A.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 655-268 'On Work on the Exploration of the Moon and Mastery of Space--piloted LK-1 circumlunar and L3 lunar landing projects and the Ye-6M lunar lander' was issued. Chelomei was to develop the three-stage UR-500K booster and LK-1 spacecraft for the manned lunar flyby. Korolev was to develop the totally different N1 booster and L3 spacecraft complex for the manned lunar landing. First launch of the N1 was to be by the first quarter 1966, with manned lunar landings in 1967 to 1968. Reprioritization led to work being stopped on Korolev's Zvezda 6-man orbiting weapons platform by mid-1965, after a huge mockup had been built.
Korolev felt that if he had the full support of the Communist Party, the military, and industry he could achieve this goal, and this decree ordered such support. The USSR would be first on the moon. But in truth the draft project behind the decree had not solved all of the technical problems, or provided a solution on how to achieve the required payload on either the booster or spacecraft side. New technology features required for success of the scheme included an advanced guidance system in the N1 third stage equipment bay, the enormous fuel tanks in the N1 first stage, and the Lox/LH2 fuel cells needed for the LOK lunar orbiter. But the real technical problem with the N1-L3 design was the total lack of any weight growth reserve. Even thought the systems had not even been developed yet, engineers were fighting over tens of grams in their weight allocations, let alone the kilograms normally at issue.
Development of Korolev's Soyuz A-B-V, a competing circumlunar project, was evidently still authorised, although it duplicated Chelomei's LK-1.
1964 September 1 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
1964 September 14 - .
- Voskhod abort system - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Komarov,
Korolev,
Krylov,
Lazarev,
Volynov,
Yegorov.
Program: Voskhod,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Voskhod 1.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Voskhod.
Kamanin reviews the Voskhod abort system with Korolev. Up to T+27 seconds, there is no possibility of saving the crew in the event of a booster failure; from T+27 seconds to T+44 seconds, escape would be difficult, but is possible; and from T+44 seconds to T+501 seconds abort should be possible, with the capsule landing on Soviet territory. Afterwards, Korolev speaks with Kamanin secretly and privately. Korolev reveals that he has discussed a greater VVS role in space with Marshal Krylov, but that Krylov is adamantly opposed to the VVS assuming such a mission. Korolev is seeking a resolution from the Communist Party that will authorise him to develop a manned lunar flyby and landing system using his N1 booster. He believes that Chelomei's UR-500 booster will not have sufficient payload to mount a manned flyby - a docking in low earth orbit will be required. But Chelomei has rejected the use of docking, and is even designing his UR-700 to allow a lunar landing without the use of docking.
Finally Korolev gets to the purpose of the secret meeting. He wants Feoktistov to be aboard Voskhod 1, despite the opinion of Kamanin and the physicians. Kamanin reiterates that the most qualified crew would be Komarov, Volynov, and Lazarev; and if he gives in on Feoktistov, then Komarov, Feoktistov, Lazarev. But Korolev is opposed to Lazarev, and insists that the crew should be Komarov, Feoktistov, and Yegorov. From Kamanin's point of view this is flying a space mission with two invalids aboard. Lazarev is a qualified and fit flight surgeon, a qualified pilot as well as a physician with 15 years of research experience in aviation medicine. Korolev is adamant that the two passengers should be civilian, not military. No agreement is possible.
1964 October 28 - .
- Lunar project orders issued to industry. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1, Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, LK-1, Luna Ye-8, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Military-Industrial Commission (VPK) Decree 'On assignment of lunar programs to OKB-52 and OKB-1' was issued..
1964 October 31 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-700.
- UR-700 project cancelled - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS.
Spacecraft: LK-700.
Following the August decree that gave the circumlunar project to Chelomei and the lunar landing project to Korolev, further work on development of the UR-700 by Chelomei was cancelled. However development of the RD-270 engine was continued and Chelomei continued to do UR-700 design studies.
November 1964 - .
- Korolev's admits that N1 cannot attain payload needed for single-launch mission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Brezhnev,
Chelomei,
Khrushchev,
Korolev,
Kozlov,
Lavochkin,
Ustinov,
Yangel.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-700,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Korolev speaks privately to Chertok. Kozlov has told him it will be impossible to build an N1 with the 93 tonne payload capability until the fourth flight article. The L3 concept was still the same as in the August decree - 2 cosmonauts aboard the LOK orbiter, one aboard the LK lander. Korolev asks Chertok to take 800 kg out of the weight budget for the L3. Chertok informs him that they are already 500 kg over the August budget. This is still without all the unknowns of the automated lunar landing being solved. Additional Details: here....
During 1965 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 development issues - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev,
Pilyugin,
Raushenbakh.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Luna E-6,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
There were two camps on the N1-L3 control systems. One group was within OKB-1, and had developed the systems for the Vostok and Zenit spacecraft, under the personal oversight of Korolev. They stressed the maximum quality and reliability in their systems. The second group had worked with Pilyugin, and had designed the systems for the Mars, Venus, Luna E-6 probes, the R-9, RT-1, RT-2, and GR-1 missiles; and piloted spacecraft. Their design emphasis was on maximum usability and output. Pilyugin had been named chief designer of the control system for the N1-L3. Additional Details: here....
1965 February 2 - .
- Cosmonaut organisation - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi,
Malinovskiy,
Nikolayev.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz PPK,
Soyuz R,
Soyuz V.
Kamanin will organise the cosmonauts into two groups: the first group will be commanded by Nikolayev, and the latest group by Beregovoi. They will be assigned to support and train seven missions: military space (reconnaissance, interceptor, and combat spacecraft); space navigation; life support and rescue systems; communications and telemetry systems; scientific orbital stations; lunar fly-by; and lunar landing expeditions. All of this may be for nought, since Marshall Malinovskiy has said that heavy launch vehicles and lunar flights have no military utility and should be funded and handled by the Academy of Science.
1965 February 10 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- L3 single-launch spacecraft draft project approved. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Korolev,
Pilyugin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Interdepartmental Scientific-Technical Council on Space Research (MNTS-KI) Decree 'On approval of the L3 draft project' was issued. The decree followed a review by a Keldysh-led Academy of Sciences state commission the previous December. The decree moved the first flight of the N1 to the end of 1966. Additional Details: here....
Spring 1965 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Guidance system for N1 cannot support planned schedule - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Korolev, Pilyugin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, Soyuz 7K-LOK. By the second quarter of 1965 Pilyugin was already notifying OKB-1 that he could never have the booster guidance system ready for the planned first launch in 1968 - not to even mention the systems for the LOK and LK..
1965 March 2 - .
- Babakin takes over Lavochkin OKB - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Chelomei,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: Luna E-6,
Luna Ye-8.
Former Lavochkin bureau, part of Chelomei, regained status of a separate design bureau with former Korolev deputy GN Babakin as its head. By the end of 1965 all materials on the E-6, Ye-8, and planetary probes were passed by Korolev to the Lavochkin Bureau, who took over responsibility for all future lunar and planetary unmanned probes.
1965 September 1 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1 1964.
- Voskhod/Soyuz crewing plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Artyukhin,
Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Katys,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Korolev,
Matinchenko,
Nikolayev,
Ponomaryova,
Solovyova,
Volynov.
Program: Voskhod,
Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Voskhod 3,
Voskhod 5.
Spacecraft: LK,
LK-1,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Voskhod.
Kamanin meets with Korolev at 15:00 to discuss crew plans. As Soyuz pilot candidates, Kamanin proposes Gagarin, Nikolayev, Bykovsky, Komarov, Kolodin, Artyukhin, and Matinchenko. Korolev counters by proposing supplemental training of a supplemental group of engineer-cosmonauts from the ranks of OKB-1. He calls Anokhin, his lead test pilot, informs Korolev that there are 100 engineers working at the bureau that are potential cosmonauts candidates, of which perhaps 25 would complete the selection process. Kamanin agrees to assist OKB-1 in flight training of these engineer-cosmonauts. Kamanin again proposes Volynov and Katys as prime crew for the Voskhod 3 12-15 day flight. Korolev reveals that, even though Kamanin will have the crew ready by October, the spacecraft for the flight may not yet even be ready by November - Kamanin thinks January 1966 is more realistic. The discussion turns to the female EVA flight - Ponomaryova as pilot, Solovyova as spacewalker. It is decided that a group of 6 to 8 cosmonauts will begin dedicated training in September for lunar flyby and landing missions. Korolev advises Kamanin that metal fabrication of the N1 superbooster first article will be completed by the end of 1965. The booster will have a payload to low earth orbit of 90 tonnes, and later versions with uprated engines will reach 130 tonnes payload. Korolev foresees the payload for the first N1 tests being a handful of Soyuz spacecraft.
1965 December 20 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Decision to use analogue guidance in early N1 launches - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Keldysh, Korolev, Pilyugin, Ryazanskiy. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Pilyugin called Keldysh to tell him he had heard that Keldysh again wanted to form an expert commission to study guidance system development problems with the N1, with Bushuyev as the head.. Additional Details: here....
1966 February 1 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
1966 February 14 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 redesign to increase payload to 95 tonnes - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Following Korolev's death, Mishin discovered that growth of the mass of the L3 payload had taken the low earth orbit payload requirement to 95 tonnes, beyond the 75 tonne lifting capability of the N1. To achieve the 95 tonne payload, changes in plans and redesign of the N1 would be necessary. The measures taken were: reduction of the orbital inclination for the initial earth orbit from 65 degrees to 52 degrees; reduce the altitude of the lunar orbit from 300 km to 220 km; increase the propellant mass by supercooling the propellants prior to loading in the lunach vehicle (the kerosene to be at -15 to -20 degrees Centigrade, the liquid oxygen to -191 degrees centigrade); add six engines to the first stage; increase thrust of all the engines on the first, second, and third stages by 2%; add a fourth stabilizer. The result of all of these measures would increase the launch mass to 2800 tonnes and the payload to the required 95 tonnes.
1966 February 17 - .
- Soviet Lunar Landing Plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Kamanin presents his plan to train 5 to 6 crews for the lunar landing mission over a 30 month period. Only experienced cosmonauts, with prior spaceflight experience, will be assigned to these crews. Kamanin lays out for the VVS leadership the complex series of events the cosmonauts will have to complete in the L3 lunar-orbit rendezvous scheme, including transfer between spacecraft of a single lunar landing cosmonaut in free space in lunar orbit. Crews need to be formed immediately, with two cosmonauts per crew - the L3 mission commander, and the second cosmonaut who will land on the moon. In order to accomplish the mission on schedule, a new air regiment needs to be formed, with the necessary flying laboratories, simulators and trainers, space suits, test stands and surface simulators, and other equipment necessary to train the crew for the mission.
1966 May 11 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Mishin selected as Korolev's replacement after four-month delay - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Keldysh,
Khrushchev,
Korolev,
Mishin,
Mozzhorin,
Okhapkin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
From 1963-1965 Ustinov was both head of the Soviet for the National Economy and the First Secretary of the Presidium of Soviet Ministers. He supported civilian space projects and instructed the military to co-operate in them. But after Khrushchev was ousted, Ustinov had less influence with the Ministry of Defence.
After the death of Korolev in January, a letter was sent to the Central Committee requesting that Mishin be appointed director of OKB-1. Ustinov tried to line up support for Mishin, but by the time of the first first Saturn IB orbital flight on 26 February 1966, no decision had been made. America was progressing on the path to the moon, but Russia was stalled. An alternate that had been considered was Sergei Okhapkin, another Deputy Chief Designer at TsKBEM. But Okhapkin knew only spacecraft, he had never developed complete launch-booster-spacecraft systems. By the time Mishin was appointed, it was clear that the race was lost. The American's planned their first Saturn V launch in September 1967 and their first manned flight in 1968. Mishin could not expect trials of the LK lunar lander until 1969 at the earliest. There were insufficient funds allocated, and the schedule had no allowance for test flight failures. Ustinov, Morozhin, and Keldysh pointed fingers as to who had presented such unrealistic schedules to the Politburo. Keldysh now supported unmanned robot lunar landers in development by Babakin. Even these would not land until 1970, allowing three years of flight trials to achieve reliability. Khrushchev, it seemed, was to blame for such enormous unaffordable projects. This in turn put Ustinov in danger, as Khrushchev's point man for space.
1966 July 10 - .
- Komarov announces that USSR will beat US to moon - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Komarov. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Komarov announces in Japan that USSR would beat the US to moonlanding by one year..
1966 July 28 - .
- Industrial problems - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Kamanin is having a difficult time getting two additional Tu-104 aircraft for zero- and partial-gravity training and tests for the L1 and L3 lunar projects. The type is not in the VVS inventory, and he has to go through the Ministry of Civil Aviation to obtain and maintain the aircraft. There seems to be no acceptable bureaucratic method to do this. Vershinin has completed and forwarded to the Central Committee the VVS letter refuting the attempt by MOM to take over manned spaceflight.
1966 August 2 - .
- Letter to Central Committee on OKB-1 actions. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Malinovskiy. Program: Soyuz, Lunar L1, Lunar L3. Malinovskiy decides to send the letter to the Central Committee complaining about MOM and OKB-1's after two days of indecision..
September 1966 - .
- N1 two-launch moon scenario proposed - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK,
Molniya-1,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Bushuyev proposed a two launch variation on Korolev's single-launch scheme. The increased-payload version of the N1 with six additional engines was not planned to fly until vehicle 3L. 1L and 2L were to be technology articles for ground test with only the original 24 engine configuration. At that time the first Apollo test flight was planned by the end of 1966, and the US moon landing no later than 1969. The Soviets expected the first test of their LK lander in 1969, and concluded they could not expect to land a Soviet man on the moon until 1972. Additional Details: here....
1966 September 2 - .
- Cosmonaut civilian program training groups - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bykovsky,
Dobrovolsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Kolodin,
Komarov,
Leonov,
Nikolayev,
Shatalov,
Volynov,
Voronov,
Zholobov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing,
Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3,
Soyuz s/n 3/4,
Soyuz s/n 5/6,
Voskhod 3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Kamanin organises the cosmonauts into the following training groups:
- Soyuz 7K-OK: Gagarin, Komarov, Nikolayev, Bykovsky, Khrunov, Gorbatko, Voronov, Kolodin
- L1: Volynov, Dobrovolskiy, Voronov, Kolodin, Zholobov, Komarov, Bykovskiy
- L3: Leonov, Gorbatko, Khrunov, Gagarin, Nikolayev, Shatalov
Rudenko agrees with Kamanin's plan, except he urges him to assign more cosmonauts to the Soyuz 7K-OK group, and include OKB-1 cosmonauts in the 7K-OK, L1, and L3 groups, and Academy of Science cosmonauts in the L1 and L3 groups.
These cosmonaut assignments were in constant flux, and many cosmonauts were assigned to train for more than one program - resulting in multiple claims in later years that 'I was being trained for the first moon flight'.
1966 October 5 - .
- Council for the Problem of the Conquest of the Moon - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Karas,
Sokolov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
A government resolution has created a Council for the Problem of the Conquest of the Moon. The chairman will be Minister Afanasyev; the members, other ministers, deputy ministers, academicians, and the chief designers. The only member from the Defense Ministry will be lieutenant generals Karas and Sokolov. There are no VVS members, but Kamanin has already received a request that General Ioffe report to the council on VVS plans for search and recovery of unmanned lunar precursor spacecraft.
1966 November 10 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Lunar coordination problems - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. Kamanin diary complains of lunar coordination problems..
1966 November 15 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur. Launch Vehicle: N1.
1966 November 16 - .
- Government go-ahead for N-1 use in lunar program - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Keldysh,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: LK-700,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Mishin's draft plan for the Soviet lunar landing was approved by an expert commission headed by Keldysh. The first N-1 launch was set for March 1968. At same meeting, Chelomei made a last ditch attempt to get his revised UR-700/LK-700 direct landing approach approved in its place. Although Chelomei had lined up the support of Glushko, and Mishin was in a weak position after Korolev's death, Keldysh managed to ensure that the N1-L3 continued. However continued design work on the LK-700, the UR-700 booster, and development of the RD-270 engine were authorised.
1966 November 19 - .
- First Soyuz Launch Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Grechko,
Keldysh,
Kerimov,
Krylov,
Kurushin,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Mnatsakanian,
Pashkov,
Petrovskiy,
Pravetskiy,
Rudenko,
Ryazanskiy,
Serbin,
Smirnov,
Tkachev,
Ustinov,
Vershinin,
Zakharov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing,
Soyuz 1,
Soyuz 2A,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 2,
Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Rudenko has reached agreement with Mishin that L1 and L3 crews will also consist of a VVS pilot as commander, and an OKB-1 flight engineer. Kamanin is depressed. Despite the support six marshals (Malinovskiy, Grechko, Zakharov, Krylov, Vershinin and Rudenko), Mishin has won this argument with the support of Ustinov, Serbin, Smirnov, Pashkov, Keldysh, Afanasyev, and Petrovskiy. Later the State Commission meets, for the first time in a long time at Tyuratam. Kerimov chairs the session, with more than 100 attendees, including Mishin, Rudenko, Krylov, Pravetskiy, Kurushin, Ryazanskiy, Mnatsakanian, and Tkachev. All is certified ready,. Launch of the active spacecraft is set for 26 November, and the passive vehicle on 27 November.
1966 December 28 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-700.
- Almaz and LK-700 development status - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Almaz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK-1,
LK-700,
Raketoplan.
Kamanin accompanies 17 generals and other officers of the VVS in a tour of Chelomei's OKB-52. Chelomei spends five hours personally acquainting the visitors with his bureau's space technology capabilities. It was the first in-depth meeting Kamanin and Vershinin have had with Chelomei, despite meeting with him occasionally since 1961. They have mainly interacted with Korolev and now Mishin. Additional Details: here....
During 1967 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 development progress - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. The KORD system detected and controlled the parameters of 42 engines (30 first stage + 8 second stage + 4 third stage) This involved processing 1600 data elements.. Additional Details: here....
1967 February 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Government approves landing on moon by end 1968 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Soviet government approves plan to land cosmonaut on moon by end 1968. N-1 test plan approved, envisioning third quarter 1967 as beginning of flight hardware construction. Fall-back project would be manned circumlunar mission. First manned L1 mission imagined as early as June 1967. First N1 launch by March 1968.
1967 February 4 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- L1/L3 launch schedules set - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The following is the schedule set be decree for the L1 and L3 projects:
Serial # Mission Date 2P Develop Block D stage Feb or Mar 67 3P same Mar 67 4L Unmanned lunar flyby May 67 5L Unmanned lunar flyby Jun 67 6L Manned lunar flyby Jun or Jul 67 7L&8L Manned lunar flybys Aug 67 9L&10L Manned lunar flybys Sep 67 11L&12L Manned lunar flybys Oct 67 13L Reserve spacecraft N1-3L Serial # Mission Date 3L Develop LV & Blocks G&D Sep 67 4L Reserve 5L LOK/LK unmanned Dec 67 6L LOK/LK unmanned Feb 68 7L Manned LOK/unmanned LK Apr 68 8L Manned LOK/unmanned LK Jun 68 9L Piloted LOK/unmanned LK with LK landing on moon Aug 68 10L First men land on moon Sep 68 11L Reserve 12L ReserveKamanin's personal opinion of this schedule - manned L1 flights may occur before the end of 1967, but there will be no lunar landing until 1969.
1967 March 14 - .
- Lunar flyby/landing program plan reviewed - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-L1A,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
UR-500K/L1 project will consist of three phases. Phase I will be dedicated to development of the Block D translunar stage, using prototype, incomplete L1 spacecraft. Phase II will conduct lunar flybys with complete but unmanned L1 spacecraft. Phase III will fly Soviet cosmonauts around the moon. The N1/L3 project will consist of five phases. Phase I will use the N1 and the 7K-L1A spacecraft. This will be used primarily to test out the Block G translunar and Block D lunar orbit insertion stages, but will also conduct lunar flybys, returning photographs of the lunar surface to the earth. Phase II will use N1's to fly L3 spacecraft with an unpiloted LOK lunar orbiter and an unpiloted LK lunar lander. Phase III, the first manned missions, will use N1's to fly L3 spacecraft with a piloted LOK lunar orbiter and an unpiloted LK lunar lander. Phase IV will fly a piloted LOK lunar orbiter and an unpiloted LK lunar lander, that will be landed on the lunar surface. In Phase V N1-L3 number 10L is to launch the first manned landing on the moon in September 1968. N1-L3 numbers 11L and 12L were back-ups, in the event any of the planned earlier missions failed. Additional Details: here....
1967 March 15 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- CIA reports on Soviet space developments - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. CIA reports accurately development of N-1, Almaz, Proton, etc.... even states 100,000 kg large space station in development for launch by N-1 by 1969. CIA does not expect lunar landing until early 1970's..
1967 March 31 - .
- Soviet lunar maps prepared. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Kamanin examines maps of the moon, executed at scales of 1:5,000,000 and 1:10,000,000. 2000 are to be printed for use by the cosmonauts in preparation for the Soviet lunar landings. Mishin doesn't see the point - he is very aggressively anti-pilot for his lunar spacecraft.
1967 June 15 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1M.
- First test of liquid hydrogen/LOX engine for N1M - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. First test of the 11D56 in an iron stand version. First test of an engine with these propellants in USSR for use in a space launch vehicle..
1967 August 2 - .
- Manned spacecraft trainer status - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Bykovsky, Feoktistov, Nikolayev. Program: Lunar L3, Lunar L1, Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-LOK, Soyuz 7K-OK. The Volga and Soyuz trainers are to be finally operational on 10 and 20 August respectively. The L1 trainer is not progressing and the L3 trainer exists only on paper.. Additional Details: here....
1967 August 15 - .
- L3 quarantine discussed. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Sterilisation and quarantine of the L3 spacecraft on its return from the moon is discussed..
1967 August 31 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. Launch Vehicle: N1.
1967 September 20 - .
- Review of N1 progress. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Pashkov,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK-700,
Spiral OS.
The booster was supposed to be launched by 1966, but there is no way it will be finished this year, and it is highly questionable it will even get off the ground in 1968. The N1 tanks are pressurised to 2 atmospheres, and can go up to three atmospheres in an emergency. In the enormous MIK assembly hall are three N1's - one 'iron bird' ground test model and two flight vehicles. The first roll out of the mock-up will take place in 1967, and the first launch attempt is still expected in 1968 (the first launch will not be attempted until the second and third stages complete stand tests. There is no test stand for the first stage, it will be fired for the first time in flight). An explosion would destroy the pad, requiring several years of repairs. There are two pads, but even that would not be a guarantee of the availability of the rocket due to the poor expected initial reliability. The N1 project is costing 10 billion roubles, not including considerable investment required by the military. To Kamanin the whole thing is a boondoggle, showing the necessity for development of lighter air-launched boosters. He believes there are many mistakes in design and construction, but Mishin, Pashkov, Smirnov, and Ustinov support these doubtful projects of Korolev and Mishin, instead of technically sound projects such as Chelomei's UR-700 or MiG's air-launched spacecraft. If Mishin thinks the current Proton/L1 reliability is only 0.6, then that of the completely unproved N1/L3 must be even less...
1967 October 3 - .
- Mishin's errors means Kamanin will not see a Soviet man on the moon in his lifetime. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Lunar L1, Lunar L3. The moon landing has already been delayed three to four years due to the mistakes of Mishin. Kamanin feels his mortality, the limited number of years remaining in his life, and is furious that Mishin is wasting time when life is so short for everyone..
1967 October 10 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Lunar Soviet - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Chelomei,
Keldysh,
Kuznetsov,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: L5.
The meeting is headed by Afanasyev. The first N1 will have a payload of only 76 tonnes, versus the 95 tonnes required for the L3 lunar landing complex. In order to land two cosmonauts on the moon, as the Americans are planning, a 105 tonne low earth orbit payload would be needed. This would require new engines in the first and second stages. Kuznetsov says that his 153 tonne engine could be uprated to 170 tonnes without any basic changes. Lox/LH2 engines would be needed for the upper stages. Keldysh questions the safety of the current plan of landing only one cosmonaut on the moon. Mishin replies that putting two cosmonauts on the moon simply is not possible with the N1. Chelomei raises a question - How is it possible that the Americans have built he Saturn V, which can put 130 tonnes in low earth orbit, in order to land two men on the moon, and Mishin says he can do the same mission with 105 tonnes? Mishin claims that this is due to the lighter design and construction of the L3. The following decisions are made:
- The first Soviet flight to he moon will use the current plan - one N1 launch, one cosmonaut on the moon.
- Special measures must be taken to ensure the safety of that single cosmonaut
- A new N1 model is to be developed to land the new L5 spacecraft (which will be able to handle 4 to 5 crew, 1.5 to 2.0 tonnes of scientific equipment, and spend three months on the lunar surface). This is to be ready two to three years after the first landing.
- The Academy of Sciences, the Ministry of Defence, and MOM are to develop a program of military and scientific experiments to be carried aboard the L3
- The next meeting of the lunar soviet will be in November/December 1967
1967 October 15 - .
- Meeting on crew selections for the L3 program. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Artyukhin,
Bykovsky,
Gagarin,
Gorbatko,
Khrunov,
Kubasov,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Nikolayev,
Popovich,
Rukavishnikov,
Voronov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Attending are Kuznetsov, Gagarin, Khlebnikov. There are three training groups: Soyuz, L1, and L3. Mishin and the MOM are holding up further training of cosmonauts until the VVS agrees to accept Mishin's candidates from TsKBEM. In any case, Mishin's attitude is that 'automation in space is everything. Humans in space are only supposed to monitor the operation of automated systems'. L3 cosmonauts selected by the VVS are: Leonov, Bykovsky, Nikolayev, Popovich, Voronov, Khrunov, Gorbatko, Artyukhin, Kubasov, Makarov, and Rukavishnikov. The official requirements: balanced composition of a crew according to mass requirements (no more than 70 kg weight per cosmonaut), and the ability to monitor fully automated function of the L3. According to official documents, the crew's primary function is to guide the flight, but now Mishin intends that their primary role will be as subjects of psychological and physical observations to establish the adaptation of the human organism to space flight).
1967 October 21 - .
- Lunar crew controversy rages. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Anokhin,
Feoktistov,
Kerimov,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
First Mishin was pushing the 60-year-old Anokhin for spaceflight, now the invalid Feoktistov. Feoktistiov suffers from gastrointestinal ulcers. Tyulin and Kerimov are of one voice in the matter - this is not even a question that can be raised - sick is sick, period. The L1 and L3 crews will have to endure eight to ten days of orbital flight. They can only be between 170 and 175 cm tall, and can have a maximum weight of 70 kg. Mishin insists that he doesn't even need military pilots for the L1 and L3, and therefore doesn't need to decide crew compositions until the middle of 1968, and then only 'his' engineer cosmonauts from TsKBEM should be considered. The Marshal interrupts Mishin, angrily reminding him that the space program is a national enterprise, not something being accomplished by 'your' spacecraft or 'your' cosmonauts. A three hour-long bitter debate ensues, with no resolution on crew selections. The final conclusions are only that the crews will consist of one pilot, and one engineer, and that Feoktistov will never be allowed to go into space.
1967 October 29 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Cosmos 188 launch scrubbed. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soyuz-B ('Baikal') launch was delayed to 30 October due to problems with the celestial navigation system aboard Cosmos 186. Later that day an N1-L3 review is held. The first launch vehicle will be completed in two to three weeks, but the launch complex will not be ready until next January. The first trials of the booster on the pad will begin in February-March 1968, with the first launch in the second half of the year.
1967 November 13 - .
- Kamanin's thoughts on first Saturn V launch. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Pashkov,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Apollo.
The first Saturn V and Surveyor 6 have been launched by the Americans. Kamanin catalogues why the Americans are beating them: bad organisation, on the parts of Ustinov, Smirnov, Pashkov, Malinovskiy, and Grechko; technical errors and an undisciplined approach to the fulfilment of government decrees concerning the Soyuz and N1 on the parts of Chief Designers Korolev and Mishin; lack of coordination between the institutes and design bureaux compared to the United States; and finally, the Americans are spending several times more money than has been dedicated to the Soviet space program.
1967 November 25 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N-1 mockup 1M1 rolled out to launch pad - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Stays on pad until 12 December for facilities checks. Photographed by US reconnsat on 11 December. 1M1 mockup scrapped in 1975..
1967 December 2 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Lunar Soviet. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Apollo.
A panel headed by Afanasyev and Mishin reviews the readiness of the N1. The mock-up booster is to complete pad compatibility tests by 30 March 1968. The first launch is still supposed to take place in the second half of 1968. The launch of the American Saturn V in November has reenergized the workers at Tyuratam. Kamanin is impressed - he was less sure of success, knowing all the problems of a project that requires the labour of thousands of persons. Afanasyev then turns to crew selection issues. The original resolution said that a cosmonaut was to be launched by an N1-L3 by April 1968. Mishin says he will be able to make two launches in the second half of 1968. It will take 18 to 24 months to train crews. But to date, Mishin still won't agree to crew selections, despite dozens of contacts and letters from Kamanin to Ustinov and Smirnov. There are still no simulators for the L3. Mishin wants to launch to the moon only engineers from TsKBEM. He is given an ultimatum: either the VVS will leave the space program, requiring Mishin to take over all training and crew responsibilities, or reach an agreement on crew composition in the next few days. Afansyev orders the commission to convene again in two to three days.
1967 December 3 - .
- L3 trainer controversy. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Mishin wants only his organisation to build L3 trainers, not the VVS. A whole series of previously-unmentioned trainers and simulators are mentioned, included the Turbolet, a V-10 helicopter with a lunar cabin, etc. For the L3 simulator Mishin wants to develop the specification documents without inputs from the VVS and have it built only to Mishin's requirements. This is rejected by Kamanin, who insists on a decision by 20 December, with issuance of the specifications for the L3 trainers with the input of VVS. If two simulators are buit, one must be installed at TsPK and the other at TsKBEM. If only one is built, it will have to be at TsPK.
1967 December 15 - .
- L3 issues - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Feoktistov. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. There is still no enabling resolution for the L3. Many meetings are held, discussing the L3, L3 trainers, and Feoktistov's assignment as a cosmonaut..
1967 December 27 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Mishin to remain in charge until first L3 launches. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Feoktistov,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Afanasyev holds meetings on the L3 lunar expedition program. Kamanin recites Mishin's failings. Afanasyev replies that he has talked to Ustinov about it, but Ustinov will leave the current management in charge until N1 flight tests begin. If they are unsuccessful, then Mishin alone will have to answer for it. Afansyev also assures Kamanin that although Feoktistov should be allowed to train for a space flight, he and Ustinov will make sure he never flies.
1968 January 17 - .
- Afanasyev inspects the TsPK. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
He is shown the Volga and L1 trainers, takes a seat in the trainer, and is given a simulated space flight. At the air base he reviews the aircraft and the TBK-60 altitude chamber. Throughout the tour, Mishin constantly wore a soft expression and used coarse language. Afanasyev was briefed on and recognised problems with development and delivery of the Salyut digital computer needed for the L1 guidance system. But he was not told that cooperation had broken down totally on the L3 simulator development and crew selection.
1968 January 23 - .
- Three-launch Soviet lunar expedition pitched - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Chelomei,
Glushko,
Grechko, Andrei,
Keldysh,
Kuznetsov,
Mishin,
Nadiradze,
Pilyugin,
Tolubko,
Ustinov,
Yangel.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: L3M-1970,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The 'big' Soviet of Chief Designers meets and the three-launch landing concept developed a month earlier is presented in detail. Pilyugin pointed out that this was a typical contradiction. Mishin had just made a presentation to the expert commission justifying that the one-launch scheme was safe and reliable. Now they wanted to put forward a new scheme because the one-launch scheme was unsafe and unfeasible. Additional Details: here....
1968 January 28 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Sergei Osipovich Okhapkin put in charge of the N1 at TsKBEM - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin, Okhapkin. Program: Lunar L3. This decision led to one of Mishin's famous 'illnesses', putting him out of action for a period..
1968 February 3 - .
- Ye-8-5 robot lunar soil return plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Luna,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
VVS Party Conference. It is clear to Kamanin that there is no support from the Air Force for manned spaceflight. Kamanin only heard yesterday that Babakin is working on an automatic soil sample return spacecraft. He will need a minimum of two to three years to complete it. Kamanin complained that it would interfere with plans for the L1 program. An uninterrupted series of flights will be needed to complete the L1 spacecraft qualification, and the Ye-8, using the same booster, could be an interference in achieving that goal.
1968 February 8 - .
- VVS officers inspect TsPK. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Popovich.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS.
It is currently organised in three cosmonaut detachments: Nikolayev commands the first detachment, which is training for L3, L1, and Soyuz fiights. Popovich commands the second, training for Almaz and 7K-VI military space missions. Nikeryasov commands the third, which is the 'observer' detachment.
1968 March 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Originally planned N-1 first launch - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. Slipped to May..
1968 March 7 - .
- Soyuz parachute recertification holding up all manned programs. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Tkachev.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
Mishin certified to MAP on 5 March that the Soyuz parachute system development is complete, but Tkachayev has dissented, saying that the system was unreliable and overweight (this from the same chief designer that certified the previous design as having an 0.999 reliability!). The parachute trials will not be finished until May - meaning there will be no manned Soyuz launch in April. This problem is holding up the L1, L3, and Almaz projects as well.
1968 March 13 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- L3 project plan. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Titov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Titov is going to Italy, Feoktistov to Hungary. The 30 month program for the L3 lunar landing is settled. The cosmonauts already began training in January. The first LK lunar lander will be tested in low earth orbit in the second half of 1969. The first Soviet manned lunar landing cannot take place any earlier than 1970-1971. The resolution had set the date as 1967-1968, but the N1 and L3 will not be ready in time. The L3 is still conceptual, a purely paper spacecraft. The first N1 was to have been moved to the pad by March of this year, but it won't even make that milestone by May.
1968 March 14 - .
- Soviets review American plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Apollo,
Lunar L3.
Six Apollo spacecraft are to be flown into earth orbit in 1968, four unmanned and two manned. Five flights are planned for 1969, including the first landing on the moon. Beyond this is the Apollo Applications Program. Expenditures for this are planned as $179 million in 1968 and $435 million in 1969, leading to the first orbital laboratory in 1970.
1968 March 20 - .
- Lunar spacesuit review. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Severin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Krechet,
LK,
Luna Ye-8,
Orlan.
Meeting with Gay Ilyich Severin. Two spacesuits are being developed for the L3 program: the Krechet-94 and Orlan. Both have been in development for two years. The Krechet-94 will allow six hours of lunar surface activity, the Orlan, 2.5 hours. Both weigh about 90 kg. There are consumables for a total of 52 hours of life support in the LK and the LT Lunar Cart. Kamanin feels the suits are too heavy, due to Mishin's demand for a 5 km range from the LK over a three day traverse with the LT. Severin could have instead developed the spacesuit used by Leonov to have a four hour autonomous operation, but Mishin insisted on doubling of the capacity.
1968 April 4 - .
- Soviet view on Saturn V - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Apollo.
The second successful launch of the Saturn V stunned the Soviet engineers. They could not believe the variety and volume of data telemetered back in real-time to the launch centre. They viewed with jealousy the launch room set-up at Cape Canaveral - where each engineering speciality could sit in their own comfortable chair, viewing data as the booster ascended on a computer screen.
1968 April 7 - . 10:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC1. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Molniya 8K78M.
- Luna 14 - .
Payload: E-6LS s/n 113. Mass: 1,700 kg (3,700 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Luna E-6.
Spacecraft: Luna E-6LS.
USAF Sat Cat: 3178 . COSPAR: 1968-027A.
Lunar Orbiter; studied lunar gravitational field, Earth-Moon gravitational relationship, and conducted further scientific experiments in circumlunar space. Not revealed until years later was that the E-6LS was primarily intended to test tracking and communications networks for the Soviet manned lunar program. The Luna 14 spacecraft entered a 140 x 870 km x 42 degree lunar orbit on April 10, 1966. The spacecraft instrumentation was similar to that of Luna 10 and provided data for studies of the interaction of the earth and lunar masses, the lunar gravitational field, the propagation and stability of radio communications to the spacecraft at different orbital positions, solar charged particles and cosmic rays, and the motion of the Moon. This flight was the final flight of the second generation of the Luna series.
1968 April 18 - .
1968 April 21 - .
- L1 on schedule; N1 in trouble. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
This was a reserve day in the L1 countdown, in case of problems in preparation. However all is on schedule for the launch. The same cannot be said for the N1. There are many delays. Mishin promised the first N1 rollout in the first half of March, but it is still in the assembly building, with no end in sight of preparations. The weather at the cosmodrome is -5 deg at night, clear pleasant days. The Hotel Kosmonavt was finished on 15 April. Although it has all of its furniture, it was not completely painted before the furniture was moved in!
1968 May 7 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 booster 4L erected at launch complex 110 east - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
A September 1968 flight test was planned. However the first stage LOX tank developed hairline cracks during ground tests. 4L was removed from the pad in June 1968. The first stage was cannibalized; the upper stages were incorporated into the 1M1 mockup for further training of the launch crews.
1968 June 23 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- First test of N1 stages - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev,
Kuznetsov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Construction of the test facilities at Zagorsk for the N1 were directed by Tabakov's NII-229. First static test of the EU-15 test article of the N1's 1200 tonne thrust Block B second stage began on 23 June 1968. Test of the EU-16 Block V third stage began in early 1969, with three trials tests completed. But for the Block A first stage, only single engine tests were undertaken at Kuznetsov's OKB-236. Additional Details: here....
1968 June 30 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 ground vehicle 1M1 moved to launch pad 110 east - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. While the next N1, 3L was being built, the 1M1 was moved back to the pad for further ground tests and launch crew training. It remained there until the end of September..
1968 July 10 - .
- L3 recovery controversy. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Mishin,
Ryabikov,
Zakharov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Marshal Zakharov has consulted with Ryabikov at Gosplan on what commitments Grechko has made from Ministry of Defence funds for L3 recovery forces. Gosplan advised him that 800 million roubles and 21,000 staff were committed, but the justification for these amounts were not methodically developed. Mishin is now saying that hundreds, not thousands of cadres will be required, see he can set the return capsule down in within the confines of the cosmodrome.
1968 July 12 - .
- L3 recovery controversy. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
VVS has been charged with arranging for ocean recovery of the L3 capsule in case it splashes down in the Indian Ocean since 1966. TsNII-30 did the research work under project 'Ellips', resulting in the recommendation that the VVS and VMF jointly develop the air and naval forces to recover the capsule at sea, at a cost of 800 million roubles. The Ellips concept requires that the L3 capsule be equipped with radio beacons and dye markers. Despite knowing this for two years, Mishin has done nothing to implement these features into the spacecraft.
1968 July 29 - .
- Reduced L3 recovery forces. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Smirnov,
Vershinin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Vershinin looks bad after his surgery. His loss would be a blow for Kamanin's cause - Vershinin was steadfast against the unobjective positions of Mishin and Smirnov. Vershinin had just sent yet another letter about the procurement of the 16 m centrifuge for the TsPK. This is a six-year long story. The VVS has been trying to procure this essential piece of cosmonaut training equipment since 1962, but it still has not been delivered. Vershinin also has issued a letter on the L3 recovery force issue. He points out that the resolution of the Central Committee ordered the expenditure of 600 million roubles and the commitment of 9,000 men for recovery services. Another 400 million roubles and 12,000 men were earmarked by the Rocket Forces. Despite this huge commitment, Mishin now says he doesn't need any of them, that he can bring his L1 and L3 spacecraft to precision landings within the confines of the cosmodrome, eliminating the need for any Indian Ocean recoveries. This optimism is not accepted, but it is agreed the total requirement can be reduced to 400 million roubles and 7,000 men, through use of lighter recovery ships of the Leninskiy Komsomol class, and the use of three airborne relay stations instead of nine.
1968 August 2 - .
- Reduced L3 recovery forces accepted. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Gagarin, Keldysh, Ryabikov, Vershinin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. Vershinin, Afanasyev, Keldysh, and Ryabikov accept the reduced recovery forces estimate. Meanwhile a letter from the cosmonauts disputes the Gagarin crash investigation finding ('pilot error resulting in an abrupt manoeuvre')..
1968 September 10 - .
- L1 preparations. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L1, Lunar L3. 23 VVS staff fly to the cosmodrome aboard an An-24 for the impending L1 launch. The State Commission will meet there on 13 September to consider the L1 preparations, and on 17 September, L3 preparations..
1968 September 19 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Bulldozer delays N1 launch by two months - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
The Zond 5 situation remains the same. The star trackers quit working, and the use of the back-up systems has not been completely successful. However the spacecraft is on course for a ballistic re-entry. At Area 112 Afanasyev heads the State Commission for the N1-L3 first launch. There are problems with the launch complex. The main electrical cable to the launch complex was accidentally bulldozed. The back-up cables were buried only 30 cm from the main line and both were destroyed. The cables were poorly marked. It will take 50 days to repair the damage. This will delay first launch until the second half of November 1968, and the second launch to February 1969. Most likely the first launch cannot take place until next year.
1968 October 24 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 - lost opportunity in 1961 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Glushko,
Isayev,
Korolev,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Glushko has a private conversation with Isayev at the N1 MIK during the Soyuz 3 launch preparations. Glushko revealed to Isayev that in 1961 he had offered Korolev a compromise - if Korolev would use the same 'packet' scheme for the N1 that he had used on the R-7, so that the individual engine modules could be individually tested on the ground before flight, Glushko would give up his insistence on the use of storable propellants. However, after checking with Mishin, Korolev would not compromise. Additional Details: here....
1968 November 15 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 1M1 mockup erected on pad with L1S payload - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1. The N1 mockup was again erected on the pad, in order to conduct tests of the L1S payload in advance of the availability of the 3L launch vehicle..
1968 November 21 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- The N1-L3 state commission meets. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The previous launch date of 25 November has been pushed back to January 1969. The N1 has completed a good cycle of ground tests, but work on the L3 has not even begun. There is no news when it will be ready. The L3 plan called for the first article to be ready in March 1968. 20 cosmonauts from the L1 and Soyuz groups were to have trained on the spacecraft. But MOM never issued the implementation plan to the industrial enterprises to begin work on the spacecraft.
1968 November 26 - .
- L1 spacecraft too unsafe to beat Apollo 8 to moon - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Apollo 8.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The primary issue in the next 3 to 4 months will be how to answer the impending American Apollo 8 flight. The Soviet Union needs to fly a manned L1 in the 8 to 12 December lunar launch window. But the spacecraft is still considered too unsafe for manned flight. The Apollo 8 mission is risky, but the US can't fly the Apollo spacecraft to the moon unmanned...
Beregovoi is to be named commander of the Gagarin Centre. Gagarin himself was being prepared for the job, but his death in a plane crash ended that plan. The other cosmonauts are not ready for command. The centre desperately needs the two planned L3 trainers: the TBK-150 and Volchuk. Kamanin has been jerked around for four months on the issue. Even if the simulators were delivered, he would still need 2 million roubles and an additional 30 to 40 staff to install and operate them.
1968 December 12 - . Launch Vehicle: Spiral 50-50.
- Kamanin catalogues the reasons the Soviet Union is losing the moon race - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Biryuzov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
- Fighting between the VVS and its 'enemies' (Ustinov etc.)
- No single state organisation is responsible for civilian spaceflight.
- Various entities are responsible for various aspects of military spaceflight (RSVN, VMF, General Staff, VVS). Kamanin notes that the state has poured 10 billion roubles into the N1 without visible effect. He believes reusable systems are needed to reduce the cost of spaceflight. The death of General Biryuzov in a plane crash meant that the Soviet Union lost a strong supporter of a robust military space program.
- Kamanin believes the VVS should be in charge of piloted spacecraft, not the RVSN.
- Furthermore the entire design approach to manned spacecraft is incorrect -- what is needed is piloted spacecraft, not cosmonauts flying as passengers in automated spacecraft. The result of the automated philosophy was that the Soyuz was not man-rated until 1968. While the qualification process was going on, the American Gemini flew ten times. The Apollo-Saturn V has flown twice, while the L3 was still just a mock-up. In effect, the Soviet Union gave the Americans a two to three year lead, allowing them to beat the Russians.
1968 December 16 - .
- Lunar Soviet. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Severin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Krechet,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
In a four-hour meeting, a number of issues are dealt with. First point was military control of the KIK control centre for lunar missions. A civilian mission control centre is requested. Next, the issue of recovery of L1 and L3 capsules in the Indian Ocean. The re-entry corridor within which landings might occur is 6000 km long and 100 km wide, stretching from Antarctica to India. To cover it will require 20 naval vessels, each with a helicopter, and 10 An-22 or Tu-95 long-range maritime reconnaissance and relay aircraft. Total cost: 600 million roubles. As Kamanin sees it, all this is due to Mishin's inability to design spacecraft capable of precision landing that also incorporates the landing and recovery aids requested by the VVS. Kamanin notes in his diary violent criticism of Mishin's disregard for the safety of the cosmonaut crews, development of crew-associated items at the last minute, unrealistic schedules and expectations, etc. etc. Severin reports that the lunar space suit he is designing will support the cosmonaut for three days, during walks extending 5 km. To do this requires a bulky suit weighing 100 kg. Kamanin disagrees, saying what is needed is to develop a simple and safe approach for the first landing, with a minimum programme for the cosmonaut - not the fantastic schemes of Mishin.
1968 December 23 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet crisis meeting mulls response to Apollo 8 - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin, Nadiradze, Pilyugin, Ustinov, Yangel. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Apollo 8. Spacecraft: LK, Soyuz 7K-LOK. Following the success of Apollo 8, Ustinov calls a crisis meeting at the Ministry of Defence. His question - how to reply to the American's success?. Additional Details: here....
1968 December 25 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- L3 lunar lander behind schedule - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Keldysh,
Malinovskiy,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Apollo,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Soyuz 7K-L1 mission 1.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
The L3 spacecraft still does not even exist in mock-up form. All of the leadership are responsible for this farce - Malinovskiy, Smirnov, Ustinov, Brezhnev. There is no single manager of the space program. The VPK and Central Committee operate on rumours. The Interagency Soviet headed by Keldysh was supposed to coordinate space activities, but in fact has not functioned in the last four to five years. There is no single military space organisation in the Ministry of Defence. Piloted flight tests are being run by former artillery officers in the RSVN. Various organizations of MAP and VVS coordinate ground and flight tests poorly. These are the reasons for the failure of the Soviet Union in space. Today in the Central Committee Ustinov asked - 'how to answer Apollo 8?' Ustinov relies on Keldysh, Keldysh supports Mishin, and Mishin is unfit for his duties. But Mishin is not even there! The program they come up with: In January 1969, 2 Venera probes will be launched, two manned Soyuz missions, and L1 s/n 13 will be sent around the moon. In February the first N1 will be launched. By the end of March the first Ye-8 robot will land on the moon and return lunar soil to the earth. This meeting is followed by a session of the VPK at 16:00. The crews are named for the Soyuz 4 and 5 flights.
1968 December 25 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviets consider lunar landing alternatives - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Pilyugin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: L3M-1970,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
A 'small Soviet' of designers was held to review whether to continue pursuing the N1 launch vehicle or not. Although a first manned lunar landing was not achievable, the N1 could still be used to establish a lunar base by the beginning of the 21st Century. Additional Details: here....
1968 December 26 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 launch vehicle 3L erected on launch pad - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. The 3L vehicle, without its payload (which was on the 1M1 mockup), is erected on the pad to test engine systems..
1968 December 30 - .
- How to beat the Americans to the lunar landing - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Chelomei,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Okhapkin,
Pilyugin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Luna.
Spacecraft: LK-1,
Luna Ye-8-5,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
Meeting of the VPK Military-Industrial Commission to discuss how to beat the Americans to the lunar landing Ustinov called the meeting to order. Mishin was 'sick' again -- Okhapkin represented TsKBEM and gave a summary of the programme to that date:
- The project had only been authorised on 3 August 1964. It consisted of two parts, circumlunar flights using Chelomei's UR-500K booster and LK-1 spacecraft, and a lunar landing using Korolev's N1 booster and L3 spacecraft.
- On 25 October 1965 the programme was redirected. Military support was ordered and the decision was made to cancel Chelomei's LK-1 spacecraft and instead use the L1 version of Korolev's Soyuz for the circumlunar flights. This was ordered by the resolution 'On organisation of construction units for support of rocket-space systems for the lunar flyby'. That resolution ordered a manned L1 flight by the end of 1967 or early 1968.
- The program actually took three years to implement rather than the two planned. Nine launches of he L1 had been made since March 1967, but it had not been possible to man-rate the UR-500K/L1 booster/spacecraft combination due to failures in both the launch vehicle and spacecraft. Flight trials of the N1 booster had not even begun yet.
Keldysh proposed that further work on the L1 be abandoned, and Proton boosters instead be used to launch the Ye-8-5 lunar soil return robot spacecraft being developed by Babakin. Babakin had been accelerating this programme since the beginning of 1968 with the support of Keldysh, even though it would only return around 100 g of lunar soil, versus the tens of kilograms the Apollo manned flights would return. However it now offered an interesting possibility - he proposed obtaining lunar soil and returning it to earth before an American manned landing. The government's organs of mass communication would say that the Soviet Union's lunar program only consisted of robot probes, emphasising that his was much safer and that Russia would never risk it's citizen's lives for mere political sensation. Additional Details: here....
1968 December 31 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
1969 January 6 - .
- Mishin a no-show. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Soyuz, Lunar L3, Lunar L1. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. There is much criticism of Mishin and Keldysh for not attending launches any longer. The opinion is that they are afraid to show their faces..
1969 January 9 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- State Commission for the first N1 launch - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kurushin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A.
The State Commission for the first N1 launch, headed by Afanasyev, convenes at Area 12 of Baikonur. All of the Chief Designers and top generals of the VVS are in attendance. Many defects are identified in the review, but there seem to be no show-stoppers. Payload integration with the booster is to begin 13 January and launch by 18 February. Then Baikonur commander General Kurushin drops a bombshell - he declares he is not prepared to attempt to launch this 'unready' rocket. Much argument and discussion ensues. Finally Afanasyev asks that the issues raised be reviewed, in preparation for the next commission meeting on 11 January.
1969 January 11 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 state commission meeting. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei. Program: Lunar L3, Lunar L1. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A. The issues raised with the N1 have been cleared up and settled. Afanasyev approves the schedule leading to an 18 February first launch of the N1..
1969 January 13 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 payload preparation and fuelling are underway. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Four N1 launches are planned in 1969: The launch of 3L will be followed by 5L, 6L, and 7L in April, June, and November. But this is probably much too optimistic due to delays in delivery of critical systems needed to complete the boosters. But at least 4L, 5L, and 6L should be launched this year.
1969 January 22 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soyuz 4/5 celebrations - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Lunar L3, Soyuz. Flight: Soyuz 4, Soyuz 4/5, Soyuz 5. TsKBEM closed down for the day, due to celebrations at Kaliningrad and at the Kremlin with the four cosmonauts from the Soyuz 4 /5 mission. Meanwhile, work at Tyuratam preparing the N1 for its first flight continued..
1969 January 23 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 stormclouds - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Mishin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft: LK, Soyuz 7K-LOK. In the morning Mishin advised his staff of comments made by Afanasyev at the Kremlin reception the previous evening. He had called a Soviet of the chief designers for 27 January to discuss the fate of the N1 programme..
1969 January 25 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Apollo vs Ye-8-5 - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Luna,
Apollo.
Flight: Apollo 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
America is preparing Apollo 9 for flight, and Kamanin muses that the Soviet reply will be the N1 and Ye-8-5, neither of which is proven or reliable. The Soviet Union would have a better chance of sending a manned L1 on a flight around the moon during the first quarter of 1969. Meanwhile Mishin's bureau has a new L3M lunar lander on the drawing boards. This will land 4 to 5 men on the moon, but require two N1 or seven UR-500K launches to assemble in orbit.
1969 January 27 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet of Chief Designers considers N1 cancellation - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Barmin,
Chelomei,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Serbin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Aelita satellite,
LK,
Mars 5NM,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Afanasyev and Keldysh chaired the unusual and extraordinary Soviet of the chief designers. Mishin opened with an emotional plea not to cancel the N1. He justified the delays and failures by saying that he had not been given sufficient budget to conduct necessary experimental and qualification tests of systems before flight. Additional Details: here....
1969 January 29 - .
- Lunar systems status - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Severin. Program: Lunar L3, Lunar L1. Spacecraft: Berkut, Krechet, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-LOK, Soyuz 7K-OK, Yastreb. Review of spacesuit development at Zvezda Factory with Gay Severin. The specifications for the moon suit are 10 hours life, 80 kg mass, able to handle a heat load of 500 kcal/hour. But this load is insufficient for heavy work.. Additional Details: here....
1969 January 30 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1/Ye-8-5 launch preparations - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin, Tyulin. Program: Lunar L3, Luna. Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8. Mishin agrees with Tyulin that he will fly to Tyuratam on 3 February to supervise launch of the Ye-8 on 18 February and the first N1 on 21 February. .
1969 January 31 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Preparations for the first N1 launch. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Mishin was staying in Korolev's cottage at the launch centre. The other chief designers were staying at the cosmodrome's hotel, while the technicians and workers were at the new apartments at Area 113. Afanasyev headed the 'Little Soviet', the State Commission, that would oversee the launch. The commission met in the conference hall in the huge horizontal assembly building for the N1 at Area 112. The commission gave the approval, and the first flight-ready N1 was rolled out of its assembly building over the 4 km of track to the launch pad. The huge dimensions of the booster had required a new method of building the booster at the launch site. Simulators were able to check all of he booster functions up to the point of engine ignition.
1969 February 3 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1/Ye-8 preparations - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Luna.
Spacecraft: LK,
Luna Ye-8.
Kamanin arrives at Tyuratam at 15:30 aboard an An-24. The State Commission for the first Ye-8 robot lunar rover mission is chaired by Tyulin at Area 31. The spacecraft will make a soft landing on the moon, deploy a mobile lunar rover that can traverse slopes up to 30 degrees. The rover will find a position that is clear of obstacles for the first Soviet manned lunar landing. It will then park there, and provide a landing beacon for the LK manned lander. The spacecraft will have a mass of 1700 kg in lunar orbit. Launch is set for 19-20 February.
1969 February 6 - .
- Volynov grounded - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Leonov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Meetings are held at the cosmonaut centre to plan for the big visit to the base by Marshal Grechko. N F Kuznetsov briefs plans for the centre with the general staff. Kamanin discusses the situation with Leonov. Leonov notes the saying from Lenin on a banner at the centre: "Know how to work!" Unfortunately, they have left out the second part: "Don't hurry!" Leonov states he is not assigning Volynov to any future flights.
1969 February 9 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Final meeting held to review the N1 before the launch. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Krylov,
Kurushin,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Marshal Krylov, Commander of the Strategic Rocket Forces, headed the meeting. The conference room was mobbed - many unfamiliar faces were in attendance - everyone wanted to witness the historic event. General Kurushin, Commander of Baikonur, stated that he was against proceeding with the launch, due to the many unresolved technical issues, unless he could somehow be persuaded otherwise. He pointed out that Mishin had made a large number of changes to the N1 to increase its payload. However these at the same time negatively impacted the booster's reliability. Additional Details: here....
1969 February 11 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Military space objectives - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Luna.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8.
The Ye-8 and N1 are on schedule for their respective launches. Kamanin discusses the cosmonaut training curriculum with Kerimov. No one has ever defined what it is cosmonauts are actually supposed to do in space. No one really knows what their purpose is --- not Keldysh, not Mishin, not Smirnov, not Ustinov. Kerimov agrees to put together a state commission to define the role of man in space and draw up plans for future space missions.
1969 February 21 - . 09:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: First stage failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 3L launch - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1S s/n 3. Mass: 6,900 kg (15,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Dorofeyev,
Kirillov,
Mishin.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A.
Decay Date: 1969-02-21 . Apogee: 30 km (18 mi).
N-1 serial number 3L was the first N-1 launched. The vehicle ran into trouble immediately at lift-off. A fire developed in the tail compartment. The engine monitoring system detected the fire, but then gave an incorrect signal, shutting down all engines at 68.7 seconds into the flight. British intelligence detected the launch attempt, but the CIA's technical means for some reason missed it and they denied for years that it had ever occurred. In retrospect the launch team at Baikonur pointed to a grave mistake - at the christening of the first N1, the champagne bottle broke against the crawler-transporter rather than the hull of the rocket. After the 3L failure everyone knew there was no chance at all of beating the Americans to the moon. Additional Details: here....
1969 March 3 - .
- Soviet/Chinese troops clash on Ussuri River - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Military on full alert; Tyuratam preempted by military through June.
1969 March 10 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Apollo 9 points to US win - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Apollo 9. Kamanin notes the successful Apollo 9 mission. In his opinion Americans will land on the moon by the end of the year. The Soviet program is 3 to 4 years behind..
1969 March 20 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet of military officers meets to review manned space plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Beregovoi.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Spiral OS.
A 50 minute presentation is given on space plans. Russia plans to fly no less than six different types of manned spacecraft in 1969-1970 - the Soyuz, L1, L3, Almaz, Soyuz VI, and Spiral. This will result in a decisive answer to the American Apollo programme within two to three years. No N1 launch with the complete L3 lunar landing spacecraft is planned until 1970. Approval is sought for the VVS to buy 10 Soyuz spacecraft for continued manned military flights in low earth orbit. Otherwise between the second half of 1970 and during all of 1971 there will be no spacecraft available for manned flights Additional Details: here....
1969 March 29 - .
- Apollo films on view in Soviet Union - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Apollo 8, Apollo 9. VVS General Staff views US documentaries on Apollo 8 and 9, and footage from the 1968 Turin Air Show..
1969 May 8 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Russian only hope is major Apollo failure - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Mishin,
Pashkov,
Serbin,
Smirnov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Apollo 11.
Mishin, Keldysh, Pashkov, Smirnov, and Serbin meet. Some of them are still expecting a big failure in the Apollo programme that will set the Americans back and still make it possible for Russia to be first on the moon. These are black days in the Soviet programme - it is clear to Kamanin that the Americans will successfully land on the moon in July, and the Russians are 2 to 3 years behind.
1969 May 10 - .
- Military space research plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kutakhov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Spiral OS.
Kamanin makes a speech to the VVS Soviet, setting forth again plans for military research in space. His presentation shows how far the USSR is behind the Americans, and the need to regain the lead. He again proposes 10 to 12 military Soyuz flights beginning in the first quarter 1970. This will fill the gap until Soyuz VI and Almaz will begin flying in 1972. Kutakhov is categorically against these Soyuz flights but, under pressure from others, still agrees to form a commission to study the matter. Reference is made to a Ministry of Defence decree of 7 January 1969.
1969 May 16 - .
- Myth 'we were never in the moon race' disseminated by the Soviet Union - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Babakin,
Keldysh.
Program: Luna,
Apollo,
Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Flight: Apollo 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Luna Ye-8.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5.
Keldysh first revealed the new 'party line' at a press conference on the semi-successful Venera 5 landing on Venus. When asked about Soviet lunar plans, he revealed that Russia would only use robot probes, that it wouldn't risk men's lives in such an endeavour. At the same time Babakin was hard at work finishing the first Ye-8-5 robot lunar soil return spacecraft, to be launched before Apollo 11.
1969 May 24 - .
- Way clear for Apollo 11 - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3, Lunar L1. Flight: Apollo 10, Apollo 11. Kamanin writes that Apollo 10 has completed its lunar mission successfully. The way is clear for the final step in American winning the moon race..
1969 May 29 - .
- N1 State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Barmin,
Bushuyev,
Chelomei,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Nadiradze,
Okhapkin,
Pashkov,
Smirnov,
Tyulin,
Yangel.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Aelita satellite,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1A,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Over two days a State Commission reviewed all of the conclusions of the N1 3L failure investigation and the readiness of N1 5L for flight. All of the fixes identified to remedy the 3L failure had been incorporated into 5L. It was felt that the behaviour of the systems in fire conditions were understood and appropriate measures had been taken. The wiring had been rerouted and insulated. Barmin wanted the system not to shut down any engines under any conditions during the first 15-20 seconds of flight, so that the booster would clear the pad and there would be no risk of the pad's destruction. But there was no time to develop such measures before the 5L launch; it could only be added in vehicle 6L. Additional Details: here....
1969 June 1 - .
- Original planned date for first LK test - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Moon. Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: LK. Original planned date for first test of LK in earth orbit..
1969 June 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet lunar plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-L1A.
Despite having no stand testing of the N1 first stage, Mishin still expected the first Soviet lunar landing to take place by the end of 1970. He began pushing Kamanin to assign L3 flight crews for the missions. Mishin's staff did not believe he had the necessary discipline to pull it off, but supported him out of solidarity. Mishin accepted the resolution to use 5L to conduct a lunar flyby. The payload consisted of the L3-S. This spacecraft used the new unified guidance system developed for the LOK by NIIAP, replacing the 7K-L1 guidance system, and functional rocket stages G and D, plus the payload bay of the LK. The only functional spacecraft system was the SAS abort tower. Although unthinkable in Korolev's time, lunar launch window constraints meant the launch had to be made at precisely 23:18 on 3 June 1969.
1969 June 10 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Revised Soviet lunar plans - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Luna.
Spacecraft: LK,
Luna Ye-8,
Luna Ye-8-5,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The VPK Military-Industrial Commission issues a decree on the schedule for the rest of 1969. There are to be five launches of Ye-8-5 lunar soil return robots, on 14 June, 13 and 28 July, 25 August, and 25 September. There are to be two launches of Ye-8 Lunokhod robot rovers on 22 October and 21 November. Further manned L1 flights are cancelled. There are no plans made for the L3 since the N1 is not ready.
1969 June 13 - .
- Leonov in trouble - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Leonov, Shatalov, Yeliseyev. Program: Lunar L3, Luna. Flight: Apollo 9, Soyuz 4/5. Leonov interviewed by Japanese reporters. He tells them that both manned and unmanned lunar spacecraft are in preparation and that lunar rocks will be returned by Soviet spacecraft by March 1970.. Additional Details: here....
1969 June 18 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Mishin and Kamanin select candidates for the lunar landing mission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Bykovsky,
Khrunov,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Mishin,
Patsayev,
Rukavishnikov,
Voronov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Lunar L3.
They are Leonov, Bykovsky, Voronov, Khrunov, Yeliseyev, Makarov, Rukavishnikov, and Patsayev. Mishin expects a landing by the end of 1970; Kamanin thinks this is impossible. Afanasyev and Mishin propose modernisation of the N1, but this will take three to four years, by which time the booster will be essentially obsolete. The second launch of the N1 is set for 3 July. It would be a welcome miracle if it flew, but it still would not be enough to erase the American lead in the moon race.
1969 June 20 - .
- Kamanin meets with Chief of Ministry of Defence General Staff Zakharov. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Zakharov. Program: Lunar L3. Zakharov is violently opposed to the Ministry of Defence spending a single kopeck on the exploration of space. It all must be paid for by the Academy of Sciences or be consigned to the waste bin..
1969 July 3 - . 20:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110R. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: First stage failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 5L launch - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1S s/n 5 / Dummy LK. Mass: 6,900 kg (15,200 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Apollo 11.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1A.
Decay Date: 1969-07-03 .
N-1 serial number 5L began to fail at 0.25 second after liftoff when the oxidizer pump of engine number 8 ingested a slag fragment and exploded. A fire ensued as the vehicle climbed past the top of the tower. Engines were shutdown until the acceleration dropped below 1 G; then the vehicle began to fall back to the pad at a 45 degree angle. The escape tower fired at the top of the brief trajectory, taking the L1S dummy descent module away from the pad. Upon impact of the base of the N1 with the pad, the vehicle exploded, destroying launch pad 110 east, which would take over 18 months to repair. This was the end of a slight Soviet hope of upstaging the US Apollo 11. Additional Details: here....
1969 July 21 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet engineers view moonwalk - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Tyulin,
von Braun.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Apollo 11.
At the same time the reconstruction schedule for the destroyed N1 launch complex was being laid out, Apollo 11 landed on the moon and the Americans won the moon race. Mishin's engineers watched the live television at TsNIIMASH. Afterwards Tyulin declared, "this is all Chertok's fault. In 1945 he should have thought of stealing Von Braun from the Americans - but he never considered that solution". "True", Chertok replied, "my adventure with Vasiliy Kharchev didn't turn out too well".
1969 July 22 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet post-mortems after Apollo 11 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Glushko,
Keldysh,
Kuznetsov,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Two sequential N1 failures could not just be blamed on the poor reliability of the first stage. It was apparent that, compared to the Americans, both the management and the development practices of the Soviet space programme were inferior to the Americans. Politically there was no consensus within the Soviet state of the need for a space programme. Glushko and Ustinov waged a perpetual struggle against Afanasyev, Keldysh, and Mishin. RVSN Commander Kirillov wrote a letter to Smirnov on behalf of Afanasyev on the root causes of the failures. His faction believed these were the continued use of artillery/military rocket development practices for large, complex systems. These outdated practices required 20 to 60 flight tests to achieve reliability before a rocket could be put into production. Additional Details: here....
1969 August 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- VPK hearing on N1 improvements - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Kuznetsov,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
The VPK Military-Industrial Commission and the Central Committee of he Party discussed the matter of delaying further N1 tests until completely redesigned engines became available. Back came the ritual reply -- a Soviet manned lunar landing must be achieved by the 100th Anniversary of the Birth of Lenin (April 22, 1970). On that date a Soviet man would plant the Red Banner and unveil a bust of Lenin on the lunar surface. Unlike the US President, Brezhnev would never get to see a manned launch to the moon. Additional Details: here....
1969 August 1 - . LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- The DOS Conspiracy begins - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Almaz,
Salyut.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
With the collapse of the work on the N1, the whole reason for Mishin's design bureau's existence simply vanished in the air. A new high-priority project was needed. Korolev had begun development of a Multi-Module Space Base (MKBS) before 1966. However MKBS was to be launched by the N1; as long as this was not available, there would be no MKBS. Almaz on the other hand did not require a new launch vehicle, although the UR-500 was in a period of intense 'baby sickness'. So while TsKBEM was in a period of analysis and instability, Chelomei's Reutov and Fili facilities were building space stations for the Ministry of Defence.
On one of these August 1969 days, three of Chelomei's TsKBM engineers came to the office of Mishin's deputy, Chertok, with a plan to get a space station orbited before the American Skylab. They wanted a collaboration between the two competing design bureaux. Their plan was to take an Almaz spaceframe, install Soyuz systems, add a new docking tunnel with a hatch to reach the interior, and presto - a space station was finished. Tentative discussions with potential allies within Chelomei's design bureau found support there as well. The DOS 'long-duration orbiting station' was the result of this 'conspiracy'.
1969 September 1 - .
- Kamanin lists the reasons the Soviets have lost the moon race. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Feoktistov,
Gagarin,
Keldysh,
Korolev,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Apollo,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Americans were able to pull equal in the race during their Gemini programme, then ahead with Apollo. The Soviet Union is now four to five years behind. Kamanin's accounting:
- No qualified Soviet government leadership in space research (Ustinov and Smirnov are a parody of proper management). They operate without rhyme or reason or plan. There is no single direction, no disciplined execution when a decision is finally made
- Korolev, Keldysh, Mishin, and Feoktistov are all dedicated to automated spacecraft - 'over-automation'
- Korolev and MIshin's rejection of Glushko's engines, and the leadership's rejection of the UR-700 as an alternative
- Ustinov and Smirnov's cancellation of the 18 day Voskhod 3 mission, even though the crews had been trained, and the associated pressure on development of Soyuz. This resulted in Soyuz being flown before it was mature, resulting in the death of Komarov and an 18 month delay in manned flights
- Death of Korolev and Gagarin both badly affected morale
- Making Mishin head of TsKBEM was a huge mistake. Mishin cannot cope with the huge number of space and missile projects assigned to his bureau
1969 September 3 - .
- L3 Trainer and Female Cosmonauts - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kuznetsova,
Pashkov,
Ponomaryova,
Smirnov,
Solovyova,
Tereshkova,
Ustinov,
Yerkina.
Program: Lunar L3,
Soyuz.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Meeting of Kamanin with S G Donevskiy. The L3 trainer will not be finished until May 1970 - and the current schedule for the first manned L3 launch is December 1970! But in any case Kamanin assesses the latter date as unrealistic -- there is no rocket or spacecraft in being yet. Later in the day Efimov, Moroz, and Kamanin meet with the female cosmonauts - Ponomaryova, Solovyova, Yerkina, and Kuznetsova. They advise them that despite the letter to the Central Committee asking for an all-female Soyuz flight, it has been rejected. Ustinov, Smirnov, and Pashkov are all opposed to the idea, as are MOM, MAP, AN, and VVS. Kamanin believes the whole female cosmonaut concept was a mistake. Flying Tereshkova in the first place started the whole thing, but now there is no follow-up.
1969 September 18 - .
- Approval is given for proceeding with the Soyuz 6-7-8 flights - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Beregovoi,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Nikolayev,
Smirnov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1.
However the board makes a big fuss over Kamanin having trained only four back-up cosmonauts to support eight prime-crew cosmonauts. A follow-up meeting is held with Smirnov and Afanasyev at 19:15, where Kamanin's training is denounced as a big failure. Nevertheless at 22:00 the word comes from the Kremlin to proceed with the missions. Kamanin points out that simultaneously with this mission he had cosmonauts in training for Soyuz s/n 17, 18, 19, 20 (Kontakt missions) and L1 circumlunar fights. Kuznetsov, Beregovoi, and several other cosmonauts are also enraged with Kamanin for bumping Nikolyaev from the Soyuz 8 crew. Kamanin maintains that in the circumstances he only had enough training resources for 8 prime + 4 back-up crew, especially for a mission scenario that would not be flown again in the future.
1969 September 19 - .
- L1 state commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Brezhnev,
Mishin,
Tyulin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Lunar L1,
Luna.
Spacecraft: Luna Ye-8-5,
Soyuz 7K-L1.
VPK Deputy Chairman Tyulin headed a state commission on the L1 programme. Mishin pushed for a manned L1 circumlunar flight in 1970. This meeting was only five days before a Ye-8-5 robot spacecraft was to have returned lunar soil from the earth. The Block D stage failed in earth orbit, and the flight was given the cover name Cosmos 300. This indicated the L1 system still did not have the necessary reliability for manned flight. Furthermore, politically, Brezhnev and the Politburo did not want to see a Khrushchev-originated project like the L1 succeed.
1969 September 24 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 on launch pad 110 west. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. This was the first new launch vehicle erection activity detected by US reconnsats after the destruction of pad 110 east in the July launch failure. The all-white launch vehicle, with no payload, is believed to be either N1 mockup 1M1 or flight vehicle 6L..
1969 October 5 - .
- DOS Conspiracy briefed to Ustinov - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Feoktistov,
Mishin,
Tyulin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Almaz,
Salyut.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Mishin was opposed to the DOS space station concept - he wanted to pursue the N1-launched MKBS. Afanasyev and Deputy Minister Tyulin wouldn't support the idea either. None of them wanted to take the risk. The only chance was to get to VPK Chairman Ustinov through Communist party channels. The opportunity came on the flight of engineers and management to Baikonur for the Soyuz 6/7/8 flight. Feoktistov had prepared a briefing on DOS, which he presented to Ustinov.
1969 October 19 - .
- DOS Conspiracy briefed to wide circle of space planners - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Bushuyev,
Chelomei,
Feoktistov,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Semenov,
Serbin,
Tyulin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Almaz,
Salyut.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
In the euphoria after the return of the Soyuz 6/7/8 crews, the problem was how to get Ustinov to meet further with the DOS 'conspirators'. Mishin had prohibited any meetings by TsKBEM staff with the Communist Party Secretary unless Mishin was also present. Another obstacle was that Feoktistov was not a party member; how could his presence at a party meeting be explained to Mishin later?
In any event these consideations were simply ignored. Feoktistov was present at a party meeting with Keldysh, Afanasyev, Tyulin, Serbin, and the Ministry of Defence's party cell: Strogonov, Kravtsev, and Popov. Keldysh was mainly worried how the project would affect the N1, but was reassured that the N1 had a dedicated work force, and the L3 lunar lander spacecraft engineers and workers that would work on DOS were currently idle and had no part of that work. It was finally decided to go ahead with the DOS no earlier than January, to allow time for Ministry Decrees, approval of a work plan by the VPK, preparation of a decree for signature by the Central Committee of the Communist Party and the Soviet Ministers. Work began on the project in December 1969 under the initial auspices of the Academy of Sciences. Additional Details: here....
1969 November - .
- Soyuz n 18 (cancelled) - . Crew: Grechko, Kuklin. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Grechko, Kuklin. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Would have simulated the passive LK lunar lander in an earth-orbit test of the Kontakt docking system..
1969 November - .
- Soyuz n 17 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz n 17.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt.
The Kontakt system designed for the lunar orbit rendezvous and docking of the LOK lunar orbiter and LK lunar lander was to be mounted on two Soyuz spacecraft and tested in earth orbit. These flights were continuously delayed after the success of Apollo 11 and finally cancelled.
1969 November 5 - .
- Press conference - lunar project raised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8.
Major press conference. Keldysh dodges questions from American reporters on the Soviet lunar landing program. The cosmonauts perform all right, no mistakes. Kamanin views Keldysh as a braking force on the space programme. He attributes the loss of the moon race to bad managers like Keldysh and Mishin.
1969 December 26 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- DOS formally authorised - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Glushko,
Kuznetsov,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Almaz,
Salyut.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Salyut 1.
Ustinov called the DOS 'conspirators' to Kuibyshev Street. Mishin was sent away to Kslovodsk and Chelomei and Glushko were not invited. No one wanted to listen to any more of Glushko's diatribes about Kuznetsov's engines.
Ustinov supported presentation of the DOS concept to the Central Committee. Chelomei categorically opposed DOS and was trying to kill it through military channels. But the allure of an '18 month' station - one which would not only beat the American Skylab, but be in space in time for the 24th Party Congress - seemed too alluring. Mishin also rejected DOS, but deputies at both design bureaux supported the concept and were eager to proceed.
DOS was therefore created only when the moon project failed. Chelomei was forced to work on DOS, and it severely impacted Almaz schedules. The Salyut name was later applied to both the DOS and Almaz stations, creating the impression in the outside world that they were built by one designer.
1969 December 31 - .
- 1969 in retrospect. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Keldysh,
Kutakhov,
Mishin,
Smirnov,
Tereshkova,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Tereshkova is on a tour of Jordan and Syria. Kamanin muses over the year 1969. He is able to rationalise that it wasn't a bad year -- they flew 9 cosmonauts on five space missions. But of course they lost the moon to the Americans. He blames Mishin, Keldysh, Smirnov, and Ustinov for this. But he also blames the attitude of the Ministry of Defence and VVS. This is indicated by the total indifference to civilian space projects of Grechko and Kutakhov. They don't support the Gagarin Centre, or Kamanin's request for 10 additional Soyuz flights in earth orbit. Kamanin views the L3 spacecraft and mission scenario as unsafe. What is needed is a new spacecraft, launched by two N1 boosters, that will take a crew of 3 to 5 to the moon.
1970 February 20 - .
- Soyuz 9 schedule; Soyuz Kontakt flights in limbo - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Serbin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 9,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz Kontakt.
It was originally planned to fly two Soyuz spacecraft in August-September 1970, but at the end of December it was ordered that this be changed to a single 20 day flight in April 1970. Kamanin was given only two days to put together a training programme that had to prepare the cosmonauts for flight by 20 March. The State Commission meets and decides to move the Soyuz 9 flight to May, even though Kamanin says he can support the April schedule. It is the scientific institutes who say they cannot finish development of their experiments - even to meet the May schedule. Kamanin blames such chaos on Smirnov, Serbin, and Ustinov.
1970 February 25 - .
- Soyuz 9 decision preempts Soyuz Kontakt flights - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kerimov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 9,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt.
Meeting with Mishin. It is clear that he wanted to continue with the original plan for a dual Soyuz flight in August. It was Afanasyev and Kerimov who were pushing for a single long-duration flight in May. There is no action by the Ministry of Defence to provide rational decision making in regard to manned spaceflight.
1970 February 26 - .
- Kamanin views DOS, continuation of N1-L3 with dismay - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Salyut,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
The Ministry of Defence and VVS approve the draft DOS resolution. Kamanin has fought against it. He would prefer to develop a single reliable Soyuz spacecraft model by building and flying ten more (there are only four left of the original production lot in assembly). Instead the space leadership keep dreaming up new projects. In Kamanin's view, the DOS and its new Soyuz ferry design join Almaz, Soyuz VI, and the L3 as 'paper spacecraft'. Mishin still thinks he will 'teach the N1 to fly' and complete the L3, but Kamanin thinks the chances of this are nil. There is no coherent plan for Soviet spaceflight.
1970 February 27 - .
- DOS schedules, Soyuz Kontakt flights still in play - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bogomolov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Salyut,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz Kontakt,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
A meeting is held on the DOS project. The Central Committee and Soviet Ministers have directed that two DOS space stations be completed by the end of 1970. TsNIIMASH thinks this is impossible - the task can be accomplished in no less than 18 to 24 months. Mishin insists it can be done in ten months, as directed. Kamanin believes he won't even have it ready by the second half of 1971. It took five to seven years to just bring the Almaz, Soyuz VI, and L1 to flight status. This DOS will stop work on all other projects. Mishin still wants to fly two Soyuz spacecraft to test Bogomolov's Kontakt docking system for the L3.
1970 February 28 - .
- Failure to achieve space objectives in Five-Year Plan - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L1,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
Kamanin is asked to assist in preparation of the next five-year plan for spaceflight (1971-1975). He muses that nothing that was to be accomplished in the last five-year plan was achieved, so what is he supposed to put in the new one? 1966-1971 was supposed to have seen Soviet manned flybys and landings on the moon; a cosmonaut contingent increased to 140 and cadres in training for military missions on the Soyuz VI and Almaz. None of this was achieved, and the cosmonaut corps actually only numbers 97.
1970 February-March - .
- Soyuz n 19 (cancelled) - . Crew: Patsayev, Shonin, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Patsayev, Shonin, Yazdovsky. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. The passive spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system. One or two of the crew would have spacewalked to the Soyuz 11 Kontakt and returned in the other spacecraft..
1970 February-March - .
- Soyuz n 20 (cancelled) - . Crew: Fartushny, Shatalov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Fartushny, Shatalov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. The active spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system..
1970 April 18 - .
- Kamanin considers the Apollo 13 mission. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Apollo.
Flight: Apollo 13.
He believes it was a 'true test' of American technical capability in space. The saving of the American astronauts demonstrated the robust redundancy in the American Saturn V - Apollo design, as compared with the Soviet N1-L3. The latter, Kamanin remarks, is a bad launch vehicle, boosting a bad spacecraft. Kamanin sees the Soviet science fiction film Solaris - and finds it too fantastic for his taste.
1970 May 18 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 erected on launch pad 110 west. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. US reconnsat detects N1 being installed on the pad. It remained there, without payload, at least through 4 June..
1970 September 23 - .
- Cosmonaut training plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bogomolov,
Bykovsky,
Mishin,
Popovich.
Program: Salyut,
Almaz,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz Kontakt,
Spiral OS.
The training plan for DOS#1 is reviewed. The station is to be launched by February 1971. Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11 will dock with it and crew the station for two to three months, according to Mishin's plan. This however will slow down flight test of Bogomolov's Kontakt docking system for the L3. This was to have been ready by January 1970, but it is still not ready for flight. On the other hand, the completion of the DOS station within four to five months is not possible. There are currently 12 cosmonauts in training for DOS, and ten for Soyuz flights. Popovich heads a group of 22 cosmonauts training for Almaz; and Bykovsky heads a group on lunar issues. The new trainers and simulators are on schedule; the existing ones are being heavily used.
1970 September 24 - .
- Mishin has new landing scenario for L3 missions. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Mishin's latest plan is land the L3 in the Indian Ocean after return from the moon, but Soyuz is not rated for swells over 3 to 4 balls. Also there is no money for the needed recovery forces. By comparison the Americans have made the sea their home. Their aircraft carriers give them control over 300 times more ocean area than the Soviet Union.
1970 October 6 - .
- Cosmonaut training centre status. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Salyut,
Almaz,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Spiral OS.
Kamanin reviews the work of the training centre in 1970-1971. There are 12 cosmonauts training for DOS missions; 22 for Almaz; 5 for Spiral; and a 'group' for the L3. They have flown 5000 flight hours in jet trainers. During the last two years Kamanin has increased the number of trainers and simulators available; achieved 100% of the training plan; and met the physical training requirements (all cosmonauts must accomplish a 10 km run).
1970 October 16 - .
- Mishin seems to have lost his fight for a water landing on L3 missions. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Grechko, Andrei,
Mishin,
Shatalov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
All will have to be on dry land. 500 million roubles would have been necessary to fund the sea forces, and the risk to the crews would have been greater. Kamanin sees the whole bogus controversy as a diversionary tactic of Mishin's to take attention away from the fact that the L3 spacecraft is in fact nonexistent - as is its N1 rocket. An additional 300 million roubles are needed to achieve a 'flying' N1. A completely new solution to the lunar landing problem needs to be worked out. Shatalov worked today with Grechko to lay out the program for French President Pompidou's visit to the Baikonur cosmodrome. Pompidou wants to see two live rocket launches, and Shatalov will show him the Soyuz spacecraft.
1970 October 23 - .
- Mishin still fighting for an ocean landing for the L3. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. He has recruited some cosmonauts and admirals to fight for the concept..
1970 October 24 - .
- Cosmonauts oppose ocean landing for the L3. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei, Mishin. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. 18 VVS officers and cosmonauts meet to discuss the L3 water landing issue. Kamanin is to draft a letter against the concept to Mishin and Afanaseyev..
1970 October 28 - .
- Zond 8 recovered, demonstrates Mishin's L3 ocean landing trajectory. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L1,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Zond 8 is recovered only 15 minutes after splashdown by the vessel Taman. Of five Zonds recovered, this was the only one to fly over the north pole. The remainder re-entered over the south pole. The reason for this was the need to fly over tracking stations on Soviet territory in order to get trajectory updates that allowed a precise landing after the second plunge into the atmosphere. This was the reason Mishin now wants a water landing for the L3. The dilemma is that after a first dip into the atmosphere over the North Pole, tracking for a precision landing is possible, but then the spacecraft cannot land on Soviet territory. Re-entering first over the South Pole means that no trajectory updates are available, but then the spacecraft can land only imprecisely somewhere on Soviet territory.
15 L1's were completed, of which only five ever returned to earth. With this successful final recovery, the programme is cancelled. The main cause of the project's failure was the unreliability of the UR-500K rocket.
1970 November 24 - . 05:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511L.
- Cosmos 379 - .
Payload: Lunar Craft T2K no. 1. Mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK.
Duration: 4,683.78 days. Decay Date: 1983-09-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 4760 . COSPAR: 1970-099A. Apogee: 232 km (144 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
LK moon lander test using the T2K version. First use of the Soyuz 11A511L booster modified especially for this purpose. The spacecraft made a series of engine burns, simulating the lunar landing profile. After 3.5 days in orbit, the first burn was made in imitation of a descent to the lunar surface after separation of the Block D lunar crasher stage. The orbit changed from 192 km X 233 km to 196 km X 1206 km orbit; delta V: 263 m/s. After 4 days in orbit, a large manoeuvre was made simulating the ascent from the lunar surface. The orbit was changed from 188 km X 1198 km to 177 km X 14,041 km; delta V: 1518 m/s. These main manoeuvres were followed by a series of small adjustments simulating rendezvous and docking with the LOK. The LK tested out without major problems and decayed from orbit on September 21, 1983.
1970 December 2 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Cosmos 382 - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1E s/n 2K. Mass: 10,380 kg (22,880 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Block D.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1E.
Duration: 8,549.30 days. USAF Sat Cat: 4786 . COSPAR: 1970-103A. Apogee: 5,269 km (3,273 mi). Perigee: 2,384 km (1,481 mi). Inclination: 55.90 deg. Period: 171.00 min.
Test of Block D upper stage in its N1 lunar crasher configuration in earth orbit. The three maneuvers simulated the lunar orbit insertion burn; the lunar orbit circularization burn; and the descent burn to bring the LK lunar lander just over the surface. Payload was a modified Soyuz 7K-L1 circumlunar spacecraft, which provided guidance to the Block D and was equipped with television cameras that viewed the behavior of the Block D stage propellants under zero-G conditions.
Maneuver Summary:
190km X 300km orbit to 303km X 5038km orbit. Delta V: 982 m/s
318km X 5040km orbit to 1616km X 5071km orbit. Delta V: 285 m/s
1616km X 5071km orbit to 2577km X 5082km orbit. Delta V: 1311 m/s
Total Delta V: 2578 m/s.
1970 December 19 - .
- Differences between VVS and Mishin enumerated. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin,
Smirnov,
Stroganov,
Ustinov.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 10.
Lunokhod-1 and Venera-7 missions continue well. The NIITsPK conference is completed, final total 88 papers. The conference has recommended a cautious build-up in manned flight durations - the next mission should be 22 days long, then 26, then 30. But Ustinov has ordered Mishin to ensure that the first flight to DOS will be 30 days long. Kamanin is categorically opposed to this. Kamanin runs through the principal differences between himself and Mishin:
- Mishin wants to continue work on the N1-L3 moon project. Kamanin thinks the whole thing should be cancelled
- Kamanin wants the L3 to land on Soviet territory. Mishin wants it to land in the Indian Ocean
- Mishin wants to make the next manned flight 30 days long. Kamanin wants to limit it to 18 days
1970 December 30 - .
- Spacecraft simulator review. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Darevskiy.
Program: Almaz,
Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Trainer review with S G Darevskiy. It is estimated that the trainers only meet 25% to 30% of the total training needs of the cosmonauts. In the next year Kamanin wants Darevskiy to exert 75% of his effort on the Almaz simulator, 20% on the DOS-7K, and only 5% on the L3. Mishin wants zero effort on Almaz, 70% on DOS-7K, and 30% on the L3.
1970 December 31 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-700.
- UR 700/LK-700/RD-270 definitively cancelled. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Moon. Type: Manned lunar spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: TKS. Spacecraft: LK-700. Further development work on the RD-270 engine, UR-700 launch vehicle, and LK-700 lunar landing project are cancelled following the successful Apollo lunar landing..
1971 January 5 - .
- VVS Reviews TsKBEM Facilities and Programs - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kutakhov,
Mishin.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Two hour meeting between the VVS leadership and Mishin at TsKBEM. Mishin claims he will fly the N1 to orbit this year, and that it will have a payload of 95 to 100 tonnes to low earth orbit. He wants to make 4 to 5 unmanned launches in 1971-1972, followed by one unmanned lunar flyby, culminating in the first Soviet cosmonaut landing on the moon in March 1973. Afterwards the VVS leaders tour the L3 and DOS-7K mock-ups. Mishin asks - Why won't the VVS support his plan for an Indian Ocean landing for the L3? Why is the VVS against a 30-day duration for the first DOS flight? Why isn't the VVS training engineer-cosmonauts as pilots? Kutakhov replies that these are decisions that have to be made by aviation specialists, not by engineers or chief designers. The General Staff supports the VVS position.
1971 February 5 - .
- Soviet view of Apollo 14. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Keldysh, Mishin, Shonin, Smirnov, Ustinov. Program: Apollo, Lunar L3. Apollo 14 successfully lands on the moon. Kamanin notes that the Soviet Union is now five to six years behind, due to the mistakes of Mishin, Keldysh, Smirnov, and Ustinov. Shonin is training on Soyuz s/n 32 at the KIS of TsKBEM..
1971 February 26 - . 05:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511L.
- Cosmos 398 - .
Payload: Lunar Craft T2K no. 2. Mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK.
Duration: 8,463.78 days. Decay Date: 1995-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 4966 . COSPAR: 1971-016A. Apogee: 1,958 km (1,216 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 106.70 min.
Second space test of the LK moon lander test using the T2K version. Followed the same programme as Cosmos 379.
Maneuver Summary:
189km X 252km orbit to 186km X 1189km orbit. Delta V: 251 m/s
186km X 1189km orbit to 200km X 10905km orbit. Delta V: 1320 m/s
Total Delta V: 2832 m/s.
Officially: Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space.
1971 March 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1-L3 loses remaining priority - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Apollo 13,
Apollo 14.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The Soviet leadership regained some interest in the N1-L3, after the near-tragedy of Apollo 13. It was felt that the Americans might cancel the remainder of the Apollo programme, leaving the road to the moon clear for the Soviet Union. However the successful flight of Apollo 14 redeemed the project, and the Central Committee lost all interest in the N1-L3. Additional Details: here....
1971 March 4 - .
- N1/L3 Expert Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Kuznetsov, Nikolai F,
Mishin,
Tereshkova.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Krechet,
LK-700,
Soyuz 7KT-OK.
Pushkin and Kuznetsov brief Kamanin on the results of the N1/L3 expert commission. They found that the N1/L3 is unreliable and that the design needs to be fundamentally re-examined. Therefore the Soviet Ministers and Central Committee passed a decree that the commission must determine by 1 May 1971 what to do with the lunar project. Kamanin's opinion: abandon the N1-L3, modify Chelomei's UR-700 design to replace it, and design a new lunar landing spacecraft for missions in 1974-1975. Mishin is afraid of such a solution. Kamanin believes that the commission, headed by Keldysh, will finally recommend continued development and flight of Mishin's bad booster and even worse spacecraft. It is true that the N1 design has been substantially reworked in the last 18 months, but Kamanin believes it to be fundamentally flawed and that nothing can make it reliable.
After Mishin pushed his Indian Ocean recovery plan for the L3, the VVS insisted on sea trials of the capsule. These showed the cosmonauts had to get out within 30 to 35 minutes before the valves to the interior started leaking seawater. The L3 is also unsafe due to the EVA method of transfer to the LK of a single unassisted cosmonaut. The Krechet spacesuit is very bulky and unmanoeuvrable.
Prague wanted Gagarin's widow for International Women's Day.since Tereshkkova couldn't go, but she wants no part of public appearances.
1971 April 13 - .
- Cosmodrome jammed for series of historic launches. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Nikolayev,
Volynov.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 10.
Spacecraft Bus: Almaz.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1.
Nikolayev and others are flying to the cosmodrome. All of the cosmonauts except Volynov will be present for the historic launch of the first space station., the first crew to the station, and the N1 launch planned for 1 May. Kamanin has an argument with the cosmonauts on the necessity of working out on the KTF trainer during the mission.
1971 April 14 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Zarya renamed Salyut - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3,
Salyut.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Shuguang 1.
All of the pressure on the N1 project was going on simultaneously with the launch preparations for DOS#1. The Central Committee had approved the name 'Zarya' (Dawn) for the station, but it was felt that this name might offend the Chinese, who's secret new manned spacecraft was also called 'Dawn' (it is interesting that Chertok and the Soviet space community was aware of this in 1970 - the existence of the nascent Chinese manned space project of that name was not revealed publicly in the West until 2002!). After some hurried consultations, it was decided to give the station the public name 'Salyut' (although the vehicle rolled out to the pad still had 'Zarya' emblazoned on the payload shroud -- but these pictures were not revealed until the 1990's).
1971 April 14 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 threatened again - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Babakin,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
An expert commission met to consider the N1-L3. Keldysh made several categorical demands:
- the laser-based Kontakt rendezvous and docking system had to either be backed up with redundancy throughout, or an independent back-up system had to be developed
- the L3 had to be designed with an internal transfer compartment, as was being done for the DOS/7K-T space station system
- each stage of the N1 had to undergo flammability tests
- the mission scenario had to be reformulated to provide support by more than one cosmonaut on the moon at a time, and use of automated landers and rovers from Babakin at Lavochkin
- landings of the capsule in the equatorial oceans of the world had to be eliminated. The capsules had to land on the territory of the USSR
1971 April 15 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Salyut preparations - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3,
Salyut,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
MKBS,
Salyut 1.
The Salyut station was prepared in a huge two story bunker built for launch vehicle / payload processing. The contrast between the money lavished by the military on this facility for Chelomei's projects and the limited funds available for a proper N1 preparation and test facilities was enormous. Here funds were available without limit. The air was controlled by a self-contained environmental control system with its own independent electrical-diesel generators. The facility was a miracle. It was shocking that this was made available for Almaz, while the military told Mishin that he would have to prepare the immense MKBS station in the uncontrolled environment, subject to frequent power blackouts, of the N1 facility. At Chelomei's facility, everything was completely checked out on earth prior to launch.
1971 May 15 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1M.
- Go-ahead to develop LH2/LOX stage for N1M - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Decision made to proceed with development of the multi-engined stage Block Sr with a propellant mass of 66.4 tonnes. This single stage would be used in place of the previously-planned Blocks S and R to insert the modernized Lunar Expeditionary Complex (LEK) into low lunar orbit. It was also to be used to insert heavy spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit and on interplanetary trajectories.
1971 May 15 - .
- Party line on Soviet space program. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Popovich,
Sevastyanov,
Shatalov.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3,
Luna.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11.
Shatalov is actively pushing his candidacy for the position of Kamanin's deputy. Popovich and Sevastyanov prepare for a trip to the Paris Air how on 2 June. They need 'correct' replies to inevitable questions about the moon race, the Salyut 1 station, and Soyuz 10's failure to dock. The line they are to follow is that the Soviet Union is fulfilling its safe and systematic exploration of space. The robots Luna-16 and Lunokhod 1 safely surveyed the moon. After the Soyuz 9 long-duration flight, Salyut 1 was launched and Soyuz 10 tested the rendezvous equipment. The line is that the USSR is not behind the USA, but is exploring space in a safe and responsible way.
1971 June 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1-6L launch commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Isayev,
Mishin,
Pilyugin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
LK,
MKBS,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The review of launch preparations veers off into a discussion of what the booster was now for. Pilyugin questioned the seriousness of intent of the TsKBEM staff. The digital control system priorities within the bureau were with DOS and Almaz -- why wasn't the N1-L3 the priority? Mishin had never been told that the N1-L3 development was lagging. It had no priority with the leadership. Top priority at TsKBEM was Nadiradze's solid propellant ICBM's, followed by the DOS Salyut station, and now Soyuz-Apollo preparations. Meanwhile it was finally recognised that a single-launch scenario was simply impossible, and two N1 launches would be needed to accomplish the lunar landing. But there was no political will to tell the Politburo the bad news -- that two N1's would be needed to be launched to accomplish the landing. The final conclusion was that the bureau needed a new direction, a project with national priority, like the DOS station. Strategic rocket work could be ruled out, as there were already too many players in that field. Additional Details: here....
1971 June 15 - .
- Soyuz Kontakt and DOS-2 crew assignments made. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Alekseyev, Semyon,
Artyukhin,
Bykovsky,
Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Gubarev,
Isakov,
Klimuk,
Kolodin,
Kovalyonok,
Lazarev,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Porvatkin,
Rukavishnikov,
Sevastyanov,
Shcheglov,
Vorobyov,
Voronov,
Yakovlev,
Yazdovsky.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Flight: DOS 2-1,
DOS 2-2,
DOS 2-3,
DOS 2-4,
Soyuz 11,
Soyuz 12 / DOS 1,
Soyuz sn 18,
Soyuz sn 19,
Soyuz sn 20,
Soyuz sn 21,
Soyuz sn 22,
Soyuz sn 23.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz Kontakt.
Crews are formed for six Soyuz (Kontakt?) flights. Soyuz s/n 18 - Filipchenko and Grechko; Soyuz s/n 19 - Lazarev and Makarov; Soyuz s/n 20 - Vorobyov and Yazdovsky; Soyuz s/n 21 - Yakovlelv and Porvatkin; Soyuz s/n 22 - Kovalyonok and Isakov; Soyuz s/n 23 - Shcheglov and [illegible]. Five crews are training for Salyut flights: Crew 1, Leonov, Rukavishnikov, and Kolodin; Crew 2, Gubarev, Sevastyanov, and Voronov. TsKBEM engineer cosmonauts are to be selected will round out the last three crews, but VVS members will be: Crew 3, Klimuk, Artyukhin; Crew 4, Bykovskyy, Alekseyev; Crew 5, Gorbatko. Leonov and Gubarev will have their crews fully ready for Soyuz 12 by 30 June, for a launch date between 15-20 July. Leonov is asking to go to East Germany for two to three days in the first week of July. Kamanin is fully opposed to this - he is thinkng not of his upcoming flight, but the exhibition of his paintings at the Prezdensk Gallery!
1971 June 24 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soyuz 11 Day 19 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dobrovolsky,
Karas,
Patsayev,
Volkov.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Dobrovolsky and Patsayev successfully complete the Svinets experiment, fixing the position of a rocket launched at night. The N1 launch has been delayed again. Karas reports that telemetry shows many problems with the rocket, even just sitting on the pad. Kamanin sees this lousy rocket as a heavy cross for Soviet cosmonautics to bear. As for Soyuz 11, the Landing Commission discusses moving the landing from the 3rd to 2nd revolution on 30 July. But then the crew will land in the dark, while for the 3rd revolution landing they will touch down 24 minutes before sunrise. It is decided to continue planning for the third revolution, in case the crew needs immediate medical assistance.
1971 June 26 - . 23:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: First stage failed.. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 6L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-LOK / LK Mockups. Mass: 9,850 kg (21,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Decay Date: 1971-07-21 . Apogee: 1.00 km (0.60 mi).
Superbooster failure of N1 serial number 6L. This was a substantially improved vehicle, incorporating filters in the propellant lines to prevent any foreign objects from getting into the pumps. The shape of the tail of the booster was modified, and ventilation and refrigeration systems were added to keep the engine compartment cool. It was painted white overall to reduce temperatures while sitting on the pad. After liftoff and ascent, an axial rotation was introduced by gas dynamics interactions of the thirty engines with the air slipstream. The launch vehicle developed a roll beyond the capability of the control system to compensate. and began to break up as it went through Max Q. Control was lost at 50.2 seconds into the flight and it was destroyed by range safety a second later. The engines functioned well and did not shut down up to the point of vehicle destruction. No functional payload was carried. It has been stated that this launch did not have a working launch escape system. Additional Details: here....
1971 June 27 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soyuz 11 Day 22 - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dobrovolsky,
Isayev,
Keldysh,
Mishin,
Patsayev,
Smirnov,
Ustinov,
Volkov.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7KT-OK.
The shocking news of rocket engine designer Isayev's premature death is received at the Soyuz 11 control point at Yevpatoriya. This is followed by the news that the third N1 failed 57 seconds into its flight. A total of 13 N1's were built, and all three launched so far have exploded. Kamanin agreed to cancellation of the entire project three years ago, but Ustinov, Smirnov, Keldysh, and Mishin continued in their grandiose charade, wasting billions of roubles in the process. Meanwhile on the 22nd day of Soyuz 11's flight, the crew is up and about. Volkov is especially active, which should improve his readaptation when he returns to earth.
1971 June 29 - .
- Soyuz 11 day 24 - final preparations for landing. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dobrovolsky,
Mishin,
Patsayev,
Volkov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7KT-OK.
Big dramas are being played out at the cosmodrome over the N1 failure, but Mishin seems protected by someone very high up and is untouchable in the blame game. This is the last full day aloft of the Soyuz 11 crew. At 19:30 the State Commission at the command point authorises the Soyuz 11 crew to undock from the Salyut space station. A communications session begins on the 15th orbit of the day at 19:45. Dobrovolsky and Volkov confirmed that the station was completely mothballed, all material to be returned was stowed in the Soyuz capsule, the crew was wearing their anti-G suits, and had completed shut-down of the station. Yeliseyev advised the crew that ground telemetry showed that they had not turned on the noxious gas filters in the station. Volkov argues that this must be a ground control error, but after checking admits the crew made a mistake.
After the crew has left the station, taken their seats in the capsule, and closed the hatch between the Soyuz BO orbital module and SA re-entry capsule, the strained voice of Volkov comes from space: 'Hatch not hermetically sealed? What's happening? What's going on?'. All this response to the fact that the caution and warning panel 'Hatch open' light has not gone out. Yeliseyev calmly advises the crew, 'Don't panic. Open the hatch, and move the wheel to the left to open. Close the hatch, and then move the wheel to the right six turns with full force'. The crew does this several times, but the light still won't go out. On a final attempt, with 6.5 turns of the wheel, the light goes out. On the second half of he 15th orbit, the crew lowers the pressure in the BO to 160 mm, and the hatch proves to be air-tight.
On the 16th orbit the crew separates their Soyuz from the Salyut station. At 21:35 they report normal separation and that they 'can see how the station moves away from the spacecraft'. They have enough propellant to stop the separation velocity, and take photographs of the station from 10 to 15 m away. They then back away to 30-40 m, and Patsayev takes another set of photographs documenting the condition of the station.
1971 July 4 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soyuz 11 failure investigation - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Dobrovolsky,
Patsayev,
Severin,
Tereshkova,
Volkov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Salyut.
Flight: Soyuz 11.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-T,
Soyuz 7KT-OK.
This was a very difficult time for TsKBEM. All work at the bureaus came to a complete halt after the loss of Soyuz 11 and N1 6L. Simultaneous expert commissions investigated the loss of N1 6L and Soyuz 11. TsKBEM was seen as responsible for every failure. A virtually legal process ensued to fix guilt. Every design decision was examined and questioned. Additional Details: here....
1971 August 12 - . 05:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511L.
- Cosmos 434 - .
Payload: Lunar Craft T2K no. 3. Mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MOM.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Moon.
Type: Manned lunar lander. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: LK.
Duration: 8,296.77 days. Decay Date: 1981-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 5407 . COSPAR: 1971-069A. Apogee: 1,253 km (778 mi). Perigee: 193 km (119 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 99.30 min.
Final LK moon lander test using the T2K version.
Maneuver Summary:
188km X 267km orbit to 190km X 1261km orbit. Delta V: 266 m/s
188km X 1262km orbit to 180km X 11384km orbit. Delta V: 1333 m/s
Total Delta V: 1599 m/s. Ten years later the spacecraft was due to re-enter over Australia soon after the Skylab scare. The Soviet Union told the people of Australia not to worry, it was only an experimental lunar cabin - the first inadvertent admission that their manned lunar project even existed!
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 18 (cancelled) - . Crew: Filipchenko, Grechko. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Filipchenko, Grechko. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 18 would have been the active spacecraft of the first dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 19 (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Lazarev, Makarov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 19 would have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. Would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 18 . A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 January 1 - .
- TsKBEM reorganised - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bushuyev,
Dorofeyev,
Mishin,
Semenov,
Shabarov.
Program: Lunar L3,
Soyuz,
Almaz.
Spacecraft: LK,
Mars 5NM,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz 7K-S,
Soyuz 7K-T,
Soyuz 7K-TM.
TsKBEM was given a completely new structure as a result of the findings of the expert commissions on the disasters for the previous year, Mishin remained as the Chief Designer for the organisation, but each programme now had its own chief designer:
- N1: Boris Dorofeyev
- 8K98P solid propellant ICBM: Igor Sadovskiy
- N1 payloads: Vladimir Brorov [check]
- Soyuz 7K-TM, or Soyuz M, for Soyuz-Apollo: Konstantin Bushuyev
- Soyuz 7K-T: Yuri Semenov
- Soyuz 7K-S or Soyuz VI: Yevgeni Shabarov
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 21 (cancelled) - . Crew: Dobrovolsky, Sevastyanov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Dobrovolsky, Sevastyanov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 21. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 21 equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. Would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 20 . A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 20 (cancelled) - . Crew: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 20 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 - .
- Soyuz sn 22 (cancelled) - . Crew: Isakov, Kovalyonok. Backup Crew: Shcheglov. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 22. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 22 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system..
1972 - .
- Soyuz sn 23 (cancelled) - . Crew: Shcheglov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Shcheglov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 23. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 23 would have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. The spacecraft would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 22. In Kamanin's diary, the name of the second crewmember is illegible..
1972 June 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet Lunar Landing (cancelled) - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Soviet Lunar Landing.
The Russians were never able to have enough success with the N1 booster to have a serious schedule for the first Soviet lunar landing. In January 1969, before the first N1 launch, it was not expected that a Soviet landing would take place until 1972 at the earliest. In such circumstances only a disaster leading to cancellation of the Apollo program would allow the Russians to be first to the moon. After the explosions of the first two N1 rockets, and the success of Apollo 11, Russian engineering efforts were diverted into crash development of the Salyut space station in order to beat the American Skylab. Cosmonauts trained for L3 lunar landing missions until October 1973, when the last training group was dissolved. By that time actual manned flight of the original single-launch L3 LOK/LK spacecraft to the moon had been abandoned. Instead work was underway on the N1F-L3M, a twin launch scenario that would put the L3M lander on the surface in 1978 for extended operations, and eventually, a lunar base. This in turn was cancelled with the entire N1 program in 1974.
1972 August 15 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 7L launch readiness review - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Mishin. Program: Lunar L3. Mishin held a Soviet of N1 chief designers to confirm launch readiness..
1972 August 21 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 7L State Commission - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kuznetsov,
Lapygin,
Mishin,
Okhapkin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
The State Commission was held to verify readiness of N1 7L for launch. Mishin was 'sick' the whole week of the hearings and had to be represented by his deputies. However neither Mishin or his first deputy Okhapkin were available - both were in the hospital. The commission nearly ruled that until Mishin was available, no launch could be approved. However the review continued. Additional Details: here....
1972 September 20 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Final N1 components arrive at Baikonur - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. The replacement transformers for the VP53 digital to analogue converters were delivered to Baikonur..
1972 October 14 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
1972 November 16 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Flight readiness review for the N1. - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
There were still three defects in the new digital computer systems and controversy as to whether to fly the fuel cells in the LOK. But without the fuel cells, there could be no translunar mission. The only power available would then be the batteries in the Block G, limiting the flight to low earth orbit. But the launch manager continued to insist there was danger in handling liquid hydrogen. This was simply a bureaucratic hold-up - only 600 kg of LH2 would be flying, which did not represent a real safety issue. Finally a waiver was agreed and the it was decided the LOK would fly with fuel cells.
All else seemed ready to go. The estimated engine reliability was 93%. The turbogenerators had achieved 100% reliability in test stands. There were still dissenting voices on the use of LH2 - the final vote was 7 for flying with it, and 2 against.
1972 November 21 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- State Commission was held to formally approve launch of N1 7L. - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
1972 November 23 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Final N1 preparations - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK. At 17:00 fuelling of N1 7L began. Lox fuelling was completed at 23:40..
1972 November 23 - . 06:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC110L. LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N-1 11A52. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- N1 7L - .
Payload: Soyuz 7K-LOK / LK Mockups. Mass: 9,850 kg (21,710 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: RVSN.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Decay Date: 1972-11-23 . Apogee: 40 km (24 mi).
Unmanned test of manned lunar mission launch vehicle serial number 7L. This article incorporated significant changes to the previous model, including roll 'steering' engines to prevent the loss of control that destroyed 6L. The rocket ascended into the sky, and the engines ran 106.93 seconds, only seven seconds before completion of first stage burnout. Programmed shutdown of some engines to prevent overstressing of the structure led to propellant line hammering, rupture of propellant lines, and an explosion of engine number 4. The vehicle disintegrated. Additional Details: here....
1973 January 1 - . LV Family: N1. Launch Vehicle: N1F-L3M.
- N1-L3M - . Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Spacecraft Bus: L3M. Spacecraft: L3M-1972. The first lunar expedition project, the N1-L3M, was studied in 1973..
1973 Early - .
- Soyuz Kontakt P (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Backup Crew: Fartushny, Klimuk. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz Kontakt P. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The Kontakt-P Soyuz would have been the passive spacecraft, simulating the LK lunar lander..
1973 Early - .
- Soyuz Kontakt A (cancelled) - . Crew: Filipchenko, Gorbatko. Backup Crew: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz Kontakt A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The launches were delayed and then cancelled due to continuing problems with the N1 lunar booster..
1974 May 1 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1 cancellation imminent - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Keldysh,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: L3M-1972,
LK,
Mars 5NM,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Ustinov achieved a leadership consensus to kill the N1 by the beginning of May 1974. He achieved the agreement of the other Ministers on the Military-Industrial Commission, and finally Keldysh. Projects that were ongoing that were linked with the N1 included: the lunar base, MKBS space station, Mars robotic soil return spacecraft and manned expedition, a space radio telescope with a 100 m antenna, and multiple channel communications satellites. All of these died with the cancellation. If 8L had been successful, then after 1 or 2 further test launches, the N1-L3M could begin flying. That meant that the Soviet Union was within 3 to 4 years of establishing long-term lunar expeditions and a moon base. The Americans would have been leapfrogged. Instead, the leadership decided to develop a completely new heavy-lift launch vehicle, which never became operational before the Soviet Union collapsed.
1974 May 2 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- N1-L3 program is cancelled - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Glushko,
Kozlov,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station.
The N1 program was cancelled before the next test flight. Mishin was removed as head of NPO Energia. Kozlov is first asked to replace him, but he prefers to stay in Samara. Glushko is appointed as the second choice. Two fully assembled (serial numbers 8L and 9L), and four partially assembled rockets were available at time of cancellation. These would have been the first to use the new modernized series NK-33/NK-39 engines. 8L was planned for launch in the fourth quarter of 1974. Confidence was high that, based on the massive telemetry received on the 7L flight, that all problems would have been rectified. A total of 3.6 billion rubles was spent on the N1-L3 program, of which 2.4 billion rubles went into N1 development. Those on the project felt that they were within months of finally providing the Soviet Union with a heavy-lift booster. Instead the work was discarded, and Glushko began design of the RLA/Vulkan with entirely new configuration and engines.
1974 August 13 - .
- N1 work cancelled - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Glushko,
Keldysh,
Korolev,
Kuznetsov,
Mishin,
Ustinov.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Buran,
LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
Glushko formally cancelled the N1 within the new NPO Energia on 13 August 1974 with the support of Ustinov, even though he had no decree of the VPK Military-Industrial Commission or the Central Committee authorising such an act. The N1-L3 itself was not officially closed down until the resolution of February 1976 starting work on the Energia/Buran boosters. By that time 6 billion roubles had been spent on the N1 over 17 years. Additional Details: here....
1974 August 14 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Glushko meets with TsKBEM staff - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Glushko,
Korolev.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LK,
Soyuz 7K-LOK.
He solicited their support in the reorganization and new projects for the bureau. Glushko was sartorially perfect, and had an aristocratic air, never using the familiar forms of address in Russian. He only loosened up a little in the last years of his life. He was a nitpicker, correcting Russian syntax in documents. He was capable of clear logic but did not have the intuitive genius of Korolev (according to Barmin, while Korolev did not look after his appearance, he possessed a pure 'Russian' intelligence).
1975 January 1 - .
- Vulkan Lunar Base - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Barmin,
Bushuyev,
Glushko,
Mishin.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: LEK,
Lunokhod LEK,
LZhM,
LZM.
Mishin and Barmin, using budget provided by the Ministry of Defence, had designed a lunar base for launch by the N1 in 1969-1974. After the cancellation of the N1, Glushko pleaded with the Military-Industrial Commission for the work to be taken from Barmin and be given to NPO Energia. Glushko's alternative, Vulkan-launched base was elaborated within his bureau. Bushuyev developed spacecraft for the base. Prudnikova developed a modular lunar city, with living modules, factory modules, a nuclear reactor power module, and a lunar crawler with a 200 km radius of action. The project work was only finally cancelled after the Apollo-Soyuz flights.
1976 May 1 - .
- Plea for revival of N1 project - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Buran.
The workers on the project put together a letter to the 25th Party Congress, saying that N1 development should continue, and that N1 s/n's 8, 9, and 10 should be flown. The Party did not accept the letter. They had been assured by the leadership that the population of the city of Leninsk, the extensive facilities and housing built for the N1, would all be used for the MKTS Soviet shuttle. Iosifiyan considered the N1 fundamentally flawed, a project that was only approved due to Kremlin politics.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use