Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
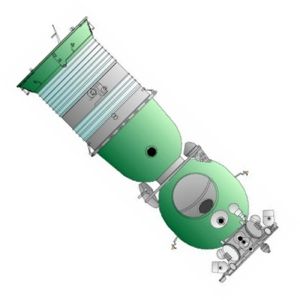
Soyuz Kontakt
AKA: 11F615. Status: Cancelled 1974. Thrust: 4.09 kN (919 lbf). Gross mass: 6,560 kg (14,460 lb). Unfuelled mass: 6,060 kg (13,360 lb). Specific impulse: 282 s. Height: 7.95 m (26.08 ft). Span: 9.80 m (32.10 ft).
Kontakt was developed for the lunar orbit rendezvous of the 7K-OK manned lunar orbiter and LK lunar lander. It utilized a hexagonal grid on the passive craft and a three-pronged grappler on the active spacecraft to allow a soft docking between the two spacecraft. The Kontakt system used manual optical methods for rendezvous and docking rather than the heavier automatic Igla radar system mounted on the 7K-OK. No hard docking was possible and crew transfer was by extravehicular activity.
The 7K-OK adaptation would have involved launch of two Soyuz by 11A511 boosters, with rendezvous and crew transfer in earth orbit. Crews were trained for these tests but due to delays and final cancellation of the N1-L3 lunar orbit rendezvous mission, the spacecraft never flew.
Crew Size: 3. Orbital Storage: 35 days. Habitable Volume: 9.00 m3. Spacecraft delta v: 390 m/s (1,270 ft/sec). Electric System: 0.50 average kW.
Family: Manned spacecraft. Country: Russia. Engines: KTDU-35. Launch Vehicles: R-7. Propellants: Nitric acid/Hydrazine. Agency: Korolev bureau. Bibliography: 344, 376.
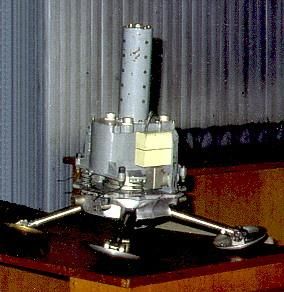 | Kontakt Docking Mech Kontact docking grappler. The three arms at the bottom faced outward from the docking assembly. MAI, March 1994 Credit: © Dietrich Haeseler |
1966 March 23 - .
- Inconsistent Soviet lunar program - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chertok.
Spacecraft: Block D,
Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-L1,
Soyuz 7K-LOK,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt.
Acting director Mishin held a brainstorming session with this top managers to address "...our inconsistent lunar program". He noted then-current contradictory approaches: 1. Return to a two-launch scheme (podsadka, as baseline); 2. Keep with direct landing; 3. Use a Block D with storable propellants; 4. Use the 7K-OK as the designated return spacecraft. He noted that the L1 program was a diversion for the bureau to the core objective of landing a cosmonaut on the moon (the L3 program). Among the advantages of continuing with the L1, he noted that it "Utilizes the 7K-OK" - evidently there was no purpose for the spacecraft beyond the L1 mission in the podsadka scenario. He asks for frank opinions from his managers. V Rauschenbach noted that they "..have to do the L-1 … and therefore we will have to use a 2-launch scheme based on the L1-S". BE Chertok: discussed the rendezvous and docking systems for the various spacecraft: L1-S - "Igla"; LOK - "Kontakt" (since "Igla" cannot be used on the LOK (due to mass considerations); or a new system for the LOK. (Mishin Diaries 1-226) Here we have an indication that the L1 podsadka version did use the Igla system, which makes complete sense, since the Soyuz 7K-OK missions conducted dress rehearsals for podsadka using this system to rendezvous and dock two 7K-OK spacecraft in earth orbit.
1968 February 1 - .
- The LKR rescue lunar lander plan was disclosed to the other Chief Designers. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chertok,
Ryazanskiy.
Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt,
LK,
LKR.
Chertok compared the "Kontakt" and "Liga" systems, and noted that the "Liga" elements in the control loop control system simplified LK landing. MS Ryazanskiy noted that this contradicted a decision two years ago to have the LK make an autonomous landing on the moon (LK homing on and landing near a beacon was postponed at that time). But AS Mnatsanakyan supported the approach, saying it was necessary to speed up the development of the "Liga"; it provided a precision landing on the moon within 50 to 100 m of the target. (Mishin Diaries 2-120).
1969 April 26 - .
- Soyuz program review - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Kolodin,
Kubasov,
Kuklin,
Nikolayev,
Sevastyanov,
Shonin,
Volkov,
Volynov.
Program: Soyuz.
Flight: Soyuz 5,
Soyuz 6,
Soyuz 7,
Soyuz 8,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt.
The commission considers plans for the rest of the Soyuz production. Spacecraft s/n 14, 15, and 16 are to fly in August 1969, 17 and 18 in November 1969, and 19 and 20 in February-March 1970. Crews selected for the August flights are: for spacecraft 14, Shonin and Kubasov; for 15, Filipchenko, Volkov, and Gorbatko; for 16, Nikolayev and Sevastyanov. Back-ups will be Kuklin, Grechko, and Kolodin. All of the spacecraft will fly 4 to 5 day missions. Spacecraft 15 and 16 will dock and remain together 2 or 3 days to form an 'orbital station'. Experiments planned for the flight are:
- Visual observation of rocket launch plumes using the Svinets device
- Film and photography of the spacecraft 15-16 docking from spacecraft 14
- Demonstration of welding in weightless vacuum conditions using the Vulkan device
- Demonstration of autonomous navigation by the cosmonauts using a sextant
- Medium wave radio communications
- Test of new television sensors for the Soyuz orientation system
Spacecraft 17 through 20 will fly 15 to 16 day missions to demonstrate the new SZhO life support system for the L3, and conduct rendezvous and docking operations using the L3's Kontakt system. Additional Details: here....
1969 November - .
- Soyuz n 17 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrunov,
Yeliseyev.
Program: Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz n 17.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt.
The Kontakt system designed for the lunar orbit rendezvous and docking of the LOK lunar orbiter and LK lunar lander was to be mounted on two Soyuz spacecraft and tested in earth orbit. These flights were continuously delayed after the success of Apollo 11 and finally cancelled.
1969 November - .
- Soyuz n 18 (cancelled) - . Crew: Grechko, Kuklin. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Grechko, Kuklin. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Would have simulated the passive LK lunar lander in an earth-orbit test of the Kontakt docking system..
1970 February 20 - .
- Soyuz 9 schedule; Soyuz Kontakt flights in limbo - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Serbin,
Smirnov,
Ustinov.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 9,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz Kontakt.
It was originally planned to fly two Soyuz spacecraft in August-September 1970, but at the end of December it was ordered that this be changed to a single 20 day flight in April 1970. Kamanin was given only two days to put together a training programme that had to prepare the cosmonauts for flight by 20 March. The State Commission meets and decides to move the Soyuz 9 flight to May, even though Kamanin says he can support the April schedule. It is the scientific institutes who say they cannot finish development of their experiments - even to meet the May schedule. Kamanin blames such chaos on Smirnov, Serbin, and Ustinov.
1970 February 25 - .
- Soyuz 9 decision preempts Soyuz Kontakt flights - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Afanasyev, Sergei,
Kerimov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Lunar L3.
Flight: Soyuz 9,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz.
Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt.
Meeting with Mishin. It is clear that he wanted to continue with the original plan for a dual Soyuz flight in August. It was Afanasyev and Kerimov who were pushing for a single long-duration flight in May. There is no action by the Ministry of Defence to provide rational decision making in regard to manned spaceflight.
1970 February 27 - .
- DOS schedules, Soyuz Kontakt flights still in play - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bogomolov,
Mishin.
Program: Soyuz,
Salyut,
Lunar L3,
Almaz.
Flight: Soyuz 10,
Soyuz 11,
Soyuz n 17,
Soyuz n 18,
Soyuz n 19,
Soyuz n 20.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz Kontakt,
Soyuz OB-VI,
Soyuz VI.
A meeting is held on the DOS project. The Central Committee and Soviet Ministers have directed that two DOS space stations be completed by the end of 1970. TsNIIMASH thinks this is impossible - the task can be accomplished in no less than 18 to 24 months. Mishin insists it can be done in ten months, as directed. Kamanin believes he won't even have it ready by the second half of 1971. It took five to seven years to just bring the Almaz, Soyuz VI, and L1 to flight status. This DOS will stop work on all other projects. Mishin still wants to fly two Soyuz spacecraft to test Bogomolov's Kontakt docking system for the L3.
1970 February-March - .
- Soyuz n 19 (cancelled) - . Crew: Patsayev, Shonin, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Patsayev, Shonin, Yazdovsky. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. The passive spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system. One or two of the crew would have spacewalked to the Soyuz 11 Kontakt and returned in the other spacecraft..
1970 February-March - .
- Soyuz n 20 (cancelled) - . Crew: Fartushny, Shatalov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Fartushny, Shatalov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz n 20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. The active spacecraft in the second planned test of the Kontakt lunar rendezvous/docking system..
1970 September 23 - .
- Cosmonaut training plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Bogomolov,
Bykovsky,
Mishin,
Popovich.
Program: Salyut,
Almaz,
Lunar L3.
Spacecraft: Almaz OPS,
Soyuz Kontakt,
Spiral OS.
The training plan for DOS#1 is reviewed. The station is to be launched by February 1971. Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11 will dock with it and crew the station for two to three months, according to Mishin's plan. This however will slow down flight test of Bogomolov's Kontakt docking system for the L3. This was to have been ready by January 1970, but it is still not ready for flight. On the other hand, the completion of the DOS station within four to five months is not possible. There are currently 12 cosmonauts in training for DOS, and ten for Soyuz flights. Popovich heads a group of 22 cosmonauts training for Almaz; and Bykovsky heads a group on lunar issues. The new trainers and simulators are on schedule; the existing ones are being heavily used.
1970 December 13 - .
- Kontakt test flights - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-OK, Soyuz Kontakt. Plans were underway for Kontakt test flights using 7K-OK spacecraft: 7K-OK number 18, 19 with "Kontakt". (Mishin Diaries 2-299).
1971 January 4 - .
- Preparation for Kontakt flights - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Meetings in January 1971 continue the level of coordination in preparation for Kontakt flights (4, 10, 12 January. (Mishin Diaries 2-314))..
1971 June 15 - .
- Soyuz Kontakt and DOS-2 crew assignments made. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Alekseyev, Semyon,
Artyukhin,
Bykovsky,
Filipchenko,
Gorbatko,
Grechko,
Gubarev,
Isakov,
Klimuk,
Kolodin,
Kovalyonok,
Lazarev,
Leonov,
Makarov,
Porvatkin,
Rukavishnikov,
Sevastyanov,
Shcheglov,
Vorobyov,
Voronov,
Yakovlev,
Yazdovsky.
Program: Salyut,
Lunar L3.
Flight: DOS 2-1,
DOS 2-2,
DOS 2-3,
DOS 2-4,
Soyuz 11,
Soyuz 12 / DOS 1,
Soyuz sn 18,
Soyuz sn 19,
Soyuz sn 20,
Soyuz sn 21,
Soyuz sn 22,
Soyuz sn 23.
Spacecraft: Salyut 1,
Soyuz Kontakt.
Crews are formed for six Soyuz (Kontakt?) flights. Soyuz s/n 18 - Filipchenko and Grechko; Soyuz s/n 19 - Lazarev and Makarov; Soyuz s/n 20 - Vorobyov and Yazdovsky; Soyuz s/n 21 - Yakovlelv and Porvatkin; Soyuz s/n 22 - Kovalyonok and Isakov; Soyuz s/n 23 - Shcheglov and [illegible]. Five crews are training for Salyut flights: Crew 1, Leonov, Rukavishnikov, and Kolodin; Crew 2, Gubarev, Sevastyanov, and Voronov. TsKBEM engineer cosmonauts are to be selected will round out the last three crews, but VVS members will be: Crew 3, Klimuk, Artyukhin; Crew 4, Bykovskyy, Alekseyev; Crew 5, Gorbatko. Leonov and Gubarev will have their crews fully ready for Soyuz 12 by 30 June, for a launch date between 15-20 July. Leonov is asking to go to East Germany for two to three days in the first week of July. Kamanin is fully opposed to this - he is thinkng not of his upcoming flight, but the exhibition of his paintings at the Prezdensk Gallery!
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 19 (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Lazarev, Makarov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 19. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 19 would have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. Would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 18 . A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 18 (cancelled) - . Crew: Filipchenko, Grechko. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Filipchenko, Grechko. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 18. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 18 would have been the active spacecraft of the first dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 20 (cancelled) - . Crew: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 20. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 20 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system. A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 Early - .
- Soyuz sn 21 (cancelled) - . Crew: Dobrovolsky, Sevastyanov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Dobrovolsky, Sevastyanov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 21. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 21 equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. Would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 20 . A crew transfer using the Krechet spacesuit would presumably have taken place..
1972 - .
- Soyuz sn 22 (cancelled) - . Crew: Isakov, Kovalyonok. Backup Crew: Shcheglov. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 22. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 22 would have been the active spacecraft of the second dual launch to test the Kontakt lunar orbit rendezvous system..
1972 - .
- Soyuz sn 23 (cancelled) - . Crew: Shcheglov. Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Shcheglov. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz sn 23. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Soyuz s/n 23 would have been equipped with the passive Kontakt rendezvous/docking system of the LK lunar lander. The spacecraft would have served as a docking target for Soyuz s/n 22. In Kamanin's diary, the name of the second crewmember is illegible..
1972 June 16 - .
- Kontakt docking system to be used in MKBS. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chertok.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt,
MKBS.
The reason for continuing with development of the L3 Kontakt docking system even after the L3 was cancelled was that it was to be used in MKBS. The note reads: Chertok - 7K-OK number 18 - rework using the propulsion system from number 36. Work on "Kontakt" to continue, as it can be used in the MKBS).
1972 June 16 - .
- Mishin notes problems with 7KS at Omsk and the rationale for continued testing of Kontak. - .
Related Persons: Mishin,
Chertok.
Spacecraft: Soyuz,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz Kontakt,
MKBS,
Soyuz 7K-S.
"1. Klyucharev VM: Omsk plant (Director Kolupaev) - Delayed production of 7KS living compartments. ZEM - develop work and schedules to recover schedule for completion of 7KS modules. 2. Chertok: 7K-OK number 18 - rework using the proulsion system from number 36. Work on "Kontakt" to continue, as it can be used in the MKBS'.
1973 Early - .
- Soyuz Kontakt A (cancelled) - . Crew: Filipchenko, Gorbatko. Backup Crew: Vorobyov, Yazdovsky. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz Kontakt A. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The launches were delayed and then cancelled due to continuing problems with the N1 lunar booster..
1973 Early - .
- Soyuz Kontakt P (cancelled) - . Crew: Lazarev, Makarov. Backup Crew: Fartushny, Klimuk. Nation: Russia. Program: Lunar L3. Flight: Soyuz Kontakt P. Spacecraft Bus: Soyuz. Spacecraft: Soyuz Kontakt. Final crews selected for a dual Soyuz mission in Earth orbit to test the Kontakt docking system to be used on the lunar landing LOK and LK spacecraft. The Kontakt-P Soyuz would have been the passive spacecraft, simulating the LK lunar lander..
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use