Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Kosmoplan
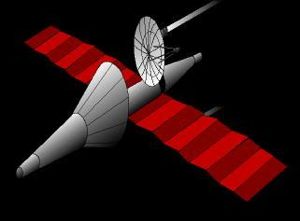 Kosmoplan - Mars Kosmoplan - Mars reconnaissance version Credit: © Mark Wade |
AKA: K. Status: Cancelled 1965. Gross mass: 12,000 kg (26,000 lb).
These would include highly maneuverable high performance storable liquid propellant engine modules; nuclear reactor modules for high power space applications; ion engine units for inter-orbital transfer and interplanetary flight; and re-entry vehicles permitting return of payloads from space with landing at conventional airfields.
Chelomei's design bureau originally designed cruise missiles, beginning with the 10X pulse-jet powered copy of the German V-1, continuing through a series of increasingly sophisticated designs in the 1950's. However it became apparent by the middle of the decade that the ballistic missile, for which no defense could be developed for decades, would win out over the cruise missile as a weapon system. Furthermore the ICBM opened up the possibility of exploration and colonization of space. Chelomei, invariably described as charming and ambitious, was anxious to be involved in the much more exciting arena of space flight. When Korolev's R-7 experienced a long string of launch failures in the summer of 1957, Chelomei was quick to criticize Korolev and ask to be put in charge of the development. But the decisive event in getting a piece of the space action was Chelomei's hiring of Nikita Khrushchev's son, Sergei, on March 8, 1958. This gave Chelomei sudden and immediate access to the highest possible patron in the hierarchy. He was rewarded with his own design bureau, OKB-52, in 1959.
Under Chelomei's direction the P-6 (SS-N-3 Shaddock) naval cruise missile was being developed. These missiles were made for long-term storage in environmentally-controlled capsules aboard Soviet warships. Chelomei saw that this technology could be applied to ballistic missiles and spacecraft as well.
Chelomei proposed use of this container approach for the UR-100 light ICBM, the Soviet answer to the US Minuteman. This most numerous of Russian ICBM's was a sealed unit, which could be stored fuelled for ten years before being fired within three minutes of launch command.
Beginning in the late 1950's, Chelomei began studying use of his encapsulated cruise missile technology for spacecraft. A whole family of unmanned spacecraft, dubbed Kosmoplans, would be built using modular elements. These would include highly maneuverable high performance storable liquid propellant engine modules; nuclear reactor modules for high power space applications; ion engine units for inter-orbital transfer and interplanetary flight; and re-entry vehicles permitting return of payloads from space with landing at conventional airfields.
These re-entry vehicles were of unique concept and consisted of a high-fineness oblique conical heat shield with petal-like maneuvering flaps at the base. These were capable of very large cross-range maneuvers (up to 3000 km) at hypersonic speed as well as controlled re-entry at very high velocities from planetary return trajectories. A similar configuration was tested by the US Air Force in the late 1960's as the Boost Glide Re-entry Vehicle (perhaps based on intelligence of Chelomei's design?). The external shell enclosed an adaptation of Chelomei's naval cruise missiles, a cylindrical fuselage with snap-out wings and a cruise turbojet. After re-entry, the conical shield would explosively separate at Mach 2. The internal craft would deploy its wings and turbojet air inlet, start its engine, and then cruise to a radio-guided precision landing at an airfield on Soviet territory.
This approach eliminated the very difficult hot structure problems encountered by other chief designers in their spaceplane designs of the same period. Since the hot heat shield would be jettisoned, the contents did not have to be designed to handle thermal equilibrium temperatures of 400 degrees or more. The same vehicle could also deliver a larger payload under a parachute, or a nuclear warhead.
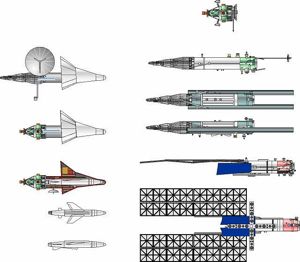
Kosmoplans were to be launched by Chelomei's equally modular family of 'UR' universal rockets, capable of both ICBM and space launch missions. Chelomei proposed variants of Kosmoplans for studies of the earth's upper atmosphere, television communications, meteorology, military photo-reconnaissance, naval radar and signals reconnaissance, and interception and destruction of enemy satellites. Civilian Kosmoplans would engage in exploration of near earth space and the planets. The same modular principles but larger re-entry vehicles would be used for manned interceptor combat Raketoplans. While the UR-200 rocket would be used for launch of smaller earth orbital Kosmoplans, a cluster of UR-200's would create the much larger UR-500 launch vehicle. The UR-500 would be used for launch of manned, lunar landing, and interplanetary Kosmoplan / Raketoplan designs.
In 1959, as Chelomei laid out these plans, he knew a tremendous struggle would be required to wrest a piece of the space program from Chief Designer Korolev. Korolev was interested in military projects only so far as they provided financing for his dreams of space exploration. He jealously wished to keep all manned, lunar, and planetary space projects to himself. But Chelomei had stacked the deck against Korolev by hiring Khrushchev's son as a lead engineer at his OKB.
The opening shot was contained in a letter sent by Korolev to the Central Committee of the Communist Part in January 1960. Korolev proposed an aggressive program for Communist conquest of space - entirely by Korolev's OKB. He pledged to place before the Central Committee in the third quarter of 1960 comprehensive plans for development of the new projects. This letter was followed by a meeting with Khrushchev on the subject on 3 March 1960. Korolev believed it would be truly possible with backing from the very top to have a large rocket in the USSR in a very short span of time. Unfortunately at the meeting Korolev made a slip of the tongue he would always regret, admitting that his plan had not been agreed among all of the Chief Designers. This resulted in Khrushchev throwing the matter back for a consensus plan.
By 30 May 1960 Korolev was back with a plan that now included participation of his rivals, Chelomei and Yangel. The consolidated plan included the following elements allocated to Chelomei:
- Theme K - Development of unpiloted Kosmoplans for flight to Mars and Venus with return to earth and landing at conventional airfields. These would use new exotic chemical systems, low thrust nuclear engines (nuclear-plasma, ion, atomic hydrogen). The preferred variant consisted of the Kosmoplan re-entry vehicle + equipment section + ion engines on booms + nuclear reactor. Sub-variants with a total mass of 10 to 12 metric tons and 25 metric tons would be developed in 1965-1966. Draft project to be completed in 1962. This authority extended to design of combat orbital Kosmoplans with nuclear warheads for maneuvering re-entry after launch by GR-1 (UR-200) or GR-2 (UR-500) rockets. These would use the re-entry vehicle without the air-breathing lander + the liquid propulsion module.
- Development of a 600 metric ton gross lift-off mass rocket using new chemical propellants for sending spacecraft to nearby planets. Draft project to be completed in 1962. This would become the UR-500 Proton booster. But it was likely that the actual primary purpose of this rocket was also not mentioned in the declassified document. The Proton was originally designed for the GR-2 (Global Rocket 2) requirement. The GR-2 was to be a kind of enormous multiple-warhead FOBS (fractional orbit bombing system). The payload of the rocket was to be six independently maneuvering nuclear armed vehicles. Each vehicle had a 1,500 kg 2.2 MT nuclear warhead. They would separate from the final stage, and make violent maneuvers using independent guidance systems to put each warhead in a different low 160 km altitude orbit. At the end of a 10,000 to 12,000 km journey along their separate orbital paths, the warheads would appear on US radar screens at the last moment with minimal warning. The total spread of the warheads would be 1800 km from left to right; two such global rockets could devastate America's major cities from coast to coast in an unstoppable first strike. The Kosmoplan re-entry vehicle would use aerodynamic horizontal and vertical maneuvering to penetrate enemy space defenses and be practically invulnerable.
- Theme R - Manned Raketoplan spacecraft for orbital maneuvering flight and recovery at conventional airfields. Total mass to be 10 to 12 metric tons, total gliding range during re-entry 2,500 to 3,000 km. Unpiloted version to be developed in 1960 to 1961, followed by piloted version in 1963 to 1965. Satellite interceptor operational version to be tested in 1962 to 1964.
- Theme US - Upravlenniye Sputnik - Naval reconnaissance satellite using P6 nuclear reactor. To be developed in 1962 to 1964. This variant use an active radar system to track American warships and would consist of the Kosmoplan nuclear reactor + equipment module + specialized radar equipment. This Kosmoplan variants went into service, but late to schedule.
- Theme IS - Istrebitel Sputnik - Anti-satellites - the Ministry of Defense was to decide by July 1960 whether to develop an R-7 launched system for annihilation of enemy reconnaissance satellites. Chelomei was later authorized to proceed with this project. The Chelomei IS ASAT would use the Kosmoplan maneuvering bus and be the first variant to fly. He planned for launch of the production model on the UR-200. But this was cancelled and production ASAT's flew in the late 1960's, launched by Yangel Tsiklon rockets.
Chelomei was authorized by Decree 715-296 of 23 June 1960 'On the Production of Various Launch Vehicles, Satellites, Spacecraft for the Military Space Forces in 1960-1967' to complete a draft project on unpiloted Kosmoplans. Chelomei managed a first flight test of a subscale unpiloted version of the Kosmoplan / Raketoplan re-entry vehicle on 21 March 1961.
The Kosmoplan's UR-200 (8K81) launch vehicle was approved for production on 16 March and 1 August 1961 by the Central Committee and Politburo. The UR-200 was designed not only to send a thermonuclear warhead over a range of 12,000 km, but also to orbit all of the Kosmoplan military variants: the IS ASAT; the US nuclear-powered naval intelligence satellite; and the Kosmoplan combat re-entry vehicle. The Kosmoplan and UR-200 draft projects were completed in July 1962. The rocket's technical characteristics would be similar to those of Korolev's R-9 and Yangel's R-16. Trial flights of the ICBM version ran from 4 November 1963 to 20 October 1964.
Approval to proceed with the UR-500 (8K82) was provided in the Central Committee decree of 24 April 1962. The draft project UR-500 was completed in 1963. The fundamental technological problems of the project had been solved by the end of 1964. In the early fall of that year, Khrushchev and the political leadership of the country visited Baikonur. Chelomei with great pride guided Khrushchev around a dummy UR-500 installed in its launch gantry at the new launch complex, presented the heavy transporters for the launch vehicle and showed a scale model of the launch silo planned for the combat version. Khrushchev's comment was 'what should we build - communism or silos for the UR-500?" It was clear that Khrushchev was not very supportive of the military version of the UR-500.
On October 13, 1964, Khrushchev was ousted from power. The new leadership, under Brezhnev, was adverse to all projects Khrushchev had supported. These included those of Chelomei and his OKB-52. An expert commission under M V Keldysh was directed to examine all of Chelomei's projects and make recommendations as to which should be cancelled. Keldysh found that Yangel's R-36 universal rocket and fractional orbital bombing system was superior to Chelomei's UR-200 / Kosmoplan combat re-entry vehicle. The UR-200 and Kosmoplan were accordingly cancelled. The IS and US Kosmoplans were redesigned for launch by the R-36. The UR-500 development was continued, but only in the 8K82K space launch version for sending the surviving Raketoplan, the LK-1 manned circumlunar spacecraft, around the moon.
The LK-1 was in turn cancelled in late 1965 as Korolev finally regained control of all manned lunar projects. The military Kosmoplans went on to greater success. The IS anti-satellite, US nuclear naval reconnaissance both went into military service. A derivative of the US for detection of US ship positions using passive radio techniques saw long service with the Soviet military. And the UR-500K became the Proton rocket, Russia's most successful commercial launch vehicle.
| Polyot Russian military anti-satellite system. First prototype model of Chelomei's ASAT, used in an interceptor control and propulsion test. ASAT technology satellite, Russia. Launched 1963. |
| Polyot 2 / I1P 1 Null |
| US-AO Ocean surveillance, active radar satellite, Russia. Launched 1965 - 1969. Used US-Bus. |
| US-A Russian military naval surveillance radar satellite. The US-A (later known as RLS) was a nuclear powered RORSAT (Radar Ocean Reconnaissance Satellite). Ocean surveillance, active radar satellite, Russia. Launched 1970 - 1988. Used US-Bus. |
| I2-BM ASAT satellite built by TsNII Kometa, Russia. Launched 1967. |
| IS-A Russian military anti-satellite system. First operational ASAT. Tested in 1967-1971 and deployed through the late 1970's. Design as revised by Yangel and Korolev from Chelomei's original. ASAT satellite built by TsNII Kometa, Russia. Launched 1976 - 1982. |
| IS-P Russian military anti-satellite system target satellite. ASAT Target, launched by R-36. Evidently a derivative of the first IS-A ASAT itself. |
| I2P Manufacturer's designation for [IS-A] military anti-satellite system. |
| IS-GVM Dummy payload of the IS satellite. |
| US-K (73D6) Null |
| US-P Russian military naval radarsat. The US-P (later known as RTR) was a solar powered EORSAT (Electronic Ocean Reconnaissance Satellite). Ocean surveillance, passive satellite, Russia. Launched 1974 - 1991. Used US-Bus. |
| US-KS (74Kh6) Null |
| Plasma-A Technology, nuclear reactor satellite, Russia. Launched 1987. Used US Bus. |
| Pirs-1 Russian military naval surveillance radar satellite. 2 launches, 1987.02.02 and 1987.07.10 . |
| Plazma-A Russian ion engine technology satellite. In 1987 two experimental Plazma-A satellites (Cosmos 1818 and 1867) were launched with new-generation Topaz reactors. |
| IS-MU Russian military anti-satellite system. Reportedly deployed in 1990. Improved modernized ASAT/ABM. Reportedly deployed in 1980's without flight test, replacing IS-A. Accepted into military service in 1991. ASAT satellite built by TsNII Kometa, USSR. |
| US-KMO (71Kh6) Null |
| Obzor Russian earth resources radar satellite. Study 1992. The Arsenal Design Bureau proposed converting its military ocean reconnaissance spacecraft bus (EORSAT) into a civil remote sensing platform. |
| US-PU Ukrainian military naval radarsat. Ocean surveillance, passive satellite, Russia. Launched 1993 - 2006. Used US-Bus. |
| Konus-A Russian gamma ray astronomy satellite. Study 1995. The Konus-A scientific satellite was developed in 1995-1997 for the Russian Academy of Science and flown as Cosmos 2326. |
| Kupon Russian military communications satellite. Kupon was originally developed by Lavochkin for the third generation GKKRS (Global Space Command and Communications System). Other satellites in the network included Potok and Geizer. Communication satellite built by Lavochkin (prime), NPO Elas (transponders) for Central Bank of the Russian Federation, Russia. Launched 1997. Used US-KMO-Bus. |
| Obzor-R Earth Observation, cosmic rays satellite built by TsSKB-Progress for Roskosmos. |
Family: Mars orbiter. Country: Russia. Launch Vehicles: Mars tactical rocket, UR-500, UR-200. Agency: Chelomei bureau. Bibliography: 283, 304, 474.
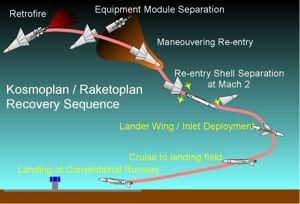 | Kosmoplan profile Kosmoplan landing profile Credit: © Mark Wade |
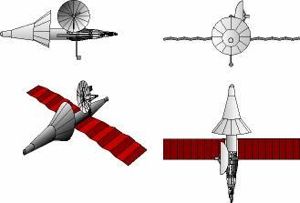 | Kosmoplan - 3 view Kosmoplan - 3 view drawing - Mars reconnaissance, nuclear electric engine version Credit: © Mark Wade |
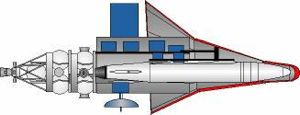 | Kosmoplan - cutaway Kosmoplan - cutaway - conceptual drawing, showing air-breathing lander inside manoeuvring re-entry shell Credit: © Mark Wade |
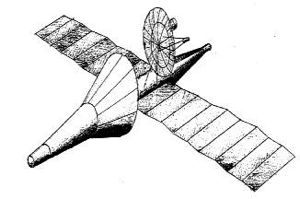 | Kosmoplan - Mars Kosmoplan - Mars reconnaissance, nuclear electric engine version Credit: © Mark Wade |
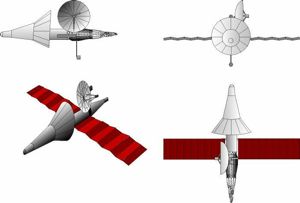 | Kosmoplan - 3 view Kosmoplan - 3 view drawing - Mars reconnaissance, nuclear electric engine version Credit: © Mark Wade |
1958 March 8 - .
- Chelomei's bureau acquires GSNII-642. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Khrushchev.
Spacecraft: Kosmoplan.
Ministry of Aviation Industry (MAP) Decree 293-140 'On subordinating GSNII-642 to OKB-52' was issued. On the same day Chelomei hired Nikita Khrushchev's son, Sergei, to work as an engineer in his design bureau. This gave Chelomei sudden and immediate access to the highest possible patron in the hierarchy. He was rewarded with his own design bureau, OKB-52, in 1959. This would lead to Chelomei being a key figure in the Soviet space program, even after Khruschev's ouster in 1964.
1959 During the Year - .
- Kosmoplans proposed by Chelomei. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Spacecraft: Kosmoplan.
Chelomei began studying use of his encapsulated cruise missile technology for spacecraft. A whole family of unmanned spacecraft, dubbed Kosmoplans, would be built using modular elements. These would include highly manoeuvrable high performance storable liquid propellant engine modules; nuclear reactor modules for high power space applications; ion engine units for inter-orbital transfer and interplanetary flight; and re-entry vehicles permitting return of payloads from space with landing at conventional airfields.
1960 January - .
- Korolev proposed an aggressive program for Communist conquest of space. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Korolev. Spacecraft: Kosmoplan. In a letter sent by Korolev to the Central Committee of the Communist Part, he pledged to provide a comprehensive plan by the third quarter of 1960 comprehensive plans for development of the new projects..
1960 March 3 - .
- Korolev-Khruschev meeting on space plans. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Khrushchev,
Korolev.
Spacecraft: Kosmoplan.
Korolev believed it would be truly possible with backing from the very top to have a large rocket in the USSR in a very short span of time. Unfortunately at the meeting Korolev made a slip of the tongue he would always regret, admitting that his plan had not been agreed among all of the Chief Designers. This resulted in Khrushchev throwing the matter back for a consensus plan.
1960 May 30 - .
- Korolev space development plan - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei, Korolev, Yangel. Spacecraft: Kosmoplan. Korolev revised his earlier, disapproved plan with one that now included participation of his rivals, Chelomei and Yangel..
1961 March 6 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- US RORSAT authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decree 420·1741 'On approval of work on the US satellite and UR-200 launch vehicle / ICBM' was issued..
1961 March 16 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- UR-200 (8K81) launch vehicle development authorised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft: IS-A,
Kosmoplan,
OGCh,
US-A,
US-P.
An enabling decree was issued on 1 August 1961 by the Central Committee and Politburo. The UR-200 was designed not only to send a thermonuclear warhead over a range of 12,000 km, but also to orbit all of the Kosmoplan military variants: the IS ASAT; the US nuclear-powered naval intelligence satellite; and the Kosmoplan combat re-entry vehicle.
1961 May 13 - . Launch Vehicle: N1.
- Soviet response to Apollo program - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Spacecraft: Elektron-A,
Elektron-B,
Kosmoplan,
LK-1,
Raketoplan.
Soviet Decree 'On the Revision of Plans for Space Objects for Accomplishing Goals of Defence Designations--heavy boosters, course of work on Elektron, and suspension of work of work on the Kosmoplan and Raketoplan with continuation of new Raketoplan work' was issued. The decree set the end of 1965 as the date for the first launch of the N1. It also authorised Chelomei to stop work on Kosmoplan interplanetary probes and instead concentrate on a specific Raketoplan design - the LK-1 manned lunar flyby spacecraft.
1962 June 3 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- US RORSAT development plans. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decree 'On course of work on the US reconnaissance satellite system launched on the UR-2OO' was issued..
1962 July - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- Kosmoplan and UR-200 draft projects completed. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: IS-A, Kosmoplan, US-A. Trial flights of the ICBM version ran from 4 November 1963 to 20 October 1964. Versions of the Kosmoplan would fly as the reactor-powered US-A and solar-powered US-P ELINT satellites and the I2P ASAT..
1963 November 1 - . 08:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Sputnik 11A59.
- Polet 1; Polyot 1 - .
Payload: I-2B s/n 1. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei.
Agency: Korolev bureau.
Class: Military.
Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: Polyot.
Decay Date: 1982-10-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 683 . COSPAR: 1963-043A. Apogee: 1,420 km (880 mi). Perigee: 331 km (205 mi). Inclination: 58.90 deg. Period: 102.40 min.
ASAT interceptor control and propulsion test. Launched by Korolev R-7 because Chelomei's own UR-200 was not yet available. Purpose - elaboration of system providing for the extensive manoeuvring of space apparatuses. Flight was considered a great success. Micro-engine fired 350 times and main stabilizing engine fired 300 times. Orbit given is final orbit after manoeuvres.
1964 April 12 - . 09:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Sputnik 11A59.
- Polet 2; Polyot 2 - . Payload: I-2B s/n 2. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: Korolev bureau. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: Polyot. Decay Date: 1966-06-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 783 . COSPAR: 1964-019A. Apogee: 479 km (297 mi). Perigee: 303 km (188 mi). Inclination: 58.10 deg. Period: 92.30 min. ASAT interceptor control and propulsion test. Elaboration of systems providing for the extensive manouevring of space apparatuses..
1964 May 22 - .
- Kosmoplan and Raketoplan canceled, except for LK-1 manned circumlunar spacecraft. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: Kosmoplan, LK-1, Raketoplan. Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On termination of work on the Kosmoplan and Raketoplan at OKB-52 and approval for the LK-1' was issued..
1964 October 13 - .
- Khrushchev ousted from power. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei, Khrushchev. Spacecraft: IS-A, Kosmoplan, LK-1, OGCh, US-A, US-P. Brezhnev faction assumes control of Politubro. Brezhnev was adverse to all projects Khrushchev had supported. These included those of Chelomei and his OKB-52..
1964 October 20 - .
- Final UR-200 launch. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: Kosmoplan. The rocket had already been cancelled after the fall of Khrushchev..
1965 December 27 - . 22:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A510.
- Cosmos 102 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1966-01-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 1867 . COSPAR: 1965-111A. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 89.20 min. Prototype RORSAT hardware using chemical batteries in place of nuclear reactor..
1966 July 20 - . 09:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A510.
- Cosmos 125 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1966-08-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 2351 . COSPAR: 1966-067A. Apogee: 260 km (160 mi). Perigee: 204 km (126 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Prototype RORSAT hardware using chemical batteries in place of nuclear reactor. Lost on the 52nd revolution as a result of a possible failure in the chemical power units placed on board instead of the nuclear BES-5..
1967 March 30 - .
- PKO Anti-satellite Force created. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Ministry of Defence Decree 'On formation of Anti-Space and Anti-Missile Forces of the Air Defence Forces (PKO) to operate General Soviet ASAT systems' was issued..
1967 October 27 - . 02:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 185 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1969-01-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 3013 . COSPAR: 1967-104A. Apogee: 887 km (551 mi). Perigee: 518 km (321 mi). Inclination: 64.20 deg. Period: 98.80 min. First test of Istrebitel Sputnik. Only tested engine; no target launched. First launch of Tsykon launch vehicle..
1967 December 27 - . 11:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 198 - . Payload: US-A no. 1. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1968-01-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 3082 . COSPAR: 1967-127B. Apogee: 927 km (576 mi). Perigee: 907 km (563 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.40 min. Prototype RORSAT hardware using chemical batteries in place of BES-5 nuclear reactor. First satellite to be boosted to 900 km storage orbit..
1968 March 22 - . 09:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 209 - . Payload: US-A no. 2. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1968-04-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 3162 . COSPAR: 1968-023C. Apogee: 927 km (576 mi). Perigee: 876 km (544 mi). Inclination: 65.30 deg. Period: 103.00 min. RORSAT hardware, representative of production hardware, but using chemical batteries in place of BES-5 nuclear reactor..
1968 April 24 - . 16:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 217 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system target. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-P. Decay Date: 1968-04-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 3216 . COSPAR: 1968-036A. Apogee: 179 km (111 mi). Perigee: 140 km (80 mi). Inclination: 62.30 deg. Period: 87.70 min. Unsuccessful launch of ASAT target. Satellite did not separate from last rocket stage. Planned launch of interceptor cancelled..
1968 October 19 - . 04:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 248 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system target. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-P. Decay Date: 1980-02-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 3503 . COSPAR: 1968-090A. Apogee: 543 km (337 mi). Perigee: 475 km (295 mi). Inclination: 62.30 deg. Period: 94.80 min. ASAT target. Intercepted repeatedly by Cosmos 249 on 20 October; destroyed by Cosmos 252 on 1 November..
1968 October 20 - . 04:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 249 - .
Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: PKO.
Class: Military.
Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: IS-A.
Decay Date: 1968-10-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 3504 . COSPAR: 1968-091A. Apogee: 2,075 km (1,289 mi). Perigee: 498 km (309 mi). Inclination: 62.30 deg. Period: 111.30 min.
ASAT interceptor. Intercepted Cosmos 248 target on second orbit. Repeatedly approached Cosmos 248, verifying primary and reserve homing and guidance systems. Destroyed itself in test of on-board destruct system. Counted as a failure by Western observers because that target was not destroyed; but this was not an objective of the test. Left 109 fragments in orbit, of which 54 were still in orbit in 1996.
1968 November 1 - . 00:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 252 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1968-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3530 . COSPAR: 1968-097A. Apogee: 2,104 km (1,307 mi). Perigee: 535 km (332 mi). Inclination: 62.30 deg. Period: 112.00 min. ASAT interceptor. Intercepted and destroyed Cosmos 248 target satellite within one day of launch. Left 139 fragments in orbit, the largest of any ASAT test..
1969 January 25 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A. FAILURE: Payload propulsion system failed; no orbit.. Failed Stage: P.
- US-A Mass Model - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1969-01-24 . COSPAR: F690125A. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). RORSAT hardware, representative of production hardware, but using chemical batteries in place of BES-5 nuclear reactor..
1969 August 6 - . 05:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 291 - . Payload: IS-P Mass Model. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system target. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-P. Decay Date: 1969-09-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 4058 . COSPAR: 1969-066A. Apogee: 548 km (340 mi). Perigee: 144 km (89 mi). Inclination: 62.20 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Test of Tsyklon 2 booster; ASAT target mass model. Did not enter typical target orbit due to lack of on-board engine. Simulated launch of ASAT interceptor planned for the next day was cancelled..
1969 December 23 - . 09:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 316 - .
Payload: IS-A Mass Model. Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: PKO.
Class: Military.
Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: IS-A.
Decay Date: 1970-08-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 4282 . COSPAR: 1969-108A. Apogee: 1,638 km (1,017 mi). Perigee: 152 km (94 mi). Inclination: 49.50 deg. Period: 102.80 min.
Test of Tsyklon 2 booster; mass model of ASAT. When the satellite decayed over US Midwest on 28 August 1970, teams of the USAF 1127th Special Group were able to recover six pieces from five locations in Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas. These showed that the necessary operational systems - translation engines, sensors, weapons systems - were dummied by steel weights. However factory markings on the recovered material proved to the Air Force analysts that they were dealing with an ASAT weapon.
1970 October 3 - . 10:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 367 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1970-10-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 4566 . COSPAR: 1970-079C. Apogee: 1,022 km (635 mi). Perigee: 915 km (568 mi). Inclination: 65.30 deg. Period: 104.50 min. Ocean surveillance; probably used chemical batteries..
1970 October 20 - . 05:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 373 - . Mass: 650 kg (1,430 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system target. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-P. Decay Date: 1980-03-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 4590 . COSPAR: 1970-087A. Apogee: 1,103 km (685 mi). Perigee: 510 km (310 mi). Inclination: 62.90 deg. Period: 101.00 min. ASAT target. Maneuvered twice to provide target for Cosmos 374 and 375 interceptors..
1970 October 23 - . 04:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 374 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1970-10-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 4594 . COSPAR: 1970-089A. Apogee: 1,464 km (909 mi). Perigee: 531 km (329 mi). Inclination: 63.00 deg. Period: 105.10 min. ASAT interceptor. Intercepted Cosmos 374 on second orbit. Blown up on instructions from ground..
1970 October 30 - . 02:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 375 - .
Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: PKO.
Class: Military.
Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: IS-A.
Decay Date: 1970-10-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 4598 . COSPAR: 1970-091A. Apogee: 1,986 km (1,234 mi). Perigee: 579 km (359 mi). Inclination: 62.80 deg. Period: 111.20 min.
ASAT interceptor. Intercept on second orbit. Blown up on instructions from ground. Dual launch of interceptors was intended to help ground staff perfect computational methods for quick-response launches when orbital methods of target were not precisely known.
1971 February 25 - . 11:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 397 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. USAF Sat Cat: 4964 . COSPAR: 1971-015A. Apogee: 2,164 km (1,344 mi). Perigee: 572 km (355 mi). Inclination: 65.70 deg. Period: 113.10 min. ASAT interceptor. Intercept and destruction of target successful on second orbit..
1971 April 1 - . 11:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 402 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1971-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 5107 . COSPAR: 1971-025B. Apogee: 1,011 km (628 mi). Perigee: 965 km (599 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.90 min. Ocean surveillance; probably used chemical batteries..
1971 April 4 - . 14:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 404 - .
Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: PKO.
Class: Military.
Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: IS-A.
Decay Date: 1971-04-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 5113 . COSPAR: 1971-027A. Apogee: 1,010 km (620 mi). Perigee: 802 km (498 mi). Inclination: 65.70 deg. Period: 103.10 min.
ASAT interceptor. Conducted an extended test flight to shake out homing system and engine function. Tested new redundant ranging systems. Tested effectiveness of new approach trajectory to target, whereby target was approached from above rather than below. Following completion of tests and verification of system functions via telemetry, spacecraft was commanded to a destructive reentry over the Pacific Ocean.
1971 December 3 - . 13:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 462 - .
Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: PKO.
Class: Military.
Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: IS-A.
Decay Date: 1975-04-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 5646 . COSPAR: 1971-106A. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Perigee: 229 km (142 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 105.40 min.
ASAT interceptor. Successfully intercepted and destroyed Cosmos 459 target. This completed state trials test series and in 1972 the Istrebitel Sputnik was adopted as armament for the Soviet Army. Cosmos 462 produced the lowest number of fragments (27) of any of the ASAT's tested.
1971 December 25 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 469 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1972-02-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 5737 . COSPAR: 1971-117B. Apogee: 1,006 km (625 mi). Perigee: 948 km (589 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 104.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered. First RORSAT flight confirmed by Russian source to have had BES-5 nuclear reactor..
1972 August 21 - . 10:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 516 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1972-10-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 6199 . COSPAR: 1972-066C. Apogee: 1,038 km (644 mi). Perigee: 906 km (562 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 104.50 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1973 April 25 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2. FAILURE: Payload propulsion system failed; no orbit.. Failed Stage: P.
- RORSAT failure - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1973-04-25 . COSPAR: F730425A. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered. Last launch of original US-A design by Savin's KB. American 'sniffer' aircraft flew over the Pacific after this failure looking for radioisotopes traces in order to characterise the reactor..
1973 December 27 - . 20:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 626 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1974-03-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 7115 . COSPAR: 1973-108D. Apogee: 982 km (610 mi). Perigee: 907 km (563 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered. First test of modernised design by KB Arsenal..
1974 May 15 - . 07:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 651 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1974-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 7388 . COSPAR: 1974-029C. Apogee: 946 km (587 mi). Perigee: 890 km (550 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 103.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1974 May 17 - . 06:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 654 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1974-09-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 7397 . COSPAR: 1974-032D. Apogee: 1,006 km (625 mi). Perigee: 924 km (574 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1974 December 24 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 699 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1977-10-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 7587 . COSPAR: 1974-103A. Apogee: 440 km (270 mi). Perigee: 428 km (265 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring; exploded 4/17/75..
1974 December 31 - .
- Plasma-A satellite authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: Plazma-A. Ministry of General Machine Building (MOM) Decree 314 'On development of the Topaz-1 thermionic nuclear reactor for Plasma-A spacecraft' was issued..
1975 April 2 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 723 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1975-07-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 7797 . COSPAR: 1975-024D. Apogee: 961 km (597 mi). Perigee: 899 km (558 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 103.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1975 April 7 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 724 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1975-08-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 7922 . COSPAR: 1975-025B. Apogee: 943 km (585 mi). Perigee: 852 km (529 mi). Inclination: 65.60 deg. Period: 102.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1975 October 1 - . LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- US-A and Tsiklon-2 accepted into military service. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On adoption of US-A with Tsiklon-2 into armaments' was issued..
1975 October 29 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 777 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1976-06-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 8416 . COSPAR: 1975-102A. Apogee: 442 km (274 mi). Perigee: 425 km (264 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring; exploded 1/76..
1975 December 12 - . 12:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 785 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1976-02-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 8480 . COSPAR: 1975-116C. Apogee: 1,004 km (623 mi). Perigee: 907 km (563 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 104.20 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered; failed immediately after reaching orbit..
1976 February 16 - . 08:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 804 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1976-02-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 8694 . COSPAR: 1976-015A. Apogee: 702 km (436 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 93.10 min. ASAT interceptor. After intercept with target deorbited using on-board engine..
1976 April 13 - . 17:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 814 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1976-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 8806 . COSPAR: 1976-034A. Apogee: 480 km (290 mi). Perigee: 118 km (73 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 90.50 min. ASAT interceptor. After intercept with target deorbited using on-board engine..
1976 July 2 - . 10:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 838 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1977-08-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 8932 . COSPAR: 1976-063A. Apogee: 440 km (270 mi). Perigee: 428 km (265 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean surveillance. Exploded June/July '76..
1976 July 21 - . 15:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 843 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1976-07-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 9043 . COSPAR: 1976-071A. Apogee: 346 km (214 mi). Perigee: 132 km (82 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 89.30 min. ASAT interceptor. Intercepted Cosmos 839. Deorbited after test..
1976 October 17 - . 18:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 860 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1976-12-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 9531 . COSPAR: 1976-103B. Apogee: 995 km (618 mi). Perigee: 923 km (573 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 104.30 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1976 October 21 - . 16:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 861 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1977-02-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 9631 . COSPAR: 1976-104C. Apogee: 987 km (613 mi). Perigee: 928 km (576 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.20 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1976 November 26 - . 14:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 868 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1978-07-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 9561 . COSPAR: 1976-113A. Apogee: 444 km (275 mi). Perigee: 422 km (262 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min.
1976 December 10 - .
- Plasma-A construction authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: Plazma-A. Military-Industrial Commission (VPK) Decree 342 'On development of the Topaz-1 thermionic nuclear reactor for Plasma-A spacecraft' was issued..
1976 December 27 - . 12:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 886 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1976-12-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 9634 . COSPAR: 1976-126A. Apogee: 2,291 km (1,423 mi). Perigee: 593 km (368 mi). Inclination: 65.80 deg. Period: 114.70 min. ASAT interceptor. Intercepted and destroyed Cosmos 880 target..
1977 May 23 - . 12:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 910 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1977-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 10014 . COSPAR: 1977-037A. Apogee: 506 km (314 mi). Perigee: 149 km (92 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 91.00 min. ASAT interceptor. Failed to intercept Cosmos 909. Deorbited using on-board engine..
1977 June 17 - . 07:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 918 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1977-06-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 10065 . COSPAR: 1977-050A. Apogee: 197 km (122 mi). Perigee: 125 km (77 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 87.70 min. ASAT interceptor. Failed to intercept Cosmos 909. Deorbited using on-board engine..
1977 August 24 - . 07:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 937 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1978-10-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 10278 . COSPAR: 1977-077A. Apogee: 444 km (275 mi). Perigee: 424 km (263 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1977 September 16 - . 14:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 952 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1977-11-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 10399 . COSPAR: 1977-088B. Apogee: 990 km (610 mi). Perigee: 911 km (566 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1977 September 18 - . 13:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 954 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1978-01-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 10361 . COSPAR: 1977-090A. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 251 km (155 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered; re-entered over Canada, spreading radioactive debris..
1977 October 26 - . 05:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 961 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1977-10-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 10434 . COSPAR: 1977-104A. Apogee: 1,421 km (882 mi). Perigee: 269 km (167 mi). Inclination: 66.40 deg. Period: 101.80 min. ASAT interceptor. Succeeded in intercept of Cosmos 959. Deorbited using on-board engine..
1977 December 21 - . 10:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 970 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1977-12-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 10531 . COSPAR: 1977-121A. Apogee: 1,138 km (707 mi). Perigee: 936 km (581 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 105.90 min. ASAT interceptor. Intercepted Cosmos 970 target. Ordered to self-destruct following interception..
1978 May 19 - . 00:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1009 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1978-05-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 10904 . COSPAR: 1978-050A. Apogee: 1,364 km (847 mi). Perigee: 966 km (600 mi). Inclination: 65.90 deg. Period: 108.60 min. ASAT interceptor. Succeeded in intercept of Cosmos 970. Deorbited using on-board engine..
1979 April 18 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1094 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1979-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 11333 . COSPAR: 1979-033A. Apogee: 442 km (274 mi). Perigee: 426 km (264 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1979 April 25 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1096 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1979-11-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 11346 . COSPAR: 1979-036A. Apogee: 442 km (274 mi). Perigee: 428 km (265 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1980 March 14 - . 10:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1167 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1981-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11729 . COSPAR: 1980-021A. Apogee: 442 km (274 mi). Perigee: 426 km (264 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1980 April 18 - . 00:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1174 - .
Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: MO.
Class: Military.
Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: IS-A.
Decay Date: 1980-04-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 11765 . COSPAR: 1980-030A. Apogee: 1,419 km (881 mi). Perigee: 372 km (231 mi). Inclination: 66.10 deg. Period: 102.90 min.
ASAT interceptor. First test of ASAT after extended storage. Missed Cosmos 1171 target by a large distance; over the two following days two more attempts were made with the backup engine, but all failed. On 20 April the satellite was ordered to self-destruct in orbit, ending the longest ASAT interceptor mission.
1980 April 29 - . 11:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1176 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1980-10-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 11968 . COSPAR: 1980-034B. Apogee: 962 km (597 mi). Perigee: 873 km (542 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 103.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered; test flight of modified safer design..
1980 November 4 - . 15:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1220 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1982-06-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 12054 . COSPAR: 1980-089A. Apogee: 759 km (471 mi). Perigee: 526 km (326 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 97.60 min. Ocean monitoring..
1981 February 2 - . 02:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1243 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1981-02-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 12160 . COSPAR: 1981-010A. Apogee: 1,013 km (629 mi). Perigee: 294 km (182 mi). Inclination: 65.80 deg. Period: 97.80 min. ASAT interceptor. Approached within 50 m of target, but explosive charge did not go off as planned. Deorbited to destructive reentry in the atmosphere..
1981 March 5 - . 18:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1249 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1981-07-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 12552 . COSPAR: 1981-021D. Apogee: 976 km (606 mi). Perigee: 904 km (561 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1981 March 14 - . 16:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1258 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1981-03-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 12337 . COSPAR: 1981-024A. Apogee: 1,022 km (635 mi). Perigee: 299 km (185 mi). Inclination: 65.80 deg. Period: 97.90 min. ASAT interceptor. Failed to intercept Cosmos 1241 target. Deorbited to destructive reentry in the atmosphere..
1981 March 20 - . 23:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1260 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1982-05-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 12364 . COSPAR: 1981-028A. Apogee: 444 km (275 mi). Perigee: 425 km (264 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1981 April 21 - . 03:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1266 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1981-05-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 12429 . COSPAR: 1981-037B. Apogee: 941 km (584 mi). Perigee: 911 km (566 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 103.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1981 August 4 - . 08:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1286 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1982-10-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 12631 . COSPAR: 1981-072A. Apogee: 442 km (274 mi). Perigee: 430 km (260 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.20 min. Ocean monitoring..
1981 August 24 - . 16:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1299 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1981-09-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 12809 . COSPAR: 1981-081E. Apogee: 962 km (597 mi). Perigee: 926 km (575 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1981 September 14 - . 20:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1306 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1982-07-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 12828 . COSPAR: 1981-089A. Apogee: 424 km (263 mi). Perigee: 168 km (104 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min. Ocean monitoring; replaced Cosmos 1260..
1982 February 11 - . 01:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1337 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1982-07-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 13061 . COSPAR: 1982-010A. Apogee: 444 km (275 mi). Perigee: 426 km (264 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1982 April 29 - . 09:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1355 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1984-03-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 13150 . COSPAR: 1982-038A. Apogee: 295 km (183 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 90.20 min. Ocean monitoring..
1982 May 14 - . 19:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1365 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1982-10-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 13593 . COSPAR: 1982-043C. Apogee: 979 km (608 mi). Perigee: 881 km (547 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1982 June 1 - . 13:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1372 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1982-09-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 13411 . COSPAR: 1982-052B. Apogee: 966 km (600 mi). Perigee: 919 km (571 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1982 June 18 - . 11:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1379 - . Mass: 1,400 kg (3,000 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Class: Military. Type: Anti-satellite system. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: IS-A. Decay Date: 1982-06-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 13281 . COSPAR: 1982-060A. Apogee: 546 km (339 mi). Perigee: 144 km (89 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 91.40 min. ASAT interceptor. Succeeded in intercept of Cosmos 1375 target. Deorbited using on-board engine. Final test of series..
1982 August 30 - . 10:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1402 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1983-01-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 13441 . COSPAR: 1982-084A. Apogee: 266 km (165 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1982 September 4 - . 17:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1405 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1984-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 13508 . COSPAR: 1982-088A. Apogee: 443 km (275 mi). Perigee: 425 km (264 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1982 October 2 - . 00:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1412 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1982-12-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 13645 . COSPAR: 1982-099B. Apogee: 998 km (620 mi). Perigee: 886 km (550 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1983 May 7 - . 10:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1461 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1985-05-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 14064 . COSPAR: 1983-044A. Apogee: 803 km (498 mi). Perigee: 574 km (356 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 98.50 min. Ocean monitoring..
1983 October 29 - . 08:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1507 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1987-08-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 14455 . COSPAR: 1983-110A. Apogee: 325 km (201 mi). Perigee: 298 km (185 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 90.80 min. Ocean monitoring..
1984 May 30 - . 18:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1567 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1988-04-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 15009 . COSPAR: 1984-053A. Apogee: 369 km (229 mi). Perigee: 353 km (219 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 91.80 min. Ocean monitoring..
1984 June 29 - . 00:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1579 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1984-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 15328 . COSPAR: 1984-069C. Apogee: 970 km (600 mi). Perigee: 914 km (567 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1984 August 7 - . 22:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1588 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1986-02-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 15167 . COSPAR: 1984-083A. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 331 km (205 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 91.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1984 October 31 - . 12:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1607 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1985-03-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 15502 . COSPAR: 1984-112B. Apogee: 994 km (617 mi). Perigee: 908 km (564 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1985 January 23 - . 19:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1625 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1985-01-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 15492 . COSPAR: 1985-008A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 118 km (73 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Ocean monitoring..
1985 April 18 - . 21:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1646 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1987-11-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 15653 . COSPAR: 1985-030A. Apogee: 399 km (247 mi). Perigee: 378 km (234 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.30 min. Ocean monitoring..
1985 August 1 - . 05:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1670 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1985-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 16196 . COSPAR: 1985-064C. Apogee: 1,007 km (625 mi). Perigee: 893 km (554 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1985 August 23 - . 22:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1677 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1985-12-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 16192 . COSPAR: 1985-075B. Apogee: 1,001 km (621 mi). Perigee: 880 km (540 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1985 September 19 - . 01:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1682 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1986-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 16054 . COSPAR: 1985-082A. Apogee: 446 km (277 mi). Perigee: 341 km (211 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.40 min. Ocean surveillance..
1986 February 27 - . 01:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1735 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1988-11-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 16620 . COSPAR: 1986-021A. Apogee: 442 km (274 mi). Perigee: 419 km (260 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 93.20 min. Ocean surveillance..
1986 March 21 - . 10:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1736 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1986-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 16806 . COSPAR: 1986-024B. Apogee: 995 km (618 mi). Perigee: 936 km (581 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1986 March 25 - . 19:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1737 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1986-12-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 16648 . COSPAR: 1986-025A. Apogee: 426 km (264 mi). Perigee: 414 km (257 mi). Inclination: 73.40 deg. Period: 93.00 min. Ocean surveillance..
1986 August 4 - . 05:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1769 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1987-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 16895 . COSPAR: 1986-059A. Apogee: 383 km (237 mi). Perigee: 287 km (178 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 91.20 min. Ocean surveillance..
1986 August 20 - . 12:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1771 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1986-11-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 17036 . COSPAR: 1986-062D. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Perigee: 909 km (564 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.20 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1987 February 1 - . 23:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1818 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: Plazma-A. USAF Sat Cat: 17369 . COSPAR: 1987-011A. Apogee: 803 km (498 mi). Perigee: 774 km (480 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 100.60 min. Test of new Topaz reactor, new systems, and ion engines aboard US-AM bus..
1987 April 8 - . 03:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1834 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1988-10-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 17847 . COSPAR: 1987-031A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1987 June 18 - . 21:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1860 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1987-09-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 18240 . COSPAR: 1987-052C. Apogee: 992 km (616 mi). Perigee: 900 km (550 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.00 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1987 July 10 - . 15:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1867 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: Plazma-A. USAF Sat Cat: 18187 . COSPAR: 1987-060A. Apogee: 803 km (498 mi). Perigee: 776 km (482 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 100.70 min. Test of new Topaz reactor, new systems, and ion engines aboard US-AM bus - Tested Plasma-2 SPT electric engine..
1987 October 10 - . 21:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1890 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1988-12-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 18396 . COSPAR: 1987-086A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1987 December 12 - . 05:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1900 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. USAF Sat Cat: 18665 . COSPAR: 1987-101A. Apogee: 735 km (456 mi). Perigee: 696 km (432 mi). Inclination: 66.10 deg. Period: 99.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
- Cosmos 1900 - . Mass: 4,300 kg (9,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. COSPAR: 1987-101xx. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1988 March 14 - . 14:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1932 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1988-06-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 19160 . COSPAR: 1988-019B. Apogee: 1,008 km (626 mi). Perigee: 920 km (570 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 104.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered - last launch of the US-AM. Programme cancelled by Gorbachev..
1988 May 28 - . 02:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1949 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1990-04-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 19193 . COSPAR: 1988-045A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1988 November 18 - . 00:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1979 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1989-12-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 19647 . COSPAR: 1988-101A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1989 July 24 - . 00:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2033 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1991-01-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 20147 . COSPAR: 1989-058A. Apogee: 322 km (200 mi). Perigee: 196 km (121 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1989 September 27 - . 16:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2046 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1991-04-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 20259 . COSPAR: 1989-079A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1989 November 24 - . 23:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2051 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1990-01-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 20334 . COSPAR: 1989-092A. Apogee: 310 km (190 mi). Perigee: 293 km (182 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 90.60 min. Ocean surveillance..
1990 March 14 - . 15:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2060 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1991-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20525 . COSPAR: 1990-022A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. Ocean surveillance..
1990 August 23 - . 16:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2096 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1992-08-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 20765 . COSPAR: 1990-075A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1990 November 14 - . 06:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2103 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1991-04-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 20933 . COSPAR: 1990-096A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1990 December 4 - . 00:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2107 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1991-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 20985 . COSPAR: 1990-108A. Apogee: 416 km (258 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. Ocean surveillance..
1991 January 18 - . 11:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2122 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-P. Decay Date: 1993-03-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 21065 . COSPAR: 1991-005A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. Ocean surveillance..
1993 March 30 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2238 - . Payload: US-PU s/n 1. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Duration: 567.00 days. Decay Date: 1994-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 22585 . COSPAR: 1993-018A. Apogee: 416 km (258 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.70 min. First launch of new EORSAT, first of at 120 degree intervals on the same orbit with a 0 degree ascending node. Ocean surveillance..
1993 April 28 - . 03:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2244 - . Payload: US-PU s/n 2. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Duration: 657.00 days. Decay Date: 1995-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 22643 . COSPAR: 1993-029A. Apogee: 416 km (258 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. Second launch of new EORSAT, second of three stationed at 120 degree intervals on the same orbit with a 0 degree ascending node..
1993 July 7 - . 07:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2258 - . Payload: US-PY s/n 3. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Duration: 603.00 days. Decay Date: 1995-06-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 22709 . COSPAR: 1993-044A. Apogee: 417 km (259 mi). Perigee: 400 km (240 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. Third launch of new EORSAT, final of three stationed at 120 degree intervals on the same orbit with a 0 degree ascending node. Ocean surveillance..
1993 September 17 - . 00:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2264 - . Payload: US-PM s/n 4. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Duration: 564.00 days. Decay Date: 1995-08-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 22808 . COSPAR: 1993-060A. Apogee: 417 km (259 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. EORSAT, first of three to be stationed at 120 degree intervals on the same orbit with a 215 degree ascending node. However cutbacks in program resulted in the constellation not being completed. Ocean surveillance..
1994 November 2 - . 01:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2293 - . Payload: US-PM s/n 5. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Duration: 497.00 days. Decay Date: 1996-05-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 23336 . COSPAR: 1994-072A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 65.03 deg. Period: 92.78 min. Second launch of new EORSAT, second of three to be stationed at 120 degree intervals on the same orbit with a 215 degree ascending node. However cutbacks in program resulted in the constellation not being completed. Ocean surveillance..
1995 June 8 - . 04:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2313 - . Payload: US-PM s/n 6. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Duration: 685.00 days. Decay Date: 1997-07-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23596 . COSPAR: 1995-028A. Apogee: 419 km (260 mi). Perigee: 410 km (250 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 87.60 min. EORSAT, first of three to be stationed at 120 degree intervals on the same orbit with a 143 degree ascending node. However cutbacks in program resulted in the constellation not being completed. Ocean surveillance..
1995 December 20 - . 00:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2326 - . Payload: US-PM s/n 7. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Duration: 660.00 days. Decay Date: 1997-11-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 23748 . COSPAR: 1995-071A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 406 km (252 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 87.20 min. EORSAT, placed in 215 degree ascending node orbital slot. Ocean surveillance; also performed astrophysics research..
1996 December 11 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2335 - . Payload: US-PM s/n 8. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Decay Date: 1999-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 24670 . COSPAR: 1996-069A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 403 km (250 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. EORSAT, second of three to be stationed at 120 degree intervals on the same orbit with a 143 degree ascending node. However cutbacks in program resulted in the constellation not being completed. Still in operation as of December 1997..
1997 November 12 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/DM-2M.
- Kupon - .
Payload: Kupon K95K. Nation: Russia.
Agency: TsBank.
Manufacturer: Lavochkin bureau.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: Kupon.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-03-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 25045 . COSPAR: 1997-070A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,435.50 min.
Geosynchronous. Kupon is the first communications satellite for the Russian banking system, and the first commercial communications satellite sold by the Lavochkin, who have in the past been more commonly associated with planetary probes and early warning satellites. Kupon, owned by the Russian Federation Central Bank (and possibly Global Information Systems of Moscow), relays financial data for the Bankir network. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 55 deg E in 1997-1998 As of 1 September 2001 located at 86.25 deg E drifting at 0.142 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 78.29E drifting at 0.156E degrees per day.
1997 December 9 - . 07:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2347 - . Payload: US-PM s/n 9. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Decay Date: 1999-12-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 25088 . COSPAR: 1997-079A. Apogee: 417 km (259 mi). Perigee: 403 km (250 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. EORSAT, in the 217 degree ascending node slot. Still in operation as of December 1997..
1999 December 26 - . 08:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2367 - .
Payload: US-PM s/n 10. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: VMF.
Manufacturer: Arsenal.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: US-PU.
Decay Date: 2002-07-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 26040 . COSPAR: 1999-072A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 404 km (251 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg.
Passive naval electronic intelligence satellite. The satellite was placed in an initial 147 km x 442 km orbit at 65 degree inclination. The US-PM's propulsion module fired at apogee to circularize the orbit. Replaced the only previous remaining US-PM satellite which ended operations in November and reentered earlier in December 1999.
2001 December 21 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2383 - .
Payload: US-PM s/n 11. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia.
Agency: VMF.
Manufacturer: Arsenal.
Program: EORSAT.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan.
Spacecraft: US-PU.
Decay Date: 2004-03-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 27053 . COSPAR: 2001-057A. Apogee: 415 km (257 mi). Perigee: 404 km (251 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg.
Signal Intelligence Satellite. Launch delayed December 19. The booster put the satellite into an initial orbit of 145 x 405 km x 65.0 deg. At apogee the satellite ignited its own propulsion system to increase velocity by about 70-80 m/s and circularize the orbit.
2004 May 28 - . 06:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2405 - . Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VMF. Manufacturer: Arsenal. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Decay Date: 2006-06-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 28350 . COSPAR: 2004-020A. Apogee: 417 km (259 mi). Perigee: 405 km (251 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.80 min. Original reported name Cosmos 2407..
2006 June 24 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 2421 - . Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: VMF. Manufacturer: Arsenal. Program: EORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-PU. Decay Date: 2006-06-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 29246 . COSPAR: 2006-026A. Apogee: 414 km (257 mi). Perigee: 384 km (238 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 92.50 min.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use