
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
US-A
 US-A Credit: © Mark Wade |
AKA: 17F16;17K114;US-AM. Status: Operational 1965. First Launch: 1965-12-27. Last Launch: 1988-03-14. Number: 38 . Gross mass: 4,300 kg (9,400 lb).
It used an active radar to track naval vessels from space in darkness and all weather.
The RLS was an element in the integrated Soviet weapons system devoted to destruction of the US Navy's surface and submarine forces. The system used space-based platforms to obtain the location of enemy forces at sea. This targeting information was provided to aircraft, surface vessels, and submarines and fed into anti-ship missiles that would attack the US forces from over the horizon. The US-A had a complex development history, with three chief designers overseeing its development. It was conceived and designed by Chelomei in 1959-1964; redesigned and flight tested by Savin in 1965-1969; and finally completed and put into service by KB Arsenal from 1969 on. The nuclear reactor aboard the US-A crashed to earth several times, causing international incidents. Furthermore the RLS had the lowest reliability and most quality problems of any Soviet space system. Nevertheless the system eventually allowed the Soviet Union to continuously monitor naval traffic throughout the oceans of the world.
The spacecraft was equipped with two side-looking radar antenna structures, guaranteeing the capability of locating naval targets in all weather, day or night, including those maintaining radio silence. The spacecraft bus provided 3 axis stabilization and the nuclear reactor was put in a safe graveyard orbit after completion of the mission. In the event of failure to place the reactor in the graveyard orbit, a backup system ejected the reactor core and dispersed the fuel during re-entry, spreading the radioactive material in the upper atmosphere so that a safe radiation exposure standard was reached. The multi-function engine section kept the spacecraft oriented during flight, maintained the orbital altitude, and deorbited the spacecraft at the end of the mission. The overall system was designated 17K114 (space complex for naval space reconnaissance and targeting purposes). The spacecraft had the article number 17F16.
Beginning in the late 1950's, Chelomei began studying use of his encapsulated cruise missile technology for spacecraft. A whole family of unmanned spacecraft, dubbed Kosmoplans, would be built using modular elements. One variant of the Kosmoplan would conduct naval radar and signals reconnaissance, launched by the UR-200 rocket.
In 1959, as Chelomei laid out these plans, he knew a tremendous struggle would be required to wrest a piece of the space program from Chief Designer Korolev. But Chelomei had stacked the deck against Korolev by hiring Khrushchev's son as a lead engineer at his OKB. By 30 May 1960 Korolev presented to the Soviet leadership a plan that now included participation of Chelomei. One project allocated to Chelomei was theme US - Upravlenniye Sputnik - a naval reconnaissance satellite using a P6 nuclear reactor for active tracking and targeting American warships. This was to be developed in 1962 to 1964. Chelomei was authorized by Decree 715-296 of 23 June 1960 'On the Production of Various Launch Vehicles, Satellites, Spacecraft for the Military Space Forces in 1960-1967' to complete a draft project on unpiloted Kosmoplans.
At the beginning of the 1960's the Soviet Union had developed anti-ship missiles of very long range but the problem of locating the missile's targets had not been solved. The first resolution for development of a Kosmoplan-derived Naval Space Reconnaissance and Targeting System (MKRTs) was issued in March 1961. The Kosmoplan's UR-200 (8K81) launch vehicle was approved for production on 16 March and 1 August 1961 by the Central Committee and Politburo. The Kosmoplan and UR-200 draft projects were completed in July 1962. Trial flights of the ICBM version of the UR-200 ran from 4 November 1963 to 20 October 1964.
Basic research on the concept was conducted by several rocket, radio-technical, and electro-technical design bureaus and research institutes. These included work done by FEI and the Kurchatov Nuclear Research Institute on a compact reactor to power the satellite. Theoretical research in the optimum orbit for the system was undertaken at the Academy of Sciences under Keldysh. The spacecraft was developed by Chelomei at OKB-52 and A A Raspletin at KB-1 MRP. M M Bondaryuk, G M Gryaznov, and V I Serbin at OKB-670 developed a thermal analogue of the nuclear power plant.
On October 13, 1964, Khrushchev was ousted from power. The new leadership, under Brezhnev, was adverse to all projects Khrushchev had supported, particularly those of Chelomei. An expert commission under M V Keldysh decided to cancel the UR-200, while the US was assigned to KB-1. Manager for the system at KB-1 was A I Savin, who was head of the renamed TsNII Kometa after 1973. The spacecraft was to be redesigned for launch by the Tsyklon 2 version of Yangel's R-36 rocket.
Two separate versions of the spacecraft were to be developed. The reactor-powered US-A would use active radar to track naval vessels in any weather. The solar-powered US-P would provide SIGINT services for the Soviet Navy and track naval ships passively. The spacecraft was still by TsKBM MOM (Chelomei) and the US-A's radar by NPO Vega GKRE. The project was jointly managed by the VMF Soviet Navy's Directorate for Rocket-Artillery Forces (URAV) and the GUKOS Military Space Force.
By the end of the 1960's development was largely complete, including flight tests from 1965 of mass models and experimental prototypes equipped with orientation, stabilization, and radio-control systems. But the principal radar system had not completed development and was not available for flight test. Finally it was decided that Chelomei's NPO Mash just didn't have the resources to bring the project to completion. Furthermore the design bureau had additional tasks with development of the Almaz and DOS space stations. Therefore Afanasyev decided to transfer the entire project to NPO Arsenal in May 1969. Arsenal had proven itself in development of the RT-2, RT-15, and D-II solid propellant ballistic missiles and had extensive test stands available that could be used for spacecraft development.
Work on spacecraft at KB Arsenal began in 1969 with the turnover to Arsenal of the documentation on these Chelomei-designed unmanned spacecraft. Arsenal was made responsible for series production and development of new variants. V F Kalabin was named head of the new space section.
MKRTs still consisted of two satellites. The RLS (ex-US-A) satellite would be equipped with an RLS radar location system powered by a YaEU nuclear reactor. The documentation handed over to Arsenal on the RLS was nearly complete and Chelomei's NPO Mash was pressured to complete the RLS drawings and release them to the factory.
Ye K Ivanov was Chief of the Design Bureau and Director of the Factory at KB Arsenal. Head project engineers for MKRTs were N N Kazakov and I A Abramov. The following were the principal subcontractors:
- Radio controls and spacecraft control systems: KB-1/Savin
- Orientation/Stabilization System - TsKB Almaz, MRO/P M Kirillov
- RLS - Moscow NII Priborstraonenniy MRP/I A Brakhanskiy, P O Salugavik
- ELINT - Kaluga NIRTI MRP/S I Baburin, V L Grechko
- Engine Unite - MKB Soyuz MAP, Turayev / V U Stepanov, D D Gelevich
- Telemetry - NII Pirborosrenniy MOM, V V Khrunov, V B Kharin
The RLS had the worst reliability and quality problems of any Soviet system. It was not available often enough for good exploitation of the data. Between 1979 and 1989 a phased modernization of the MKRTs was undertaken, providing better accuracy, localization of targets, and one-time observation capability. Flight durations were increased five to ten times. The entire surface of the world's ocean was continuously monitored, a feat not achieved by any other system. The system's effectiveness was proven in the 1982 Falklands War, when MKRTs monitored the British forces and was able to advise the General Staff of the Soviet Navy of the exact moment of the British landing.
The nuclear spacecraft component had redundant systems for placing the reactor into a safe high storage orbit at the end of spacecraft operations. The YaEU nuclear reactor was equipped with an automatic system to place it into a higher safe orbit after operations were completed.
More at: US-A.
Family: Medium earth orbit, Naval surveillance radarsat, Surveillance. Country: Russia. Engines: Stepanov IS/US 16 kgf. Launch Vehicles: R-7, UR-200, Tsiklon, Soyuz 11A510, Tsiklon-2, Tsiklon-2A. Projects: RORSAT. Launch Sites: Baikonur, Baikonur LC31, Baikonur LC90/19. Agency: MO, Arsenal. Bibliography: 102, 2, 279, 290, 376, 42, 474, 6, 7008, 13317, 13318.
 | USA Tracking |
 | USA Ground Equipment |
 | USA Fissile Material |
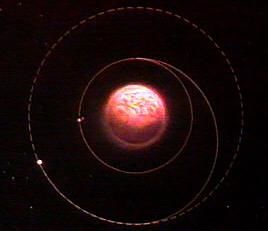 | USA Reactor Disposal |
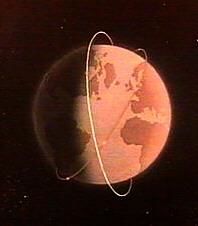 | USA Coverge |
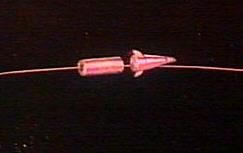 | USA Separation |
 | Cosmos 125 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1961 March 6 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- US RORSAT authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decree 420·1741 'On approval of work on the US satellite and UR-200 launch vehicle / ICBM' was issued..
1961 March 16 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- UR-200 (8K81) launch vehicle development authorised. - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft: IS-A,
Kosmoplan,
OGCh,
US-A,
US-P.
An enabling decree was issued on 1 August 1961 by the Central Committee and Politburo. The UR-200 was designed not only to send a thermonuclear warhead over a range of 12,000 km, but also to orbit all of the Kosmoplan military variants: the IS ASAT; the US nuclear-powered naval intelligence satellite; and the Kosmoplan combat re-entry vehicle.
1962 June 3 - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- US RORSAT development plans. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decree 'On course of work on the US reconnaissance satellite system launched on the UR-2OO' was issued..
1962 July - . Launch Vehicle: UR-200.
- Kosmoplan and UR-200 draft projects completed. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: IS-A, Kosmoplan, US-A. Trial flights of the ICBM version ran from 4 November 1963 to 20 October 1964. Versions of the Kosmoplan would fly as the reactor-powered US-A and solar-powered US-P ELINT satellites and the I2P ASAT..
1964 June 18 - .
- USSR five-year military space plan issued. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Malinovskiy.
Spacecraft: MiG 105-11,
Raketoplan,
Soyuz R,
Spiral OS,
US-A,
US-P,
Zenit-2M satellite,
Zenit-4M.
Ministry of Defence Decree 'On military space programs for 1964-69, including the R spaceplane' was issued. The decree was issued by Defence Ministry Marshal Rodiono Yakovlevich Malinovksiy. Included in this plan were new versions of the automatic Zenit, Morya-1 (US series) spacecraft, the Spiral spaceplane, the Soyuz-R manned combat spacecraft, and others. Chelomei's Raketoplan spaceplane was cancelled.
1964 October 13 - .
- Khrushchev ousted from power. - . Nation: Russia. Related Persons: Chelomei, Khrushchev. Spacecraft: IS-A, Kosmoplan, LK-1, OGCh, US-A, US-P. Brezhnev faction assumes control of Politubro. Brezhnev was adverse to all projects Khrushchev had supported. These included those of Chelomei and his OKB-52..
1965 August 24 - .
- Development of R-36-O and Tsyklon launch vehicles authorised - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Chelomei,
Keldysh,
Yangel.
Spacecraft: IS-A,
OGCh,
US-A.
Decree 'On Creation of an R-36 Based Carrier Rocket for Launching the IS and US KA--start of work on an R-36-based launch vehicle for the IS and US programs' was issued. After Khrushchev was ousted from power, Chelomei's projects were examined by an expert commission under M V Keldysh. It was found that Yangel's R-36 rocket was superior to Chelomei's UR-200. The UR-200 was cancelled; the IS and US satellites would be launched by the R-36 11K67. The Tsyklon 2 definitive operational version replaced the 11K67 launch vehicle from 1969.
1965 December 27 - . 22:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A510.
- Cosmos 102 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1966-01-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 1867 . COSPAR: 1965-111A. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 205 km (127 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 89.20 min. Prototype RORSAT hardware using chemical batteries in place of nuclear reactor..
1966 July 20 - . 09:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A510.
- Cosmos 125 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1966-08-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 2351 . COSPAR: 1966-067A. Apogee: 260 km (160 mi). Perigee: 204 km (126 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 89.10 min. Prototype RORSAT hardware using chemical batteries in place of nuclear reactor. Lost on the 52nd revolution as a result of a possible failure in the chemical power units placed on board instead of the nuclear BES-5..
1967 July 1 - . LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Tsiklon-2 launch vehicle authorised. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft: IS-A, Meteor, US-A. Council of Soviet Ministers (SM) Decree 'On use of the R-36-based launcher for the Kosmos and Meteor satellites' was issued..
1967 July 21 - .
- US Project reassigned; R-36-O booster development approved; Yantar-2K and Zvevda 7K-VI approved. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Kozlov.
Spacecraft: Soyuz VI,
US-A,
US-P,
Yantar-2K,
Yantar-4K1.
Decree 715-240 'On the Creation of Space Systems for Naval Reconnaissance Comprising the US sat and the R-36-based booster -further work on the US naval reconnaissance satellite, approval of work on the Yantar-2K, and course of work on 7K-VI Zvezda'.
An entire family of Yantar spacecraft was proposed by Kozlov's design bureau during the initial development; information on two film return models has been declassified. Yantar was initially derived from the Soyuz spacecraft, including systems developed for the Soyuz VI military model. During design and development this changed until it had very little in common with Soyuz.
Following numerous problems in the first flight tests of the Soyuz 7K-OK, Kozlov ordered a complete redesign of the 7K-VI manned military spacecraft. The new spacecraft, with a crew of two, would have a total mass of 6.6 tonnes and could operate for a month in orbit. The new design switched the positions of the Soyuz descent module and the orbital modules and was 300 kg too heavy for the standard 11A511 launch vehicle. Therefore Kozlov designed a new variant of the Soyuz launch vehicle, the 11A511M. The project was approved by the Central Committee of the Communist Party, with first flight to be in 1968 and operations to begin in 1969. The booster design, with unknown changes to the basic Soyuz, did not go into full production.
1967 December 27 - . 11:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 198 - . Payload: US-A no. 1. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1968-01-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 3082 . COSPAR: 1967-127B. Apogee: 927 km (576 mi). Perigee: 907 km (563 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.40 min. Prototype RORSAT hardware using chemical batteries in place of BES-5 nuclear reactor. First satellite to be boosted to 900 km storage orbit..
1968 March 22 - . 09:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A.
- Cosmos 209 - . Payload: US-A no. 2. Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1968-04-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 3162 . COSPAR: 1968-023C. Apogee: 927 km (576 mi). Perigee: 876 km (544 mi). Inclination: 65.30 deg. Period: 103.00 min. RORSAT hardware, representative of production hardware, but using chemical batteries in place of BES-5 nuclear reactor..
1969 January 25 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2A. FAILURE: Payload propulsion system failed; no orbit.. Failed Stage: P.
- US-A Mass Model - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1969-01-24 . COSPAR: F690125A. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). RORSAT hardware, representative of production hardware, but using chemical batteries in place of BES-5 nuclear reactor..
1970 October 3 - . 10:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 367 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: PKO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1970-10-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 4566 . COSPAR: 1970-079C. Apogee: 1,022 km (635 mi). Perigee: 915 km (568 mi). Inclination: 65.30 deg. Period: 104.50 min. Ocean surveillance; probably used chemical batteries..
1971 April 1 - . 11:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 402 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1971-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 5107 . COSPAR: 1971-025B. Apogee: 1,011 km (628 mi). Perigee: 965 km (599 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.90 min. Ocean surveillance; probably used chemical batteries..
1971 December 25 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 469 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1972-02-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 5737 . COSPAR: 1971-117B. Apogee: 1,006 km (625 mi). Perigee: 948 km (589 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 104.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered. First RORSAT flight confirmed by Russian source to have had BES-5 nuclear reactor..
1972 August 21 - . 10:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 516 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1972-10-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 6199 . COSPAR: 1972-066C. Apogee: 1,038 km (644 mi). Perigee: 906 km (562 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 104.50 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1973 April 25 - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2. FAILURE: Payload propulsion system failed; no orbit.. Failed Stage: P.
- RORSAT failure - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1973-04-25 . COSPAR: F730425A. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered. Last launch of original US-A design by Savin's KB. American 'sniffer' aircraft flew over the Pacific after this failure looking for radioisotopes traces in order to characterise the reactor..
1973 December 27 - . 20:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 626 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1974-03-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 7115 . COSPAR: 1973-108D. Apogee: 982 km (610 mi). Perigee: 907 km (563 mi). Inclination: 65.40 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered. First test of modernised design by KB Arsenal..
1974 May 15 - . 07:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 651 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1974-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 7388 . COSPAR: 1974-029C. Apogee: 946 km (587 mi). Perigee: 890 km (550 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 103.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1974 May 17 - . 06:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 654 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1974-09-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 7397 . COSPAR: 1974-032D. Apogee: 1,006 km (625 mi). Perigee: 924 km (574 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1975 April 2 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 723 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1975-07-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 7797 . COSPAR: 1975-024D. Apogee: 961 km (597 mi). Perigee: 899 km (558 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 103.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1975 April 7 - . 11:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/20. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 724 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1975-08-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 7922 . COSPAR: 1975-025B. Apogee: 943 km (585 mi). Perigee: 852 km (529 mi). Inclination: 65.60 deg. Period: 102.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1975 October 1 - . LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- US-A and Tsiklon-2 accepted into military service. - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On adoption of US-A with Tsiklon-2 into armaments' was issued..
1975 December 12 - . 12:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 785 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1976-02-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 8480 . COSPAR: 1975-116C. Apogee: 1,004 km (623 mi). Perigee: 907 km (563 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 104.20 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered; failed immediately after reaching orbit..
1976 October 17 - . 18:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 860 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1976-12-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 9531 . COSPAR: 1976-103B. Apogee: 995 km (618 mi). Perigee: 923 km (573 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 104.30 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1976 October 21 - . 16:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 861 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1977-02-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 9631 . COSPAR: 1976-104C. Apogee: 987 km (613 mi). Perigee: 928 km (576 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.20 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1977 September 16 - . 14:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 952 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1977-11-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 10399 . COSPAR: 1977-088B. Apogee: 990 km (610 mi). Perigee: 911 km (566 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1977 September 18 - . 13:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 954 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1978-01-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 10361 . COSPAR: 1977-090A. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 251 km (155 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered; re-entered over Canada, spreading radioactive debris..
1980 April 29 - . 11:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1176 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1980-10-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 11968 . COSPAR: 1980-034B. Apogee: 962 km (597 mi). Perigee: 873 km (542 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 103.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered; test flight of modified safer design..
1981 March 5 - . 18:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1249 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1981-07-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 12552 . COSPAR: 1981-021D. Apogee: 976 km (606 mi). Perigee: 904 km (561 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1981 April 21 - . 03:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1266 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1981-05-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 12429 . COSPAR: 1981-037B. Apogee: 941 km (584 mi). Perigee: 911 km (566 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 103.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1981 August 24 - . 16:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1299 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1981-09-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 12809 . COSPAR: 1981-081E. Apogee: 962 km (597 mi). Perigee: 926 km (575 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1982 May 14 - . 19:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1365 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1982-10-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 13593 . COSPAR: 1982-043C. Apogee: 979 km (608 mi). Perigee: 881 km (547 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1982 June 1 - . 13:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1372 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1982-09-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 13411 . COSPAR: 1982-052B. Apogee: 966 km (600 mi). Perigee: 919 km (571 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1982 August 30 - . 10:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1402 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1983-01-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 13441 . COSPAR: 1982-084A. Apogee: 266 km (165 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1982 October 2 - . 00:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1412 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1982-12-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 13645 . COSPAR: 1982-099B. Apogee: 998 km (620 mi). Perigee: 886 km (550 mi). Inclination: 64.80 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1984 June 29 - . 00:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1579 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1984-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 15328 . COSPAR: 1984-069C. Apogee: 970 km (600 mi). Perigee: 914 km (567 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1984 October 31 - . 12:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1607 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1985-03-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 15502 . COSPAR: 1984-112B. Apogee: 994 km (617 mi). Perigee: 908 km (564 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1985 August 1 - . 05:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1670 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1985-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 16196 . COSPAR: 1985-064C. Apogee: 1,007 km (625 mi). Perigee: 893 km (554 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 104.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1985 August 23 - . 22:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1677 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1985-12-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 16192 . COSPAR: 1985-075B. Apogee: 1,001 km (621 mi). Perigee: 880 km (540 mi). Inclination: 64.70 deg. Period: 103.90 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1986 March 21 - . 10:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1736 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1986-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 16806 . COSPAR: 1986-024B. Apogee: 995 km (618 mi). Perigee: 936 km (581 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1986 August 20 - . 12:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1771 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1986-11-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 17036 . COSPAR: 1986-062D. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Perigee: 909 km (564 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.20 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1987 June 18 - . 21:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1860 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1987-09-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 18240 . COSPAR: 1987-052C. Apogee: 992 km (616 mi). Perigee: 900 km (550 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 104.00 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1987 December 12 - . 05:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1900 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. USAF Sat Cat: 18665 . COSPAR: 1987-101A. Apogee: 735 km (456 mi). Perigee: 696 km (432 mi). Inclination: 66.10 deg. Period: 99.10 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
- Cosmos 1900 - . Mass: 4,300 kg (9,400 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: UNKS. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. COSPAR: 1987-101xx. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered..
1988 March 14 - . 14:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC90/19. Launch Pad: LC90/pad?. LV Family: R-36. Launch Vehicle: Tsiklon-2.
- Cosmos 1932 - . Mass: 3,800 kg (8,300 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MO. Program: RORSAT. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: Kosmoplan. Spacecraft: US-A. Decay Date: 1988-06-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 19160 . COSPAR: 1988-019B. Apogee: 1,008 km (626 mi). Perigee: 920 km (570 mi). Inclination: 65.10 deg. Period: 104.40 min. Ocean surveillance; nuclear powered - last launch of the US-AM. Programme cancelled by Gorbachev..
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use