
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Shuttle
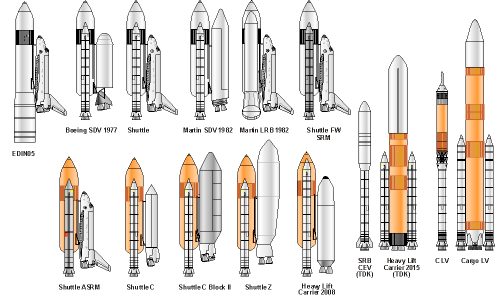
Shuttle Evolution
Improvements suggested to the shuttle derived from the design as flown.
Credit: © Mark Wade
AKA: Space Transportation System;STS. First Launch: 1981-04-12. Last Launch: 2011-07-08. Number: 135 . Payload: 24,400 kg (53,700 lb). Thrust: 2,625,932.00 kN (590,332,997 lbf). Gross mass: 2,029,633 kg (4,474,574 lb). Height: 56.00 m (183.00 ft). Diameter: 8.70 m (28.50 ft). Apogee: 600 km (370 mi).
In the mid-1960's the US Air Force conducted a series of classified studies on next-generation space transportation systems. These were to reduce the cost of launching military payloads while supporting a projected robust manned military presence in space - including large space stations and reconnaissance and strike missions. These Air Force studies finally concluded that a partially reusable vehicle was the most attractive, epitomized by Lockheed's Starlifter, which had a large drop tank but returned the engines and avionics of the vehicle for reuse. The Air Force probably spent around $ 1 billion on 'black' technology development tests at this time, including work on linear aerospike engines and high fineness lifting body shapes that would re-emerge again 30 years later in Lockheed's X-33 space shuttle successor.
NASA also had ambitious plans - for large space stations, lunar bases, nuclear interplanetary rocket stages, and manned Mars expeditions. NASA went through a long iterative process in designing and selecting the space shuttle, leading ultimately to the same conclusion as the Air Force.
By mid-1969, the ambitious new NASA Administrator, Tom Paine, had proposed an extensive manned space exploration program as the logical follow-on to Apollo. A new, modular, reusable space transportation system would be required to set up bases on the Moon and Mars during the 1970s and 1980s. This system would consist of a reusable space shuttle to low earth orbit space stations and interorbital and interplanetary nuclear and chemical space tugs. The first major goal was a 12-man space station by 1975. NASA awarded $2.9-million study contracts to North American Rockwell and McDonnell-Douglas in July 1969. The space station was to evolve into a 50-man space base by 1980. Additional way-stations to Mars would be deployed in geostationary, lunar and Mars orbit during the 1980s.
George Mueller headed the space shuttle portion of this effort, which accelerated as the Apollo project grew to a close. NASA awarded four $0.3-million space shuttle / Integral Launch and Re-entry Vehicle ILRV Phase A study contracts to North American Rockwell, McDonnell-Douglas, Lockheed and General Dynamics in January 1969. Martin Marietta's bid was rejected, but the company continued to participate using its own funds. The ILRV requirement was for a booster/spacecraft combination with 12-crew / 2.3 - 22.7 metric ton payload capability, a 720 km re-entry cross range, and first flight by 1974. The most important mission was expected to be space station resupply payloads weighing about 11,300 kg. 120 different permutations were investigated by the contractors.
The assumption of a massive cost-is-no-object future space program was that only fully reusable vertical takeoff/horizontal landing, two-stage-to-orbit concepts for the space shuttle were considered at first. NASA's Shuttle task group had already calculated the potential life-cycle costs of three classes of 22,680-kilogram payload reusable launch vehicles based on prior USAF studies:
- An advanced low-cost expendable rocket plus reusable spacecraft would cost $2.5 billion to develop and $43.1 million per launch.
- An ILRV/Starlifter-type partially reusable single-stage-to-orbit vehicle would cost of $3.9 billion to develop and $5.3-12.6 million per launch, depending on the estimated cost of the expendable propellant tanks.
- A fully reusable two-stage-to-orbit configuration such as the General Dynamics Triamese concept would cost $4.5 billion to develop but only $3.2 million per launch.
Space Shuttle Mission Model (mid-1969)
| 1975 | 1976 | 1977 | 1978 | 1979 | 1980 | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | TOTAL | |
| UNMANNED SATELLITES | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 22 |
| UNMANNED PLANETARY PROBES | 7 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 51 |
| SPACE STATION (ROTATE 12-CREW EVERY 3 MTHS.) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 35 | ||||||
| SPACE BASE (5 FLIGHTS/QUARTER TO ROTATE ENTIRE 50-CREW) | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 138 | |||||
| LUNAR PROGRAM (6-MAN LUNAR ORBITAL STATION + 6-MAN MOONBASE) | 48 | 48 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 300 | |||
| =TOTAL UNMANNED FLIGHTS | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 29 |
| =TOTAL MANNED FLIGHTS | 7 | 7 | 7 | 55 | 55 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 473 |
| TOTAL SHUTTLE FLIGHTS: | 16 | 10 | 17 | 60 | 61 | 65 | 64 | 61 | 66 | 64 | 62 | 546 |
Space Shuttle Mission Requirements (mid-1969)
| ORBITAL CHARACTERISTICS | SPACE STATION / BASE LOGISTICS SUPPORT | PLACEMENT AND RETRIEVAL OF SATELLITES | DELIVERY OF PROPULSION STAGES & PAYLOAD | DELIVERY OF PROPELLANTS | SATELLITE SERVICING & MAINTENANCE | SHORT DURATION ORBITAL MISSIONS |
| ALTITUDE (KM) | 370 TO 555KM | 185 TO 1480KM | 185 TO 230KM | 370 TO 555KM | 185 TO 1480KM | 185 TO 555KM |
| INCLINATION (DEG.) | 28.5 - 90 | 28.5 - 98 | 28.5 - 55 | 28.5 - 55 | 28.5 - 98 | 28.5 - 90 |
| DURATION (DAYS) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 TO 15 | 7 TO 30 |
| PAYLOAD CHARACTERISTICS | SPACE STATION / BASE LOGISTICS SUPPORT | PLACEMENT AND RETRIEVAL OF SATELLITES | DELIVERY OF PROPULSION STAGES & PAYLOAD | DELIVERY OF PROPELLANTS | SATELLITE SERVICING & MAINTENANCE | SHORT DURATION ORBITAL MISSIONS |
| CREW | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| PASSENGERS (MIN.) | 50 MEN / QTR | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| PAYLOAD DIAMETER (M) | 4.57 | 4.57 | 4.57 | 4.57 | 4.57 | 4.57 |
| ASCENT PAYLOAD WT. | 31750KG / QTR | 4536-22680KG | 11340-22680KG | 22680KG | 2268-6804KG | 11340-22680KG |
| ASCENT PAYLOAD VOL. | 142-283 M3 | 283 M3 | 283 M3 | 142-283 M3 | 113-170 M3 | |
| RETURN PAYLOAD WT. | 20412KG / QTR | 4536-22680KG | -- | -- | 6804KG | 22680KG |
| RETURN PAYLOAD VOL. | -- | 142-283 M3 | -- | -- | 142-283 M3 | 113-170 M3 |
In August 1969, in post-moon landing euphoria, NASA directed the Phase A contractors to concentrate only on fully reusable shuttle concepts. These were two stages, both either winged or lifting bodies, and both recovered at the launch site for reuse. Only as an afterthought, some alternate concepts were still evaluated, including Lockheed's LS200 single orbiter with drop tank, and Chrysler's SERV ballistic single-stage-to-orbit vehicle.
The Phase B designs were more refined but still used the same two-stage approach. Mueller set up a NASA space shuttle task group headed by LeRoy Day to evaluate potential uses of the vehicle. The shuttle requirements had changed considerably as a result of the new post-Apollo program which required a total of 546 shuttle launches in 1975-85. In May 1970, Mueller instructed the task group to increase the payload capability to 22,680 kg to comply with US Air Force requirements, but also because there would be a need to launch vast quantities of low-density rocket propellants into Earth orbit for future space stations in geostationary and lunar orbit. The mission requirements also grew significantly more complex and diverse as the Shuttle also now had to be capable of launching unmanned satellites and planetary probes. At this point a controversy developed over the basic design approach. There were over large cross-range winged designs, medium cross-range lifting body designs, and minimal cross-range stub-wing designs. NASA's Max Faget, who had dictated the spacecraft design for the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs, advocated the stub-wing design.
Then the Nixon administration burst NASA's balloon. The future NASA budget would be only a fraction of Apollo-program levels. There would be no moon bases, no flights to Mars, no nuclear interplanetary stages, no space stations, no more Saturn V's, no space tugs. There wouldn't even be a space shuttle unless NASA could get the development cost down and also convince the US Air Force to use the shuttle for its launch requirements. A USAF requirement was a large cross-range to allow recovery of the shuttle orbiter at the Vandenberg AFB launch point after a single polar orbit of the earth. This was necessary for abort-once-around, quick satellite deployment, strike, or quick-look reconnaissance scenarios. This, together with wind tunnel studies indicating that Faget's straight wing was unstable at re-entry speeds, drove NASA to the delta wing. The reduction in development cost led NASA to throw away the concept of reusing anything but the engines and guidance systems. Instead the shuttle would be boosted by cheap solid fuel boosters and, taking a concept from the Air Force, the propellants would be put in a big expendable drop tank.
Following the usual charade of competitive bidding, NASA picked the same prime contractor as for X-15 and Apollo, who could be trusted to build precisely the vehicle NASA had in mind. North American Rockwell was selected to build the orbiter, with its Rocketdyne Division making the main engines. Thiokol was selected on political grounds for the solid rocket boosters. Martin Marietta would build the External Tank, but at the government Saturn IC factory at Michoud.
To finance the Shuttle, already-built Apollo hardware that would have supported a second Skylab mission was sent to museums and American manned space flight went into a long hiatus in the 1970's. Budget cuts and overruns eventually reduced the number of shuttles built from five to four and delayed the first flight from 1978 to 1981 (thereby ruining the plan to save Skylab 1 on an early shuttle mission). But the development cost was indeed minimized - the shuttle ended up costing $ 6.744 billion in 1971 dollars, versus $ 5.15 billion estimated - less than a quarter of the Apollo program cost and a very modest overrun in comparison to some other programs.
The pretext for the shuttle was that it would be much cheaper than expendable launch vehicles and would replace them all. Production was accordingly terminated by the US government of Delta, Atlas, and Titan vehicles. NASA staff and contractors were under incredible pressure to justify this decision by increasing the shuttle launch rate, lowering the turn-around time, and thereby reducing the cost per launch. When the shuttle Challenger exploded and the entire US space lift program was shut down for almost a year, the fallacy of this decision was exposed. The US Air Force and commercial users returned to use of expendable launch vehicles. When the shuttle began flying again, it was only for NASA programs.
In the final analysis the shuttle came up short in three areas. First, the shuttle orbiter ended up almost 20% over its specified weight - resulting in it being unable to boost the US Air Force's payloads into polar orbits from Vandenberg. Lighter filament-wound casing Solid Rocket Boosters were being developed for use in flights from Vandenberg, but even this did not seem enough. After the Challenger explosion the USAF was able to extricate itself from the Shuttle program. The Vandenberg launch complex, built at the cost of billions, was mothballed. The Air Force started a new costly development program to design the Titan 4 expendable rocket for its large military payloads.
The second shortcoming of the shuttle was that it failed utterly to reduce the cost of putting payloads into orbit. The shuttle program inherited from Apollo huge fixed costs - the Manned Spaceflight Center in Houston, the cadres of government and contractor workers at the Kennedy Space Center, and so on. The result was that there was a fixed base cost of around $ 2.8 billion per year, just to keep all those people and facilities in place, even if no flights were undertaken at all (as occurred after the shuttle disaster). The marginal cost of each flight added to this base was under $ 100 million. Seen this way the shuttle was almost competitive expendable boosters - but didn't come anywhere near the reductions NASA promised when development started. But if the usual number of flights per year was divided by the total annual costs, the cost per launch was $ 245 million, significantly more than a Titan or Proton launch with the same payload.
The final shortcoming was that the shuttle was designed as if it had the inherent operating safety of an airliner. It was not equipped with any provision for crew rescue in case of booster failure during ascent to orbit, or being stranded in orbit, or structural failure during re-entry. The crew was not even provided with spacesuits, despite the lessons of the Soviet space program. This seemed an extraordinary act of engineering hubris, given that contemporary military aircraft were equipped with pressure suits and ejection seats. But the weight problem also meant that there was no margin for crew safety measures without (to NASA) unacceptable impact to the net payload.
If the shuttle failed as a space truck, it succeeded in keeping America in the manned spaceflight business in the face of low public interest and political support. With the excuse of delivering payloads to orbit, NASA got to fly up to seven astronauts and run a host of supplementary experiments and payloads with each flight.
With construction of the international space station beginning, NASA was looking forward to finally using the shuttle for its intended purpose. Due to the lower than planned flight rate, NASA's contractors were confident they could keep the existing shuttles flying through 2030. The real test came when (as was inevitable) another shuttle was lost. Following the Columbia disaster, NASA finally realized it could not make the shuttle safe. The only way to continue American manned spaceflight would be to develop a replacement manned spacecraft with an escape system, and meanwhile fly the shuttle as little as possible. NASA decided to complete the International Space Station in order to keep its international partners happy, then retire the shuttle by 2010. It was to be replaced by a modernized Apollo capsule, dubbed the Orion. The shuttle turned out to be a fifty-year detour to nowhere.
When the Orion program started, NASA hoped to have the sort of lunar base by 2020 they would have had by 1980 if Apollo had been continued in lieu of the shuttle. Instead the Constellation program to go to the moon or Mars was in turn cancelled by the Obama administration. In order to keep Congressman happy, the Orion spacecraft continued a costly slow-paced development program for possible future deep-space missions. For access to the International Space Station, the United States had to pay for seats aboard the Russian Soyuz spacecraft. Bizarrely, instead of completing Orion in a timely manner, NASA funded two other American replacements, the SpaceX Dragon and Boeing CST-100. These would not fly until 2017, only a few years before the planned retirement of the ISS.
More at: Shuttle.
| Spacemaster American winged orbital launch vehicle. Martin-Marietta shuttle Phase A design. X-24B type lifting body orbiter with unique catamaran-configuration booster. |
| MURP American manned spaceplane. The McDonnell Douglas Space Shuttle Phase A studies were conducted under contract NAS9-9204. Their Class I vehicle was dubbed MURP - Manned Upper Reusable Payload. |
| Shuttle FR-3 American winged orbital launch vehicle. General Dynamics shuttle proposal phase A of October 1969. Unwinged flat-bottom configuration booster and orbiter with V butterfly-tails. |
| Shuttle LS A American winged orbital launch vehicle. Lockheed shuttle proposal phase A of December 1969. X-24B lifting body orbiter with delta-wing booster. |
| Shuttle NAR A North American's Phase A shuttle design was completed under contract NAS9-9205 in December 1969. North American had learned that the way to win a NASA design competition was to adhere to the design favored by Max Faget, so they proposed a two-stage-to-orbit vehicle, with both booster and orbiter being of Faget's straight-wing, low cross-range configuration. |
| Shuttle MDC American winged orbital launch vehicle. The McDonnell Douglas Space Shuttle Phase A studies were conducted under contract NAS9-9204. Their baseline Class III vehicle design was completed in November 1969 after 13 alternate configurations had been considered. The two-stage-to-orbit vehicle had a gross mass of 1,550,000 kg and a 11,300 kg payload was accommodated in a 4.6 m x 9.2 m payload bay. |
| Shuttle MDC A Alternate American winged orbital launch vehicle. McDonnell-Douglas shuttle proposal phase A of November 1969. Delta wing first stage and HL-10 lifting body second stage. |
| Shuttle HCR American winged orbital launch vehicle. McDonnell-Douglas/Martin Marietta shuttle high cross-range proposal phase B of December 1970. Swept wing booster, delta wing orbiter. |
| Shuttle LCR American winged orbital launch vehicle. McDonnell-Douglas/Martin Marietta shuttle low cross-range proposal phase B of December 1970. Swept-wing booster, Faget straight wing orbiter. |
| Shuttle DC-3 American winged orbital launch vehicle. Marshall Spaceflight Center shuttle concept of April 1970 using Faget low cross range stub-winged booster and orbiter. |
| Shuttle R134C American winged orbital launch vehicle. Rockwell/General Dynamics shuttle proposal phase B, November 1970. Delta wing high-cross range orbiter and booster. |
| Shuttle R134G American winged orbital launch vehicle. Rockwell/General Dynamics shuttle proposal phase B, November 1970. Straight wing low-cross range orbiter. |
| Shuttle LS200 American winged orbital launch vehicle. Lockheed Skunk Works alternate shuttle proposal of June 1971. X-24B lifting body orbiter with wrap-around external tank. |
| Shuttle H33 American winged orbital launch vehicle. Grumman/Boeing alternate shuttle proposal of July 1971. Shuttle orbiter with drop tanks, delta booster. |
| SERV American VTOVL orbital launch vehicle. Chrysler ballistic single stage to orbit alternate shuttle proposal of June 1971. This was the most detailed design study ever performed on a VTOVL SSTO launch vehicle. The 2,040 metric ton SERV was designed to deliver a 53 metric ton payload to orbit in a capacious 7 m x 18 m payload bay. |
| Mini-shuttle American manned rocketplane. Study 1972. In August 1972 it was proposed to test a subscale version of the shuttle to test the aerodynamics. The 13,750 kg vehicle would be 11 m long and have a wingspan of 7 m. |
| Shuttle LRB 1972 American winged orbital launch vehicle. Original design for a shuttle with liquid rocket boosters, completed in March 1972 as part of the shuttle design decision process |
| Saturn Shuttle American orbital launch vehicle. A winged recoverable Saturn IC stage was considered instead of solid rocket boosters after the final shuttle design was selected. |
| Enterprise American manned spaceplane. Study 1974. Enterprise was the first Space Shuttle Orbiter. It was rolled out on September 17, 1976. |
| EDIN05 American winged orbital launch vehicle. In February 1976 this version of the shuttle was proposed. A single liquid rocket booster under the external tank would replace the two solid rocket boosters. |
| Boeing SDV American orbital launch vehicle. The Boeing SDV Class I vehicle would lead to the Shuttle-C, using the shuttle aft fuselage with SSME engines to power a cargo canister into orbit. |
| IHLLV American orbital launch vehicle. Same concept as Shuttle C. Shuttle orbiter replaced by recoverable pod with shuttle main engines and payload canister. Quick way for US to obtain heavy payload capability and reduce shuttle cost per kg to orbit by 3 X. |
| Space Shuttle American winged orbital launch vehicle. The version of the space shuttle that went into production. Redesign of the shuttle with reliability in mind after the Challenger disaster reduced maximum payload to low earth orbit from 27,850 kg to 24,400 kg. |
| Columbia American manned spaceplane. Columbia, the first orbiter in the Shuttle fleet, was named after the sloop that accomplished the first American circumnavigation of the globe. |
| Challenger American manned spaceplane. |
| Martin Marietta SDV American orbital launch vehicle. The Martin Marietta Class I SDV would lead to the Shuttle-C, using the shuttle aft fuselage with SSME engines to power a cargo canister into orbit. |
| Discovery American manned spaceplane. merican manned spaceplane. |
| Shuttle LRB American winged orbital launch vehicle. Shuttle with Liquid Rocket Boosters in place of Solid Rocket Boosters. |
| Atlantis American manned spaceplane. The space shuttle Atlantis was the fourth orbiter to become operational at Kennedy Space Center, and the last of the original production run. |
| Shuttle II American orbital launch vehicle. In May 1988 NASA Langley studied a new-technology approach to improving the shuttle's payload capability. The design would allow 9,000 to 18,000 kg of additional payload to be carried in an external payload container or in the orbiter. |
| Shuttle LRB 1989 American orbital launch vehicle. In July 1989 a NASA Langley/George Washington University joint study was made of various Liquid Rocket Booster configurations. |
| Shuttle C American orbital launch vehicle. NASA Marshall design for a cargo version of the shuttle system. The shuttle orbiter would be replaced by an unmanned recoverable main engine pod. The same concept was studied earlier as the Interim Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle (IHLLV) and as the Class I Shuttle Derived Vehicle (SDV). The Phase I two-SSME configuration would have a payload of 45,000 kg to low earth orbit. Design carried to an advanced phase in 1987-1990, but then abandoned when it was found the concept had no cost advantage over existing expendable launch vehicles. |
| Low Cost Cargo Vehicle American orbital launch vehicle. This variant of the Shuttle C was envisioned for delivery of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen to orbit. |
| Shuttle C Block II American orbital launch vehicle. In August 1989 NASA studied a version of the Shuttle-C with two Advanced Solid Rocket Motors (ASRM's) in place of the standard RSRM's. This would increase the payload by 4500 kg, but also require use of a new 10 m x 30 m payload module. |
| Shuttle Z American orbital launch vehicle. Shuttle-Z was Shuttle-C on steroids, the ultimate development of the shuttle to be used to put Mars expeditions into orbit. It would use 4 SSME's, and a third stage with 181,000 kg of propellant powered by 1 SSSME. But such designs would require new handling facilities due to the extra height of the vehicle. |
| Ares Mars Direct American orbital launch vehicle. The Ares launch vehicle was designed for support of Zubrin's Mars Direct expedition. It was a shuttle-derived design taking maximum advantage of existing hardware. It would use shuttle Advanced Solid Rocket Boosters, a modified shuttle external tank for handling vertically-mounted payloads, and a new LOx/LH2 third stage for trans-Mars or trans-lunar injection of the payload. Ares would put 121 metric tons into a 300 km circular orbit , boost 59 metric tons toward the moon or 47 metric tons toward Mars. Without the upper stage 75 metric tons could be placed in low earth orbit. |
| Endeavour American manned spaceplane. merican manned spaceplane. Built as a replacement after the loss of the Challenger; named after the first ship commanded by James Cook. |
| Shuttle ASRM American winged orbital launch vehicle. Shuttle using Advanced Solid Rocket Motors (development cancelled 1993). |
| Shuttle ISS American winged orbital launch vehicle. Redesign of the shuttle with reliability in mind after the Challenger disaster reduced maximum payload to low earth orbit from 27,850 kg to 24,400 kg. When the decision was made to move the International Space Station to a high-inclination 51.6 degree orbit, net payload to the more challenging orbit dropped to unacceptable limits. The situation was improved by introduction of the Super Lightweight External Tank, which used 2195 Aluminum-Lithium alloy as the main structural material in place of the 2219 aluminum alloy of the original design. This saved 3,500 kg in empty mass, increasing shuttle payload by the same amount. The tank was first used on STS-91 in June 1998. |
| Ares American heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle. The design selected to boost America's Orion manned spacecraft into space in the 21st Century was a family of launch vehicles dubbed Ares. Originally sold as being derivatives of space shuttle technology, tinkering by NASA engineers and necessary changes during development quickly resulted in the designs being essentially all-new. Following inevitable cost growth and schedule slippage, it was cancelled in 2010. However continued development and eventual production of one derivative or another continued to be funded by Congress for many years afterwards. |
| Cargo LV American orbital launch vehicle. September 2005 NASA baseline heavy-lift vehicle to renew manned lunar exploration by 2018. |
| Ares I-X American heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle. Shuttle-derived launch vehicle design selected by NASA Administrator Mike Griffin to boost the manned CEV Crew Exploration Vehicle into low earth orbit. A single five-segment version of the shuttle solid rocket booster would be mated with a LOx/LH2 upper stage powered by a single J-2S engine. |
| Shuttle Flights Shuttle Flights |
Country: USA. Engines: OME. Spacecraft: ANDE, PSSC, Quasar, SSF, DSP, Spacebus 100, LAGEOS, GAS, HS 376, Insat 1, DoD 82-1, DSCS III, TDRS, SPAS, DFI, PFTA, Spacelab, IRT, LDEF, HS 381, ERBS, LFC/ORS, Shuttle MMU, Magnum, NUSAT, Spartan, CRNE, PDP, ASC, Atlantis, GLOMR, AS 4000, EASE/ACCESS, OEX Target, MSL-2, Lacrosse (satellite), Magellan, SDS-2, Galileo orbiter, Galileo probe, SSBUV, HS 601, Misty, HST, Ulysses, BBXRT, GRO, AFP-675, CRO, IBSS, MPEC, STP-1, UARS, EOIM, Eureca, CTA, USS, SHOOT, Spacehab, ACTS, BremSat, ODERACS, OAST, MAPS, WSF, Mir-Shuttle Docking Module, OAST-Flyer, TSS, GBA, IAE satellite, PAMS, TEAMS, ORFEUS, FSS, Second Axial Carrier, SLP, IEH, Technology Applications and Science Experiment, AERCam, EDO, USMP, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, EAL/ODS, SAC-A, ISS Unity, MightySat 1, Starshine, Chandra, ISS Leonardo, Simplesat, MEPSI, Cubesat, Ares spaceplane. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral. Bibliography: 4988, 7718.
 | Shuttle Cockpit Upgraded Shuttle MEDS Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
1968 October 30 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Phase A Space Shuttle studies. - .
Nation: USA.
NASA began the design, bidding, and source selection process leading to a single national space shuttle. At the beginning the design was known by the same nomenclature previously used by the USAF - Integrated Launch and Re-entry Vehicle (ILRV). The development program was seen as: Phase A: Advanced Studies; Phase B: Project Definition; Phase C: Vehicle Design; and Phase D: Production and Operations. Four contractors or contractor teams were to be selected in Phase A; two contractors or teams for Phase B; and then a single contractor for Phases C and D (which were later combined). NASA Houston and Huntsville jointly issued the Request for Proposal for eight-month Phase A ILRV studies. The requirements were for 2,300 to 23,000 kg of payload to be delivered into a 500-km altitude orbit. The re-entry vehicle should have a cross range of at least 725 km (NASA persisted in this requirement even though it knew the USAF needed more). General Dynamics, Lockheed, McDonnell-Douglas, Martin Marietta, and North American Rockwell all were invited to bid.
The Space Shuttle Main Engine competition was run in parallel with the main shuttle development project, and also had four phases. Oversight for this program came from the USAF Space Division and its subcontractor, the Aerospace Corporation. Despite promising classified work on linear and conventional aerospike engines at the time, NASA dictated that the design had to use a conventional bell nozzle.
February 1969 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Space Shuttle Phase A contracts - .
Nation: USA.
Following evaluation of proposals submitted against the October 1968 request for proposal, NASA issued Advanced Design contracts for the shuttle to General Dynamics, Lockheed, McDonnell Douglas, and North American Rockwell. Martin Marietta did not receive a contract but was allowed to continue using company funds.
Rocketdyne and Pratt & Whitney were selected for the Phase A, advanced study phase of the competition. The same basic engine (combustion chamber and turbomachinery) was to be used in both stages of the planned two-stage fully-recoverable shuttle. The orbiter would be equipped with a two-position deployable nozzle, with expansion ratios of 58:1 for the low altitude portion of the ascent, and 120:1 with the extension deployed for the vacuum portion of the flight to orbit. The engine was to have a thrust of 270,000 kgf in vacuum, 235,000 kgf at sea level, and be throttleable from 73% to 100% of the rated thrust. The engine for the booster was to use a 5:1 ratio expansion nozzle, producing 227,000 kgf at sea level. Pratt & Whitney seemed to have a clear lead in this portion of the competition, having produced the XLR-129-P-1, a prototype high-pressure Lox/LH2 engine under USAF contract. This produced 188,000 kgf using a smaller fixed nozzle. Most of the shuttle bidders proposed use of this engine in their Phase A vehicle designs.
The Space Task Group put together to run the shuttle design process was composed of various agencies of the federal government. Each group favoured differing basic configurations for the shuttle, reflecting controversies extending back over ten years to the time of DynaSoar development. Faget at NASA Houston favoured a straight-wing orbiter, the bottom surface being essentially a cross shape cut out of the spherical section of one of the Apollo or Mercury heat shields he had designed. This had minimal cross range, but was supposed to have the advantages of minimum weight and good subsonic glide performance. NASA Langley and Edwards AFB favoured a lifting body, based on the HL-10 shape under test there. This had supposed weight advantages over a winged vehicle, more cross range than Faget's straight wing, but less cross range than a delta wing. USAF Flight Dynamics Laboratory and Draper Laboratories favoured a swept delta wing spaceplane, like the Dynasoar, for maximum cross range on re-entry.
Faget favoured a small net payload to orbit (6800 kg) while the other government centres favoured heavier payloads, at least 11,300 kg, and up to 29,500 kg. As in the case of earlier USAF ILRV studies, the Space Task Group had initially considered three categories of launch solutions. Class I used an existing expendable launch vehicle (the Titan 3MV or Saturn IB) and a reusable orbiter. Class II were 1.5 stage to orbit designs, using an orbiter vehicle and a drop tank. Class III were fully reusable two-stage-to-orbit designs. In contrast to the USAF studies, which favoured immediate development of a Class I vehicle, followed by a Class II vehicle, Task Group's preferred solution was to proceed immediately with a Class III vehicle.
1969 February 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Nixon forms Space Task Group - .
Nation: USA.
Vice President Agnew was made chairman of the group, which was to formulate a Post-Apollo Space Program, providing policy direction for future American efforts after the moon landing. The Groups final report proposed three alternate future programs:
- At a funding level of $8 to $ 10 billion a year indefinitely, NASA could do it all - a manned expedition to Mars, permanent manned space bases in lunar orbit and the lunar surface, a 50-person space station in earth orbit, and a reusable space shuttle to support all of these projects on an economical basis
- All of the objectives could be achieved, but the funding level kept at $ 8 billion per year, by deleting the manned lunar orbit station
- At $ 5 billion per year, a program consisting of just the earth orbit station and the space shuttle could be funded - but no further manned exploration of the moon or planets
Nixon rejected all of the alternatives and wanted something even cheaper.
1969 April 21 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Space Shuttle Task Group formed - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. The Director of Apollo Test in the NASA Hq. Apollo Program Office, LeRoy E. Day, was detailed to head the MSF Space Shuttle Task Group. The group would provide NASA with material for a report on the Space Shuttle to the President's Space Task Group..
1969 May - . Launch Vehicle: Shuttle.
- USAF selects three companies to prepare design concepts for a reusable space vehicle for the STS. - . SAMSO selected General Dynamics/Convair, Lockheed Missiles and Space Company, North American Rockwell, and McDonnell Douglas to prepare design concepts for a reusable space vehicle for the STS..
1969 June 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Faget shuttle concept attacked - .
Nation: USA.
The first report comes out attacking the Faget straight wing design. Another follows in November 1969; with the dispute becoming public with AIAA papers published in October 1970 and January 1971. These dissidents at other NASA centres calculated that a Faget orbiter was unsafe, as it could not withstand the re-entry thermal environment and aerodynamic stresses. NASA's Flight Research Center pushed a lifting body design, while the US Air Force noted that in any case the Faget design did not meet its cross-range requirements.
1969 June 16 - . Launch Vehicle: Shuttle.
- USAF contracts to study Space Transportation System (STS) design concepts. - .
SAMSO awarded contracts to North American Rockwell, McDonnell Douglas, General Dynamics/Convair, and Lockheed Missiles and Space Company to study Space Transportation System (STS) design concepts. SAMSO awarded contracts to North American Rockwell, McDonnell Douglas, General Dynamics/Convair, and Lockheed Missiles and Space Company to study Space Transportation System (STS) design concepts.
Fall 1969 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- No government approval for NASA's shuttle program - .
Nation: USA.
NASA decided to take the minimum program proposed by the Space Task Group (just the space station and the shuttle), and then implement it over a very long period in phases. At first only a reusable space shuttle would be developed. When that was completed, work on a space station could start. However as of the fall of 1970, NASA was unable to obtain the Nixon administration's approval of even this limited program.
1969 September 11 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Two major directions were identified for NASA manned space flight in the next decade. - .
Nation: USA.
Program: Skylab.
Flight: Skylab B.
Spacecraft: Columbia,
Skylab.
Two major directions were identified for manned space flight in the next decade. These were further exploration of the Moon, with possibly the establishment of a lunar surface base, and the continued development of manned flight in Earth orbit, leading to a permanent manned space station supported by a low-cost shuttle system. To maintain direction, the following key milestones were proposed: 1972 - AAP operations using a Saturn V launched Workshop 1973 - Start of post-Apollo lunar exploration 1974 - Start of suborbital flight tests of Earth to orbit shuttle - Launch of a second Saturn V Workshop 1975 - Initial space station operations - Orbital shuttle flights 1976 - Lunar orbit station - Full shuttle operations 1977 - Nuclear stage flight test 1978 - Nuclear shuttle operations-orbit to orbit 1979 - Space station in synchronous orbit By 1990 - Earth orbit space base - Lunar surface base - Possible Mars landing
1969 October 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- NASA and the Air Force agree on shuttle development - . NASA and the Air Force agreed on development of a reusable space vehicle that would meet both civilian and military space requirements. NASA proposed a two-stage shuttle with a cargo area 60x15 feet..
1970 January 23 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- NASA Houston in-house study of shuttle concepts - .
Nation: USA.
The study was in an attempt to resolve disputes between the centres as to the best approach. Houston's Faget straight-wing two-stage vehicle was in competition with concepts from other centres - recoverable versions of Saturn boosters, and an advanced single-stage-to-orbit Aerospaceplane. Payload for the Faget vehicle was to be only 5,700 to 6,800 kg to low earth orbit, and the system was to be operational by the end of 1975, after the last Apollo flight.
1970 February 17 - . Launch Vehicle: Shuttle.
- Space Transportation System (STS) for both NASA and USAF - .
Space Transportation System (STS) to provide maximum utility to both military and civilian users at lower operating costs. NASA would manage STS development, and a NASA-USAF Committee would review the program to guarantee that it met Defense Department and NASA requirements.
1970 May 4 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- DC-3 drop tests - . Nation: USA. NASA conducted drop tests of a 1/10 scale model of Faget's 'DC-3' straight-wing shuttle design. The model was 4 m long, weighed 270 kg, and was dropped from 3,700 m altitude. Recovery was by parachute..
June 1970 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Independent studies of NASA's shuttle ordered. - .
Nation: USA.
The new NASA Administrator, James Fletcher, had found that the NASA internal estimates of the cost to develop and operate the space shuttle were treated by the Office of Management of the Budget with great scepticism. Therefore he authorised several independent studies. Lockheed was to report on how the shuttle could reduce payload costs. Aerospace Corporation was to make an independent estimate of the cost of developing and operating the shuttle. Mathematica was to use these studies to make a definitive report comparing the cost of the shuttle with that of using existing expendable boosters.
The Mathematica study would become notorious, for it forecast enormous savings in the use of the shuttle. It became very influential in government and congressional circles in shifting opinion to support the project. This, as NASA Administrator Low would dryly comment later, was 'unfortunate'. All earlier studies for the USAF and NASA, notably a RAND study in 1970, showed no cost advantage for reusable boosters when research and development costs were taken into account. RAND had concluded that a manned space station supported by expendable boosters would be cheaper, and more flexible and useful.
Fletcher also directed NASA to take US Air Force requirements for the shuttle into account. The US Defence Department's requirements included the ability to carry 18 m long payloads, and deliver a mass of 18,000 kg to a polar orbit from Vandenberg AFB, or 30,000 kg to a low earth orbit from Cape Canaveral. The 4.5 m diameter for the payload bay was a NASA requirement, established by the planned diameter of future space station modules. 18 m x 4.5 m also corresponded to the dimensions of a liquid hydrogen tank with a mass of 30,000 kg, the lowest-density payload imaginable. The USAF also wanted an 1800 to 2400 km cross range on re-entry, and an initial operational capability of December 1977.
The Aerospace Corporation study of NASA Phase A proposals concluded that the weight of a shuttle's thermal protection system would vary in relation to the fourth root of the required cross range. Aerospace also believed that sequential ignition of the booster and orbiter was a better approach than the triamese-type all-engines running at lift-off. It also declared that the USAF's desired operational date was unrealistic -- the earliest a shuttle could be available was mid to late 1979.
1970 June 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- NASA completes Shuttle Phase A evaluations - .
Nation: USA.
After over 200 man-years of NASA and contractor effort, the Agency reached the following conclusions at the end of Phase A:
- The common orbiter/booster engine planned would have to have a lower thrust then proposed, with more used per booster. This was due to the need for the orbiter to have several engines instead of one or two in order to give it abort capabilities in the event of a single engine failure. It was recommended that a 180,000 kgf engine be developed for the shuttle instead of the 230,000 kgf previously planned.
- Lifting body configurations were not suited for the launch vehicle application. This was due to the required complex internal arrangement of tanks and equipment within the curving hull, difficulty of fabricating the airframe and tanks, and poor subsonic lift/drag performance.
- Variable geometry wings were not desirable, since they resulted in a heavier weight to body area ratio during re-entry, and thereby more re-entry heating problems. They also required complex mechanical and pneumatic/hydraulic systems for operation, which meant more maintenance, more complexity, and extra failure modes. There considerable advantages - a lower spacecraft weight fraction and the highest lift/drag in subsonic flight - did not offset these disadvantages.
- Two-stage-to-orbit, vertical takeoff, horizontal landing configuration
- Initial operational capability by the end of 1977
- 6,800 kg payload to a 500 km, 55 deg inclination orbit when launched from Cape Canaveral
- 4.6 m x 18.3 m payload bay
- Two orbiter alternates were to be proposed by the contractors, one with a 370 km cross-range (NASA requirement), one with a 2784 km cross range (USAF requirement). This implied a minimum L/D for the high cross-range vehicle of 1.8, and a total heat load 5 to 7 times greater than the low cross-range alternative.
- Seven-day orbital mission capability.
- Go-around capability on landing in case of a missed approach. This implied the use of airbreathing engines. Phase A studies showed that use of gaseous H2 from the orbiter's tanks as fuel for such engines drastically reduced the orbiter weight compared to use of conventional JP-4 jet fuel housed in separate tanks.
- Design to be capable of 25 to 70 launches a year, with a turnaround time of two weeks
- G-forces limited to 3G on ascent
- Two crew housed in a pressure cabin without spacesuits
- 43 hour countdown time after assembly
- Stage separation without the use of rocket devices
- No in-flight refuelling allowed
- Capable of landing under FAA Category 2 conditions on a 3,000 m runway
- All systems fail-operational - e.g. they would remain operational after any single component failure, and remain fail-safe for crew survival even after two subsystem failures
- Quick safeing of vehicle systems after landing
- No propellant cross-feed allowed between booster and orbiter
1970 July 6 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Phase B Contracts - .
Nation: USA.
Phase B contracts were issued for preliminary design for a space shuttle to two industrial teams - McDonnell Douglas and Martin Marietta; and North American Rockwell and General Dynamics. The specifications were as laid out in the NASA specificaiton on 1 June. In addition, both teams were mandated to study, as a baseline, alternate orbiters, consisting of the MSC-002 straight-wing Faget configuration for the low cross-range alternative, and a delta wing configuration for the high cross-range alternative. The booster configuration, on the other hand, was left up to the contractors.
Engine contracts were let to Pratt and Whitney, Rocketdyne, and Aerojet. The engine specification called for a Lox/LH2 engine with a bell nozzle, capable of gimballing plus/minus 7 deg, producing 188,000 kgf at sea leval and 216,000 kgf at altitude. The booster engines would be equipped with a 6:1 expansion nozzle, and the orbiter with a two-position nozzle to bring the expansion ratio up to 120:1 at altitude. The engine had to throttle between 50% and 115% of the rated thrust (the latter rating for abort engine-out situations). The engine was to be equipped with a digital engine controller and be compact and reusable.
1970 July 7 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Alternate Space Shuttle Concepts (ASSC) - .
Nation: USA.
NASA Huntsville, dissatisfied with the shuttle concepts being pursued by NASA Houston, let contracts to Chrysler and Lockheed for alternate technical approaches to the configuration dictated to Phase B contractors by NASA Houston. Later a further contract was let to a Grumman/Boeing team. In all, 29 configurations of partially reusable to fully-reusable vehicles were explored. The baseline engine for these studies had a thrust of 250,000 kgf and a two-position bell nozzle.
1970 September 23 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle specifications revised - .
Nation: USA.
In response to US Air Force criticism, the payload requirement was increased to 11,500 kg (still well short of the USAF 30,000 kg requirement). The use of JP-4 jet fuel was required for the airbreathing flyback engines. The payload by was to be capable of carrying a passenger module for ferry of space station crews.
1970 November 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle specifications revised - . Nation: USA. Further minor changes were made as a result of the NASA 90-day review in October..
1970 December 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Phase B preliminary proposals - . Nation: USA. The teams of McDonnell Douglas/Martin Marrietta and North American Rockwell/General Dynamics made their preliminary proposals under shuttle Phase B contracts..
1970 December 29 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle external tank concept studied - .
Nation: USA.
On 29 December 1970 Grumman and Boeing received contract NAS9-11160 to study two-stage-to-orbit shuttle configurations using both internal and external liquid hydrogen tanks. Reviews with NASA in January and March 1971 showed there could be significant weight, risk, and cost reductions through use of a booster with a heat-sink airframe and an orbiter equipped with an external liquid hydrogen tank.
1971 February 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME Award - .
Nation: USA.
North American Rockwell's Rocketdyne division was awarded NASA contract NAS8-40000 for development of the space shuttle main engine, beating out Pratt and Whitney and Aerojet. This was the only large liquid propellant rocket motor scheduled to be developed in the United States for decades and a crushing blow to the losers. Both felt that their designs were superior to that of Rocketdyne, but Rocketdyne had become NASA's 'house' for main rocket engines.
1971 March 26 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Phase B Final Reports - .
Nation: USA.
Taking into account NASA and USAF comments on the draft proposals, and specification revisions, the teams of McDonnell Douglas/Martin Marrietta and North American Rockwell/General Dynamics made their final proposals under shuttle Phase B contracts. Based on the strict specifications of NASA, the low cross-range and high-cross range versions of the orbiter stages were similar. The associate contractors provided considerably different winged booster stage designs. One common feature was the use of aluminium structures and non-metallic thermal protection systems. In late 1969 the USAF had indicated a preference for all-aluminium structures in the shuttle due to a titanium shortage. This requirement forced a move to non-metallic thermal protection systems, which at the time it was thought would weigh 15% less but cost 300% more. Thermal protection shingles for a titanium structure would weigh 2300 to 4500 kg less, but an aluminium structure would weight about 1800 kg more - meaning there was no essential weight difference between the two approaches. Therefore at the aluminium structure was accepted as a specification requirement. In retrospect it could hardly have been necessary to apply this requirement on a project where only a few flight vehicles were be built. It made the shuttle much more vulnerable to any breach of heat shield integrity and would lead to the death of the Columbia crew 35 years later. The resulting need for a non-metallic thermal protection system would also have enormous cost and schedule consequences for the actual program.
1971 April 21 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME Protest - . Nation: USA. Pratt and Whitney filed a protest against NASA's award to Rocketdyne of the SSME contract. This action prevented further work on Rocketdyne's contract until the issue was adjudicated..
1971 April 27 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- James C Fletcher sworn in as NASA Administrator - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Fletcher,
Low, George,
Nixon,
Paine.
Program: Apollo.
James C. Fletcher was sworn in as NASA Administrator at a White House ceremony. Fletcher decided to push for Congressional approval of the stalled space shuttle program, but found that would only be forthcoming if the US Air Force agreed to participate. In order for that to happen, NASA would have to incorporate the USAF requirements for the shuttle that it had so far ignored (greater payload, higher cross-range). In another attempt to share the cost of the shuttle with other nations, previous NASA Administrator Thomas Paine had already tried to obtain international partners. But the only remnants of that effort were the Canadian robotic arm for the shuttle, and the European Space Agency Spacelab module. Neither represented a significant amount of the total program cost.
President Nixon had nominated Fletcher for the position on March 1, and the Senate had confirmed the nomination on March 11. George M. Low, NASA Deputy Administrator, had been Acting Administrator since the resignation of Paine on September 15, 1970.
1971 May 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- NASA budget constraints - .
Nation: USA.
Nixon's Office of Management of the Budget (OMB) tells NASA to expect no budget increases in the next five years (e.g. $ 3.2 billion per year, meaning no more than $1 billion per year could be spent on the shuttle). Since the peak funding to develop a two-stage-to-orbit shuttle as defined in Phase B studies would be $2 billion, this meant that development of a fully reusable shuttle would not be possible.
1971 June 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle design decision - .
Nation: USA.
Based on funding constraints defined in May, NASA decides its shuttle configuration will have to be a partially reusable orbiter, with an external liquid hydrogen tank. Grumman had been the main advocate of this approach, but it was the same conclusion reached in the USAF ILRV studies in 1968. The in-house design reflecting this change was MSC-020, with a liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen tank housing all propellants outside of the orbiter.
1971 August 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle delta wings - . Nation: USA. NASA Houston finally abandoned its straight wing design and studied a series of delta wing orbiters with external tanks through the summer of 1971 (MSC-020B, MSC-036, MSC-046, MSC-040)..
Fall 1971 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Delta wing selected for shuttle - .
Nation: USA.
NASA, taking note of the criticisms of the Faget straight-wing design by NASA Flight Research Center and the US Air Force, officially selected a delta wing configuration as the most stable and the one best able to meet the USAF cross-range requirement. But NASA Houston stubbornly continued to push the configuration anyway - even after its own studies showed the orbiter would have a tendency to spin at hypersonic speeds and couldn't take the thermal environment on re-entry. Houston refused to give up, and continued to tinker with aspect ratio, wing sweep, and tail location, reaching the 43th design iteration - MSC-043 - at the end of 1971. One of the alternatives studied was the 'Blue Goose' design of 1970, perhaps the ugliest spacecraft ever conceived. The wing of the long-necked abomination shifted 3.7 m during flight to compensate for centre of gravity changes. The payload bay was forward, followed by the liquid oxygen, then the liquid hydrogen tank. The design was found to have *extreme* aerodynamic heating and structural problems!
1971 September 12 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Phase B-Prime - .
Nation: USA.
The Phase B contractors, plus Grumman/Boeing and Lockheed, are given further study contracts to produce shuttle designs based on the expendable external tank approach. Lockheed was asked to evaluate the NASA Houston design using an MSC-040 configuration orbiter, external tank, including the MSC040C using three high-performance engines. While the USAF was driving the shuttle design criteria, it had so far not committed to any significant funding for the shuttle. The USAF contribution was limited to allowing NASA use the government-owned Plant 42 at Palmdale, paying for any launch facilities at Vandenberg AFB needed for USAF launches, and providing flight test support at Edwards AFB.
1971 October 30 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Phase C/D Request for Proposal - .
Nation: USA.
Request for Proposals were sent to Grumman/Boeing, McDonnell-Douglas/Martin Marrietta, and North American Rockwell for final proposals for Shuttle full-scale development. However the NASA specifications kept shifting. In December 1971 NASA decided to require parallel burn of the shuttle orbiter and booster stages, so the bid due date was shifted from 15 December 1971 to 1 June 1972.
1971 November 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Phase B Double Prime - .
Nation: USA.
In yet another iteration of shuttle design studies, $ 2.8 million contracts were given to Grumman/Boeing, Lockheed, McDonnell-Douglas/Martin Marrietta, and North American Rockewell. The development costs for the Phase B Prime contracts had still been over the Nixon administration's budget cap, and still further ways to reduce development cost had to be found. The studies were to run through 15 March 1972 and study lower cost booster concepts: a fully recoverable stage but with a new pressure-fed engine; a Saturn V first stage modified to serve as a flyback booster; and solid rocket motors. The staging velocity was to be under 6600 kph (e.g. lower than in earlier studies). The studies assumed a series burn, with the shuttle orbiter igniting at altitude.
The studies indicated :
- The Saturn S-IC flyback booster would use expendable engines, considered a drawback.
- The new-design pressure fed liquid propellant booster would cost $4.2 billion to develop, plus a recurring cost of $275/kg to orbit.
- Solid boosters would stage at 5800 kph. A solid booster shuttle would have a 2,221,000 gross lift-off weight equipped with 2 x 156 inch diameter solid rocket motors, loaded with 1.25 million kg of propellant and having a 130 second burn time. Lift-off thrust would be 1,332,000 kgf. Development cost would be $ 3.7 billion, and recurring shuttle cost to orbit would be $ 500/kg.
1972 January 5 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Nixon announces $5.5 billion space shuttle program - . Related Persons: , Nixon. President Richard M. Nixon announced that NASA would manage a $5.5 billion program to develop a space shuttle to be the workhorse of future U.S. space efforts and replace all present launch vehicles..
1972 March 15 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle booster decision - .
Nation: USA.
NASA decided that the shuttle booster will be 2 x 156 inch solid rocket motors. This would reduce the total development cost by $700 million, from $ 5.85 billion to $ 5.15 billion. It was also decided to delete the requirement for the shuttle to be equipped with air-breathing engines for final approach and ferry, and to add Abort Solid Rocket Motors that would pull the shuttle away from the external tank in case of a failure of the solid rocket boosters or external tank during the first portion of the ascent to orbit.
1972 March 31 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME Judgement - . Nation: USA. Pratt and Whitney's protest against the award of the shuttle engine development contract was rejected. Contract award to Rocketdyne could now proceed..
1972 April 6 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Request for proposals for the Space Shuttle. - . NASA asked the aerospace industry to submit proposals for the development of the Space Shuttle..
1972 April 14 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral, Vandenberg. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle.
- Kennedy Space Center and Vandenberg AFB to be the operational bases for the Shuttle. - .
Related Persons: ,
Kennedy.
NASA announced that the Kennedy Space Center in Florida and Vandenberg AFB in California would be the operational bases for the future Space Transportation System (STS). The research and development launches of the Space Shuttle would be made from Cape Canaveral, as would the civilian space launches, while the military Space Shuttle launches would be from Vandenberg AFB. SAMSO was the responsible Defense Department agency for defining the military applications and requirements for the Space Shuttle and for cooperating with NASA in the development of the STS.
1972 April 21 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME Contract - . Nation: USA. Rocketdyne finally receives the contact for development of the shuttle main engine. By the end of the century the total value will have exceeded $5.6 billion..
1972 June 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Phase C/D Proposals - .
Nation: USA.
Given that NASA had dictated in great detail the final design, the contractors' proposals differed only in detail. Grumman's orbiter had a 747-type hump-backed configuration, while Lockheed's featured a double-deck crew space. McDonnell-Douglas proposed an alternate auxiliary liquid propellant rocket motor for aborts in place of the mandated Abort Solid Rocket Motors. North American Rockwell's design featured a rounded double-delta wing. All contractors struggled with thermal protection system issues. Ablative materials were lighter, but the bad experience with the use of spray-on ablator on the X-15A-2 made such a solution for an operational vehicle problematic.
1972 July 7 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle orbiter contract - .
Nation: USA.
North American Rockwell received NASA contract NAS9-14000, valued at $2.6 billion, for development of the space shuttle orbiter. Included are two flight articles, the STA Structural Test Article, and the MPTA Main Propulsion Test Article. Later production of two additional orbiters will be added, bringing the final contract value to $ 5.815 billion by 1996.
1972 July 12 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Safety in Earth Orbit - .
Nation: USA.
North American Rockwell issues a study on safety concepts for the space shuttle. These include putting an Apollo command module in the shuttle payload bay as an emergency re-entry capsule in case of inability of the shuttle to re-enter due to heat shield damage or a propulsion system failure. The study finds that all solutions have unacceptable weight penalties, and that any upper stages carried in the payload bay had to be man-rated in order to ensure crew safety. Liquid propellant upper stages (such as Centaur and the planned Space Tug) were probably too dangerous to be taken to orbit by the shuttle.
1972 July 26 - .
- Contract awarded for shuttle OV-102. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1972 July 26 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Contract for development of the Space Shuttle. - . NASA awarded a $2.6 billion contract to North American Rockwell (now Rockwell International) for the development of the national Space Transportation System (STS) and the Space Shuttle..
1972 August 9 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle go-ahead. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Rockwell receives authority to proceed, space shuttle orbiter.
1973 May 14 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- DOD to develop the shuttle's Interim Upper Stage. - . An Air Force Program Memorandum on DOD Space Shuttle Utilization was completed that assumed the DOD would develop the shuttle's Interim Upper Stage (IUS) needed for high energy missions..
1973 August 16 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle solid rocket booster contract - . Nation: USA. United Space Boosters and Thiokol receive the contract..
1973 August 16 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle external tank contract - . Nation: USA. Boeing Michoud received the production contract, using facilities already built for Saturn V first stage construction. By 1996 the contract will have totalled $6.7 billion and covered the production of 120 external tanks..
1974 March 8 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Air Force plan for the Space Transportation System. - . The Air Force completed a revised Program Memorandum on DoD Space Shuttle Utilization that was to become the basis for Air Force planning for the Space Transportation System..
1974 June 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle configuration changes - . Nation: USA. Between the March 1972 Authority to Proceed and June 1974 six major configuration changes are made to the shuttle design..
1974 June 4 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Enterprise construction begins. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Structural assembly of the crew module for shuttle Enterprise (OV-101) begins at Plant 42 in Palmdale..
1974 June 4 - .
- Structural assembly of crew module for OV-102 begun. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1974 July 18 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle carrier aircraft purchased - .
Nation: USA.
NASA purchases used American Airlines 747 N9668 for use as a carrier to ferry the shuttle orbiter between factory, landing sites, and launch sites. Modification of a 747 to carry the orbiter on its back was chosen over two more costly alternatives that would have suspended it from a wing connecting two fuselages: a new design proposed by NASA LaRC, and a Lockheed proposal for two C-5A transports joined together.
1974 August 26 - .
- Shuttle Enterprise fuselage assembly starts. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Start structural assembly aft fuselage, Enterprise (OV-101).
1974 October 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS studies begun. - .
The Air Force awarded firm-fixed-price (FFP) level of effort contracts of about $635,000 to $640,000 each to Martin Marietta Corporation, Lockheed Missiles and Space Company, General Dynamics Convair Division, The Boeing Company, and McDonnell Douglas Astronautics Company for nine-month IUS System Study efforts.^ These companies had in-production, existing operational upper stages and the studies would provide baseline data for future acquisition efforts.
1975 January 23 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- DOD space shuttle mission operations to be controlled by a predominantly NASA team. - .
HQ USAF issued a Program Management Directive specifying that initial DOD space shuttle mission operations would be planned and controlled by a predominantly NASA team rather than by a DOD team. The Program Management Directive also directed that action be taken to minimize the impact of DOD communications security requirements on shuttle operations.
1975 February 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Lower-cost shuttle external tank - .
Nation: USA.
Grumman completes a study of a lower-cost external tank. It would use a Nomex core, aluminium liner, and E-glass/epoxy exterior. Although lower in cost than the baseline aluminium tank, it would be slightly heavier. Given the critical weight growth problem with the shuttle, it was not proceeded with. In fact, a continuous program of weight reduction for the baseline tank was introduced. Batch 1 External Tanks were already from 500 to 1040 kg lighter than the first tank. Batch 2, set for delivery from June 1982 to Vandenberg AFB for USAF launches, were 2700 kg lighter. The final "lightweight tank" was over 4500 kg lighter. All of these translated into equivalent additional payload for the shuttle.
1975 March 27 - .
- Shuttle Enterprise fuselage complete. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1975 March 27 - .
- Shuttle Columbia fuselage assembly starts. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Start long-lead fabrication aft fuselage, Columbia (OV-102).
1975 May 23 - .
- Enterprise wings complete. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Wings on dock, Palmdale-less elevons, seals and main gear doors-Enterprise (OV-101).
1975 May 27 - .
- Enterprise vertical stabilizer complete. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Vertical stabilizer on dock, Palmdale (main fin box only), Enterprise (OV-101).
1975 July 23 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME engine chamber Test - . Nation: USA. The first full thrust chamber test is completed..
1975 August 25 - .
- Shuttle Enterprise final assembly. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Start final assembly and closeout system installation, Enterprise (OV-101).
1975 September 4 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Interim Upper Stage for use with the Space Transportation System. - . Dr. Walter LaBerge, Assistance Secretary of the Air Force for Research and Development, announced an Interim Upper Stage to be developed for use with the Space Transportation System..
1975 September 5 - .
- Enterprise aft fuselage complete. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Aft fuselage on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101).
1975 October 17 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME first test. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Space shuttle main engine first main stage test at NSTL.
1975 October 31 - .
- Enterprise lower fuselage complete. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Lower forward fuselage on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101).
1975 November 17 - .
- Columbia crew module started. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Start long-lead fabrication of crew module, Columbia (OV-102).
1975 Dec - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- DOD to use NASA's mission operations system for the space shuttle - . HQ USAF decided that the DOD would not acquire its own mission operations system for the space shuttle but would use NASA's system instead..
1975 December 1 - .
- Enterprise upper forward fuselage complete. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Upper forward fuselage on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101).
1975 December 20 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
1976 January 16 - .
- Crew module on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 February 27 - . LV Family: Titan, Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/IUS.
- Interim Upper Stage to be used with the Titan III - .
A joint DOD/NASA study was carried out on the consolidation of expendable launch vehicles during transition to the space shuttle. The study recommended that the Interim Upper Stage, being developed for the space shuttle, be used with the Titan III during the transition period.
1976 March 3 - .
- Payload bay doors on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Payload bay doors on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101).
1976 March 12 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME Test - . Nation: USA. The full engine is run at 65% power for 42.5 seconds before a fuel turbopump failure curtails the test (50 second duration planned)..
1976 March 12 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise final assembly complete. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Complete final assembly and closeout system installation..
1976 March 15 - .
- Start functional checkout, Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Start functional checkout, Enterprise (OV-101)..
1976 Apr - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle.
- $125 million to modify NASA's space shuttle mission control center for use by the DOD. - . A joint USAF/NASA study concluded that it would cost $125 million to modify NASA's space shuttle mission control center so that it could be used by the DOD..
1976 April 22 - .
- Body flap on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 June 25 - .
- Complete functional checkout, Enterprise (OV-101) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 June 28 - .
- Start horizontal ground vibration tests Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Start horizontal ground vibration tests and proof load tests, Enterprise (OV-101).
1976 June 30 - .
- SSME dummy set on dock, Palmdale. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. SSME dummy set on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101).
1976 Jul - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Optimum configuration for the space shuttle launch pad at Vandenberg AFB. - . Tests were conducted at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center to determine the optimum configuration for the space shuttle launch pad to be built at Vandenberg AFB..
1976 July 22 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Design criteria for space shuttle facilities at Vandenberg. - . Contract FO4701-76-C-0081 was distributed to Martin Marietta for the preparation of design criteria for space shuttle facilities at Vandenberg AFB. The target price of the contract was $28 million..
1976 August 2 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle carrier aircraft - . Nation: USA. Work begins on modification of 747 N9668 to carry the shuttle on its back in a $30 million contract. After completion the aircraft is rolled out as N905NA..
1976 August 23 - .
- Start Delta F modification, Enterprise (OV-101) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 August 27 - .
- Shuttle Enterprise - dummy OMS pods delivered. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Reaction control system/orbital maneuvering system pods (simulated), approach and landing tests, on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise.
1976 September 3 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Contract for validation phase of the Interim Upper Stage. - . A contract was distributed to the Boeing Aerospace Company for the validation phase of the Interim Upper Stage development program. The contract carried a target price of $21 million..
1976 September 10 - .
- Complete Delta F modifications, Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 September 13 - .
- Start preparations for first rollout, Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 September 17 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- The roll-out of the first space shuttle vehicle took place. - .
1976 September 20 - .
- Start Delta F retest, Enterprise (OV-101) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 October 26 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle ejection seat tests - . Nation: USA. Tests begin on the rocket sled at Holloman AFB of the ejection seats to be used in shuttle Columbia, using an upper fuselage. The test series is completed on November 18..
1976 October 29 - .
- Complete Delta F retest, Enterprise (OV-101) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 November 26 - .
- Complete integrated checkout, Enterprise (OV-101) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1976 Dec - . LV Family: Titan, Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC, Shuttle.
- Process selected for manufacturing hydrazine fuels for the Titan III and the space shuttle. - . SAMSO selected the Sisler process as the best of three competing methods for manufacturing hydrazine fuels for the Titan III and the space shuttle..
1976 December 7 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- DOD mission operations system for the space shuttle. - .
Briefings were presented to HQ AFSC, HQ USAF, and SAF/SS outlining three alternative methods of providing the DOD with a mission operations system for the space shuttle. These were: modification of NASA facilities at the Johnson Space Center, expansion of the Air Force Satellite Control Facility, and construction of an all-new DOD facility to be called the STS Operations and Planning Center.
1976 December 13 - .
- Start assembly upper forward fuselage, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1977 Jan - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Space shuttle facilities at Vandenberg AFB, California. - . The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers began designing the mate/demate facility, the airfield, and the tow route to be used by the space shuttle at Vandenberg AFB, California..
1977 January 3 - .
- Start assembly vertical stabilizer, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1977 January 14 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Boeing 747 shuttle carrier aircraft delivered - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Boeing 747 shuttle carrier aircraft delivered to Edwards.
1977 January 31 - .
- Mockup SSME's delivered for Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Mass simulated SSMEs on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 January 31 - .
- Mass simulated SSMEs on dock, Palmdale, Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1977 January 31 - . Launch Site: Edwards.
- Enterprise (OV-101) transported to Edwards AFB - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise.
1977 February 7 - .
- Enterprise (OV-101)/shuttle carrier aircraft mate - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Enterprise (OV-101)/shuttle carrier aircraft mate start.
1977 February 10 - .
- Midfuselage on dock, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1977 February 15 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards.
- Enterprise (OV-101)/shuttle carrier aircraft mated - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Complete Enterprise (OV-101)/shuttle carrier aircraft mated.
1977 February 18 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- First inert captive flight - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Conduct first inert captive flight, Edwards (2 hours, 5 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 February 22 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Second inert captive flight - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Conduct second inert captive flight, Edwards (3 hours, 13 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 February 25 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Third inert captive flight - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Conduct third inert captive flight, Edwards (2 hours, 28 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 February 28 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Fourth inert captive flight - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Conduct fourth inert captive flight, Edwards (2 hours, 11 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 March 2 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Fifth inert captive flight - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Conduct fifth inert captive flight, Edwards (1 hour, 39 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 April 27 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME Tests resumed - . Nation: USA. 25 tests will be run on two engines over the next year..
1977 May 5 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle ejection seat tests - . Nation: USA. Another test series is held at Holloman at speeds of zero to 725 kph in support of the impending ALT shuttle glide tests..
1977 June 7 - .
- Complete integrated checkout of Enterprise - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Complete integrated checkout and hot-fire ground test, Edwards, Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 June 10 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS 85-second test firing. - . A rocket nozzle for the IUS was subjected to an 85 second test firing at the Rocket Propulsion Laboratory. The test was successful. A second successful test took place on 15 July..
1977 June 15 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SRB Drop test - . Nation: USA. An unloaded shuttle solid rocket motor is dropped from an NB-52 in a test of the parachute recovery system..
1977 June 18 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 1 - . Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Fullerton, Haise. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fullerton, Haise. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. First manned captive active flight. Enterprise (OV-101)/shuttle carrier aircraft, Edwards (55 minutes, 46 seconds).
1977 June 20 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Titan 34D/IUS launch vehicle begun. - . HQ USAF directed AFSC to begin developing the Titan 34D/IUS launch vehicle..
1977 June 24 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle MPTA shipped to National Space Technology Laboratories - . Nation: USA. The test article of the shuttle orbiter's aft structure is mated to External Tank MPTA-ET (ET number one) and three prototype SSME engines..
1977 June 28 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 2 - . Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Engle, Truly. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Engle, Truly. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Second manned captive active flight. Enterprise (OV-101)/shuttle carrier aircraft, Edwards (1 hour, 2 minutes).
1977 Jul - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Secure use of NASA's Johnson Space Center for classified DOD missions. - .
A joint DOD/NASA committee was formed to find an economical method of securing NASA's Johnson Space Center so that it could be used for mission control when classified DOD missions were flown. The committee handed in its final report in November, recommending that the Johnson Space Center be secured through what it called the "controlled mode" of operation.
1977 July 18 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- DM-1 Shuttle SRB development static firing - . Nation: USA. The first firing of a shuttle Solid Rocket Booster motor..
1977 July 26 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 3 - . Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Fullerton, Haise. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fullerton, Haise. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Third manned captive active flight. Enterprise (OV-101)/shuttle carrier aircraft, Edwards (59 minutes, 50 seconds).
1977 Aug - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Launch complex for the space shuttle at Vandenberg AFB - . Sverdrup and Parcel began designing the launch complex to be used by the space shuttle at Vandenberg AFB, California..
1977 August 4 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SRB Drop test - . Nation: USA. An unloaded shuttle solid rocket motor is dropped from an NB-52 in a test of the parachute recovery system..
1977 August 12 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 4. The space shuttle made its first free flight. - .
Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Fullerton,
Haise.
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Fullerton,
Haise.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Enterprise.
After being carried aloft by a Boeing 747, it was released and made an unassisted landing at Edwards AFB, California. This was part of a series of approach and landing tests carried out at Edwards from February to October. Conduct first free flight, ALT, tail cone on, Edwards (5 minutes, 21 seconds), Enterprise (OV-101), lake bed Runway 17
1977 August 26 - .
- Deliver wings on dock, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1977 September 7 - .
- Lower forward fuselage on dock, Palmdale, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1977 September 13 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 5 - . Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Engle, Truly. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Engle, Truly. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Second free flight, ALT, tail cone on, Edwards (5 minutes, 28 seconds), Enterprise (OV-101), lake bed Runway 17.
1977 September 23 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 6 - . Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Fullerton, Haise. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fullerton, Haise. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Third free flight , ALT, tail cone on, Edwards (5 minutes, 34 seconds), Enterprise (OV-101), lake bed Runway 15.
1977 September 30 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- SRB Hydroburst test - . Nation: USA. A flight-representative shuttle Solid Rocket Booster was subjected to water pressure until the casing burst..
1977 September 30 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Contract to integrate payloads into the space shuttle. - . Martin Marietta was awarded a contract to develop plans, procedures, analytical tools and models, and general expertise that would be required to integrate payloads into the space shuttle..
1977 Oct - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Large USAF structure to be carried into orbit aboard the shuttle. - . Competitive contracts were awarded to the Denver Division of Martin Marietta and the Convair Division of General Dynamics to design a large structure to be carried into orbit aboard the shuttle..
1977 October 7 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Rocket nozzle for the IUS tested - . A rocket nozzle for the IUS was subjected to a 145 second test firing at the Rocket Propulsion Laboratory. The test was successful..
1977 October 12 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 7 - . Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Engle, Truly. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Engle, Truly. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Fourth free flight, ALT, first tail cone off, Edwards (2 minutes, 34 seconds), Enterprise (OV-101), lake bed Runway 17.
1977 October 26 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Enterprise flight 8 - . Call Sign: Enterprise. Crew: Fullerton, Haise. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fullerton, Haise. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Fifth free flight, ALT, final tail cone off, Edwards (2 minutes, 1 second), Enterprise (OV-101), concrete Runway 04.
1977 October 28 - .
- Lower forward fuselage on dock, Palmdale, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1977 November 4 - .
- Deliver aft fuselage on dock, Palmdale, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1977 November 7 - .
- Start final assembly Columbia. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Start final assembly and closeout system installation, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102).
1977 November 15 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- First ferry flight test, Edwards - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. First ferry flight test, Edwards (3 hours, 21 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 November 16 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Second ferry flight test, Edwards - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Second ferry flight test, Edwards (4 hours, 17 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 November 17 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Third ferry flight test, Edwards - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Third ferry flight test, Edwards (4 hours, 13 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 November 18 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Fourth ferry flight test, Edwards - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Fourth ferry flight test, Edwards (3 hours, 37 minutes), Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 December 9 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Complete approach and landing flight tests - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Complete approach and landing flight tests, including ferry flights, Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 December 12 - .
- Start modification of Enterprise for ground vibe tests - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Start removal for mated vertical ground vibration test modification at Edwards, Enterprise (OV-101).
1977 December 13 - . Launch Vehicle: Shuttle.
- STS Program Office reorganized - . The Deputy for Launch Vehicles reorganized the STS Program Office to support expanding STS programs..
1977 December 14 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SRB Drop test - . Nation: USA. An unloaded shuttle solid rocket motor is dropped from an NB-52 in a test of the parachute recovery system..
1977 December 15 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS program status - . The status of the IUS program was briefed to the Air Force Systems Acquisition Review Council. The Council requested additional information on funding, requirements and costs, and program alternatives.
1977 December 19 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS motor test fired - . A full scale IUS motor was successfully test fired at the Arnold Engineering Development Center..
1978 January 10 - .
- Vertical stabilizer on dock, Palmdale, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 January 18 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- DM-2 Shuttle SRB development static firing - . Nation: USA. The second firing of a shuttle Solid Rocket Booster motor..
1978 February 7 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Space shuttle environmental impact statement - .
The final version of the space shuttle environmental impact statement was released to the Council on Environmental Quality. The statement described how the construction and operation of space shuttle facilities would affect the environment of Vandenberg AFB.
1978 February 10 - .
- Complete final assembly, STA-099, Palmdale - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger.
1978 February 14 - .
- STA-099 on dock, Lockheed facility, Palmdale - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger.
1978 February 17 - .
- Crew module on dock, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 February 24 - .
- Body flap on dock, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 March 3 - .
- Complete modification for mated vibe tests. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Complete modification for mated vertical ground vibration test, Edwards, Enterprise (OV-101).
1978 March 6 - .
- Upper forward fuselage on dock, Palmdale, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 March 10 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards.
- Ferry Enterprise from Edwards to Texas. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry Enterprise (OV-101) atop shuttle carrier aircraft from Edwards to Ellington Air Force Base, Texas (approximately 3 hours, 38 min).
1978 March 12 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Enterprise delivered. - . Nation: USA.
1978 March 13 - .
- Ferry Enterprise from Texas to Huntsville - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry Enterprise (OV-101) atop shuttle carrier aircraft from Ellington AFB to Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala..
1978 March 19 - .
- Aft payload bay doors on dock, Palmdale, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 March 23 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Validation phase of the Inertial Upper Stage completed. - .
SAMSO briefed the Defense Systems Acquisition Review Council (DSARC) on the results of the validation phase of the development of the space shuttle's Inertial Upper Stage. The DSARC recommended that the program be allowed to continue into full scale development.
1978 April 6 - . LV Family: Titan, Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Titan III 34D/IUS not to be used as backup for launch of a Tracking and Data Relay Satellite. - . Spacecraft: TDRS. NASA withdrew its requirement for a Titan III 34D/IUS to be used as backup for a space shuttle launch of a Tracking and Data Relay Satellite in 1980..
1978 April 14 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Contract for space shuttle's Inertial Upper Stage - . A contract for full-scale development of the space shuttle's Inertial Upper Stage was distributed to the Boeing Aerospace Company..
1978 April 21 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Cost growth in the Titan III 34D/IUS development program. - . SAMSO representatives briefed HQ AFSC officials on possible alternatives to deal with the cost growth problem in the Titan III 34D/IUS development program..
1978 April 21 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle MPTA First test - . Nation: USA. For the first time three SSME engines are run on the MPTA test article mated to an external tank - for 2.5 seconds..
1978 April 23 - .
- Columbia ready for power-on. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Complete final assembly and closeout system installation, ready for power-on, Columbia (OV-102).
1978 April 24 - .
- Start precombined systems test, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 April 28 - .
- Forward payload bay doors on dock, Columbia. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Forward payload bay doors on dock, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102).
1978 May - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Space Shuttle Orbiter 101 began vibration tests - . Space Shuttle Orbiter 101 began undergoing vibration tests at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama..
1978 May - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Contract for integration of payloads into the space shuttle's Inertial Upper Stage. - . A contract for integration of payloads into the space shuttle's Inertial Upper Stage was distributed to the Boeing Aerospace Company. The value of the contract was $10.72 million..
1978 May 10 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SRB Drop test - . Nation: USA. An unloaded shuttle solid rocket motor is dropped from an NB-52 in a test of the parachute recovery system..
1978 May 10 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Modifications to the main engine of the space shuttle orbiter - . Modifications to the main engine of the space shuttle orbiters began to be evaluated in a series of test firings..
1978 May 26 - .
- Upper forward fuselage mate, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 May 26 - .
- Complete forward RCS structure, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 May 26 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- New carbon-carbon nozzle for Inertial Upper Stage. - . A carbon-carbon nozzle, manufactured for the space shuttle's Inertial Upper Stage propulsion system by a new low-cost process, underwent a test firing at the Air Force Rocket Propulsion Laboratory..
1978 May 30 - .
- Start Enterprise (OV-101)/ ET mated vibe test - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Start Enterprise (OV-101)/ ET mated vertical ground vibration test, MSFC.
1978 Jun - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Ground support system for the space shuttle at Vandenberg AFB. - . Martin Marietta was awarded a follow-on contract to perform systems integration during the acquisition of the ground support system for the space shuttle at Vandenberg AFB..
1978 June 6 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral, Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Radio guidance for Titan 34D. - .
SAMSO was authorized by the Office of the Secretary of the Air Force to develop a radio guidance system for Titan III34Ds launched from Vandenberg instead of the IUS inertial guidance system. This program change would reduce development costs for the Titan III34D program.
1978 July 7 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle MPTA long duration test - . Nation: USA. The engine assembly is run for several minutes, and engine restart is demonstrated..
1978 July 7 - .
- Complete mate payload bay doors, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Complete mate forward and aft payload bay doors, Columbia (OV-102).
1978 July 13 - .
- Reconfigure from boost to launch, vibe test - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Reconfigure from boost to launch, mated vertical ground vibration test, MSFC, Enterprise (OV-101).
1978 July 18 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Test failure of space shuttle main engine - . Testing of modifications to the main engine of the space shuttle orbiters was suspended when a high pressure oxygen pump failed..
1978 July 26 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SRB Drop test - . Nation: USA. An unloaded shuttle solid rocket motor is dropped from an NB-52 in a test of the parachute recovery system..
1978 Aug - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Shuttle computer equipment installation begun at Vandenberg AFB. - . Installation of the Vandenberg Launch Processing System began at Vandenberg AFB. The system was made up of data processing equipment that would be used in conducting launch operations for the shuttle..
1978 August 11 - .
- Complete forward RCS, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 August 12 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Testing of the main engine of the space shuttle orbiters .. resumed. - . Testing of the main engine of the space shuttle orbiters was resumed after a failure of the high pressure oxygen pump was determined to have been caused by test instrumentation..
1978 September 12 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SRB Drop test - . Nation: USA. An unloaded shuttle solid rocket motor is dropped from an NB-52 in a test of the parachute recovery system..
1978 September 15 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle tests at NASA Huntsville - .
Nation: USA.
The shuttle Enterprise is first mated to an external tank for vertical ground vibration tests and simulated high-altitude aborts. Thereafter two SRB's are mounted for the first full-size shuttle static tests. This initial test series is completed on 5 December 1978.
1978 September 25 - .
- Start precombined system test, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 Oct - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Johnson Space Center to support DoD shuttle operations. - . HQ USAF directed the implementation of the so-called controlled mode at the Johnson Space Center. This was a special method of operation that would allow the Center to support DoD shuttle operations..
1978 October 11 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Shuttle Structural Test began structural bending tests. - . Space Shuttle Orbiter 99, the Structural Test Article, began undergoing structural bending tests..
1978 October 19 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Test of the Kevlar case for the large Inertial Upper Stage motor. - . A test was conducted on the Kevlar case used to hold propellant in the space shuttle's large Inertial Upper Stage motor. The case burst at a pressure lower than the predicted pressure..
1978 October 19 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- DM-3 Shuttle SRB development static firing - . Nation: USA. The third firing of a shuttle Solid Rocket Booster motor..
1978 Dec - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Space shuttle to include additional strap-on solid rocket motors. - . NASA decided to augment the thrust of the space shuttle orbiter by attaching a single strap-on solid rocket motor to each of the orbiter's two solid rocket boosters..
1978 December 15 - .
- Complete precombined system test, Columbia. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1978 December 27 - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Failure of the main engine of the space shuttle orbiter. - .
Testing of the main engine of the space shuttle orbiters was suspended when the engine failed, apparently because of a malfunctioning of its main oxidizer valve. This and previous test failures caused the scheduling of the first orbiter test flight to slip from March 1979 to the end of CY 1979 or the beginning of CY 1980.
1979 January 19 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- The Army Corps of Engineers awarded a $3.8 million contract to Morrison-Knudsen, Inc. - . It was for site preparation at the space shuttle launch facility, Vandenberg AFB. Site preparation was the first phase of a three-phase construction effort at the launch facility. Ground-breaking took place on 24 January..
1979 February 3 - .
- Complete combined systems test, Palmdale, Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1979 February 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- DM-4 Shuttle SRB development static firing - . Nation: USA. The fourth firing of a shuttle Solid Rocket Booster motor..
1979 February 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle, Titan 34D.
- A Critical Design Review was held for the Inertial Upper Stage. - .
SAMSO felt that the design presented at this Review was not really complete, and it directed the contractor, Boeing, to do further work in the areas of software, rocket motors, and interface with the space shuttle and the Satellite Control Facility. Boeing was to present the results of its efforts at a follow-on design review to be held later in the year.
1979 February 14 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Space shuttle launch facilities at Vandenberg AFB delayed. - .
HQ USAF stretched out the schedule for construction of space shuttle launch facilities at Vandenberg AFB, and it changed the Initial Operational Capability date for those facilities from mid-1983. The extra time was needed because NASA was adding strap-on solid rocket motors to the shuttle to augment its performance, and the launch facilities had to be modified to accommodate those motors.
1979 February 16 - .
- Airlock on dock, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1979 February 26 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Final shuttle tests at NASA Huntsville - . Nation: USA. These verified loadings on the full mated shuttle stack with the external tank and solid rocket motors loaded with water to simulate the weights at various flight phases. 36 x 670 N and 20 x 4400 N exciters were used to vibrate the vehicle..
1979 February 26 - .
- Complete mated vertical ground vibe test program - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Complete mated vertical ground vibration test program at MSFC, Enterprise (OV-101).
1979 March 5 - .
- Complete postcheckout, Palmdale, Columbia (OV-102) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia.
1979 March 6 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Improved IUS performance - . A change order was added to the IUS contract, directing the contractor to take various steps to improve the performance of the vehicle.
1979 March 8 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards.
- Columbia (OV-102) transported overland to Edwards. - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Columbia (OV-102) transported overland from Palmdale to Edwards (38 miles).
1979 March 9 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle carrier aircraft/Columbia test flight - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Shuttle carrier aircraft/Columbia (OV-102) test flight at NASA Edwards.
1979 March 16 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle, Titan 34D.
- Large rocket motor for the Inertial Upper Stage was fired - .
The large rocket motor for the Inertial Upper Stage was test fired at the Arnold Engineering Development Center. The firing lasted 145 seconds and generated more than 50,000 pounds of thrust. This was the first development test firing of the large motor, and it was entirely successful.
1979 March 20 - .
- Ferry flight, Edwards to El Paso - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Columbia (OV-102) from Edwards to Biggs Army Air Base, El Paso, Texas (3 hours, 20 minutes).
1979 March 22 - .
- Ferry flight El Paso to Kelly AFB - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Columbia (OV-102) from Biggs Army Air Base to Kelly AFB, San Antonio, Texas (1 hr, 39 min).
1979 March 23 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. LV Family: Shuttle.
- Shuttle orbiter 102 flown from Edwards to Cape Canaveral,. - . NASA brought space shuttle orbiter 102 from Edwards AFB, California, to Cape Canaveral, Florida. Orbiter 102 would be the first orbiter to go into space, and Cape Canaveral would be the launch site..
1979 March 23 - .
- Ferry flight, Kelly AFB to Eglin AFB, Fla - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Columbia (OV-102) from Kelly AFB to Eglin AFB, Fla. (2 hours, 12 minutes).
1979 March 24 - .
- Ferry flight, Eglin AFB to KSC - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Columbia (OV-102) from Eglin AFB to KSC (1 hour, 33 minutes).
1979 April 10 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Enterprise delivered to Kennedy Space Centre - .
Nation: USA.
The decision was taken not to convert the Enterprise to a flight orbiter due to the numerous structural design changes made since its construction. Static test article OV-099 would be used for that instead. So Enterprise became a pathfinder vehicle at Cape Canaveral to verify fit and handling of ground facilities in the Vertical Assembly Building and LC39.
1979 April 10 - .
- Ferry flight, MSFC to KSC - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101) from MSFC to KSC (1 hour, 52 minutes).
1979 April 18 - .
- Complete left-hand OMS/RCS Phase I qualification - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Complete left-hand OMS/RCS Phase I qualification, WSTF May 1 Enterprise (OV-101)/ ET/SRBs mated on mobile launcher platform,.
1979 May 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- First shuttle roll-out - . Nation: USA. Non-flight shuttle Enterprise, mated to External Tank number 2, and two inert solid rocket motors, is rolled out to LC39A for facility checks..
1979 May 10 - .
- Deliver right-hand OMS/RCS for Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Deliver right-hand OMS/RCS from McDonnell Douglas, St. Louis, to KSC, Columbia (OV-102).
1979 May 15 - .
- Deliver left-hand OMS/RCS for Columbia - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Deliver left-hand OMS/RCS from McDonnell Douglas to KSC, Columbia (OV-102).
1979 Jun - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- USAF space shuttle mission controllers. - . SAMSO Det 2 was established at NASA's Johnson Space Center to train AF officers to become space shuttle mission controllers..
1979 June 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- QM-1 Shuttle SRB qualification static firing - . Nation: USA. The fifth firing of a shuttle Solid Rocket Booster motor..
1979 June 21 - .
- Start assembly crew module, Challenger (OV-099) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger.
1979 June 25 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle, Titan 34D.
- First test firing of the small motor for the Inertial Upper Stage . - . The small rocket motor for the Inertial Upper Stage was test fired at the Arnold Engineering Development Center. This was the first development test firing of the small motor..
1979 July 2 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Major Shuttle SSME failure - . Nation: USA. Engine 2002 explodes violently during a test run due to a hydrogen leak. The MPTA test article sustains major structural damage due to overpressure of the heat shield support..
1979 July 12 - . Launch Vehicle: Shuttle.
- Consolidated Space Operations Center (CSOC). - .
A special working group with HQ USAF finished a concept of operations for the Consolidated Space Operations Center (CSOC). CSOC would serve both the space shuttle program and the Air Force Satellite Control Facility, functioning as a Shuttle Operations and Planning Center and a Satellite Operations Center.
1979 July 23 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A.
- First test STS stack move from VAB to LC39A - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Enterprise (OV-101), ET, SRBs transported on mobile launcher platform from Launch Complex 39-A to Vehicle Assembly Building at KSC.
1979 August 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Start long-lead fabrication crew module, Discovery - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery.
1979 August 6 - .
- Complete limit test (STA-099) - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Complete limit test (STA-099), Lockheed facility, Palmdale.
1979 August 10 - .
- Ferry flight, KSC to Atlanta - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101), KSC to Atlanta (1 hour, 55 minutes).
1979 August 11 - .
- Ferry flight, Atlanta to St. Louis - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101), Atlanta to St. Louis (1 hour, 50 minutes).
1979 August 12 - .
- Ferry flight, St. Louis to Tulsa - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101), St. Louis to Tulsa (1 hour, 35 minutes).
1979 August 13 - .
- Ferry flight, Tulsa to Denver - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101), Tulsa to Denver (2 hours).
1979 August 14 - .
- Ferry flight, Denver to Hill AFB, Ogden, Utah - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101), Denver to Hill AFB, Ogden, Utah (1 hour, 30 minutes).
1979 August 15 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg.
- Ferry flight, Ogden to Vandenberg AFB - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101), Ogden to Vandenberg AFB (2 hours, 20 minutes).
1979 August 16 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards.
- Ferry flight, Vandenberg AFB to Edwards - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Ferry flight, shuttle carrier aircraft/Enterprise (OV-101), Vandenberg AFB to Edwards (1 hour, 10 minutes).
1979 August 23 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards.
- Enterprise / shuttle carrier demate, Edwards - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. Enterprise (OV-101)/ shuttle carrier demate, Edwards.
1979 August 27 - .
- Start long-lead fabrication crew module, Discovery - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery.
1979 Sep - . LV Family: Shuttle.
- Teal Ruby to be flown on the space shuttle in November 1982. - . Under Secretary of Defense William J. Perry decided that Teal Ruby would be built and flown on the space shuttle in November 1982. His decision was made in response to earlier suggestions within DOD that the program be cancelled because of cost overruns..
1979 Late - .
- STS-2A (cancelled) - .
Crew: Haise,
Lousma.
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Haise,
Lousma.
Program: STS.
Flight: STS-2A.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
In late 1977 shuttle orbital missions were due to start in 1979. STS-2, the second shuttle flight, was to have rendezvoused with the Skylab space station and released a small Skylab Reboost Module. This would dock to Skylab and boost the station to a higher orbit for later use. But the shuttle program also was hit with delays and before the first shuttle flew, Skylab burned up in the atmosphere and crashed into the Australian outback on July 11, 1979.
1979 September 4 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle SSME Failure - . Nation: USA. In a test run, a liquid oxygen turbopump fails 9.7 seconds into the burn..
1979 September 27 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- QM-2 Shuttle SRB qualification static firing - . Nation: USA. The sixth firing of a shuttle Solid Rocket Booster motor..
1979 December 17 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- First Shuttle SSME full-duration test - .
Nation: USA.
The first completely successful firing of the orbiter's engines is completed Three engines are run from 100% to 70% thrust for 514 seconds. Engines 2004, 2005, 2006, and 2007 were to have been certified ready for flight in the first half on 1979. This involved each engine being given a 1.5 second start verification firing; a 100 second calibration firing; and a 520 second flight demonstration test. But continued failures resulted in multiple rebuilds of each engine to add required modifications. The result was a two-year delay to this schedule.
During 1980 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle TPS Tests - . Nation: USA. Shuttle thermal protection system tiles are tested mounted of F-15 and F-104 aircraft at speeds of up to Mach 1.4 and dynamic pressures of 470 N / sq m..
1980 February 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- QM-3 Shuttle SRB qualification static firing - . Nation: USA. The seventh and final firing of a shuttle Solid Rocket Booster motor prior to the first launch. None of the ground tests subjected the motors to expected flight loads..
1980 April 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle ejection seat tests - . Nation: USA. Another series of tests of the shuttle ejection seat are held at Holloman AFB in support of the first shuttle orbital flights..
1980 September 19 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- SRB Hydroburst test - . Nation: USA. A production-representative shuttle Solid Rocket Booster was subjected to water pressure until the casing burst..
1981 January 17 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle MPTA-098 625-second firing. - . Nation: USA. This firing used the three flight engines, which had been removed from Columbia..
1981 February 20 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle flight readiness firing - . Nation: USA. The 20 second test on the pad at Cape Canaveral finally cleared the engines for the first shuttle launch..
1981 April 12 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-1 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Crippen, Young. Payload: Columbia F01 / DFI. Mass: 4,909 kg (10,822 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Crippen, Young. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-1. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 2.26 days. Decay Date: 1981-04-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 12399 . COSPAR: 1981-034A. Apogee: 251 km (155 mi). Perigee: 240 km (140 mi). Inclination: 40.30 deg. Period: 89.40 min. First flight of Space Transportation System (aka Space Shuttle).. Payloads: Development Flight Instrumentation and Aerodynamic Coefficient Identification Package..
- DFI - . Payload: DFI PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: DFI. Decay Date: 1981-04-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 12399 . COSPAR: 1981-034xx. Apogee: 272 km (169 mi). Perigee: 260 km (160 mi). Inclination: 40.30 deg. Period: 89.80 min.
1981 November 12 - . 15:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-2 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Engle, Truly. Payload: Columbia F02 / DFI. Mass: 8,517 kg (18,776 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Engle, Truly. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-2. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 2.26 days. Decay Date: 1981-11-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 12953 . COSPAR: 1981-111A. Apogee: 231 km (143 mi). Perigee: 222 km (137 mi). Inclination: 38.00 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Second shuttle test flight. Payloads: Office of Space and Terrestrial Applications (OSTA)-1 experiments, Orbiter Experiments (OEX)..
- DFI - . Payload: DFI PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: DFI. Decay Date: 1981-11-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 12953 . COSPAR: 1981-111xx. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 255 km (158 mi). Inclination: 38.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
- OSTA-1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1981-11-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 12953 . COSPAR: 1981-111xx. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 255 km (158 mi). Inclination: 38.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
1982 March 22 - . 16:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-3 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Fullerton, Lousma. Payload: Columbia F03 / OSS-1. Mass: 10,301 kg (22,709 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fullerton, Lousma. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-3. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 8.00 days. Decay Date: 1982-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 13106 . COSPAR: 1982-022A. Apogee: 249 km (154 mi). Perigee: 241 km (149 mi). Inclination: 38.00 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Manned two crew. Payloads: Office of Space Science (OSS) experiments, Monodisperse Latex Reactor (MLR), Electro-phoresis Verification Test (EEVT), Plant Lignification Experiment..
- OSS-1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1982-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 13106 . COSPAR: 1982-022xx. Apogee: 245 km (152 mi). Perigee: 220 km (130 mi). Inclination: 38.00 deg. Period: 89.20 min.
- DFI - . Payload: DFI PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: DFI. Decay Date: 1982-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 13106 . COSPAR: 1982-022xx. Apogee: 245 km (152 mi). Perigee: 220 km (130 mi). Inclination: 38.00 deg. Period: 89.20 min.
1982 June 27 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-4 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Hartsfield,
Mattingly.
Payload: Columbia F04 / DoD 82-1. Mass: 11,109 kg (24,491 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Hartsfield,
Mattingly.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 7.05 days. Decay Date: 1982-07-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 13300 . COSPAR: 1982-065A. Apogee: 302 km (187 mi). Perigee: 295 km (183 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.30 min.
Manned two crew. Fourth space shuttle test flight. Payloads: Induced Environment Contamination Monitor (IECM), Monodisperse Latex Reactor (MLR), Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES), Development Flight Instrumentation (DFl), Orbiter Experiments (OEX), first NASA getaway special (GAS), Night/Day Optical Survey of Lightning (NOSL) experiment, Vapor Phase Compression (VPC) freezer heat exchanger dynamics for freezing samples, Aerodynamic Coefficient Identification Package (AClP) experiment.
- DFI - . Payload: DFI PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: DFI. Decay Date: 1982-07-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 13300 . COSPAR: 1982-065xx. Apogee: 319 km (198 mi). Perigee: 306 km (190 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
- DoD 82-1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: DoD 82-1. Decay Date: 1982-07-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 13300 . COSPAR: 1982-065xx. Apogee: 319 km (198 mi). Perigee: 306 km (190 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.80 min. Cirris cryogenic infrared radiance instrument to obtain spectra of rocket and aircraft target exhausts. Lens cap failed to deploy..
1982 November 11 - . 12:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-5 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Allen,
Brand,
Lenoir,
Overmyer.
Payload: Columbia F05 / SBS 3 [PAM-D] / Anik C3 [PAM-D]. Mass: 14,551 kg (32,079 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Allen,
Brand,
Lenoir,
Overmyer.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 5.09 days. Decay Date: 1982-11-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 13650 . COSPAR: 1982-110A. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 294 km (182 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
Manned four crew. First mission to deploy commercial communications satellites (SBS 3, Anik C3). Payloads: : Satellite Business Systems (SBS)-C with Payload Assist ; (PAM)-D; Telesat-E (Canadian communications satellite) with PAM-D. Monodisperse Latex Reactor (MLR), Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES), three getaway specials (GAS), Student experiments, GLOW experiment, Vestibular experiment, Oxygen Interaction With Materials experiment.
- Anik C3 (Telesat 6) - .
Payload: Anik C3 [PAM-D]. Mass: 632 kg (1,393 lb). Nation: Canada.
Agency: Telesat.
Program: Anik.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1997-06-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 13652 . COSPAR: 1982-110C. Apogee: 35,902 km (22,308 mi). Perigee: 35,871 km (22,289 mi). Inclination: 7.90 deg. Period: 1,441.20 min.
Deployed from STS-5 11 November 1982. Telecommunications, operated by Telesat Canada. Transmit power 11.2 W per frequency at input of transmit antenna (typical saturated carrier). Anik C-3 Transmit frequency (MHz): 11730, 11743, 11791, 11804, 11852 , 11865, 11913, 11926, 11974, 11987, 12035, 12048, 12096, 12109 , 12157, 12170. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 117.5 deg W in 1982-1989; 115 deg W in 1989-1997 As of 5 September 2001 located at 15.95 deg E drifting at 1.305 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 114.85W drifting at 1.353W degrees per day.
- SBS 3 - .
Payload: SBS 3 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,117 kg (2,462 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SBS.
Program: SBS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 13651 . COSPAR: 1982-110B. Apogee: 35,910 km (22,310 mi). Perigee: 35,855 km (22,279 mi). Inclination: 7.80 deg. Period: 1,441.00 min.
Deployed from STS-5 11 November 1982. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 94 deg W in 1982-1983; 95 deg W in 1983-1993; 74 deg W in 1994-1995 As of 4 September 2001 located at 41.59 deg E drifting at 1.235 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 117.46E drifting at 1.221W degrees per day. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
- DFI - . Payload: DFI PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: DFI. Decay Date: 1982-11-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 13650 . COSPAR: 1982-110xx. Apogee: 287 km (178 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
1983 April 4 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-6 - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Bobko,
Musgrave,
Peterson,
Weitz.
Payload: Challenger F01 / TDRS 1 [IUS]. Mass: 21,305 kg (46,969 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bobko,
Musgrave,
Peterson,
Weitz.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 5.02 days. Decay Date: 1983-04-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 13968 . COSPAR: 1983-026A. Apogee: 295 km (183 mi). Perigee: 288 km (178 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
Manned four crew. First flight of space shuttle Challenger; deployed TDRSS. Payloads: Deployment of Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS)-A with Inertial Upper Stage (lUS)-2, Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES), Monodisperse Latex Reactor (MLR), Night/Day Optical Survey of Lightning (NOSL) experiment, three getaway specials (GAS).
- TDRS 1 - .
Payload: TDRS A. Mass: 2,268 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: TDRS.
USAF Sat Cat: 13969 . COSPAR: 1983-026B. Apogee: 35,976 km (22,354 mi). Perigee: 35,835 km (22,266 mi). Inclination: 7.40 deg. Period: 1,442.20 min.
Element of satellite communications network, deployed from STS-6 5 April 1983. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 67 deg W in 1983; 41 deg W in 1983-1989; 79 deg W in 1989-1990; 170 deg W in 1990-1993; 85 deg E in 1994-1995; 49 deg W in 1996-on. As of 5 September 2001 located at 49.36 deg W drifting at 0.010 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 48.98W drifting at 0.029W degrees per day.
1983 April 8 - . 21:05 GMT - .
- EVA STS-6-1 - . Crew: Musgrave, Peterson. EVA Duration: 0.17 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Musgrave, Peterson. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-6. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Tested EMU Manoeuvring Unit. Tested EVA emergency procedures..
1983 June 18 - . 11:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-7 - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Crippen,
Fabian,
Hauck,
Ride,
Thagard.
Payload: Challenger F02 / OSTA-2. Mass: 16,839 kg (37,123 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Crippen,
Fabian,
Hauck,
Ride,
Thagard.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-7.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 6.10 days. Decay Date: 1983-06-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 14132 . COSPAR: 1983-059A. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 299 km (185 mi). Inclination: 28.30 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed Anik C2, Palapa B1; deployed and retrieved SPAS platform. Payloads: Office of Space and Terrestrial Applications (OSTA)-2 experiments, deployment of PALAPA-B1 communications satellite for Indonesia with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D and Telesat-F communications satellite for Canada with PAM-D, German Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS)-01, seven getaway specials (GAS), Monodisperse Latex Reactor (MLR), Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES).
- Anik C2 (Telesat 7) - .
Payload: Anik C2 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,238 kg (2,729 lb). Nation: Canada.
Agency: Telesat.
Program: Anik.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-01-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 14133 . COSPAR: 1983-059B. Apogee: 36,273 km (22,538 mi). Perigee: 35,949 km (22,337 mi). Inclination: 7.80 deg. Period: 1,452.70 min.
Deployed by STS-7 6/19/83. Telecommunications. Operating entity TELESAT Canada. Longitude 110 W. Transmit power 11.2 W on each frequency. Frequencies 11730, 11743, 11791, 11804, 11852, 11865, 11913, 11926, 11974, 11987, 12035, 12048, 12096, 12109, 12157, 12170 MHz. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 112 deg W in 1983; 105 deg W in 1983-1985; 110 deg W in 1985-1991; 109 deg W in 1991-1993;76 deg W in 1993-1997; 115 deg W in 1997-1998 As of 4 September 2001 located at 113.76 deg E drifting at 4.144 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 68.60E drifting at 4.154W degrees per day.
- OSTA-2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1983-06-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 14132 . COSPAR: 1983-059xx. Apogee: 295 km (183 mi). Perigee: 289 km (179 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
- Palapa B1 - .
Payload: Palapa B1 [PAM-D. Mass: 1,200 kg (2,600 lb). Nation: Indonesia.
Agency: Perumtel.
Program: Palapa.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-10-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 14134 . COSPAR: 1983-059C. Apogee: 35,840 km (22,260 mi). Perigee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Inclination: 8.60 deg. Period: 1,437.90 min.
Deployed by STS-7 6/18/83. Palapa B satellites were four times as powerful and twice the size of their predecessors, the Palapa A series. While the A series was designed for domestic/regional communications within Indonesia, the new system also served the Philippines, Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore. Palapa B2 was originally placed into a useless orbit due to malfunctions of its PAM-D upper stage. The Indonesian government claimed $75 million insurance and ordered a replacement (B2P), which was successfully orbited 3 years later. The original B2 was recovered by the STS-51A mission on November 12, 1984 under an arrangement between the satellite's insurers, NASA and Hughes. The satellite was then sold by the insurers to an intermediary company, refurbished, and then resold back to Indonesia following its launch in 1990. Spacecraft: Based on Hughes HS-376 design. Cylindrical structure. Spin stabilised. Hydrazine propulsion system for attitude control, orbit maintenance. Body mounted solar cells provide 1060 W BOL. Despun antenna platform. Payload: Each carried 24 C-band transponders (+6 spares). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 108 deg E in 1983-1990; 118 deg E in 1990-1992; 134 deg E in 1992-1995 As of 1 September 2001 located at 156.84 deg E drifting at 0.192 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 169.93W drifting at 0.283W degrees per day.
- SPAS-01 - .
Payload: Challenger F2 / SPAS 1. Mass: 3,230 kg (7,120 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: MBB.
Class: Military.
Type: Strategic defense satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads.
Spacecraft: SPAS.
Decay Date: 1983-06-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 14142 . COSPAR: 1983-059F. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi). Perigee: 295 km (183 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
Ten experiments mounted on Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS-01) performed research in forming metal alloys in microgravity and use of remote sensing scanner. Orbiter's small control rockets fired while SPAS-01 held by remote manipulator system to test movement on extended arm.
1983 August 30 - . 06:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-8 - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Bluford,
Brandenstein,
Gardner,
Thornton, Bill,
Truly.
Payload: Challenger F03 / PFTA. Mass: 13,642 kg (30,075 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bluford,
Brandenstein,
Gardner,
Thornton, Bill,
Truly.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-8.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 6.05 days. Decay Date: 1983-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 14312 . COSPAR: 1983-089A. Apogee: 313 km (194 mi). Perigee: 306 km (190 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.70 min.
First night launch and night landing. Deployed Insat 1B. Payloads: Deployment of INSAT (lndia communica-tion satellite) with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D, Payload Flight Test Article (PFTA)/ Payload Deployment Retrieval System (PDRS), Continuous Flow Electrophoresis (CFES), biomedical experiments. 250,000 express mail envelopes with special cachet for U.S. Postal Service were carried for a first-day cover.
- DFI/USPS - . Payload: DFI PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: DFI. Decay Date: 1983-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 14312 . COSPAR: 1983-089xx. Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 216 km (134 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
- PFTA - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: PFTA. Decay Date: 1983-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 14312 . COSPAR: 1983-089xx. Apogee: 223 km (138 mi). Perigee: 216 km (134 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
- Insat 1B - .
Mass: 1,152 kg (2,539 lb). Nation: India.
Agency: ISRO.
Program: Insat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Insat 1.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-08-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 14318 . COSPAR: 1983-089B. Apogee: 35,824 km (22,259 mi). Perigee: 35,811 km (22,251 mi). Inclination: 3.60 deg. Period: 1,437.70 min.
Released from STS 8 8/31/83; also carried transponders for domestic communications. Operational multipurpose satellite for telecommunications, meteorological imaging and data relay, radio and television programme distribution and direct television broadcasting for community reception. Geostationary longitude 74.0 +/ - 0.1 deg E. Deployment from US Space Transportation System flight no 8, orbiter Challenger, on 31 Aug 1983. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 74 deg E in 1983-1992; 93 deg E in 1992-1993 As of 26 August 2001 located at 125.27 deg E drifting at 0.152 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 80.35E drifting at 0.392E degrees per day.
1983 November 28 - . 16:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-9 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Garriott,
Lichtenberg,
Merbold,
Parker,
Shaw,
Young.
Payload: Columbia F06 / Spacelab 1 Pallet. Mass: 15,088 kg (33,263 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Garriott,
Lichtenberg,
Merbold,
Parker,
Shaw,
Young.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-9.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 10.32 days. Decay Date: 1983-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 14523 . COSPAR: 1983-116A. Apogee: 254 km (157 mi). Perigee: 241 km (149 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.50 min.
Carried ESA Spacelab. Payloads: Payload: Spacelab-1 experiments, habitable Spacelab and pallet, carried 71 experiments. The six-man crew was divided into two 12-hour-day red and blue teams to operate experiments. First high-inclination orbit of 57 degrees.
- Spacelab 1 Pallet - . Payload: SL 1 PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1983-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 14523 . COSPAR: 1983-116xx. Apogee: 239 km (148 mi). Perigee: 231 km (143 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.20 min.
- Spacelab 1 - . Payload: SL 1 LM. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1983-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 14523 . COSPAR: 1983-116xx. Apogee: 239 km (148 mi). Perigee: 231 km (143 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.20 min.
1984-1986 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Columbia overhauled at Palmdale. - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
The ejection seats and flight instrumentation used for the first manned shuttle flights were removed. Head-up display and GPS avionics were installed. Orbiter 5.4 structural modifications were made; the disconnect valves, thermal protection system, and brakes were brought up to date. Provisions were made for use of the Manned Maneuvering Unit and 231 Master Change Requests were implemented.
1984 February 3 - . 13:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-41-B - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Brand,
Gibson,
McCandless,
McNair,
Stewart.
Payload: Challenger F04 / SPAS 1A. Mass: 15,362 kg (33,867 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brand,
Gibson,
McCandless,
McNair,
Stewart.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41-B.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 7.97 days. Decay Date: 1984-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 14681 . COSPAR: 1984-011A. Apogee: 316 km (196 mi). Perigee: 307 km (190 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed Westar 6, Palapa B2; tested Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU). Payloads: PALAPA-B2 (Indonesian communications satellite) with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D and WESTAR (Western Union communications satellite)-Vl with PAM-D. Both satellites were deployed but the PAM-D in each satellite failed to ignite, leaving both satellites in earth orbit. Both satellites were retrieved and returned to earth for renovation on the STS-51-A mission. The manned maneuvering unit (MMU) was tested with extravehicular astronauts as free flyers without tethers as far as 98 m from the orbiter. Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS)-01 experiments, Monodisperse Latex Reactor (MLR), Isoelectric Focusing Experiment (lEF), Acoustic Containerless Experiment System (ACES), Cinema 360 cameras, five getaway specials (GAS), Aerodynamic Coefficient Identification (ACIP)/High Resolution Accelerom-eter Package (HIRAP).
- Palapa B2 - . Payload: Palapa B2 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,200 kg (2,600 lb). Nation: Indonesia. Agency: Perumtel. Program: Palapa. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376. Decay Date: 1984-11-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 14692 . COSPAR: 1984-011D. Apogee: 1,190 km (730 mi). Perigee: 280 km (170 mi). Inclination: 28.20 deg. Period: 99.50 min. Deployed from STS 41B 4 February 1984; failed to reach proper orbit; recovered by STS-51A..
- SPAS 1A - . Mass: 3,230 kg (7,120 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Military. Type: Strategic defense satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SPAS. Decay Date: 1984-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 14681 . COSPAR: 1984-011xx. Apogee: 294 km (182 mi). Perigee: 270 km (160 mi). Inclination: 28.60 deg. Period: 90.20 min. German-built Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS), first flown on STS-7, became first satellite refurbished and flown again. SPAS remained in payload bay due to electrical problem with Remote Manipulator System (RMS)..
- MMU 2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: Shuttle MMU. COSPAR: 1984-011xx.
- MMU 3 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: Shuttle MMU. COSPAR: 1984-011xx.
- Westar 6 - .
Payload: Westar 6 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,200 kg (2,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: WUTC.
Program: Westar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Decay Date: 1984-11-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 14688 . COSPAR: 1984-011B. Apogee: 1,220 km (750 mi). Perigee: 307 km (190 mi). Inclination: 27.70 deg. Period: 100.10 min.
Deployed from STS 41B 4 February 1984; failed to reach proper orbit; recovered by STS-51A. The Westar series of geostationary spacecraft provide commercial communications services for Western Union. Westar 6 failed to achieve geosynchronous orbit after being deployed from the Space Shuttle. It was later retrieved by another Shuttle mission (November 14, 1984) and returned for refurbishment and relaunch. All Westars have been launched by NASA on a reimbursable basis. Spacecraft: Westar uses the Hughes HS-376 spacecraft design. Spin stabilised with a despun antenna section. Body mounted solar cells. Once on orbit, an outer cylinder deploys downward in 'dixie-cup' fashion to increase the solar panel area. Payload: Westar spacecraft typically carried 12 to 24 transponders in the 4-6 GHz range. A single antenna reflector (72 inch diameter) is used with an array of offset feed horns. The reflector uses two polarisation-selective surfaces for horizontal and vertical polarised signals.
- IRT - . Payload: Challenger F4 / Westar 6 [PAM-D] / Palapa B2 [PAM-. Mass: 91 kg (200 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: IRT. Decay Date: 1984-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 14689 . COSPAR: 1984-011C. Apogee: 288 km (178 mi). Perigee: 279 km (173 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.20 min. Deployed from STS 41B on 5 February 1984; Integrated Rendezvous Target..
1984 February 7 - .
- EVA STS-10-1 - . Crew: McCandless, Stewart. EVA Duration: 0.23 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: McCandless, Stewart. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-10. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Tested MMU manoeuvring unit in free flight..
1984 February 9 - .
- EVA STS-10-2 - . Crew: McCandless, Stewart. EVA Duration: 0.25 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: McCandless, Stewart. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-10. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Tested MMU manoeuvring unit in free flight..
1984 April 6 - . 13:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-41-C - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Crippen,
Hart,
Nelson,
Scobee,
van Hoften.
Payload: Challenger F05 / LDEF 1 / MMU 3. Mass: 17,357 kg (38,265 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Crippen,
Hart,
Nelson,
Scobee,
van Hoften.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41-C.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 6.99 days. Decay Date: 1984-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 14897 . COSPAR: 1984-034A. Apogee: 468 km (290 mi). Perigee: 222 km (137 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Manned five crew. First repair on orbit of a satellite, Solar Maximum Mission, by James van Hoften and George Nelson. Deployed LDEF. Payloads:Solar Maximum Mission (SMM) repair, manned maneuvering unit (MMU) satellite support, deployment of Long-Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) in earth orbit free drift. LDEF contained 57 experiments and weighed about 10,000 kg. Cinema 360 and IMAX 70-mm cameras.
- MMU 2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: Shuttle MMU. Decay Date: 1984-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 14897 . COSPAR: 1984-034xx. Apogee: 496 km (308 mi). Perigee: 494 km (306 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 94.50 min.
- LDEF - . Payload: Challenger F5 / LDEF 1. Mass: 3,625 kg (7,991 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Langley. Class: Earth. Type: Micrometeoroid satellite. Spacecraft: LDEF. Decay Date: 1990-01-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 14898 . COSPAR: 1984-034B. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 344 km (213 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Long Duration Exposure Facility; deployed from STS 41C 7 April 1984; retrieved by STS-32 20 January 1990. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
- SMRM-FSS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: FSS. Decay Date: 1984-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 14897 . COSPAR: 1984-034xx. Apogee: 496 km (308 mi). Perigee: 494 km (306 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 94.50 min.
- MMU 3 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: Shuttle MMU. Decay Date: 1984-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 14897 . COSPAR: 1984-034xx. Apogee: 496 km (308 mi). Perigee: 494 km (306 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 94.50 min.
1984 April 8 - . 14:18 GMT - .
- EVA STS-41-C-1 - . Crew: Nelson, van Hoften. EVA Duration: 0.12 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Nelson, van Hoften. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41-C. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Attempted capture of Solar Max satellite..
1984 April 11 - . 08:58 GMT - .
- EVA STS-41-C-2 - . Crew: Nelson, van Hoften. EVA Duration: 0.30 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Nelson, van Hoften. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41-C. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Successfully captured and repaired Solar Max satellite..
1984 June 26 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Discovery Pad Abort - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-41-D. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. The countdown for the second launch attempt for Discovery's maiden flight ended at T- 4 seconds when the orbiter's computers detected a sluggish valve in main engine #3. The main engine was replaced and Discovery was finally launched on August 30, 1984..
1984 July - .
- STS-41-E (cancelled) - . Crew: Buchli, Detroye, Mattingly, Onizuka, Shriver. Backup Crew: Sundberg. Support Crew: Watterson. Payload: DoD Mission. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-41-E. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned Department of Defense shuttle mission. Cancelled due to IUS failure..
1984 August - .
- STS-41-F (cancelled) - . Crew: Bobko, Griggs, Hoffman, Seddon, Williams, Donald. Payload: Communications satellites. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Bobko, Griggs, Hoffman, Seddon, Williams, Donald. Program: STS. Flight: STS-41-F. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Planned shuttle mission for deployment of commercial communications satellites. Cancelled due to payload delays..
1984 August 30 - . 12:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-41-D - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Coats,
Hartsfield,
Hawley,
Mullane,
Resnik,
Walker.
Payload: Discovery F01 / SBS 4[PAM-D] / Telstar 302[PAM-D]. Mass: 21,552 kg (47,514 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Coats,
Hartsfield,
Hawley,
Mullane,
Resnik,
Walker.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41-D.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 6.04 days. Decay Date: 1984-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 15234 . COSPAR: 1984-093A. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned six crew. First flight of space shuttle Discovery; deployed SBS 4, Leasat 1, Telstar 3C. Payloads: Satellite Business System (SBS)-D commu-nications satellite with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D deployment, Syncom IV-2 communica-tions satellite with its unique stage deployment, Telstar (American Telephone and Telegraph) 3-C with PAM-D deployment, Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology (OAST)-1 experiments. Deployment and restowing of large solar array. Continuous Flow Electrophoresis (CFES). IMAX camera.
- Telstar 3C - .
Payload: Telstar 302 [PAM-D]. Mass: 625 kg (1,377 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: ATT.
Program: Telstar series.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1997-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 15237 . COSPAR: 1984-093D. Apogee: 35,948 km (22,337 mi). Perigee: 35,901 km (22,307 mi). Inclination: 5.70 deg. Period: 1,443.20 min.
Released from STS 41D 9/1/84; stationed at 125 deg W. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 86 deg W in 1984-1987; 85 deg W in 1987-1997; 97 deg W in 1997 As of 26 August 2001 located at 148.40 deg W drifting at 1.778 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 128.46W drifting at 1.794W degrees per day.
- Syncom IV-2 - .
Payload: Discovery F1 / SBS 4 [PAM-D] / Telstar 302 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,315 kg (2,899 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 381.
Completed Operations Date: 1996-10-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 15236 . COSPAR: 1984-093C. Apogee: 36,741 km (22,829 mi). Perigee: 36,448 km (22,647 mi). Inclination: 13.00 deg. Period: 1,477.60 min.
Released from STS 41D 8/31/84; 105 deg W; leased to U.S. government. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 105 deg W in 1984-1987; 177 deg W in 1987; 72 deg E in 1988-1990; 177 deg W in 1990-1996 As of 1 September 2001 located at 17.02 deg W drifting at 10.139 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 57.99E drifting at 10.147W degrees per day.
- OAST 1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: OAST. Decay Date: 1984-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 15234 . COSPAR: 1984-093xx. Apogee: 297 km (184 mi). Perigee: 294 km (182 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
- SBS 4 - .
Payload: SBS D / PAM-D. Mass: 1,117 kg (2,462 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SBS.
Program: SBS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
USAF Sat Cat: 15235 . COSPAR: 1984-093B. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 6.80 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Released from STS 41D 8/31/84; 101 deg W. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 101 deg W in 1984-1985; 91 deg W in 1985-1993; 77 deg W in 1993-on. As of 1 September 2001 located at 77.06 deg W drifting at 0.019 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 113.88W drifting at 5.445W degrees per day.
1984 October 5 - . 11:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-41-G - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Crippen,
Garneau,
Leestma,
McBride,
Ride,
Scully-Power,
Sullivan.
Payload: Challenger F06 / ERBS / LFC / ORS. Mass: 10,643 kg (23,463 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Crippen,
Garneau,
Leestma,
McBride,
Ride,
Scully-Power,
Sullivan.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41-G.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 8.22 days. Decay Date: 1984-10-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 15353 . COSPAR: 1984-108A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.00 min.
Manned seven crew. Deployed ERBS; performed high resolution Earth imagery. Payloads: Earth Radiation Budget Satellite (ERBS) deployment, Office of Space and Terrestrial Applications (OSTA)-3 experiments, Large Format Camera (LFC). First use of Orbital Refueling System (ORS) with extravehicular activity (EVA) astronauts, IMAX camera.
- LFC/ORS - . Payload: MPESS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: LFC/ORS. Decay Date: 1984-10-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 15353 . COSPAR: 1984-108xx. Apogee: 227 km (141 mi). Perigee: 214 km (132 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Larger Format Camera/ Orbital Refueling System payload carried in shuttle bay..
- OSTA-3 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1984-10-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 15353 . COSPAR: 1984-108xx. Apogee: 227 km (141 mi). Perigee: 214 km (132 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
- ERBS - . Payload: Challenger F6 / ERBS. Mass: 226 kg (498 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: ERBS. USAF Sat Cat: 15354 . COSPAR: 1984-108B. Apogee: 589 km (365 mi). Perigee: 576 km (357 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 96.30 min. Earth Radiation Budget Satellite. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1984 October 11 - .
- EVA STS-41-G-1 - . Crew: Leestma, Sullivan. EVA Duration: 0.15 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Leestma, Sullivan. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41-G. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Simulated refuelling of satellite..
1984 November 8 - . 12:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-A - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Allen,
Fisher,
Gardner,
Hauck,
Walker, Dave.
Payload: Discovery F02 / PLT. Mass: 20,550 kg (45,300 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Allen,
Fisher,
Gardner,
Hauck,
Walker, Dave.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-A.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 7.99 days. Decay Date: 1984-11-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 15382 . COSPAR: 1984-113A. Apogee: 297 km (184 mi). Perigee: 289 km (179 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
Manned five crew. First retrieval of two satellites (PALAPA B-2 and WESTAR Vl) for return to earth. Deployed Anik D2, Leasat 2; recovered Westar 6, Palapa B2. Payloads: Telesat (Canada communications satellite)-H with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D deploy-ment, Syncom IV-1 communications satellite deployment with its unique stage, retrieval of PALAPA B-2 and WESTAR VI communications satellites with PAM-D which failed to ignite on the STS-41-B mission. Manned maneuvering unit (MMU) used for retrieval. Diffusive Mixing of Organic Solutions (DMOS) experiment.
- Syncom IV-1 - .
Payload: Discovery F2 / Anik D2 / Syncom-4 1. Mass: 1,315 kg (2,899 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 381.
Completed Operations Date: 1992-09-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 15384 . COSPAR: 1984-113C. Apogee: 36,403 km (22,619 mi). Perigee: 36,152 km (22,463 mi). Inclination: 7.60 deg. Period: 1,461.20 min.
Released from STS 51A 10 November 1984; 105 deg W; leased to U.S. government. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 15 deg W in 1984-1992 As of 3 September 2001 located at 170.37 deg W drifting at 6.220 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 100.08W drifting at 6.233W degrees per day.
- Anik D2 - .
Payload: Anik D2 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,100 kg (2,400 lb). Nation: Canada.
Agency: Telesat.
Program: Anik.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-02-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 15383 . COSPAR: 1984-113B. Apogee: 36,271 km (22,537 mi). Perigee: 36,076 km (22,416 mi). Inclination: 6.70 deg. Period: 1,455.90 min.
Released 9 November 1984 from STS 51A; 82 deg W. Telecommunications. Longitude 111.5 deg W. Operating entity Telesat Canada. Transmitter power 8.9 watts at each frequency. Frequencies 3720 to 4180 MHz spaced by 20 MHz. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 111 deg W in 1984-1986; 110 deg W in 1986-1991; 82 deg W in 1991-1993; 20 deg E in 1993-1995 As of 28 August 2001 located at 178.69 deg W drifting at 4.912 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 25.98W drifting at 4.913W degrees per day.
1984 November 12 - . 13:25 GMT - .
- EVA STS-51-A-1 - . Crew: Allen, Gardner. EVA Duration: 0.26 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Allen, Gardner. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Retrieved Palapa satellite..
1984 November 14 - .
- EVA STS-51-A-2 - . Crew: Allen, Gardner. EVA Duration: 0.25 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Allen, Gardner. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Retrieved Westar satellite..
1984 November 16 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg.
- The Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise arrives - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Enterprise. The Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise arrived at Vandenberg AFB for a series of facility verification tests..
1985 January 24 - . 19:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-C - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Buchli,
Mattingly,
Onizuka,
Payton,
Shriver.
Payload: Discovery F03 / Magnum 1 [IUS]. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Buchli,
Mattingly,
Onizuka,
Payton,
Shriver.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-C.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 3.06 days. Decay Date: 1985-01-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 15496 . COSPAR: 1985-010A. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 332 km (206 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed USA 8 (Aquacade ELINT spacecraft). Orbits of Earth: 48. Landed at: Runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Landing Speed: 342 kph. Touchdown miss distance: 839.00 m. Landing Rollout: 2,240.00 m. Payloads: Department of Defence classified payloads.
- USA 8 - . Payload: Orion 1. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Magnum. USAF Sat Cat: 15543 . COSPAR: 1985-010B. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min. New Magnum model geostationary ELINT satellite model replaced earlier Rhyolite/Aquacade. Deployed from STS-51C 24 January 1985. Boosted to geostationary orbit. As of 2003 Apr 30 located at 69.16E drifting at 0.038W degrees per day..
1985 March - .
- STS-51-E (cancelled) - . Crew: Baudry, Bobko, Garn, Griggs, Hoffman, Seddon, Williams, Donald. Payload: TDRS/IUS. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Baudry, Bobko, Garn, Griggs, Hoffman, Seddon, Williams, Donald. Program: STS. Flight: STS-51-E. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned TDRS/IUS deployment shuttle mission. Cancelled due to IUS failure..
1985 April - .
- STS-51-AA (cancelled) - . Crew: Creighton, Fabian, Jarvis, Lucid, Nagel, Walker. Backup Crew: Konrad. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-51-AA. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Planned shuttle mission. Cancelled due to payload delays..
1985 April 12 - . 13:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-D - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bobko,
Garn,
Griggs,
Hoffman,
Seddon,
Walker,
Williams, Donald.
Payload: Discovery F04 / Anik C1[PAM-D] / Syncom-4 3 /Orbus. Mass: 16,249 kg (35,822 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bobko,
Garn,
Griggs,
Hoffman,
Seddon,
Walker,
Williams, Donald.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-D.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 7.00 days. Decay Date: 1985-04-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 15641 . COSPAR: 1985-028A. Apogee: 535 km (332 mi). Perigee: 445 km (276 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 94.40 min.
Manned seven crew. Payloads: Telesat (Canada communications satellite)-I with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D deployment, Syncom IV-3 communications satellite deploy-ment with its unique stage (unique stage failed to ignite), Continuous Flow Electrophoresis (CFES), Phase Partitioning Experiment (PPE), student experiments, two getaway specials (GAS) Informal science studies (Toys in Space).
- Syncom IV-3 - .
Payload: Discovery F4 / Anik C1 [PAM-D] / Syncom-4 3 [Orbus. Mass: 1,315 kg (2,899 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 381.
Completed Operations Date: 1996-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 15643 . COSPAR: 1985-028C. Apogee: 37,080 km (23,040 mi). Perigee: 36,401 km (22,618 mi). Inclination: 14.40 deg. Period: 1,485.10 min.
Released by STS 51D 4/13/85; failed to orbit and subsequently repaired by STS 51-I on 8/31/85; 178 deg E; leased by U.S. government. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 175 deg W in 1985-1987; 105 deg W in 1987-1996 As of 31 August 2001 located at 106.85 deg E drifting at 11.920 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 158.41W drifting at 11.917W degrees per day.
- Anik C1 - .
Payload: Anik C1 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,238 kg (2,729 lb). Nation: Canada.
Agency: Telesat.
Program: Anik.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 2000-04-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 15642 . COSPAR: 1985-028B. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Released by STS 51D 4/13/85; 107.5 deg W. Telecommunications. Operating entity TELESAT Canada. Longitude 107.5 W. Transmit power 11.2 W on each frequency. Frequencies 11730, 11743, 11791, 11804, 11852, 11865, 11913, 11926, 11974, 11987, 12035, 12048, 12096, 12109, 12157, 121 70 MHz. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 107 deg W in 1985-1991; 109 deg W in 1991-1993; 72 deg W in 1993-1997; 118 deg W in 1997-1998; 106 deg W in 1998-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 63.20 deg W drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 2 located at 112.29E drifting at 2.201W degrees per day.
1985 April 16 - .
- EVA STS-51-D-1 - . Crew: Griggs, Hoffman. EVA Duration: 0.13 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Griggs, Hoffman. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-D. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. RMS 'Ryswatters' installed..
1985 April 29 - . 16:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-B - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Gregory,
Lind,
Overmyer,
Thagard,
Thornton, Bill,
van den Berg, Lodewijk,
Wang.
Payload: Challenger F07 / SL 3 MPESS. Mass: 14,245 kg (31,404 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gregory,
Lind,
Overmyer,
Thagard,
Thornton, Bill,
van den Berg, Lodewijk,
Wang.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-B.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 7.01 days. Decay Date: 1985-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15665 . COSPAR: 1985-034A. Apogee: 353 km (219 mi). Perigee: 346 km (214 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
Manned seven crew. Deployed Nusat; carried Spacelab 3. Payloads: Spacelab-3 experiments, habitable Spacelab and mission peculiar experiment support structure. The experiments represented a total of five different disciplines: materials processing in space, environmental observa-tions, life science, astrophysics, and technology experiments. Two getaway specials (GAS). The flight crew was split into gold and silver shifts working 12-hour days during the flight.
- NUSAT-1 - . Payload: Challenger F7 / Nusat / GLOMR [1]. Mass: 52 kg (114 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Weber. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: NUSAT. Decay Date: 1986-12-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 15666 . COSPAR: 1985-034B. Apogee: 354 km (219 mi). Perigee: 345 km (214 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Air traffic control radar calibration. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
- Spacelab 3 - . Payload: SL 3 LM. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1985-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15665 . COSPAR: 1985-034xx. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 346 km (214 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
- SL 3 MPESS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1985-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15665 . COSPAR: 1985-034xx. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 346 km (214 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
- GLOMR - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: GLOMR. Decay Date: 1985-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15665 . COSPAR: 1985-034xx. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 346 km (214 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
1985 June 17 - . 11:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-G - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Al-Saud,
Baudry,
Brandenstein,
Creighton,
Fabian,
Lucid,
Nagel.
Payload: Discovery F05 / Morelos 1[PAM-D] / Telstar 303. Mass: 20,174 kg (44,476 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Al-Saud,
Baudry,
Brandenstein,
Creighton,
Fabian,
Lucid,
Nagel.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-G.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 7.07 days. Decay Date: 1985-06-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 15823 . COSPAR: 1985-048A. Apogee: 369 km (229 mi). Perigee: 358 km (222 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
Deployed and retrieved Spartan 1; launched Morelos 1, Arabsat 1B, Telstar 3D.Payloads: Shuttle Pointed Autono-mous Research Tool for Astronomy (SPARTAN)-1; Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (ADSF); High Precision Tracking Experiment (HPTE); Orbiter Experiments (OEX); French Echocardiograph Experiment (FEE) and French Pocket Experiment (FPE).
- Telstar 3D - .
Payload: Telstar 303 / PAM-D. Mass: 630 kg (1,380 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: ATT.
Program: Telstar series.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1999-02-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 15826 . COSPAR: 1985-048D. Apogee: 35,911 km (22,314 mi). Perigee: 35,888 km (22,299 mi). Inclination: 5.40 deg. Period: 1,441.90 min.
Released by STS 51G 19 June 1985; stationed at 76 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 125 deg W in 1985-1992; 123 deg W in 1992-1996; 120 deg W in 1996-1999 As of 31 August 2001 located at 16.95 deg W drifting at 1.400 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 6.47W drifting at 1.400W degrees per day.
- Morelos 1 - .
Payload: Morelos-A / PAM-D. Mass: 512 kg (1,128 lb). Nation: Mexico.
Agency: Morelos.
Program: Morelos.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1994-03-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 15824 . COSPAR: 1985-048B. Apogee: 36,030 km (22,380 mi). Perigee: 35,999 km (22,368 mi). Inclination: 6.30 deg. Period: 1,447.80 min.
Released by STS 51G 17 June 1985; 113.5 deg W. Coverage of the national territory with television, radio and telephony signals and data transmission. Geostationary satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 113 deg W in 1985-1994 As of 4 September 2001 located at 123.32 deg W drifting at 2.909 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 176.84E drifting at 2.883W degrees per day.
- Arabsat 1B - . Payload: Discovery F5 / Morelos 1 [PAM-D] / Telstar 303 [PA. Mass: 592 kg (1,305 lb). Nation: Arab States. Agency: Arabsat. Program: Arabsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 100. Completed Operations Date: 1992-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 15825 . COSPAR: 1985-048C. Apogee: 35,746 km (22,211 mi). Perigee: 35,737 km (22,205 mi). Inclination: 1.90 deg. Period: 1,433.80 min. Released by STS 51G 18 June 1985; 26 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 26 deg E in 1985-1992 As of 5 September 2001 located at 135.45 deg W drifting at 0.555 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 165.57E drifting at 0.400E degrees per day..
- Spartan 1 - . Payload: Spartan 101. Mass: 1,008 kg (2,222 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1985-06-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 15831 . COSPAR: 1985-048E. Apogee: 395 km (245 mi). Perigee: 359 km (223 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 92.10 min. Released by STS 51G 20 June 1985, retrieved 22 June 1985..
1985 July - .
- STS-51-DA (cancelled) - . Crew: Cleave, O Connor, Shaw, Spring. Payload: TDRS/IUS. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Cleave, O Connor, Shaw, Spring. Program: STS. Flight: STS-51-DA. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned TDRS/IUS deployment shuttle mission. Cancelled due to IUS failure..
1985 July 12 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Challenger Pad Abort - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-51-F. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. The countdown for Challenger's launch was halted at T-3 seconds when on-board computers detected a problem with a coolant valve on main engine #2. The valve was replaced and Challenger was launched on July 29, 1985..
1985 July 29 - . 21:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-F - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Acton,
Bartoe,
Bridges,
England,
Fullerton,
Henize,
Musgrave.
Payload: Challenger F08 / PDP / Spacelab 2 PLT. Mass: 15,603 kg (34,398 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Acton,
Bartoe,
Bridges,
England,
Fullerton,
Henize,
Musgrave.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-F.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 7.95 days. Decay Date: 1985-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15925 . COSPAR: 1985-063A. Apogee: 337 km (209 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 49.50 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
Manned seven crew. At 5 minutes, 45 seconds into ascent the number one engine shut down prematurely due to a a sensor problem and an abort to orbit was declared. Despite the anomaly the mission continued. Launched PDP; carried Spacelab 2. Payloads: Spacelab-2 with 13 experiments, Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX), Protein Crystal Growth (PCG). The flight crew was divided into a red and blue team. Each team worked 12-hour shifts for 24-hour-a-day operation.
- Spacelab 2 PLT - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1985-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15925 . COSPAR: 1985-063xx. Apogee: 328 km (203 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 49.50 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
- Spacelab 2 PLT - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1985-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15925 . COSPAR: 1985-063xx. Apogee: 328 km (203 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 49.50 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
- Spacelab 2 PLT - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1985-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15925 . COSPAR: 1985-063xx. Apogee: 328 km (203 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 49.50 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
- PDP - . Payload: Challenger F8 / PDP. Mass: 285 kg (628 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Huntsville. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: PDP. Decay Date: 1985-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15929 . COSPAR: 1985-063B. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 311 km (193 mi). Inclination: 49.50 deg. Period: 90.90 min. Plasma Diagnostics Package; released by STS 51F 8/1/85, retrieved 8/2/85. .
- CRNE - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: CRNE. Decay Date: 1985-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 15925 . COSPAR: 1985-063xx. Apogee: 328 km (203 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 49.50 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
1985 August 27 - . 10:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-I - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Covey,
Engle,
Fisher, William,
Lounge,
van Hoften.
Payload: Discovery F06 / Syncom-4 4 [Orbus-7S] / Aussat A1. Mass: 19,952 kg (43,986 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Covey,
Engle,
Fisher, William,
Lounge,
van Hoften.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-I.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 7.10 days. Decay Date: 1985-09-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 15992 . COSPAR: 1985-076A. Apogee: 364 km (226 mi). Perigee: 351 km (218 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.70 min.
Manned five crew. Launched Aussat 1, ASC 1, Leasat 4; repaired Leasat 3. Payloads: Deploy ASC (American Satellite Company)-1 with Payload Assist Modue (PAM)-D. Deploy AUSSAT (Australian communications satellite)-1 with PAM-D. Deploy Syncom IV-4 communications satellite with its unique stage. Retrieve Leasat-3 communications satellite, repair and deploy by extravehicular activity (EVA) astronauts. Physical Vapor Transport Organic Solids (PVTOS) experiment.
- Aussat A1 - .
Payload: Aussat A1 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,260 kg (2,770 lb). Nation: Australia.
Agency: Aussat.
Program: Aussat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-08-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 15993 . COSPAR: 1985-076B. Apogee: 35,934 km (22,328 mi). Perigee: 35,922 km (22,320 mi). Inclination: 7.00 deg. Period: 1,443.30 min.
Released by STS 51I 8/27/85. Aussat A1 was decommissioned in early 1993 at the ned of its nominal life. It is currently in a non-synchronous graveyard orbit.. It spent its active life at 160 deg. E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 160 deg E in 1985-1993 As of 5 September 2001 located at 174.28 deg W drifting at 1.831 deg W per day. As of 2007 Feb 27 located at 120.19E drifting at 1.838W degrees per day.
- ASC-1 - .
Mass: 1,271 kg (2,802 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: new.
Program: GTE.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: AS 3000.
Spacecraft: ASC.
Completed Operations Date: 1994-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 15994 . COSPAR: 1985-076C. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Released by STS 51I 8/27/85; stationed at 81 deg E. C, Ku band communications satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 128 deg W in 1985-1994 As of 5 September 2001 located at 99.97 deg W drifting at 0.156 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 119.21W drifting at 0.126W degrees per day.
- Syncom IV-4 - .
Payload: Discovery F6 / Syncom-4 4 [Orbus-7S] / Aussat A1 [. Mass: 1,388 kg (3,060 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 381.
Completed Operations Date: 1996-10-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 15995 . COSPAR: 1985-076D. Apogee: 36,503 km (22,681 mi). Perigee: 36,486 km (22,671 mi). Inclination: 9.50 deg. Period: 1,472.40 min.
Released by STS 51I 8/29/85; 178 deg E; leased by U.S. government. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 177 deg W in 1985-1987 As of 3 September 2001 located at 149.81 deg W drifting at 8.908 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 84.34W drifting at 8.912W degrees per day.
1985 August 31 - .
- EVA STS-51-I-1 - . Crew: Fisher, William, van Hoften. EVA Duration: 0.31 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fisher, William, van Hoften. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-I. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Captured Syncom F3 and began repairs..
1985 September 1 - .
- EVA STS-51-I-2 - . Crew: Fisher, William, van Hoften. EVA Duration: 0.19 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fisher, William, van Hoften. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-I. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Completed Syncom F3 repairs and redeployed satellite..
1985 October 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- SLC-6 at Vandenberg declared operation for shuttle flights. - .
Nation: USA.
The launch complex and support buildings had been built on the old Manned Orbiting Laboratory facilities at a total cost of $ 5.5 billion. Checks of the facilities with non-flight shuttle Enterprise, an external tank, and inert solid rocket boosters were conducted from late 1984 to early 1985. Later fundamental design flaws were found that would cost another $1 billion and two years to fix. The US Air Force was no longer interested in the shuttle as a booster for its payloads, and the facility was mothballed without ever launching a shuttle.
1985 October 3 - . 15:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-J - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Bobko,
Grabe,
Hilmers,
Pailes,
Stewart.
Payload: Atlantis F01 / DSCS-3 2 / DSCS-3 3 [IUS]. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bobko,
Grabe,
Hilmers,
Pailes,
Stewart.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-J.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 4.07 days. Decay Date: 1985-10-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 16115 . COSPAR: 1985-092A. Apogee: 486 km (301 mi). Perigee: 476 km (295 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 94.20 min.
Manned five crew. Atlantis (first flight); deployed USA 11, USA 12. Reusable space transportation system.
Orbits of Earth: 63. Landed at: Runway 23 dry lake bed at Edwards Air Force Base, . Touchdown miss distance: 754.00 m. Landing Rollout: 2,455.00 m. Payloads: Classified DoD Mission - Record altitude (as of 5/93).
- USA 11 - . Payload: DSCS III F-2. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 16116 . COSPAR: 1985-092B. Apogee: 35,963 km (22,346 mi). Perigee: 35,434 km (22,017 mi). Inclination: 0.30 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Released from STS 51J 10/4/85. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit; at 12 deg W in 1986; 42 deg W in 1995..
- USA 12 - .
Payload: DSCS III F-3. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III.
USAF Sat Cat: 16117 . COSPAR: 1985-092C. Apogee: 35,963 km (22,346 mi). Perigee: 35,633 km (22,141 mi). Inclination: 0.30 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Released from STS 51J 4 October 1985; boosted into orbit with DSCS 3 F3 on single IUS booster. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit; at 180 deg E in 1994.
1985 October 30 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-61-A - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Bluford,
Buchli,
Dunbar,
Furrer,
Hartsfield,
Messerschmid,
Nagel,
Ockels.
Payload: Challenger F09 / GLOMR 1. Mass: 14,451 kg (31,859 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bluford,
Buchli,
Dunbar,
Furrer,
Hartsfield,
Messerschmid,
Nagel,
Ockels.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-61-A.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 7.03 days. Decay Date: 1985-11-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 16230 . COSPAR: 1985-104A. Apogee: 331 km (205 mi). Perigee: 319 km (198 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.00 min.
Manned eight crew. Launched GLOMR; carried Spacelab D1. Payloads: Spacelab D-1 with habitable module and 76 experiments. Six of the eight crew members were divided into a blue and red team working 12-hour shifts for 24-hour-a-day operation. The remaining two crew members were 'switch hitters.'.
- GLOMR; GLOMAR - . Payload: Challenger F9 / GLOMR 1. Mass: 52 kg (114 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: GLOMR. Decay Date: 1986-12-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 16231 . COSPAR: 1985-104B. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 317 km (196 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.00 min. Released from STS 61A 11/1/85. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
- Spacelab D-1 - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1985-11-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 16230 . COSPAR: 1985-104xx. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 322 km (200 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.10 min.
- USS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USS. Decay Date: 1985-11-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 16230 . COSPAR: 1985-104xx. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 322 km (200 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.10 min.
1985 November 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-H (cancelled) - . Payload: EOM-1. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-51-H. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Planned EOM-1/2 shuttle mission. Cancelled due to payload delays..
1985 November 27 - . 00:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-61-B - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Cleave,
Neri Vela,
O Connor,
Ross,
Shaw,
Spring,
Walker.
Payload: Atlantis F02 / EASE / ACCESS. Mass: 21,791 kg (48,040 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Cleave,
Neri Vela,
O Connor,
Ross,
Shaw,
Spring,
Walker.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-61-B.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 6.88 days. Decay Date: 1985-12-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 16273 . COSPAR: 1985-109A. Apogee: 370 km (220 mi). Perigee: 361 km (224 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
Manned seven crew. Deployed Morelos 2, Aussat 2, Satcom K2, OEX. Payloads: Deploy SATCOM (RCA-Satellite Communi-cations) Ku-2 with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D II. Deploy Morelos (Mexico communications satellite)-B with PAM-D. Deploy AUSSAT (Australian communications satellite)-2 with PAM-D. EASE/ACCESS (Assembly of Structures— Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures) by extravehicular activity (EVA) astronauts, Continuous Flow Electrophore-sis System (CFES), Diffusive Mixing of Organic Solutions (DMOS), IMAX camera, one getaway special (GAS), Linhof camera and Hasseblad camera.
- OEX Target - . Payload: Atlantis F2 / Aussat A2 [PAM-D] / Morelos 2 [PAM-D. Mass: 16 kg (35 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Technology. Type: Technology satellite. Spacecraft: OEX Target. Decay Date: 1987-03-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 16277 . COSPAR: 1985-109E. Apogee: 386 km (239 mi). Perigee: 373 km (231 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 92.10 min. Released from STS 61B 11/30/85; shuttle autopilot software test target. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
- Morelos 2 - .
Payload: Morelos-B / PAM-D. Mass: 645 kg (1,421 lb). Nation: Mexico.
Agency: Morelos.
Program: Morelos.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
USAF Sat Cat: 16274 . COSPAR: 1985-109B. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Released by STS 61B 11/27/85. Coverage of the national territory with television, radio and telephony signals and data transmission. Geostationary satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 116 deg W in 1985-1998; 120 deg W in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 120.20 deg W drifting at 0.004 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 148.53W drifting at 2.555W degrees per day.
- Aussat A2 - .
Payload: Aussat A2 [PAM-D]. Mass: 1,259 kg (2,775 lb). Nation: Australia.
Agency: Aussat.
Program: Aussat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376.
USAF Sat Cat: 16275 . COSPAR: 1985-109C. Apogee: 35,886 km (22,298 mi). Perigee: 35,866 km (22,286 mi). Inclination: 6.70 deg. Period: 1,440.70 min.
Released by STS 61B 11/28/85; 156 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 156 deg E in 1985-1993; 164 deg E in 1993-1999 As of 1 September 2001 located at 24.67 deg W drifting at 1.153 deg W per day. As of 2007 Feb 27 located at 133.30E drifting at 1.163W degrees per day.
- EASE/ACCESS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EASE/ACCESS. Decay Date: 1985-12-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 16273 . COSPAR: 1985-109xx. Apogee: 385 km (239 mi). Perigee: 323 km (200 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
- Satcom K2 - .
Payload: Satcom-K 2 / PAM-D2. Mass: 1,812 kg (3,994 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: RCA Amer.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Satcom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 4000.
USAF Sat Cat: 16276 . COSPAR: 1985-109D. Apogee: 36,002 km (22,370 mi). Perigee: 35,944 km (22,334 mi). Inclination: 4.20 deg. Period: 1,445.60 min.
Released by STS 61B 11/28/85; 81 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 81 deg W in 1985-1996; 85 deg W in 1996-1997; 81 deg W in 1997-1999 As of 6 September 2001 located at 80.95 deg W drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 157.11W drifting at 2.398W degrees per day.
1985 November 29 - .
- EVA STS-61-B-1 - . Crew: Ross, Spring. EVA Duration: 0.23 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Ross, Spring. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-61-B. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Began EASE/ACCESS (Assembly of Structures / Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures) structural assembly experiments..
1985 December 1 - .
- EVA STS-61-B-2 - . Crew: Ross, Spring. EVA Duration: 0.28 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Ross, Spring. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-61-B. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Completed EASE/ACCESS (Assembly of Structures / Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures) structural assembly experiments..
1986 January 12 - . 11:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-61-C - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Bolden,
Cenker,
Chang-Diaz,
Gibson,
Hawley,
Nelson,
Nelson, Bill.
Payload: Columbia F07 Satcom-K 1 [PAM-D2]. Mass: 14,724 kg (32,460 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bolden,
Cenker,
Chang-Diaz,
Gibson,
Hawley,
Nelson,
Nelson, Bill.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-61-C.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 6.09 days. Decay Date: 1986-01-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 16481 . COSPAR: 1986-003A. Apogee: 338 km (210 mi). Perigee: 331 km (205 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Manned seven crew. Launched Satcom K1. Payloads: Deploy SATCOM (RCA-Satellite Communi-cations) Ku-1 with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D II. Materials Science Laboratory, Comet Halley Active Monitoring Experiment (CHAMP), Hitchhiker (HH) Goddard (G)-1, thirteen getaway specials (GAS), student experiment, Initial Blood Storage Equipment (lBSE), Characterization of Space Motion Sickness (SMS).
- Satcom K1 - . Payload: Satcom-K 1 / PAM-D2. Mass: 1,923 kg (4,239 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: RCA Amer. Manufacturer: Lockheed. Program: Satcom. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 4000. Completed Operations Date: 1997-07-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 16482 . COSPAR: 1986-003B. Apogee: 36,016 km (22,379 mi). Perigee: 35,965 km (22,347 mi). Inclination: 4.50 deg. Period: 1,446.50 min. Stationed at 81 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 85 deg W in 1986-1997; 87 deg W in 1997 As of 31 August 2001 located at 61.19 deg W drifting at 2.593 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 125.55E drifting at 2.586W degrees per day..
- GBA-1 - . Payload: GAS Bridge. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1986-01-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 16481 . COSPAR: 1986-003xx. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 322 km (200 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
- MSL-2 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads.
Spacecraft: MSL-2.
Decay Date: 1986-01-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 16481 . COSPAR: 1986-003xx. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 322 km (200 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
The Material Science Laboratory was a carrier system designed to utilize the residual space of the Shuttle cargo bay. Based on the multi-purpose experiment support structure (MPESS) carrier, it offered a full complement of power, data, and thermal control services to payloads mounted on it.
1986 January 28 - . 16:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle. FAILURE: Seal on SRB failed, allowed hot gas to burn through External Tank.. Failed Stage: 0.
- STS-51-L - . Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Jarvis, McAuliffe, McNair, Onizuka, Resnik, Scobee, Smith. Payload: Challenger F10 / TDRS 2 [IUS]. Mass: 116,670 kg (257,210 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Jarvis, McAuliffe, McNair, Onizuka, Resnik, Scobee, Smith. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51-L. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Duration: 0.0008 days. Decay Date: 1986-01-28 . Apogee: 15 km (9 mi). Exploded 73 seconds after launch, all 7 crewmembers were killed; carried TDRSS satellite..
- TDRS B - . Payload: TDRS B. Mass: 2,240 kg (4,930 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: TDRS. Apogee: 15 km (9 mi).
- Spartan-Halley - .
Payload: Spartan-Halley. Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads.
Spacecraft: Spartan.
Apogee: 15 km (9 mi).
The Spartan series consists of low-cost, Shuttle-launched, short-duration, sounding-rocket-type payloads. The payloads were retrievable and reusable with a turnaround time of 6 to 9 months. Spartan operated as an autonomous sub-satellite, and the data was stored on an internal tape recorder. Pointing and stabilization were achieved by an attitude control system capable of three-axis stabilized pointing to any target within +/- 3 arc-minutes. The main objective of this spacecraft was to obtain UV spectra of the coma and tail of Comet Halley in January 1986 shortly before its perihelion. This spacecraft was lost when Space Shuttle Challenger exploded on launch.
1986 March - .
- STS-61-E (cancelled) - . Crew: Durrance, Hoffman, Leestma, McBride, Parise, Parker, Richards. Backup Crew: Nordsieck. Payload: Astro-1. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-E. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Planned Astro-1 shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 May - .
- STS-61-F (cancelled) - . Crew: Bridges, Hauck, Hilmers, Lounge. Payload: Ulysses. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Bridges, Hauck, Hilmers, Lounge. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-F. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned shuttle mission for deployment of Ulysses spacecraft. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 May - .
- STS-61-G (cancelled) - . Crew: Grabe, Thagard, van Hoften, Walker, Dave. Payload: Galileo. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Grabe, Thagard, van Hoften, Walker, Dave. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-G. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Planned shuttle mission for deployment of Galileo spacecraft. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 June - .
- STS-61-H (cancelled) - . Crew: Blaha, Buchli, Coats, Fisher, Springer, Sudarmono, Wood, Nigel. Backup Crew: Akbar, Farrimond. Payload: Communications satellites. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-H. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Planned shuttle mission for deployment of commercial communications satellites. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 July - .
- STS-62-A (cancelled) - . Crew: Aldridge, Crippen, Gardner, Gardner, Guy, Mullane, Ross, Watterson. Backup Crew: Odle. Payload: DoD Mission. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-62-A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Planned Department of Defense shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. Would have been first launch from the ill-fated SLC-6 launch site at Vandenberg, California..
1986 July - .
- STS-61-M (cancelled) - . Crew: Fisher, William, Lee, O Connor, Ride, Shriver, Wood, Robert. Backup Crew: Walker. Payload: TDRS/IUS. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-M. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned TDRS/IUS deployment shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 September - .
- STS-61-N (cancelled) - . Crew: Adamson, Brown, Mark, Casserino, Leestma, McCulley, Shaw. Backup Crew: Joseph. Payload: DoD Mission. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-N. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Planned Department of Defense shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 September - .
- STS-61-I (cancelled) - . Crew: Bagian, Bhat, Carter, Dunbar, Smith, Williams, Donald. Backup Crew: Nair. Payload: LDEF(Recovery). Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-I. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned shuttle LDEF (Long Duration Exposure Facility) recovery mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 September - .
- STS-62-B (cancelled) - . Crew: Roberts. Payload: DoD Mission. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Roberts. Program: STS. Flight: STS-62-B. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Planned Department of Defense shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1986 October - .
- STS-61-K (cancelled) - . Crew: Brand, Garriott, Griggs, Lampton, Lichtenberg, Nicollier, Stevenson, Stewart. Backup Crew: Chappell, Frimout. Payload: EOM-1/2. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-K. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Planned EOM-1 shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. No crew named, later combined with STS-61K.
1986 November - .
- STS-61-L (cancelled) - . Crew: Konrad. Backup Crew: Cunningham, Stephen. Payload: Communications satellites. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-61-L. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Planned shuttle mission for deployment of commercial communications satellites. Would have launched the first American journalist in space from Launch Complex 39B. Cancelled after Challenger disaster..
1986 December - .
- STS-71-B (cancelled) - . Crew: Jones, Charles. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Jones, Charles. Program: STS. Flight: STS-71-B. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1987 January - .
- STS-71-A (cancelled) - . Crew: Nordsieck. Payload: Astro-2. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Nordsieck. Program: STS. Flight: STS-71-A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Planned Astro-2 shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1987 January - .
- STS-71-C (cancelled) - . Crew: Longhurst. Backup Crew: Holmes. Payload: Communications satellites. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-71-C. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Planned shuttle mission for deployment of commercial communications satellites. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1987 February - .
- STS-71-D (cancelled) - . Crew: Wood, Robert. Backup Crew: Walker. Payload: Communications satellites. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-71-D. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Planned shuttle mission for deployment of commercial communications satellites. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1987 March - .
- STS-71-E (cancelled) - . Crew: Gaffney, Phillips. Backup Crew: Hughes-Fulford. Payload: SLS-1. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-71-E. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned SLS-1 shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1987 March - .
- STS-71-F (cancelled) - . Crew: MacLean. Backup Crew: Tryggvason. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-71-F. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Planned shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1987 June 8 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle crash barrier tests. - . Nation: USA. Non-flight shuttle orbiter Enterprise was brought out of storage to test crash barrier designs to be used in case of an orbiter runway overrun. After this it was sent to the National Air and Space Museum for storage..
1987 August - .
- STS-71-M (cancelled) - . Crew: Nordsieck. Payload: Astro-3. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Nordsieck. Program: STS. Flight: STS-71-M. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Planned Astro-3 shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1988 February - .
- STS-81-G (cancelled) - . Crew: Mohri, Mukai. Backup Crew: Doi. Payload: Spacelab-J. Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-81-G. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned Spacelab-J shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1988 July - .
- STS-81-M (cancelled) - . Crew: Hughes-Fulford. Payload: SLS-2. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Hughes-Fulford. Program: STS. Flight: STS-81-M. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Planned SLS-2 shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. .
1988 September 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51-K (cancelled) - . Payload: Spacelab-D1 . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Flight: STS-51-K. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Challenger. Planned Spacelab-D1 shuttle mission. Cancelled after Challenger disaster. No crew selected; renamed STS-61A.
1988 September 29 - . 15:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-26 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Covey,
Hauck,
Hilmers,
Lounge,
Nelson.
Payload: Discovery F07 / PDP. Mass: 21,082 kg (46,477 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Covey,
Hauck,
Hilmers,
Lounge,
Nelson.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-26.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 4.04 days. Decay Date: 1988-10-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 19547 . COSPAR: 1988-091A. Apogee: 306 km (190 mi). Perigee: 301 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned five crew. First shuttle reflight after Challenger disaster. Deployed TDRS 3. Payloads: Deploy IUS (lnertial Upper Stage) with Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS)-C. 3M's Physical Vapor Transport Organics Solids 2 experiment (PVTOS), Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (ADSF), Infrared Communi-cations Flight Experiment (lRCFE), Protein Crystal Growth Il (PCG), Isoelectric Focusing (ISF)-2, Phase Partitioning Experiment (PPE), Aggrega-tion of Red Blood Cells (ARC)-2, Mesoscale Lightning Experiment (MLE)-1, Earth Limb Radiance (ELRAD), Orbiter Experiments (OEX), Autonomous Supporting Instrumentation System (OASlS)-I, two Shuttle Student Involvement Project (SSIP) experiments.
- TDRS 3 - .
Payload: TDRS C. Mass: 2,200 kg (4,800 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: TDRS.
USAF Sat Cat: 19548 . COSPAR: 1988-091B. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.50 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
NASA communications; 171 deg W; deployed from STS-26 . Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 151 deg W in 1988; 171 deg W in 1989-1990; 174 deg W in 1990-1991; 62 deg W in 1991-1994;171 deg W in 1994-1995; 85 deg E in 1995-1999 As of 26 August 2001 located at 85.17 deg E drifting at 0.007 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 84.98E drifting at 0.004W degrees per day.
1988 December 2 - . 14:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-27 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Gardner, Guy,
Gibson,
Mullane,
Ross,
Shepherd.
Payload: Atlantis F03 / Lacrosse 1. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gardner, Guy,
Gibson,
Mullane,
Ross,
Shepherd.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-27.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 4.38 days. Decay Date: 1988-12-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 19670 . COSPAR: 1988-106A. Apogee: 447 km (277 mi). Perigee: 437 km (271 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 93.40 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed a classified payload. Orbits of Earth: 68. Landed at: Runway 17 dry lake bed at Edwards Air Force Base, . Landing Speed: 359 kph. Touchdown miss distance: 447.00 m. Landing Rollout: 2,171.00 m. Payloads: DoD Mission.
- USA 34 - . Payload: Lacrosse 1. Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Manufacturer: Martin. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military Radarsat. Spacecraft: Lacrosse satellite. Decay Date: 1997-03-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 19671 . COSPAR: 1988-106B. Apogee: 447 km (277 mi). Perigee: 437 km (271 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 93.40 min. Deployed from STS-27. Operations completed March 1997..
1989 March 13 - . 14:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-29 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bagian,
Blaha,
Buchli,
Coats,
Springer.
Payload: Discovery F08 / SHARE. Mass: 17,280 kg (38,090 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bagian,
Blaha,
Buchli,
Coats,
Springer.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-29.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 4.99 days. Decay Date: 1989-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 19882 . COSPAR: 1989-021A. Apogee: 308 km (191 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed TDRS 4. Payloads: Deploy IUS (Inertial Upper Stage) with Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS)-D. Protein Crystal Growth (PCG); Chromosome and Plant Cell Division in Space; IMAX 70mm camera; Shuttle Student Involvement Project (SSIP) experiments: SSIP 82-8, Effects of Weightlessness in Space Flight on the Healing of Bone Fractures, and SSIP 83-9, Chicken Embryo Development in Space; Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) experiment.
- TDRS 4 - .
Payload: TDRS D. Mass: 2,120 kg (4,670 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: TDRS.
USAF Sat Cat: 19883 . COSPAR: 1989-021B. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 4.60 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Deployed from STS 29 13 March 1989; NASA communications; 41 deg W. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 41 deg W in 1989-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 41.04 deg W drifting at 0.010 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 45.81W drifting at 0.008W degrees per day.
1989 May 4 - . 18:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-30 - . Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Cleave, Grabe, Lee, Thagard, Walker, Dave. Payload: Atlantis F04 / Magellan [IUS]. Mass: 20,833 kg (45,928 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Cleave, Grabe, Lee, Thagard, Walker, Dave. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-30. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Duration: 4.04 days. Decay Date: 1989-05-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 19968 . COSPAR: 1989-033A. Apogee: 366 km (227 mi). Perigee: 361 km (224 mi). Inclination: 28.90 deg. Period: 91.80 min. Manned five crew. Deployed Magellan Venus probe. Payloads: Deploy IUS with Magellan spacecraft. Fluids Experiment Apparatus (FEA). Mesoscale Lightning Experiment (MLE), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) experiment..
- Magellan - .
Payload: Atlantis F4 / Magellan [IUS]. Mass: 3,444 kg (7,592 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft: Magellan.
Decay Date: 1994-10-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 19969 . COSPAR: 1989-033B.
SAR radar imaging of the Venusian surface, gravitational field mapping. The Magellan spacecraft was deployed from shuttle STS-30 on May 5, 1989, arrived at Venus on August 10, 1990 and was inserted into a near-polar elliptical orbit with a periapsis altitude of 294 km at 9.5 deg. N. The primary objectives of the Magellan mission were to map the surface of Venus with a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and to determine the topographic relief of the planet. At the completion of radar mapping 98% of the surface was imaged at resolutions better than 100 m, and many areas were imaged multiple times. The mission was divided up into 'cycles', each cycle lasted 243 days (the time necessary for Venus to rotate once under the Magellan orbit - i.e. the time necessary for Magellan to 'see' the entire surface once.) The mission proceeded as follows: 10 Aug 1990 - Venus orbit insertion and spacecraft checkout;15 Sep 1990 - Cycle 1: Radar mapping (left-looking); 15 May 1991 - Cycle 2: Radar mapping (right-looking); 15 Jan 1992 - Cycle 3: Radar mapping (left-looking); 14 Sep 1992 - Cycle 4: Gravity data acquisition; 24 May 1993 - Aerobraking to circular orbit; 3 Aug 1993 - Cycle 5: Gravity data acquisition; 30 Aug 1994 - Windmill experiment; 12 Oct 1994 - Loss of radio signal; 13 Oct 1994 - Loss of spacecraft. A total of 4225 usable SAR imaging orbits was obtained by Magellan. Magellan showed an Earth-sized planet with no evidence of Earth-like plate tectonics. At least 85% of the surface is covered with volcanic flows, the remainder by highly deformed mountain belts. Even with the high surface temperature (475 C) and high atmospheric pressure (92 bars), the complete lack of water makes erosion a negligibly slow process, and surface features can persist for hundreds of millions of years. Some surface modification in the form of wind streaks was observed. Over 80% of Venus lies within 1 km of the mean radius of 6051.84 km. The mean surface age is estimated to be about 500 million years. A major unanswered question concerns whether the entire surface was covered in a series of large events 500 million years ago, or if it has been covered slowly over time. The gravity field of Venus is highly correlated with the surface topography, which indicates the mechanism of topographic support is unlike the Earth, and may be controlled by processes deep in the interior. Details of the global tectonics on Venus were still unresolved.
1989 August 8 - . 12:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-28 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Adamson,
Brown, Mark,
Leestma,
Richards,
Shaw.
Payload: Columbia F08 / DoD. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Adamson,
Brown, Mark,
Leestma,
Richards,
Shaw.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-28.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 5.04 days. Decay Date: 1989-08-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 20164 . COSPAR: 1989-061A. Apogee: 306 km (190 mi). Perigee: 289 km (179 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed 2 classified satellites. Landed at: Runway 17 dry lake bed at Edwards Air Force Base, . Landing Speed: 287 kph. Touchdown miss distance: 1,618.00 m. Landing Rollout: 1,833.00 m. Payloads: DoD Mission.
- USA 41 - . Nation: USA. Agency: DARPA. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1989-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 20172 . COSPAR: 1989-061C. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 296 km (183 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.50 min. Deployed from STS-28 8/8/89. Believed to be one-off ferret satellite under COBRA BRASS measurement and signature intelligence experiment..
- USA 40 - . Payload: SDS B-1. Mass: 5,900 kg (13,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 20167 . COSPAR: 1989-061B. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min. Deployed from STS-28 8 August 1989..
1989 October 18 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Galileo Probe - . Mass: 339 kg (747 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Outer planets. Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft Bus: Galileo. Spacecraft: Galileo Probe. COSPAR: 1989-084E. Atmospheric probe; deployed from Galileo 7/13/95; entered Jupiter atmosphere 12/7/95. Entry into Jupiter Dec 7.
- STS-34 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Baker,
Chang-Diaz,
Lucid,
McCulley,
Williams, Donald.
Payload: Atlantis F05 / Galileo [IUS]. Mass: 22,064 kg (48,642 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Baker,
Chang-Diaz,
Lucid,
McCulley,
Williams, Donald.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-34.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 4.99 days. Decay Date: 1989-10-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 20297 . COSPAR: 1989-084A. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 298 km (185 mi). Inclination: 34.30 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed Galileo .Payloads: Deploy IUS with Galileo spacecraft. Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet (SSBUV), Polymer Morphology (PM) experiments, IMAX camera project, Mesoscale Lightning Experiment (MLE), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) experiment, Growth Hormone Concentration and Distribution (GHCD) in Plants experiment, Sensor Technology Experiment (STEX), SSIP Student Experiment (SE) 82-15, Ice Crystals Experiment. First flight at this inclination.
- Galileo Probe - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Galileo. Spacecraft: Galileo Probe. Decay Date: 1989-10-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 20297 . COSPAR: 1989-084xx. Apogee: 333 km (206 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 34.30 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
- SSBUV-2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SSBUV. Decay Date: 1989-10-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 20297 . COSPAR: 1989-084xx. Apogee: 333 km (206 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 34.30 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
- Galileo - .
Payload: Atlantis F5 / Galileo [IUS]. Mass: 3,881 kg (8,556 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Class: Outer planets.
Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft Bus: Galileo.
Spacecraft: Galileo probe.
Decay Date: 2003-09-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 20298 . COSPAR: 1989-084B.
Deployed from STS-34 18 October 1989; entered Jupiter orbit 7 December 1995 and conducted investigations of Jupiter's moons, atmosphere, and magnetosphere. Although the antenna failed to deploy, NASA developed workarounds and the spacecraft cruised the Jovian system for eight years. Its propellant then depleted, it was maneuvered to enter the Jovian atmosphere on September 21, 2003, at 18:57 GMT. Entry was at 48.2 km/s from an orbit with a periapsis 9700 km below the 1-bar atmospheric layer. The spacecraft continued transmitting at least until it passed behind the limb of Jupiter at 1850:54 GMT, at which point it was 9283 km above the 1-bar level, surprising Galileo veterans who feared it might enter safemode due to the high radiation environment. On its farewell dive, it had crossed the orbit of Callisto at around 1100 on September 20, the orbit of Ganymede at around 0500 on September 21, Europa's orbit at about 1145, Io's orbit at about 1500, Amalthea's orbit at 1756, and the orbits of Adrastea and Metis at 1825. Galileo was destroyed to prevent the possibility that its orbit would eventually be perturbed in such a way that it would crash on and biologically contaminate Europa, which was considered a possible place to search for life. Light travel time from Jupiter to Earth was 52 min 20 sec at the time of impact, and the final signal reached Earth at 1943:14 GMT.
- SSBUV-1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SSBUV. Decay Date: 1989-10-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 20297 . COSPAR: 1989-084xx. Apogee: 333 km (206 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 34.30 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
1989 November 23 - . 00:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-33 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Blaha,
Carter,
Gregory,
Musgrave,
Thornton.
Payload: Discovery F09 / Magnum 2 [IUS]. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Blaha,
Carter,
Gregory,
Musgrave,
Thornton.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-33.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 5.00 days. Decay Date: 1989-11-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 20329 . COSPAR: 1989-090A. Apogee: 214 km (132 mi). Perigee: 207 km (128 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed a classified payload. Orbits of Earth: 78. Distance traveled: 3,218,687 km. Landed at: Concrete runway 04 at Edwards Air Force Base, Cali. Landing Speed: 368 kph. Touchdown miss distance: 570.00 m. Landing Rollout: 2,366.00 m. Payloads: DoD Mission - third space shuttle night launch.
- USA 48 - . Payload: Orion 2. Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Magnum. USAF Sat Cat: 20355 . COSPAR: 1989-090B. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min. Second Magnum model ELINT satellite. Code name changed to Orion. Deployed from STS-33 November 23, 1989, and boosted to geostationary orbit. As of 2003 May 4 located at 88.13E drifting at 0.048W degrees per day..
1990 January 9 - . 12:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-32 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Brandenstein,
Dunbar,
Ivins,
Low,
Wetherbee.
Payload: Columbia F09 / Syncom-4 5 [Orbus-7S]. Mass: 12,014 kg (26,486 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brandenstein,
Dunbar,
Ivins,
Low,
Wetherbee.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-32.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 10.88 days. Decay Date: 1990-01-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 20409 . COSPAR: 1990-002A. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 296 km (183 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.10 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed Leasat 5, retrieved LDEF. Night landing. Payloads: Deployment of Syncom IV-5, retrieval of Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF), Fluids Experiment Apparatus (FEA)-3, Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) III-2, Latitude/Longitude Locator (L3), American Flight Echocardiograph (AFE), Characterization of Neurospora Circadian Rhythms in Space (CNCR)-01, Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS)-4, Mesoscale Lightning Experiment (MLE), IMAX, Interim Operational Contamination Monitor (lOCM).
- Leasat 5 - .
Payload: Columbia F9 / Syncom-4 5 [Orbus-7S]. Mass: 3,400 kg (7,400 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Program: Leasat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 20410 . COSPAR: 1990-002B. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 4.40 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Deployed from STS 32 1/10/89; 177 deg W; leased to U.S. government. The Leasat series was developed as a commercial venture to provide dedicated communications services to the U. S. military. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 178 deg E in 1990; 72 deg E in 1990-1997; 77 deg E in 1997-1998; 155 deg E in 1998-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 155.70 deg E drifting at 0.023 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 100.05E drifting at 0.003E degrees per day. Additional Details: here....
1990 February 28 - . 07:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-36 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Casper,
Creighton,
Hilmers,
Mullane,
Thuot.
Payload: Atlantis F06 / KH-12 1. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Casper,
Creighton,
Hilmers,
Mullane,
Thuot.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-36.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 4.43 days. Decay Date: 1990-03-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 20512 . COSPAR: 1990-019A. Apogee: 204 km (126 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 62.00 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed a classified payload. Landed at: Runway 23 dry lake bed at Edwards Air Force Base, . Landing Speed: 368 kph. Touchdown miss distance: 494.00 m. Landing Rollout: 2,407.00 m. Payloads: DoD Mission - Record altitude (through 5/93).
- USA 53 - .
Payload: KH-12 no. 1. Mass: 19,600 kg (43,200 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Misty.
Decay Date: 1990-03-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 20516 . COSPAR: 1990-019B. Apogee: 207 km (128 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 62.00 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Deployed from STS-36 February 28, 1990. Said to be designated 'Misty', and believed to be the first maneouvering stealth satellite. Barely visible, it was rediscovered by amateur observors in October 1990, with a ground track that repeated every nine days. It maneouvered again in early November 1990, changing its inclination by 1.2 degrees and entering a lower orbit with a three-day repeating ground track. Amateurs again found it in 1996 and 1997 in a 66.2 degree orbit with a 99.4 minute period. The decay date for the active satellite is believed to refer instead to debris; the actually satellite was probably deorbited after 1997, perhaps after USA 144 (Misty 2?) was put into operation.
1990 April 24 - . 12:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-31 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bolden,
Hawley,
McCandless,
Shriver,
Sullivan.
Payload: Discovery F10 / Hubble Space Telescope. Mass: 13,005 kg (28,671 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bolden,
Hawley,
McCandless,
Shriver,
Sullivan.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-31.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 5.05 days. Decay Date: 1990-04-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 20579 . COSPAR: 1990-037A. Apogee: 615 km (382 mi). Perigee: 585 km (363 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.70 min.
Deployed HST (Hubble Space Telescope). Payloads: Deployment of Hubble Space Telescope, IMAX camera in payload bay and in crew compartment, Protein Crystal Growth III-03, Investigation Into Polymer Membrane Process-ing- 01, Air Force Maui Optical Site-05, Radiation Monitoring Equipment III-01, Student Experiment 82-16, and Ascent Particle Monitor 01.
- HST Hubble Space Telescope - . Payload: Hubble Space Telescope. Mass: 10,863 kg (23,948 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Class: Astronomy. Type: Astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: HST. USAF Sat Cat: 20580 . COSPAR: 1990-037B. Apogee: 596 km (370 mi). Perigee: 590 km (360 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.50 min. Hubble Space Telescope; deployed from STS-31 4/25/90. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1990 October 6 - . 11:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-41 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Akers,
Cabana,
Melnick,
Richards,
Shepherd.
Payload: Discovery F11 / Ulysses [IUS + PAM-S]. Mass: 22,140 kg (48,810 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Akers,
Cabana,
Melnick,
Richards,
Shepherd.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-41.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 4.09 days. Decay Date: 1990-10-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 20841 . COSPAR: 1990-090A. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed Ulysses spacecraft. Payloads: Deploy Ulysses, Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet, Intelsat Solar Array Coupon, Solid-Surface Combustion Experiment, Investigations Into Polymer Membrane Processing, Chromo-some and Plant Cell Division in Space, Physiological Systems Experiment, Voice Command System, Radiation Monitoring Equipment III, Air Force Maui Optical Site.
- Ulysses - .
Payload: Discovery F11 / Ulysses [IUS + PAM-S]. Mass: 367 kg (809 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Class: Astronomy.
Type: Solar satellite. Spacecraft: Ulysses.
USAF Sat Cat: 20842 . COSPAR: 1990-090B. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi). Perigee: 285 km (177 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 90.10 min.
Deployed from STS 41 10/6/90; solar research. Ulysses is a scientific spacecraft, within the framework of the international solar/polar mission. It will be the first spacecraft to fly over the poles of the sun. Frequency 2111.6073/2293.1481 MHz, 8408.2099 MHz., interplanetary trajectory i nto a polar flyby over the sun. Designator ESA/90/01. Also registered by the United States in ST/SG/SER.E/250, orbital data are taken from that document.
1990 November 15 - . 23:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-38 - . Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Covey, Culbertson, Gemar, Meade, Springer. Payload: Atlantis F07 / DoD. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Covey, Culbertson, Gemar, Meade, Springer. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-38. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Duration: 4.91 days. Decay Date: 1990-11-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 20935 . COSPAR: 1990-097A. Apogee: 226 km (140 mi). Perigee: 78 km (48 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 87.50 min. Manned five crew. Deployed a classified payload. Orbits of Earth: 79. Payloads: DoD Mission..
- USA 67 - . Mass: 2,500 kg (5,500 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval signals intelligence satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 20963 . COSPAR: 1990-097B. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min. Deployed from STS 38 15 November 1990. Boosted to geostationary orbit. Last known longitude (31 December 1990) 99.16 deg W drifting at 0.050 deg W per day..
1990 November 20 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Backup shuttle carrier aircraft. - . Nation: USA. In the event of loss of N905NA, which has been in service for 15 years, NASA purchases a second 747, N911NA, for use as a shuttle carrier..
1990 December 2 - . 06:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-35 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Brand, Durrance, Gardner, Guy, Hoffman, Lounge, Parise, Parker. Payload: Columbia F10 / BBXRT. Mass: 11,943 kg (26,329 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Brand, Durrance, Gardner, Guy, Hoffman, Lounge, Parise, Parker. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-35. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 8.96 days. Decay Date: 1990-12-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 20980 . COSPAR: 1990-106A. Apogee: 362 km (224 mi). Perigee: 352 km (218 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.70 min. Manned seven crew. Carried ASTRO-1 observatory. Payloads: Ultraviolet Astronomy TeIescope (Astro), Broad-Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS)..
- BBXRT - . Payload: BBXRT/TAPS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: BBXRT. Decay Date: 1990-12-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 20980 . COSPAR: 1990-106xx. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 339 km (210 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
- Astro 1 Fwd - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1990-12-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 20980 . COSPAR: 1990-106xx. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 339 km (210 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
- Astro 1 Aft - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1990-12-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 20980 . COSPAR: 1990-106xx. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 339 km (210 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
1991 April 5 - . 14:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-37 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Apt,
Cameron,
Godwin,
Nagel,
Ross.
Payload: Atlantis F08 / Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. Mass: 16,611 kg (36,620 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Apt,
Cameron,
Godwin,
Nagel,
Ross.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-37.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 5.98 days. Decay Date: 1991-04-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 21224 . COSPAR: 1991-027A. Apogee: 462 km (287 mi). Perigee: 450 km (270 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.70 min.
Manned five crew. Unscheduled EVA to manually deploy the Gamma-Ray Observatory's high-gain antenna, which failed to deploy upon ground command. Payloads: Gamma-Ray Observatory (GRO), Crew/ Equipment Translation Aids (part of Extravehicular Activity Development Flight Experiment), Ascent Particle Monitor (APM), Bioserve Instrumentation Technology Associates Materials Dispersion Apparatus (BlMDA), Protein Crystal Growth (PCG)-Block Il, Space Station Heatpipe Advanced Radiator Element (SHARE)-ll, Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX)-ll, Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME)-lIl, Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) Calibration Test.
- Compton Observatory - .
Payload: Gamma Ray Observatory. Mass: 15,620 kg (34,430 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Class: Astronomy.
Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: GRO.
Decay Date: 2000-06-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 21225 . COSPAR: 1991-027B. Apogee: 453 km (281 mi). Perigee: 448 km (278 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.60 min.
Astrophysical laboratory for gamma ray observations; deployed from STS-37 4/7/91; renamed Compton Gamma Ray Observatory. The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory was intentionally deorbited on by NASA over the objections of the scientific community on June 3, 2000. NASA decided to end the mission after several orientation gyroscope failures. They felt that if another gyroscope was lost, the heavy spacecraft might eventually reenter out of control.
1991 April 7 - .
- EVA STS-37-1 - . Crew: Apt, Ross. EVA Duration: 0.19 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Apt, Ross. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-37. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Manually deployed Gamma-Ray Observatory's high-gain antenna..
1991 April 8 - .
- EVA STS-37-2 - . Crew: Apt, Ross. EVA Duration: 0.25 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Apt, Ross. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-37. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Tested CETA (Crew / Equipment Translation Aids - rail with cart for moving astronauts around exterior of International Space Station)..
1991 April 28 - . 11:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-39 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bluford,
Coats,
Hammond,
Harbaugh,
Hieb,
McMonagle,
Veach.
Payload: Discovery F12. Mass: 9,712 kg (21,411 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bluford,
Coats,
Hammond,
Harbaugh,
Hieb,
McMonagle,
Veach.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-39.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 8.31 days. Decay Date: 1991-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 21242 . COSPAR: 1991-031A. Apogee: 263 km (163 mi). Perigee: 248 km (154 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
Manned seven crew. Deployed USA 70, CRO A, CRO B, CRO C; deployed and retrieved IBSS. Payloads: Infrared Background Signature Survey (lBSS), Air Force Program (AFP)-675, Space Test Payload (STP)-I, Multi-Purpose Experiment Canister (MPEC), Cloud Logic to Optimize Use of Defense Systems (CLOUDS)-1A, Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME)-lll.
- CRO-C - . Payload: Discovery F12 / IBSS-SPAS 02 / CRO A / CRO B / CRO. Mass: 197 kg (434 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SDIO. Class: Military. Type: Strategic defense satellite. Spacecraft: CRO. Decay Date: 1991-05-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 21245 . COSPAR: 1991-031D. Apogee: 85 km (52 mi). Perigee: 67 km (41 mi). Inclination: 56.90 deg. Period: 85.70 min. Chemical Release Observation; deployed 2 May 1991; released gases for observation by IBSS..
- IBSS - . Payload: SPAS-2. Mass: 1,901 kg (4,190 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SDIO. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: IBSS. Decay Date: 1991-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 21244 . COSPAR: 1991-031B. Apogee: 255 km (158 mi). Perigee: 245 km (152 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.50 min. Infrared Background Signature Survey; sensor technology test; retrieved 2 May 1991..
- CRO-B - . Payload: Discovery F12 / IBSS-SPAS 02 / CRO A / CRO B / CRO. Mass: 197 kg (434 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SDIO. Class: Military. Type: Strategic defense satellite. Spacecraft: CRO. Decay Date: 1991-05-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 21246 . COSPAR: 1991-031E. Apogee: 88 km (54 mi). Perigee: 68 km (42 mi). Inclination: 56.90 deg. Period: 85.80 min. Chemical Release Observation; deployed 2 May 1991; released gases for observation by IBSS..
- AFP-675 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: AFP-675. Decay Date: 1991-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 21242 . COSPAR: 1991-031xx. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
- STP-1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: STP-1. Decay Date: 1991-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 21242 . COSPAR: 1991-031xx. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
- USA 70 - . Payload: MPEC. Nation: USA. Agency: DARPA. Program: STS. Class: Technology. Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft: MPEC. USAF Sat Cat: 21262 . COSPAR: 1991-031C. Classified subsatellite released from shuttle..
- SPAS-II - . Payload: SPAS. Mass: 3,230 kg (7,120 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Military. Type: Strategic defense satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SPAS. COSPAR: 1991-031xx. Apogee: 263 km (163 mi). Perigee: 248 km (154 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Shuttle Pallet Satellite-II (SPAS-II) experiments were carried out on this classified mission. No details on whether SPAS was released or nature of experiments..
- CRO-A - . Payload: Discovery F12 / IBSS-SPAS 02 / CRO A / CRO B / CRO. Mass: 197 kg (434 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SDIO. Class: Military. Type: Strategic defense satellite. Spacecraft: CRO. Decay Date: 1991-05-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 21247 . COSPAR: 1991-031F. Apogee: 236 km (146 mi). Perigee: 215 km (133 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Chemical Release Observation; deployed 3 May 1991; released gases for observation by IBSS..
1991 June 5 - . 13:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-40 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Bagian,
Gaffney,
Gutierrez,
Hughes-Fulford,
Jernigan,
O Connor,
Seddon.
Payload: Columbia F11 / GBA-2. Mass: 11,767 kg (25,941 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bagian,
Gaffney,
Gutierrez,
Hughes-Fulford,
Jernigan,
O Connor,
Seddon.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-40.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 9.09 days. Decay Date: 1991-06-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 21399 . COSPAR: 1991-040A. Apogee: 296 km (183 mi). Perigee: 287 km (178 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
Carried Spacelab life sciences module. Payloads: Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS)-1 with long module, getaway special bridge assembly with 12 getaway specials, Physiological Monitoring System (PMS), Urine Monitoring System (UMS), Animal Enclosure Modules (AEM), Middeck Zero-gravity Dynamics Experiment (MODE), 7 Orbiter Experiments Program experiments.
- Spacelab SLS 1 - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1991-06-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 21399 . COSPAR: 1991-040xx. Apogee: 289 km (179 mi). Perigee: 276 km (171 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
- GBA-2 - . Payload: GAS Bridge. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1991-06-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 21399 . COSPAR: 1991-040xx. Apogee: 289 km (179 mi). Perigee: 276 km (171 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
1991 August 2 - . 15:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-43 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Adamson,
Baker, Mike,
Blaha,
Low,
Lucid.
Payload: Atlantis F09 / TDRS 5 [IUS]. Mass: 21,265 kg (46,881 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Adamson,
Baker, Mike,
Blaha,
Low,
Lucid.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-43.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 8.89 days. Decay Date: 1991-08-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 21638 . COSPAR: 1991-054A. Apogee: 306 km (190 mi). Perigee: 301 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed TDRS 5 satellite. Payloads: Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS)-E/lnertial Upper Stage (lUS), Space Station Heatpipe Advanced Radiator Element (SHARE)-ll, Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet (SSBUV) instrument 03, Optical Communications Through the Shuttle Window (OCTW), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) Calibration Test, Auroral Photography Experiment (APE)-B, Bioserve-lnstrumentation Technology Associates Materials Dispersion Apparatus (BlMDA)-02, Investigations Into Polymer Membrane Processing (IPMP)-03, Protein Crystal Growth Ill Block Il, Space Acceleration Measure-ment System (SAMS), Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE)-02, Tank Pressure Control Experiment (TPCE).
- TDRS 5 - .
Payload: TDRS E. Mass: 2,200 kg (4,800 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: TDRS.
USAF Sat Cat: 21639 . COSPAR: 1991-054B. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
NASA communications; 174 deg W; deployed from STS-43 8/2/91. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 174 deg W in 1991-1999 As of 1 September 2001 located at 174.28 deg W drifting at 0.011 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 171.61W drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
1991 August 10 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Columbia overhauled at Palmdale - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
The orbiter returned to service on 9 February 1992. 62 modifications were made, including replacement of the nose cap; removal of the SEADS and SUMS experiment packages; new Auxiliary Power Units installed; carbon brakes and a drag chute installed; Orbiter 6.0 structural modifications made; AP-101S General Purpose Computers replaced the older AP-101P's; and the Thermal Protection System was reworked.
1991 September 12 - . 23:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-48 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Brown, Mark,
Buchli,
Creighton,
Gemar,
Reightler.
Payload: Discovery F13 / UARS. Mass: 7,854 kg (17,315 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brown, Mark,
Buchli,
Creighton,
Gemar,
Reightler.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-48.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 5.35 days. Decay Date: 1991-09-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 21700 . COSPAR: 1991-063A. Apogee: 580 km (360 mi). Perigee: 575 km (357 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 96.20 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed UARS; conducted materials and biological research. Payloads: Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS), Ascent Particle Monitor (APM)-03, Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experiment (PARE)-01, Protein Crystal Growth (PCG)-ll-2, Middeck Zero-Gravity Dynamics, Experiment (MODE)-01, Investigations Into Polymer Membrane Processing (IPMP)-04, Cosmic Radiation Effects and Activation Monitor (CREAM-02), Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME)-lll-06, Shuttle Activation Monitor (SAM)-03, Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) Calibration Test.
- UARS - .
Payload: Discovery F13 / UARS. Mass: 6,795 kg (14,980 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Class: Earth.
Type: Ionosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: MMS.
Spacecraft: UARS.
Decay Date: 2011-09-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 21701 . COSPAR: 1991-063B. Apogee: 582 km (361 mi). Perigee: 574 km (356 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 96.20 min.
Upper Atmospheric Research Satellite; deployed from STS-48 on 15 Sepetember 1991. It studied the depletion of the ozone layer, confirming that CFCs cause the `ozone hole', and improved models of upper atmosphere chemistry, including studies of methane in the Antarctic, sulphur dioxide from volcanoes, and global wind measurements. Some media hysteria surrounded its reentry on 24 September 2011, but it apparently came down unobserved in the Pacific Ocean east of Hawaii.
1991 November 24 - . 23:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-44 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Gregory,
Hennen,
Henricks,
Musgrave,
Runco,
Voss.
Payload: Atlantis F10 / DSP 16 [IUS]. Mass: 20,242 kg (44,625 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gregory,
Hennen,
Henricks,
Musgrave,
Runco,
Voss.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-44.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 6.95 days. Decay Date: 1991-11-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 21795 . COSPAR: 1991-080A. Apogee: 371 km (230 mi). Perigee: 363 km (225 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
Manned six crew. Deployed Defense Support Program satellite. Payloads: Defense Support Program satellite/ Inertial Upper Stage, Interim Operational Contamination Monitor, Terra Scout, Military Man in Space, Shuttle Activation Monitor, Cosmic Radiation Effects and Activation Monitor, Radiation Monitoring Equipment Ill, Air Force Maui Optical Site Calibration Test, Ultraviolet Plume Instrument, Visual Function Tester 1.
- USA 75 - .
Payload: DSP-1 Block 14 F16. Mass: 2,360 kg (5,200 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 21805 . COSPAR: 1991-080B. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Inclination: 2.50 deg. Period: 1,421.90 min.
DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite, deployed from shuttle STS-44 on 25 November 1991. Only DSP launched from the shuttle before the Challenger disaster moved the payload to the Titan 4. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 130 deg W in 1992; 70 deg E in 1992; 8 deg E in 1999; 40 deg W in 2000. Still in service as of March 2007.
1992 January 22 - . 14:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-42 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bondar,
Grabe,
Hilmers,
Merbold,
Oswald,
Readdy,
Thagard.
Payload: Discovery F14 / GBA-3. Mass: 13,001 kg (28,662 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bondar,
Grabe,
Hilmers,
Merbold,
Oswald,
Readdy,
Thagard.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-42.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 8.05 days. Decay Date: 1992-01-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 21846 . COSPAR: 1992-002A. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 291 km (180 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
Manned seven crew. Carried International Microgravity Laboratory-1. Payloads: International Microgravity Laboratory (lML)-1, getaway special (GAS) bridge with 10 getaway specials, IMAX camera, Gelation of Sols: Applied Microgravity Research (GOSAMR)-1, Investigations Into Polymer Mem-brane Processing (IPMP), Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME)-lll, Student Experiment 81-09: Convection in Zero Gravity, Student Experiment 83-02: Capillary Rise of Liquid Through Granular Porous Media.
- GBA-3 - . Payload: GAS Bridge. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1992-01-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 21846 . COSPAR: 1992-002xx. Apogee: 299 km (185 mi). Perigee: 286 km (177 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
- Spacelab IML-1 - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1992-01-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 21846 . COSPAR: 1992-002xx. Apogee: 299 km (185 mi). Perigee: 286 km (177 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
1992 February 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Discovery OMDP-1 - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Shuttle Discovery undergoes its OMDP-1 Orbiter Maintenance Down Period at the Kennedy Space Center. These are undertaken every 10 to 12 shuttle missions. 70 modifications are made, including addition of a brake chute, structural inspection, and thermal protection system refit.
1992 March 24 - . 13:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-45 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Bolden,
Duffy,
Foale,
Frimout,
Leestma,
Lichtenberg,
Sullivan.
Payload: Atlantis F11 / Atlas 1 Fwd. Mass: 8,020 kg (17,680 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bolden,
Duffy,
Foale,
Frimout,
Leestma,
Lichtenberg,
Sullivan.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-45.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 8.92 days. Decay Date: 1992-04-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 21915 . COSPAR: 1992-015A. Apogee: 294 km (182 mi). Perigee: 282 km (175 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.30 min.
Manned seven crew. Carried ATLAS-1 experimental package. Payloads: Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS)-1, Shuttle Solar Backscat-ter Ultraviolet (SSBUV)-4, Getaway Special Experiment G-229, Space Tissue Loss (STL)-1, Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME)-lIl, Visual Function Tester (VFT)-lI, Cloud Logic To Opti-mize Use of Defense Systems (CLOUDS)-1A, Investigations Into Polymer Membrane Process-ing (IPMP), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX)-Il, Ultraviolet Plume Instrument (UVPl).
- Atlas 1 Fwd - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1992-04-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 21915 . COSPAR: 1992-015xx. Apogee: 293 km (182 mi). Perigee: 283 km (175 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.30 min.
- Atlas 1 Aft - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1992-04-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 21915 . COSPAR: 1992-015xx. Apogee: 293 km (182 mi). Perigee: 283 km (175 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.30 min.
1992 May 7 - . 23:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-49 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Akers,
Brandenstein,
Chilton,
Hieb,
Melnick,
Thornton,
Thuot.
Payload: Endeavour F01 / Intelsat 6 SRM. Mass: 14,786 kg (32,597 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Akers,
Brandenstein,
Chilton,
Hieb,
Melnick,
Thornton,
Thuot.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-49.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 8.89 days. Decay Date: 1992-05-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 21963 . COSPAR: 1992-026A. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 268 km (166 mi). Inclination: 28.30 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Retrieved Intelsat 6 and attached new SRM. First active dual rendezvous of two orbiting spacecraft (Endeavour and Intelsat-Vl). First deployment of a drag chute on the orbiter fleet. Payloads: Intelsat-Vl reboost mission hardware, Assembly of Station by EVA Methods (ASEM), Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) Calibration Test, Ultraviolet Plume Instrument (UVPl).
- MPESS-ASEM - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1992-05-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 21963 . COSPAR: 1992-026xx. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 344 km (213 mi). Inclination: 28.30 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Space shuttle bay Multi Purpose Experiment Support Structure and ASEM Node Carrier, providing stowage for EVA equipment..
- Intelsat Cradle - . Nation: International. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Decay Date: 1992-05-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 21963 . COSPAR: 1992-026xx. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 344 km (213 mi). Inclination: 28.30 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
1992 May 11 - . 20:40 GMT - .
- EVA STS-49-1 - . Crew: Hieb, Thuot. EVA Duration: 0.16 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Hieb, Thuot. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-49. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Attempted capture of Intelsat V1..
1992 May 12 - . 21:05 GMT - .
- EVA STS-49-2 - . Crew: Hieb, Thuot. EVA Duration: 0.23 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Hieb, Thuot. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-49. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Second attempted capture of Intelsat V1..
1992 May 14 - . 21:17 GMT - .
- EVA STS-49-3 - . Crew: Akers, Hieb, Thuot. EVA Duration: 0.35 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Akers, Hieb, Thuot. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-49. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Intelsat V1 finally captured in first three-person spacewalk..
1992 May 15 - .
- EVA STS-49-4 - . Crew: Akers, Thornton. EVA Duration: 0.32 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Akers, Thornton. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-49. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Tested tools and techniques for assembly of the International Space Station..
1992 June 25 - . 16:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-50 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Baker,
Bowersox,
DeLucas,
Dunbar,
Meade,
Richards,
Trinh.
Payload: Columbia F12 / USML-1 / OAST. Mass: 11,153 kg (24,588 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Baker,
Bowersox,
DeLucas,
Dunbar,
Meade,
Richards,
Trinh.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-50.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 13.81 days. Decay Date: 1992-07-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22000 . COSPAR: 1992-034A. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 302 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Carried United States Microgravity Laboratory. First extended-duration mission. Payloads: United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML)-1; Orbital Acceleration Research Experiment (OARE); Investigations Into Polymer Membrane Processing (IPMP), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX)-ll; Ultraviolet Plume Instrument (UVPl) .
- USML-1 - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1992-07-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22000 . COSPAR: 1992-034xx. Apogee: 301 km (187 mi). Perigee: 245 km (152 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1992-07-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22000 . COSPAR: 1992-034xx. Apogee: 301 km (187 mi). Perigee: 245 km (152 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
1992 July 31 - . 13:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-46 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Allen, Andy,
Chang-Diaz,
Hoffman,
Ivins,
Malerba,
Nicollier,
Shriver.
Payload: Atlantis F12 / Eureca 1 / TSS 1. Mass: 12,965 kg (28,582 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Allen, Andy,
Chang-Diaz,
Hoffman,
Ivins,
Malerba,
Nicollier,
Shriver.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-46.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 7.97 days. Decay Date: 1992-08-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 22064 . COSPAR: 1992-049A. Apogee: 437 km (271 mi). Perigee: 425 km (264 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.20 min.
Manned seven crew. Deployed Eureca-1; failed to deploy Italian tether probe TSS-1. Payloads: Tethered Satellite System (TSS)-1; European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA)-1L; Evaluation of Oxygen Integration with Materials (EOlM)-lll/ Thermal Energy Management Processes (TEMP)-2A; Consortium for Materials Development In Space Complex Autonomous Payloads (CONCAP)-ll and Ill; IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC); Limited Duration Space Environment Candidate Materials Exposure (LDCE); Pituitary Growth Hormone Cell Function (PHCF); Ultravio-let Plume Instrument (UVPl).
- TSS-1 PLT - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1992-08-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 22064 . COSPAR: 1992-049xx. Apogee: 233 km (144 mi). Perigee: 226 km (140 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
- Eureca-1 - .
Payload: Atlantis F12 / Eureca 1 / TSS 1. Mass: 4,491 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: ESA.
Class: Materials.
Type: Materials science satellite. Spacecraft: Eureca.
Decay Date: 1993-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22065 . COSPAR: 1992-049B. Apogee: 509 km (316 mi). Perigee: 484 km (300 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 94.60 min.
Microgravity experiments; deployed from STS-46 8/2/92; retrieved by STS-57; European Retrievable Carrier. EURECA is a European scientific and technology mission, launched by the US Space Transportation System. The spacecraft is scheduled to be retrieved likewise by the US/STS in late spring/early summer 1993. Designator ESA/92/01. Frequency plan: 2053.4583/22 30 MHz, 28 GHz/ 18 GHz (data-relay via Olympus).
- EOIM-3/TEMP2A-3 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EOIM. Decay Date: 1992-08-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 22064 . COSPAR: 1992-049xx. Apogee: 233 km (144 mi). Perigee: 226 km (140 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
- TSS-1 MPESS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1992-08-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 22064 . COSPAR: 1992-049xx. Apogee: 233 km (144 mi). Perigee: 226 km (140 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
1992 September 12 - . 14:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-47 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Apt,
Brown,
Davis,
Gibson,
Jemison,
Lee,
Mohri.
Payload: Endeavour F02 / Spacelab-J. Mass: 12,772 kg (28,157 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Apt,
Brown,
Davis,
Gibson,
Jemison,
Lee,
Mohri.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-47.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 7.94 days. Decay Date: 1992-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 22120 . COSPAR: 1992-061A. Apogee: 310 km (190 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned seven crew. Carried Spacelab-J with microgravity and biology experiments. Payloads: Spacelab-J, nine getaway special canister experiments, Israel Space Agency Investigation About Hornets (ISAIAH), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II, Solid Surface Combus-tion Experiment (SSCE).
- GAS Bridge - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1992-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 22120 . COSPAR: 1992-061xx. Apogee: 308 km (191 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
- Spacelab J LM - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1992-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 22120 . COSPAR: 1992-061xx. Apogee: 308 km (191 mi). Perigee: 297 km (184 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
1992 October 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Atlantis OMDP-1 - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Shuttle Atlantis undergoes its OMDP-1 Orbiter Maintenance Down Period at the Palmdale, returning to service in May 1994. These are undertaken every 10 to 12 shuttle missions. Modifications made include: nose wheel steering changes, EDO cargo pallet provisions, and Mir ODS docking system fitting. Provisions for the Long Duration Orbiter 28-day pallet are installed, and 331 Master Change Requests are implemented.
1992 October 22 - . 17:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-52 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Baker, Mike,
Jernigan,
MacLean,
Shepherd,
Veach,
Wetherbee.
Payload: Columbia F13 / Lageos 2 [Iris] / CTA. Mass: 9,106 kg (20,075 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Baker, Mike,
Jernigan,
MacLean,
Shepherd,
Veach,
Wetherbee.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-52.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 9.87 days. Decay Date: 1992-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22194 . COSPAR: 1992-070A. Apogee: 307 km (190 mi). Perigee: 304 km (188 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Deployed Lageos 2, CTA. Payloads: Laser Geodynamic Satellite (LAGEOS) II/ Italian Research Interim Stage (IRIS), Canadian Experiments (CANEX) 2, United States Micro-gravity Payload (USMP) 1, Attitude Sensor Pack-age (ASP), Tank Pressure Control Experiment (TPCE), Physiological Systems Experiment (PSE), Heat Pipe Performance (HPP) experiment, Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG), Shuttle Plume Impingement Experiment (SPIE), Commercial Materials ITA Experiment (CMIX), Crystals by Vapor Transport Experiment (CVTE).
- USMP-1 Fwd - . Payload: MPESS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1992-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22194 . COSPAR: 1992-070xx. Apogee: 215 km (133 mi). Perigee: 206 km (128 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
- USMP-1 Aft - . Payload: MPESS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1992-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22194 . COSPAR: 1992-070xx. Apogee: 215 km (133 mi). Perigee: 206 km (128 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
- CTA - . Payload: Columbia F13 / Lageos 2 [Iris] / CTA. Mass: 82 kg (180 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: CSA. Program: STS. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: CTA. Decay Date: 1992-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22214 . COSPAR: 1992-070C. Apogee: 219 km (136 mi). Perigee: 212 km (131 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Canadian Target Assembly; deployed from STS-52 10/22/92. .
- Lageos 2 - . Payload: Columbia F13 / Lageos 2 [Iris] / CTA. Mass: 400 kg (880 lb). Nation: Italy. Agency: ASI. Class: Earth. Type: Geodetic satellite. Spacecraft: Lageos. USAF Sat Cat: 22195 . COSPAR: 1992-070B. Apogee: 5,952 km (3,698 mi). Perigee: 5,616 km (3,489 mi). Inclination: 52.70 deg. Period: 222.50 min. 60 cm diameter sphere with laser reflectors; deployed from STS-52 10/23/92..
1992 November 8 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Columbia OMDP-1 - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Shuttle Columbia begins its OMDP-1 Orbiter Maintenance Down Period at the Palmdale, returning to service in 1995 for the STS-73 mission. These are undertaken every 10 to 12 shuttle missions. Modifications made included a complete mid-life refurbishment, corrosion control on the wing leading edge spar, and implementation of 96 Master Change Requests.
1992 December 2 - . 13:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-53 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bluford,
Cabana,
Clifford,
Voss,
Walker, Dave.
Payload: Discovery F15 / USA-89. Mass: 11,868 kg (26,164 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bluford,
Cabana,
Clifford,
Voss,
Walker, Dave.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-53.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 7.31 days. Decay Date: 1992-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22259 . COSPAR: 1992-086A. Apogee: 376 km (233 mi). Perigee: 365 km (226 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 92.00 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed classified military satellite USA 89. The ODERACS payload was unable to be deployed because of payload equipment malfunction. Payloads: Department of Defense (DOD)1; Glow Experiment/Cryogenic Heat Pipe Experiment Payload (GCP); Orbital Debris Radar Calibration System (ODERACS); Battlefield Laser Acquisition Sensor Test (BLAST); Cloud Logic To Optimize Use of Defense Systems (CLOUDS) 1A; Cosmic Radiation Effects and Activation Monitor (CREAM); Fluid Acquisition and Resupply Equipment (FARE); Hand-held, Earth-oriented, Real-time, Cooperative, User-friendly, Location-targeting and Environmental System (HER-CULES); Microencapsulation in Space (MIS)-1; Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME) III; Spare Tissue Loss (STL); Visual Function Tester (VFT)2.
- ODERACS A - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1992-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22259 . COSPAR: 1992-086xx. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 317 km (196 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.90 min.
- ODERACS B - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1992-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22259 . COSPAR: 1992-086xx. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 317 km (196 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.90 min.
- ODERACS C - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1992-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22259 . COSPAR: 1992-086xx. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 317 km (196 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.90 min.
- ODERACS D - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1992-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22259 . COSPAR: 1992-086xx. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 317 km (196 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.90 min.
- ODERACS F - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1992-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22259 . COSPAR: 1992-086xx. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 317 km (196 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.90 min.
- USA 89 - . Payload: SDS B-3. Mass: 5,900 kg (13,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 22518 . COSPAR: 1992-086B. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min. Deployed from STS-53 12/2/92..
- ODERACS E - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1992-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 22259 . COSPAR: 1992-086xx. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 317 km (196 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.90 min.
1993 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle ASRM.
- Shuttle using Advanced Solid Rocket Motors (development cancelled 1993). - . Nation: USA.
1993 January 13 - . 13:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-54 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Casper,
Harbaugh,
Helms,
McMonagle,
Runco.
Payload: Endeavour F03 / TDRS 6 [IUS]. Mass: 21,156 kg (46,640 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Casper,
Harbaugh,
Helms,
McMonagle,
Runco.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-54.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 5.98 days. Decay Date: 1993-01-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 22313 . COSPAR: 1993-003A. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 302 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Manned five crew. Deployed TDRSS 6. Payloads: Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS)-F/Inertial Upper Stage (IUS); Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer (DXS); Chromosome and Plant Cell Division in Space (CHROMEX); Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGBA) A; Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experiment (PARE) 02; Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE).
- TDRS 6 - .
Payload: TDRS F. Mass: 2,530 kg (5,570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: TDRS.
USAF Sat Cat: 22314 . COSPAR: 1993-003B. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.70 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
NASA communications; deployed from STS-54 1/13/93. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 150 deg W in 1993; 138 deg W in 1993; 46 deg W in 1994-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 46.99 deg W drifting at 0.017 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 173.51W drifting at 0.006E degrees per day.
1993 January 17 - .
- EVA STS-54-1 - . Crew: Harbaugh, Runco. EVA Duration: 0.18 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Harbaugh, Runco. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-54. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Tested tools and techniques for extravehicular activity..
1993 March 22 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Columbia Pad Abort - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Flight: STS-55.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
The countdown for Columbia's launch was halted by on-board computers at T-3 seconds following a problem with purge pressure readings in the oxidizer preburner on main engine #2 Columbia's three main engines were replaced on the launch pad, and the flight was rescheduled behind Discovery's launch on STS-56. Columbia finally launched on April 26, 1993.
1993 April 8 - . 05:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-56 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Cameron,
Cockrell,
Foale,
Ochoa,
Oswald.
Payload: Discovery F16 / Spartan 201-F1 / Atlas-2. Mass: 7,441 kg (16,404 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Cameron,
Cockrell,
Foale,
Ochoa,
Oswald.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-56.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 9.26 days. Decay Date: 1993-04-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 22621 . COSPAR: 1993-023A. Apogee: 299 km (185 mi). Perigee: 291 km (180 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
Manned five crew. Carried Atlas-2; deployed and retrieved Spartan 201. Payloads: Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS) 2, Shuttle Solar Backscat-ter Ultraviolet (SSBUV) A, Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy (SPARTAN) 201 (Solar Wind Generation Experi-ment), Solar Ultraviolet Experiment (SUVE), Commercial Material Dispersion Apparatus (CMIX), Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experiment (PARE), Hand-held, Earth-oriented, Real-time, Cooperative, User-friendly, Location-targeting, and Environmental System (HER-CULES), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II, Space Tissue Loss (STL), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS), Cosmic Radiation Effects and Activation Monitor (CREAM), Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME) III.
- Atlas-2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1993-04-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 22621 . COSPAR: 1993-023xx. Apogee: 293 km (182 mi). Perigee: 280 km (170 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
- SPTN-SFSS - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads.
Spacecraft: Spartan.
Decay Date: 1993-04-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 22621 . COSPAR: 1993-023xx. Apogee: 293 km (182 mi). Perigee: 280 km (170 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.20 min.
Spartan Flight Support Structure was an MPESS class cross-bay truss structure on which Spartan 204 was mounted. The Spartan satellites were small free flyers deployed by the RMS robot arm for a couple of days and then retrieved. SPTN-204 carried NRL's FUVIS Far Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph which was used to study the Shuttle environment and make astronomical observations. This was the first Spartan mission to be sponsored by the USAF Space Test Program rather than NASA.
- Spartan 201 - . Mass: 1,289 kg (2,841 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: STS. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1993-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 22623 . COSPAR: 1993-023B. Apogee: 298 km (185 mi). Perigee: 291 km (180 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min. Studied solar corona and galaxy; deployed from STS-56 4/11/93; Shuttle Point Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy; retrieved 4/13/93..
1993 April 26 - . 14:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-55 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Harris, Henricks, Nagel, Precourt, Ross, Schlegel, Walter. Payload: Columbia F14/USS/Spacelab D-2 LM. Mass: 12,185 kg (26,863 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Harris, Henricks, Nagel, Precourt, Ross, Schlegel, Walter. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-55. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 9.99 days. Decay Date: 1993-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 22640 . COSPAR: 1993-027A. Apogee: 312 km (193 mi). Perigee: 304 km (188 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.70 min. Manned seven crew. Carried German Spacelab-D2. Payloads: Spacelab D-2 with long module, unique support structure (USS), and Reaction Kinetics in Glass Melts (RKGM) getaway special, Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II..
- USS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USS. COSPAR: 1993-027xx.
- Spacelab D-2 LM - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. COSPAR: 1993-027xx.
1993 June 21 - . 13:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-57 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Currie,
Duffy,
Grabe,
Low,
Voss, Janice,
Wisoff.
Payload: Endeavour F04 / GBA-5. Mass: 8,931 kg (19,689 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Currie,
Duffy,
Grabe,
Low,
Voss, Janice,
Wisoff.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-57.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 9.99 days. Decay Date: 1993-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22684 . COSPAR: 1993-037A. Apogee: 471 km (292 mi). Perigee: 402 km (249 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.30 min.
Manned six crew. Carried Spacehab 1; retrieved Eureca-1 spacecraft. Payloads: Spacehab 01, retrieval of European Retriev-able Carrier (EURECA) Satellite, Superfluid Helium On-Orbit Transfer (SHOOT), Consortium for Materials Development in Space Complex Autonomous Payload (CONCAP)-IV, Fluid Acquisition and Resupply Experiment (FARE), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II, Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS), GAS bridge assembly with 12 getaway special payloads.
- GBA-5 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1993-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22684 . COSPAR: 1993-037xx. Apogee: 472 km (293 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.20 min.
- Spacehab SH-01 - . Payload: Spacehab 1. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1993-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22684 . COSPAR: 1993-037xx. Apogee: 472 km (293 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.20 min.
- SHOOT - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SHOOT. Decay Date: 1993-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22684 . COSPAR: 1993-037xx. Apogee: 472 km (293 mi). Perigee: 391 km (242 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.20 min. Superfluid Helium On-Orbit Transfer Flight Demonstration, an experiment carried on the space shuttle STS-57 mission in June 1993. The experiment transferred a superfluid between two dewars in a low gravity environment at different flow rates..
1993 August 12 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Discovery Pad Abort - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Flight: STS-51.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
The countdown for Discovery's third launch attempt ended at the T-3 second mark when on-board computers detected the failure of one of four sensors in main engine #2 which monitor the flow of hydrogen fuel to the engine. All of Discovery's main engines were ordered replaced on the launch pad, delaying the Shuttle's fourth launch attempt until September 12, 1993.
1993 September 12 - . 11:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-51 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bursch,
Culbertson,
Newman,
Readdy,
Walz.
Payload: Discovery F17 / ACTS [TOS-21H] / Orfeus-SPAS 01. Mass: 19,360 kg (42,680 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bursch,
Culbertson,
Newman,
Readdy,
Walz.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 9.84 days. Decay Date: 1993-09-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 22795 . COSPAR: 1993-058A. Apogee: 308 km (191 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Deployed and retrieved Orfeus-SPAS. During the EVA conducted tests in support of the Hubble Space Telescope first servicing mission and future EVAs, including Space Station assembly and maintenance. First night landing at KSC. Payloads: Advanced Communication Technology Sat-ellite (ACTS)/Transfer Orbit Stage (TOS), Orbiting Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer—Shuttle Pallet Satellite (ORFEUS-SPAS) with Remote IMAX Camera System (RICS), Limited Duration Space Environ-ment Candidate Materials Exposure (LDCE) (Beam Configuration C), Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG Block II), Chromosome and Plant Cell Division in Space (CHROMEX), High Resolution Shuttle Glow Spectroscopy-A (HRSGS-A), Auroral Photography Experiment-B (APE-B), Investigation into Polymer Membrane Processing (IPMP), Radiation Monitoring Equip-ment (RME-III), Air Force Maui Optical Site Cal-ibration Test (AMOS), IMAX In-Cabin Camera.
- ORFEUS-SPAS - . Payload: ASTRO-SPAS 01. Mass: 3,202 kg (7,059 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: DARA. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SPAS. Decay Date: 1993-09-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 22798 . COSPAR: 1993-058C. Apogee: 331 km (205 mi). Perigee: 301 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.90 min. Deployed from STS-51..
- ACTS - .
Payload: Discovery F17 / ACTS [TOS-21H] / Orfeus-SPAS 01. Mass: 2,767 kg (6,100 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Cleveland.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 4000.
USAF Sat Cat: 22796 . COSPAR: 1993-058B. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,767 km (22,224 mi). Inclination: 3.20 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
NASA experimental communications; Advanced Communications Technology Satellite; deployed from STS-51 9/12/93; 100 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 100 deg W in 1993-1999 105 deg W in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 105.36 deg W drifting at 0.007 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 105.14W drifting at 0.004W degrees per day.
1993 September 16 - . 08:40 GMT - .
- EVA STS-51-1 - . Crew: Newman, Walz. EVA Duration: 0.30 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Newman, Walz. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-51. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Tested tools and techniques for extravehicular activity..
1993 October 18 - . 14:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-58 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Blaha, Fettman, Lucid, McArthur, Searfoss, Seddon, Wolf. Payload: Columbia F15 / EDO. Mass: 10,517 kg (23,186 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Blaha, Fettman, Lucid, McArthur, Searfoss, Seddon, Wolf. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-58. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 14.01 days. Decay Date: 1993-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22869 . COSPAR: 1993-065A. Apogee: 294 km (182 mi). Perigee: 284 km (176 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.30 min. Biological, microgravity experiments aboard Spacelab 2. Payloads: Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS) 2, Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II..
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1993-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22869 . COSPAR: 1993-065xx. Apogee: 277 km (172 mi). Perigee: 259 km (160 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
- Spacelab SLS 2 LM - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1993-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22869 . COSPAR: 1993-065xx. Apogee: 277 km (172 mi). Perigee: 259 km (160 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
1993 December 2 - . 09:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-61 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Akers,
Bowersox,
Covey,
Hoffman,
Musgrave,
Nicollier,
Thornton.
Payload: Endeavour F05 / FSS. Mass: 8,011 kg (17,661 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Akers,
Bowersox,
Covey,
Hoffman,
Musgrave,
Nicollier,
Thornton.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-61.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 10.83 days. Decay Date: 1993-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 22917 . COSPAR: 1993-075A. Apogee: 576 km (357 mi). Perigee: 291 km (180 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.30 min.
Manned seven crew. Hubble repair mission. Conducted the most EVAs (5) on a Space Shuttle Flight to that date. Payloads: Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Servicing Mission (SM) 1, IMAX Camera, IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS).
- FSS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: FSS. Decay Date: 1993-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 22917 . COSPAR: 1993-075xx. Apogee: 600 km (370 mi). Perigee: 592 km (367 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.60 min.
- ORUC - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1993-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 22917 . COSPAR: 1993-075xx. Apogee: 600 km (370 mi). Perigee: 592 km (367 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.60 min.
- SAC - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Second Axial Carrier. Decay Date: 1993-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 22917 . COSPAR: 1993-075xx. Apogee: 600 km (370 mi). Perigee: 592 km (367 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.60 min.
1994 February 3 - . 12:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-60 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bolden,
Chang-Diaz,
Davis,
Krikalyov,
Reightler,
Sega.
Backup Crew: Titov, Vladimir.
Payload: Discovery F18 / GBA-6. Mass: 13,006 kg (28,673 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-60.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 8.30 days. Decay Date: 1994-02-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 22977 . COSPAR: 1994-006A. Apogee: 351 km (218 mi). Perigee: 348 km (216 mi). Inclination: 56.40 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
Deployed ODERACS A-F, Bremsat, carried Wake Shield Facility. Payloads: Wake Shield Facility (WSF) 1 and SPACEHAB 02. Getaway special bridge assembly experiments: Capillary Pumped Loop (CAPL), Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Spheres (ODERACS), University of Bremen Satellite (BREMSAT), G-514, G-071, and G-536. Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II; Auroral Photography Experiment (APE-B).
- ODERACS A - . Payload: Discovery F18 / WSF 1 / BremSat 1 / ODERACS A, .... Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1994-10-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 22990 . COSPAR: 1994-006B. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 327 km (203 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.30 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Sphere; deployed from STS-60. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- ODERACS E - . Payload: Discovery F18 / WSF 1 / BremSat 1 / ODERACS A, .... Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1995-03-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 22994 . COSPAR: 1994-006F. Apogee: 356 km (221 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Sphere; deployed from STS-60. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- BremSat 1 - . Payload: Discovery F18 / WSF 1 / BremSat 1 / ODERACS A, .... Mass: 63 kg (138 lb). Nation: Germany. Agency: Bremen, DARA. Class: Technology. Type: Re-entry test vehicle. Spacecraft: BremSat. Decay Date: 1995-02-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 22998 . COSPAR: 1994-006H. Apogee: 160 km (90 mi). Perigee: 156 km (96 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 87.70 min. Atomic oxygen, dust particle, microgravity, reentry experiments. .
- ODERACS F - . Payload: Discovery F18 / WSF 1 / BremSat 1 / ODERACS A, .... Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1995-02-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 22995 . COSPAR: 1994-006G. Apogee: 356 km (221 mi). Perigee: 338 km (210 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Sphere; deployed from STS-60. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- ODERACS C - . Payload: Discovery F18 / WSF 1 / BremSat 1 / ODERACS A, .... Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1994-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 22992 . COSPAR: 1994-006D. Apogee: 353 km (219 mi). Perigee: 329 km (204 mi). Inclination: 56.90 deg. Period: 91.35 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Sphere; deployed from STS-60. .
- ODERACS D - . Payload: Discovery F18 / WSF 1 / BremSat 1 / ODERACS A, .... Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1994-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 22993 . COSPAR: 1994-006E. Apogee: 353 km (219 mi). Perigee: 329 km (204 mi). Inclination: 56.90 deg. Period: 91.35 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Sphere; deployed from STS-60. .
- GBA-6 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1994-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 22977 . COSPAR: 1994-006xx. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
- Wake Shield Facility - . Payload: WSF. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: WSF. Decay Date: 1994-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 22977 . COSPAR: 1994-006xx. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
- Spacehab SH-02 - . Payload: Spacehab 2. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1994-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 22977 . COSPAR: 1994-006xx. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
- ODERACS B - . Payload: Discovery F18 / WSF 1 / BremSat 1 / ODERACS A, .... Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1994-10-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 22991 . COSPAR: 1994-006C. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 332 km (206 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Sphere; deployed from STS-60. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1994 March 4 - . 13:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-62 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Allen, Andy,
Casper,
Gemar,
Ivins,
Thuot.
Payload: Columbia F16 / USMP-2 / OAST-2. Mass: 8,870 kg (19,550 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Allen, Andy,
Casper,
Gemar,
Ivins,
Thuot.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-62.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 13.97 days. Decay Date: 1994-03-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 23025 . COSPAR: 1994-015A. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 246 km (152 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
Carried USMP-2, OAST-2, SAMPIE, TES, EISG. Payloads: United States Microgravity Payload (USMP) 2, Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology (OAST) 2, Dexterous End Effector (DEE), Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet/A (SSBUV/A), Limited-Duration Space Environment Candidate Material Exposure (LDCE), Advanced Protein Crystal Growth (APCG), Physiological Systems Experiment (PSE), Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG), Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGBA), Auroral Photography Experiment Phase B (APE-B), Middeck Zero-Gravity Dynamics Experiment (MODE), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) Calibration Test, Bioreactor Demonstration System A.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1994-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23025 . COSPAR: 1994-015xx. Apogee: 253 km (157 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
- OAST-2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: OAST. Decay Date: 1994-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23025 . COSPAR: 1994-015xx. Apogee: 253 km (157 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
- USMP-2 Aft - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1994-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23025 . COSPAR: 1994-015xx. Apogee: 253 km (157 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
- USMP-2 Fwd - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1994-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23025 . COSPAR: 1994-015xx. Apogee: 253 km (157 mi). Perigee: 200 km (120 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
1994 April 9 - . 11:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-59 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Apt,
Chilton,
Clifford,
Godwin,
Gutierrez,
Jones.
Payload: Endeavour F06 / MAPS. Mass: 12,490 kg (27,530 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Apt,
Chilton,
Clifford,
Godwin,
Gutierrez,
Jones.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-59.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 11.24 days. Decay Date: 1994-04-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 23042 . COSPAR: 1994-020A. Apogee: 204 km (126 mi). Perigee: 194 km (120 mi). Inclination: 56.90 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
Carried SIR-C SAR radar. Payloads: Space Radar Laboratory (SRL) 1; Consortium for Materials Development in Space Complex Autonomous Payload (CONCAP) IV; three getaway special (GAS) payloads; Space Tissue Loss (STL) A, B; Visual Function Tester (VFT) 4; Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II.
- MAPS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: MAPS. Decay Date: 1994-04-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23042 . COSPAR: 1994-020xx. Apogee: 211 km (131 mi). Perigee: 202 km (125 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Air pollution experiment carried in shuttle bay..
- SRL-1 - . Payload: SRL PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1994-04-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23042 . COSPAR: 1994-020xx. Apogee: 211 km (131 mi). Perigee: 202 km (125 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
1994 July 8 - . 16:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-65 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Cabana,
Chiao,
Halsell,
Hieb,
Mukai,
Thomas,
Walz.
Backup Crew: Favier.
Payload: Columbia F17 / EDO. Mass: 10,811 kg (23,834 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-65.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 14.75 days. Decay Date: 1994-07-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 23173 . COSPAR: 1994-039A. Apogee: 249 km (154 mi). Perigee: 239 km (148 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
Carried IML-2; microgravity, biology experiments. Payloads: International Microgravity Laboratory (IML) 2, Orbital Acceleration Research Experiment (OARE), Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS), Military Applications of Ship Tracks (MAST), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX).
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1994-07-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 23173 . COSPAR: 1994-039xx. Apogee: 249 km (154 mi). Perigee: 239 km (148 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
- Spacelab IML 2 - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1994-07-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 23173 . COSPAR: 1994-039xx. Apogee: 249 km (154 mi). Perigee: 239 km (148 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
1994 August 18 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Shuttle Endeavour Pad Abort - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Flight: STS-68.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
The countdown for Endeavour's first launch attempt ended 1.9 seconds before liftoff when on-board computers detected higher than acceptable readings in one channel of a sensor monitoring the discharge temperature of the high pressure oxidizer turbopump in main engine #3. A test firing of the engine at the Stennis Space Center in Mississippi on September 2nd confirmed that a slight drift in a fuel flow meter in the engine caused a slight increase in the turbopump's temperature. The test firing also confirmed a slightly slower start for main engine #3 during the pad abort, which could have contributed to the higher temperatures. After Endeavour was brought back to the Vehicle Assembly Building to be outfitted with three replacement engines, NASA managers set October 2nd as the date for Endeavour's second launch attempt.
1994 September 9 - . 22:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-64 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Hammond,
Helms,
Lee,
Linenger,
Meade,
Richards.
Payload: Discovery F19 / Spartan / LITE. Mass: 9,260 kg (20,410 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Hammond,
Helms,
Lee,
Linenger,
Meade,
Richards.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-64.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 10.95 days. Decay Date: 1994-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23251 . COSPAR: 1994-059A. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 233 km (144 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.30 min.
Payloads: Lidar In-Space Technology Experiment (LITE), Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy (SPARTAN) 201-II, Robot-Operated Materials Processing System (ROMPS), Shuttle Plume Impingement Flight Experiment (SPIFEX), getaway special (GAS) bridge assembly with ten GAS experiments, Trajectory Control Sensor (TCS), Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER), Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE), Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) III, Radiation Monitoring Experiment (RME) III, Military Applications of Ship Tracks (MAST), Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II, Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) Calibration Test.
- Spartan 201 - . Mass: 1,288 kg (2,839 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: STS. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1994-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23253 . COSPAR: 1994-059B. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 252 km (156 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.68 min. Deployed from STS-64 9/13/94; retrieved 9/15/94; solar studies..
- GBA-7 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1994-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23251 . COSPAR: 1994-059xx. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 233 km (144 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.30 min.
- LITE - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1994-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23251 . COSPAR: 1994-059xx. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 233 km (144 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Lidar In-Space Technology Experiment, carried in shuttle payload bay. Measured the Earth's cloud cover and tracked particles in the atmosphere..
1994 September 16 - . 14:42 GMT - .
- EVA STS-64-1 - . Crew: Lee, Meade. EVA Duration: 0.29 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Lee, Meade. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-64. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Tested SAFER emergency manoeuvring backpack..
1994 September 30 - . 11:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-68 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Baker, Mike,
Bursch,
Jones,
Smith, Steven,
Wilcutt,
Wisoff.
Payload: Endeavour F07 / SRL-2. Mass: 12,510 kg (27,570 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Baker, Mike,
Bursch,
Jones,
Smith, Steven,
Wilcutt,
Wisoff.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-68.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 11.24 days. Decay Date: 1994-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23285 . COSPAR: 1994-062A. Apogee: 212 km (131 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
Carried SIR-C SAR. Landed at Edwards Air Force Base on October 11. Payloads: Space Radar Laboratory (SRL) 2, five Getaway Special payloads, Chromosome and Plant Cell Division in Space (CHROMEX) 5, Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) 01, Cosmic Radiation Effects and Activation Monitor (CREAM), Military Application of Ship Tracks (MAST), Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG).
- SRL-2 - . Payload: SRL PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1994-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23285 . COSPAR: 1994-062xx. Apogee: 212 km (131 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Space Radar Laboratory (SRL) 2..
- MAPS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: MAPS. Decay Date: 1994-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23285 . COSPAR: 1994-062xx. Apogee: 212 km (131 mi). Perigee: 199 km (123 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
1994 November 3 - . 16:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-66 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Brown,
Clervoy,
McMonagle,
Ochoa,
Parazynski,
Tanner.
Payload: Atlantis F13 / Atlas-3. Mass: 10,544 kg (23,245 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brown,
Clervoy,
McMonagle,
Ochoa,
Parazynski,
Tanner.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-66.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 10.94 days. Decay Date: 1994-11-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 23340 . COSPAR: 1994-073A. Apogee: 301 km (187 mi). Perigee: 284 km (176 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
Carried Atlas-3 laboratory; deployed and retrieved CRISTA-SPAS. Payloads: Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS) 3, Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmo-sphere (CRISTA)-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS) 1, Experiment of the Sun for Complement-ing the ATLAS Payload for Education (ESCAPE) II, Inter-Mars Tissue Equivalent Proportional Counter (ITEPC), Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet (SSBUV) A, Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experiment (PARE/NIH-R), Protein Crystal Growth (PCG-TES and PCG-STES), Space Tissue Loss (STL/NIH-C-A), Shuttle Acceleration Measurement System (SAMS), Heat Pipe Performance (HPP).
- Atlas-3 - . Payload: Atlas-3 PLT/Igloo. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1994-11-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 23340 . COSPAR: 1994-073xx. Apogee: 301 km (187 mi). Perigee: 284 km (176 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
- CRISTA-SPAS - . Mass: 3,260 kg (7,180 lb). Nation: Germany. Agency: DLR. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SPAS. Decay Date: 1994-11-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 23341 . COSPAR: 1994-073B. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 294 km (182 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.55 min. Released by STS-66 11/4/94; retrieved 11/12/95; atmospheric research..
1995 February 3 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- ODERACS IIF - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1996-11-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 23476 . COSPAR: 1995-004H. Apogee: 258 km (160 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 98.30 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Reentered? .
- STS-63 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Collins, Eileen,
Foale,
Harris,
Titov, Vladimir,
Voss, Janice,
Wetherbee.
Backup Crew: Krikalyov.
Payload: Discovery F20 / Spacehab SH03 / CGP / ODERACS. Mass: 8,641 kg (19,050 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-18 Mir LD-4,
Soyuz TM-20,
STS-63.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 8.27 days. Decay Date: 1995-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23469 . COSPAR: 1995-004A. Apogee: 342 km (212 mi). Perigee: 275 km (170 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
Deployed ODERACS 2A-2E; deployed and retrieved Spartan 204. Discovery rendezvoused with Russia's space station, Mir, to a distance of 11 m and performed a fly-around, but did not dock with Mir. Payloads: SPACEHAB 03, Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy (SPARTAN) 204, Cryo Systems Experiment (CSE)/GLO-2 Experi-ment Payload (CGP)/Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Spheres (ODERACS) 2, Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE), Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS), IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC)
- ODERACS 2E - . Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1995-02-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 23475 . COSPAR: 1995-004G. Apogee: 270 km (160 mi). Perigee: 261 km (162 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.80 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration spheres; deployed from STS 63 2/4/95. Reentered Feb 27 .
- ODERACS 2D - . Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1995-03-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 23474 . COSPAR: 1995-004F. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 246 km (152 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 89.60 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration spheres; deployed from STS 63 2/4/95. Reentered Mar 2 .
- Spartan 204 - . Mass: 1,195 kg (2,634 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRL. Program: STS. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1995-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23470 . COSPAR: 1995-004B. Apogee: 389 km (241 mi). Perigee: 388 km (241 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.30 min. Retrievable payload to observe galactic dust in far UV; deployed from STS 63 2/7/95, retrieved 2/9/95..
- ODERACS 2C - . Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1996-02-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 23473 . COSPAR: 1995-004E. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration spheres; deployed from STS 63 2/4/95. Reentered? .
- ODERACS 2A - . Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1996-03-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 23471 . COSPAR: 1995-004C. Apogee: 280 km (170 mi). Perigee: 268 km (166 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 87.10 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration spheres; deployed from STS 63 2/4/95..
- Spacehab SH-03 - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1995-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23469 . COSPAR: 1995-004xx. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 386 km (239 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
- CGP/ODERACS - . Payload: HH-M. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1995-02-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 23469 . COSPAR: 1995-004xx. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 386 km (239 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
- ODERACS 2B - . Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: ODERACS. Decay Date: 1995-09-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23472 . COSPAR: 1995-004D. Apogee: 179 km (111 mi). Perigee: 177 km (109 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.10 min. Orbital Debris Radar Calibration spheres; deployed from STS 63 2/4/95. Reentered Sep 29 .
1995 February 9 - . 11:56 GMT - .
- EVA STS-63-1 - . Crew: Foale, Harris. EVA Duration: 0.19 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Foale, Harris. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-63. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Tested tools and techniques for extravehicular activity..
1995 March 2 - . 06:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-67 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Durrance,
Gregory, William,
Grunsfeld,
Jernigan,
Lawrence,
Oswald,
Parise.
Payload: Endeavour F08 / ASTRO-2 Fwd. Mass: 13,116 kg (28,915 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Durrance,
Gregory, William,
Grunsfeld,
Jernigan,
Lawrence,
Oswald,
Parise.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-67.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 16.63 days. Decay Date: 1995-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23500 . COSPAR: 1995-007A. Apogee: 305 km (189 mi). Perigee: 305 km (189 mi). Inclination: 28.45 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
Carried Astro 2 astronomy payload with 3 UV telescopes.(attached to Endeavour).Payloads: Ultraviolet Astronomy (ASTRO) 2; Middeck Active Control Experiment (MACE); Protein Crystal Growth—Thermal Enclosure System (PCG-TES) 03; Protein Crystal Growth—Single-Locker Thermal Enclosure System (PCG-STES) 02; Commercial Materials Dispersion Apparatus Minilab/Instrumentation Technology Associates, Inc. Experiments (CMIX) 03; Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II; two getaway special experiments.
- ASTRO-2 Fwd - . Payload: ASTRO-2 PLT + Igloo. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1995-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23500 . COSPAR: 1995-007xx. Apogee: 363 km (225 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1995-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23500 . COSPAR: 1995-007xx. Apogee: 363 km (225 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
- ASTRO-2 Aft - . Payload: ASTRO-2 PLT. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1995-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23500 . COSPAR: 1995-007xx. Apogee: 363 km (225 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
1995 June 27 - . 19:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-71 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Baker,
Budarin,
Dunbar,
Gibson,
Harbaugh,
Precourt,
Solovyov.
Backup Crew: Onufrienko,
Usachyov.
Payload: Atlantis F14 / Spacelab-Mir LM. Mass: 12,191 kg (26,876 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-21,
STS-71,
STS-71 Mir EO-19.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 9.81 days. Decay Date: 1995-07-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 23600 . COSPAR: 1995-030A. Apogee: 342 km (212 mi). Perigee: 342 km (212 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
Mir Expedition EO-19. Transferred Budarin, Solovyov to Mir, returned Soyuz TM-21 crew to Earth. After undocking from Mir on July 4, Atlantis spent several days on orbit, carrying out medical research work with the Spacelab-Mir module in the cargo bay. Payloads: Shuttle/Mir Mission 1, Spacelab-Mir, IMAX camera, Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX).
- Spacelab-Mir LM - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Flight: Soyuz TM-21, STS-71, STS-71 Mir EO-19. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1995-07-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 23600 . COSPAR: 1995-030xx. Apogee: 396 km (246 mi). Perigee: 48 km (29 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-21, STS-71, STS-71 Mir EO-19. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1995-07-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 23600 . COSPAR: 1995-030xx. Apogee: 396 km (246 mi). Perigee: 48 km (29 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.90 min.
1995 July 13 - . 13:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-70 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Currie,
Henricks,
Kregel,
Thomas,
Weber, Mary.
Payload: Discovery F21 / TDRS 7 [IUS]. Mass: 20,159 kg (44,442 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Currie,
Henricks,
Kregel,
Thomas,
Weber, Mary.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-70.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 8.93 days. Decay Date: 1995-07-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 23612 . COSPAR: 1995-035A. Apogee: 257 km (159 mi). Perigee: 257 km (159 mi). Inclination: 28.45 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
Deployed TDRS 7. Payloads: Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) G/ Inertial Upper Stage (IUS); Bioreactor Demon-stration System (BDS) B; Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC); Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG); Hand-Held, Earth-Oriented, Real-Time, Cooperative, User-Friendly, Location-Targeting and Environmental System (HER-CULES); Microcapsules in Space (MIS) B; Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experiment (PARE)/National Institutes of Health (NIH) Rodents (R); Radiation Monitoring Experiment (RME) III; Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II; Space Tissue Loss (STL)/National Institutes of Health (NIH) Cells (C); Military Applications of Ship Tracks (MAST); Visual Function Tester (VFT) 4; Window Experiment (WINDEX).
- TDRS 7 - .
Payload: TDRS G. Mass: 2,120 kg (4,670 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: TDRS.
USAF Sat Cat: 23613 . COSPAR: 1995-035B. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 5.30 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
NASA communications; deployed from STS-70 on 7/13/95. Stationed at 149.8 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 150 deg W in 1995-1996; 171 deg W in 1996-1999 As of 3 September 2001 located at 171.48 deg W drifting at 0.017 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 150.85W drifting at 0.002E degrees per day.
1995 September 7 - . 15:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-69 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Cockrell,
Gernhardt,
Newman,
Voss,
Walker, Dave.
Payload: Endeavour F09 / Spartan / WSF. Mass: 11,499 kg (25,350 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Cockrell,
Gernhardt,
Newman,
Voss,
Walker, Dave.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-69.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 10.85 days. Decay Date: 1995-09-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23667 . COSPAR: 1995-048A. Apogee: 321 km (199 mi). Perigee: 321 km (199 mi). Inclination: 28.45 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Deployed and retrieved Spartan 201, WSF 2. Payloads: Wake Shield Facility (WSF) 2; Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for As-tronomy (SPARTAN) 201; International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH)1; Inter-Mars Tissue Equivalent Proportional Counter (ITEPC); Extravehicular Activity Development Flight Test (EDFT) 2; Capillary Pumped Loop (CAPL) 2/ getaway special (GAS) bridge assembly with five GAS payloads; Auroral Photography Experiment (APE) B; Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC); Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGBA), Configuration A; Electrolysis Perfor-mance Improvement Concept Study (EPICS); Space Tissue Loss (STL)/National Institutes of Health (NIH) Cells (C); Commercial Middeck Instrumentation Technology Associates Experiment (CMIX).
- IEH-1 - . Payload: IEH-1/HH-M. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: IEH. Decay Date: 1995-09-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23667 . COSPAR: 1995-048xx. Apogee: 345 km (214 mi). Perigee: 339 km (210 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
- Spartan 201 - . Mass: 1,195 kg (2,634 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: STS. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1995-09-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23668 . COSPAR: 1995-048B. Apogee: 376 km (233 mi). Perigee: 368 km (228 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 92.00 min. Released by STS-69 9/8/95; retrieved 9/10/95; examined solar corona..
- WSF 2 - . Payload: Wake Shield Facility. Mass: 1,935 kg (4,265 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SII. Class: Materials. Type: Materials science satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: WSF. Decay Date: 1995-09-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23669 . COSPAR: 1995-048C. Apogee: 405 km (251 mi). Perigee: 397 km (246 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 92.60 min. Wake Shield Facility; released by STS-69 9/11/95; retrieved 9/14/95; semiconductor materials research. Retrieved by Endeavour Sep 14 .
- GBA-8/CAPL - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1995-09-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 23667 . COSPAR: 1995-048xx. Apogee: 345 km (214 mi). Perigee: 339 km (210 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
1995 September 16 - . 08:20 GMT - .
- EVA STS-69-1 - . Crew: Gernhardt, Voss. EVA Duration: 0.28 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Gernhardt, Voss. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-69. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Tested tools and techniques for extravehicular activity..
1995 September 27 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Discovery OMDP-2 - .
Nation: USA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
During this overhaul 96 Master Change Requests are made, including installation of the Orbiter Docking System for space station operations, installation of the EDO cargo pallet, and repair and update of the thermal protection system. Discovery is returned to service in July 1996.
1995 October 20 - . 13:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-73 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Bowersox, Coleman, Catherine, Leslie, Lopez-Alegria, Rominger, Sacco, Thornton. Payload: Columbia F18 / Spacelab LM / EDO. Mass: 15,250 kg (33,620 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Bowersox, Coleman, Catherine, Leslie, Lopez-Alegria, Rominger, Sacco, Thornton. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-73. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 15.91 days. Decay Date: 1995-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 23688 . COSPAR: 1995-056A. Apogee: 241 km (149 mi). Perigee: 241 km (149 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Carried USML-2 for microgravity experiments (attached to Columbia). Payloads: United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML) 2, Orbital Acceleration Research Experiment (OARE)..
- Spacelab USML-2 - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1995-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 23688 . COSPAR: 1995-056xx. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 256 km (159 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1995-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 23688 . COSPAR: 1995-056xx. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 256 km (159 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
1995 November 12 - . 12:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-74 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Cameron,
Hadfield,
Halsell,
McArthur,
Ross.
Payload: Atlantis F15 / 316GK SM. Mass: 6,134 kg (13,523 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Cameron,
Hadfield,
Halsell,
McArthur,
Ross.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-22,
STS-74.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 8.19 days. Decay Date: 1995-11-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23714 . COSPAR: 1995-061A. Apogee: 342 km (212 mi). Perigee: 257 km (159 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Rendezvoused and docked with Mir space station on November 15. Delivered the Russian-built 316GK Shuttle-Mir docking module to Mir.Payloads: Shuttle-Mir Mission 2; docking module with two attached solar arrays; IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC); Glow Experiment (GLO-4)/ Photogrammetric Appendage Structural Dynamics Experiment (PASDE) Payload (GPP); Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-22, STS-74. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1995-11-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23714 . COSPAR: 1995-061xx. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
- Mir-Shuttle Docking Module - . Payload: DM 316GK s/n 1. Mass: 6,134 kg (13,523 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: NASA. Manufacturer: Korolev bureau. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Flight: Soyuz TM-22, STS-74. Spacecraft Bus: Mir. Spacecraft: Mir-Shuttle Docking Module. Duration: 8.19 days. COSPAR: 1995-061xx. Apogee: 342 km (212 mi). Perigee: 356 km (221 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Atlantis rendezvoused and docked with Mir space station on Nov 15. After departure the Russian-built 316GK Shuttle-Mir docking module remained attached to Mir to provide easier docking capability in the future..
1996 January 11 - . 09:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-72 - . Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Barry, Chiao, Duffy, Jett, Scott, Winston, Wakata. Payload: Endeavour F10 / OAST / FSU. Mass: 6,510 kg (14,350 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Barry, Chiao, Duffy, Jett, Scott, Winston, Wakata. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-72. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Duration: 8.92 days. Decay Date: 1996-01-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23762 . COSPAR: 1996-001A. Apogee: 310 km (190 mi). Perigee: 302 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min. Deployed and retrieved OAST Flyer; retrieved SFU Space Flyer Unit. Beside the two satellite retrievals, the mission included two spacewalks..
- OAST-Flyer - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: OAST-Flyer. Decay Date: 1996-01-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23763 . COSPAR: 1996-001B. Apogee: 311 km (193 mi). Perigee: 301 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min. GPS receiver, amateur radio tests; examined effect of solar radiation on satellite explosive devices; deployed from STS 72 1/14/96; retrieved 1/16/96..
- SLA-1/GAS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: GAS. Decay Date: 1996-01-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 23762 . COSPAR: 1996-001xx. Apogee: 310 km (190 mi). Perigee: 302 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
1996 January 15 - . 05:35 GMT - .
- EVA STS-72-1 - . Crew: Barry, Chiao. EVA Duration: 0.26 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Barry, Chiao. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-72. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Tested tools and techniques for extravehicular activity..
1996 January 17 - . 05:40 GMT - .
- EVA STS-72-2 - . Crew: Chiao, Scott, Winston. EVA Duration: 0.29 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Chiao, Scott, Winston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-72. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Tested tools and techniques for extravehicular activity..
1996 February 22 - . 20:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-75 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Allen, Andy,
Chang-Diaz,
Cheli,
Guidoni,
Hoffman,
Horowitz,
Nicollier.
Payload: Columbia F19 / USMP-3 Aft. Mass: 10,592 kg (23,351 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Allen, Andy,
Chang-Diaz,
Cheli,
Guidoni,
Hoffman,
Horowitz,
Nicollier.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-75.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 15.74 days. Decay Date: 1996-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 23801 . COSPAR: 1996-012A. Apogee: 320 km (190 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
Carried TSS-1R tether satellite; satellite tether broke during deployment, making TSS-1R an unintentional free flyer
Payloads: Tethered Satellite System (TSS) Reflight (1R); Orbital Acceleration Research Experiment (OARE) (part of United States Microgravity Payload 3); USMP-3; Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG) 09, Block IV; Middeck Glovebox Experiment (MGBX) (part of USMP-3). During the deployment of TSS, the tether broke and the satellite was lost.
- TSS-1 - . Payload: TSS-1R. Nation: Italy. Agency: ASI. Program: STS. Class: Technology. Type: Tether technology satellite. Spacecraft: TSS. Decay Date: 1996-03-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 23805 . COSPAR: 1996-012B. Apogee: 189 km (117 mi). Perigee: 173 km (107 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 88.10 min. LEO. Tether deployment test; 20 km long tether; satellite unintentionally deployed when tether broke 2/25/96 Reentered Mar 19..
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1996-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 23801 . COSPAR: 1996-012xx. Apogee: 320 km (190 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
- TSS-1R Deployer - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft: TSS. Decay Date: 1996-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 23801 . COSPAR: 1996-012xx. Apogee: 320 km (190 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
- TSS-1R MPESS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1996-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 23801 . COSPAR: 1996-012xx. Apogee: 320 km (190 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
- USMP-3 Fwd - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1996-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 23801 . COSPAR: 1996-012xx. Apogee: 320 km (190 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
- USMP-3 Aft - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1996-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 23801 . COSPAR: 1996-012xx. Apogee: 320 km (190 mi). Perigee: 277 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
1996 March 22 - . 08:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-76 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Chilton,
Clifford,
Godwin,
Lucid,
Searfoss,
Sega.
Payload: Atlantis F16 / Spacehab-SM. Mass: 6,753 kg (14,887 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Chilton,
Clifford,
Godwin,
Lucid,
Searfoss,
Sega.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-23,
STS-76,
STS-76 Mir NASA-1.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 9.22 days. Decay Date: 1996-03-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 23831 . COSPAR: 1996-018A. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 394 km (244 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
Shuttle-Mir Mission 3. Docked with the Mir space station 24 March 1996; Shannon Lucid was left on Mir for an extended stay. First American EVA on Mir. Payloads: SPACEHAB/Mir 03; KidSat; Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) II, Configuration M; RME 1304—Mir/ Environmental Effects Payload (MEEP); orbiter docking system RME 1315; Trapped Ions in Space Experiment (TRIS); Extravehicular Activity Development Flight Test (EDFT) 04.
- Spacehab-SM - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Flight: Soyuz TM-23, STS-76, STS-76 Mir NASA-1. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1996-03-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 23831 . COSPAR: 1996-018xx. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 34 km (21 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Flight: Soyuz TM-23, STS-76, STS-76 Mir NASA-1. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1996-03-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 23831 . COSPAR: 1996-018xx. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 34 km (21 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
1996 May 19 - . 10:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-77 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Brown,
Bursch,
Casper,
Garneau,
Runco,
Thomas, Andrew.
Payload: Endeavour F11 / GBA-9. Mass: 12,233 kg (26,969 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brown,
Bursch,
Casper,
Garneau,
Runco,
Thomas, Andrew.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-77.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 10.03 days. Decay Date: 1996-05-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23870 . COSPAR: 1996-032A. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 274 km (170 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.10 min.
Deployed and retrieved Spartan 2; deployed PAMS-STU; carried Spacehab module. Payloads: Shuttle Pointed Research Tool for Astronomy (SPARTAN) 207/Inflatable Antenna Experiment (IAE); Technology Experiments Advancing Missions in Space (TEAMS) 01 (includes Vented Tank Resupply Experiment (VTRE), Global Positioning System (GPS) Attitude and Navigation Experiment (GANE) (RME 1316), Liquid Metal Test Experiment (LMTE) and Passive Aerodynami-cally Stabilized Magnetically Damped Satellite (PAMS) Satellite Test Unit (STU); SPACEHAB-4; Brilliant Eyes Ten-Kelvin Sorption Cryocooler Experiment (BETSCE); 12 getaway specials attached to a GAS bridge assembly (GAS 056, 063, 142, 144, 163, 200, 490, 564, 565, 703, 741 and the Reduced-Fill Tank Pressure Control Experiment (RFTPCE); Aquatic Research Facility (ARF) 01; Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) 07, Block III.
- IAE - . Payload: Inflatable Antenna Experiment. Nation: USA. Agency: JPL. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: IAE satellite. Decay Date: 1996-05-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 23872 . COSPAR: 1996-032C. Apogee: 201 km (124 mi). Perigee: 180 km (110 mi). Inclination: 39.10 deg. Period: 88.30 min. LEO. Inflatable Antenna Experiment; deployed from Spartan 207 5/20/96; test of inflatable antenna technology. Reentered May 22..
- Spartan 207 - . Mass: 1,195 kg (2,634 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL. Program: STS. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1996-05-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23871 . COSPAR: 1996-032B. Apogee: 288 km (178 mi). Perigee: 278 km (172 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.20 min. LEO. Deployed from STS 77 on 5/20/96; retrieved 5/21/96; deployed IAEsatellite during free flight..
- Spacehab 4 - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1996-05-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23870 . COSPAR: 1996-032xx. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 274 km (170 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.10 min.
- TEAMS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: TEAMS. Decay Date: 1996-05-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23870 . COSPAR: 1996-032xx. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 274 km (170 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.10 min. Time-of-flight/energy/angle mass spectrograph to study electrons and ions. Instrument mounted in shuttle bay..
- PAMS STU - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: PAMS. Decay Date: 1996-10-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 23876 . COSPAR: 1996-032D. Apogee: 138 km (85 mi). Perigee: 132 km (82 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 87.20 min. LEO. Passive Aerodynamically Stabilized Magnetically Damped Satellite; deployed from STS 77 5/22/96; attitude control technology test. Reentered Oct 26..
- GBA-9 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: GBA. Decay Date: 1996-05-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23870 . COSPAR: 1996-032xx. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 274 km (170 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 90.10 min.
1996 June 20 - . 14:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-78 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Brady,
Favier,
Helms,
Henricks,
Kregel,
Linnehan,
Thirsk.
Payload: Columbia F20 / EDO. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brady,
Favier,
Helms,
Henricks,
Kregel,
Linnehan,
Thirsk.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-78.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 16.91 days. Decay Date: 1996-07-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 23931 . COSPAR: 1996-036A. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 246 km (152 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
Columbia carried Terence T Henricks, Kevin R Kregel, Susan J Helms, Richard M Linnehan, Charles E Brady, Jr, Jean-Jacques Favier, and Robert Brent Thirsk to orbit. Main payload was the Life and Microgravity Spacelab for conducting human biological and microgravity experiments. Columbia landed safely at Kennedy Space Center on July 7.
- Spacelab LMS 1 - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1996-07-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 23931 . COSPAR: 1996-036xx. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 246 km (152 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1996-07-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 23931 . COSPAR: 1996-036xx. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 246 km (152 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
1996 August 6 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Endeavour OMDP-1 - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Shuttle Endeavour undergoes its OMDP-1 Orbiter Maintenance Down Period at Palmdale, returning to service on 4 April 1997. These overhauls are undertaken every 10 to 12 shuttle missions..
1996 September 16 - . 08:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-79 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Akers,
Apt,
Blaha,
Readdy,
Walz,
Wilcutt.
Payload: Atlantis F17 / External Airlock/ODS. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Akers,
Apt,
Blaha,
Readdy,
Walz,
Wilcutt.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-24,
STS-76 Mir NASA-1,
STS-79,
STS-79 Mir NASA-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 10.14 days. Decay Date: 1996-09-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 24324 . COSPAR: 1996-057A. Apogee: 386 km (239 mi). Perigee: 368 km (228 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.10 min.
On September 19 Atlantis docked with the Russian Mir space station. Aboard Atlantis in the payload bay were the Orbiter Docking System, the modified Long Tunnel, and the Spacehab Double Module, containing supplies for the Mir. Astronaut John Blaha relieved Shannon Lucid as NASA resident on the complex. Atlantis undocked from the Mir complex on September 23 at 23:33 GMT. Valeriy Korzun, Aleksandr Kaleri and John Blaha remain on Mir. On September 26 Atlantis closed its payload bay doors, and at 11:06 GMT fired its OMS engines for a three minute long deorbit burn. After entry interface at 11:42 GMT the spaceship flew across Canada and the US for a landing at the Kennedy Space Center's Runway 15 at 12:13 GMT.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: Orbiter Docking System. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1996-09-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 24324 . COSPAR: 1996-057xx. Apogee: 386 km (239 mi). Perigee: 368 km (228 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.10 min.
- Spacehab Double Module - . Payload: Spacehab FU2/STA. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1996-09-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 24324 . COSPAR: 1996-057xx. Apogee: 386 km (239 mi). Perigee: 368 km (228 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.10 min. Remained attached to OV-104.
1996 November 19 - . 19:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-80 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Cockrell,
Jernigan,
Jones,
Musgrave,
Rominger.
Payload: Columbia F21 / Orfeus / WSF. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Cockrell,
Jernigan,
Jones,
Musgrave,
Rominger.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-80.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 17.66 days. Decay Date: 1996-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 24660 . COSPAR: 1996-065A. Apogee: 375 km (233 mi). Perigee: 318 km (197 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
Mission STS-80 carried the Orfeus astronomy satellite, the Wake Shield Facility, and spacewalk equipment. The Orfeus satellite was deployed on November 20. It carried an ultraviolet telescope and spectrographs. Wake Shield Facility was deployed on November 22 and retrieved on November 26 . On 1996 Nov 29, crewmembers Tamara Jernigan and Thomas Jones were to conduct the first of several planned EVAs. However the shuttle's exit hatch would not open and NASA cancelled this and the other planned spacewalks of the mission. On December 4 at the astronauts retrieved the Orfeus satellite using the RMS arm. Reentry attempts on Dec 5 and Dec 6 were called off due to bad weather. Columbia finally landed at 11:49 GMT December 7 on Runway 33 at Kennedy Space Center, making STS-80 the longest shuttle mission to that date .
- ORFEUS - . Payload: ASTRO-SPAS. Nation: USA. Agency: DLR. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: ORFEUS. Decay Date: 1996-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 24661 . COSPAR: 1996-065B. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 346 km (214 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Retrieved Dec 4.
- WSF - . Payload: Wake Shield Facility. Mass: 1,935 kg (4,265 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SII. Class: Materials. Type: Materials science satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: WSF. Decay Date: 1996-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 24662 . COSPAR: 1996-065C. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 347 km (215 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.60 min. Retrieved Nov 26.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1996-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 24660 . COSPAR: 1996-065xx. Apogee: 375 km (233 mi). Perigee: 318 km (197 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
1997 January 12 - . 09:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-81 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Baker, Mike,
Grunsfeld,
Ivins,
Jett,
Linenger,
Wisoff.
Payload: Atlantis F18 / Spacehab Double Module. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Baker, Mike,
Grunsfeld,
Ivins,
Jett,
Linenger,
Wisoff.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-24,
STS-79 Mir NASA-2,
STS-81,
STS-81 Mir NASA-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 10.20 days. Decay Date: 1997-01-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 24711 . COSPAR: 1997-001A. Apogee: 380 km (230 mi). Perigee: 343 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
After a night launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis, the Shuttle docked with Mir at 03:55 GMT on January 14. STS-81 transferred 2,715 kg of equipment to and from the Mir, the largest transfer of items to that date. During the docked phase, 640 kg of water, 515 kg of U.S. science equipment, 1,000 kg of Russian logistics, and 120 kg of miscellaneous material were transferred to Mir. Returned to Earth aboard Atlantis were 570 kg of U.S. science material, 405 kg of Russian logistics and 98 kg of miscellaneous material. At 02:16 GMT January 19, Atlantis separated from Mir after picking up John Blaha, who had arrived aboard STS-79 on September 19, 1996, and dropping off Jerry Linenger, who was to stay aboard Mir for over four months. The Shuttle backed off along the -RBAR (i.e. toward the Earth) to a distance of 140 m before beginning a flyaround at 02:31 GMT. Most of the flyaround was at a distance from Mir of 170 m. The first 'orbit' around Mir was complete at 03:15, and the second was completed at 04:02 GMT. Then the Orbiter fired its jets to drift away from the orbit of Mir. NASA's first Shuttle mission of 1997 came to a close with a landing at the Kennedy Space Center at 14:22 GMT on January 22 (after the first opportunity was waved off due to cloud cover at the Cape).
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1997-01-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 24711 . COSPAR: 1997-001xx. Apogee: 380 km (230 mi). Perigee: 343 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
- Spacehab Double Module - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1997-01-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 24711 . COSPAR: 1997-001xx. Apogee: 380 km (230 mi). Perigee: 343 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
1997 February 11 - . 08:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-82 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Bowersox,
Harbaugh,
Hawley,
Horowitz,
Lee,
Smith, Steven,
Tanner.
Payload: Discovery F22 / SAC. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bowersox,
Harbaugh,
Hawley,
Horowitz,
Lee,
Smith, Steven,
Tanner.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-82.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 9.98 days. Decay Date: 1997-02-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 24719 . COSPAR: 1997-004A. Apogee: 618 km (384 mi). Perigee: 584 km (362 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.70 min.
After a spectacular night launch, the Shuttle completed its rendezvous with Hubble Space Telescope on February 13. Over the next four days five spacewalks were undertaken to renovate Hubble.
The Hubble Space Telescope was released back into orbit at 06:41 GMT on February 19. Discovery landed on Runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center at 08:32 GMT on February 21.
- ORUC - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SLP. Decay Date: 1997-02-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 24719 . COSPAR: 1997-004xx. Apogee: 618 km (384 mi). Perigee: 584 km (362 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.70 min.
- FSS - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: FSS. Decay Date: 1997-02-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 24719 . COSPAR: 1997-004xx. Apogee: 618 km (384 mi). Perigee: 584 km (362 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.70 min.
- SAC - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Second Axial Carrier. Decay Date: 1997-02-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 24719 . COSPAR: 1997-004xx. Apogee: 618 km (384 mi). Perigee: 584 km (362 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.70 min.
- External Airlock - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1997-02-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 24719 . COSPAR: 1997-004xx. Apogee: 618 km (384 mi). Perigee: 584 km (362 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.70 min.
1997 April 4 - . 19:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-83 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Crouch,
Gernhardt,
Halsell,
Kilrain,
Linteris,
Thomas,
Voss, Janice.
Backup Crew: Coleman, Catherine.
Payload: Columbia F22 / Spacelab LM Unit 1 / EDO. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-83.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 3.97 days. Decay Date: 1997-04-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 24755 . COSPAR: 1997-013A. Apogee: 302 km (187 mi). Perigee: 298 km (185 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
The launch of STS-83, the first Microgravity Science Laboratory (MSL-1) mission, was postponed for a day to replace some insulation around a water coolant line in Columbia's payload bay. Liftoff was further delayed 20 minutes due to anomalous oxygen readings in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-83 was cut short due to a problem with one of the three fuel cells that provide electricity and water to Columbia (flight rules required that all three must be operating). At 14:30 GMT on April 6 the crew were ordered to begin a Minimum Duration Flight (MDF). On April 8 the OMS engines ignited at 17:30 GMT for the deorbit burn, and Columbia landed on Runway 33 at Kennedy Space Center at 18:33 GMT.
With delays in International Space Station construction leaving ample room in the shuttle schedule, NASA made the unique decision to leave the equipment installed in Columbia and refly this mission with the same crew later in 1997 as STS-94.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1997-04-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 24755 . COSPAR: 1997-013xx. Apogee: 302 km (187 mi). Perigee: 298 km (185 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
- MSL-1 Spacelab - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module 1. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Manufacturer: Bremen. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1997-04-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 24755 . COSPAR: 1997-013xx. Apogee: 302 km (187 mi). Perigee: 298 km (185 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min. Remained attached to OV-102.
1997 May 15 - . 08:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-84 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Clervoy,
Collins, Eileen,
Foale,
Kondakova,
Lu,
Noriega,
Precourt.
Backup Crew: Titov, Vladimir.
Payload: Atlantis F19 / Spacehab Double Module. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-25,
STS-81 Mir NASA-3,
STS-84,
STS-84 Mir NASA-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 9.22 days. Decay Date: 1997-05-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 24804 . COSPAR: 1997-023A. Apogee: 393 km (244 mi). Perigee: 377 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
Atlantis blasted off on a night launch to Mir, docking with the station on May 17 at 02:33 GMT. Jerry Linenger, who had begun his stay on Mir in mid-January aboard STS-81, would return aboard STS-84. Michael Foale would be left at the station for his stint as the American crew member of Mir. The crew transfered to Mir 466 kg of water, 383 kg of U.S. science equipment, 1,251 kg of Russian equipment and supplies, and 178 kg of miscellaneous material. Returned to Earth aboard Atlantis were 406 kg of U.S. science material, 531 kg of Russian logistics material, 14 kg of ESA material and 171 kg of miscellaneous material. Atlantis undocked from Mir at 01:04 GMT on May 22. After passing up its first landing opportunity due to clouds over the landing site, the Shuttle fired its OMS engines on the deorbit burn at 12:33 GMT on May 24. Atlantis landed at 13:27 GMT at Kennedy Space Center's runway 33.
- Spacehab Double Module - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1997-05-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 24804 . COSPAR: 1997-023xx. Apogee: 393 km (244 mi). Perigee: 377 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1997-05-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 24804 . COSPAR: 1997-023xx. Apogee: 393 km (244 mi). Perigee: 377 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
1997 July 1 - . 18:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-94 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Crouch,
Gernhardt,
Halsell,
Kilrain,
Linteris,
Thomas,
Voss, Janice.
Payload: Columbia F23 / Spacelab LM Unit 1 / EDO. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Crouch,
Gernhardt,
Halsell,
Kilrain,
Linteris,
Thomas,
Voss, Janice.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Bremen.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-94.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 15.70 days. Decay Date: 1997-07-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 24849 . COSPAR: 1997-032A. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi). Perigee: 296 km (183 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
STS-94 was the reflight, with the same equipment and crew, of the curtailed STS-83 mission. Cargo Bay Payloads:
- MSL-1: The Microgravity Science Laboratory included the first test of the International Space Station's EXPRESS Rack. MSL-1 also contained numerous other experiment payloads to test materials and combustion processes in zero gravity.
- CRYOFD: The Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) heat pipe was a Hitchhiker payload.
- OARE: The Orbital Acceleration Research Experiment was a self-calibrating instrument that monitored extremely small accelerations and vibrations experienced during orbit of the Shuttle.
The mission this time went for its full two week duration and the crew completed the full list of experiments. The deorbit burn was on July 17, 1997 at 09:44 GMT and Columbia landed on KSC's Runway 33 at 10:46:34 GMT.
- Spacelab MSL-1R - . Payload: Spacelab Long Module. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Manufacturer: Bremen. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1997-07-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 24849 . COSPAR: 1997-032xx. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi). Perigee: 296 km (183 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min. Remained attached to OV-102.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1997-07-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 24849 . COSPAR: 1997-032xx. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi). Perigee: 296 km (183 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.50 min.
1997 August 7 - . 14:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-85 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Brown,
Curbeam,
Davis,
Robinson,
Rominger,
Tryggvason.
Payload: Discovery F23 / CRISTA-SPAS-2. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brown,
Curbeam,
Davis,
Robinson,
Rominger,
Tryggvason.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-85.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 11.85 days. Decay Date: 1997-08-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 24889 . COSPAR: 1997-039A. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 249 km (154 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
Deployed and retrieved the CRISTA-SPAS-2 (the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2) designed to study Earth's middle atmosphere. The CRISTA-SPAS-2 was making its second flight on the Space Shuttle and represented the fourth mission in a cooperative venture between the German Space Agency (DARA) and NASA.
CRISTA-SPAS was deployed by the RMS arm at 22:27 GMT on August 7 and was recaptured by Discovery's RMS arm at 15:14 GMT on August 16. Because of unfavorable weather conditions at the primary shuttle landing site at the Kennedy Space Center, Discovery was waved off for its scheduled August 18 landing. STS-85 landed the next day, at Kennedy Space Center at 11:08 GMT.
- TAS-1 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: STS.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads.
Spacecraft: Technology Applications and Science Experiment.
Decay Date: 1997-08-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 24889 . COSPAR: 1997-039xx. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 249 km (154 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
Technology Applications and Science experiment, mounted in space shuttle bay, from NASA-Goddard's Hitchhiker-M program. TAS-01 used a number of GAS cans with science experiments, including the second flight of the Shuttle Laser Altimeter and an instrument to measure the absolute bolometric flux of the Sun.
- IEH-2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: IEH. Decay Date: 1997-08-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 24889 . COSPAR: 1997-039xx. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 249 km (154 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
- MFD - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Decay Date: 1997-08-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 24889 . COSPAR: 1997-039xx. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 249 km (154 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
- CRISTA - . Payload: ASTRO-SPAS. Mass: 3,230 kg (7,120 lb). Nation: Germany. Agency: DLR. Manufacturer: Bremen. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: SPAS. Decay Date: 1997-08-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 24890 . COSPAR: 1997-039B. Apogee: 296 km (183 mi). Perigee: 282 km (175 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 90.30 min. Recaptured August 16..
1997 September 26 - . 02:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-86 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Bloomfield,
Chretien,
Lawrence,
Parazynski,
Titov, Vladimir,
Wetherbee,
Wolf.
Payload: Atlantis F20 / Spacehab-DM. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bloomfield,
Chretien,
Lawrence,
Parazynski,
Titov, Vladimir,
Wetherbee,
Wolf.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-26,
STS-84 Mir NASA-4,
STS-86,
STS-86 Mir NASA-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 10.81 days. Decay Date: 1997-10-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 24964 . COSPAR: 1997-055A. Apogee: 381 km (236 mi). Perigee: 354 km (219 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
Atlantis was launched on a mission to the Russian Mir space station. The TI rendevous terminal initiation burn was carried out at 17:32 GMT on September 27, and Atlantis docked with the SO (Docking Module) on the Mir complex at 19:58 GMT. The crew exchange was completed on September 28, with David Wolf replacing Michael Foale on the Mir crew. On October 1 cosmonaut Titov and astronaut Parazynski conducted a spacewalk from the Shuttle payload bay while Atlantis was docked to Mir. They retrieved four MEEP (Mir Environmental Effects Payload ) exposure packages from Mir's SO module and installed the Spektr solar array cap. The MEEP experiments had been attached to the Docking Module by astronauts Linda Godwin and Rich Clifford during Shuttle mission STS-76 in March 1996. In addition to retrieving the MEEP, Parazynski and Titov were to continue an evaluation of the Simplified Aid For EVA Rescue (SAFER), a small jet-backpack designed for use as a type of life jacket during station assembly.
Atlantis undocked from Mir at 17:28 GMT on October 3 and conducted a flyaround focused on the damaged Spektr Module to determine the location of the puncture in its hull. The Mir crew pumped air into the Spektr Module using a pressure regulator valve, and the Shuttle crew observed evidence that, as expected, the leak seemed to be located at the base of the damaged solar panel. Final separation of Atlantis from Mir took place around 20:28 GMT. After two landing attempts were waved off on October 5 due to heavy cloud cover, the crew fired the engines to deorbit at 20:47 GMT on October 6 and landed at Kennedy Space Center at 21:55.
- Spacehab Double Module - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1997-10-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 24964 . COSPAR: 1997-055xx. Apogee: 381 km (236 mi). Perigee: 354 km (219 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.90 min. Remained attached to OV-104.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1997-10-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 24964 . COSPAR: 1997-055xx. Apogee: 381 km (236 mi). Perigee: 354 km (219 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
1997 November 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- Atlantis OMDP-2 - . Nation: USA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Atlantis is overhauled at Palmdale, returning to service in mid-1998. This was the last OMDP accomplished at Palmdale; future work would be done at the Kennedy Space Center..
1997 November 19 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- AERCam-Sprint - . Payload: AERCam/SAFER. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Manufacturer: Houston. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft: AERCam. COSPAR: 1997-073C. Retrieved by OV-102 Dec 3..
- STS-87 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Chawla,
Doi,
Kadenyuk,
Kregel,
Lindsey,
Scott, Winston.
Payload: Columbia F24 / Spartan / USMP-4 Aft. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Chawla,
Doi,
Kadenyuk,
Kregel,
Lindsey,
Scott, Winston.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-87.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 15.69 days. Decay Date: 1997-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 25061 . COSPAR: 1997-073A. Apogee: 279 km (173 mi). Perigee: 273 km (169 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
OV-102 Columbia was launched on a microgravity science mission. Spartan 201 was released a day late on November 21. However the satellite did not start its automatic orientation maneuver because the crew failed to send it the correct commands prior to release.
Spartan was recaptured by hand, during a spacewalk by Takao Doi and Winston Scott on November 25. Tests of space station tools went well, but the free-flying Sprint camera subsatellite was not deployed due to lack of time.
NASA decided not to redeploy Spartan on this mission. During an EVA on Dec 3, Doi and Scott carried out more tests of the Space Station crane. They also deployed the AERCam/Sprint 'football' remote-controlled camera for a free flight in the payload bay.
Columbia landed on December 5, with a deorbit burn at 11:21 GMT. Touchdown was at 12:20 GMT at Kennedy Space Center.
- AERCam/Sprint - . Payload: AERCam/Sprint. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Spacecraft: AERCam. COSPAR: 1997-073xx.
- EDO - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EDO. Decay Date: 1997-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 25061 . COSPAR: 1997-073xx. Apogee: 279 km (173 mi). Perigee: 273 km (169 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
- USMP-4 Aft - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1997-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 25061 . COSPAR: 1997-073xx. Apogee: 279 km (173 mi). Perigee: 273 km (169 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
- Spartan 201 - . Mass: 1,195 kg (2,634 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: STS. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1997-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 25062 . COSPAR: 1997-073B. Apogee: 284 km (176 mi). Perigee: 278 km (172 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.10 min. Retrieved by OV-102 Nov 25.
- USMP-4 Forward - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: STS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: USMP. Decay Date: 1997-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 25061 . COSPAR: 1997-073xx. Apogee: 279 km (173 mi). Perigee: 273 km (169 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.00 min.
1997 November 25 - . 00:02 GMT - .
- EVA STS-87-1 - . Crew: Doi, Scott, Winston. EVA Duration: 0.32 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Doi, Scott, Winston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-87. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Retrieved Spartan free-flier. Tested EVA tools and techniques..
1997 December 3 - . 09:09 GMT - .
- EVA STS-87-2 - . Crew: Doi, Scott, Winston. EVA Duration: 0.21 days. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Doi, Scott, Winston. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-87. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Tested tools and techniques for extravehicular activity..
1998 January 23 - . 02:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-89 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Anderson,
Dunbar,
Edwards, Joe,
Reilly,
Sharipov,
Thomas, Andrew,
Wilcutt.
Payload: Endeavour F12 / Spacehab Double Module. Mass: 116,277 kg (256,346 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Anderson,
Dunbar,
Edwards, Joe,
Reilly,
Sharipov,
Thomas, Andrew,
Wilcutt.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Douglas.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-26,
STS-86 Mir NASA-5,
STS-89,
STS-89 Mir NASA-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 8.82 days. Decay Date: 1998-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 25143 . COSPAR: 1998-003A. Apogee: 382 km (237 mi). Perigee: 359 km (223 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.00 min.
Penultimate Shuttle mission to Mir. Andy Thomas replaced David Wolf as the resident NASA astronaut. Endeavour docked with the SO module on Mir at 20:14 GMT on January 24, 1998.
Payloads included:
- Orbiter middeck: CEBAS (German/US biological module with fish and snails); dinosaur skull (part of a museum educational program)
- Bay 1: Tunnel Adapter
- Bay 3: Orbiter Docking System/External Airlock
- Bay 4-7: Transfer Tunnel
- Bay 8-12: Spacehab Double Module (payloads included supplies for Mir, X-ray crystallography detector planned for the International Space Station)
- Bay 13P: Getaway Special GABA carrier with G-141, G-145 (German materials processing experiments)
- Bay 13S: Getaway Special GABA carrier with G-093 (University of Michigan fluid dynamics experiment), G-432 (Chinese materials processing experiment)
Despite fits problems with his Sokol emergency spacesuit, Andy Thomas replaced David Wolf as a Mir crew member on January 25. Endeavour undocked from Mir on January 29 at 16:57 GMT and made one flyaround of the station before departing and landing at Kennedy Space Center's runway 15 at 22:35 GMT on January 31.
- Spacehab Double Module - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. COSPAR: 1998-003xx.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1998-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 25143 . COSPAR: 1998-003xx. Apogee: 382 km (237 mi). Perigee: 359 km (223 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.00 min.
1998 April 17 - . 18:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-90 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Altman,
Buckey,
Hire,
Linnehan,
Pawelczyk,
Searfoss,
Williams, Dave.
Backup Crew: Dunlap,
Mukai.
Payload: Columbia F25 / Spacelab LM Eurolab. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Bremen.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-90.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 15.91 days. Decay Date: 1998-05-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 25297 . COSPAR: 1998-022A. Apogee: 274 km (170 mi). Perigee: 247 km (153 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
Columbia rolled out to pad 39B on March 23. Payloads:
- Spacelab transfer tunnel
- Spacelab Long Module, with Neurolab experiments for the following life science studies:
- Chronic Recording of Otolith Nerves in Microgravity
- Development of the Aortic Baroreflex under Conditions of Microgravity
- Neural-Thyroid Interaction on Skeletal Isomyosin Expression in OG
- Spatial Orientation of the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex and Velocity Storage
- Autonomic Neuroplasticity in Weightlessness
- Extended Duration Orbiter pallet
- Two Get Away Special beams with canisters G-197, G-467, G-772 (Colorado's COLLIDE experiment, which collided small particles into each other to simulate the formation of planets and rings).
The Neurolab mission was managed by NASA-Johnson at Houston, unlike earlier Spacelab flights which were NASA-Marshall/Huntsville's responsibility. Landed at Kennedy Space Center May 3 1998.
- Neurolab - . Payload: Spacelab. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Spacelab. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft: Spacelab. Decay Date: 1998-05-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 25297 . COSPAR: 1998-022xx. Apogee: 274 km (170 mi). Perigee: 247 km (153 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min.
1998 June 2 - . 22:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-91 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Chang-Diaz,
Gorie,
Kavandi,
Lawrence,
Precourt,
Ryumin.
Payload: Discovery F24 / Spacehab. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Chang-Diaz,
Gorie,
Kavandi,
Lawrence,
Precourt,
Ryumin.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: Mir.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TM-27,
STS-89 Mir NASA-6,
STS-91.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 9.83 days. Decay Date: 1998-06-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 25356 . COSPAR: 1998-034A. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
The final shuttle-Mir mission, STS-91 recovered NASA astronaut Andy Thomas from the Mir station and took Russian space chief and ex-cosmonaut Valeri Ryumin to Mir for an inspection tour of the ageing station. This was the first test of the super lightweight Aluminium-Lithium alloy external tank, designed to increase shuttle payload to the Mir / International Space Station orbit by 4,000 kg. At 22:15 GMT Discovery entered an initial 74 x 324 km x 51.6 deg orbit, with the OMS-2 burn three quarters of an hour later circulising the chase orbit. Discovery docked with the SO module on Mir at 17:00 GMT on June 4. NASA equipment was retrieved from the station, and Discovery undocked at 16:01 GMT on June 8, and landed on Runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center at 18:00 GMT on June 12.
- Spacehab - . Payload: Spacehab FU1. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. COSPAR: 1998-034xx.
- External Airlock/ODS - . Payload: EAL/ODS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: EAL/ODS. Decay Date: 1998-06-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 25356 . COSPAR: 1998-034xx. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
- Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer - . Payload: AMS. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer. COSPAR: 1998-034xx.
- Spacehab - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mir. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1998-06-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 25356 . COSPAR: 1998-034xx. Apogee: 373 km (231 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
1998 October 29 - . 19:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-95 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Brown,
Duque,
Glenn,
Lindsey,
Mukai,
Parazynski,
Robinson.
Payload: Discovery F25. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brown,
Duque,
Glenn,
Lindsey,
Mukai,
Parazynski,
Robinson.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Douglas.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-95.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 8.91 days. Decay Date: 1998-11-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 25519 . COSPAR: 1998-064A. Apogee: 557 km (346 mi). Perigee: 536 km (333 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 95.60 min.
The flight of STS-95 provoked more publicity for NASA than any other flight in years, due to the presence of ex-astronaut Senator John Glenn on the crew, which also included the first Spanish astronaut, Pedro Duque. The US Navy PANSAT student satellite was deployed on Oct 30 into a 550 km x 561 x 28.5 degree orbit. The Spartan 201 satellite was deployed from Discovery on November 1 and retrieved on November 3. Spartan 201 was on its fifth mission to observe the solar corona. The data on this mission would be used to recalibrate the SOHO satellite which recently resumed observation of the Sun following loss of control. Discovery landed at 17:03:31 GMT November 7 on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center.
- Spartan 201 - . Mass: 1,195 kg (2,634 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: STS. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Spartan. Decay Date: 1998-11-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 25521 . COSPAR: 1998-064C. Apogee: 560 km (340 mi). Perigee: 549 km (341 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 95.74 min. Retrieved by Discovery November 3 1998..
- Spacehab - . Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Manufacturer: Douglas. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. Decay Date: 1981-04-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 25519 . COSPAR: 1998-064xx. Apogee: 560 km (340 mi). Perigee: 550 km (340 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 95.75 min.
1998 December 4 - . 08:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-88 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Cabana,
Currie,
Krikalyov,
Newman,
Ross,
Sturckow.
Payload: Endeavour F13. Mass: 116,277 kg (256,346 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Cabana,
Currie,
Krikalyov,
Newman,
Ross,
Sturckow.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-88.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 11.80 days. Decay Date: 1998-12-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 25549 . COSPAR: 1998-069A. Apogee: 399 km (247 mi). Perigee: 382 km (237 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
First attempted launch of STS-88 was scrubbed at 09:03 GMT on December 3 due to a problem with a hydraulic system sensor. Launch came the next day, with Endeavour entering an initial 75 km x 313 km x 51.6 degree orbit. Half an orbit after launch, at 09:19 GMT, Endeavour fired its OMS engines to raise the orbit to 180 km x 322 km x 51.6 degree.
On December 5 at 22:25 GMT Nancy Currie unberthed the Unity space station node from the payload bay using the RMS arm. She then moved the Unity to a position docked to the Orbiter Docking System in the payload bay in readiness for assembly with the Russian-launched Zarya FGB ISS component. After rendezvous with the Zarya FGB module, on December 6 at 23:47 GMT Endeavour grappled Zarya with the robot arm, and at 02:07 GMT on December 7 it was soft docked to the PMA-1 port on Unity. After some problems hard dock was achieved at 02:48 GMT. Unity and Zarya then formed the core of the future International Space Station. Ross and Newman made three space walks to connect cables between Zarya and Unity, on December 7, 9 and 12. On the last EVA a canvas tool bag was attached to the exterior of Unity to provide tools for future station assembly workers. Docking cables were disconnected to prevent Unity and Zarya from inadvertently undocking. Following an internal examination of the embryonic space station, Endeavour undocked at 20:30 GMT on December 13. The SAC-A and Mightysat satellites were ejected from the payload bay on December 14 and 15. Deorbit burn was December 16 at 03:48 GMT, and Endeavour landed at 04:53:29 GMT, on Runway 15 at the Kennedy Space Center.
Payloads included:
- Sill: RMS arm No. 303
- Bay 1-2: Tunnel Adapter 002
- Bay 3-4: Orbiter Docking System/External Airlock (Boeing/Palmdale)
- Bay 7-13: Unity (Node 1) (Boeing/Huntsville), including the PMA-1 and PMA-2 docking adapters (Boeing/Huntington Beach)
- Bay 2 Port: GABA adapter with SAC-A satellite
- Bay 4 Starboard: Carrier with Tool Stowage Assembly
- Bay 5 Port: GABA adapter with two PFR space walk platforms and one PFR stanchion.
- Bay 5 Starboard: GABA adapter with two more PFR space walk platforms and one PFR stanchion.
- Bay 6 Port: GABA adapter with Mightysat
- Bay 6 Starboard: APC carrier with TCS laser rendezvous sensor
- Bay 7 Starboard: APC carrier with TCS laser rendezvous sensor
- Bay 13 Port: GABA adapter with SEM-7 and G-093 canisters
- Bay 13 Starboard: GABA adapter with IMAX Cargo Bay Camera
- Unity - . Mass: 11,600 kg (25,500 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Manufacturer: Douglas. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: ISS Unity. Decay Date: 1972-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 25575 . COSPAR: 1998-069F. Apogee: 400 km (240 mi). Perigee: 387 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 92.43 min.
- SAC-A - . Mass: 68 kg (149 lb). Nation: Argentina. Agency: CONAE. Manufacturer: INVAP. Program: SAC. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: SAC-A. Decay Date: 1999-10-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 25550 . COSPAR: 1998-069B. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 381 km (236 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. SAC-A was to provide engineering bench testing for new space science technology instruments and equipment that will be used in a more complex spacecraft for the Argentine space program..
- Mightysat 1 - . Mass: 320 kg (700 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: McLean. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Mightysat 1. Decay Date: 1999-11-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 25551 . COSPAR: 1998-069C. Apogee: 395 km (245 mi). Perigee: 381 km (236 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. First flight of a USAF Philips Laboratory/Space Experiments Directorate ejectable technology demonstration platform. Four advanced technologies demonstrated, including composite structure, advanced solar cells, advanced electronics, and a shock device..
1999 May 27 - . 10:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-96 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Barry,
Husband,
Jernigan,
Ochoa,
Payette,
Rominger,
Tokarev.
Payload: Discovery F26 / Spacehab-DM. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Barry,
Husband,
Jernigan,
Ochoa,
Payette,
Rominger,
Tokarev.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-96.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 9.80 days. Decay Date: 1999-06-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 25760 . COSPAR: 1999-030A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 384 km (238 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Discovery docked at the PMA-2 end of the International Space Station PMA-2/Unity/PMA-1/Zarya stack. The crew transferred equipment from the Spacehab Logistics Double Module in the payload bay to the interior of the station. Tammy Jernigan and Dan Barry made a space walk to transfer equipment from the payload bay to the exterior of the station. The ODS/EAL docking/airlock truss carried two TSA (Tool Stowage Assembly) packets with space walk tools. The Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC), built by Energia and DASA-Bremen, carried parts of the Strela crane and the US OTD crane as well as the SHOSS box which contains three bags of tools and equipment to be stored on ISS's exterior.
The STS-96 payload bay manifest:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System/External Airlock
- Bay 3-4: Tunnel Adapter S/N 001
- Bay 5-7: Spacehab Tunnel
- Bay 5: Keel Yoke Device (KYD) and Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC)
- Bay 8-12: Spacehab Logistics Double Module
- Bay 13 Port: Adapter Beam (ABA) with IVHM
- Bay 13 Stbd: Adapter Beam (ABA) with SVF/Starshine
- Sill: RMS Arm S/N 303
On May 30 at 02:56 GMT Tammy Jernigan and Dan Barry entered the payload bay of Discovery from the tunnel adapter hatch, and made a 7 hr 55 min space walk, transferring equipment to the exterior of the station.
On May 31 at 01:15 GMT the hatch to Unity was opened and the crew began several days of cargo transfers to the station. Battery units and communications equipment were replaced and sound insulation was added to Zarya. Discovery undocked from ISS at 22:39 GMT on June 3 into a 385 x 399 km x 51.6 degree orbit, leaving the station without a crew aboard. On June 5 the Starshine satellite was ejected from the payload bay. The payload bay doors were closed at around 02:15 GMT on June 6 and the deorbit burn was at 04:54 GMT. Discovery landed on runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center at 06:02 GMT.
- Spacehab-DM - . Payload: Spacehab-DM. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space laboratory. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: Spacehab. COSPAR: 1999-030x.
- Starshine - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: ISS.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Starshine.
Decay Date: 2000-02-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 25769 . COSPAR: 1999-030B. Apogee: 324 km (201 mi). Perigee: 311 km (193 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg.
At 0:721 GMT on June 5 the Starshine satellite was ejected into a 379 x 396 km x 51.6 degree orbit from a canister at the rear of STS-96 Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay. The small Starshine satellite, built by NRL, was to be observed by students as part of an educational exercise.
1999 July 23 - . 04:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-93 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Ashby,
Coleman, Catherine,
Collins, Eileen,
Hawley,
Tognini.
Payload: Columbia F26 / Chandra. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Ashby,
Coleman, Catherine,
Collins, Eileen,
Hawley,
Tognini.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-93.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 4.95 days. Decay Date: 1999-07-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 25866 . COSPAR: 1999-040A. Apogee: 280 km (170 mi). Perigee: 260 km (160 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
STS-93 was first rolled out to pad 39B on June 7 1999. The Chandra/IUS-27 vehicle was placed in the payload canister on June 19. The first launch attempt was on July 20, but controllers aborted the launch at T-6 seconds, just before main engine ignition, due to a data spike in hydrogen pressure data. This was determined to be due to a faulty sensor and a second attempt was on July 22. A lightning storm prevented launch during the 46 minute window, and the launch was again scrubbed. Finally the vehicle lifted off the pad on July 23, but five seconds after launch a short in an electrical bus brought down two of the three main engine controllers. Backup controllers took over, but a further failure on the backup controller bus would have resulted in engine shutdown and the first ever attempt at an RTLS (Return To Launch Site) abort. To further complicate matters engine 3 (SSME 2019) had a hydrogen leak throughout the ascent, causing the engine to run hot. Controllers sweated as temperatures neared redline. The hot engine's controller compensated as programmed by using additional liquid oxygen propellant. The final result was that the shuttle ran out of gas - main engine cut-off (MECO) was at 04:39 GMT, putting Columbia into a 78 km x 276 km x 28.5 degree transfer orbit. Columbia was 1,700 kg short of oxygen propellant and 5 meters/sec slower than planned. The OMS-2 engine burn at 05:12 GMT circularised the orbit 10 km lower than planned.
The orbiter payload bay contained only the Chandra spacecraft, the IUS, and the IUS tilt tableTthe following payloads were carried in the shuttle's cabin: STL-B (Space Tissue Loss), CCM (Cell culture module), SAREX-II (Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment), EarthKam, PGIM (Plant Growth Investigations in Microgravity), CGBA (Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus), MEMS (Micro-electric Mechanical System), and BRIC (Biological Research in Canisters) and SWUIS (the Southwest Ultraviolet Imaging System, an 0.18-m UV telescope to be used for airglow and planetary observations); GOSAMR (the Gelation of Sols: Applied Microgravity Research experiment) and LFSAH, the Lightweight Flexible Solar Array Hinge. MSX and SIMPLEX experiments were also to be carried out.
Chandra/IUS-27 was deployed from Columbia at 11:47 GMT July 23. Flight duration was limited; this was the heaviest shuttle (122,534 kg) and heaviest payload (19,736 kg) to that date. Columbia landed at 03:20 GMT on July 28 on runway 33 at Kennedy Space Center. Post-flight inspection found the presence of holes in the cooling lines on the nozzle of SSME 2019 (engine 3) which caused a hydrogen leak. A loose repair pin in the engine broke free and caused the failure. The cause of the short was found to be chaffed wiring inside the shuttle. The entire fleet was grounded for inspection and replacement of wiring as necessary.
- Chandra - .
Payload: OV-102. Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Huntsville.
Manufacturer: TRW.
Class: Astronomy.
Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: Chandra.
USAF Sat Cat: 25867 . COSPAR: 1999-040B. Apogee: 128,769 km (80,013 mi). Perigee: 20,046 km (12,455 mi). Inclination: 45.10 deg. Period: 3,808.60 min.
The Chandra Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility was one of NASA's four Great Observatories (along with Hubble Space Telescope, Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, and the SIRTF). Chandra will study the composition and nature of galaxies, stellar objects and interstellar phenomena as well as basic issues in theoretical physics using the most sensitive X-ray telescope ever built. The IUS under-performed and placed Chandra in an orbit about 900 km lower than planned. Therefore Chandra's own IPS propulsion system had to be used to make up the difference. The first such manoeuvre was at 01:11 GMT on July 25 when the IPS engines fired for 5 minutes to raise perigee to 1192 km. Further perigee burns on July 31, August 4, and August 7 raised the orbit to its final 10,000 km x 140.000 km. Additional Details: here....
1999 December 20 - . 00:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-103 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Brown,
Clervoy,
Foale,
Grunsfeld,
Kelly, Scott,
Nicollier,
Smith, Steven.
Payload: Discovery F27. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Brown,
Clervoy,
Foale,
Grunsfeld,
Kelly, Scott,
Nicollier,
Smith, Steven.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-103.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 7.97 days. Decay Date: 1999-12-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 25996 . COSPAR: 1999-069A. Apogee: 609 km (378 mi). Perigee: 563 km (349 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 96.40 min.
Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission SM-3A, delayed repeatedly by technical problems with the shuttle fleet after the near-disastrous previous launch. Finally launched after the last possible day to avoid Y2K computer problems; one spacewalk was cancelled so that the shuttle could return by December 28. Hubble was in a 591 km x 610 km x 28.5 deg orbit at launch. After separation of the external tank ET-101 the Orbiter was in a 56 km x 587 km x 28.5 deg transfer orbit. The OMS 2 burn at 0134 UTC raised the orbit to 313 km x 582 km. The payload bay contained:
- Bay 1-2: External airlock/ODS
- Bay 7-8: ORU Carrier (Spacelab pallet). Carried Hubble replacement spares arranged as follows: COPE protective enclosure with three RSU gyros, a new solid state recorder, and an S-band transmitter; LOPE enclosure with an HST-486 computer and voltage improvement kit; ASIPE enclosure with a spare HST-486 and spare RSU; FSIPE enclosure with a replacement FGS-2 fine guidance sensor; and NPE enclosure with New Outer Blanket Layer insulation.
- Bay 11: Flight Servicing System (FSS). Contained the BAPS (Berthing and Positioning System) used to dock with the aft end of the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Bay 8: APC carrier with foot restraint
- Bay 12: APC carrier with HST foot retstraint
2000 February 11 - . 17:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-99 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Gorie,
Kavandi,
Kregel,
Mohri,
Thiele,
Voss, Janice.
Payload: Endeavour F14. Mass: 116,277 kg (256,346 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gorie,
Kavandi,
Kregel,
Mohri,
Thiele,
Voss, Janice.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-99.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 11.23 days. Decay Date: 2000-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 26088 . COSPAR: 2000-010A. Apogee: 234 km (145 mi). Perigee: 226 km (140 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
On an extremely successful mission the space shuttle Endeavour deployed the 61 metre long STRM mast. This was a side-looking radar that digitally mapped with unprecedented accuracy the entire land surface of the Earth between latitudes 60 deg N and 54 deg S. Sponsors of the flight included the US National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA), NASA, and the German and Italian space agencies. Some of the NIMA data would remain classified for exclusive use by the US Department of Defense.
2000 May 19 - . 10:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-101 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Halsell,
Helms,
Horowitz,
Usachyov,
Voss,
Weber, Mary,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Payload: Atlantis F21. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Halsell,
Helms,
Horowitz,
Usachyov,
Voss,
Weber, Mary,
Williams, Jeffrey.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-101.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 9.84 days. Decay Date: 2000-05-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 26368 . COSPAR: 2000-027A. Apogee: 381 km (236 mi). Perigee: 352 km (218 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
ISS Logistics flight. Launch delayed three times by weather. Objective of mission STS-101 was repair, resupply and construction tasks aboard the international space station. This was the first launch with new electronic cockpit displays and other upgrades. The solid boosters separated at 10:13 GMT and the main engines cutoff at 10:19 GMT. The external tank, ET-102 then separated, with both orbiter and ET-102 in a 52 x 320 km initial orbit. At 10:54 GMT the OMS engines fired to raise perigee to 159 x 329 km x at 51.6 deg. Atlantis docked with the International Space Station's PMA-2 docking adapter on the Unity node at 04:31 GMT on May 21. At that time the ISS was in a 332 x 341 km orbit.
On May 22 mission specialists Jeff Williams and James carried out external maintenance work on the ISS.
On May 23 at 00:03 GMT the Atlantis crew opened the first hatch to PMA-2 and entered the Station. The crew replaced a set of batteries in Zarya, installed fans and ducting to improve airflow, and delivered supplies and equipment. Three hour-long orbit raising burns on May 24 and 25 by the RCS engines on Atlantis raised the station to a 372 x 380 km x 51.6 deg orbit.
The STS-101 crew left the station on May 26, closing the PMA-2 hatch at 08:08 GMT and undocking at 23:03 GMT. Atlantis performed a 180 degree flyaround of the station and departed the vicinity around 23:44 GMT.
Atlantis closed its payload bay doors around 02:30 GMT on May 29 and fired the OMS engines for deorbit at 05:12 GMT. The vehicle landed on RW15 at Kennedy Space Center at 06:20 GMT. Atlantis was to be turned around for the next ISS shuttle flight, STS-106.
Left in orbit was the renovated International Space Station, equipped with an upgraded electrical system, new fans, filters, fire extinguishers, smoke detectors and communications gear.
2000 September 8 - . 12:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-106 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Altman,
Burbank,
Lu,
Malenchenko,
Mastracchio,
Morukov,
Wilcutt.
Payload: Atlantis F22. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Altman,
Burbank,
Lu,
Malenchenko,
Mastracchio,
Morukov,
Wilcutt.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-106.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 11.80 days. Decay Date: 2000-09-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 26489 . COSPAR: 2000-053A. Apogee: 387 km (240 mi). Perigee: 375 km (233 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.20 min.
Atlantis was launched from Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39B. Solid rocket boosters RSRM-75 and external tank ET-103 were used to loft the orbiter into space. The inital orbit of 72 x 328 km x 51.6 deg was circularised by the Shuttle's OMS engines at apogee.
Atlantis docked with the PMA-2 adapter on the International Space Station at 05:51 GMT on September 10. The orbiter's small RCS engines were used to gently reboost the station's orbit several times.
Astronauts Lu and Malenchenko made a spacewalk on September 11 beginning at 04:47 GMT. They rode the RMS arm up to Zvezda and began installing cables, reaching a distance of 30 meters from the airlock when installing Zvezda's magnetometer. Total EVA duration was 6 hours 21 minutes.
During their 12-day flight, the astronauts spent a week docked to the International Space Station during which they worked as movers, cleaners, plumbers, electricians and cable installers. In all, they spent 7 days, 21 hours and 54 minutes docked to the International Space Station, outfitting the new Zvezda module for the arrival of the Expedition One crew later this fall.
The Shuttle undocked from ISS at 03:44 GMT on September 18 and made two circuits of the station each lasting half an orbit, before separating finally at 05:34 GMT. The payload bay doors were closed at 04:14 GMT on September 20 and at 06:50 GMT the OMS engines ignited for a three minute burn lowering the orbit from 374 x 386 km x 51.6 deg to 22 x 380 km x 51.6 deg. After entry interface at 07:25 GMT, the orbiter glided to a landing on runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center with main gear touchdown at 07:56:48 GMT for a mission duration of 283 hr 11min.
2000 October 11 - . 23:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-92 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Chiao,
Duffy,
Lopez-Alegria,
McArthur,
Melroy,
Wakata,
Wisoff.
Payload: Discovery F28. Mass: 115,127 kg (253,811 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Chiao,
Duffy,
Lopez-Alegria,
McArthur,
Melroy,
Wakata,
Wisoff.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-92.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 12.90 days. Decay Date: 2000-10-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 26563 . COSPAR: 2000-062A. Apogee: 394 km (245 mi). Perigee: 386 km (240 mi). Inclination: 51.57 deg. Period: 92.28 min.
ISS Logistics flight. 100th shuttle flight. Launch delayed from October 6. STS-92 brought the Z-1 Truss (mounted on a Spacelab pallet), Control Moment Gyros, Pressurised Mating Adapter-3 (PMA-3) and two DDCU (Heat pipes) to the International Space Station.
The RSRM-76 solid rocket boosters separated at 23:19 GMT and main engine cut-off (MECO) came at 23:25 GMT. External tank ET-104 separated into a 74 x 323 km x 51.6 deg orbit. At apogee at 00:01 GMT on Oct 12, Discovery's OMS engines fired to raise perigee to a 158 x 322 km x 51.6 deg orbit; ET-104 re-entered over the Pacific around 00:30 GMT. At Oct 12 on 03:01 GMT the NC1 burn raised the orbit to 180 x 349 km; NC3 on Oct 12 to 311 x 375 km; and the TI burn at 14:09 GMT on Oct 13 to 375 x 381 km x 51.6 deg. Discovery's rendezvous with the International Space Station came at 15:39 GMT on Oct 13, with docking at 17:45 GMT. The spaceship docked with PMA-2, the docking port on the +Y port of the Space Station's Unity module. Hatch was open to PMA-2 at 20:30 GMT the same day.
STS-92 Cargo Manifest
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System + 3 EMU spacesuits
- Bay 5 Port: Adapter Beam with DDCU-HP control unit
- Bay 5 Starboard: Adapter Beam with DDCU-HP control unit
- Bay 7-8: Spacelab Pallet MD003 with PMA-3
- Bay 10-12: ISS Z1 first segment of the space station truss
- Bay 13 Adapter Beam with IMAX Cargo Bay Camera
- Sill: Canadarm RMS 301
Total payload bay cargo: ca. 14,800 kg
The Z1 first segment of the space station truss was built by Boeing/Canoga Park and was 3.5 x 4.5 meters in size. It was attached to the +Z port on Unity. Z1 carried the control moment gyros, the S-band antenna, and the Ku-band antenna.
PMA-3, built by Boeing/Huntington Beach, was docked to the -Z port opposite Z1. PMA-3 was installed on a Spacelab pallet for launch.
On October 14 at 16:15 GMT the Z1 segment was unberthed from the payload bay and at around 18:20 GMT it was docked to the zenith port on the Unity module.
On October 15 at 14:20 GMT the ODS airlock was depressurised, beginning a spacewalk by Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao. Official NASA EVA duration (battery power to repress) was 6 hours 28 minutes.
The second spacewalk was on October 16, with Jeff Wisoff and Mike Lopez-Alegria. The suits went to battery power at 14:15 GMT and Wisoff left the airlock at 14:21 GMT. Repressurisation began at 21:22 GMT for a duration of 7 hours 07minutes.
Leroy Chiao and Bill McArthur began the third STS-92 EVA at 15:30 GMT on October 17, completing their work at 22:18 GMT for a total time of 6 hours 48 minutes.
After the spacewalk, Discovery completed the second of the three station reboosts scheduled for STS-92. They fired reaction control system jets in a series of pulses of 1.4 seconds each, over a 30-minute period, gently raising the station's orbit by about 3.1 km.
The last of four successful spacewalks began on 18 October at 16:00 GMT and ended at 22:56 GMT, lasting 6 hours and 56 minutes. Jeff Wisoff and Mike Lopez-Alegria each jetted slowly through space above Discovery's cargo bay.
After the space walk, Discovery completed the third and final reboost of the space station.
On 19 October the astronauts worked within the ISS. They completed connections for the newly installed Z1 external framework structure and transferred equipment and supplies for the Expedition One first resident crew of the Station. The crew also tested the four 290-kg gyroscopes in the truss, called Control Moment Gyros, which will be used to orient the ISS as it orbits the Earth. They will ultimately assume attitude control of the ISS following the arrival of the U.S. Laboratory Destiny. The tests and the transfer of supplies into the Russian Zarya Module took longer than expected. As a result, the crew's final departure from the Station's Unity module was delayed. Melroy and Wisoff took samples from surfaces in Zarya to study the module's environment. They then unclogged the solid waste disposal system in the Shuttle's toilet, which was restored to full operation after a brief interruption in service.
Discovery undocked from the ISS at 16:08 GMT on 20 October. The final separation burn was executed about 45 minutes after undocking. The crew had added 9 tonnes to the station's mass, bringing it to about 72 tonnes. The return to earth, planned for 22 October, was delayed repeatedly due to high winds at the Kennedy landing site. The landing was finally made at Edwards Air Force Base, California, on October 24, at 22:00 GMT.
2000 December 1 - . 03:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-97 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Bloomfield,
Garneau,
Jett,
Noriega,
Tanner.
Payload: Endeavour F15. Mass: 120,742 kg (266,190 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bloomfield,
Garneau,
Jett,
Noriega,
Tanner.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: North American.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-97.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 10.83 days. Decay Date: 2000-12-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 26630 . COSPAR: 2000-078A. Apogee: 365 km (226 mi). Perigee: 352 km (218 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.70 min.
Endeavour was launched on an assembly mission to the to the International Space Station (ISS). The main mission was to install a 72 m x 11.4 m, 65 kW double-wing solar panel on the Unity module of the ISS. The external tank and the Orbiter entered a 74 x 325 km orbit at 0314 GMT. Endeavour's OMS burn raised its perigee to 205 km at around 0347 GMT; the ET re-entered over the Pacific. Endeavour docked with the Station's PMA-3 docking port at 1959 GMT on December 2. Astronauts then installed the P6 solar panel truss to the station during a series of spacewalks. The P6 was made up of the LS (Long Spacer), PV-1 IEA (Integrated Equipment Assembly) and the PVAA (Photovoltaic Array). The LS carried two Thermal Control Systems with radiators to eject waste heat from the Station; these radiators were to be moved to truss segments S4 and S6 later in assembly. The PVAA had solar array wings SAW-2B and SAW-4B, which deployed to a span of 73 meters. Only after completion of three station assembly space walks on December 3, 5, and 7 did the Endeavour crew enter the station (at 1436 GMT on December 8), delivering supplies to Alpha's Expedition One crew. Hatches were closed again at 1551 GMT December 9, and Endeavour undocked at 1913 GMT the same day. After one flyaround of the station, Endeavour fired its engines to depart the vicinity at 2017 GMT December 9. The deorbit burn was at 2158 GMT on December 11, changing the orbit from 351 x 365 km to 27 x 365 km, with landing at Runway 15 of Kennedy Space Center at 2303 GMT.
The payload bay of Endeavour for STS-97 contained a total cargo of 18740 kg:
- Bay 1-2:
- Orbiter Docking System 1800 kg
- 3 EMU spacesuits (S/N unknown) 360 kg
- FPPU experiment (in airlock) 23 kg. The FPPU (Floating Potential Probe Experiment) was installed on P6 to measure charge build-up as the arrays pass through the ionosphere plasma. P6 had devices to bleed off excess charge, and FPPU would monitor their effectiveness.
- APCU Assembly Power Converter Unit 35 kg
- APCU Assembly Power Converter Unit 35 kg
- Bay 3-6:
- ITS P6 Long Spacer 4000 kg
- TCS radiator (aft) 500 kg
- TCS radiator (starboard) 500 kg
- Bay 8-11:
- ITS P6 Integrated Equipment Assembly 7200 kg
- PV radiator P6 500 kg
- Bay 12-13:
- ITS P6 Photovoltaic Array/Beta Gimbal Assembly. 1000 kg
- Solar array wing 2B 1070 kg
- Solar array wing 4B 1070 kg
- Bay 13S: IMAX Cargo Bay Camera 238 kg
- Sill: Canadarm RMS 303 410 kg
- Bay 1-2:
2001 February 7 - . 23:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-98 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Cockrell,
Curbeam,
Ivins,
Jones,
Polansky.
Payload: Atlantis F23. Mass: 90,225 kg (198,912 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Cockrell,
Curbeam,
Ivins,
Jones,
Polansky.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-98.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 12.89 days. Decay Date: 2001-02-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 26698 . COSPAR: 2001-006A. Apogee: 337 km (209 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 51.30 deg. Period: 89.71 min.
ISS Assembly flight. Launch delayed from January 18 and February 6. International Space Station assembly mission; delivered the Destiny and PMA-2 modules. Destiny was an American ISS module, an 8.4 meter long and 4.2 meter wide cylindrical structure with a mass of 15 tonnes. It was to function as a science and technology module and the primary control module for the ISS. The shuttle orbiter was placed in an initial 74 x 323 km x 51.6 deg orbit. At 2357 GMT the OMS engines fired for the OMS-2 burn which raised Atlantis' orbit to 204 x 322 km x 51.6 deg. Atlantis docked with the Station at 1651 GMT on February 9 at the PMA-3 port on Unity's nadir. At 1500 GMT on Feb 10 Marsha Ivins used the RMS arm to unberth the PMA-2 docking port from Unity. Tom Jones and Bob Curbeam then conducted three spacewalks on Februay 10 to 14 to attach the Destiny and PMA-2 modules to the station. The crew also delivered over a tonne of food, fuel and equipment to the ISS. Atlantis undocked from Alpha at 1406 GMT on February 16. Atlantis landed at Edwards AFB on February 20; plans to land on February 18 and 19 were called off due to persistent wind problems at Kennedy Space Center. The deorbit burn was at 1927 GMT and lowered the orbit from 370 x 386 km to about 50 x 380 km. The nominal entry interface at 122 km came at 2002 GMT and touchdown on runway 22 was at 20:33 GMT. On March 1 Atlantis was flown on the back of NASA's SCA 911 carrier aircraft to Altus AFB, Oklahoma, en route to Kennedy.
2001 March 8 - . 11:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP3. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-102 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Helms,
Kelly, James,
Richards, Paul,
Thomas, Andrew,
Usachyov,
Voss,
Wetherbee.
Payload: Discovery F29. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Helms,
Kelly, James,
Richards, Paul,
Thomas, Andrew,
Usachyov,
Voss,
Wetherbee.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-102,
STS-102 ISS EO-2.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 12.83 days. Decay Date: 2001-03-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 26718 . COSPAR: 2001-010A. Apogee: 381 km (236 mi). Perigee: 370 km (220 mi). Inclination: 51.50 deg. Period: 92.06 min.
STS 102 was an American shuttle spacecraft that carried a crew of seven astronauts (six American and one Russian). The primary mission was to deliver a multi-rack Italian container (Leonardo MultiPurpose Logistics Module, LMPLM) to the Destiny Module of the International Space Station, ISS. It docked with the ISS at 05:34 UT on 9 March. The 6.4 m x 4.6 m cylindrical LMPLM delivered new equipment to Destiny, and retrieved used/unwanted equipment, and trash back to the shuttle. The crew did a few spacewalks to install a platform on the ISS to support a Canadian robot arm when it arrives next month. The STS 102 left behind three of the astronauts (two American and one Russian) and brought back the three astronauts (one American and two Russian) who had been inhabiting the ISS for about four and a half months. It landed at Cape Canaveral at 07:31 UT on 21 March.
Discovery was launched on mission STS-102 (Space Station flight 5A.1) into an initial 60 x 222 km x 51.6 deg orbit. The mission was delivery of supplies and equipment, and changeout of the Expedition One and Expedition Two station crews. STS-102 carried the Leonardo Multi Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), built by Alenia Spazio (Torino), to the International Space Station. The 6.4 m x 4.6 m cylindrical MPLM was a descendant of the Spacelab long modules. Also carried was a Spacehab/Energia unpressurized Integrated Cargo Carrier with LCA/MTSAS-A, RU, and PFCS. A sidewall adapter beam with two GAS canisters (G-783 and WSVFM) was also on board. WSVFM measured vibration during launch. Another adapter beam, probably at the rear of the payload bay, carried SEM-9. SEM-9 and G-783 contained high school microgravity experiments.
Leonardo carried 16 'racks' of equipment, including the Human Research Facility Rack (Rack 13) which allowed the astronauts to do extensive medical experiments, the CHeCS Rack (28), the DDCU-1 and DDCU-2 racks (7 and 9), the Avionics-3 (Rack 6), and the MSS Avionics/Lab (Rack 11) and Avionics/Cupola (Rack 12) racks for a total of 7 equipment racks to be installed on Destiny. Three Resupply Stowage Racks (50, 51, 52) and four Resupply Stowage Platforms (180, 181, 182 and 188) remained installed on Leonardo, with their equipment bags being individually transferred to the Station. System Racks 2, 3, 4, 5 and 8 were already on Destiny together with stowage racks 110 through 117. Each rack had a mass of 150-300 kg.
The orbiter fired its OMS engines at 1221 GMT to raise the orbit to 185 x 219 km. Discovery docked with the PMA-2 port on the Station at 0639 GMT on March 10. The LCA (Lab Cradle Assembly) was attached to Destiny's +Z side during an EVA. It was to be used on the next mission to temporarily place a Spacelab pallet on Destiny during installation of the Station's robot arm. Later, it would be the site for the main Station truss, beginning with segment S0.
The PMA-3, on Unity at the -Z nadir position, had to be moved to the port position to make room for Leonardo. An external stowage platform was attached to Destiny and the External Stowage Platform and the PFCS Pump Flow Control System were added to the port aft trunnion on Destiny. A rigid umbilical (RU) was connected to the PDGF grapple fixture on Destiny to support the Station's future robot arm. Leonardo was docked to Unity at -Z for a while so that its cargo could be transferred to the station easily; it was then be returned to the payload bay and brought back to earth.
At 0232 GMT on March 19 command of ISS was transferred to Expedition 2 and the hatches were closed. Discovery undocked at 0432 GMT and flew once around the station before departing at 0548 GMT. ISS mass after undocking was 115527 kg. The OMS engines fired for the deorbit burn at 0625 GMT on March 21, and Discovery touched down on runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center at 0731 GMT.
2001 April 19 - . 18:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-100 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Ashby,
Guidoni,
Hadfield,
Lonchakov,
Parazynski,
Phillips,
Rominger.
Payload: Endeavour F16 / Raffaello, Canadarm-2. Mass: 103,506 kg (228,191 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Ashby,
Guidoni,
Hadfield,
Lonchakov,
Parazynski,
Phillips,
Rominger.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-100.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 11.90 days. Decay Date: 2001-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 26747 . COSPAR: 2001-016A. Apogee: 404 km (251 mi). Perigee: 378 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.40 min.
Space Shuttle OV-105 Endeavour was launched on mission STS-100 to carry out International Space Station Flight 6A continued the outfitting of the Station. The crew of four Americans, one Russian, one Canadian and one Italian were to install an 18 meter, 1,700 kg Canadian robotic arm named Canadarm-2 on the ISS, and to transport an Italian cargo container, Raffaello, which delivered 4,500 kg of supplies and equipment to the station. Total payload of 13,744 kg consisted of:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System, External Airlock, 3 EMU spacesuits - 2160 kg including 360 kg for the 3 suits
- Bay 3 Starboard: Adapter Beam with DCSU switching unit - 180kg
- Bay 5: Spacelab Pallet with Canadarm-2 SSRMS (Space Station Remote Manipulator System, 1800 kg mass), LDA, and 56 kg UHF antenna - 3256 kg
- Bay 6 Port: Adapter Beam with IMAX Camera - 238 kg
- Bay 8-12: Rafaello Module (MPLM-2) with MPLM racks and 3400 kg cargo - 7500 kg
- Sill: Canadarm RMS 303 - 410 kg
On 23 April the SSRMS station manipulator was unberthed from the SLP Spacelab pallet at 1114 GMT and latched on to the PDGF fixture on the Destiny ISS module at 1416 GMT. This was followed at 1458 GMT with the MPLM-2 Raffaello module being moved from Endeavour's payload bay by the Shuttle's RMS and berthed to the nadir port on the ISS Unity module at 1600 GMT. Over the next few days, the cargo racks on the MPLM were transferred to Destiny. Raffaello was then unberthed from Unity at 2003 GMT on April 27 and reberthed in the rear of Endeavour's bay for return to earth at 2059 GMT.
Undocking of Endeavour was delayed by a series of computer problems at the Station. Failures in the Station's command and control computers left only one of the three computers operating.
They were all restarted by April 29, and the Shuttle RMS grappled the Spacelab pallet at 2044 GMT . The station's Canadarm-2 released it at 2106 GMT, and the RMS berthed the pallet back in the Shuttle cargo bay. Endeavour undocked from the Station at 1734 GMT on April 29. The weather in Florida was bad at the planned May 1 landing time, so Endeavour landed in California. The deorbit burn was at 1502 GMT on May 1, with landing at 1610:42 GMT on runway 22 at Edwards. Endeavour returned to the Kennedy Space Center atop a Boeing 747 SCA aircraft on May 9.
2001 July 12 - . 09:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-104 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Gernhardt,
Hobaugh,
Kavandi,
Lindsey,
Reilly.
Payload: Atlantis F24 / Quest. Mass: 117,127 kg (258,220 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gernhardt,
Hobaugh,
Kavandi,
Lindsey,
Reilly.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-104.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 12.77 days. Decay Date: 2001-07-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 26862 . COSPAR: 2001-028A. Apogee: 395 km (245 mi). Perigee: 378 km (234 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
STS-104 was an American ISS Assembly shuttle flight with a crew of five American astronauts and a major space station module, the Quest Airlock. Orbiter OV-104 Atlantis main engine cutoff and external tank separation was at 0913 GMT. Atlantis was then in an orbit of 59 x 235 km x 51.6 deg. The OMS-2 burn at 0942 GMT increased velocity by 29 m/s and raised the orbit to 157 x 235 km x 51.6 deg and another burn at 1240 GMT raised it further to 232 x 305 km. Atlantis docked with the International Space Station at 0308 GMT on July 14. The main payload on STS-104 was the Quest Joint Airlock, built by Boeing/Huntsville. It consisted of an Equipment Lock for storage and the Crew Lock, based on the Shuttle airlock. The 13,872 kg payload consisted of:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System/External Airlock - 2160 kg including 3 EMU spacesuits
- Bay 4-5: Spacelab Pallet (Fwd) with O2-1/O2-2 oxygen tanks - 2500 kg
- Bay 6-7: Spacelab Pallet (Aft) with N2-1/N2-2 nitrogen tanks - 2500 kg
- Bay 8-12: Station Joint Airlock Adapter beam (6064 kg) with IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (238 kg)
- Sill: RMS arm - 410 kg
The six tonne Airlock consisted of two cylinders of four meters diameter and a total length six meters. The Airlock could be pressurized by the externally-mounted high pressure oxygen-nitrogen tanks, and was to be the sole unit through which all future EVAs were to take place. (Until that point, all EVA entries/exits had been through a Russian module in ISS, with non-Russians having to wear Russian space suits). Another payload was the "EarthKAM" of middle/high school interest. It was to allow pupils to command picture-taking of chosen spots on Earth; they were expected to target 2,000 spots. The shuttle also carried out pulsed exhaust tests during maneuvers to enable better understanding of the formation of HF echoes from the shuttle exhaust. The echoes were obtained by ground based radars in an experiment called SIMPLEX (Shuttle Ionospheric Modification with Pulsed Local EXhaust). The STS-104 crew returned to Atlantis on July 22, and undocked at 0455 GMT. After flying around the station they departed the vicinity at 0615 GMT. Atlantis landed at 0338:55 GMT on July 25, touching down at Kennedy Space Center runway 15.
2001 August 10 - . 21:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-105 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Barry,
Culbertson,
Dezhurov,
Forrester,
Horowitz,
Sturckow,
Tyurin.
Payload: Discovery F30 / Leonardo. Mass: 116,914 kg (257,751 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Barry,
Culbertson,
Dezhurov,
Forrester,
Horowitz,
Sturckow,
Tyurin.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-105,
STS-105 ISS EO-3.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 11.88 days. Decay Date: 2001-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 26888 . COSPAR: 2001-035A. Apogee: 402 km (249 mi). Perigee: 373 km (231 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
STS 105 was an American shuttle that carried a crew of ten (including three crew for the ISS - one American and two Russian), five tonnes of supplies, hardware, and a bedroom suite to accommodate a third astronaut in the Destiny module. The crew installed in the station two new science experiment racks that were carried in the Leonardo container which was first lifted out of the shuttle and bolted to the Unity module. Leonardo then carried back all the trash from the ISS back to the shuttle. They crew installed the MISSE (Materials International Space Station Experiment) container outside the ISS to test the effect of radiation on materials and some low-cost science experiments such as microgravity cell growth studies inside the station.
The 15,107 kg payload consisted of:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System/External Airlock and 3 EMU spacesuits - 2160 kg
- Bay 4P: Adapter beam with G-780 (Mayo High School, Rochester, Minnesota experiment to study germination of faba beans) and PSP-1 (NASA-GSFC canister with passive experiments and ballast) - 200 kg
- Bay 5: Integrated Cargo Carrier/KYD - 1280 kg, with the Early Ammonia Servicer for the station's P6 truss- 640 kg and two small exposure experiments PEC-1 and PEC-2, to be installed on the be installed on the ISS Quest module as part of the MISSE materials exposure program
- Bay 7-12: MPLM FM1 (Leonardo) module - 9800 kg total including 3300 kg of payload to be transferred to the Station
- Bay 13P: Adapter beam with G-774 (Microgravity Smoldering Combustion (MSC) experiment) and SEM-10 (canister with 11 school experiments) - 410 kg
- Bay 13S: Adapter beam with Simplesat and ACE avionics - 355 kg
- Sill: RMS arm - 410 kg
The Leonardo MPLM module was lifted out of Discovery's payload bay at 1326 GMT on August 13 and docked to Unity's nadir at 1554 GMT. 3300 kg of cargo from Leonardo was transferred to the Station. Then 1700 kg of station garbage and materials were loaded into Leonardo. It was unberthed from Unity at 1816 GMT on August 19 and returned to the payload bay for the return to Earth at 1917 GMT.
Discovery undocked at 1452 GMT on August 20 with the Expedition 2 crew aboard, leaving Expedition 3 at the Station.
At 1830 GMT on August 20 the Simplesat test satellite was ejected from a GAS canister in the cargo bay. Discovery landed at Kennedy Space Center at 1822:58 GMT on August 22 on runway 15, after a deorbit burn at 1715 GMT. The Expedition Two crew of Usachyov, Voss and Helms had been in space for 167 days. Discovery was taken out of service after the flight for structural inspections. Its last maintenance down period was in 1995-1996.
- Simplesat - . Mass: 52 kg (114 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: Simplesat. Decay Date: 2002-01-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 26889 . COSPAR: 2001-035B. Apogee: 135 km (83 mi). Perigee: 130 km (80 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 87.10 min. Simplesat was small astronomical test satellite ejected from a GAS Cannister in shuttle Discovery's payload bay. No contact was ever made with Simplesat after its release; evidently the satellite failed. .
2001 December 5 - . 22:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-108 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Bursch,
Godwin,
Gorie,
Kelly, Mark,
Onufrienko,
Tani,
Walz.
Payload: Endeavour F17 / Raffaello. Mass: 105,000 kg (231,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bursch,
Godwin,
Gorie,
Kelly, Mark,
Onufrienko,
Tani,
Walz.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-108,
STS-108 ISS EO-4.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 11.82 days. Decay Date: 2001-12-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 26995 . COSPAR: 2001-054A. Apogee: 377 km (234 mi). Perigee: 353 km (219 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.80 min.
ISS Logistics flight, launch delayed from November 30 and December 4. Gorie, Kelley, Godwin, Tani, Onufrikeno, Bursch, Walz STS-108 flew the UF-1 Utilization Flight mission to the International Space Station. The UF designation distinguished this from earlier Station flights which were considered assembly flights. The shuttle would deliver the Expedition-4 crew of Onufrikeno, Bursch, and Walz to the station and return the Expedition-3 crew to earth. In addition to the crew swap, UF-1 brought supplies to the Station aboard the Raffaello module, and Godwin and Tani conducted a spacewalk to add thermal blankets to the gimbals on the Station's solar arrays. Endeavour reached an orbit of approximately 58 x 230 km (according to the NASA PAO) at 2228 GMT. At 2259 GMT it fired its OMS engines to raise perigee to 225 km. Mass after OMS-2 was 114,692 kg. Endeavour soft docked with the International Space Station at 2003 GMT on December 7. Problems with aligning the vehicles delayed hard dock until 20:51 GMT, and the hatch was opened at 22:43 GMT. The Raffaello module was unberthed from Endeavour at 1701 GMT on December 8 and berthed to the Unity module of the station at 1755 UTC.
STS-108 cargo bay payload was dominated by the Raffaello (MPLM-2) logistics module with 4 RSP and 8 RSR resupply racks. Also in the cargo bay were the MACH-1 and LMC experiment trusses flown under the Goddard small payloads program. MACH-1 was an MPESS-type Hitchhiker bridge carrying the CAPL-3 capillary thermal control experiment on top. On its forward side was the Starshine-2 launch canister, the CAPL-3 avionics plate, the Hitchhiker avionics plate, and the SEM-15 canister. On the aft side was the G-761 canister containing experiments from Argentina, the PSRD synchrotron detector (a prototype for the AMS antimatter experiment which will fly on Station later), and the COLLIDE-2 and SEM-11 canisters. The SEM (Space Experiment Modules) are collections of high school experiments. LMC, the Lightweight MPESS Carrier carried four canisters with materials science and technology experiments: SEM-12, G-785, G-064 and G-730. In addition, an adapter beam on the starboard sidewall carried G-221 and G-775, with materials science and biology experiments.
Raffaello was transferred back to the Shuttle payload bay on December 14. Endeavour undocked from the Station at 17:28 UTC on December 15 and made a half loop around the station before making a small separation burn at 1822 UTC. The Starshine-2 reflector satellite was ejected from the MACH-1 bridge in Endeavour's payload bay at 1502 UTC on December 16. Endeavour landed on runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center at 1755 UTC on December 17. The Expedition 3 crew of Culbertson, Dezhurov and Tyurin returned to Earth aboard Endeavour, leaving the Expedition 4 crew of Onufrienko, Bursch and Walz in charge of the Station.
2002 March 1 - . 11:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-109 - .
Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Altman,
Carey,
Currie,
Grunsfeld,
Linnehan,
Massimino,
Newman.
Payload: Columbia F27. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Altman,
Carey,
Currie,
Grunsfeld,
Linnehan,
Massimino,
Newman.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-109.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Columbia.
Duration: 10.92 days. Decay Date: 2002-03-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 27388 . COSPAR: 2002-010A. Apogee: 578 km (359 mi). Perigee: 486 km (301 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 95.30 min.
Hubble Servicing Mission 3B. STS-109 main engine cutoff came at 1130 UTC with Columbia in a 55 x 574 km x 28.5 deg transfer orbit. The OMS-2 burn at about 1207 UTC raised perigee to about 195 km. There was a problem with a freon cooling loop on the Orbiter, but it wasn't quite bad enough to affect the mission. The Hubble Space Telescope closed its aperture door on March 2 in preparation for the rendezvous. Columbia got within 100m of HST by 0852 UTC on March 3 and grappled it with the RMS at 0931 UTC. HST was berthed on the FSS in Columbia's payload bay by 1032 UTC.
In the course of five spacewalks, the crew installed new equipment on HST. This was the first flight of Columbia since the launch of Chandra in 1999 following refurbishment. In the first two spacewalks, two new solar arrays were installed, and the two old arrays stowed on the RAC carrier. The RWA-1R reaction wheel assembly on the MULE carrier replaced the faltering RWA-1 in the telescope. The third spacewalk was the most difficult, as HST was entirely powered down while astronauts replaced its power controller unit, not designed for on-orbit replacement. On the fourth spacewalk the astronauts removed the European FOC camera, aboard HST since launch in 1990, and replaced it with the new ACS (Advanced Camera for Surveys). They also installed the CASH wire harness, part of the aft shroud cooling system. On the final spacewalk, the astronauts installed the NCS (NICMOS cooling system) cryocooler in the aft shround and the associated NCS radiator on the telescope's exterior. The NICMOS infrared camera had been idle since its original thermal control system failed. With the removal of FOC, the COSTAR device (which deployed contact lenses for the original instruments) became obsolete, since the newer instruments made the corrections to the incorrect HST mirror internally. Cargo manifest:
- Middeck:4 EMU spacesuits - 480 kg
- Bay 4: RAC (Rigid Array Carrier) - 2393 kg. The RAC carried the two folded SA-III rigid solar arrays which replaced the SA-II roll-up arrays. It calso carried the DBA2 diode box assembly which controlled the arrays, and a wire harness and containers associated with the NICMOS cooling system.
- Bay 7-8: SAC (Second Axial Carrier) - 2517 kg. The SAC was a specially designed pallet that flew on the first two Hubble SM flights, STS-61 and STS-82. On this flight it carried the ACS camera up (and the FOS camera down) as well as the NCS cryocooler, the PCU-R power controller, the CASH wire harness, and the thermal covers used in the PCU replacement.
- Bay 11: FSS (Flight Support System) - 2111 kg. The FSS first flew on STS 41-C (the Solar Max Repair) and was reused for each of the HST SM flights. It carried the BAPS Berthing and Positioning System, which was the docking ring for HST. Stowed on the FSS were a support post for BAPS and a cover for the HST low gain antenna.
- Bay 12: MULE (Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier) - 1409 kg. The MULE carried the NCS radiator, the NCS electronics support module, and the RWA-1R reaction wheel unit. MULE first flew on STS-48 carrying the UARS satellite, and then on STS-95 carrying the HOST payload which tested out the NCS.
- Sill: RMS arm No 201 - 410 kg
2002 April 8 - . 20:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-110 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Bloomfield,
Frick,
Morin,
Ochoa,
Ross,
Smith, Steven,
Walheim.
Payload: Atlantis F25 / SO. Mass: 100,000 kg (220,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bloomfield,
Frick,
Morin,
Ochoa,
Ross,
Smith, Steven,
Walheim.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-110.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 10.82 days. Decay Date: 2002-04-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 27413 . COSPAR: 2002-018A. Apogee: 402 km (249 mi). Perigee: 309 km (192 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.70 min.
Launch delayed from March 22, April 4. Space Shuttle Atlantis entered an orbit of approximately 59 x 229 km x 51.6 deg at 2052 UTC, and separated from the External Tank, ET-114. ET-114 reached apogee around 2122 UTC and reentered over the Pacific about 2150 UTC at the end of its first orbit. Atlantis fired its OMS engines at apogee to raise its perigee to 155 km. Further orbit changes will lead to a rendezvous with the Space Station on Station mission 8A. STS-110 carried the S0 truss segment to the Station. The truss was the first segment of the main backbone of the Station which was to grow to carry the large solar panel wings and radiators. Cargo manifest:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System - 1800 kg + 3 EMU spacesuits - 360 kg
- Bay 4-13: S0 Truss - 12623 kg. The S0 truss, built by Boeing/Huntington Beach, was 13.4 m long and 4.6 m in diameter. The main truss had a hexagonal cross section. One face carried fluid, power and data cables, while another face carried the rails for the Mobile Transporter. The S0 contained avionics, GPS antennae, and a radiation dose monitor. The S0 would be attached to the LCA (Lab Cradle Assembly) which was attached to the top of the Destiny lab module in 2001. Attached to S0 were:
- 4 x MTS (Module to Truss Structure) struts. These were used to connect it to the Destiny module
- Airlock Spur. This was a 4.2 m beam that hinged out to connect to the Quest module and had handrails for spacewalkers
- Mobile Transporter (MT). This was made by TRW Astro Aerospace in Carpinteria and was an 885 kg, 2.7 m long truck which moved on the S0 rails to transfer heavy cargo along the truss.
- Sill: RMS arm - 410 kg
- Total: 15193 kg
2002 June 5 - . 21:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-111 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Chang-Diaz,
Cockrell,
Korzun,
Lockhart,
Perrin,
Treshchev,
Whitson.
Payload: Endeavour F18 / Leonardo. Mass: 105,000 kg (231,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Chang-Diaz,
Cockrell,
Korzun,
Lockhart,
Perrin,
Treshchev,
Whitson.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-111,
STS-111 ISS EO-5.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour .
Duration: 13.86 days. Decay Date: 2002-06-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 27440 . COSPAR: 2002-028A. Apogee: 387 km (240 mi). Perigee: 349 km (216 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
Launch delayed from May 2, 6, 30, 31 and June 4. STS-111 reached a 58 x 224 km x 51.6 deg orbit at 2131 UTC and separated from the External Tank. It coasted to apogee at 2201 UTC and carried out the OMS-2 burn to raise the orbit to 158 x 235 km. The mission of STS-111 (UF-2 ISS utilization flight) was to swap the Expedition 4 and 5 crews and deliver the MBS Mobile Base System and some interior experiment racks. Endeavour docked with the Station at 1625 UTC on June 7. The Leonardo MPLM module was attached to the Station on June 8. Cargo manifest:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System - 1800 kg + 2 EMU spacesuits - 240 kg
- Bay 4: Mobile Base System (MBS) - 1600 kg. The Mobile Base System was made by MD Robotics of Brampton, Ontario. It was to be attached to the Mobile Transporter and used to mount the SSRMS Canadarm-2 arm and heavy payloads.
- Bay 6P: Adapter Beam / Wrist Roll Joint - 150 kg. The WRJ (Wrist Roll Joint) would be swapped with the broken one on the SSRMS arm.
- Bay 7-12: MPLM FM1 "Leonardo" - 10557 kg. The Leonardo module carried 8 Resupply Stowage Racks and 4 Resupply Stowage Plaftorms, with equipment to be transferred to the station. It also carried two science racks: the MSG (Microgravity Science Glovebox) and Express-3, which would be installed on Destiny. Leonardo, built by Alenia Spazio in Torino, also flew on STS-102 and STS-105.
- Bay 13P: ICAPC Beam / PGDF - 75 kg. The PGDF (Power-Data Grapple Fixture) would be installed on the P6 truss.
- Bay 13S: Adapter Beam / SMDP - 200 kg. The Service Module Debris Panels (SMDP) package contained 6 panels which would be stowed on PMA-1 until a later spacewalk attached them to the Zvezda module to protect it from space debris hits.
- Total: 14622 kg
2002 October 7 - . 19:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-112 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Ashby,
Magnus,
Melroy,
Sellers,
Wolf,
Yurchikhin.
Payload: Atlantis F26 / S1. Mass: 116,640 kg (257,140 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Ashby,
Magnus,
Melroy,
Sellers,
Wolf,
Yurchikhin.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-112.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 10.83 days. Decay Date: 2002-10-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 27537 . COSPAR: 2002-047A. Apogee: 405 km (251 mi). Perigee: 273 km (169 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
ISS Assembly flight delayed from March 22, April 4, August 22, September 28, October 2 due to payload delays and then SSME problems. American shuttle spacecraft STS-112 carried a crew of five Americans and one Russian to the International Space Station (ISS). During the 11-day mission, the crew extended the truss system of the exterior rail line with a 14-m, 13-ton girder. The crew also tested a manual cart on the rails. The cart, named CETA (Crew and Equipment Transportation Aid), was designed to increase mobility of crew and equipment during the later installation phases. STS-112 landed back in Cape Canaveral at 15:43 UT on 2002 October 18 carrying the same crew of six.
2002 November 24 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- MEPSI - .
Mass: 2.00 kg (4.40 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: MEPSI.
Decay Date: 2003-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 27562 . COSPAR: 2002-052B. Apogee: 349 km (216 mi). Perigee: 332 km (206 mi). Inclination: 51.70 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
MEPSI (Micro-Electromechanical-based Picosat Satellite Inspection Experiment) consisted of two 1 kg boxes attached to each other by a 15-m tether. The boxes included an imaging camera and a MEM transceiver. They were ejected from the PLA (Picosat Launch Assembly) of shuttle Endeavour, a 6 kg box attached to an Adaptive Payload Carrier (APC) on the payload bay side wall.
- STS-113 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Bowersox,
Budarin,
Herrington,
Lockhart,
Lopez-Alegria,
Pettit,
Wetherbee.
Payload: Endeavour F19 / P1. Mass: 115,000 kg (253,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bowersox,
Budarin,
Herrington,
Lockhart,
Lopez-Alegria,
Pettit,
Wetherbee.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-113,
STS-113 ISS EO-6.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 13.78 days. Decay Date: 2002-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 27556 . COSPAR: 2002-052A. Apogee: 397 km (246 mi). Perigee: 379 km (235 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.30 min.
ISS assembly mission ISS-11A delayed from August 22, September 6, 19, October 6, November 2, 10, 11, 19 and 23 due to SSME problems and then damage to the Shuttle's manipulator arm. Shuttle mission STS-113 carried a crew of seven astronauts (six American and one Russian) and a 13.7-m truss of 12.5 tons to the International Space Station (ISS). During several hours of EVA, the crew installed and secured the truss assembly. The truss was to provide structural support for the station's thermal control radiators, and brought the total mass of the ISS to over 200 tons. Prior to leaving the ISS, the shuttle released a pair of tethered (15-m long) picosatellites. It was to leave the ISS on December 2.
2003 January 16 - . 15:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-107 - . Call Sign: Columbia. Crew: Anderson, Brown, David, Chawla, Clark, Husband, McCool, Ramon. Payload: Columbia F28 / Spacehab. Mass: 115,900 kg (255,500 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Anderson, Brown, David, Chawla, Clark, Husband, McCool, Ramon. Agency: NASA. Manufacturer: Boeing. Program: STS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-107. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Columbia. Duration: 15.94 days. Decay Date: 2003-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 27647 . COSPAR: 2003-003A. Apogee: 276 km (171 mi). Perigee: 263 km (163 mi). Inclination: 39.00 deg. Period: 89.90 min. The last solo shuttle earth orbit mission ended in tragedy when the shuttle Columbia disintegrated during re-entry at an altitude of 63.15 km and a speed of Mach 18. Launch delayed from May 23, June 27, July 11 and 19, November 29, 2002..
2004 January 15 - .
- STS-119 (cancelled) - . Crew: Fincke, Gernhardt, Kelly, Mark, Kononenko, Lindsey, Noriega, Padalka. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Fincke, Gernhardt, Kelly, Mark, Kononenko, Lindsey, Noriega, Padalka. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-119A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. STS-119 was to have flown ISS Assembly mission ISS-15A and have carried out a crew rotation..
2004 February 19 - .
- STS-120 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Foreman,
Halsell,
Lawrence,
Poindexter,
Sellers,
Wilson.
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Foreman,
Halsell,
Lawrence,
Poindexter,
Sellers,
Wilson.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Flight: STS-120A.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. STS-120 was to have flown ISS Assembly mission ISS-10A. It would have delivered to the station the second of three station connecting modules, Node 2. With this mission the redefined ISS US Core would have been completed.
Mid-2004 - .
- STS-121 (cancelled) - . Crew: Chiao, Phillips, Sharipov. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Chiao, Phillips, Sharipov. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-121A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-121 was to have flown ISS Assembly mission ISS-9A.1, delivering the SPP with 4 Solar Arrays to the station, and have carried out a crew rotation..
Late 2004 - .
- STS-124 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-124 ISS EO-17. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-124 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-1J/A. It would have delivered the Japanese JEM ELM PS module and SPP to the station..
April 2005 - .
- STS-126 (cancelled) - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Flight: STS-126A.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-126 was to have flown ISS resupply mission ISS-UF3. It would have carried an MPLM module and Express Pallet for delivery of equipment and supplies to the station.
June 2005 - .
- STS-127 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-127 ISS EO-20. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-127 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-1E. It would have delivered the European Lab - Columbus (APM) to the station..
2005 July 26 - . 14:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-114 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Camarda,
Collins, Eileen,
Kelly, James,
Lawrence,
Noguchi,
Robinson,
Thomas, Andrew.
Payload: Discovery F31 / Raffaello. Mass: 116,884 kg (257,685 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Camarda,
Collins, Eileen,
Kelly, James,
Lawrence,
Noguchi,
Robinson,
Thomas, Andrew.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-6,
STS-114.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 13.90 days. Decay Date: 2005-08-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 28775 . COSPAR: 2005-026A. Apogee: 350 km (210 mi). Perigee: 313 km (194 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Return to flight after loss of Columbia. Delayed extensively as NASA attempted to fix the external tank foam-shedding problem that resulted in the loss of Columbia (first planned for September 12, 2004, the launch slipped to March; May 14, 15 and 22; July 13, 2005). Discovery safely reached orbit at a total mass of 121,485 kg, but extensive video coverage detected external tank foam shedding during ascent. Discovery docked at the Pirs module of the ISS on 28 July 28 at 11:18 GMT. Following replenishment of the station (using the Raffaello MPLM-6 module with 8240 kg of supplies), a series of spacewalks verified the integrity of the shuttle's heat shield and tested repair techniques, Discovery undocked from the ISS at 07:24 GMT on 6 August and landed safely on Runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base at 12:11 GMT on 9 August. However the shuttle fleet was immediately grounded again while NASA attempted to find a permanent fix to the external tank foam woes.
Early 2006 - .
- STS-130 (cancelled) - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Flight: STS-130A.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-130 was to have flown ISS resupply mission ISS-UF5. Equipment and supplies would have been delivered to the station aboard an MPLM and Express Pallet in the cargo bay.
Spring 2006 - .
- STS-131 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-131A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-131 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-14A. 4 SPP Arrays and the MMOD would have been delivered to the station..
Late Spring 2006 - .
- STS-132 (cancelled) - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Flight: STS-132A.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-132 was to have flown ISS resupply mission ISS-UF6. Supplies and equipment would have been delivered via an MPLM and EXPRESS Pallet in the cargo bay.
2006 July 4 - . 18:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-121 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Fossum,
Kelly, Mark,
Lindsey,
Nowak,
Reiter,
Sellers,
Wilson.
Return Crew: Fossum,
Kelly, Mark,
Lindsey,
Nowak,
Sellers,
Wilson.
Payload: Discovery F32 / Leonardo. Mass: 121,094 kg (266,966 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Fossum,
Kelly, Mark,
Lindsey,
Nowak,
Reiter,
Sellers,
Wilson.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-8,
STS-121,
STS-121 Astrolab.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 12.78 days. Decay Date: 2006-07-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 29251 . COSPAR: 2006-028A. Apogee: 351 km (218 mi). Perigee: 332 km (206 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
The shuttle was launched using external tank ET-119 and solid motors RSRM-93. Cameras revealed that large chunks of foam were still shed from the external tank during the ascent to orbit. However examination of the heat shield using a new extension and sensors attached to the shuttle's robot arm revealed no significant damage. Discovery docked with the PMA-2 adapter on the Destiny module of the ISS at 14:52 GMT on 6 July. On July 7 the Leonardo cargo module was moved from the shuttle payload bay by the robot arm and docked to the Unity Module of the ISS between 09:42 and 11:50 GMT. The crew then began unloading the spare parts and supplies in the module to the station. A series of three EVAs conducted on 8 to 12 July tested the new equipment and techniques for repairing the shuttle heat shield in case of damage, and did some preliminary installations on the exterior of the ISS to pave the way for continued station assembly missions. On 14 July, the station's SSRMS robot moved the Leonardo module from the station back to the shuttle cargo bay between 13:08 and 14:50 GMT. The shuttle separated from the ISS, and fired its engines at 12:07 GMT on 17 July to make a 92 m/s deorbit maneuver. Discovery landed at the Kennedy Space Center at 13:14 GMT. European astronaut Reiter was left behind to make up part of the EO-13 resident crew on the station.
Summer 2006 - .
- STS-133 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-133A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-133 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-20A. Node 3 would have been delivered to the station..
2006 September 9 - . 15:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-115 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Burbank,
Ferguson,
Jett,
MacLean,
Stefanyshyn-Piper,
Tanner.
Payload: Atlantis F27 / P3, P4. Mass: 122,400 kg (269,800 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Burbank,
Ferguson,
Jett,
MacLean,
Stefanyshyn-Piper,
Tanner.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-8,
Soyuz TMA-9,
STS-115.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 11.80 days. Decay Date: 2006-09-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 29391 . COSPAR: 2006-036A. Apogee: 350 km (210 mi). Perigee: 335 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Atlantis docked with the International Space Station at the PMA-2 port at 10:48 GMT on 11 September. At the Shuttle RMS robot arm connected to the enormous P3/P4 truss in the payload pay and handed it off to the Station's robot arm between 14:52 and 15:03 GMT the same day. The station arm then connected to the P3/P4 truss to the station's P1 truss at 07:27 on 12 September. Three EVA's were made by the shuttle crew over the next three days to complete installation of the truss and deply its solar panels. The Shuttle undocked from the station at 12:50 GMT on 20 September. There was a one-day delay in landing due to weather at the Cape and some concern about several small objects seen floating near the spacecraft. These were believed to be plastic shims that had worked loose from between the tiles and were not a concern. Atlantis landed at Kennedy Space Center at 10:21 GMT on 21 September.
Late 2007 - .
- STS-138 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-138A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-138 was to have flown ISS resupply mission ISS-UF7. The Centrifuge Accomodations Module (CAM) would have been delivered to the station..
Late 2006 - .
- STS-134 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-134A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-134 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-16A. The Habitation module would have been delivered to the station..
2006 December 10 - . 01:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-116 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Curbeam,
Fuglesang,
Higginbotham,
Oefelein,
Patrick,
Polansky,
Williams.
Return Crew: Curbeam,
Fuglesang,
Higginbotham,
Oefelein,
Patrick,
Polansky,
Reiter.
Payload: Discovery F32 / P5. Mass: 120,420 kg (265,480 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Curbeam,
Fuglesang,
Higginbotham,
Oefelein,
Patrick,
Polansky,
Reiter,
Williams.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-9,
STS-116,
STS-121 Astrolab.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 12.86 days. Decay Date: 2006-12-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 29647 . COSPAR: 2006-055A. Apogee: 358 km (222 mi). Perigee: 326 km (202 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
The mission used solid rocket booster pair RSRM-95 and external tank ET-123. At SSME burnout Discovery was in a 58 km x 220 km x 51.6 deg preliminary burn. The OMS-2 burn at 02:25 GMT placed the shuttle in a stable 225 x 250 km orbit from which rendezvous maneuvers began. Discovery docked with the ISS at 22:12 GMT on December 11. In the most demanding ISS assembly mission ever, the crew would require an additional spacewalk to complete installation of the P5 truss, retraction of the recalcitrant port P6 solar array wing, and activation of the truss electrical and cooling system. Sunita Williams rode the shuttle to the station, and remained behind with the EO-14 crew; ESA astronaut Thomas Reiter, already aboard the station, was returned to earth. Due to weather problems a landing at White Sands was considered; but in the end Discovery landed safely at Kennedy Space Center, after which it was to enter a year-long overhaul cycle.
Early 2007 - .
- STS-135 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-135A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-135 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-17A. An MPLM would have delivered Destiny lab racks and a CBA to the station..
Spring 2007 - .
- STS-136 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-136A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-136 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-18A. The first US Crew Return Vehicle (CRV) would have been delivered to the station..
2007 June 8 - . 23:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-117 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Anderson, Clayton,
Archambault,
Forrester,
Olivas,
Reilly,
Sturckow,
Swanson.
Return Crew: Archambault,
Forrester,
Olivas,
Reilly,
Sturckow,
Swanson,
Williams.
Payload: Atlantis F28 / S3, S4. Mass: 122,685 kg (270,474 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Anderson, Clayton,
Archambault,
Forrester,
Olivas,
Reilly,
Sturckow,
Swanson,
Williams.
Agency: NASA.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-10,
STS-117,
STS-117 ISS EO-15,
STS-117 ISS EO-15.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 13.84 days. Decay Date: 2007-06-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 31600 . COSPAR: 2007-024A. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 330 km (200 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
The shuttle delivered the S3 and S4 truss segments to the starboard side of the International Space Station. The crew made three spacewalks to install these truss segments, conduct other station reconfiguration and installation work, deploy the solar arrays and prepare them for operation. A fourth spacewalk was added to repair loose re-entry insulation on the shuttle and get-ahead installation work on the outside of the station. The shuttle delivered NASA long-term ISS crew member Clayton Anderson to the station; and returned Suni Williams to earth. At the conclusion of this mission the station finally achieved its full-power, dual-boom configuration first conceived for Space Station Freedom in the 1980's.
Mid-2007 - .
- STS-137 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Flight: STS-137A. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Flight delayed after the Columbia disaster. No crew had been named at the time of the loss of Columbia. STS-137 was to have flown ISS assembly mission ISS-19A. An MPLM and other station hardware would be delivered..
2007 August 8 - . 22:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-118 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Caldwell,
Drew,
Hobaugh,
Kelly, Scott,
Mastracchio,
Morgan,
Williams, Dave.
Payload: Endeavour F20 / S5, Spacehab. Mass: 121,823 kg (268,573 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Caldwell,
Drew,
Hobaugh,
Kelly, Scott,
Mastracchio,
Morgan,
Williams, Dave.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-10,
STS-117 ISS EO-15,
STS-118.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 12.75 days. Decay Date: 2007-08-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 32008 . COSPAR: 2007-035A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Space Shuttle Endeavour was launched on Aug 8 at 2236 UTC. The STS-118 stack comprised Orbiter OV-105, solid rockets RSRM-97 and external tank ET-117. The solid boosters separated 2 min after launch. At 2245 UTC the orbiter main engines cut off and ET-117 separated into an approximately 57 x 225 km x 51.6 deg orbit. The OMS-2 burn at 2313 UTC put Endeavour in a higher 229 x 317 km orbit as the ET fell back to reentry around 2346 UTC.
During ascent a large chunk of external tank foam was observed to hit the underside of the orbiter. Examination in orbit using the robotic arm showed a hole in a heat shield tile that went down to the felt mounting pad. There was considerable press discussion of the danger, but as the mission drew to a close NASA decided that no lasting damage would be incurred during reentry to the orbiter structure, and called off a potential extra spacewalk to repair the tile.
Endeavour docked at the PMA-2 adapter on the Station at 18:02 GMT on 10 August; the hatches were opened at 20:04.
The 14036 kg of cargo broke down as follows:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System, 1800 kg
- Bay 1-2: EMU 3010, 130 kg
- Bay 1-2: EMU 3017, 130 kg
- Bay 3: Tunnel Adapter, 112 kg
- Bay 5-7: Spacehab-SM Single Module, 5480 kg: Loaded with research experimental equipment and consumables to be left at the station.
- Bay 8P: SPDU: Station Power Distribution Unit, will be left at the ISS and allow the Orbiter to draw electricity from the station while docked, allowing longer missions
- Bay 8-10: S5 Truss, 1584 kg: a short spacer truss installed at the end of the ISS S4 truss during the mission, to eliminate interference with the S6 solar panels when they would be added later
- Bay 11-12: ESP-3, 3400 kg: External Stowage Platform 3, left at the ISS, provided external storage for spare parts, and was delivered with a spare nitrogen tank for the truss cooling system, a spare truss battery charge/discharge unit (BCDU), a spare Canadarm-2 robot arm pitch roll joint, and a replacement Control Moment Gyro for the Z1 truss
- Bay 11-12: CMG-3R ORU, 540 kg
- Sill: OBSS, 450 kg
- Sill: RMS 201, 410 kg
Following successful completion of all cargo delivery and station assembly tasks, the crew returned to Endeavour on 18 August, undocking the next day at 11:56 GMT. Landing was moved up a day ahead of schedule because of concern a hurricane might force evacuation of the Houston Control Center on the originally-planned return date. Endeavour began its deorbit burn at 15:25 GMT on August 21 and lowered its orbit from 336 x 347 km to -28 x 342 km. It landed on runway 15 at Kennedy Space Center at 16:32 GMT. Landing mass was 100,878 kg.
2007 October 23 - . 15:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-120 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Melroy,
Nespoli,
Parazynski,
Tani,
Wheelock,
Wilson,
Zamka.
Return Crew: Anderson, Clayton,
Melroy,
Nespoli,
Parazynski,
Wheelock,
Wilson,
Zamka.
Payload: Discovery F33 / Harmony / ISS-10A. Mass: 123,400 kg (272,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Anderson, Clayton,
Melroy,
Nespoli,
Parazynski,
Tani,
Wheelock,
Wilson,
Zamka.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-10,
Soyuz TMA-11,
STS-117 ISS EO-15,
STS-120,
STS-120 ISS EO-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 15.10 days. Decay Date: 2007-11-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 32272 . COSPAR: 2007-050A. Apogee: 344 km (213 mi). Perigee: 340 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Main mission objectives were delivery of the Harmony module to the station, and external work to move the P6 truss to its final location and put the ISS into its full-power configuration for the first time. Discovery docked with the ISS at the Destiny module at 12:40 GMT on 25 October. The cargo of 17,390 kg was as follows:
- Orbiter Docking System - Bay 1-2 - 1800 kg
- Spacesuit EMU 3004 - 130 kg
- Spacesuit EMU 3003 - 130 kg
- Station Power Distribution Unit SPDU - Bay 3P - 100 kg
- Fixture for return of S-band Antenna - SASA FSE - Bay 3P - 4S - 100 kg
- Power/Data Grapple Fixture for Node-2 - PDGF - Bay 5P - 50 kg
- Main Bus Switching Unit - MBSU - Bay 6S - 238 kg
- MBSU adapter - Bay 6S - 122 kg
- Station Power Distribution Unit - SPDU - Bay 6S - 7P - 100 kg
- Node-2 Harmony module - Bays 8-12 - 14,300 kg
- OBSS 203 - Sill 450 kg
- RMS 301 - Sill 410 kg
2008 February 7 - . 19:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-122 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Eyharts,
Frick,
Love,
Melvin,
Poindexter,
Schlegel,
Walheim.
Payload: Atlantis F29 / Columbus. Mass: 117,850 kg (259,810 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Eyharts,
Frick,
Love,
Melvin,
Poindexter,
Schlegel,
Walheim.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-11,
STS-120 ISS EO-16,
STS-122,
STS-122 ISS EO-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 12.77 days. Decay Date: 2008-02-20 14:07:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 32486 . COSPAR: 2008-005A. Apogee: 343 km (213 mi). Perigee: 329 km (204 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
ISS flight 1E's primary mission was the long-delayed delivery and installation of the European Columbus module. The shuttle entered an initial 58 km x 230 km orbit at 19:54 GMT. The OMS-2 circularization burn at 20:23 GMT put it into a 215 km x 233 km chase orbit. Atlantis docked with the PMA-2 port of the ISS at 17:17 GMT on 9 February. Eyharts was dropped off at the station, Tani, already aboard the ISS, returned to Earth on Atlantis. Atlantis undocked from the ISS on 20 February at 09:24 GMT; began its deorbit burn at 12:59; and landed at the Kennedy Space Center at 14:07.
2008 March 11 - . 06:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-123 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Behnken,
Doi,
Foreman,
Gorie,
Johnson, Gregory H,
Linnehan,
Reisman.
Payload: Endeavour F21 / Dextre, Kibo ELM-PS. Mass: 118,950 kg (262,230 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Behnken,
Doi,
Foreman,
Gorie,
Johnson, Gregory H,
Linnehan,
Reisman.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-11,
STS-122 ISS EO-16,
STS-123,
STS-123 ISS EO-16.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 15.76 days. Decay Date: 2008-03-27 00:40:41 . USAF Sat Cat: 32699 . COSPAR: 2008-009A. Apogee: 346 km (214 mi). Perigee: 341 km (211 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Endeavour's main task was delivery of the Canadian Dextre robotic manipulator (fitted to the end of the Canadarm-2 robotic arm already installed on the station) and the Japanese Kibo ELM-PS Experiment Logistics Module - Pressurized. It also brought astronaut Reisman to the station, replacing Eyharts on the long-duration crew. The orbiter was placed in an initial 58 km x 220 km orbit at main engine shutdown, adjusted by the OMS-2 firing 38 minutes later to a 220 km x 233 km chase orbit. On 13 March the shuttle docked with the PMA-2 port of the International Space Station at 03:49 GMT. Mission accomplished, Endeavour undocked at 00:25 GMT on March 25, completed the customary ISS flyaround at 01:36 GMT, deorbited at 23:33 GMT the next day, and landed at 00:39 GMT at Kennedy Space Center.
2008 May 31 - . 21:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-124 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Chamitoff,
Fossum,
Garan,
Ham,
Hoshide,
Kelly, Mark,
Nyberg.
Payload: Discovery F34 / Kibo PM / ISS-1J. Mass: 119,190 kg (262,760 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Chamitoff,
Fossum,
Garan,
Ham,
Hoshide,
Kelly, Mark,
Nyberg.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-12,
STS-123 ISS EO-16,
STS-124,
STS-124 ISS EO-17.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 13.76 days. Decay Date: 2008-06-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 32960 . COSPAR: 2008-027A. Apogee: 351 km (218 mi). Perigee: 338 km (210 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Discovery delivered to the International Space Station the Kibo Pressurized Module, the primary element of the Japanese portion of the station. Half an earth away from jettison of external tank ET-128, a 76 m/s OMS-2 burn at 21:40 GMT put the Shuttle in its low-altitude chase lorbit. Discovery docked at the PMA-2 port of the station at 18:03 GMT on 2 June. Using the shuttle and station's robotic arms, with assistance from spacewalking astronauts, the Kibo module was attached to the station's Harmony module at 23:01 GMT on 4 June. The previously-delivered Japanese Logistics Module was transferred from Harmony to Kibo on 6 June at 20:04 GMT. The Shuttle undocked from the station on 11 June at GMT and landed on 14 June at 15:15 GMT at the Kennedy Space Center.
2008 November 15 - . 00:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-126 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Boe,
Bowen,
Ferguson,
Kimbrough,
Magnus,
Pettit,
Stefanyshyn-Piper.
Return Crew: Boe,
Bowen,
Ferguson,
Kimbrough,
Magnus,
Pettit,
Stefanyshyn-Piper.
Payload: Endeavour F22 / MPLM-1 / ULF-2. Mass: 116,500 kg (256,800 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Boe,
Bowen,
Ferguson,
Kimbrough,
Magnus,
Pettit,
Stefanyshyn-Piper.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-13,
STS-124 ISS EO-17,
STS-126,
STS-126 ISS EO-18.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 15.85 days. Decay Date: 2008-11-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 33441 . COSPAR: 2008-059A. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 344 km (213 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
ISS resupply and internal outfitting flight, docked at the Harmony module of the sation at 22:01 GMT on 16 November. The Leonardo module contained 6956 kg of cargo, mainly devoted to allowing a future full ISS crew of six: two crew quarters racks, a Galley rack, a Waste and Hygiene Compartment rack, two Water Recovery System racks, an experiment rack, a Combustion integration rack, and miscellaneous supplies in three Resupply Stowage Racks and six Resupply Stowage Platforms. On 17 November at 17:09 GMT the ISS robot arm moved the Leonardo module from the shuttle's payload bay to the Harmony module nadir port for unloading. The mission also rotated the ISS long-term NASA crew member, replacing Chamitoff with Magnus. Four spacewalks were conducted, primarily to repair a broken ISS Solar Array Rotary Joint.
The unloaded Leonardo module was returned to the shuttle bay on 26 November. The shuttle undocked from the ISS at 14:47 GMT on 28 November. The next day, at 20:33 GMT, it released a 7 kg PicoSat Solar Cell Testbed Experiment, a prototype for a later picosat mission to geostationary transfer orbit to study degradation of solar cells while passing through the earth's radiation belts.
Following two wave-offs for a Kennedy Space Center landing due to weather, Endeavour made its 89 m/s deorbit maneuver at 20:19 on 29 November, and landed at Runway 04L/22R at Edwards AFB at 21:25 GMT.
Cargo Manifest, Total = 17,370 kg:
- Bay 1-2: Orbiter Docking System = 1800 kg + EMUs 3005 and 3011 = 260 kg
- Bay 3 Port: APC/SPDU = 100 kg
- Bay 3 Starboard: APC/SSPL Picosat launcher = 50 kg + PSSC Picosats = 7 kg
- Bay 7 Starboard: ROEU 751 umbilical = 50 kg
- Bay 7-12: Leonardo (MPLM-1) = 12748 kg
- Bay 13: Lightweight MPESS Carrier (LMC)= 1495 kg
- Sill: RMS 201 = 410 kg + OBSS = 450 kg
2009 March 15 - . 23:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-119 - . Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Acaba, Antonelli, Archambault, Arnold, Ricky, Phillips, Swanson. Payload: Discovery F35 /. Mass: 120,860 kg (266,450 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-119. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Duration: 12.81 days. Decay Date: 2009-03-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 34541 . COSPAR: 2009-012A. Apogee: 353 km (219 mi). Perigee: 335 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Crew: Archambault, Antonelli, Phillips, Swanson, Acaba, Arnold. ISS assembly mission. Delivered to the ISS and installed the fourth starboard truss segment (ITS S6) and fourth set of solar arrays and batteries..
2009 May 11 - . 18:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-125 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Altman,
Feustel,
Good,
Grunsfeld,
Johnson, Gregory C,
Massimino,
McArthur, Megan.
Payload: Atlantis F30 /. Mass: 119,820 kg (264,150 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Hubble.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-14,
STS-125.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 12.90 days. Decay Date: 2009-05-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 34933 . COSPAR: 2009-025A. Apogee: 566 km (351 mi). Perigee: 302 km (187 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 93.30 min.
Hubble Servicing Mission SM-4. Atlantis rendezvoused with the Hubble space observatory, grappled it with the RMS arm, and secured it in the payload bay at 18:12 GMT on 13 May. After repairs and upgrades over four EVA's, the satellite was released at 12:57 GMT on 19 May. Atlantis landed at Edwards AFB at 15:39 GMT on 24 May.
2009 July 15 - . 22:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-127 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Cassidy,
Hurley,
Kopra,
Marshburn,
Payette,
Polansky,
Wolf.
Payload: Endeavour F23 / ISS 2J/4. Mass: 120,000 kg (260,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-14,
Soyuz TMA-15,
STS-127.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 15.60 days. Decay Date: 2009-07-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 35633 . COSPAR: 2009-038A. Apogee: 336 km (208 mi). Perigee: 328 km (203 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Crew: Polansky, Hurley, Cassidy, Marshburn, Wolf, Payette. Deliver to the ISS and install the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility (JEM EF); Kibo Japanese Experiment Logistics Module - Exposed Section (ELM-ES); and Spacelab Pallet - Deployable 2 (SLP-D2).
- Dragonsat - .
Mass: 3.00 kg (6.60 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Clemson.
Class: Technology.
Type: Technology satellite. Spacecraft: Cubesat.
Decay Date: 2010-03-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 35690 . COSPAR: 2009-038B. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 326 km (202 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.10 min.
Ejected from the Endeavour on 30 July at 12:34 GMT. Dragonsat consisted of two 1.5 kg cubesats, BEVO-1 from the University of Texas at Austin and Aggiesat 2 from Texas A&M University. The two satellites were ejected attached to each other, but failed to separate as planned.
- ANDE Passive(Pollux) - . Nation: USA. Agency: Clemson. Class: Earth. Type: Climate satellite. Spacecraft: ANDE. Decay Date: 2010-03-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 35690 . COSPAR: 2009-038E. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 326 km (202 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.10 min. Ejected from the Endeavour on 30 July at 12:33 GMT. Upper atmosphere studies..
- ANDE Active (Castor) - . Nation: USA. Agency: Clemson. Class: Earth. Type: Climate satellite. Spacecraft: ANDE. Decay Date: 2010-03-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 35690 . COSPAR: 2009-038F. Apogee: 332 km (206 mi). Perigee: 326 km (202 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.10 min. Ejected from the Endeavour on 30 July at 12:33 GMT. Upper atmosphere studies..
2009 August 29 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-128 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Ford, Kevin,
Forrester,
Fuglesang,
Hernandez,
Olivas,
Stott,
Sturckow.
Payload: Discovery F36 /. Mass: 121,420 kg (267,680 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-14,
Soyuz TMA-15,
STS-128.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery .
Duration: 13.87 days. Decay Date: 2009-09-12 00:53:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 35811 . COSPAR: 2009-045A. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 310 km (190 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min.
Crew: Sturckow, Ford, Forrester, Hernandez, Fuglesang, Olivas. Deliver to the ISS and install the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM); Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC); Three-crew quarters, galley, and second treadmill (TVIS2); and the Crew Health Care System 2 (CHeCS 2).
- Leonardo - . Nation: USA. Agency: Clemson. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: ISS. Spacecraft: ISS Leonardo. COSPAR: 2009-045x.
2009 October 28 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39B. Launch Platform: MLP1. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Ares I-X.
- Ares I-X - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: Clemson.
Spacecraft Bus: FLTP/FESTIP.
Spacecraft: Ares spaceplane.
First flight test of the Ares/Constellation program. The Ares I-X rocket consisted of the modified Shuttle RSRM-91A solid rocket booster, a dummy Upper Stage Simulator, and a dummy Ares command module / launch abort system. It was launched from the newly modified LC39B at Kennedy Space Center to test the aerodynamics of the vehicle within the atmosphere and provide real-world data to ameliorate concerns regarding the vibration level created by the SRB for any crew in a future mission. The SRB reached 46 km altitude before descending to the Atlantic for recovery.
2009 November 16 - . 19:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-129 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Bresnik,
Foreman,
Hobaugh,
Melvin,
Satcher,
Wilmore.
Payload: Atlantis F31 / ExPRESS Logistics Carrier. Mass: 120,848 kg (266,424 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-15,
Soyuz TMA-16,
STS-129.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 10.80 days. Decay Date: 2009-11-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 36094 . COSPAR: 2009-062A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
The mission was to deliver and place spare components outside the ISS station. The 11-day flight included three spacewalks. The payload bay carried two large ExPRESS Logistics Carriers holding two spare gyroscopes, two nitrogen tank assemblies, two pump modules, an ammonia tank assembly, a spare latching end effector for the station's robotic arm, a spare trailing umbilical system for the Mobile Transporter, and a high-pressure gas tank.
2010 February 8 - . 09:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-130 - . Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Behnken, Hire, Patrick, Robinson, Virts, Zamka. Payload: Endeavour F24 / Tranquility / Cupola. Mass: 121,320 kg (267,460 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: Behnken, Hire, Patrick, Robinson, Virts, Zamka. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-16, Soyuz TMA-17, STS-130. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Endeavour. Duration: 13.75 days. Decay Date: 2010-02-22 03:20:00 . USAF Sat Cat: 36394 . COSPAR: 2010-004A. Apogee: 348 km (216 mi). Perigee: 334 km (207 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. Docked with the ISS at 05:06 GMT on 10 February. Primary payloads were the Tranquility module and the Cupola, a robotic control station with six windows around its sides and another in the center, providing a 360-degree view around the station..
2010 April 5 - . 10:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-131 - . Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Anderson, Clayton, Dutton, Mastracchio, Metcalf-Lindenburger, Poindexter, Wilson, Yamazaki. Payload: Discovery F37 /. Mass: 121,047 kg (266,862 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-17, Soyuz TMA-18, STS-131. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Discovery. Duration: 15.12 days. Decay Date: 2010-04-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 36507 . COSPAR: 2010-012A. Apogee: 346 km (214 mi). Perigee: 322 km (200 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.20 min. Crew: Poindexter;Dutton;Metcalf-Lendenburger;Wilson;Mastracchiio;Yamazaki;Anderson,Clayton. Contingency flight to assure ISS completion; nominal payload EXPRESS Logistics Carrier 3 (ELC3) and EXPRESS Logistics Carrier 4 (ELC4)..
2010 May 14 - . 18:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-132 - . Call Sign: Atlantis. Crew: Antonelli, Bowen, Good, Ham, Reisman, Sellers. Payload: Atlantis F32 / Node 3. Mass: 110,000 kg (240,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: ISS. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-17, Soyuz TMA-18, STS-132. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle. Spacecraft: Atlantis. Duration: 11.77 days. Decay Date: 2010-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 36572 . COSPAR: 2010-019A. Apogee: 359 km (223 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Crew: Ham;Antonelli;Good;Sellers;Bowen;Reisman. Deliver to the ISS and install Node 3 with Cupola. With this mission ISS assembly was completed..
2011 February 24 - . 21:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-133 - .
Call Sign: Discovery. Crew: Barratt,
Boe,
Bowen,
Drew,
Lindsey,
Stott.
Payload: Discovery F38 /. Mass: 121,840 kg (268,610 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-01M,
Soyuz TMA-20,
STS-133.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Discovery.
Duration: 12.80 days. Decay Date: 2011-03-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 37371 . COSPAR: 2011-008A. Apogee: 355 km (220 mi). Perigee: 318 km (197 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.30 min.
Final flight of the space shuttle Discovery. The spaceplane docked with the International Space Station at 19:14 GMT on 26 February. The ELC-4 Express Logistics Carrier 4 was transferred from the Shuttle to the S3 station truss on 27 February. The station's SSRMS robot arm moved the Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module from the shuttle to the nadir port of the Unity module between 13:46 and 15:05 UTC on 1 March. Following cargo unloading and three spacewalks devoted to station repair and assembly, Discovery undocked from the station for the last time at 12:00 GMT on 7 March, landing at the Kennedy Space Center at 16:57 GMT on 9 March.
2011 May 16 - . 12:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-134 - .
Call Sign: Endeavour. Crew: Chamitoff,
Feustel,
Fincke,
Johnson, Gregory H,
Kelly, Mark,
Vittori.
Payload: Endeavour F25 / ELC-3 / AMS-02. Mass: 121,830 kg (268,580 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-21,
STS-134.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Endeavour.
Duration: 15.74 days. Decay Date: 2011-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 37577 . COSPAR: 2011-020A. Apogee: 345 km (214 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min.
Final space station assembly mission. Also delivered spare parts. Endeavour docked with the Station at 10:14 GMT on 18 May. The ELC-3 carrier was unberthed from the shuttle at 13:27 GMT and installed on the Station's truss at 16:09 GMT. The AMS-02 Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer was unberthed at 06:59 GMT on 19 May and bolted to the Station's S3 truss at 09:46 GMT. Cargo Bay Manifest:
- External Airlock/ODS: 1800 kg
- EMU spacesuits 3004, 3018: 260
- RMS arm 201: 410 kg
- Orbiter Boom Sensor System: 382 kg
- Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (particle detector to search for antimatter): 6917
- STORRM (lidar to test rendezvous and docking technology for the Orion spacecraft): 17 kg
- PPSU-2 electronics box: 17 kg
- SPDU: 17 kg kg
- ROEU 755 umbilical for ELC-3: 90 kg
- ROEU 751 umbilical for AMS-02: 78 kg
- MISSE carriers (3): 171 kg
- MISSE 8 experiment (studies the effect of exposing various materials to space): 45 kg
- Express Logistics Carrier:
- ELC-3 plus support hardware: 3207 kg
- Cargo Transport Container: 476 kg
- SASA-2R S-band antenna: 116 kg
- SASA-3R S-band antenna: 116 kg
- SPDM Arm 3/OCTM: 342 kg
- SPDM support hardware: 269 kg
- HPGA oxygen tank: 552 kg
- ATA-2 ammonia tank: 772 kg
- STP-H3 experiment package (set of US DoD Space Test Program experiments, including thermal control systems and space environment sensors): 500 kg
- Total Payload: 16,554 kg
2011 July 8 - . 07:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- PSSC-2 - . Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Technology. Type: Technology satellite. Spacecraft: PSSC. Decay Date: 2011-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 37752 . COSPAR: 2011-031B. Apogee: 338 km (210 mi). Perigee: 307 km (190 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 91.00 min. Picosatellite Solar Cell Testbed 2. Ejected from STS-135 prior to re-entry..
- STS-135 - .
Call Sign: Atlantis. Payload: Atlantis F33 / Rafaello MPLM-2. Mass: 120,000 kg (260,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Program: ISS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: Soyuz TMA-02M,
Soyuz TMA-21,
STS-135.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Atlantis.
Duration: 12.77 days. Decay Date: 2011-07-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 37736 . COSPAR: 2011-031A. Apogee: 385 km (239 mi). Perigee: 371 km (230 mi). Inclination: 51.60 deg. Period: 92.10 min.
Final Space Shuttle flight, denoting the end of the space age. Atlantis docked with the Harmony module of the ISS on 10 June at 15:07 GMT. Primary payload was the Raffaello MultiPurpose Logistics Module delivering consumables and spare parts to the station sufficient to support the six crew members through the end of 2012 should delays occur in NASA's commercial robotic resupply program. Main crew task while docked with the station was to unload Rafaello and return of the station's failed coolant Pump Module for analysis. Atlantis undocked on 19 July at 06:28 GMT. The Picosat Solar Cell Experiment satellite was released from the cargo bay on 20 July. Atlantis made the final shuttle landing at the Kennedy Space Center on 21 July at 09:57 GMT. Payload delivered was:
- External Airlock/ODS: 1800 kg
- EMU spacesuits 3015, 3006: 260 kg
- RMS arm 301: 410 kg
- Orbiter Boom Sensor System: 382 kg
- MPLM-2 Rafaello: 11,556 kg
- SPDU: 17 kg
- ROEU 755 umbilical for MPLM: 78 kg
- Lightweight MPESS Carrier: 1050 kg
- Robotic Refuelling Mission: 300 kg
- Picosat Launcher: 22 kg
- PSSC-2/MTV Aerospace Corporation Picosat Solar Cell Experiment satellite: 4 kg
- Total payload: 15,879 kg
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use