
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Titan
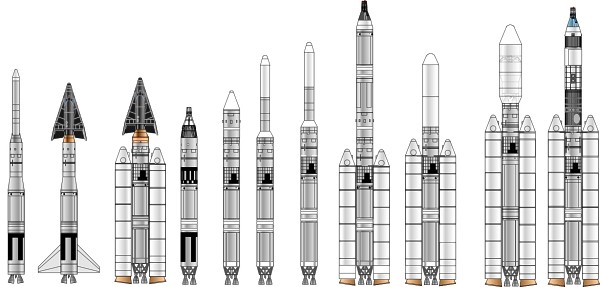
Titan
Credit: (c) Mark Wade
AKA: HGM-25A;HTM-25B;LGM-25;LGM-25C;SM-68. Status: Retired 2005.
The reasons given for developing the booster in parallel with the NASA Saturn I of the same class were that the solid fuel boosters and storable (although corrosive and toxic) liquid propellants of the core provided a vehicle with improved readiness compared to the Saturn. However USAF 'ownership' (no NASA claims of priority) and the NIH (Not Invented Here) syndrome were probably more important factors.
Whatever the controversies at its genesis, the Titan has outlived the Saturn and will continue in use in the 21st century. It was originally conceived as a carrier of manned military spacecraft - first the X-20A Dynasoar, then the Gemini B and Manned Orbiting Laboratory, and finally lifting body spaceplanes in support of MOL follow-on space stations. All of these projects were cancelled in turn. Titans have been used instead to launch unmanned military spacecraft, ranging from heavy photoreconnaissance platforms in low earth orbit to geosynchronous communications, missile launch detection, and ELINT satellites.
After NASA junked the Saturn launch vehicle family in the mid-1970's, and the Challenger disaster in the 1980's, Titans were used for launching NASA deep-space probes. Whatever trouble NASA managed to get itself into, the Titan was still there to keep its planetary exploration program going.
More at: Titan.
| Barbarian MM American heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle. The Zenith Star space-based chemical laser missile defense weapon required a launch vehicle capable of placing a 45,000 kg payload into low earth orbit. Martin and Aerojet turned to their work 20 years earlier on advanced Titans for the MOL program. These earlier studies were combined with new concepts for tank construction and materials. The Martin Barbarian was a 4.57 m diameter Titan vehicle (instead of the customary 3.05 m) with four LR-87 engines on the first stage, and a single LR-87 engine on the second stage. |
| Commercial Titan 3 American orbital launch vehicle. Commercial version of Titan 34D military booster. It differed in having a lengthened second stage and a 4 m diameter payload shroud to handle shuttle-class or Ariane-type dual payloads. |
| Soltan American orbital launch vehicle. The progenitor of the Titan 3 was this design, which used two, 3 segment, 100 inch diameter solid rocket boosters. The 100 inch segmented boosters had already been ground-fired by Aerojet. However the final decision was to develop the more-capable Titan 3C with 5 segment, 120 inch diameter solid rocket boosters. |
| Titan 23B American orbital launch vehicle. Basic Titan 3A core, originally developed for Titan 3C, with Agena D upper stage replacing Transtage. New radio guidance system, 1.5 m diameter fairing atop Agena. Payload remained attached to the Agena. |
| Titan 23C American orbital launch vehicle. Post-MOL standardization of Titan 3C, with man-rated systems removed, upgraded first stage engines, digital avionics, blowdown solid rocket motor thrust vector control in place of pressure-regulated system, simplified Transtage attitude control system. |
| Titan 23G Star-37S-ISS American orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Titan 23G Star-37XFP-ISS American orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Titan 23S American orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Titan 24B American orbital launch vehicle. Stretched first stage, originally developed for the cancelled MOL program, with Agena D upper stage. Radio guidance system, 1.5 m diameter fairing atop Agena. Payload remained attached to the Agena. |
| Titan 2B American intercontinental ballistic orbital launch vehicle. Space launch version of Titan 2 ICBM, obtained through minimal modification of ICBM (new wiring and avionics only, and use of existing ICBM re-entry vehicle shroud). Proposed in the late 1980's but never developed. |
| Titan 2L American intercontinental ballistic orbital launch vehicle. Version of refurbished Titan 2 ICBM with two liquid propellant strap-on stages. Proposed in the late 1980's but never developed. |
| Titan 2S American intercontinental ballistic orbital launch vehicle. Version of refurbished Titan 2 ICBM with two to eight Castor 4A solid-propellant strap-on stages. Proposed in the late 1980's but never developed. |
| Titan 33B American orbital launch vehicle. Basic Titan 3A core, except guidance provided by the Agena upper stage. The Agena and its payload were completely enclosed in a new 3.05 m diameter shroud. 'Ascent Agena' separated after orbital insertion and did not remain attached to the payload. |
| Titan 34B American orbital launch vehicle. Stretched Titan core, originally developed for Titan 3M MOL, with Agena D upper stage. Guidance provided by the Agena upper stage. The Agena and its payload were completely enclosed in a 3.05 m diameter shroud. 'Ascent Agena' separated after orbital insertion and did not remain attached to the payload. |
| Titan 34D American orbital launch vehicle. Stretched Titan core designed for use with 5 1/2 segment solid rocket motors. IUS (Interim/Inertial Upper Stage) solid upper stages, Transtage, or used without upper stages. |
| Titan 34D/IUS American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 34D with IUS upper stages. |
| Titan 34D/Transtage American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 34D with Transtage upper stage. |
| Titan 3BAS2 American orbital launch vehicle. Configuration of Titan 3B proposed by Martin in mid-1960's. Titan 3B for deep space missions with Centaur upper stage, Algol strapons for liftoff thrust augmentation. Never flown. |
| Titan 3C7 American orbital launch vehicle. Variant of Titan 3C with seven segment solid motors. Proposed by Martin for precise delivery of payloads beyond Titan 3C capacity into geosynchronous orbit. Never flown. |
| Titan 3L2 American orbital launch vehicle. Variant of Titan with 15 foot Large Diameter Core, 2 x 7 segment strap-ons. Man-rated, optimized for delivery of heavy payloads into LEO. Never developed. |
| Titan 3L4 American orbital launch vehicle. Variant of Titan with 15 foot Large Diameter Core, 4 x 7 segment strap-ons. Man rated, optimized for delivery of 40,000 pound manned payloads into 250 nm / 50 deg space station orbit. |
| Titan 3M American orbital launch vehicle. Man-rated launch vehicle designed for MOL and other missions of the 1970's. Malfunction Detection System initiated abort procedures during launch. Also suited for launch of 'bulbous and lifting body payloads'. 7 segment UA1207 motors developed but not used until Titan 4 in 1990's. Cancelled with MOL program in 1969. |
| Titan 4 American orbital launch vehicle. Developed to handle military payloads designed for launch on Shuttle from Vandenberg before the USAF pulled out of the Shuttle program after the Challenger disaster. Further stretch of core from Titan 34, 7-segment solid rocket motors (developed for MOL but not used until 25 years later). Enlarged Centaur G used as upper stage (variant of stage designed for Shuttle but prohibited for flight safety reasons after Challenger). Completely revised electronics. All the changes resulted in major increase in cost of launch vehicle and launch operations. |
| Titan 401A/Centaur Version of Titan 4 with Centaur T upper stage. |
| Titan 401B/Centaur Version of Titan 4B with Centaur T upper stage. |
| Titan 402A/IUS American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 4 with IUS upper stages. |
| Titan 402B/IUS American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 4B with IUS upper stage. |
| Titan 403A American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 4 with no upper stage, configured for launch of lower-mass, higher-orbit Lacrosse, SDS and NOSS-2 payloads from Vandenberg. |
| Titan 403B American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 4B with no upper stage, configured for launch from Vandenberg. |
| Titan 404A American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 4 with no upper stage, configured for launch of heavy-weight, low altitude KH-12 and Improved CRYSTAL payloads from Vandenberg. |
| Titan 404B American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 4B with no upper stage, configured for launch from Vandenberg. |
| Titan 405A American orbital launch vehicle. Version of Titan 4 with no upper stage, configured for launch of lower-mass, higher-orbit SDS and NOSS-2 payloads from Cape Canaveral. |
| Titan 405B Null |
| Titan 4B American orbital launch vehicle. Titan 4 with Upgraded Solid Rocket Motors replacing UA1207. Developed to improve performance for certain missions, and reduce number of field joints in motor after Challenger and Titan 34D explosions involving segmented motors. |
| Titan 5 American orbital launch vehicle. Proposed Titan upgrade with cryogenic core as replacement for NLS. |
| Titan C American orbital launch vehicle. The Titan C, a Titan II booster stage topped by a new liquid oxygen/hydrogen upper stage, was the launch vehicle selected in November 1959 for the DynaSoar orbital flight program. Despite the fact the upper stage engine was secretly tested in 1958-1960, after many political twists and turns, it was cancelled in favor of the Titan 3C in July 1961 |
| Titan I American intercontinental ballistic missile. ICBM, built as back-up to Atlas, using two stages instead of one and a half, and conventional tank construction in lieu of balloon tanks. It was also to have been used for suborbital tests of the X-20A Dynasoar manned space plane. For unknown reasons never refurbished for use as space launcher and scrapped after being replaced by the Titan II in the missile role in mid-1960's. |
| Titan II American intercontinental ballistic missile. ICBM, developed also as the launch vehicle for the manned Gemini spacecraft in the early 1960's. When the ICBM's were retired in the 1980's they were refurbished and a new series of launches began. |
| Titan II GLV American intercontinental ballistic orbital launch vehicle. Version for launch of Gemini manned spacecraft. Developed in parallel with ICBM version. Differed in having redundancy features in systems and MDS (Malfunction Detection System) installed. |
| Titan II SLV American intercontinental ballistic orbital launch vehicle. Space launch version, obtained through minimal refurbishment of decommissioned ICBM's. |
| Titan IIIA American orbital launch vehicle. Titan with Transtage third stage. Core for Titan 3C. |
| Titan IIIB American orbital launch vehicle. Titan core with Agena upper stage. Found to be more cost effective and higher performance than using Transtage. |
| Titan IIIC American orbital launch vehicle. Titan 3A with five segment solid motors. Man-rated design originally developed for Dynasoar spaceplane. |
| Titan IIID American orbital launch vehicle. Titan 3C without transtage. |
| Titan IIIE American orbital launch vehicle. Titan 3D with Centaur D-1T upper stage. Used by NASA for deep space missions in 1970's. |
| Titan IIIE Centaur-D1T Star-37E American orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Titan-Vanguard American orbital launch vehicle. The Martin Company proposed to the Department of Defense that the first stage of the Titan I intercontinental ballistic missile be combined with the Vanguard rocket to provide a launch vehicle capable of placing an instrument package into lunar orbit and on the lunar surface. NASA was instead given the mission and used Atlas/Agena and Atlas/Centaur for this purpose instead. |
| Winged Titan American winged orbital launch vehicle. The only trace of this winged version of the Titan launch vehicle are some drawings in popular magazines ca. 1960. |
Family: orbital launch vehicle. Country: USA. Spacecraft: BCP-2000, EIS, Intruder, Quasar, Avco Project 7969, Bell Project 7969, Goodyear Project 7969, Martin Project 7969, Gemini, Gemini Fuel Cell, Gemini LOR, Mercury Mark I, Oscar, G4C, ERS, Gemini-Centaur, SSF, Dynasoar, Gemini Transport, Gemini Ferry, Gemini Pecan, OV1, LES, LCS, Gemini - Double Transtage, G5C, OV2, Extended Mission Gemini, Gemini Satellite Inspector, GGTS, IDCSP, KH-8, MOL, OV4, Gemini Paraglider, Rescue Gemini, Winged Gemini, Advanced Vela, OV5, DODGE, IS-A, Solrad, TACSAT, Big Gemini, Gemini B AM, Gemini B RM, DSP, Jumpseat, SESP, KH-9, DSCS II, NOSS, Sphinx, Viking, S73-7 Cal Balloon, ATS-6, X-24C, Helios, NOSS-Subsat, SDS, KH-11, Voyager, ECS/OTS, Chalet, Tiros N, DSCS III, DMSP Block 5D-2, Advanced Tiros N, HL-20, Singleton, Lacrosse (satellite), HS 393, SDS-2, Misty, NOSS-2, NOSS-2 subsatellite, CRAF, Star Lite, Mars Observer, Improved Crystal, ERTA, Landsat 6, Clementine, ISA Interstage Adapter, ISAS satellite, Milstar, Trumpet, Mercury ELINT, Advanced Orion, TiPS, Cassini, Huygens, HL-42, QuikScat, DMSP Block 5D-3, Coriolis. Agency: Martin. Bibliography: 126, 127, 128, 16, 17, 172, 18, 2, 216, 22, 223, 26, 278, 279, 281, 296, 33, 34, 376, 42, 455, 5, 552, 554, 563, 583, 594, 6, 60, 61, 69, 88.
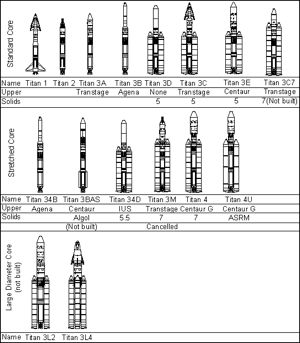 | Titan Geneology Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 1 Credit: via Andreas Parsch |
 | Titan 1 Credit: US Air Force |
 | Titan 1 Credit: US Air Force |
 | Winged Titan Credit: via Mark C Goll |
 | Titan 2 Gemini The Titan 2 ICBM was used for launch of the Gemini manned spacecraft. Credit: NASA |
 | Titan 2 SLV Credit: NASA |
 | Titan 2 Gemini The Titan 2 ICBM was used for launch of the Gemini manned spacecraft. Credit: NASA |
 | Titan 2 Large Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 2 Small Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 3A Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 3A Large Credit: © Mark Wade |
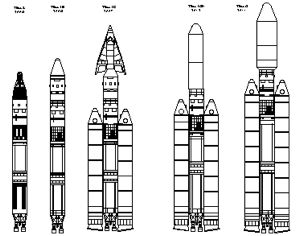 | Titan LVs Small Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 23B Titan 23B - COSPAR 1977-019 |
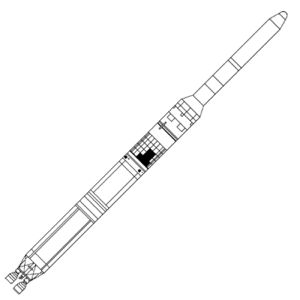 | Titan 34B Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 3B Titan 3B - COSPAR 1969-007 |
 | Titan 3C Titan 3C - COSPAR 1966-099 |
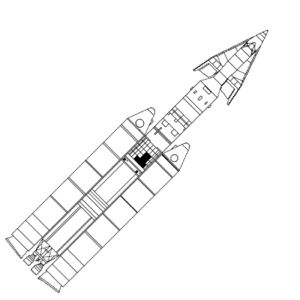 | Titan 3C Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 3 Early Credit: © Mark Wade |
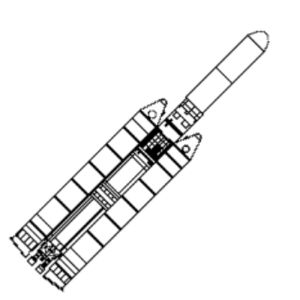 | Titan 3 Small Credit: © Mark Wade |
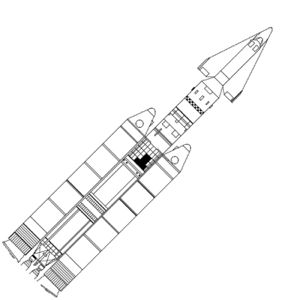 | Titan 3 LV with X-20 The original mission of the Titan 3 booster was to launch the X-20 Dynasoar manned spaceplane into orbit. Credit: © Mark Wade |
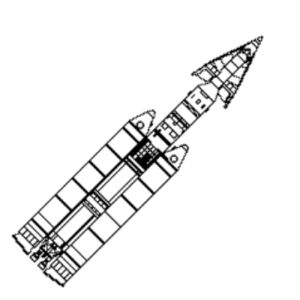 | Titan 3 with X-20 Titan 3 with X-20 Large Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 3D Titan 3D - COSPAR 1978-060 |
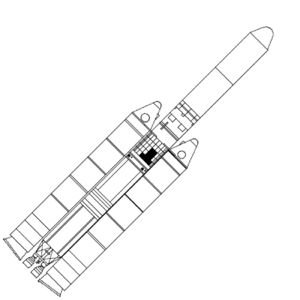 | Titan 3D Credit: © Mark Wade |
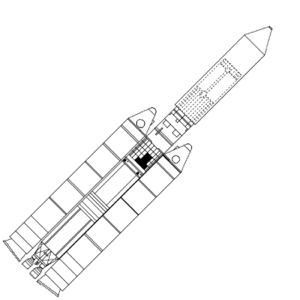 | Titan 3E Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 34D Titan 34D - COSPAR 1986-0F3 |
 | Titan 34D Titan 34D - COSPAR 1982-016 |
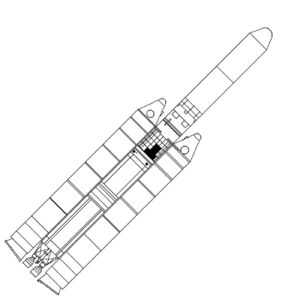 | Titan 34D Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | IUS Credit: NASA |
 | Commercial Titan Commercial Titan with Mars Observer Credit: Lockheed Martin |
 | Titan3E Credit: NASA |
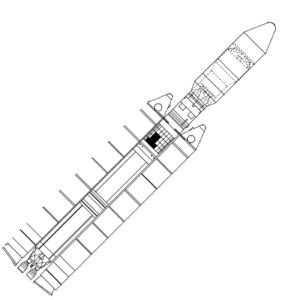 | Titan 4 Credit: © Mark Wade |
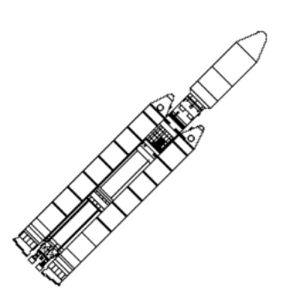 | Titan 4 Large Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Titan 4 Launch Credit: Lockheed Martin |
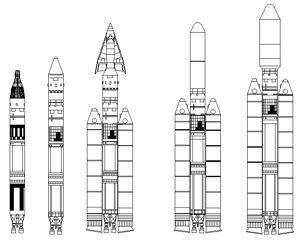 | Titan LVs Large Credit: © Mark Wade |
1954 August 23 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Atlas alternate propulsion system contractor. - .
Related Persons: Schriever.
General Schriever forwarded two important recommendations to Headquarters ARDC. First, he recommended that an alternate propulsion system contractor be introduced into the Atlas program as a back-up. Second, he presented the results of the Atlas management study of 18 August and recommended Ramo-Wooldridge for the SE/TD role in the project.
1954 October 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan program initiated. - .
Related Persons: Schriever,
Power.
The early results of missile configuration studies conducted by Lockheed, the Glenn L. Martin Company, and the newly formed Guided Missile Research Division (GMRD) of Ramo-Wooldridge, supported by other Air Force studies, indicated the numerous advantages of a two-stage missile. Therefore, General Schriever recommended to LtGeneral Thomas S. Power, Commander, ARDC, that a second, or alternate, configuration and staging approach be introduced into the program to take full advantage of more advanced concepts and to stimulate competition.
1955 January 4 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan begins as alternate configuration and staging approach to the Atlas missile. - . The Air Force ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee recommended that an alternate configuration and staging approach to the present Atlas missile be introduced into the ballistic missile program..
1955 January 12 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan proposed as a competitor and backup to the Atlas program. - . Related Persons: Schriever. General Schriever formally proposed to Hq ARDC that an alternate, two-stage configuration intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) be developed as a competitor and backup to the Atlas program..
1955 January 14 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Contract for Titan liquid oxygen-hydrocarbon ICBM engines. - .
The Western Development Division (WDD) and the Special Aircraft Project Office (SAPO) awarded a contract to Aerojet-General Corporation for development of liquid oxygen-hydrocarbon ICBM engines. The contract covered design and fabrication of booster, sustainer, and vernier engines and was intended to provide an alternate propulsion system should the North American Aviation effort encounter delays.
1955 February 16 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, . Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Contract for ballisitc missile all-inertial guidance system. - . Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) was awarded a contract for the research and development of an all-inertial guidance system. AC Spark Plug Company was to work with MIT and would fabricate and test the completed guidance system..
1955 March 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Alternate configuration ICBM to be authorized - . Hq ARDC recommended to Hq USAF that an alternate configuration ICBM be authorized for development..
1955 April 12 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Contract for all-inertial guidance for a ballistic missile. - . The Arma Division of American Bosch Arma Corporation received a contract to design, develop, fabricate, and test a complete airborne all-inertial guidance system for a ballistic missile system..
1955 April 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Alternate ICBM approved. - . Secretary of the Air Force Harold E. Talbott approved development of an alternate ICBM..
1955 May 2 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan ICBM contractor selection. - . Hq USAF authorized AEDC to proceed with the selection of an alternate source for the development of the ICBM. The alternate airframe configuration was to be a two-stage missile, later dubbed Titan..
1955 May 2 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan 1 begun. - . Nation: USA. USAF approved Western Development Division proposals to inaugurate a second ICBM airframe, which became the Titan ICBM (SM-68)..
1955 July 12 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Requirement for an intercontinental ballistic missile. - . General Operational Requirement (GOR) Number 104 was issued for a long-range intercontinental ballistic missile..
1955 July 27 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Maximum acceleration of the Atlas program. - . Development Directive 76 was issued for an ICBM weapon system. The directive called for maximum acceleration of the Atlas program and confirmed the assignment of the highest Air Force priority..
1955 September 14 - . LV Family: Titan, . Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Martin wins Titan ICBM contract. - . After evaluating the Douglas Aircraft Company, Lockheed, and the Glenn L. Martin Aircraft Company proposals for the alternate ICBM, the Air Materiel Command (AMC) declared the Martin Company winner..
1955 October 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Martin given contract for the Titan ICBM. - . The Glenn L. Martin Aircraft Company of Baltimore, Maryland, was given a contract authorizing the design, development, and testing of the two-stage Titan ICBM (XSM-68) - Weapon System 107A-2..
1955 December 1 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, . Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Highest priority for both ICBMs and IRBMs. - . Related Persons: , Eisenhower. President Eisenhower officially assigned highest and equal priority to the development of the Atlas and Titan ICBMs and the Thor and Jupiter IRBMs. This decision led to the resignation of ICBM program advocate Gardner..
1956 January 30 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- ICBM and IRBM equal priority. - . Headquarters ARDC directed WDD to treat the ICBM and IRBM with equal priority..
1956 February 10 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Trevor Gardner resigned as Assistant Secretary of the Air Force. - .
Trevor Gardner, who was instrumental in the actions leading to the acceleration of the Air Force ballistic missile program two years earlier, resigned as Assistant Secretary of the Air Force. He protested the Pentagon's policies concerning missiles and lack of stronger emphasis on the programs.
1956 February 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan missile development moved from Baltimore to Denver. - . Related Persons: , Quarles. Secretary of the Air Force Donald Quarles approved the Glenn L. Martin Aircraft Company proposal to move its development effort for Titan (XSM-68) from Baltimore, Maryland, to the Denver, Colorado..
1956 April 13 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Production funding for guided missiles increased. - . As per authority of the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee (AF/BMC), Procurement Authorization 56-GM-20 increased the production funding for guided missiles to $279.05 million..
1956 May 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 1.
- First test firing of a 150,000-pound thrust engine for Titan's first stage. - . Aerojet-General conducted the first test firing of a 150,000-pound thrust engine subassembly of the XLR-87-AJ-1 liquid rocket engine that would be used in the Titan's first stage..
1956 July 9 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Hardened bases for ICBMs studied - . The Western Development Division began studying hardened bases for ICBM operational deployment..
1956 Aug - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Full-duration firing of the sustainer engine for Titan - .
The first full-duration, 300-second firing of the North American Aviation 60,000-pound thrust sustainer engine for Titan was successfully completed. During the month, Aerojet-General completed maximum duration test firings of the Titan booster engines (XLR-87-AJ-1) for 130 seconds and the sustainer engine (XLR-91-AJ-1) for 155 seconds.
1956 Oct - . LV Family: Titan, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Thor.
- Radio inertial guidance system for Titan and Thor. - . WDD decided to eliminate the inertial platform from the Bell Telephone Laboratories (BTL) radio inertial guidance system for Titan and Thor..
1956 Oct - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Back-up sustainer engine for Titan's second stage cancelled. - . Western Development Division cancelled the North American Aviation development effort on a back-up sustainer engine for Titan's second stage..
1956 November 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan operational missile site hardening. - . Brigadier General Osmond J. Ritland, WDD Vice Commander, ordered planning to be conducted on how to harden the Titan operational missile sites..
1956 November 26 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, Thor, Jupiter, Redstone, Pershing.
- All missiles over 200 miles range assigned to USAF. - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson issued a memo to the Armed Forces Policy Council to end the argument between the Air Force and Army on responsibility for missile programs. In an effort to settle the areas of jurisdiction for the services, Secretary Wilson ruled that all long-range missiles, ICBMs as well as IRBMs, with a range of more than 200 miles, would be given to the Air Force.
1957 January 10 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Highest priority for ICBM/IRBM contracts - . The Defense Department assigned the highest priority to ICBM/IRBM contracts and purchase orders to expedite the programs..
1957 January 18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First firing of a complete, two-chamber Stage I engine for the Titan ICBM. - . Aerojet-General conducted the first firing of a complete, two-chamber Stage I prototype engine (XLR-87-AJ-1) for the Titan ICBM..
1957 January 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Contract for production of Titan missiles. - . A definitive contract was signed with the Glenn L. Martin Company for the continued development and production of Titan missiles..
1957 Mar - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First full-duration firing of the Stage I engine for Titan - . The first full-duration firing of the prototype XLR-87-AJ-1 Stage I engine for Titan was completed..
1957 July 29 - . LV Family: Titan, Saturn I, .
- Follow-on ballistic missiles and space programs - .
AFBMD presented the Air Force Scientific Advisory Board's Ad Hoc Committee with a summary of follow-on ballistic missile weapon systems and advanced space programs that could be undertaken. Included among the programs was the proposed development of high-thrust space vehicles for orbital and lunar flights.
1957 August 1 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Ballistic missile programs reoriented. - .
The National Security Council approved a Defense Department recommendation to reorient and cut back the ballistic missile programs. Atlas retained its priority, but the Titan program was reduced to second priority. The Thor and Jupiter IRBM programs were to be combined and evaluated by a joint Office of the Secretary of Defense-Air Force-Army Committee that would choose between them for future development.
1957 August 9 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor.
- Missile production rates curtailed. - .
In an attempt to reduce program costs, Defense Secretary Charles E. Wilson curtailed the planned production rates for Atlas, Titan, and Thor missiles to four missile each per month for the ICBMs. He also requested a study of the effects of a monthly production rate of 2-2-2 for the three programs.
1957 August 16 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E, Titan I.
- US ICBM production limited to four Atlas and two Titan missiles per month - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson directed that the ICBM program be limited to a maximum monthly production of four Atlas and two Titan missiles rather than the "4-4" program ordered on 9 August. With other areas also reduced, the Titan program became essentially a research and development effort.
1957 September 11 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E, Titan I, Thor.
- Air Force Ballistic Missile program cuts - .
The Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee reviewed the revised AFBMD FY 1958 program that resulted from OSD decisions and directives of August that cut the program from $1,135 billion to $944 million. A 4-4-2 monthly production rate was approved for Atlas, Titan, and Thor missiles, and program slippages were accepted in response to Secretary Wilson's guidance of 9 August. The program was later submitted to OSD/BMC and approved on 5 October 1957.
1957 Oct - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First production Stage I engine for Titan delivered - . The first production version of the XLR 87-AJ-l Stage I engine for Titan was delivered by Aerojet-General..
1957 October 5 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Atlas, Thor, Titan.
- Approval of the revised AFBMD ballistic missile program. - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson approved the revised AFBMD ballistic missile program submitted to the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee on 12 September. A total of $991 million was approved; $437 million for Atlas, $335 million for Titan, and $148 million for Thor. AFBMD's original FY58 budget submission of October 1956 had requested $1,672 billion for the ballistic missile programs.
1957 October 5 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter.
- Studies to accelerate missile programs. - . In anticipation of directives to revise the objectives of the United States missile programs in light of the Russian success with Sputnik, AFBMD began studies for accelerating its programs..
1957 October 6 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, .
- Restrictions on US missile production removed. - . The Defense Department removed the restrictions placed on missile production on 16 August, while the production rates and operational deployment schedules were revised..
1957 Nov - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First R&D Stage II engine for Titan. - . The Aerojet-General Corporation delivered the first R&D XLR 91-AJ-l Stage II engine for Titan..
1957 November 14 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D, Atlas E, Titan I.
- USAF augmented program for ballistic missiles - .
Headquarters USAF presented its revised and augmented program for ballistic missile development to the Secretary of Defense and the Armed Forces Policy Council. Nine Atlas squadrons were proposed, the first to become operational in June 1959 and the ninth in June 1963 and eight Titan squadrons, the first to be operational in March 1961 and the last in June 1963.
1957 December - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan-Vanguard.
- Titan plus Vanguard proposed to place instrument package into lunar orbit - .
Nation: USA.
The Martin Company proposed to the Department of Defense (DOD) that a stage of the Titan intercontinental ballistic missile be combined with the Vanguard rocket to provide a launch vehicle capable of placing an instrument package into lunar orbit and, ultimately, on the lunar surface.
1957 December 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- AVCO Corporation proposed development of a manned satellite system to the Air Force. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
The basic elements of the proposal included a Titan rocket to boost a manned satellite into a 110 nautical mile earth orbit. The satellite would be a spherical capsule containing instrumentation and a life support system capable of sustaining one man for three or four days. A novel feature of the system would be development of a stainless steel cloth parachute which would lower the capsule safely through re-entry deceleration. As the air pressure increased the parachute would automatically expand to its full size and land the capsule at a survival, if bone jarring, rate of 35 feet per second. AVCO asked $500,000 for a three month study and mockup of the capsule device and estimated, as a rough guess", a total development cost of $100 million. The ballistic missile division, however, was not convinced that this was the best approach to the manned reentry problem. The division' s position was that when the Air Force identified its space goals and established specific technical requirements it would then be wiser to "ask for bids and put it (development) on an open competitive basis. " (Memo, Col L. D. Ely, to Col C. H. Terhune, 17 Dec 57, subj: AVCO Proposal for Manned Satellite.)
1957 December 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First Titan operational wing be located near Denver, Colorado. - . The Ballistic Missile Site Selection Panel recommended that the first Titan (SM-68) operational wing be located in the area of Denver, Colorado..
1958 February 3 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Thor, Atlas E, Jupiter.
- Highest priority to ballistic missiles, spy satellites, and ballistic missile early detection. - .
Related Persons: ,
Eisenhower.
Spacecraft: WS-117.
President Eisenhower directed the highest and equal national priority for Atlas, Titan, Thor, Jupiter, the WS 117L advanced military satellite system, and WS 224A BMEWS. This action returned the Titan program to its previous highest national priority status.
1958 February 11 - . LV Family: Thor, Atlas, Titan, Navaho. Launch Vehicle: Thor Able, Thor Agena A.
- 14 Thor boosters to be used during year for space and ICBM missions. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
The ballistic missile division informed command headquarters that as many as 14 Thor boosters would be available during the calendar year for special purpose flights. These were tentatively allocated as follows: three were assigned to Phase I "Able" series flights, six were assigned to the program for recoverable satellites, and five were assigned to Phase II "Able" for continued development leading to a Thor ICBM capability. (For a time Thor plus a second stage and warhead was considered as a means of acquiring an early emergency ICBM inventory well ahead of Atlas and Titan.) However, only eight additional launchings could be scheduled through 1958--three for Phase I "Able", three for recoverable satellites to be launched one a month beginning in October, and two in support of Phase II "Able" precisely guided reentry vehicles. Thus this appeared to be the maximum effort possible in the category of space related experimental flights essential to a more advance program. If a greater effort was desirable it would be necessary to obtain additional launching facilities, a problem that might be quickly and easily solved by modifying Navaho launch stands to accept Thor vehicles. (Msg, WDT 2-7E, AFBMD to ARDC, 11 Feb 58.)
1958 March 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Contract for all-inertial guidance for the Titan ICBM. - . American Arma Bosch was awarded a contract to develop and produce an all-inertial guidance system for the Titan ICBM..
1958 April 10 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter.
- Equal priority for all ICBM and IRBM programs - . Related Persons: , Eisenhower. President Dwight D. Eisenhower reaffirmed the highest and equal national priority for Atlas, Titan, Thor, and Jupiter..
1958 April 25 - . LV Family: Thor, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Thor Able, Titan C.
- USAF goal to to "...land a man on the moon and return him safely to earth". - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
Lunex.
The Air Force Ballistic Missile Division published the development plan for an Air Force Manned Military Space Systems Program. The objective was to ". achieve an early capability to land a man on the moon and return him safely to earth. The program represented a reasonable level of accomplishment with a minimum of time and money and called for start of a high priority program (similar to that enjoyed by ballistic missiles) characterized by "concurrency" and single Air Force agency management. The complete program would be carried out in four phases: first, "Man-In-Space-Soonest," was to determine functional capabilities and limitations of man in space by means of earth orbital flights--beginning with an instrumented 2,900 pound re-entry body, then a primate passenger and, finally, a manned capsule. The second, designated "Man-In-Space-Sophisticated," would use a drag type 3, 200 pound re-entry vehicle, capable of a 14 day manned space flight. This device would be used for earth orbital flight only but it would perform experiments essential to the final phase of the lunar program. The third phase, "Lunar Reconnaissance," would explore the moon by television camera and by means of a soft landing of an instrumented package on the moonIs surface. The final phase of the projected program was "Manned Lunar Landing and Return, " which would first test equipment by circumlunar flights returning to earth with instrumented capsules containing animals. At this stage of project development payload capacity would be increased to 9,000 pounds. The spacecraft would then undertake a full scale flight to the moon and safe return to earth with an animal passenger. The climax of the entire project would then be a manned lunar landing, brief surface exploration, and return to earth. This would be followed by other circumlunar flights to fully explore the moon's surface and gather additional physical data. The program was scheduled for completion in December of 1965 at a total estimated cost of $1.5 billion. Program cost estimates were based on use of Air Force rocket hardware and available ground facilities thus eliminating much new development and construction funding. However, new launch vehicle combinations would have to be developed progressing in performance as follows: a Thor-Vanguard second stage, a Thor-fluorine second stage, a "super" Titan with a fluorine-hydrazine second and third stages. Methods of landing involved use of retrorockets to insure a soft landing on the moon and return to earth through re-entry to a predetermined landing area. (USAF Manned Military Space Syst.em Development Plan, 25 Apr 58, prep by AFBMD.)
1958 May 21 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . Headquarters USAF announced that Lowry Range near Denver, Colorado, would be the first operational site for the Titan missiles (SM-68) that were to be built in Martin's Denver plant..
1958 May 26 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Inertial guidance system transferred from the Titan to Atlas. - .
American Bosch Arma Corporation's contract for an all-inertial guidance system was transferred from the Titan (XSM-68) development program to Atlas (XSM-65) that was to become operational sooner. The Bell Telephone Laboratories (BTL) radio-guidance system would be used on all Titan research and development missiles and for the first four Titan operational squadrons.
1958 June 16 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan C.
- Dynasoar Phase I contracts announced. - .
Nation: USA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar.
Phase I contracts for the Dyna-Soar boost-glide orbital spacecraft are awarded by the USAF to two teams of contractors: one headed by Boeing (Aerojet, General Electric, Ramo-Wooldridge, North American, and Chance Vought), and one headed by Martin (Bell, American Machine & Foundry, Bendix, Goodyear, and Minneapolis-Honeywell). Under the $ 9 million one-year contracts each team was to refine its design, leading to a competitive down-select.
1958 June 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Delivery of the first Titan missile - . The Air Force accepted delivery of the first Titan missile (A-l) from the Martin Company's Denver Division..
1958 July - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Advanced Titan considered. - . Nation: USA. USAF reviews improvements (inertial guidance, storable fuel, 1 x 9 basing, both stages constant 3.05 m diameter, in silo launch) to the Titan I..
1958 July 28 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . Deployment of Titan squadrons in a 3x3 hardened and dispersed configuration was approved for the Lowry, Ellsworth, and Mountain Home squadrons..
1958 August 29 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Centaur upper stage to be used with either Atlas or Titan boosters. - .
ARPA issued order Number 19-59 establishing the Centaur program that would provide a high energy, liquid-fuel upper stage for use with either the Atlas or Titan boosters. Pratt and Whitney was to develop the liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen engines for the upper stage vehicle to be developed by Convair/Astronautics. The development goal was to produce an upper stage vehicle that could place a satellite into a 24-hour, synchronous orbit 23,000 miles above the equator.
1958 October 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan missile A-2 exploded - . Titan missile A-2, scheduled for the first flight test, exploded during captive tests at Denver..
1958 October 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First Titan flight test missile delivered - . Titan missile A-3, now scheduled for the first Titan flight test, was delivered to the Air Force by the Martin Company..
1959 January 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Silo-launched Titan approved. - . Nation: USA. Major General Schriever approves conversion of future Titan facilities from silo-lift to in-silo launch..
1959 February 6 - . 21:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). First test launch of USAF Titan ICBM (A-3) from Cape Canaveral. Dummy second stage (500 km range)..
1959 February 25 - . 19:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1959 Mar - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- LR87-AJ-3 engine for Titan authorized - . As a result of numerous refinements evolved during prototype development of the LR87-AJ-1 engine for Titan, an advanced propulsion system - the AJ-3 - was authorized for development..
1959 March 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Non-cryogenic propellants for Titan - . AFBMD recommended that non-cryogenic propellants be introduced into the Titan program with the seventh squadron..
1959 Apr - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . Construction began on the operational facilities for the first Titan (SM-68) squadron at Lowry AFB, Colorado..
1959 Apr - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contractor for Titan all-inertial guidance system. - . AC Spark Plug was selected as the contractor to build the Titan all-inertial guidance system..
1959 April 3 - . 17:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1959 May 4 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1959 May 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Exploded during static testing. Failed Stage: 1.
- Titan 1 B-4 - . Nation: USA. Exploded during static testing..
1959 May 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First prototype XLR87-AJ-3 engine for Titan completed. - . The first prototype of the XLR87-AJ-3 engine for Titan was completed..
1959 June 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan C.
- Dyna-Soar contractors Boeing and Martin selected. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Dynasoar.
The Dyna-Soar source selection board completed its evaluation of the proposals of the Boeing Airplane Company and the Martin Company. The board recommended the development of the Boeing glider but also favored the employment of the orbtal Titan C booster offered by Martin.
1959 June 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer and the Aerozine-50 fuel blend selected for Titan II. - . Studies of possible non-cryogenic propellants for use on Titan indicated that the most promising combination was a nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer and the Aerozine-50 fuel blend..
1959 July 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Exploded during static testing. Failed Stage: 1.
- Titan 1 B-3 - . Nation: USA. Exploded during static testing..
1959 August 14 - . 16:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
- Test mission - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 0 km (0 mi).
Titan missile B-5, scheduled to be the first fully powered-flight test missile, was heavily damaged when a faulty release mechanism allowed an earlier-than-planned liftoff that resulted in engine shutdown and the missile's dropping back on the launch pad.
1959 August 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- In-silo launch capability for Titan missiles beginning in October 1962. - .
The Department of Defense and the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee approved an in-silo launch capability for Titan missiles beginning with the seventh squadron (October 1962). As a result of changes initiated during 1959, the Titan missiles from the seventh squadron on would have all-inertial guidance systems, storable non-cryogenic propellants, and an in-silo launch capability.
1959 September 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II would commence with the seventh Titan squadron. - .
Secretary of the Air Force James H. Douglas, Jr., recommended approval of the Titan II (WS 107C) program that would commence with the seventh squadron to be deployed to SAC. The Titan II would be an advanced system, with all-inertial guidance, non-cryogenic propellants, and in-silo launch capability for vastly improved reaction time and reduced vulnerability through hardened and dispersed (H&D) configurations.
1959 September 16-18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Plans for advanced launch vehicles - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Glennan.
Program: Apollo.
The ARPA-NASA Booster Evaluation Committee appointed by Herbert F. York, DOD Director of Defense Research and Engineering, April 15, 1959, convened to review plans for advanced launch vehicles. A comparison of the Saturn (C-1) and the Titan-C boosters showed that the Saturn, with its substantially greater payload capacity, would be ready at least one year sooner than the Titan-C. In addition, the cost estimates on the Titan-C proved to be unrealistic. On the basis of the Advanced Research Projects Agency presentation, York agreed to continue the Saturn program but, following the meeting, began negotiations with NASA Administrator T. Keith Glennan to transfer the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (and, therefore, Saturn ) to NASA.
1959 September 21 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor.
- USAF responsible for all military spacecraft. - .
Related Persons: ,
LeMay.
General Curtis E. LeMay, Vice Chief of Staff, USAF, informed Headquarters ARDC that the Secretary of Defense had assigned responsibility to the Air Force for developing and launching all military spacecraft. The Air Force was also to perform all required systems integration for military space systems. The decision was made for reasons of efficiency and economy.
1959 September 23 - . LV Family: Polaris, Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Responsibility for military space programs assigned to USAF - .
Spacecraft: WS-117,
Transit,
Midas,
Samos.
Once again, the Defense Department reorganized its space program. Primary responsibility for military space programs was assigned to the Air Force. ARPA retained responsibility for advanced research on missile defense, solid propellants, and several other projects. Existing projects were reassigned to the military services from ARPA - MIDAS and SAMOS to the Air Force,the Transit navigation satellite to the Navy, and NOTUS to the Army. These reassignments were not immediately effective, but the move toward Air Force development, production, and launching of military space vehicles was quite clear.
1959 Nov - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First production -3 engines for the Titan program. - . Aerojet-General delivered the first production XLR87-AJ-3 Stage I and XLR91-AJ-3 Stage II engine for the Titan program..
1959 November 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Titan II.
- Development contracts for the Dyna-Soar space glider. - . Spacecraft: Dynasoar. The development contracts for the Dyna-Soar space glider were finally awarded by the Air Force - Boeing was to build the glider stage and Martin would provide the first stage booster..
1959 November 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Contractor selection for Dynasoar and Titan I announced. - .
Nation: USA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar.
Boeing and Martin selected by USAF to develop Dynasoar and Titan I launch vehicle. The compromise project reformulation a week earlier led to this announcement by the Secretary of the Air Force. Boeing was the winner of the DynaSoar design competition on 9 November 1959 - but for the glider and total system only. Martin was selected as an associate contractor for booster development. Dynasoar received the designation WS-620A on 17 November 1959
1959 November 18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Titan II.
- 14-squadron Titan force and Titan II development approved. - . The Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee approved planning for a 14-squadron Titan force and the development of the Titan II weapon system (XSM-68B, WS 107C)..
1959 December 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II authorized - . Headquarters USAF authorized the initiation of development for an improved Titan missile, the Titan II..
1959 December 12 - . 17:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Exploded just above pad. Failed Stage: 1.
- RVX-3 Re-entry Vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 0 km (0 mi). The first flight testing of Titan staging and second stage engine ignition was unsuccessful when Titan C-3 exploded at liftoff due to a faulty relay in the command destruct system. First Titan ICBM launching testing second stage was unsuccessful at AMR..
1960 Jan - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Ablestar second stage completed - .
Aerojet-General Corporation completed development of the Ablestar second stage for use with Atlas, Titan, or Thor boosters. Primary improvements over the previous Able vehicles were increased propellant capacity, multiple restart capability, and full-time attitude control.
1960 Jan - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contracts for Titan II engines. - .
AFBMD awarded contracts for development of first and second stage Titan engines that would use non-cryogenic (storable) pro-pellants. Aerozine 50 (50 per cent UDMH and 50 per cent hydrazine) was the fuel selected to be used with nitrogen tetroxide as the oxidizer.
1960 February 2 - . 18:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Test mission - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
Titan test missile B7A completed a 2,200-mile flight, achieving successful staging and ignition of the second stage engine at high altitude. The Stage II engine, XLR-91-AJ-1, performed as planned, and the missile impacted almost exactly on target. This was the first successful Titan launch and flight since 4 May 1959.
1960 February 5 - . 21:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
1960 February 24 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- RVX-4 test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
Titan flight test missile G-4 was launched from Cape Canaveral and completed all test objectives in the first successful long-range flight, with the reentry vehicle impacting 4,335-NM downrange. This flight was the longest to date by a Titan and demonstrated the integrity of all basic design parameters as well as Bell Telephone Laboratories radio-inertial guidance systems.
1960 March 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II RV and basing decisions - .
Two important decisions were made on the Titan II program during the month. AFBMD received program approval to proceed with the development of the Mark 6 reentry vehicle specifically for use on the Titan II. Configuration for the Titan II operational squadrons was set at nine hardened and dispersed underground silo missile launchers (1x9) in strategic missile wings of two squadrons each (18 missile launchers).
1960 March 8 - . 18:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
1960 March 22 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- RVX-4 test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). USAF Titan fired 5,000 statute miles / 8000 km and data capsule recovered..
1960 April 8 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 April 21 - . 20:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 April 28 - . 20:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 May - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contract for production of the Titan II. - . The Air Force gave the Martin Company a letter contract for development, captive and flight testing, and production of the Titan II (WS 107C)..
1960 May 13 - . 21:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 May 27 - . 17:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 June - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin awarded a contract to develop the Titan 2 ICBM. - . Nation: USA.
1960 Jun - . Launch Site: Little Rock AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Little Rock AFB site for the 11th and 12th Titan squadrons. - . The Defense Department announced the selection of Little Rock AFB, Arkansas, as the site for the 11th and 12th Titan operational squadrons..
1960 June 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Martin to develop the Dyna-Soar booster airframe. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. The Air Force gave the Martin Company responsibility for the development of the Dyna-Soar booster airframe..
1960 June 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Production contract for Titan II - .
The Air Force (AFBMD) placed a production contract with the Martin Company for the Titan II (SM-68B) ICBM. This was designed to use storable, non-cryogenic fuels, an all-inertial guidance system, in-silo launch facilities, and to have greater range and payload capabilities than the Titan I (SM-68).
1960 June 24 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 June 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Aero-Jet to develop booster engines for the Dyna-Soar system. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. The Air Force authorized the Aero-Jet General Corporation to develop booster engines for the Dyna-Soar system..
1960 July 1 - . 17:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Destroyed 90 m above pad. Failed Stage: 1.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1.00 km (0.60 mi). The attempt to launch the first operational configuration Titan I ICBM (J-2) from Cape Canaveral was a failure. Titan 1 J (Mk 4 RV).
1960 July 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Mark 6 reentry vehicle for the Titan II. - . General Electric was awarded the contract to develop the Mark 6 reentry vehicle for the Titan II..
1960 July 28 - . 21:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: 130 km range. Failed Stage: 1.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). Titan 1 J (Mk 4 RV).
1960 August 10 - . 22:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
The first successful launch and flight of an operational prototype Titan I occurred on 10 August 1960. After two previous failures, Titan missile J-7 was the first operational prototype to be launched and complete a successful flight test down the Atlantic Missile Range. Titan 1 J (Mk 4 RV)
1960 August 30 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 Sep - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II prototype booster and sustainer engines built. - . Aerojet-General Corporation completed fabrication of the Titan II (XLGM-25C) prototype booster (XLR 87-AJ-5) and sustainer (XLR 91-AJ-5) engines..
1960 September 28 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 September 29 - . 14:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 October 7 - . 15:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 October 24 - . 23:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Titan ICBM fired 6,100 miles / 9800 km, 100 miles longer than any previous shot, with tactical-type nose cone..
1960 October 31 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First operational Titan I missile - . The Air Force accepted the first operational Titan I missile (HGM-25A) from the Martin Company..
1960 Nov - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First full-duration test firing of the Stage II engine for the Titan II ICBM. - . Aerojet-General conducted the first successful, full-duration test firing of the XLR91-AJ-5 Stage II engine intended for use in the advanced Titan II ICBM..
1960 November 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Titan II.
- Titan II instead of Titan I for Dyna-Soar. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. The Assistant Secretary of the Air Force requested ARDC to examine the feasiblity of employing Titan II instead of Titan I for Dyna-Soar suborbital flights..
1960 December 2 - . Launch Site: Ellsworth AFB. Launch Complex: Ellsworth AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Ellsworth AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 850th SMS activated at Ellsworth AFB.
1960 December 4 - . 05:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1960 December 20 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
1960 December 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- First segmented solid motor test. - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. Successful firing of a solid-propellant rocket motor using "building block" method was announced by NASA..
1961 Jan - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First production R&D Stage II engine for Titan II - . The first production R&D XLR91-AJ-5 Stage II engine for Titan II was delivered by Aerojet-General..
1961 January 9 - . LV Family: Atlas, Saturn I, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3.
- USAF need for a space launch vehicle with 15,000 lb payload - . Headquarters USAF instructed AFBMD to continue its efforts to define the need for a space launch vehicle with a payload capacity between the Atlas/Centaur (9,000 lbs) and the early Saturn (19,000 lbs).
1961 January 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Titan II.
- Titan II to be the Dyna-Soar suborbital Step I booster. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. Air Force headquarters announced that Titan II would be the suborbital Step I booster..
1961 January 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- USAF changes Dynasoar launch vehicle to Titan II - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar.
1961 January 20 - . 20:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
1961 January 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The Titan II selected as booster for the Dyna-Soar - . Spacecraft: Dynasoar. The Titan II was selected as the booster for the Air Force Dyna-Soar I hypersonic boost-glide research vehicle..
1961 January 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Large solid-propellant motor segment tested. - . Aerojet-General Corporation successfully test fired a 20-ton, 65-inch diameter, solid-propellant motor segment that produced 400,000 pounds of thrust for 18 seconds..
1961 February 1 - . Launch Site: Beale AFB. Launch Complex: Beale AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Beale AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 851st SMS activated at Beale AFB.
1961 February 1 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. Launch Complex: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 848th SMS activated at Lowry AFB.
1961 February 10 - . 05:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 February 20 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 Mar - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First full-duration test of the Stage I engine for the Titan II - . The first successful, full-duration test of the XLR87-AJ-5 Stage I engine for the Titan II was completed..
1961 March 3 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
1961 March 7 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- First Titan in-silo captive test firing - . The first Titan in-silo captive test firing took place at the Silo Launch Test Facility at Vandenberg'AFB, California..
1961 March 28 - . LV Family: Titan, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan force reduced from 14 to 12 squadrons. - .
Related Persons: ,
Kennedy.
President John F. Kennedy reduced the FY 1962 budget for the Titan force from 14 to 12 squadrons. Accordingly, the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee cancelled the two Titan II squadrons planned for Griffiss AFB, New York. In addition, the President deferred the current plans for three mobile Minuteman missile squadrons.
1961 March 28 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 March 31 - . 19:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
aaa - . Launch Site: Larson AFB. Launch Complex: Larson AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Larson AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 568th SMS activated at Larson AFB.
1961 May 3 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLTF. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Demonstration launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 60 km (37 mi). The 6565th Test Wing (Development) successfully conducted the first launch of a Titan (VS-1) from an underground silo at Vandenberg AFB. The nation's first silo launch of a Titan I at Vandenberg AFB..
1961 May 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II proposed for lunar landing program - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gilruth,
Seamans,
Silverstein.
Program: Apollo.
Spacecraft Bus: Gemini.
Spacecraft: Gemini LOR.
Albert C. Hall of The Martin Company proposed to Robert C. Seamans, Jr., NASA's Associate Administrator, that the Titan II be considered as a launch vehicle in the lunar landing program. Although skeptical, Seamans arranged for a more formal presentation the next day. Abe Silverstein, NASA's Director of Space Flight Programs, was sufficiently impressed to ask Director Robert R. Gilruth and STG to study the possible uses of Titan II. Silverstein shortly informed Seamans of the possibility of using the Titan II to launch a scaled-up Mercury spacecraft.
1961 May 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin briefed NASA on the Titan II weapon system. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gilruth,
Seamans.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Mercury Mark I.
Martin Company personnel briefed NASA officials in Washington, D.C., on the Titan II weapon system. Albert C. Hall of Martin had contacted NASA's Associate Administrator, Robert C. Seamans, Jr., on April 7 to propose the Titan II as a launch vehicle for a lunar landing program. Although skeptical, Seamans nevertheless arranged for a more formal presentation. Abe Silverstein, NASA Director, Office of Space Flight Programs, was sufficiently impressed by the Martin briefing to ask Director Robert R. Gilruth and Space Task Group to study possible Titan II uses. Silverstein shortly informed Seamans of the possibility of using the Titan II to launch a scaled-up Mercury spacecraft.
1961 May 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Martin C plan for Dyna-Soar Step IIA booster. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. A Dyna-Soar technical evaluation board recommended the Martin C plan for a Step IIA booster..
1961 May 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Plan for development of Titan III. - . SSD presented a preliminary plan for development of a high-lift booster that would wrap large solid-propellant booster engines around a liquid-rocket second stage center core vehicle..
1961 May 23 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 June 1 - . Launch Site: Mountain Home AFB. Launch Complex: Mountain Home AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan I ICBM 569th SMS activated at Mountain Home AFB - . Nation: USA.
1961 Jun - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First production R&D Stage I engine for the Titan II - . The first production model R&D XLR87-AJ-5 Stage I engine for the Titan II were delivered..
1961 June 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Solid-propellant rocket motor of 500,000 pounds of thrust test fired. - . Aerojet-General test fired a large solid-propellant rocket motor generating 500,000 pounds of thrust at its Sacramento, California, test facility..
1961 June 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Solid booster program meeting requirements of both NASA and the Air Force. - . Undersecretary of the Air Force Joseph V. Charyk instructed Headquarters USAF to prepare a solid booster program that would satisfy the requirements of NASA and the Air Force..
1961 June 24 - . 03:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 10 km (6 mi).
Titan I (M-l) was the first Series M missile and first inertially-guided Titan missile to be launched from Cape Canaveral. Essentially a Titan I with a Titan II inertial guidance system, M-l was only a partial success due to a second stage hydraulic failure and loss of control after sustainer engine ignition.
1961 July - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin proposal for a Titan-boosted Mercury vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft Bus: Mercury.
Spacecraft: Mercury Mark I.
James L. Decker of Martin Company submitted a proposal for a Titan-boosted Mercury vehicle. A Mercury-Titan program, expected to span an 18-month flight schedule, would benefit from the Air Force's booster development and test of the ballistic missile system and the considerable design and test that the Air Force had expended in the Dyna-Soar program to adapt the vehicle to manned spaceflight. The Titan, with its sea-level rating of 430,000 pounds of thrust in the first stage and 100,000 pounds in the second stage, was capable of lifting significantly heavier spacecraft payloads than the Mercury-Atlas. Its hypergolic propulsion system, using storable liquid propellants, was a much simpler system than the cryogenic propellant system in Atlas. A highly reliable booster could be provided, employing complete redundancy in the flight control systems in the form of a three-axis reference system, autopilot, servo, electrical, and hydraulic systems. The short time he proposed would depend on the availability of pad 19 at Cape Canaveral, planned for conversion to the Titan II configuration. Pad 19, unlike the other three Titan I pads, had been intended for space applications and was better designed for required prelaunch test programs.
1961 Jul - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First production Stage I engine for Titan II. - . Aerojet-General delivered the first production XLR87-AJ-5 Stage I engine for Titan II..
1961 July 21 - . 02:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 July 25 - . 19:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Titan missile M-2 completed the first full-range (4,342-NM) flight test of a Titan I equipped with an all-inertial guidance system. .
1961 August 1 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. Launch Complex: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 849th SMS activated at Lowry AFB.
1961 Aug - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First production Stage II engine for Titan II - . The first production XLR91-AJ-5 Stage II engine for Titan II was delivered by Aerojet-General..
1961 August 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin briefed Space Task Group on Titan II technical characteristics and performance. - .
Nation: USA.
Representatives of Martin Company briefed Director Robert R. Gilruth and some of the senior staff of Space Task Group on Titan II technical characteristics and expected performance. At a senior staff meeting four days later, August 7, Gilruth commented on the Titan II's promise for manned spaceflight, particularly its potential ability to place larger payloads in orbit than could Atlas, which would make it 'a desirable booster for a two-man spacecraft.' Martin had estimated the cost of procuring and launching nine Titan II boosters, with cost of ancillary equipment, at $47.889 million spread over fiscal years 1962 through 1964.
1961 August 4 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 August 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Solid motor segment test. - .
Nation: USA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar.
Segmented solid-propellent rocket engine fired by United Technology Corp. at Sunnyvale, generating over 200,000 pounds of thrust in 80-second firing. Developed under NASA contract, center section of engine contained over 55,000 pounds of propellant, the largest single piece yet manufactured in the United States.
1961 August 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First Titan II production engine delivered - . The first Titan II production engine was delivered to the Air Force..
1961 September 7 - . 01:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). USAF Titan successfully launched from Atlantic Missile Range, making 6,100-mile flight..
1961 September 8 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 September 23 - . 20:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle research and development mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Launched from Titan II silo.
1961 September 29 - . 01:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 October - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II to be selected as the launch vehicle for NASA's advanced Mercury. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Martin Company received informal indications from the Air Force that Titan II would be selected as the launch vehicle for NASA's advanced Mercury. Martin, Air Force, and NASA studied the feasibility of modifying complex 19 at Cape Canaveral from the Titan weapon system configuration to the Mercury Mark II launch vehicle configuration.
1961 October 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III to be a standard military space launch vehicle. - . Space Systems Division provided Headquarters AFSC with a special study of the Titan II with strap-on solid boosters as the concept for a standard military space launch vehicle - named Titan III..
1961 October 7 - . 01:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). USAF Titan I launched from Cape Canaveral carrying Titan II guidance system..
1961 October 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Early program definition actions for the Titan III. - . Dr. Harold Brown, Director of Defense Research and Engineering (DDR&E), authorized the Air Force to begin early program definition actions for the development of the Titan III..
1961 October 24 - . 23:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 October 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First Titan II missiles delivered. - . The Air Force accepted the first Titan II (XLGM-25C) missiles..
1961 November 22 - . 00:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). BSD's 6555th ATWg at Cape Canaveral completed the first successful launch of a Titan I (J-22) by an entire Air Force crew..
1961 November 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Bleymaier Director of Titan III Program - . Colonel Joseph S. Bleymaier was appointed Director of Titan III Program (Program 624) at Headquarters SSD..
1961 November 29 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 December 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II for the Mercury Mark II - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: McNamara.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Recommendation that the weapon system of the Titan II, with minimal modifications, be approved for the Mercury Mark II rendezvous mission. On the basis of a report of the Large Launch Vehicle Planning Group, Robert C. Seamans, Jr., NASA Associate Administrator, and John H. Rubel, Department of Defense Deputy Director for Defense Research and Engineering, recommended to Secretary of Defense Robert S. McNamara that the weapon system of the Titan II, with minimal modifications, be approved for the Mercury Mark II rendezvous mission. The planning group had first met in August 1961 to survey the Nation's launch vehicle program and was recalled in November to consider Titan II, Titan II-1/2, and Titan III. On November 16, McNamara and NASA Administrator James E. Webb had also begun discussing the use of Titan II.
1961 December 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- DOD/NASA coordination for Mercury Mark II - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: McNamara,
Seamans,
Webb.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
NASA Associate Administrator Robert C. Seamans, Jr., and DOD Deputy Director of Defense Research and Engineering John H. Rubel recommended to Secretary of Defense Robert S. McNamara and NASA Administrator James E. Webb that detailed arrangements for support of the Mercury Mark II spacecraft and the Atlas-Agena vehicle used in rendezvous experiments be planned directly between NASA's Office of Manned Space Flight and the Air Force and other DOD organizations. NASA's primary responsibilities would be the overall management and direction for the Mercury Mark II/ Agena rendezvous development and experiments. The Air Force responsibilities would include acting as NASA contractor for the Titan II launch vehicle and for the Atlas-Agena vehicle to be used in rendezvous experiments. DOD's responsibilities would include assistance in the provision and selection of astronauts and the provision of launch, range, and recovery support, as required by NASA.
1961 December 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- First test of UTC 1205 rocket motors. - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. Solid-propellent rocket motor generating nearly 500,000 pounds of thrust was fired in a static test of 80-second duration by United Technology Corp. at Sunnyvale, Calif., under USAF contract..
1961 December 13 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 December 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III program office. - . SSD established a Deputy for Titan III (Program 624A) program office to develop a space standard launch vehicle (SLV) and system built around a Titan II with two strap-on, 120-inch diameter motors..
1961 December 15 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1961 December 18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- New method to steer large-size solid-propellant rockets. - .
United Technology Center (UTC) announced the successful test of a new experimental method to steer large-size solid-propellant rockets. Called liquid thrust vector control (TVC), this technique used a gas or liquid that was sprayed into the exhaust path of rocket engine exhaust, thus deflecting the exhaust and thereby turning the vehicle. The test was conducted on a 450,000-pound thrust solid-fuel engine.
1961 December 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Production contract for the solid-propellant rocket motor for the Titan III. - . SSD awarded a contract to United Technology Center for production of the 120-inch diameter, solid-propellant rocket motor for the Titan III..
1961 December 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II to be used for the Mercury Mark II program. - .
Nation: USA.
Manned Spacecraft Center directed Air Force Space Systems Division to authorize contractors to begin the work necessary to use the Titan II in the Mercury Mark II program. On December 27, Martin-Baltimore received a go-ahead on the launch vehicle from the Air Force. A letter contract for 15 Gemini launch vehicles and associated aerospace ground equipment followed on January 19, 1962.
1961 December 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Dynasoar suborbital tests deleted from program. - .
Nation: USA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar.
Development time schedule for Dyna-Soar was reduced when DOD authorized the USAF to move directly from B-52 drop tests to unmanned and then manned orbital flights. This eliminated the previous interim stage of suborbital flights to be powered by the Titan II. This required renegotiation of the development contract held by the Martin Co. and negotiating of a new contract for a larger booster.
1961 December 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan 2 first static ground test. - . Nation: USA. Titan 2 was successfully captive-fired for the first time at the Martin Co.'s Denver facilities..
1961 December 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan 2 first ground test. - .
Nation: USA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: Gemini.
Titan II, an advanced ICBM and the booster designated for NASA's two-man orbital flights, was successfully captive-fired for the first time at the Martin Co.'s Denver facilities. The test not only tested the flight vehicle but the checkout and launch equipment intended for operational use.
1961 December 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- USAF announces Titan III for Dynasoar - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spaceplane. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. With continued weight growth USAF announces Titan III to be developed for Dynasoar orbital missions..
1961 December 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II captive-fired for the first time - . A Titan II was successfully captive-fired for the first time at Martin's test stand facilities near Denver, Colorado..
1962 January 1 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. Launch Complex: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Davis-Monthan AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan 2 390th SMW and 570th SMS (9 missiles) activated at Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona..
1962 January 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Statement of Work for the procurement of Titan II launch vehicles for the Gemini program. - .
Nation: USA.
Manned Spacecraft Center prepared a Statement of Work to be accomplished by Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) in its role as contractor to NASA for the procurement of Titan II launch vehicles for the Gemini program. The launch vehicle would retain the general aerodynamic shape, basic systems, and propulsion concepts of the missile. Modifications, primarily for crew safety, were to be kept to a minimum. The Statement of Work accompanied a purchase request for $27 million, dated January 5, 1962, for 15 Titan launch vehicles. Pending ratification of the Gemini Operational and Management Plan, however, funding was limited to $3 million. To oversee this work, SSD established a Gemini Launch Vehicle Directorate, headed by Colonel Richard C. Dineen, on January 11. Initial budgeting and planning were completed by the end of March, and a final Statement of Work was issued May 14; although amended, it remained in effect throughout the program.
1962 January 11 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini Launch Vehicle Directorate established. - . Spacecraft: Gemini. Headquarters Space Systems Division established the Gemini Launch Vehicle Directorate (SSVL) under Colonel R.C. Dineen as part of the Deputy for Launch Vehicles (SSV)..
1962 January 19 - . LV Family: Titan.
- Contract for 15 Titan Gemini Launch Vehicles - . Spacecraft: Gemini. The Martin Marietta Corporation was awarded a letter contract for the development and production of 15 Titan Gemini Launch Vehicles and related aerospace ground equipment (AGE)..
1962 January 21 - . 00:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A3. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1962 January 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II plans to ensure flight safety and enhance reliability. - .
Nation: USA.
After investigating potential malfunction problems of the modified Titan II/Gemini launch vehicle, Martin-Baltimore prepared a study report with plans to provide the components necessary to ensure flight safety and enhance reliability. Martin defined the malfunction problem quantitatively in terms of the probability of each cause and its characteristic effect on the system and vehicle. Martin intended to keep the launch vehicle as much like the weapon system as possible; thus the data obtained from the Air Force's weapon system development program would be applicable to the launch vehicle. Only minimal modifications to enhance probability of mission success, to increase pilot safety, and to accommodate the Gemini spacecraft as the payload were to be made. These included a malfunction detection system; backup guidance, control, and hydraulic systems; and selective electrical redundancies.
1962 January 29 - . 23:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). The 47th, and final, Titan I research and development flight test missile (M-7) was successfully fired from Cape Canaveral. Of the launches, 34 were rated successes, nine partials, and only four as failures. .
1962 February 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Aerospace Corporation to support of the Gemini Launch Vehicle Program. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division issued a Technical Operating Plan to Aerospace Corporation, El Segundo, California, for support of the Gemini Launch Vehicle Program; a contract followed on March 15. Aerospace was to assume responsibility for general systems engineering and technical direction of the development of the launch vehicle and its associated subsystems. Aerospace had already established a Gemini Launch Vehicle Program Office in January.
1962 February 16 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II explodes in first silo test - . The 6595th Aerospace Test Wing at Vandenberg AFB conducted the first and development test missile (N-7) from an underground silo. In this first silo launch of a Titan II, the missile destroyed itself .
1962 February 16 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Design criteria for the Titan III. - . Space Systems Division awarded a contract to the Martin Marietta Corporation to study the design criteria for the Titan III standardized space launch vehicle..
1962 February 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Proposal for redundant subsystems for the Gemini launch vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Inertial Guidance System.
Martin-Baltimore submitted its initial proposal for the redundant flight control and hydraulic subsystems for the Gemini launch vehicle; on March 1, Martin was authorized to proceed with study and design work. The major change in the flight control system from Titan II missile to Gemini launch vehicle was substitution of the General Electric Mod IIIG radio guidance system (RGS) and Titan I three-axis reference system for the Titan II inertial guidance system. Air Force Space Systems Division issued a letter contract to General Electric Company, Syracuse, New York, for the RGS on June 27. Technical liaison, computer programs, and ground-based computer operation and maintenance were contracted to Burroughs Corporation, Paoli, Pennsylvania, on July 3.
1962 February 23 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
- Research and development Cat II / operational test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 50 km (31 mi).
1962 March 1 - . Launch Site: McConnell AFB. Launch Complex: McConnell AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- McConnell AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan 2 381st SMW and 532nd SMS (9 missiles) activated at McConnell AFB, Kansas..
1962 Mar - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Construction work for Titan I completed. - . Construction work for all six Titan I squadrons was completed..
1962 March 16 - . 18:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Mk 6 re-entry vehicle test launch - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
The 6555th Aerospace Test Wing launched the first Titan II (XLGM-25C) research and development flight test missile (N-2) from Cape Canaveral. The Titan II was the most powerful ICBM yet launched by the U.S., its first stage engines generating 430,000 pounds of thrust and the second stage engine 100,000 pounds. The flight of N-2 also marked the first successful test of the AC Spark Plug inertial guidance system. The Air Force successfully launched a Titan II intercontinental ballistic missile. This was the first full-scale test of the vehicle; it flew 8000 km out over the Atlantic Ocean.
1962 March 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contract to Aerojet-General for 15 propulsion systems for the Gemini launch vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division awarded a letter contract to Aerojet-General Corporation, Azusa, California, for the research, development, and procurement of 15 propulsion systems for the Gemini launch vehicle. It also included the design and development of the related aerospace ground equipment. Aerojet had been authorized to go ahead with work on the engines on February 14, 1962, and the final engine was scheduled for delivery by April 1965.
1962 March 21 - . LV Family: Titan.
- Contract for Titan Gemini engines - . Spacecraft: Gemini. Aerojet-General Corporation was given a letter contract for research, development, and manufacture of 15 sets of Titan Gemini Launch Vehicle propulsion systems and associated ground equipment..
1962 March 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Development Plan for the Gemini Launch Vehicle - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division published the "Development Plan for the Gemini Launch Vehicle System". From experience in Titan II and Mercury programs, the planners estimated a budget of $164.4 million, including a 50 percent contingency for cost increases and unforeseen changes.
1962 March 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Design philosophy for Gemini Titan II - .
Nation: USA.
Martin-Baltimore submitted a "Description of the Launch Vehicle for the Gemini Spacecraft" to Air Force Space Systems Division. This document laid the foundation for the design of the Gemini launch vehicle by defining the concept and philosophy of each proposed subsystem.
1962 April 1 - . Launch Site: Little Rock AFB. Launch Complex: Little Rock AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Little Rock AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan 2 308th SMW and 373rd SMS (9 missiles) activated at Little Rock AFB, Arkansas.
1962 April 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan IIIC solid-propellant booster contractor - . A Titan III source selection board recommended United Technology Center as the developer of the solid-propellant booster motors..
1962 April 12 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - .
The Ballistic Systems Division Site Activation Task Force (SATAF) at Lowry AFB, Colorado, turned over Complex A, the first three-missile Titan I (HGM-25A) launch complex, to the 724th SMW. These were the first of 54 Titan I launchers programmed for SAC's operational inventory. All Titan I squadrons featured silo-lift facilities, that is, storage in an underground silo and erection to an above ground launch position.
1962 April 14 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- United Technology Center selected for the solid-propellant rocket motors for the Titan III. - . Space Systems Division selected the proposal submitted by United Technology Center for the 120-inch diameter, solid-propellant rocket motors for the Titan III..
1962 April 18 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. Launch Complex: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 848th SMS (nine missiles) declared operational at Lowry AFB.
1962 April 19 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . The last Titan I (HGM-25A) complex was turned over to the 724th Strategic Missile Squadron of the 451st Strategic Missile Wing (SAC) at Lowry AFB, Colorado. This completed activation..
1962 May 1 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. Launch Complex: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Davis-Monthan AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan 2 571st SMS (9 missiles) activated within the 390th SMW at Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona..
1962 May 4 - . 21:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Research and development Category II test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Titan I flight test missile was the 100th major space and ballistic vehicle to be launched from Vandenberg AFB since 16 December 1958. A total of 21 Thors, 32 Atlases, 5 Titans, and 42 space boosters had been launched from the base..
1962 May 10 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. Launch Complex: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - .
Nation: USA.
Titan I ICBM 849th SMS (nine missiles) declared operational at Lowry AFB. The second Titan I (HGM-25A) squadron at Lowry AFB, Colorado, the 725th Strategic Missile Squadron of SAC's 451st Strategic Missile Wing, became operational with the turnover of the last of three, three-missile launch complexes. All launch facilities were silo-lift.
1962 May 16-17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- A Launch Vehicle-Spacecraft Interface Working Group was established. - .
Nation: USA.
Gemini Project Office (GPO) and Aerospace had agreed on the need for such a group at a Gemini-Titan coordination meeting on May 11. The main function of the group, composed of Martin and McDonnell personnel with a McDonnell representative as chairman, was to provide mutual exchange of design and physical data on mechanical, electrical, and structural details between the spacecraft contractor and the booster contractor. The group would make no policy decisions; its actions were to be reviewed at regularly scheduled coordination meetings held by GPO.
1962 May 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contract to convert pad 19 at Cape Canaveral for Gemini flights. - .
Nation: USA.
Amendment No. 6 to the Gemini launch vehicle procurement contract assigned $2.609 million to fund the construction necessary to convert pad 19 at Cape Canaveral for Gemini flights. The Air Force had originally constructed pad 19 for the Titan I development program. Following the final Titan I development flight (January 29) from the Cape, design of the required modifications had begun in February. In April, Gemini Project Office decided that Pad 19 would have an erector rather than a gantry, the upper third of which would be designed as a white room. The final design review of pad 19 modifications took place July 9-10, and the Army Corps of Engineers awarded the construction contract to Consolidated Steel, Cocoa Beach, Florida. Construction began in September. Work was completed and pad 19 was activated on October 17, 1963.
1962 May 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Avco proposal for a space station. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: MOL.
Representatives from Avco Manufacturing Corporation made a presentation to MSC on a proposal for a space station. Prime purpose of the station, company spokesmen said, was to determine the effects of zero-g on the crew's ability to stand reentry and thus fix the limit that man could safely remain in orbit. Avco's proposed station design comprised three separate tubes about 3 m in diameter and 6 m long, launched separately aboard Titan IIs and joined in a triangular shape in orbit. A standard Gemini spacecraft was to serve as ferry vehicle.
1962 May 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Avco proposal for Titan-launched space station. - . Nation: USA. Avco's proposed station design comprised three separate tubes about 3 m in diameter and 6 m long, launched separately aboard Titan 2s and joined in a triangular shape in orbit. A standard Gemini spacecraft was to serve as ferry vehicle..
1962 June 7 - . 18:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1962 June 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Combined Titan I liquid-fueled engine - solid-propellant rocket motor test fired to validate Titan III. - .
A Titan I liquid-fueled engine was strapped to the side of a 175-ton solid-propellant rocket motor, and the configuration was test fired by Aerojet-General Corporation. This evaluated the compatibility of liquid and solid engines for SSD's Titan III space launch vehicle. The combination generated 700,000 pounds of thrust.
1962 June 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin-Baltimore's airborne systems functional test stand went into operation at Baltimore. - .
Nation: USA.
In this 3000-square-foot facility, all airborne systems in the Gemini launch vehicle - including flight control, hydraulic, electrical, instrumentation, and malfunction detection - were assembled on tables and benches; actual engines, but simulated propellant tanks and guidance, were used. In addition to individual and combined systems tests, the facility was used to check system design changes and trouble-shoot problems encountered in other test programs.
1962 July 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Plan for flight testing the malfunction detection system (MDS) for the Gemini launch vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Martin prepared a plan for flight testing the malfunction detection system (MDS) for the Gemini launch vehicle on development flights of the Titan II weapon system. Gemini Project Office (GPO) had requested Martin to prepare Systems Division and Aerospace approved the plan and won GPO concurrence early in August. This so-call 'piggyback plan' required installing the Gemini MDS in Titan II engines on six Titan II flights to demonstrate its reliability before it was flown on Gemini.
1962 July 11 - . 18:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1962 July 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan Launch Operations Committee. - .
Nation: USA.
A technical team at Air Force Missile Test Center, Cape Canaveral, Florida - responsible for detailed launch planning, consistency of arrangements with objectives, and coordination - met for the first time with official status and a new name. The group of representatives from all organizations supplying major support to the Gemini-Titan launch operations, formerly called the Gemini Operations Support Committee, was now called the Gemini-Titan Launch Operations Committee.
1962 July 25-26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Reliability review of the Titan II launch vehicle engine system. - .
Nation: USA.
A reliability review of the Titan II launch vehicle engine system was held in Sacramento, California, at Aerojet-General's Liquid Rocket Plant, the site where the engines were being developed. Gemini engines had to be more reliable than did intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) engines. This requirement meant supplementing the ICBM engine reliability program, a task being performed by Aerojet under Air Force Space Systems Division direction.
1962 July 25 - . 16:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1962 August 1 - . Launch Site: McConnell AFB. Launch Complex: McConnell AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- McConnell AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan 2 533rd SMS (9 missiles) activated within the 381st SMW at McConnell AFB, Kansas..
1962 August 16 - . Launch Site: Mountain Home AFB. Launch Complex: Mountain Home AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mountain Home AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 569th SMS (nine missiles) declared operational at Mountain Home AFB.
1962 August 16 - . Launch Site: Mountain Home AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Mountain Home AFB - . With the transfer of Complex A, the turnover of the 569th Strategic Missile Squadron to SAC was completed. All nine Titan I missiles were now operational at Mountain Home AFB, Idaho..
1962 August 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III to be operational by 1965. - .
The Defense Department announced plans to develop the Titan III launch vehicle that was to be operational by 1965. Martin Marietta Corporation would be the systems integration (prime) contractor for the Titan III program that was managed by AFSC's Space Systems Division.
1962 August 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- US Department of Defense announced Titan III launch vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: McNamara.
The Department of Defense announced plans to develop a Titan III launch vehicle powered by both solid and liquid fuel rocket motors with a total thrust of over 11 million newtons (2.5 million Ibs). .Scheduled to become operational in 1965, the Titan III would be used to launch the Air Force's X-20 (Dyna Soar) manned spacecraft, as well as heavy unmanned military satellites. Martin Marietta Corporation had been selected as prime contractor for the project, at an estimated cost of between $500 million and $1 billion. At a news conference the following day, Defense Secretary Robert S. McNamara cited the Titan III as a major step toward overtaking the Soviet Union in various phases of military space development.
1962 August 31 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First Titan II operational missile was accepted by the Air Force. - . The first Titan II (LGM-25C) operational missile was accepted by the Air Force. This missile was delivered to Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona, on 11 December 1962..
1962 September 1 - . Launch Site: Little Rock AFB. Launch Complex: Little Rock AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Little Rock AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan 2 374th SMS (9 missiles) activated within the 308th SMW at Little Rock AFB, Arkansas.
1962 September 8 - . Launch Site: Beale AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Beale AFB - . The nine Titan I missile launchers at Beale AFB, California, were turned over to SAC's 851st Strategic Missile Squadron..
1962 September 8 - . LV Family: Titan.
- Focal point for space projects within Headquarters USAF. - .
Spacecraft: Dynasoar,
Midas.
Headquarters USAF announced that the Deputy Chief of Staff for Research and Development (DCS/R&D) would be the focal point for space projects within Headquarters USAF. Lt General James Ferguson, DCS/R&D, would possess Air Force headquarters responsibility for programs such as MIDAS, Titan III, Dyna-Soar, and others.
1962 September 8 - . Launch Site: Beale AFB. Launch Complex: Beale AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Beale AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 851st SMS (nine missiles) declared operational at Beale AFB..
1962 September 12 - . 15:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1962 September 26 - . Launch Site: Ellsworth AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Ellsworth AFB - . The last complex of the 850th Strategic Missile Squadron (Titan I) at Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota, was turned over to SAC..
1962 September 26 - . Launch Site: Larson AFB. Launch Complex: Larson AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Larson AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 568th SMS (nine missiles) declared operational at Larson AFB.
1962 September 28 - . Launch Site: Larson AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Larson AFB - .
The last of the six operational Titan I squadrons, the 568th Strategic Missile Squadron at Larson AFB, Washington, was transferred to SAC. This brought the Titan I operational force to its programmed strength of six radio-guidance squadrons and 54 silo-lift launchers.
1962 September 28 - . Launch Site: Ellsworth AFB. Launch Complex: Ellsworth AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Ellsworth AFB - . Nation: USA. Titan I ICBM 850th SMS (nine missiles) declared operational at Ellsworth AFB.
1962 October 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Air Force Space Systems Division revised the Development Plan for the Gemini launch vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
The budget was raised to $181.3 million. Cost increases in work on the vertical test facility at Martin's Baltimore plant, on the conversion of pad 19 at Cape Canaveral, and on aerospace ground equipment had already generated a budget increase to $172.6 million during September. The new Development Plan also indicated that the first launch date had slipped to December 1963.
1962 October 6 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Research and development Category II test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1962 October 10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- X-20 flight dates compatible with Titan IIIC schedules. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. The Dyna-Soar program completed a system package program, which made the X-20 flight dates compatible with projected Titan IIIC schedules..
1962 October 12 - . 16:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1962 October 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III research and development begun. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Dynasoar.
Following Congressional approval of development funding, Air Force headquarters issued System Program Directive 9, authorizing research and development of Titan III, System 624A. By this time the funding and schedule for development of the Titan IIIC booster was the pacing item in the Dynasoar project. The launch schedule had to be revised and reduced yet once again. Delivery of the first Dyna-Soar was to be made by October 1964 and first orbital launch by the end of 1965. While the first glider test would be 14 months later than the original July 1957 schedule, the first orbital flight was expected six months earlier.
1962 October 26 - . 17:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1962 November 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan I SATAF discontinued - . Ballistic Systems Division's Site Activation Task Forces (SATAFs) for Titan I at Larson, Lowry, and Mountain Home AFBs were discontinued..
1962 November - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contract for Phase I of the Gemini launch vehicle program. - .
Nation: USA.
During the first three weeks of the month, Air Force Space Systems Division and Martin-Baltimore negotiated the terms of the contract for Phase I of the Gemini launch vehicle program. The resulting cost-plus-fixed-fee contract included an estimated cost of $52.5 million and a fixed fee of $3.465 million. This contract covered the development and procurement of the first launch vehicle and preparations for manufacturing and procuring the remaining 14 vehicles required by the Gemini program.
1962 November 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for Phase II development of the solid-propellant rocket motors for Titan III. - . Space Systems Division awarded a $173 million contract to United Technology Center for Phase II development of the five-segment, 120-inch diameter, solid-propellant rocket motors for Titan III..
1962 November 29 - . Launch Site: Edwards. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Edwards AFB solid-rocket motor test facility. - .
Ground was broken at Edwards AFB, California for construction of the largest and most heavily instrumented solid-rocket motor test facility. It was designed to test the five-segment, 120-inch solid-propellant motors for the Titan III program but could handle engines up to and including 156 inches in diameter.
1962 December - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Aerojet-General contract for the first phase of the Gemini launch vehicle engine program. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division and Aerojet-General negotiated a cost-plus-fixed-fee contract for the first phase of the Gemini launch vehicle engine program, February 14, 1962, through June 30, 1963. The contract required delivery of one set of engines, with the remaining 14 sets included for planning purposes. Estimated cost of the contract was $13.9 million, with a fixed fee of $917,400 for a total of $14,817,400.
1962 December 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Development phase of the Titan III program begins. - . The Martin Marietta Corporation was awarded a contract for Titan III airframe, systems, integration, and testing..
1962 December 5 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Research and development Category II test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1962 December 6 - . 20:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II. FAILURE: Failure.
- Mk 4 re-entry vehicle test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 500 km (310 mi).
Titan II flight N-11, the eighth in a series being conducted by the Air Force to develop the weapon system, was launched from Cape Canaveral. It carried a design change intended to reduce the amplitude of longitudinal oscillations which had appeared during first stage operation on all seven previous Titan II flights. This phenomenon, which subsequently became known as POGO, generated g-forces as high as nine in the first stage and over three at the position on the missile corresponding to the location of the spacecraft on the Gemini launch vehicle. Fearing the potentially adverse effect on astronaut performance of such superimposed g-forces, NASA established 0.25g at 11 cycles per second as the maximum level tolerable for Gemini flights. As a first try at solving the POGO problem, Titan II N-11 carried standpipes in each leg of the stage I oxidizer feed lines to interrupt the coupling between the missile's structure and its propulsion system. This coupling was presumed to be the cause of the instability. Postflight analysis, however, revealed that the POGO fix was unsuccessful; longitudinal oscillation had actually been multiplied by a factor of two.
1962 December 19 - . 20:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1962 December 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for solid rocket motors for the Titan 3. - . USAF awarded a $30 million contract to United Technology Center (UTC) for the design, development, delivery, and flight of large, segmented, solid rocket motors for the Titan 3..
1962 December 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini Launch Vehicle Configuration Control Board. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division established the Gemini Launch Vehicle Configuration Control Board to draw up and put into effect procedures for approving and disapproving specifications and engineering change proposals for the Gemini launch vehicle. It formally convened for the first time on March 5, 1963.
1962 December 27 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First operational Titan II missile installed at Davis-Monthan AFB. - .
The first operational Titan II (LGM-25C) missile was installed in the lead complex of the 570th Strategic Missile Squadron at Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona. This was a major milestone in the transition of the Titan II from research and development to fully operational status with the Strategic Air Command.
1963 January 10 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II. FAILURE: Failure.
1963 January 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- McNamara requests review of the Titan III nd Gemini programs. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar, Gemini. The Secretary of Defense directed a review of the Titan III program and the Gemini program of NASA..
1963 January 29-30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II development flight failures caused by problems in the airborne radio guidance system. - .
Nation: USA.
At a launch guidance and control coordination meeting, Aerospace described three Titan II development flight failures that had been caused by problems in the General Electrical Mod III airborne radio guidance system. Although these failures did not appear to be the result of inherent design faults that might react on the Gemini program, Aerospace felt that a tighter quality assurance program was needed: 'GE has a poor MOD III (G) quality control program, basically poor workmanship.'
1963 January 29 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Research and development Category II test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1963 February 6 - . 17:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Mk 6 re-entry vehicle test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). A Titan II (N-16) completed a 6,500-mile flight down the Atlantic Missile Range carrying the heaviest payload ever to travel that far on a U.S. missile..
1963 February 16 - . 21:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II. FAILURE: Failure.
- Awful Tired - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 5.00 km (3.10 mi). Research and development launch - Mk 6 re-entry vehicle.
1963 February 18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Pilot safety philosophy and procedures would be carried over from Mercury-Atlas to Gemini-Titan. - .
Nation: USA.
In a letter transmitting copies of the Gemini Launch Vehicle Pilot Safety Program to Gemini contractors and other organizations engaged in Gemini development and operations, Air Force Space Systems Division explained that pilot safety philosophy and procedures would be carried over from Mercury-Atlas to Gemini-Titan.
1963 February 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- First static firing of one segment version of the Titan III solid rocket motor. - .
United Technology Center (UTC), the contractor for the Titan III solid-rocket motors, successfully conducted the first static firing of one segment of the large-size, 120-inch diameter motor. This would be used as the first stage (Stage 0) booster. UTC was developing a single engine of five segments as the basic booster.
1963 February 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for Titan III standard launch vehicles for space missions. - .
The Air Force announced the formal contract award to Martin Marietta Corporation for the design, development, fabrication, and delivery of Titan III standard launch vehicles for space missions. Martin Marietta would act as the systems integration contractor, while Aerojet-General would produce the liquid-fuel propulsions systems for the Titan core section and United Technology Center (UTC) would provide the solid-rocket motors (SRMs) for the booster.
1963 March 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1 to use GLV 2 tank - .
Nation: USA.
The stage II oxidizer tank from Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 was airlifted from Martin-Denver to Martin-Baltimore to be used in GLV-1. GLV propellant tank and skirt assemblies were manufactured, pressure-tested, and calibrated at Martin-Denver, then shipped to Baltimore where the GLV was assembled. Additional Details: here....
1963 March 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Study group to recommend DOD experiments for inclusion in the Gemini flight program. - .
Nation: USA.
The Gemini Program Planning Board, meeting in Washington, agreed to the establishment of an ad hoc study group to compare NASA and Department of Defense (DOD) objectives for the Gemini program and to recommend DOD experiments for inclusion in the Gemini flight program. The group met in continuous session March 25 to April 26, presenting its final report to the board on May 6. The board then recommended that a program of inflight military experiments be immediately approved, that the Air Force establish a field office at Manned Spacecraft Center to manage DOD participation in the Gemini program in general and integration of experiments in particular, and that work on preventing longitudinal oscillations in stage I and combustion instability in stage II of the Gemini launch vehicle to be urgently pursued. The board declined to recommend additional flights in the Gemini program, as suggested by the study group, to encompass experiments that would not fit into the framework of the planned Gemini program. The Secretary of Defense and NASA Administrator concurred in the Board's recommendations.
1963 March 21 - . 15:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1963 March 30 - . 08:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A2. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- NTMP K-17 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). K-17 Nike-Zeus intercept of Titan I ICBM..
1963 April 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- POGO problems in the Titan II. - .
Nation: USA.
The Titan II-Gemini Coordination Committee was established to direct efforts to reduce longitudinal vibration (POGO) in the Titan II and to improve engine reliability. Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) and Aerospace had presented to NASA and the Air Force a series of briefings on the POGO problem that culminated in a briefing to the Gemini Program Planning Board. The main problem was that POGO level satisfactory in the weapon system was too high to meet NASA standards for the Gemini program, and further reduction in the POGO level required a much more elaborate and extensive analytic and experimental program than had so far been considered necessary. The board approved the SSD/Aerospace proposals and established a committee to oversee work toward a POGO remedy. The high-level committee was composed of officials from Air Force Ballistic Systems Division, SSD, Space Technology Laboratories, and Aerospace.
1963 April 3 - . Launch Site: McConnell AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- All major site construction on the Titan II force completed. - . All major site construction on the Titan II force was completed at Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona; Little Rock AFB, Arkansas; and McConnell AFB, Kansas..
1963 April 5 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
1963 April 13 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A3. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- NTMP K-21 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). K-21 Nike-Zeus intercept of Titan I ICBM..
1963 April 17 - . LV Family: Saturn V, Saturn I, Titan.
- Large Solid Rocket Motor Program (Program 623A) begun. - .
The Defense Department announced the selection of Thiokol Chemical Corporation, Aerojet-General Corporation, and Lockheed Propulsion Company to conduct work on the development of large solid-propellant motors as part of the Space Systems Division's Large Solid Rocket Motor Program (Program 623A). Development work was divided into four tasks: (1) Thiokol and Aerojet-General were to develop 260-inch diameter, solid rocket motors of 3 million pounds of thrust for demonstration static firings; (2) Thiokol was to work on a 156-inch, 3 million-pound thrust, two-segment solid rocket motor; (3) Thiokol was to develop and static fire a 156-inch, one-segment solid rocket motor of one million pounds thrust demonstrating thrust vector control (TVC) through movable nozzles; and (4) Lockheed was to static fire a 156-inch, single segment solid rocket motor of one million pounds thrust that demonstrated TVC through jet tabs.
1963 April 19 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II. FAILURE: Failure.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 500 km (310 mi). Mk 6 re-entry vehicle.
1963 April 23-24 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini successful crew escape possible based on Titan II tests. - .
Nation: USA.
The Gemini Abort Panel met. Martin-Baltimore's analysis of the last three Titan II flight tests tended to show that successful crew escape would have been possible. McDonnell presented data on spacecraft structural capabilities, but lack of data on what to expect from Titan II catastrophic failure meant that spacecraft structural capabilities remained a problem. Also some questions had existed as to what could happen to the adapter retrosection during and after an abort. A study had been made of this problem, assuming a 70,000 foot altitude condition, and there appeared to be no separation difficulties. This study investigated the period of up to 10 seconds after separation, and there was no evidence that recontact would occur.
1963 April 27 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Dinner Party - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
Titan II (N-8) was the second research and development missile and the first successful flight test vehicle to be launched from a silo at Vandenberg AFB. This was the first successful Titan II launch and flight after three consecutive failures, one (N-7) at Vandenberg and two (N-18 and N-21) at the Atlantic range. Research and development launch. Mk 6 re-entry vehicle.
1963 May 1 - . 10:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I. FAILURE: Failure.
- Research and development launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. The Titan I research and development flight test program ended with the launch of missile V-4 from Vandenberg. V-4 self-destructed over the launch pad, recording one of the seven failures in the Titan I flight test program that began in .
1963 May 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini/Titan II improvement program. - .
Nation: USA.
The Gemini Program Planning Board approved the Air Force Systems Command development plan for the Gemini/Titan II improvement program. The plan covered the development work required to man-rate the Titan II beyond the requirements of the Titan II weapon system and included three major areas: (1) reducing longitudinal oscillation levels to NASA requirements, (2) reducing the incidence of stage II engine combustion instability, and (3) cleaning up the design of stage I and II engines and augmenting the continuing engine improvement program to enhance engine reliability. The work was to be funded by the Titan Program Office of Air Force Ballistics Systems Division and managed by the Titan II/Gemini Coordination Committee, which had been established April 1. NASA found the plan satisfactory.
1963 May 7-17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First engines for Gemini launch vehicle No. 1 - .
Nation: USA.
Aerojet-General delivered the first flight engines for Gemini launch vehicle No. 1 to Martin-Baltimore. Aerojet-General had provided a set of Type 'E' dummy engines March 18. These were installed and used to lay out tubing and wiring while the launch vehicle was being assembled. Additional Details: here....
1963 May 9 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II. FAILURE: Failure.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Mk 6 re-entry vehicle..
1963 May 13 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Flying Frog - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Research and development launch. Mk 6 re-entry vehicle..
1963 May 24 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Atlas D,E, and Titan I missiles to be phased out 1965 - 1968. - .
Headquarters USAF recommended that Atlas D,E, and Titan I missiles be phased out of SAC's active operational inventory between 1965 and 1968. The older liquid-fueled ICBMs were expensive to operate, required a large manpower commitment, were slow-reacting and thus vulnerable when compared to the more advanced Minuteman and Titan II missile that were being deployed.
1963 May 24 - . 17:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Mk 6 re-entry vehicle.
1963 May 29 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The vertical test facility (VTF) at Martin-Baltimore was activated. - .
Nation: USA.
The VTF comprised a 165-foot tower and an adjacent three-story blockhouse with ground equipment similar to that used at complex 19. In it, the completely assembled Gemini launch vehicle was tested to provide a basis for comparison with subsequent tests conducted at complex 19. Each subsystem was tested separately, then combined systems tests were performed, concluding with the Combined Systems Acceptance Test, the final step before the launch vehicle was presented for Air Force acceptance.
1963 May 29 - . 16:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC16. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II. FAILURE: Failed 55 seconds after launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Titan II flight N-20, the 19th in the series of Air Force research and development flights, was launched from Cape Canaveral. It carried oxidizer standpipes and fuel accumulators to suppress longitudinal oscillations (POGO). During the spring of 1963, static firings of this configuration had been successful enough to confirm the hypothesis that POGO was caused by coupling between the missile structure and its propulsion system, resulting in an unstable closed loop system. Standpipes and accumulators, by interrupting the coupling reduced the source of instability. Flight N-20 failed 55 seconds after launch and yielded no POGO data. Although the failure was not attributed to the installed POGO fix, Air Force Ballistics Systems Division decided officially that no further Titan II development flights would carry the POGO fix because so few test flights remained to qualify the weapon system operationally. This decision did not stand, however, and the POGO fix was flown again on N-25 (November 1), as well as on two later flights.
1963 June 2 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Stage I of Gemini launch vehicle 1 was erected in Martin-Baltimore's vertical test facility. - . Nation: USA. Stage II was erected on June 9, and posterection inspection was completed June 12. Subsystem Functional Verification Tests began June 10..
1963 June 8 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First Titan II operational squadron activated. - . The first Titan II operational squadron, the 570th Strategic Missile Squadron, was activated at Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona, and assigned to SAC's 390th Strategic Missile Wing..
1963 June 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini Titan malfunction detection system test plan. - .
Nation: USA.
Manned Spacecraft Center - Atlantic Missile Range Operations Office reported that the malfunction detection system would be flown on Titan II launches N-24, N-25, N-29, N-31, and N-32. The first launch in this so-called 'piggyback program' was scheduled for June 21. All preparations for this flight, including installation and checkout of all malfunction detection system components, were reported complete at a Titan II coordination meeting on June 14.
1963 June 20 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Thread Needle - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Research and development launch. Mk 6 re-entry vehicle..
1963 June 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin-Baltimore received the stage II fuel tank for Gemini launch vehicle 2 from Martin-Denver. - . Nation: USA. This was a new tank, replacing a tank rejected for heat treatment cracks. Stage II oxidizer tank and stage I fuel and oxidizer tanks were received July 12 after a roll-out inspection at Martin-Denver July 1-3..
1963 June 30 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Davis-Monthan AFB - . The first Titan II flight at Davis-Monthan AFB was turned over to SAC's 570th Strategic Missile Squadron..
1963 July 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Effects on pilot performance of longitudinal oscillations (POGO) of the Gemini launch vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Gemini Project Office (GPO) completed a test program on the centrifuge at Ames Research Center to evaluate the effects on pilot performance of longitudinal oscillations (POGO) of the Gemini launch vehicle. When subjected to oscillatory g-loads ranging from 0 to ± 3g superimposed on a steady-state load of 3.5g, pilot perception and performance decreased markedly above ± 0.25g. Primary effects were impaired pilot vision, reduced eye scan rate, masked sensory perception and kinesthetic cues, and degraded speech. GPO reconfirmed the need to reduce POGO to a maximum of 0.25g.
1963 July 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Backup for the first Gemini flight. - .
Nation: USA.
Acting Manager Charles W Mathews informed Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) senior staff that Gemini Project Office was exploring the possibility of backing up the first Gemini flight with a payload consisting of a boilerplate reentry module and a production adapter. Additional Details: here....
1963 July 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Approval for the continued development of the Titan III. - . Related Persons: , McNamara. After a detailed, six-month review of the Titan III program, Secretary of Defense Robert S. McNamara approved the continued development of the Titan III..
1963 July 16 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A2. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1963 July 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- World's largest solid-rocket motor test fired. - .
The first full-scale, five-segment solid-propellant booster motor for the Titan III, the world's largest solid-rocket motor (SRM), was test fired at the United Technology Center's test facility. The motor produced over 1,000,000 pounds of thrust during its 110-second firing.
1963 July 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- First test firing of Transtage propulsion system - . At its Sacramento test facility, the Aerojet-General Corporation conducted the first test firing of the twin-engine propulsion system that would power the Titan III upper stage..
1963 July 31 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Electronic-Electrical Interference (EEI) Tests of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1. - . Nation: USA. Electronic-Electrical Interference (EEI) Tests of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1 began in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore, following a review by Air Force Space Systems Division and Aerospace of data from Sub-system Verification Tests. . Additional Details: here....
1963 July 31 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan I engineering transferred to AFLC. - . The Titan I weapon system acquisition phase was completed and engineering responsibility for the Titan I (WS 107B) was transferred from Ballistic Systems Division (AFSC) to AFLC..
1963 August 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Executive management responsibility for the Titan I transferred to Norton AFB. - . Executive management responsibility for the Titan I weapon system (WS 107A-2) was transferred from BSD (AFSC) to San Bernardino Air Materiel Area (AFLC), Norton AFB, California..
1963 August 15 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). K-26 Nike-Zeus intercept of Titan I ICBM..
1963 August 21 - . 23:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development / Pod T-202 test / plume study mission - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
Titan II development flight N-24 was launched from the Atlantic Missile Range. This was the first of five flight tests in the Gemini malfunction detection system (MDS) piggyback series. All MDS parameters were lost 81 seconds after liftoff because of a short circuit in the MDS. Operation in the second flight (N-25 on November 1) was normal except for two minor instrumentation problems. Three more test flights (N-29 on December 12, 1963; N-31 on January 15, 1964; and N-33 on March 23, 1964) verified the performance of the Gemini MDS under actual conditions of flight environment and engine operation.
1963 August 30 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A3. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1963 September 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- A Mission Planning Coordination Group was established. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
A Mission Planning Coordination Group was established at the request of the Gemini Project Office to review monthly activities in operations, network guidance and control, and trajectories and orbits; and to ensure the coordination of various Manned Spacecraft Center elements actively concerned with Gemini mission planning. Additional Details: here....
1963 September 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle No. 1 - .
Nation: USA.
The formal Combined Systems Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle No. 1 was conducted in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Two preliminary CSAT dry runs had been conducted on August 2 and 17, in conjunction with Electronic-Electrical Interference (EEI) Tests. Additional Details: here....
1963 September 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Department of Defense approved the Titan II Augmented Engine Improvement Program. - .
Nation: USA.
On November 15, Aerojet-General received an Air Force contract to develop and test new engine components to correct weak and potentially dangerous problem areas of engine design. Aerojet-General had already initiated the development effort on September 30. The goal was to enhance engine reliability by a complete redesign rather than resort to piecemeal fixes as problems came up. While the primary goal was not achieved, the program did yield several side benefits, including the correction of several minor design deficiencies, the improvement of welding techniques, and the development of better assembly procedures.
1963 September 11-20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Vehicle acceptance team for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1. - . Nation: USA. The vehicle acceptance team for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1 inspected the vehicle and reviewed its manufacturing and testing history, focusing on the results of the Combined Systems Acceptance Test (CSAT) of September 6. . Additional Details: here....
1963 September 14 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini delay of three weeks in the battery qualification program. - .
Nation: USA.
Gemini Project Office reported a delay of about three weeks in the battery qualification program. McDonnell had sent a team to investigate the problem of high porosity welds in titanium battery cases. Another problem had turned up with the batteries in prequalification vibration test. The batteries vibrated excessively, although they did not fail electrically; the vibration's amplification factor was apparently low enough to be remedied by potting.
1963 September 17 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A2. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1963 September 23 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Tar Top - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Titan II (N-23) became the first Category II research and development missile to be launched successfully from Vandenberg AFB by the 6595th Aerospace Test Wing. Research and development launch. Mk 6 re-entry vehicle..
1963 September 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Backup for the injectors of the second stage engine of the Gemini launch vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division contracted with Aerojet-General for a program to develop a backup for the injectors of the second stage engine of the Gemini launch vehicle. Titan II development flights had shown the stage II engine tended toward incipient combustion instability. The Gemini Stability Improvement Program, begun as a backup, became a program aimed at maximum probability of success on December 24, 1963. The 18-month program produced a completely redesigned stage II engine injector.
1963 September 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle trainer. - .
Nation: USA.
Manned Spacecraft Center awarded its first incentive-type contract to Ling-Temco-Vought, Inc., Dallas, Texas for the fabrication of a trainer to be used in the Gemini launch vehicle training program. The fixed-price-incentive-fee contract had a target cost of $90,000, a target profit of $9,000, and a ceiling of $105,000. The incentive was based on cost only and provided for an 80/20 sharing arrangement; that is, the contractor would pay from his profit 20 percent of all savings under the target cost, or, alternatively, would receive 20 percent of all savings under the target cost. This meant that the contractor's profit would be zero after $97,500 was spent, and would be minus if costs exceeded $105,000.
1963 October 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1. - . Nation: USA. Martin-Baltimore completed its evaluation of data from the second Combined Systems Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1, found it acceptable, and presented it to the GLV-1 vehicle acceptance team (VAT). . Additional Details: here....
1963 October 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Reconsideration of flying Gemini fixes on Titan II development flights. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Schriever.
Personnel from Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD), Air Force Ballistic Systems Division (BSD), and Titan II contractors met in Los Angeles to reconsider flying Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) fixes on Titan II development flights. BSD, which was responsible for the weapon system development program, had halted the installation of GLV fixes on the Titan II flights because of the limited number of flights remaining to qualify the missile. General Bernard A Schriever, Commander of Air Force Systems Command (of which BSD and SSD were subordinate division), intervened in support of an active program to clean up launch vehicle problem areas. The incorporation of GLV fixes on Titan II flights resumed on November 1 with the flight of Titan II N-25.
1963 October 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- McNamara briefed on Titan III and Dyna-Soar. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Dynasoar. Secretary McNamara was briefed on the Titan III and Dyna-Soar programs at the Martin Company facilities in Denver, Colorado..
1963 October 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First Titan II Gemini Launch Vehicle. - . Spacecraft: Gemini. From the Martin Marietta Corporation, the Space Systems Division accepted the first Titan II Gemini Launch Vehicle..
1963 October 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 1 arrived at Atlantic Missile Range and was transferred to complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Stage I was erected in the complete vehicle erector October 28, stage II in the second stage erector October 29. The two stages were cabled together in the side-by-side configuration required for the Sequence Compatibility Firing scheduled for mid-December. A limited Electronic-Electrical Interference Test was completed November 7, and power was applied to the vehicle November 13.
1963 November 1 - . 20:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development / Pod T test / plume study mission - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
Titan II development flight N-25 was launched from the Atlantic Missile Range. It carried the oxidizer surge chamber and fuel accumulator kit intended to reduce the amplitude of longitudinal vibration which had characterized earlier flights. NASA regarded 0.25g as the maximum level tolerable in manned space flight; this flight achieved a level of 0.22g, the first to fall within acceptable limits. Although the kit had been tested on only one flight, Gemini Project Office had sufficient confidence in it to decide, on November 6, to procure several more such kits for subsequent installation in Gemini launch vehicles. Two later Titan II development flights (N-29 on December 12, 1963, and N-31 on January 15, 1964) and the flight of Gemini-Titan 1 confirmed the validity of this decision. The required kits for the remaining Gemini launch vehicles were then procured.
1963 November 9 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1963 November 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- First Titan III engine - .
Space Systems Division accepted the first Titan III engine from Aerojet-General at its Sacramento facilities. The first and second stage liquid engines, 430,000 and 100,000 pounds of thrust respectively, were for the Titan IIIA vehicle that would test the basic center core configuration (Stages 1 and 2) of the eventual Titan IIIC vehicle.
1963 November 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch schedules reexamined. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. The Gemini Management Panel, after reviewing the status of spacecraft and launch vehicle, decided that Gemini launch schedules need reexamination, especially the amount of testing at Cape Canaveral necessary to establish confidence in mission success. . Additional Details: here....
1963 November 14 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). K-24 Nike-Zeus intercept of Titan I ICBM..
1963 November 16 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Rendezvous evaluation experiment for the Gemini-Titan 4 mission. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Flight Crew Support Division reported an agreement with Flight Operations Division on a flight profile and rendezvous evaluation experiment for the Gemini-Titan 4 mission. Objective of the experiment was to stimulate normal Agena/Gemini rendezvous and to repeat part of the maneuver using loss of signal/manual technique. Basically, the mission would use circular phasing and catch-up orbit as proposed by the Flight Crew Support Division. Exact fuel requirements and ground tracking requirement were under study by Flight Operations Division.
1963 November 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- First Titan II squadron to reach fully operational status. - . The 570th Strategic Missile Squadron became fully operational and was turned over to SAC..
1963 November 27 - . Launch Site: McConnell AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- McConnell AFB - . The 533d Strategic Missile Squadron, the first Titan II squadron at McConnell AFB, Kansas, was turned over to SAC..
1963 November 29 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- All 18 Titan II launchers at Davis-Monthan AFB operational. - . All 18 Titan II launchers at Davis-Monthan AFB were operational with the turnover of the second squadron, the 571st Strategic Missile Squadron, to SAC's 390th Strategic Missile Wing..
1963 December 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Correction of Titan II deficiencies for the Gemini program. - .
Nation: USA.
The Gemini Program Planning Board issued a memorandum of understanding of the correction of the Titan II deficiencies for the Gemini program. This agreement formalized NASA specifications and Air Force plans to clean up problems related to longitudinal oscillations (POGO), combustion instability, and engine improvement. The program to alleviate the POGO effect included ground proof tests of all subsystems modified to control oscillations. Flight tests of the solutions would be flown on Titan II missiles before application to the Gemini launch vehicle. For the combustion stability program, dynamic stability would be demonstrated through the use of artificially produced disturbances, with the engines being flight tested on unmanned vehicles as final proof of man-rating. Engine improvement was a program to correct all design deficiencies that had cropped up during the Titan II development flights.
1963 December 4 - . Launch Site: McConnell AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- McConnell AFB - . The second McConnell Titan II squadron of LGM-25C missiles, the 532d Strategic Missile Squadron, was turned over to SAC..
1963 December 8 - . Launch Site: Little Rock AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Little Rock AFB - . The first operational Titan II squadron at Little Rock AFB, the 373d Strategic Missile Squadron, was transferred to SAC..
1963 December 10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIM.
- Manned Orbiting Laboratory assigned to USAF - .
Related Persons: ,
McNamara.
Spacecraft: MOL.
Secretary of Defense Robert S. McNamara assigned responsibility for the development of a near-earth Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) to the Air Force. First manned flight was tentatively planned for late 1967 or early 1968. A modified Titan III, the Titan HIM, would be used to place the laboratories in orbit from Vandenberg.
1963 December 10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 in assembly - . Nation: USA. The engine was installed December 31. An interim stage I engine was received December 29 and installed January 9, 1964. . Additional Details: here....
1963 December 12 - . 20:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development / Pod T test / plume study mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1963 December 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 3 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Martin-Baltimore received the propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 3 from Martin-Denver, which had begun fabricating them in June. Splicing the oxidizer and fuel tanks for each stage was completed April 17, 1964. Flight engines arrived from Aerojet-General on May 10, and installation was completed June 6. Final horizontal tests of the assembled launch vehicle began June 1 and were concluded on June 17 with an Air Force inspection of GLV-3 before the vehicle was erected in the vertical test facility.
1963 December 17 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development / Pod T? test / plume study mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1963 December 28 - . Launch Site: Little Rock AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Final operational Titan II squadron transferred to SAC at Little Rock AFB. - . The sixth and final operational Titan II squadron, the 374th Strategic Missile Squadron, was transferred to SAC at Little Rock AFB, Arkansas. This action completed the programmed activation..
1963 December 31 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 1 completed the Combined Systems Test (CST). - .
Nation: USA.
The two stages of Gemini launch vehicle 1, standing side by side on complex 19, completed the Combined Systems Test (CST) in preparation for Sequence Compatibility Firing (SCF). CST had been scheduled for December 13 but was delayed by late completion of the complex support systems for operational compatibility with the launch vehicle. Additional Details: here....
1964 January - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The program plan for Gemini extravehicular operations was published. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 11,
Gemini 12,
Gemini 5,
Gemini 6,
Gemini 7,
Gemini 8,
Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Objectives of the operations were to evaluate man's capabilities to perform useful tasks in a space environment, to employ extravehicular operations to augment the basic capability of the spacecraft, and to provide the capability to evaluate advanced extravehicular equipment in support of manned space flight and other national space programs. Additional Details: here....
1964 January 15 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development / Pod T test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1964 January 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Static test-to-failure of the Gemini spacecraft / launch vehicle interface - .
Nation: USA.
Martin-Baltimore conducted a static test-to-failure of the spacecraft/launch vehicle interface structure. Test results demonstrated a very satisfactory minimum structural margin of 23 percent above ultimate conditions expected to be met in the transonic buffet conditions of launch. Plans were made to hold a structures meeting in Houston on March 17-19, 1964, for final review of all load conditions, stress distribution, and margins, in readiness for the Gemini-Titan 1 mission.
1964 January 23 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1964 February 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 2 in test - . Nation: USA. Gemini launch vehicle 2 stage I and interstage were erected in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Stage II was erected February 7. Subsystems Functional Verification Tests began February 21..
1964 February 17 - . 16:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1964 February 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 1 Subsystem Functional Verification Tests (SSFVT) began on complex 19. - . Nation: USA. These repeated the SSFVT performed at Martin-Baltimore in the vertical test facility. Their purpose was to verify the vehicle's readiness to begin systems tests. SSFVT were completed on March 3..
1964 February 26 - . 20:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1964 March 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1 and spacecraft No. 1 were mechanically mated at complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Before GLV and spacecraft were electrically mated, the launch vehicle's status was reverified with a Combined Systems Test (CST) performed on March 10. A special series of Electronic-Electrical Interference (EEI) Tests began March 12 and ended March 25. Evaluation of test results confirmed that the intent of EEI testing had been accomplished, despite some persistent anomalies. A successful post-EEI systems reverification CST was performed March 27.
1964 March 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 4 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Martin-Baltimore received the propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle 4 from Martin-Denver, which had begun fabricating them in November 1963. Tank splicing was completed July 21. Aerojet-General delivered the stage II flight engine June 26, the stage I engine July 28. Engine installation was completed September 4. Final horizontal tests were completed and reviewed October 26, with Martin authorized to erect the vehicle in the vertical test facility.
1964 March 13 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). The 10th, and last, Titan II (XLGM-25C) research and development flight test missile (N-30) to be launched from Vandenberg completed a successful flight. .
1964 March 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II development problems resolved. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Mueller.
The Air Force Systems Command weekly report (inaugurated in September 1963) summarizing actions taken to resolve Titan II development problems would no longer be issued. George E. Mueller, NASA Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight, informed Associate Administrator Robert C. Seamans, Jr., that the launch vehicle 'no longer appears to be the pacing item in the Gemini program.'
1964 March 24 - . 01:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1964 March 31 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1 modifications completed. - .
Nation: USA.
Electrical and mechanical modification of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 1 airborne components was completed. GLV-1 had been shipped to the Cape equipped with several items to be used only for ground tests. These were replaced with flight units, beginning January 31. The GLV-1 Wet Mock Simulated Launch, a complete countdown exercise including propellant loading, was successfully completed April 2. Testing concluded on April 5 with a Simulated Flight Test.
1964 April 8 - . 16:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 1 - .
Payload: Gemini SC1. Mass: 3,187 kg (7,026 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: Gemini.
Decay Date: 1964-04-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 782 . COSPAR: 1964-018A. Apogee: 299 km (185 mi). Perigee: 154 km (95 mi). Inclination: 32.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min.
The first Gemini mission, Gemini-Titan I, was launched from Complex 19 at Cape Kennedy at 11:00 a.m., e.s.t. This was an unmanned flight, using the first production Gemini spacecraft and a modified Titan II Gemini launch vehicle (GLV). The mission's primary purpose was to verify the structural integrity of the GLV and spacecraft, as well as to demonstrate the GLV's ability to place the spacecraft into a prescribed earth orbit. Mission plans did not include separation of the spacecraft from the second stage of the vehicle, and both were inserted into orbit as a unit six minutes after launch. The planned mission encompassed only the first three orbits and ended about four hours and 50 minutes after liftoff. No recovery was planned for this mission, but Goddard continued to track the spacecraft until it reentered the atmosphere on the 64th orbital pass over the southern Atlantic Ocean (April 12) and disintegrated. The flight qualified the GLV and its systems and the structure of the spacecraft.
1964 April 9 - . 20:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC15. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Research and development / Pod RVIP test / plume study mission - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
The 23d, and last, Titan II research and development missile (N-3A) to be launched down the Atlantic range completed a success ful flight. With the 10 test flights from Vandenberg, a total of 33 Titan II (XLGM-25C) R&D flights had been completed since 16 March 1962 - 27 successes and only six failures. This Air Force conducted test program contributed significantly to the development of the Gemini launch vehicle; the Gemini malfunction detection system was tested on five flights, Gemini guidance components on three, and the longitudinal oscillation fix on four. In addition to flight testing these (and other) critical components, these flights also enhanced confidence in the use of the Titan II as a launch vehicle. Thirty-two Titan II test flights were analyzed to determine whether any characteristic of the flight would have demanded a Gemini abort; 22 were adjudged successful from the standpoint of a Gemini mission, nine would have required Gemini to abort, and one resulted in a prelaunch shutdown.
1964 April 14 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Electrical-Electronic Interference Tests on Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 - .
Nation: USA.
Electrical-Electronic Interference Tests began on Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Oscillograph recorders monitored 20 GLV and aerospace ground equipment (AGE) circuits, five of which displayed anomalies. Two hydraulic switchover cicuits showed voltage transients exceeding failure criteria, but a special test fixed this anomaly in the AGE rather than the GLV.
1964 April 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini manned flight could be accomplished in 1964. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
After reviewing the results of Gemini-Titan (GT) 1, the Gemini Management Panel remained optimistic that manned flight could be accomplished in 1964. According to the work schedule, GT-2 could fly on August 24 and GT-3 on November 16, with comfortable allowances for four-week slips for each mission. Some special attention was devoted to GT-2, where the spacecraft had become the pacing item, a position held by the launch vehicle on GT-1. Spacecraft No. 2 systems tests had started one month late but were proceeding well. In addition, the schedule looked tight for starting spacecraft No. 3 systems tests on June 1.
1964 April 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 completed. - . Nation: USA. The formal Combined Systems Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 was satisfactorily completed in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Three preliminary CSATs (April 17-20) had been completed and all anomalies resolved. . Additional Details: here....
1964 April 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The vehicle acceptance team (VAT) for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 convened at Martin-Baltimore. - . Nation: USA. The vehicle acceptance team (VAT) for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 convened at Martin-Baltimore. The VAT inspection was completed May 1 with GLV-2 found acceptable.. Additional Details: here....
1964 May 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle model static and dynamic loads test. - .
Nation: USA.
Langley Research Center completed tests on a model of the Gemini launch vehicle to determine the static and dynamic loads imposed on the vehicle and the launch vehicle erector by ground winds. Simulated wind velocities of 5 to 52 miles per hour did not produce loads great enough to be of concern. Tests had begun on April 15.
1964 May 11-12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan 3 crews inspect crew station mock-up - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Primary and backup crews for Gemini-Titan 3 inspected a spacecraft No.3 crew station mock-up at McDonnell. They found all major aspects of the crew station acceptable. A few items remained to be corrected but would not affect the launch schedule..
1964 May 16 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- Phase out plan for Atlas and Titan I ICBM's. - . The Defense Department tentatively established phase out of the Atlas E and Titan I missiles during the third and fourth quarters of FY1965 (January-June 1965) and that of the Atlas F in FY1968..
1964 June 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Three firms received authorization to begin work on space station studies. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: MOL.
Secretary of the Air Force Eugene M. Zuckert announced that three firms, Douglas Aircraft Company, General Electric Company, and The Martin Company, had received authorization to begin work on space station studies. Zuckert predicted also that the Titan III would be test-flown that summer and would launch the Manned Orbiting Laboratory sometime in 1967 or 1968.
1964 June 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch abort training - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Group 1 (selected April 1959) and Group 2 (September 1962) astronauts averaged approximately 100 runs each whereas Group 3 (October 1963) astronauts completed 32 runs apiece. The Gemini-Titan 3 launch profile was simulated in detail, including such cues as noise, vibration, pitch and roll programming, and other motion cues which results from various launch anomalies. The training was completed July 30.
1964 June 10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contract with Martin for 15 Gemini launch vehicles (GLV) converted. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division's cost-plus-fixed-fee contract with Martin for 15 Gemini launch vehicles (GLV) and associated aerospace ground equipment was replaced by a cost-plus-incentive-fee contract. Contract negotiations had been conducted between March 15 and April 30, 1964. The final contract contained cost, performance, and schedule incentives. Target cost was $111 million and target fee was $8.88 million. The maximum fee possible under the contract was $16.65 million as against a minimum of $3.33 million. The period of performance under the contract was July 1, 1963, through December 31, 1967, and covered the delivery of 14 GLVs (one GLV had already been delivered) and associated equipment and services, including checkout and launch.
1964 June 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Three basic plans were under study for Gemini rendezvous missions. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Christopher C. Kraft, Jr., Assistant Director for Flight Operations, Manned Spacecraft Center, reported that three basic plans were under study for rendezvous missions. Rendezvous at first apogee would probably be rejected because of possible dispersions which might necessitate plane changes. Rendezvous from concentric orbits seemed to be desirable because of the freedom in selection of the geographic position of rendezvous. Major work thus far, however, had been expended on the tangential rendezvous. Subsequently, the concentric orbit plan was chosen for Gemini-Titan 6, the first rendezvous mission.
1964 June 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Contract with Aerojet-General for engines and related aerospace ground equipment revised. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division's cost-plus-fixed-fee contract with Aerojet-General for engines and related aerospace ground equipment for the Gemini launch vehicle was replaced by a cost-plus-incentive-fee contract. Contract negotiations had been conducted between May 25 and June 17, 1964. The final contract covered the procurement of 14 sets of engines (one set had already been delivered) and associated equipment during the period from July 1, 1963, through December 31, 1967. Cost, performance, and schedule incentives made possible a maximum fee of $5,885,250 versus a minimum fee of $1,177,050. The initial target cost was $39,235,000 with a target fee of $3,138,800.
1964 June 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Stage I of Gemini launch vehicle 3 was erected in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Stage II was erected June 22. Power was first applied June 29, and subsystems functional verification testing concluded July 31..
1964 June 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 5 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Martin-Baltimore received the propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 5 from Martin-Denver, which had begun fabrication in October 1963. Aerojet-General delivered the flight engines for GLV-5 November 5. Tank splicing was completed December 5; engine installation December 9. Final horizontal tests were completed January 7, 1965.
1964 June 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- First of 17 flight test versions of the Titan III standard space launch vehicles accepted. - .
Space Systems Division accepted the first of the programmed 17 flight test versions of the Air Force Titan III standard space launch vehicles from the Martin Marietta Corporation. This vehicle was the first of five Titan IIIA (SLV-5A) missiles that would test the center core section before the two strap-on solid-rocket motors were added to form the first Titan IIIC booster vehicle.
1964 July 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IDCSP satellites as secondary payloads on Titan IIIC research and development launches. - .
Spacecraft: IDCSP.
Discussions between the Titan III System Program Office (SPO) and the Initial Defense Communications Satellite Program (IDCSP) SPO were initiated to investigate the possibility of using IDCSP satellites as secondary payloads on Titan IIIC research and development launches.
1964 Jul - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB, Titan IIID.
- Titan IIIX space booster definition - .
Space Systems Division began definition phase efforts for a new member of the Titan III family - the Titan IIIX space booster. The new vehicle would be two stages, Stage I with the man-rated components of the Titan Gemini Launch Vehicle and Stage II similar to that being used on the Titan III. The Titan IIIX would use radio rather then inertial guidance.
1964 July 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini spacecraft 2 began the second phase of Spacecraft Systems Tests. - .
Nation: USA.
Following the successful mating of its modules, Gemini spacecraft No. 2 began the second phase of Spacecraft Systems Tests (SST) at McDonnell. SST continued through September. During August and September, test operations alternated with the receipt and installation of a number of flight items in the spacecraft. Additional Details: here....
1964 July 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III contract lauded as one of the best managed. - .
Related Persons: ,
McNamara.
Secretary of Defense Robert S. McNamara reported to President Lyndon B. Johnson that Space Systems Division's Titan III contract with Martin Marietta was one of the best managed contracts in the DoD. This was said to be due to the incentives applied to the program. At present, McNamara reported that the Titan III program was one percent below cost estimates and savings were being accomplished without harm to defense posture.
1964 July 10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Plans for Gemini-Titan (GT) missions 4 through 7. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 4, Gemini 5, Gemini 6. Spacecraft: Gemini, Gemini Fuel Cell, Gemini REP. Manager Charles W. Mathews reported that the Gemini Program Office had been reviewing and evaluating plans for Gemini-Titan (GT) missions 4 through 7. GT-4 would be a four-day mission using battery power. . Additional Details: here....
1964 July 11 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 2 arrived at Eastern Test Range. - . Nation: USA. Stage I was erected at complex 19 on July 13, stage II on July 14. Electrical power was applied to the vehicle on July 20 in preparation for Subsystems Functional Verification Tests, which began July 21..
1964 July 11 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III Transtage engine was static fired - . The Titan III Transtage engine was successfully static fired for over six minutes. This test firing verified its various subsystems..
1964 July 10-25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Tests conducted on fuel cells planned for Gemini-Titan 5 mission. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Fuel Cell.
Gemini Program Office reported that tests had been conducted on section I of the fuel cells planned for the long-duration Gemini-Titan 5 mission. These tests had resulted in a failure characterized by output decay. A complete investigation was in process to determine the cause of the failure.
1964 July 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- McDivitt and White II named for the Gemini-Titan 4 mission. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Astronauts James A. McDivitt and Edward H. White II were named as command pilot and pilot, respectively, for the Gemini-Titan (GT) 4 mission scheduled for the first quarter of 1965. The backup crew for the mission would be Frank Borman, command pilot, and James A. Lovell, Jr., pilot. Additional Details: here....
1964 July 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini missions beyond the 12 originally planned considered. - .
Nation: USA.
In response to a request from NASA Headquarters, Gemini Program Office (GPO) provided a study for Gemini missions beyond the 12 originally planned. 'The Advanced Gemini Missions Conceptual Study' described 16 further missions, including a space station experiment, a satellite chaser mission, a lifeboat rescue mission, and both a circumlunar and lunar orbiting mission. On February 28, 1965, GPO reported that a preliminary proposal for Gemini follow-on missions to test the land landing system had not been approved. Spare Gemini launch vehicles 13, 14, and 15 were canceled, and there were no current plans for Gemini missions beyond the approved 12-flight program.
1964 July 30 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Cobra Skin - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). A SAC crew launched the first Titan II (LGM-25C) on a successful Demonstration and Shakedown Operation (DASO) test flight from Vandenberg AFB. DASO missions were intended to test launch techniques. Demonstration and shakedown operations launch.
1964 Aug - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- Study of the Titan IIIX/Agena - . Martin Marietta Corporation of Denver, Colorado, initiated a study of the Titan IIIX/Agena system..
1964 August 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan I completed the operational updating program. - . The six Titan I (HGM-25A) squadrons completed the operational updating program..
1964 August 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 3 - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. The formal Combined Systems Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 3 was successfully performed. The vehicle acceptance team (VAT) met August 17 to review CSAT and other test and manufacturing data. . Additional Details: here....
1964 August 11 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Double Talley - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Demonstration and shakedown operations launch.
1964 August 13 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gentle Annie - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Demonstration and shakedown operations launch.
1964 August 16 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 6 in assembly - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 6. Spacecraft: Gemini. Martin-Baltimore received the propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle 6 from Martin-Denver, which had begun fabricating them in April. After being inspected, the tanks were placed in storage where they remained until December 18..
1964 August 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Interrupted testing of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2. - . Nation: USA. A severe electrical storm in the vicinity of complex 19 interrupted testing of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2. Several observers reported a lightning strike at or near complex 19. . Additional Details: here....
1964 August 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Hurricane Cleo struck the Cape Kennedy area. - .
Nation: USA.
Stage II of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 was deerected and stored; the erector was lowered to horizontal, and stage I was lashed in its vertical position. Stage II was reerected September 1. Power was applied to the launch vehicle September 2, and Subsystem Functional Verification Tests (SSFVT) began September 3. When forecasts indicated that Hurricane Dora would strike Cape Kennedy, both stages of GLV-2 were deerected on September 8 and secured in the Missile Assembly Building. Hurricane Ethel subsequently threatened the area, and both stages remained in the hanger until September 14, when they were returned to complex 19 and reerected. SSFVT, begun again on September 18, ended successfully October 5.
1964 September 1 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIA. FAILURE: Transtage pressurization failure caused premature shutdown.. Failed Stage: U.
- Titan 3A Transtage 1 - .
Payload: Transtage 2. Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Decay Date: 1964-09-02 .
The 6555th Aerospace Test Wing launched the first Titan IIIA space booster (Vehicle #2) from the Eastern Test Range. Essentially the liquid-propellant core section of the Titan IIIC, the Titan IIIA performed satisfactorily except for a transtage (Stage 3) malfunction. After the first two stages had performed flawlessly, a premature shutdown of the transtage engine resulted from the failure of an onboard helium pressure valve and prevented the 3,750-pound dummy test payload from being injected into orbit.
1964 September 4 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 to be flown as scheduled - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD), supported by launch vehicle contractors, recommended that Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2 be flown as scheduled. Manned Spacecraft Center had proposed dropping GLV-2 from the Gemini program because of possible ill effects resulting from the electromagnetic incident of August 17 and from Hurricane Cleo. GLV-3 would then be substituted for the second Gemini mission, and the program would be shortened by one flight. After reviewing the incidents, their effects, corrective action, and retesting, SSD, Martin, Aerospace, and Aerojet-General all felt GLV-2 should fly, and NASA accepted their recommendation.
1964 September 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Final mating of Gemini spacecraft No. 3 modules began at McDonnell. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Mating operations were completed September 27. . Additional Details: here....
1964 September 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Spacecraft No. 2 arrived at Cape Kennedy - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft Bus: Gemini.
Spacecraft No. 2 arrived at Cape Kennedy and was installed in the Cryogenic Building of the Merritt Island Launch Area Fluid Test Complex. There it was inspected and connected to aerospace ground equipment (AGE), and hypergolic and cryogenic servicing was performed. Additional Details: here....
1964 September 29 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Power sources for Gemini-Titan (GT) 5 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4,
Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Fuel Cell.
Fuel cells and batteries were discussed as power sources for the Gemini-Titan (GT) 5 mission (long-duration) at a meeting of the Gemini Management Panel. A study was reviewed that proposed a combination to be used in the following manner: batteries would be used during peak load requirements; the fuel cell would supply the remaining mission power source requirements. The panal accepted the proposal, and McDonnell was directed to proceed with the plan. In addition, the group decided to remove the fuel cell from GT-4 and substitute batteries, pending the concurrence of NASA Headquarters. It also decided to fly older versions of the fuel cell in GT-2 (the redesigned version would be flown in the later manned flights) to gain flight experience with the component. Additional Details: here....
1964 September 29 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- New Gemini flight schedule resulting from the lightning strike and hurricane conditions. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3,
Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Gemini Program Manager Charles W. Mathews presented the Gemini Management Panel with the new flight schedule resulting from the lightning strike and hurricane conditions. The schedule was as follows: Gemini-Titan (GT) 2, November 17; GT-3, January 30, 1965; and GT-4, April 12. For GT-4 through GT-7, three-month launch intervals were planned; for the remainder of the program, these intervals would be reduced to two and one half months.
1964 September 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Engineering responsibility for Titan II transferred - . Engineering responsibility for the Titan II weapon system (WS 107C) program was transferred from Ballistic Systems Division to AFLC's San Bernardino Air Materiel Area (SBAMA) at Norton AFB, California.
1964 October 2 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Black Widow - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Demonstration and shakedown operations launch.
1964 October 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Combined Systems Test (CST) of Gemini launch vehicle 2 - .
Nation: USA.
The Prespacecraft Mate Combined Systems Test (CST) of Gemini launch vehicle 2 was completed at complex 19. This test, similar to CST performed at the Martin plant, comprised an abbreviated countdown and simulation of flight events, with a simulator representing electrical characteristics of the spacecraft; its purpose was to establish confidence in the launch vehicle. Electrical Electronic Interference Tests were completed October 12. Hurricane Isbell threatened the area on October 14-15, but its path was far enough south of the Cape to make deerection unnecessary, though testing was curtailed.
1964 October 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 3 review - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The vehicle acceptance team for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 3 met for the second time to review test and manufacturing data at Martin-Baltimore. The meeting concluded on October 9 with the vehicle found acceptable and Martin was authorized to remove it from the vertical test cell. After final checks, weighing, and balancing, GLV-3 passed roll-out inspection on October 27 and was turned over to the Air Force. Air Force Space Systems Division formally accepted GLV-3, following a review of launch vehicle status and correction of discrepancy items.
1964 October 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan (GT) 3 crew completed egress practice - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3,
Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Parachute.
Flight Crew Support Division reported that the Gemini-Titan (GT) 3 primary crew had completed egress practice in boilerplate No. 201 in the Ellington Air Force Base flotation tank. The backup GT-4 crew was scheduled for such training on October 23. Full-scale egress and recovery training for both the GT-3 and the GT-4 crews was scheduled to begin about January 15, when parachute refresher courses would also be scheduled.
1964 October 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Phase II of IDCSP - .
Spacecraft: IDCSP.
Headquarters USAF and AFSC directed the go-ahead for Phase II of the Initial Defense Communications Satellite Program (IDCSP) with a funding ceiling of $30 million after 14 September 1964. This action approved the launch of three IDCSP payloads on Titan IIIC research and development vehicles that were to be launched in the first half of 1966.
1964 October 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 4 was erected in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 4. Spacecraft: Gemini. Power was applied to the vehicle for the first time on November 4. Subsystems Functional Verification Tests were completed November 19..
1964 October 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Launch Vehicle for the first manned Gemini spaceflight mission turned over to the Air Force, - . Spacecraft: Gemini. The Titan II Gemini Launch Vehicle (GLV-3) for the first manned Gemini spaceflight mission (GT-3) was turned over to the Air Force at Martin Marietta's Baltimore, Maryland, plant..
1964 November 4 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- High Rider - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). The fifth, and final, Titan II demonstration and shakedown operation (DASO) launch was conducted by the SAC crew from Vandenberg. Demonstration and shakedown operations launch.
1964 November 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III solid-propellant rocket motor static test fired. - .
A 250-ton, 120-inch diameter, solid-propellant rocket motor was static test fired for 110 seconds as part of the Air Force's Titan III standard launch vehicle research and development program. Two of the 120-inch motors were to be attached to a Titan II liquid-propellant core vehicle to form the Titan IIIC space booster (SLV-5C). This test firing was important because it was the first test of the booster's flight instrumentation and the newly designed ablative nozzle-throat that replaced the former carbon throat.
1964 November 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 2 and spacecraft No. 2 were electrically mated at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. The Joint Combined Systems Test was run the following day. . Additional Details: here....
1964 November 19 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- Atlas E,F, and Titan I ICBMs to be retired from the active operational inventory. - .
Related Persons: ,
McNamara.
Secretary of Defense Robert S. McNamara officially announced his decision to retire Atlas E,F, and Titan I ICBM weapon systems from the active operational inventory. They were said to be no longer supportable from requirements, cost, or manpower use standpoints. Moreover, the relative slow-reacting, liquid-fueled Atlas and Titan I missiles had provided the initial deterrent that was necessary and would now be replaced by the less vulnerable, more easily maintained Minuteman and Titan II ICBMs.
1964 November 24 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan 2 completed the Wet Mock Simulated Launch. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Gemini-Titan (GT) 2 successfully completed the Wet Mock Simulated Launch, a full-scale countdown exercise which included propellant loading. Procedures for flight crew suiting and spacecraft ingress were practiced during simulated launch.. Additional Details: here....
1964 November 24 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 3 was scheduled to be shipped from Martin-Baltimore to Cape Kennedy. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Shipment was delayed, however, because GLV-2 had not yet been launched; and several modifications, scheduled for the Cape, were made at Baltimore instead. All work was completed by January 14, 1965; the vehicle was reinspected and was again available for delivery. Preparations for shipment were completed January 20, and stage II was airlifted to Cape Kennedy January 21, followed by stage I January 23.
1964 November 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The Combined Systems Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 4 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The vehicle acceptance team inspected the vehicle and reviewed all test and manufacturing data December 11-13 and authorized Martin to remove GLV-4 from the vertical test cell. During the next three months, while awaiting shipment to Cape Kennedy, GLV-4 had 27 engineering changes installed. Final integrity checks, weighing, and balancing were completed March 8, 1965.
1964 November 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- McDivitt and White began crew training - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Astronauts James McDivitt and Edward White, command pilot and pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 mission, began crew training on Gemini mission simulator No. 2 in Houston. The initial week of training was devoted to familiarizing the crew with the interior of the spacecraft.
1964 December 8 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A1. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- ST West Wind I operational test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1964 December 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Mission Control Center at Houston used passively in the Gemini-Titan 2 launch attempt. - .
Nation: USA.
The Mission Control Center at Houston was used passively and in parallel with the Mission Control Center at the Cape in the Gemini-Titan 2 launch attempt, primarily to validate the computer launch programs. In addition, considerable use was made of the telemetry processing program and related television display formats. The Houston control center received, processed, and displayed live and simulated Gemini launch vehicle and spacecraft data. Test results were considered very successful.
1964 December 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan (GT) 2 launch attempt. - .
Nation: USA.
Gemini-Titan (GT) 2 launch countdown began at 4:00 a.m., e.s.t., and proceeded normally, with minor holds, until about one second after engine ignition. At that point a shutdown signal from the master operations control set (MOCS) terminated the launch attempt. Loss of hydraulic pressure in the primary guidance and control system of stage I of the launch vehicle caused an automatic switchover to the secondary guidance and control system. During the 3.2-second holddown following ignition command, switchover was instrumented as a shutdown command. Accordingly, the MOCS killed the launch attempt. Subsequent investigation disclosed that loss of hydraulic pressure had been caused by failure of the primary servo-valve in one of the four tandem actuators which control movement of the stage I thrust chambers. All four stage I tandem actuators were replaced with redesigned actuators.
1964 December 10 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIA.
- Titan 3A Transtage 2 - . Payload: Transtage 1. Mass: 4,077 kg (8,988 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Decay Date: 1964-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 949 . COSPAR: 1964-081A. Apogee: 180 km (110 mi). Perigee: 166 km (103 mi). Inclination: 32.10 deg. Period: 88.00 min. The second Titan 1IIA (Vehicle #1) military space booster was launched from Cape Canaveral and achieved a completely successful test flight. Launch vehicle test. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1964 December 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The Gemini Phase II centrifuge training program was completed. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3,
Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Phase II provided refresher training for Gemini-Titan 3 and 4 flight crews, who made their runs clad in pressure suits. For astronauts not yet officially assigned to a mission the program provided familiarization training under shirt-sleeve conditions. Phase II had begun early in November.
1964 December 18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin-Baltimore removed the propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 from storage. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Cleaning the tanks and purging them with nitrogen was completed February 5, 1965. Aerojet-General delivered the flight engines for GLV-6 February 1. Tank splicing was completed February 23, engine installation, February 25. GLV-6 horizontal testing was completed April 3.
1964 December 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan I ICBM to be retired from the operational inventory by 30 June 1965. - .
Headquarters USAF directed that the Titan I ICBMs be retired from the operational inventory by 30 June 1965. There were then six Titan I Strategic Missile Squadrons of nine missile launchers each. Headquarters USAF directed that the Titan I ICBMs be retired from the operational inventory by 30 June 1965. There were then six Titan I Strategic Missile Squadrons of nine missile launchers each.
1964 December 22 - . Launch Site: Edwards. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Development of Titan III solid-rocket motor completed - .
United Technology Center (UTC) successfully fired its 120-inch diameter, one million-pound thrust, solid-propellant rocket motor at Edwards AFB. This was the fourth static test firing of the motor within two months, and it completed the development phase of the Titan III solid-rocket motor (SRM) program.
1964 December 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- Titan IIIB approved - .
A memo from the Office of the Secretary of Defense to the Secretary of the Air Force, Eugene M. Zuckert, approved the Titan IIIX program and requisite lengthening of Titan III research and development. The Titan IIIX was essentially the Titan IIIA's first and second stages plus an adapter section that would allow the vehicle to be used with the Agena D upper stage.
1965 Jan - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- Titan III upgrades to be studied. - .
Space Systems Division initiated Phase I studies with Martin Marietta Corporation, Thiokol, and United Technology Center (UTC) to determine what performance increment could be gained by strapping existing solid rocket motor segments to the Titan IIIX core vehicle. Minuteman first stages were to be considered along with two and three segments of the 120-inch diameter United Technology Center motors. The Titan IIIX/Strap-on configuration definition and acquisition phases were to be greatly compressed, with first launches from Vandenberg AFB expected in 1967. The Titan IIIX/Strap-on was subsequently designated Titan IIID.
1965 January 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acquisition phase of the Titan II program completed. - . The acquisition phase of the Titan II program was completed, and the Ballistic Systems Division Titan System Program Office was discontinued as of 31 December 1964..
1960 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3BAS2.
- Titan 3B proposed for deep space missions with Centaur upper stage. - . Nation: USA. Configuration of Titan 3B proposed by Martin in mid-1960's. Titan 3B for deep space missions with Centaur upper stage, Algol strapons for liftoff thrust augmentation. Never flown..
1965 January 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Revised Gemini-Titan (GT) 3 flight plan to cover the possibility of retrorocket failure. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3,
Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
NASA Headquarters provided Flight Operations Division with preliminary data for revising the Gemini-Titan (GT) 3 flight plan to cover the possibility of retrorocket failure. The problem was to ensure the safe reentry of the astronauts even should it become impossible to fire the retrorockets effectively. The Headquarters proposal incorporated three orbit attitude and maneuver system maneuvers to establish a fail-safe orbit from which the spacecraft would reenter the atmosphere whether the retrorockets fired or not. This proposal, as refined by Mission Planning and Analysis Division, became part of the flight plans for GT-3 and GT-4.
1965 January 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Redesigned stage I tandem actuators were received and installed in Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 2. - .
Nation: USA.
Although some retesting began shortly after the Gemini-Titan 2 mission was scrubbed on December 9, 1964, most activity in preparing GLV-2 for another launch attempt was curtailed until the new actuators arrived. Subsystems retesting then began. The final combined systems test - the Simulated Flight Test - was completed January 14, with launch scheduled for January 19.
1965 January 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- Titan IIIB/Agena D approved. - .
A Headquarters USAF program management directive (PMD) approved the acquisition program for the Titan IIIX/Agena D (Program 624B), subsequently redesignated Titan IIIB/Agena D. This newest addition to the Titan III series of boosters would consist of the Titan IIIA first and second stages, an adapter section, and an Agena D third stage - everything up to the Agena interface being the Titan IIIX launch vehicle. Contracts were later awarded for 24 Titan IIIX vehicles, with first launch planned for the summer of 1966.
1965 January 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan II Facilities Update. - .
A $9.5 million contract was awarded to Peter Kiewit Sons Company for Project Yard Fence, Titan II Facilities Update. The project was to utilize improved technology of minimize maintenance activities and to improve Titan II support equipment of the squadrons at Davis-Monthan, Little Rock, McConnell, and Vandenberg.
1965 January 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Flight tests of the zero-gravity mock-up of the Gemini spacecraft began. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The mock-up was installed in a KC-135 aircraft to provide astronauts with the opportunity to practice extravehicular activities under weightless conditions. The Gemini-Titan (GT) 3 flight crew participated in the opening exercises, which were duplicated the next day by the GT-4 flight crew.
1965 January 13 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- By June 1965, 150 more ICBM sites would be inactivated. - .
The Defense Department announced that by the end of FY1965 (June 1965), 150 more ICBM sites would be inactivated and the Atlas E, F, and Titan I missiles removed and placed in storage. The missiles werer stored at San Bernardino Air Materiel Area (SBAMA) facilities at Norton AFB, California. The retired missiles would be replaced by more advanced Minuteman missiles whose annual combat-ready costs were $100,000 per missile compared to nearly $1.0 million for each of the older, more complicated liquid-fueled ICBMs.. In addition, manpower savings would be substantial since only 12 men were required for support of each Minuteman versus approximately 80 for each Atlas or Titan.
1965 January 14 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Interval between Gemini flights reduced from three to two months. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
A task force in the Office of Manned Space Flight finished a two-month study to determine the requirements for reducing the interval between Gemini flights from three to two months. The findings and recommendations were presented to George E. Mueller, NASA Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight, on January 19. Additional Details: here....
1965 January 14 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A3. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- ST West Wind III operational test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1965 January 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Built-in holds in the GLV/Gemini countdown. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft Bus: Mercury & Gemini Spacecraft Systems Development Diaries. Spacecraft: Gemini Fuel Cell. The study of 325 missile countdowns, 205 missile launches, as well as all Titan scrubs and holds, indicated that GLV launching would be considerably improved and a great many scrubs precluded by the addition of such holds..
1965 January 19 - . 14:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 2 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Apogee: 169 km (105 mi).
The second Titan II Gemini Launch Vehicle (GLV-2) carried the unmanned, instrumented Gemini spacecraft (GT-2) for a suborbital shot preliminary to the first U.S. two-man Gemini mission. During the countdown for Gemini-Titan (GT) 2, the fuel cell hydrogen inlet valve failed to open. Efforts to correct the problem continued until it was determined that freeing the valve would delay the countdown. Work on the fuel cell ceased, and it was not activated for the flight. The fuel cell installed in spacecraft No. 2 was not a current flight design. When fuel cell design was changed in January 1964, several cells of earlier design were available. Although these cells were known to have some defects, flight testing with the reactant supply system was felt to be extremely desirable. Accordingly, it was decided to fly the entire system on GT-2, but only on a "non-interference with flight" basis. When it became clear that correcting the problem that emerged during the GT-2 countdown would cause delay, fuel cell activation for the flight was called off.
1965 January 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini 1 - .
Nation: Russia.
Kamanin observes that Gemini 1 was sent with mannequins on a suborbital trajectory, splashing down 3400 km from Cape Canaveral after 20 minutes of flight. He cannot believe this trajectory was intentional; the Soviets only fly mannequins aboard flights with the same duration as the planned manned mission. Kamanin believes this represents the third failure of the Titan 2 booster. Meanwhile, Soviet capability in centrifuges, is improving, albeit slowly. A centrifuge with a 16-m arm is to be completed by 1970, and one of 7 M in 1966.
1965 January 22 - . Launch Site: Beale AFB. Launch Complex: Beale AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Beale AFB - . Nation: USA. Last Titan I ICBM taken off alert status at Beale AFB..
1965 January 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 3 was erected at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Power was applied January 29 and Subsystems Functional Verification Tests (SSFVT) commenced. SSFVT were finished February 12. The Combined Systems Test before spacecraft mating was conducted February 15-16..
1965 January 29 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Qualification testing for Gemini-Titan 3 - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Qualification testing of the food, water, and waste management systems for the Gemini-Titan 3 mission was completed. .
1965 February 1 - . Launch Site: Ellsworth AFB. Launch Complex: Ellsworth AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Ellsworth AFB - . Nation: USA. Last Titan I ICBM taken off alert status at Ellsworth AFB.
1965 Feb - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- Contract for the Titan IIIX/Agena program. - . Space Systems Division received contract go-ahead for the Titan IIIX/Agena program..
1965 February 2 - . Launch Site: Larson AFB. Launch Complex: Larson AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Larson AFB - . Nation: USA. Last Titan I ICBM taken off alert status at Larson AFB.
1965 February 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Modifications to Gemini launch vehicle 5 completed - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Modifications to Gemini launch vehicle 5 were completed and stage I was erected in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Stage II was erected February 8. Power was applied to the vehicle for the first time on February 15, and Subsystems Functional Verification Tests were completed March 8. Another modification period followed.
1965 February 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini spacecraft No. 3 in position atop Gemini launch vehicle 3. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Gemini spacecraft No. 3 was moved to complex 19 and hoisted into position atop Gemini launch vehicle 3. Test operations began February 9 with premate systems tests, which lasted until February 13. . Additional Details: here....
1965 February 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Cooper and Conrad named as crew for the seven-day Gemini-Titan 5 mission. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 5. Spacecraft: Gemini. Manned Spacecraft Center announced the selection of L. Gordon Cooper, Jr., as command pilot and Charles Conrad, Jr., as pilot for the seven-day Gemini-Titan 5 mission. Backup crew would be Neil A. Armstrong and Elliot M. See, Jr..
1965 February 11 - . 15:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIA.
- LES 1 - .
Mass: 31 kg (68 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES.
USAF Sat Cat: 1002 . COSPAR: 1965-008C. Apogee: 2,809 km (1,745 mi). Perigee: 2,783 km (1,729 mi). Inclination: 32.10 deg. Period: 145.80 min.
Titan IIIA, Vehicle #3, was launched from Cape Canaveral. In a maneuverability test involving three separate orbits, the Transtage and two satellites were successfully placed into their programmed orbits. The primary objective of the mission was the triple ignition of the Transtage engine that was required for the three separate orbits. When it placed the Lincoln Experimental Satellite (LES-1) into orbit, the vehicle became the first Titan III to inject an operational payload into orbit. Lincoln Experimental Satellite; communications experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1965 February 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan (GT) 3 mission might be flown between March 22 and 25, 1965. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Kraft.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Director of Flight Operations Christopher C. Kraft, Jr., told the Manned Spacecraft Center senior staff that the Gemini-Titan (GT) 3 mission might be flown between March 22 and 25, although it was officially scheduled for the second quarter of 1965. In addition, the Houston control center was being considered for use in the GT-4 mission.
1965 February 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 3 and spacecraft No. 3 were mechanically mated on complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation Test was completed February 19, the Joint Guidance and Control Test on February 22. Gemini-Titan 3 combined systems testing included the Joint Combined Systems Test on February 24 and the Flight Configuration Mode Test on March 3.
1965 February 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan 3 crew egress training. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: Grissom, Young. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. During the week, the Gemini-Titan 3 prime crew participated in egress training from static article No. 5 in the Gulf of Mexico. A. Additional Details: here....
1965 February 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin-Denver delivered propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 7 to Martin-Baltimore. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 7.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Tank fabrication had begun in May 1964. Martin-Baltimore recleaned and purged the tanks with nitrogen by April 20, 1965. In the meantime, flight engines for GLV-7 arrived from Aerojet-General on April 17. Tank splicing was completed May 6 and engine installation May 20. All horizontal testing was completed June 14. A modification period followed.
1965 February 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Rehearsal of the flight crew countdown for Gemini-Titan 3 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
A full-scale rehearsal of the flight crew countdown for Gemini-Titan 3 was conducted at the launch site. Procedures were carried out for moving the flight crew from their quarters in the Manned Spacecraft Center operations building at Merritt Island to the pilot's ready room at complex 16 at Cape Kennedy. Complete flight crew suiting operation in the ready room, the transfer to complex 19, and crew ingress into the spacecraft were practiced. Practice countdown proceeded smoothly and indicated that equipment and procedures were flight ready.
1965 March 1-2 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini certified for manned space flight - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Office of Manned Space Flight held the Gemini manned space flight design certification review in Washington. Chief executives of all major Gemini contractors certified the readiness of their products for manned space flight. Gemini-Titan 3 was ready for launch as soon as the planned test and checkout procedures at Cape Kennedy were completed.
1965 March 5 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-A2. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- ST West Wind II operational test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). SAC launched the 20th, and the last, Titan I (HGM-25A) ICBM from Vandenberg as Nike target missile in support of Army requirements. Last launch of a Titan I from Vandenberg AFB (first launch on 3 May 1961)..
1965 March 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The Wet Mock Simulated Launch of Gemini-Titan 3 was successfully conducted. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 3. Spacecraft: Gemini. Countdown exercises were concluded on March 18 with the Simulated Flight Test..
1965 March 10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Roll-out inspection of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 4 - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 4. Spacecraft: Gemini. Air Force Space Systems Division formally accepted delivery of the vehicle March 21, and preparations to ship it to Cape Kennedy began at once. GLV-4 stage I arrived at the Cape March 22, followed the next day by stage II..
1965 March 23 - . 14:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 3 - .
Call Sign: Molly Brown (from Broadway play 'The Unsinkable..'. Crew: Grissom,
Young.
Backup Crew: Schirra,
Stafford.
Payload: Gemini SC3. Mass: 3,225 kg (7,109 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 3.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 0.20 days. Decay Date: 1965-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 1301 . COSPAR: 1965-024A. Apogee: 240 km (140 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 33.00 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
First manned test flight of Gemini. Virgil I. Grissom and John W. Young entered an elliptical orbit about the earth. After three orbits, the pair manually landed their spacecraft in the Atlantic Ocean, thus performing the first controlled reentry. Unfortunately, they landed much farther from the landing zone than anticipated, about 97 km (60 miles) from the aircraft carrier U.S.S. Intrepid. But otherwise the mission was highly successful. Gemini III, America's first two-manned space mission, also was the first manned vehicle that was maneuverable. Grissom used the vehicle's maneuvering rockets to effect orbital and plane changes. Grissom wanted to name the spacecraft 'Molly Brown' (as in the Unsinkable, a Debbie Reynolds/Howard Keel screen musical). NASA was not amused and stopped allowing the astronauts to name their spacecraft (until forced to when having two spacecraft aloft at once during the Apollo missions). The flight by Young was the first of an astronaut outside of the original seven. Young, who created a media flap by taking a corned beef sandwich aboard as a prank, would go on to fly to the moon on Apollo and the Space Shuttle on its first flight sixteen years later.
1965 March 25 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- Atlas and Titan I ICBMs to be retired - .
These were: two Atlas E units, the 566th Strategic Missile Squadron (SMS) at Warren and the 548th SMS at Forbes AFB, Kansas; three Atlas F squadrons, the 577th SMS at Altus, the 578th SMS at Dyess, and the 579th SMS at Walker; and three Titan I squadrons, the 851st SMS at Beale, the 850th SMS at Ellsworth, and the 568th SMS at Larson AFB, Washington.
1965 March 25 - . 02:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Arctic Sun operational test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). The first Titan II operational test (OT) missile was launched from Vandenberg. The Titan II operational test launch program was scheduled to use 25 Titan missiles through August 1966..
1965 March 26 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. Launch Complex: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . Nation: USA. Last Titan I ICBM taken off alert status at Lowry AFB.
1965 March 29 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Full EVA considered for Gemini 4. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Gilruth,
Low, George,
Mueller,
Seamans.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft Bus: Gemini space suits.
Spacecraft: G4C,
Gemini.
The possibility of doing more than the previously planned stand-up form of extravehicular activity (EVA) was introduced at an informal meeting in the office of Director Robert R. Gilruth at Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Present at the meeting, in addition to Gilruth and Deputy Director George M. Low, were Richard S. Johnston of Crew Systems Division (CSD) and Warren J. North of Flight Crew Operations Division. Johnston presented a mock-up of an EVA chestpack, as well as a prototype hand-held maneuvering unit. North expressed his division's confidence that an umbilical EVA could be successfully achieved on the Gemini-Titan 4 mission. Receiving a go-ahead from Gilruth, CSD briefed George E. Mueller, Associate Administrator for Mannned Space Flight, on April 3 in Washington. He, in turn, briefed the Headquarters Directorates. The relevant MSC divisions were given tentative approval to continue the preparations and training required for the operation. Associate Administrator of NASA, Robert C. Seamans, Jr., visited MSC for further briefing on May 14. The enthusiasm he carried back to Washington regarding flight-readiness soon prompted final Headquarters approval.
1965 March 29 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 4 was erected at complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
After the vehicle had been inspected, umbilicals were connected March 31 and power applied April 2. Subsystems Functional Verification Tests began immediately and were completed April 15. The Prespacecraft Mate Combined Systems Test was conducted the next day (April 16).
Spring 1966 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan I missiles scrapped. - . Nation: USA. Titan I missiles in storage at Mira Loma Air Force Station, Riverside County, California, are scrapped..
1965 April 1 - . Launch Site: Mountain Home AFB. Launch Complex: Mountain Home AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Last Titan I ICBM off alert status - . Nation: USA. Last Titan I ICBM taken off alert status at Mountain Home AFB.
1965 April 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Schirra and Stafford selected for Gemini-Titan 6. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Grissom,
Schirra,
Stafford,
Young.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Manned Spacecraft Center announced that Walter M. Schirra, Jr., and Thomas P. Stafford had been selected as command pilot and pilot for Gemini-Titan 6, the first Gemini rendezvous and docking mission. Virgil I. Grissom and John W. Young would be the backup crew.
1965 April 14-15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 was erected in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 6. Spacecraft: Gemini. GLV-6 was the first vehicle in the new west test cell, which Martin had finished installing and checking out in January. . Additional Details: here....
1965 April 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Martin-Denver delivered the propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle 8 to Martin-Baltimore. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Tank fabrication had begun September 25, 1964. Aerojet-General delivered the stage I engine on June 16 and the stage II on August 20. In the meantime, tank splicing was completed August 3. Engine installation was completed September 23, and all hoizontal testing ended September 27.
1965 April 15 - . Launch Site: Lowry AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Lowry AFB - . The last Titan I (HGM-25A) was removed from its silo at Lowry AFB, Colorado, in preparation for the 724th Strategic Missile Squadron's inactivation on 25 June..
1965 April 16 - . 19:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 April 18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- All Titan I missiles in storage - . Nation: USA. By this date all Titan I missiles had been shipped to storage at Mira Loma Air Force Station, Riverside County, California..
1965 April 21 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 5 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Combined Systems Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 5 was conducted in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Four earlier CSAT attempts (April 15-20) were marred by numerous minor anomalies. The vehicle acceptance team inspection began April 26 and concluded April 30, with GLV-5 found acceptable. The vehicle was removed from the test cell May 7-8, formally accepted by the Air Force May 15, and shipped to Cape Kennedy. Stage I arrived at the Cape on May 17 and stage II on May 19.
1965 April 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Abort criteria for Gemini-Titan (GT) 4 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4,
Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Abort Panel met to review abort criteria for Gemini-Titan (GT) 4 and decided that GT-3 rules would suffice. Alternate procedures for delayed mode 2 abort would be investigated when the Manned Spacecraft Center abort trainer became available to the GT-5 mission.
1965 April 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 4 and spacecraft No. 4 were mechanically mated at complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test were completed April 26-29. These had been separate tests for earlier vehicles, but from Gemini-Titan 4 on, the tests were combined and performed as one. The spacecraft/GLV Joint Combined Systems Test followed on April 30. The Flight Configuration Mode Test finished systems testing May 7.
1965 April 30 - . 19:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 May 6 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC20. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIA.
- LES 2 - .
Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES.
USAF Sat Cat: 1360 . COSPAR: 1965-034B. Apogee: 14,810 km (9,200 mi). Perigee: 2,771 km (1,721 mi). Inclination: 32.20 deg. Period: 309.90 min.
The fourth Titan IIIA flight test missile (Vehicle #6) was launched from Complex 20 at Cape Canaveral in a maneuverability test for the Transtage. The primary aim was for the Transtage engine to accomplish four separate ignitions, something never before attempted. In the process of successfully completing its four programmed ignitions and burns, the Transtage placed two satellites into orbit - a Lincoln Experimental Satellite (LES-2) and a hollow aluminum radar calibration sphere (LCS-1). By completing its assigned tasks, the Transtage extended the capabilities of the Titan IIIA beyond it's specific requirements. Because of this highly productive mission, the planned fifth Titan IIIA (Vehicle 7/4) launch was cancelled and the booster was converted to a Titan IIIC configuration. Experimental commsat. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- LCS 1 - .
Mass: 34 kg (74 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: LCS.
USAF Sat Cat: 1361 . COSPAR: 1965-034C. Apogee: 2,795 km (1,736 mi). Perigee: 2,786 km (1,731 mi). Inclination: 32.10 deg. Period: 145.60 min.
The fourth Titan IIIA flight test missile (Vehicle #6) was launched from Complex 20 at Cape Canaveral in a maneuverability test for the Transtage. The primary aim was for the Transtage engine to accomplish four separate ignitions, something never before attempted. In the process of successfully completing its four programmed ignitions and burns, the Transtage placed two satellites into orbit - a Lincoln Experimental Satellite (LES-2) and a hollow aluminum radar calibration sphere (LCS-1). By completing its assigned tasks, the Transtage extended the capabilities of the Titan IIIA beyond it's specific requirements. Because of this highly productive mission, the planned fifth Titan IIIA (Vehicle 7/4) launch was cancelled and the booster was converted to a Titan IIIC configuration. Aluminum sphere used for radar calibration. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1965 May 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The Wet Mock Simulated Launch (WMSL) of Gemini-Titan (GT) 4 was completed. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 4. Spacecraft: Gemini. The spacecraft was then demated from the launch vehicle in order to replace the batteries in the spacecraft adapter; flight seats were also installed and crew stowage evaluated. . Additional Details: here....
1965 May 21 - . 23:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 June 3 - . 15:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 4 - .
Call Sign: American Eagle / Little Eva. Crew: McDivitt,
White.
Backup Crew: Borman,
Lovell.
Payload: Gemini SC4. Mass: 3,574 kg (7,879 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 4.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 4.08 days. Decay Date: 1965-06-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 1390 . COSPAR: 1965-043A. Apogee: 281 km (174 mi). Perigee: 162 km (100 mi). Inclination: 32.50 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
The second manned and first long-duration mission in the Gemini program. Major objectives of the four-day mission were demonstrating and evaluating the performance of spacecraft systems in a long-duration flight and evaluating effects on the crew of prolonged exposure to the space environment. Secondary objectives included demonstrating extravehicular activity (EVA) in space, conducting stationkeeping and rendezvous maneuvers with the second stage of the launch vehicle, performing significant in-plane and out-of-plane maneuvers, demonstrating the ability of the orbit attitude and maneuver system (OAMS) to back up the retrorockets, and executing 11 experiments. The stationkeeping exercise was terminated at the end of the first revolution because most of the OAMS propellant allocated for the exercise had been used; further efforts would jeopardize primary mission objectives and could mean the cancellation of several secondary objectives. No rendezvous was attempted. The only other major problem to mar the mission was the inadvertent alteration of the computer memory during the 48th revolution in an attempt to correct an apparent malfunction. This made the planned computer-controlled reentry impossible and required an open-loop ballistic reentry. All other mission objectives were met. The flight crew began preparing for EVA immediately after terminating the stationkeeping exercise. Although preparations went smoothly, McDivitt decided to delay EVA for one revolution, both because of the high level of activity required and because deletion of the rendezvous attempt reduced the tightness of the schedule. Ground control approved the decision. The spacecraft hatch was opened at 4 hours 18 minutes into the flight and White exited 12 minutes later, using a hand-held maneuvering gun. White reentered the spacecraft 20 minutes after leaving it. The hatch was closed at 4 hours 54 minutes ground elapsed time. Drifting flight was maintained for the next two and one-half days to conserve propellant. The spacecraft landed in the Atlantic Ocean about 725 km east of Cape Kennedy - some 65 km from its nominal landing point. The crew boarded a helicopter 34 minutes after landing and was transported to the prime recovery ship, the aircraft carrier Wasp. Spacecraft recovery was completed at 2:28 p.m., a little more than 100 hours after Gemini 4 had been launched. Gemini 4 was the first mission to be controlled from the mission control center in Houston.
The space walk was hurriedly included after the Russian first in Voskhod 2. White seemed to have a lot more fun than Leonov and McDivitt took the pictures that came to symbolize man in space. With this flight the US finally started to match Russian flight durations.
1965 June 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 5 was erected at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 5. Spacecraft: Gemini. The vehicle was inspected and umbilicals connected June 9. . Additional Details: here....
1965 June 14 - . 13:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 June 18 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan 3C Transtage 5 - .
Payload: Lead Ballast / Transtage 5. Mass: 9,694 kg (21,371 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Decay Date: 1965-06-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 1412 . COSPAR: 1965-047A. Apogee: 191 km (118 mi). Perigee: 168 km (104 mi). Inclination: 32.10 deg. Period: 88.10 min.
The first Titan IIIC (SLV-5C) research and development vehicle (Vehicle #7) was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral. The Titan IIIC, the first Air Force vehicle specifically designed and developed as a military space booster under Space Systems Division management, was the first heavy-duty booster to combine the thrust of large-size, strap-on solid rocket motors with a three-stage, liquid-powered rocket. The Titan IIIC weighed more than 1.4 million pounds fully fueled but without its payload. At takeoff, the two United Technology Center solid rocket motors (SRMs) generated a peak thrust of 2,647,000 pounds - making the Titan IIIC the most powerful rocket yet launched. When the two solid motors were jettisoned two minutes after lift-off, the liquid-fueled center core section took over-Stage 1 engines producing 520,000 pounds of thrust, then Stage 2 with 100,000 pounds, and finally Stage 3 (Transtage) with its 16,000-pound thrust engines and carrying the payload. This first Titan IIIC placed a 21,000-pound test payload into a 100-NM (low earth) circular orbit - the heaviest payload yet orbited by the U.S. The Titan IIIC was capable of placing a 3,200-pound payload into a 22,000-mile, synchronous equatorial orbit. When fully operational, the new booster would provide a vast increase in the size and range of satellites that could be placed in orbit. This capability would eliminate one of the primary limitations on a number of satellite programs - the limited payload capability of the present Thor and Atlas space booster families. Launch vehicle test. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1965 June 25 - . Launch Site: Mountain Home AFB. LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- The remaining seven Atlas and Titan I squadrons assigned to SAC were inactivated. - .
These included the last Atlas E squadron, the 567th Strategic Missile Squadron (SMS) at Fairchild; three Atlas F units at Schilling (550th SMS), Lincoln (551st SMS), and Plattsburgh (556th SMS); and three Titan I squadrons, and the 569th SMS at Mountain Home along with the two units at Lowry, the 724th and 725th SMSs. These actions concluded the phase out of all Atlas and Titan I ICBMs in the SAC operational inventory.
1965 June 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 7 in test - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 7.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Stage I of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 7 was erected in the east cell of the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Stage II was erected June 28. GLV-7 was inspected and prepared for testing while GLV-6 was undergoing vertical tests in the west cell. Power was applied to GLV-7 for the first time July 26. Subsystems Functional Verification Tests were completed August 25. Systems modification and retesting followed.
1965 June 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Combined Systems Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 was completed at Martin-Baltimore. The vehicle acceptance team convened July 6 to review GLV-6 and accepted it July 10. The vehicle was demated on July 19 and formally accepted by the Air Force July 31. Stage II was delivered to Cape Kennedy the same day, and stage I on August 2. Both stages were then placed in storage pending the launch of Gemini-Titan 5.
1965 June 30 - . 14:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 July 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 5 and spacecraft No. 5 were mechanically mated at complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test began immediately and was completed July 9. The spacecraft/GLV Joint Combined Systems Test followed on July 12. The Flight Configuration Mode Test completed systems testing on July 16.
1965 July 21 - . 18:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 July 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini-Titan 5 demated. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Gemini-Titan (GT) 5 was demated following completion of the Wet Mock Simulated Launch to allow the spacecraft fuel cells to be replaced and the coolant bypass to be modified. Spacecraft and launch vehicle were remated August 5. Modified Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and the Joint Guidance and Control Tests were run on August 6. Spacecraft Final Systems Test on August 9-10 and the Simulated Flight Test on August 13 completed prelaunch testing of GT-5, scheduled for launch August 19.
1965 July 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Circumlunar flight using Gemini seriously studied - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Webb.
Program: Apollo.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
During a news conference, Kenneth S. Kleinknecht, Deputy Manager of the Gemini Project Office at MSC, affirmed that, although no firm decisions had yet been made, the concept of a circumlunar flight using a Gemini spacecraft was being seriously studied. The mission would use Titan II and III-C launch vehicles and would require rendezvousing in earth orbit. NASA, Martin-Marietta Corporation (builder of the Titan), and Aerojet-General Corporation (which manufactured upper stages for the III-C) all were studying the feasibility of such a flight. Later in the year, NASA Administrator James E. Webb eliminated the possibility of a Gemini circumlunar mission, ". . . our main reliance for operating at lunar distances . . . is the large Saturn V/Apollo system."
1965 August 9 - . Launch Site: Little Rock AFB. Launch Complex: Little Rock AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Accident at Titan 2 Silo 373-4, Little Rock AFB, kills 53. - .
Nation: USA.
A fire started in the silo during construction work. Two workers survived. The Titan 2 missile was fueled and in the silo but did not explode. The warhead had been removed from the site prior to the start of construction. The complex wass off alert status for the next 13 months during the accident investigation and repairs.
1965 August 16 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 9 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Martin-Baltimore received propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 9 from Martin-Denver, which had begun fabricating them February 25. These were the first GLV tanks to be carried by rail from Denver to Baltimore. All previous tanks had traveled by air, but shortage of suitable aircraft made the change necessary. The tanks were shipped August 9. Aerojet-General delivered the stage I engine for GLV-9 August 20 and the stage II engine September 22. Tank splicing was completed October 21, engine installation November 10. Horizontal testing concluded November 23.
1965 August 16 - . 20:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 August 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Launch of Gemini-Titan 5 scrubbed. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Inertial Guidance System.
A spacecraft computer malfunction caused a hold of the countdown 10 minutes before the scheduled launch of Gemini-Titan 5. While the problem was being investigated, thunderstorms approached the Cape Kennedy area. With the computer problem unresolved and the weather deteriorating rapidly, the mission was scrubbed and rescheduled for August 21. Recycling began with unloading propellants.
1965 August 21 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 5 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 5. Crew: Conrad,
Cooper.
Backup Crew: Armstrong,
See.
Payload: Gemini SC5/Rendezvous Evaluation Pod. Mass: 3,605 kg (7,947 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 5.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 7.96 days. Decay Date: 1965-08-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 1516 . COSPAR: 1965-068A. Apogee: 395 km (245 mi). Perigee: 304 km (188 mi). Inclination: 32.60 deg. Period: 91.50 min.
Major objectives of the eight-day mission were evaluating the performance of the rendezvous guidance and navigation system, using a rendezvous evaluation pod (REP), and evaluating the effects of prolonged exposure to the space environment on the flight crew. Secondary objectives included demonstrating controlled reentry guidance, evaluating fuel cell performance, demonstrating all phases of guidance and control system operation needed for a rendezvous mission, evaluating the capability of either pilot to maneuver the spacecraft in orbit to rendezvous, evaluating the performance of rendezvous radar, and executing 17 experiments. The mission proceeded without incident through the first two orbits and the ejection of the REP. About 36 minutes after beginning evaluation of the rendezvous guidance and navigation system, the crew noted that the pressure in the oxygen supply tank of the fuel cell system was falling. Pressure dropped from 850 pounds per square inch absolute (psia) at 26 minutes into the flight until it stabilized at 70 psia at 4 hours 22 minutes, and gradually increased through the remainder of the mission. The spacecraft was powered down and the REP exercise was abandoned. By the seventh revolution, experts on the ground had analyzed the problem and a powering-up procedure was started. During the remainder of the mission the flight plan was continuously scheduled in real time. Four rendezvous radar tests were conducted during the mission, the first in revolution 14 on the second day; the spacecraft rendezvous radar successfully tracked a transponder on the ground at Cape Kennedy. During the third day, a simulated Agena rendezvous was conducted at full electrical load. The simulation comprised four maneuvers - apogee adjust, phase adjust, plane change, and coelliptical maneuver - using the orbit attitude and maneuver system (OAMS). Main activities through the fourth day of the mission concerned operations and experiments. During the fifth day, OAMS operation became sluggish and thruster No. 7 inoperative. Thruster No. 8 went out the next day, and the rest of the system was gradually becoming more erratic. Limited experimental and operational activities continued through the remainder of the mission. Retrofire was initiated in the 121st revolution during the eighth day of the mission, one revolution early because of threatening weather in the planned recovery area. Reentry and landing were satisfactory, but the landing point was 145 km short, the result of incorrect navigation coordinates transmitted to the spacecraft computer from the ground network. Landing occurred August 29, 190 hours 55 minutes after the mission had begun. The astronauts arrived on board the prime recovery ship, the aircraft carrier Lake Champlain, at 9:25. The spacecraft was recovered at 11:51 a.m.
With this flight, the US finally took the manned spaceflight endurance record from Russia, while demonstrating that the crew could survive in zero gravity for the length of time required for a lunar mission. However the mission was incredibly boring, the spacecraft just drifting to conserve fuel most of the time, and was 'just about the hardest thing I've ever done' according to a hyperactive Pete Conrad. An accident with freeze dried shrimp resulted in the cabin being filled with little pink subsatellites.
1965 August 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIM.
- Development of Manned Orbiting Laboratory approved. - .
Spacecraft: MOL.
President Lyndon B. Johnson announced that he had approved the Defense Department plans for the development of a Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) that would cost $1. 5 billion. The Air Force was to continue its management of the MOL program. Douglas Aircraft Company was to design and build the spacecraft that would be boosted into orbit by the Titan IIIM version of the Titan IIIC space launch vehicle.
1965 August 25 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL to be launched from Canaveral and Vandenberg - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: Johnson, Lyndon. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: MOL. DoD revealed that newly-authorized Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) program (announced by President Lyndon Johnson the same day) would be launched from both the Air Force Eastern and Western Test Ranges..
1965 August 26 - . 00:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 August 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Stage I of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 was erected at complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Stage II was erected the following day. Umbilicals were connected and inspected September 1, and Subsystems Reverification Tests began September 2. These tests were completed September 15. The Prespacecraft Mate Verification Test of GLV-6 was run September 16.
1965 August 31 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan III.
- Bleymaier named Commander, Air Force Western Test Range. - .
Related Persons: Schriever.
General Bernard A. Schriever, Commander. AFSC, named Brigadier General Joseph S. Bleymaier as Commander, Air Force Western Test Range (AFWTR), with headquarters at Vandenberg AFB. General Bleymaier, former Titan III (Program 624A and 624B) program director and Deputy for Manned Systems AFSC, named Brigadier General Joseph S. Bleymaier as Commander, Air Force Western Test Range (AFWTR), with headquarters at Vandenberg AFB. General Bleymaier, former Titan III (Program 624A and 624B) program director and Deputy for Manned Systems
1965 September 16 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 10 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
During the rail trip, leaking battery acid corroded the dome of the stage II fuel tank. The tanks arrived at Martin-Baltimore September 21. The stage II fuel tank was rejected and returned to Denver. It was replaced by the stage II fuel tank from GLV-11, which completed final assembly September 25 and arrived in Baltimore November 3 after being inspected and certified. Fabrication of GLV-10 tanks had begun in April.
1965 September 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 and spacecraft No. 6 were mechanically mated at complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test was completed September 21. The spacecraft/GLV Joint Combined Systems Test was run September 23. GLV tanking test was performed September 29 and the Flight Configuration Mode Test October 1, completing systems testing for Gemini-Titan 6.
1965 September 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 7 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 7.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Combined Systems Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 7 was completed in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Inspection of GLV-7 by the vehicle acceptance team began September 27 and ended October 1, with the vehicle found acceptable. GLV-7 was deerected October 5 and formally accepted by the Air Force October 15. Stage I was airlifted to Cape Kennedy October 16, followed by stage II October 18. Both stages were placed in storage pending the launch of the Gemini VI mission.
1965 September 21 - . 14:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 September 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 8 in test - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 8 was erected in the west cell of the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Power was applied to the vehicle October 13, following the deerection of GLV-7. Subsystems Functional Verification Tests of GLV-8 were completed November 4.
1965 October 15 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC. FAILURE: Partial Failure..
- Transtage 4 - . Mass: 189 kg (416 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft: OV2. Decay Date: 1972-07-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 1624 . COSPAR: 1965-082xx. Apogee: 264 km (164 mi). Perigee: 229 km (142 mi). Inclination: 32.30 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
- OV2-01 - . Mass: 170 kg (370 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV2. Decay Date: 1972-07-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 1624 . COSPAR: 1965-082B. Apogee: 791 km (491 mi). Perigee: 708 km (439 mi). Inclination: 32.60 deg. Period: 99.80 min. Dual launch with LCS 2; upper stage broke up. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- LCS 2 - .
Payload: OV2-01 / Transtage 4. Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: LCS.
Decay Date: 1965-10-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 1624 . COSPAR: 1965-082A. Apogee: 785 km (487 mi). Perigee: 730 km (450 mi). Inclination: 32.30 deg. Period: 99.98 min.
The second Titan IIIC (Vehicle #4) was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral. This was the first Titan IIIC to carry an operational payload. Three satellites were placed in orbit - an LCS-2 radar calibration sphere, an OV 2-1 radiation sensor, and a metal-ballasted dummy payload. All systems performed well until the second planned burn of the Transtage engines just prior to the injection of the multiple payload into orbit. At this point in the mission, the Transtage exploded due to a malfunction, abruptly terminating the mission. Dual launch with OV2-1; upper stage broke up.
- LCS 2 - .
Mass: 189 kg (416 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Spacecraft: OV2.
COSPAR: 1965-082xx.
The second Titan IIIC (Vehicle #4) was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral. This was the first Titan IIIC to carry an operational payload. Three satellites were placed in orbit - an LCS-2 radar calibration sphere, an OV 2-1 radiation sensor, and a metal-ballasted dummy payload. All systems performed well until the second planned burn of the Transtage engines just prior to the injection of the multiple payload into orbit. At this point in the mission, the Transtage exploded due to a malfunction, abruptly terminating the mission.
1965 October 20 - . 18:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Power Box - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Operational missile test. Some lists give launch date as 10 October..
1965 October 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini 6 spacecraft and launch vehicle put in storage - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Gemini spacecraft No. 6 and the second stage of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 were deerected and removed from complex 19. GLV-6 stage I was deerected the next day. The GLV was placed in storage at the Satellite Checkout Building under guard, in an environment controlled for temperature and humidity. Bonded storage maintained the integrity of previously conducted tests to reduce testing that would have to be repeated. Spacecraft No. 6 was stored in the Pyrotechnics Installation Building at the Merritt Island Launch Area.
1965 October 29-30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 7 was erected at complex 19, following the deerection of GLV-6. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 7.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Power was applied to GLV-7 on October 31, and Subsystems Reverification Tests (SSRT) began immediately. SSRT ended November 9, and the Prespacecraft Mate Verification Test was performed November 10. This test now included dropping all umbilicals, eliminating the need for a Flight Configuration Mode Test (FCMT). No FCMT was performed on GLV-7 or any subsequent vehicle.
1965 November 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 11 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Martin-Baltimore received the propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 11 from Martin-Denver, which had began fabricating them June 28. They were shipped by rail October 27. The GLV-11 stage II fuel tank was used in GLV-10, and the stage II fuel tank from GLV-12 was reassigned to GLV-11, arriving by air from Martin-Denver January 16, 1966. Aerojet-General delivered the engines for GLV-11 on December 14, 1965. Stage I tank splicing and engine installation was complete by March 31, stage II by April 5. Stage I horizontal tests ended April 12 and stage II, April 25.
1965 November 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 8 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Combined Systems Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 8 was conducted at Martin-Baltimore. The vehicle acceptance team convened November 16 and completed its inspection November 19, deeming the vehicle excellent. GLV-8 was deerected December 13-14 and was formally accepted by the Air Force on December 23. Stage I was airlifted to Cape Kennedy on January 4, 1966, followed by stage II on January 6. Both stages were placed in storage.
1965 November 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 10 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The stage I engine had been delivered August 23. Martin-Baltimore completed splicing stage I January 12, 1966; stage II splicing, using the fuel tank reassigned from GLV-11, was finished February 2. Engine installation was completed February 7, and stage I horizontal tests February 11. Stage II horizontal testing ended March 2.
1965 November 27 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 November 30 - . 14:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1965 December 4 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 at complex 19 two hours after launch of Gemini VII. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6,
Gemini 7.
Spacecraft Bus: Gemini space suits.
Spacecraft: G5C,
Gemini.
Both stages of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 6 were removed from storage and arrived at complex 19 two hours after the launch of Gemini VII. Spacecraft No. 6 was returned to complex 19 on December 5. Within 24 hours after the launch of Gemini VII, both stages of GLV-6 were erected, spacecraft and launch vehicle were mated, and power was applied. Subsystems Reverification Tests were completed December 8. The only major problem was a malfunction of the spacecraft computer memory. The computer was replaced and checked out December 7-8. The Simulated Flight Test, December 8-9, completed prelaunch tests. The launch, initially scheduled for December 13, was rescheduled for December 12.
1965 December 4 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 7 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 7. Crew: Borman,
Lovell.
Backup Crew: Collins,
White.
Payload: Gemini SC7. Mass: 3,663 kg (8,075 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 6,
Gemini 7.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 13.77 days. Decay Date: 1965-12-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 1812 . COSPAR: 1965-100A. Apogee: 318 km (197 mi). Perigee: 217 km (134 mi). Inclination: 28.90 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
An Air Force Titan II Gemini Launch Vehicle lifted Gemini 7 (GT-7) into orbit from Cape Canaveral. Astronauts Frank Borman and James Lovell completed the 14-day mission, the longest U.S. space flight to date (330 hours, 35 minutes) and 206 revolutions, and were recovered on 18 December, 700 miles southwest of Bermuda. During their record flight, Borman and Lovell piloted GT-7 as the target vehicle for the first space rendezvous between manned spacecraft. Astronauts Walter Schirra and Thomas Stafford aboard Gemini 6 were launched on 15 December and completed the first space rendezvous with Gemini 7 the same day. Primary objectives of the mission were demonstrating manned orbital flight for approximately 14 days and evaluating the physiological effects of a long-duration flight on the crew. Among the secondary objectives were providing a rendezvous target for the Gemini VI-A spacecraft, stationkeeping with the second stage of the launch vehicle and with spacecraft No. 6, conducting 20 experiments, using lightweight pressure suits, and evaluating the spacecraft reentry guidance capability. All objectives were successfully achieved with the exception of two experiments lost because of equipment failure. Shortly after separation from the launch vehicle, the crew maneuvered the spacecraft to within 60 feet of the second stage and stationkept for about 15 minutes. The exercise was terminated by a separation maneuver, and the spacecraft was powered down in preparation for the 14-day mission. The crew performed five maneuvers during the course of the mission to increase orbital lifetime and place the spacecraft in proper orbit for rendezvous with spacecraft No. 6. Rendezvous was successfully accomplished during the 11th day in orbit, with spacecraft No. 7 serving as a passive target for spacecraft No. 6. About 45 hours into the mission, Lovell removed his pressure suit. He again donned his suit at 148 hours, while Borman removed his. Some 20 hours later Lovell again removed his suit, and both crewmen flew the remainder of the mission without suits, except for the rendezvous and reentry phases. With three exceptions, the spacecraft and its systems performed nominally throughout the entire mission. The delayed-time telemetry playback tape recorder malfunctioned about 201hours after liftoff, resulting in the loss of all delayed-time telemetry data for the remainder of the mission. Two fuel cell stacks showed excessive degradation late in the flight and were taken off the line; the remaining four stacks furnished adequate electrical power until reentry. Two attitude thrusters performed poorly after 283 hours in the mission. Retrofire occurred exactly on time, and reentry and landing were nominal. The spacecraft missed the planned landing point by only 10.3 km miles, touching down on December 18. The crew arrived at the prime recovery ship, the aircraft carrier Wasp, half an hour later. The spacecraft was recovered half an hour after the crew.
Far surpassing the Gemini 5 flight, Gemini 7 set a manned spaceflight endurance record that would endure for years. The incredibly boring mission, was made more uncomfortable by the extensive biosensors. This was somewhat offset by the soft spacesuits (used only once) and permission to spend most of the time in long johns. The monotony was broken just near the end by the rendezvous with Gemini 6.
1965 December 8-10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 9 in test - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Gemini launch vehicle 9 was erected in the east cell of the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. Power was applied to the launch vehicle for the first time on December 22, and Subsystems Functional Verification Tests were completed January 20, 1966.
1965 December 12 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini 6 launch aborted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6,
Gemini 7.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Titan 2 engines shut down a moment after ignition. The fault that caused the Titan to shut down saved the astronaut's lives; the quick thinking of the astronauts in not pulling the abort handles saved the mission. The scheduled launch of Gemini VI-A was aborted when the Master Operations Control Set automatically shut down the Gemini launch vehicle a second after engine ignition because an electrical umbilical connector separated prematurely. The launch was canceled at 9:54 a.m., e.s.t. Emergency procedures delayed raising the erector until 11:28, so the crew was not removed until 11:33 a.m. Launch was rescheduled for December 15. Routine analysis of the engine data, begun immediately after shutdown, revealed decaying thrust in one first stage engine subassembly before shutdown had been commanded. The problem was diagnosed as a restriction in the gas generator circuit of the subassembly, which would have caused shutdown about 1 second later than it actually occurred as a result of the umbilical disconnect. Source of the restriction proved to be a protective dust cap inadvertently left in place in the gas generator oxidizer injector inlet port. The anomalies were corrected and recycling, based on long-prepared contingency plans, proceeded without incident through launch on December 15.
1965 December 15 - . 13:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 6 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 6. Crew: Schirra,
Stafford.
Backup Crew: Grissom,
Young.
Payload: Gemini SC6. Mass: 3,546 kg (7,817 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 6,
Gemini 7.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 1.08 days. Decay Date: 1965-12-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 1839 . COSPAR: 1965-104A. Apogee: 271 km (168 mi). Perigee: 258 km (160 mi). Inclination: 28.90 deg. Period: 89.60 min.
The primary objective of the mission, crewed by command pilot Astronaut Walter M. Schirra, Jr., and pilot Astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, was to rendezvous with spacecraft No. 7. Among the secondary objectives were stationkeeping with spacecraft No. 7, evaluating spacecraft reentry guidance capability, testing the visibility of spacecraft No. 7 as a rendezvous target, and conducting three experiments. After the launch vehicle inserted the spacecraft into an 87 by 140 nautical mile orbit, the crew prepared for the maneuvers necessary to achieve rendezvous. Four maneuvers preceded the first radar contact between the two spacecraft. The first maneuver, a height adjustment, came an hour and a half after insertion, at first perigee; a phase adjustment at second apogee, a plane change, and another height adjustment at second perigee followed. The onboard radar was turned on 3 hours into the mission. The first radar lock-on indicated 246 miles between the two spacecraft. The coelliptic maneuver was performed at third apogee, 3 hours 47 minutes after launch. The terminal phase initiation maneuver was performed an hour and a half later. Two midcourse corrections preceded final braking maneuvers at 5 hours 50 minutes into the flight. Rendezvous was technically accomplished and stationkeeping began some 6 minutes later when the two spacecraft were about 120 feet apart and their relative motion had stopped. Stationkeeping maneuvers continued for three and a half orbits at distances from 1 to 300 feet. Spacecraft No. 6 then initiated a separation maneuver and withdrew to a range of about 30 miles. The only major malfunction in spacecraft No. 6 during the mission was the failure of the delayed-time telemetry tape recorder at 20 hours 55 minutes ground elapsed time, which resulted in the loss of all delayed-time telemetry data for the remainder of the mission, some 4 hours and 20 minutes. The flight ended with a nominal reentry and landing in the West Atlantic, just 10 km from the planned landing point, on December 16. The crew remained in the spacecraft, which was recovered an hour later by the prime recovery ship, the aircraft carrier Wasp.
Gemini 6 was to have been the first flight involving docking with an Agena target/propulsion stage. However the Agena blew up on the way to orbit, and the spacecraft was replaced by Gemini 7 in the launch order.
For lack of a target, NASA decided to have Gemini 6 rendezvous with Gemini 7. This would require a quick one week turnaround of the pad after launch, no problem with Russian equipment but a big accomplishment for the Americans. The first launch attempt was aborted; the Titan II ignited for a moment, then shut down and settled back down on its launch attachments. Schirra waited it out, did not pull the abort handles that would send the man catapulting out of the capsule on their notoriously unreliable ejection seats. The booster was safed; Schirra had saved the mission and the launch three days later went perfectly. The flight went on to achieve the first manned space rendezvous controlled entirely by the self-contained, on-board guidance, control, and navigation system. This system provided the crew of Gemini 6 with attitude, thrusting, and time information needed for them to control the spacecraft during the rendezvous. Under Schirra's typically precise command, the operation was so successful that the rendezvous was complete with fuel consumption only 5% above the planned value to reach 16 m separation from Gemini 7.
1965 December 21 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Transtage 8 - .
Mass: 189 kg (416 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Spacecraft: OV2.
Decay Date: 1975-08-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 1863 . COSPAR: 1965-108A. Apogee: 22,114 km (13,740 mi). Perigee: 337 km (209 mi). Inclination: 26.90 deg. Period: 387.40 min.
For the first time, Launch Complex 41, at the just completed Integrate-Launch-Transfer (ITL) complex at Cape Canaveral was used to launch the third Titan IIIC research and development space booster (Vehicle #8). As with the second vehicle, this Titan IIIC performed flawlessly throughout the liftoff and boost segments of the flight plan. However, severe difficulties were encountered when the Transtage engines malfunctioned and did not restart for the programmed third burn. Thus, the vehicle failed to reach near-synchronous equatorial orbit with its four-satellite payload. Lincoln Experimental Satellites LES-3 and LES-4 were released as was Oscar IV, but the OV2-3 payload remained attached to the Transtage.
- OV2-03 - . Mass: 193 kg (425 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV2. Decay Date: 1975-08-17 . COSPAR: 1965-108xx. Apogee: 22,846 km (14,195 mi). Perigee: 321 km (199 mi). Inclination: 26.80 deg. Period: 399.30 min. Upper stage separation failed. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- LES 4 - . Mass: 52 kg (114 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES. Decay Date: 1977-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 1870 . COSPAR: 1965-108B. Apogee: 33,632 km (20,897 mi). Perigee: 189 km (117 mi). Inclination: 26.60 deg. Period: 589.20 min. Lincoln Experimental Satellite; experimental commsat; transmitted in X-band. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- LES 3 - . Mass: 16 kg (35 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES. Decay Date: 1968-04-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 1941 . COSPAR: 1965-108D. Apogee: 4,829 km (3,000 mi). Perigee: 267 km (165 mi). Inclination: 26.50 deg. Period: 139.90 min. Radio signal source for commsat tests. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Oscar 4 - .
Mass: 13 kg (28 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: OSCAR.
Program: Oscar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Amateur radio communications satellite. Spacecraft: Oscar.
Decay Date: 1976-04-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 1902 . COSPAR: 1965-108C. Apogee: 33,549 km (20,846 mi). Perigee: 162 km (100 mi). Inclination: 26.80 deg. Period: 587.50 min.
OSCAR IV was launched piggyback with three United States Air Force satellites. The launch vehicle had a partial failure and placed the spacecraft in a low orbit preventing widespread amateur use. Orbit 29120 x 168 km. Inclination 26.8 degrees. Period 587.5 minutes. Weight 18.1 kg. Four monopole antennas. OSCAR IV was built by the TRW Radio Club of Redondo Beach, California. It had a 3 Watt 10 kHz wide linear transponder (144 MHz uplink and 432 MHz downlink). In operation until March 16, 1966. Re-entry April 12, 1976. Total operation 85 days. OSCAR IV provided the first US-Soviet amateur link.
1965 December 22 - . 14:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1966 January 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 8 was erected at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 8. Spacecraft: Gemini. After the vehicle was inspected and umbilicals connected, power was applied January 19. Subsystems Reverification Tests began the following day and lasted until January 31. . Additional Details: here....
1966 January 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- First Titan IIIB completed - . The first Titan IIIB configuration vehicle was completed by the Denver Division of the Martin Marietta Corporation..
1966 January 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 12 in assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 11,
Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Martin-Denver delivered propellant tanks for Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 12 to Martin-Baltimore by air. The GLV-12 stage II fuel tank had been reallocated to GLV-11, and GLV-12 used the stage II fuel tank originally assigned to GLV-10, which had been reworked to eliminate the damaged dome that had caused the tank reshuffling. Additional Details: here....
1966 February 3 - . 11:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1966 February 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 9 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Combined Systems Acceptance Test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 9 was successfully conducted in the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. The vehicle acceptance team convened February 14 and concluded its review on February 17 by accepting the vehicle. Deerection of GLV-9 was completed February 25, and the vehicle was formally accepted by the Air Force March 8. Stage I arrived at Cape Kennedy on March 9, stage II on March 10.
1966 February 10 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 8 and spacecraft 8 were electrically mated. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 8. Spacecraft: Gemini. The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test was completed February 14. After data from this test were reviewed (February 15), the Joint Combined Systems Test was run February 16..
1966 February 17 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The tanking test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 8 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
While the launch vehicle was being cleaned up after the test, spacecraft No. 8 Final Systems Test was completed February 23. On February 25, GLV and spacecraft were temporarily mated for an erector-cycling test. The extravehicular support package and life support system were checked out and installed in the spacecraft between February 26 and March 5, while GLV systems were modified and revalidated February 28 to March 3.
1966 February 17 - . 09:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1966 February 28 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 10 tests - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Stage I of Gemini launch vehicle 10 was erected in the east cell of the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. After completing horizontal testing March 3, stage II was erected March 7. Power was applied to the vehicle for the first time on March 14. Subsystems Functional Verification Tests were completed April 13.
1966 March 12 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Start of construction (site preparation) for SLC-6 - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: MOL. Start of construction (site preparation) for Space Launch Complex 6 facilities at former Sudden Ranch property..
1966 March 16 - . 16:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 8 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 8. Crew: Armstrong,
Scott.
Backup Crew: Conrad,
Gordon.
Payload: Gemini SC8. Mass: 3,788 kg (8,351 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 0.45 days. Decay Date: 1966-03-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 2105 . COSPAR: 1966-020A. Apogee: 264 km (164 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 28.90 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
The Atlas-Agena target vehicle for the Gemini VIII mission was successfully launched from KSC Launch Complex 14 at 10 a.m. EST March 16. The Gemini VIII spacecraft followed from Launch Complex 19 at 11:41 a.m., with command pilot Neil A. Armstrong and pilot David R. Scott aboard. The spacecraft and its target vehicle rendezvoused and docked, with docking confirmed 6 hours 33 minutes after the spacecraft was launched. This first successful docking with an Agena target vehicle was followed by a major space emergency. About 27 minutes later the spacecraft-Agena combination encountered unexpected roll and yaw motion. A stuck thruster on Gemini put the docked assembly into a wild high speed gyration. Near structural limits and blackout, Armstrong undocked, figuring the problem was in the Agena, which only made it worse. The problem arose again and when the yaw and roll rates became too high the crew shut the main Gemini reaction control system down and activated and used both rings of the reentry control system to reduce the spacecraft rates to zero. This used 75% of that system's fuel. Although the crew wanted to press on with the mission and Scott's planned space walk, ground control ordered an emergency splashdown in the western Pacific during the seventh revolution. The spacecraft landed at 10:23 p.m. EST March 16 and Armstrong and Scott were picked up by the destroyer U.S.S. Mason at 1:37 a.m. EST March 17. Although the flight was cut short by the incident, one of the primary objectives - rendezvous and docking (the first rendezvous of two spacecraft in orbital flight) - was accomplished.
Primary objectives of the scheduled three-day mission were to rendezvous and dock with the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) and to conduct extravehicular activities. Secondary objectives included rendezvous and docking during the fourth revolution, performing docked maneuvers using the GATV primary propulsion system, executing 10 experiments, conducting docking practice, performing a rerendezvous, evaluating the auxiliary tape memory unit, demonstrating controlled reentry, and parking the GATV in a 220-nautical mile circular orbit. The GATV was inserted into a nominal 161-nautical mile circular orbit, the spacecraft into a nominal 86 by 147-nautical mile elliptical orbit. During the six hours following insertion, the spacecraft completed nine maneuvers to rendezvous with the GATV. Rendezvous phase ended at 5 hours 58 minutes ground elapsed time, with the spacecraft 150 feet from the GATV and no relative motion between the two vehicles. Stationkeeping maneuvers preceded docking, which was accomplished at 6 hours 33 minutes ground elapsed time. A major problem developed 27 minutes after docking, when a spacecraft orbit attitude and maneuver system (OAMS) thruster malfunctioned. The crew undocked from the GATV and managed to bring the spacecraft under control by deactivating the OAMS and using the reentry control system (RCS) to reduce the spacecraft's rapid rotation. Premature use of the RCS, however, required the mission to be terminated early. The retrofire sequence was initiated in the seventh revolution, followed by nominal reentry and landing in a secondary recovery area in the western Pacific Ocean. The spacecraft touched down less than 10 km from the planned landing point. The recovery ship, the destroyer Leonard Mason, picked up both crew and spacecraft some three hours later. Early termination of the mission precluded achieving all mission objectives, but one primary objective - rendezvous and docking - was accomplished. Several secondary objectives were also achieved: rendezvous and docking during the fourth revolution, evaluating the auxiliary tape memory unit, demonstrating controlled reentry, and parking the GATV. Two experiments were partially performed.
1966 March 24 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 9 was removed from storage and erected at complex 19. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The vehicle was inspected and umbilicals connected by March 28. Power was applied March 29, and the Subsystems Reverification Test (SSRT) began March 30. SSRT concluded April 11. The Prespacecraft Mate Verification Combined Systems Test was completed April 12.
1966 March 25 - . 09:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1966 April 5 - . 16:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-D. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1966 April 13 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test began. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test began after Gemini launch vehicle 9 and spacecraft No. 9 were electrically mated. These activities were completed April 15. The Joint Combined Systems Test was run April 19.
1966 April 14 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 10 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The Combined Systems Acceptance Test (CSAT) of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 10 was conducted at Martin-Baltimore. The CSAT was followed by a performance data review, completed April 19. The vehicle acceptance team convened April 26 and accepted GLV-10 on April 29. The vehicle was deerected May 2-4 and formally accepted by the Air Force May 18. Stage I was flown to Cape Kennedy the same day, with stage II following May 20. Both stages were transferred to Hanger L where they were purged and pressurized with dry nitrogen and placed in controlled access storage.
1966 April 18 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 11 tests - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Stage I of Gemini launch vehicle 11 was erected in the west cell of the vertical test facility at Martin-Baltimore. After completing horizontal tests April 25, stage II was erected April 29. Power was applied to the vehicle for the first time on May 9, and Subsystems Functional Verification Tests were completed June 8.
1966 April 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The tanking test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 9 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
While the GLV was undergoing post-tanking cleanup, the spacecraft computer and extravehicular systems were retested (April 21-22), pyrotechnics were installed in the spacecraft (April 25), spacecraft final systems tests were run (April 27-28), spacecraft crew stowage was reviewed (April 29), and the astronaut maneuvering unit was reverified (April 30-May 2). Additional Details: here....
1966 April 20 - . 08:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Long Light operational test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). A SAC crew launched the 19th, and final, Titan II Operational Test (OT) missile (#62-12298) from Vandenberg. .
1966 May 24 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Silver Bullett Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). The first Titan II Follow-On Operational Test (FOT) missile to be launched from Vandenberg was a failure..
1966 June 3 - . 13:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 9 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 9. Crew: Cernan,
Stafford.
Backup Crew: Aldrin,
Lovell.
Payload: Gemini SC9. Mass: 3,668 kg (8,086 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 3.01 days. Decay Date: 1966-06-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 2191 . COSPAR: 1966-047A. Apogee: 272 km (169 mi). Perigee: 269 km (167 mi). Inclination: 28.80 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
At the first launch attempt, while the crew waited buttoned up in the spacecraft on the pad, their Agena docking target field blew up on the way to orbit. NASA decided to use an Atlas to launch an Agena docking collar only. This was called the Augmented Target Docking Adapter. Ths was successfully launched and the Gemini succeeded in rendezvousing with it. However, the ATDA shroud had not completely separated, thus making docking impossible. However three different types of rendezvous were tested with the ATDA. Cernan began his EVA, which was to include flight with a USAF MMU rocket pack but the Gemini suit could not handle heat load of the astronaut's exertions. Cernan's faceplate fogs up, forcing him to blindly grope back into the Gemini hatch after only two hours.
Seventh manned and third rendezvous mission of the Gemini program. Major objectives of the mission were to rendezvous and dock with the augmented target docking adapter (ATDA) and to conduct extravehicular activities (EVA). These objectives were only partially met. After successfully achieving rendezvous during the third revolution - a secondary objective - the crew discovered that the ATDA shroud had failed to separate, precluding docking - a primary objective - as well as docking practice - another secondary objective. The crew was able, however, to achieve other secondary objectives: an equi-period rendezvous, using onboard optical techniques and completed at 6 hours 36 minutes ground elapsed time; and a rendezvous from above, simulating the rendezvous of an Apollo command module with a lunar module in a lower orbit (completed at 21 hours 42 minutes ground elapsed time). Final separation maneuver was performed at 22 hours 59 minutes after liftoff. EVA was postponed because of crew fatigue, and the second day was given over to experiments. The hatch was opened for EVA at 49 hours 23 minutes ground elapsed time. EVA was successful, but one secondary objective - evaluation of the astronaut maneuvering unit (AMU) - was not achieved because Cernan's visor began fogging. The extravehicular life support system apparently became overloaded with moisture when Cernan had to work harder than anticipated to prepare the AMU for donning. Cernan reentered the spacecraft, and the hatch was closed at 51 hours 28 minutes into the flight. The rest of the third day was spent on experiments.
1966 June 7 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 10 was removed from storage and erected at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 10. Spacecraft: Gemini. Umbilicals were connected and power applied June 9. Subsystems Reverification Tests (SSRT) began immediately. SSRT ended June 16, and the Prespacecraft Mate Verification Combined Systems Test was conducted June 17..
1966 June 9 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The launch vehicle acceptance test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 11 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The vehicle acceptance team convened June 20 and accepted GLV-11 June 24. The vehicle was deerected June 29 and formally accepted by the Air Force on July 11. Stage I was delivered by air to Cape Kennedy the same day and stage II on July 13. Both stages were transferred to Hanger U where the tanks were purged and pressurized. The stages remained in controlled access storage until the launch pad was revalidated after the launch of Gemini X; revalidation was completed July 21.
1966 June 16 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- GGTS 1 - . Mass: 47 kg (103 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Gravity gradient technology satellite. Spacecraft: GGTS. USAF Sat Cat: 2207 . COSPAR: 1966-053A. Apogee: 33,858 km (21,038 mi). Perigee: 33,663 km (20,917 mi). Inclination: 4.20 deg. Period: 1,334.00 min. Gravity gradient stabilization tests. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- IDCSP 1-1 - .
Payload: IDCSP 1 / OPS 9311. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 2215 . COSPAR: 1966-053B. Apogee: 33,888 km (21,056 mi). Perigee: 33,656 km (20,912 mi). Inclination: 8.30 deg. Period: 1,334.40 min.
A Titan IIIC (Vehicle #11) successfully supported a record-setting mission by placing eight satellites into near-synchronous orbits 18,200 miles above the equator. Seven communication satellites and one gravity gradient experimental satellite were included in this first launch in a series designed to establish a ring of experimental communications satellites dispersed around the equator. When completed, this satellite system would provide the Defense Department with a global military communication system designated the Initial Defense Satellite Communication System (IDSCS). Each of the seven satellites could relay 600 voice or 6,000 teletype channels. Space Systems Division was responsible for the development and launch of the spaceborne elements of the IDSCS as well as the Titan IIIC booster and launch services. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- IDCSP 1-2 - . Payload: IDCSP 2 / OPS 9312. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2216 . COSPAR: 1966-053C. Apogee: 33,923 km (21,078 mi). Perigee: 33,657 km (20,913 mi). Inclination: 4.90 deg. Period: 1,335.30 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 1-3 - . Payload: IDCSP 3 / OPS 9313. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2217 . COSPAR: 1966-053D. Apogee: 33,955 km (21,098 mi). Perigee: 33,669 km (20,920 mi). Inclination: 8.30 deg. Period: 1,336.40 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 1-4 - . Payload: IDCSP 4 / OPS 9314. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2218 . COSPAR: 1966-053E. Apogee: 34,017 km (21,137 mi). Perigee: 33,694 km (20,936 mi). Inclination: 8.00 deg. Period: 1,338.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 1-5 - . Payload: IDCSP 5 / OPS 9315. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2219 . COSPAR: 1966-053F. Apogee: 34,093 km (21,184 mi). Perigee: 33,712 km (20,947 mi). Inclination: 8.90 deg. Period: 1,340.90 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 1-6 - . Payload: IDCSP 6 / OPS 9316. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2220 . COSPAR: 1966-053G. Apogee: 34,215 km (21,260 mi). Perigee: 33,707 km (20,944 mi). Inclination: 8.70 deg. Period: 1,343.90 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 1-7 - .
Payload: IDCSP 7 / OPS 9317. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 2221 . COSPAR: 1966-053H. Apogee: 34,359 km (21,349 mi). Perigee: 33,711 km (20,947 mi). Inclination: 5.00 deg. Period: 1,347.60 min.
A Titan IIIC (Vehicle #11) successfully supported a record-setting mission by placing eight satellites into near-synchronous orbits 18,200 miles above the equator. Seven communication satellites and one gravity gradient experimental satellite were included in this first launch in a series designed to establish a ring of experimental communications satellites dispersed around the equator. When completed, this satellite system would provide the Defense Department with a global military communication system designated the Initial Defense Satellite Communication System (IDSCS). Each of the seven satellites could relay 600 voice or 6,000 teletype channels. Space Systems Division was responsible for the development and launch of the spaceborne elements of the IDSCS as well as the Titan IIIC booster and launch services. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1966 June 20 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 10 and spacecraft No. 10 were electrically mated at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 10. Spacecraft: Gemini. The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test was conducted June 20-21. Following a data review, the Joint Combined Systems Test was run June 23..
1966 June 24 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The tanking test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 10 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
During the post-tanking cleanup and systems testing of the GLV, spacecraft No. 10 hypergolics were serviced (June 27-28), spacecraft Final Systems Tests were conducted (June 28-July 1), crew stowage was evaluated, and the extravehicular life support system was checked (July 1). Additional Details: here....
1966 June 29 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- Initial launch of a satellite by Titan IIIB/Agena - . Nation: USA. Nation's initial launch of a satellite by a Titan IIIB/Agena space booster (first launch of a Titan III from Vandenberg AFB)..
1966 July 18 - . 22:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 10 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 10. Crew: Collins,
Young.
Backup Crew: Bean,
Williams, Clifton.
Payload: Gemini SC10. Mass: 3,763 kg (8,295 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 2.95 days. Decay Date: 1966-07-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 2349 . COSPAR: 1966-066A. Apogee: 259 km (160 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 28.90 deg. Period: 88.70 min.
An Air Force Titan Gemini Launch Vehicle placed the Gemini 10 (GT-10) spacecraft into orbit for the three-day mission of Astronauts John Young and Michael Collins. Rendezvous and docking were accomplished with the Gemini Agena Target Vehicle (GATV) that had been launched from Cape Kennedy aboard an Atlas Booster just ahead of GT-10. Using the GATV-10 Primary Propulsion System (PPS), the docked vehicles achieved a manned-flight altitude record of 476 miles. Reentry was accomplished on 21 July and recovery was made 544 miles east of Cape Canaveral. Exciting mission with successful docking with Agena, flight up to parking orbit where Gemini 8 Agena is stored. Collins space walks from Gemini to Agena to retrieve micrometeorite package left in space all those months. Loses grip first time, and tumbles head over heels at end of umbilical around Gemini. Package retrieved on second try.
The Gemini X mission began with the launch of the Gemini Atlas-Agena target vehicle from complex 14. The Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) attained a near-circular, 162- by 157-nautical-mile orbit. Spacecraft No. 10 was inserted into a 145- by 86-nautical-mile elliptical orbit. Slant range between the two vehicles was very close to the nominal 1000 miles. Major objective of the mission was achieved during the fourth revolution when the spacecraft rendezvoused with the GATV at 5 hours 23 minutes ground elapsed time and docked with it about 30 minutes later. More spacecraft propellant was used to achieve rendezvous than had been predicted, imposing constraints on the remainder of the mission and requiring the development of an alternate flight plan. As a result, several experiments were not completed, and another secondary objective - docking practice - was not attempted. To conserve fuel and permit remaining objectives to be met, the spacecraft remained docked with the GATV for about 39 hours. During this period, a bending mode test was conducted to determine the dynamics of the docked vehicles, standup extravehicular activties (EVA) were conducted, and several experiments were performed. The GATV primary and secondary propulsion systems were used for six maneuvers to put the docked spacecraft into position for rendezvous with the Gemini VIII GATV as a passive target. The spacecraft undocked at 44 hours 40 minutes ground elapsed time, separated from the GATV, and used its own thrusters to complete the second rendezvous some three hours later. At 48 hours and 42 minutes into the flight, a 39-minute period of umbilical EVA began, which included the retrieval of a micrometorite collection package from the Gemini VIII Agena. The hatch was opened a third time about an hour later to jettison extraneous equipment before reentry. After about three hours of stationkeeping, the spacecraft separated from the GATV. At 51 hours 39 minutes ground elapsed time, the crew performed a true anomaly-adjust maneuver to minimize reentry dispersions resulting from the retrofire maneuver.
1966 July 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 11 was removed from storage and erected at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 11. Spacecraft: Gemini. After the vehicle was inspected and umbilicals connected, power was applied July 27, and Subsystems Reverification Tests (SSRT) began. SSRT ended August 4, and the Prespacecraft Mate Verification Combined Systems Test was run the following day..
1966 July 22 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Giant Train Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1966 July 29 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The launch vehicle acceptance test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 12 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The vehicle acceptance team convened August 9 and accepted the vehicle August 12. GLV-12 was deerected August 17 and formally accepted by the Air Force August 30. Stage I was airlifted to Cape Kennedy the same day. Stage II arrived September 3. Both stages were placed in controlled access storage in Hanger T pending the launch of Gemini XI and the revalidation of the launch pad, completed September 16.
1966 July 29 - . 18:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 3014 - .
Payload: KH-8 no. 01 (Gambit) / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO,
USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: KH-8.
Decay Date: 1966-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 2376 . COSPAR: 1966-069A. Apogee: 252 km (156 mi). Perigee: 154 km (95 mi). Inclination: 94.20 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
After the initial launch attempt oil the 28th was held at T minus 12 seconds, the first Titan IIIB/Agena D was successfully launched from Vandenberg AFB. All primary and secondary test objectives were met during the launch and flight which completed the research and development program for the Titan IIIB. This newest member of the Titan III (SLV-5) KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1966 August 8 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 11 and spacecraft No. 11 were electrically mated at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 11. Spacecraft: Gemini. Elecrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test was conducted August 8-9. The Joint Combined Systems Test followed August 11-12..
1966 August 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The tanking test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 11 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
While GLV post-tanking operations were being performed, the Final Systems Tests of spacecraft No. 11 were conducted August 22-23. Spacecraft and GLV were mechanically mated August 24 and erector cycling was tested. The electrical interface was revalidated August 25-29. The Simultaneous Launch Demonstration on August 31 and the Simulated Flight Test on September 1 completed prelaunch testing.
1966 August 26 - . 13:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC. FAILURE: Payload fairing broke up 78 seconds after launch.. Failed Stage: S.
- IDCSP (8) ... IDCSP (14) - . Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. Decay Date: 1966-08-26 . 8 satellites, each weighing 45 kg..
1966 September 12 - . 14:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 11 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 11. Crew: Conrad,
Gordon.
Backup Crew: Anders,
Armstrong.
Payload: Gemini SC11. Mass: 3,798 kg (8,373 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 2.97 days. Decay Date: 1966-09-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 2415 . COSPAR: 1966-081A. Apogee: 280 km (170 mi). Perigee: 161 km (100 mi). Inclination: 28.80 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
More highjinks with Conrad. First orbit docking with Agena, followed by boost up to record 800 km orbit, providing first manned views of earth as sphere. Tether attached by Gordon to Agena in spacewalk and after a lot of effort tethered spacecraft put into slow rotation, creating first artificial microgravity.
The primary objective of the Gemini XI mission was to rendezvous with the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) during the first revolution and dock. Five maneuvers completed the spacecraft/GATV rendezvous at 1 hour 25 minutes ground elapsed time, and the two vehicles docked nine minutes later. Secondary objectives included docking practice, extravehicular activity (EVA), 11 experiments, docked maneuvers, a tethered vehicle test, demonstrating automatic reentry, and parking the GATV. All objectives were achieved except one experiment - evaluation of the minimum reaction power tool - which was not performed because umbilical EVA was terminated prematurely. Umbilical EVA began at 24 hours 2 minutes ground elapsed time and ended 33 minutes later. Gordon became fatigued while attaching the tether from the GATV to the spacecraft docking bar. An hour later the hatch was opened to jettison equipment no longer required. At 40 hours 30 minutes after liftoff, the GATV primary propulsion system (PPS) was fired to raise the apogee of the docked vehicles to 741 nautical miles for two revolutions. The PPS was fired again, 3 hours 23 minutes later, to reduce apogee to 164 nautical miles. The crew then prepared for standup EVA, which began at 47 hours 7 minutes into the flight and lasted 2 hours 8 minutes. The spacecraft was then undocked to begin the tether evaluation. At 50 hours 13 minutes ground elapsed time, the crew initiated rotation. Initial oscillations damped out and the combination became very stable after about 20 minutes; the rotational rate was then increased. Again, initial oscillations gradually damped out and the combination stabilized. At about 53 hours into the mission, the crew released the tether, separated from the GATV, and maneuvered the spacecraft to an identical orbit with the target vehicle. A fuel cell stack failed at 54 hours 31 minutes, but the remaining five stacks shared the load and operated satisfactorily. A rerendezvous was accomplished at 66 hours 40 minutes ground elapsed time, and the crew then prepared for reentry.
1966 September 16 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Black River Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1966 September 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 12 was removed from storage and erected at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini. Umbilicals were connected after GLV inspection September 21. Power was applied the next day and Subsystems Reverification Tests (SSRT) began September 23. SSRT ended October 2 and Prespacecraft Mate Verification Combined Systems Test was run October 4..
1966 September 28 - . 19:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 4096 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 02 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1966-10-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 2433 . COSPAR: 1966-086A. Apogee: 287 km (178 mi). Perigee: 146 km (90 mi). Inclination: 93.90 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 October 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Gemini launch vehicle 12 and spacecraft No. 12 were electrically mated at complex 19. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini. The Electrical Interface Integrated Validation and Joint Guidance and Control Test was conducted October 5-6, and data was reviewed the following day. The Joint Combined Systems Test was run on October 10..
1966 October 11 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- The tanking test of Gemini launch vehicle (GLV) 12 was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
While the GLV was being cleaned up after the tanking test, the Final Systems Test of spacecraft No. 12 was conducted October 17-19. Spacecraft and GLV were mechanically mated October 25 and the erector was cycled. The spacecraft guidance system was retested October 26-27, and the spacecraft/GLV electrical interface was revalidated October 28. The Simultaneous Launch Demonstration on November 1 and the Simulated Flight Test on November 2 completed prelaunch testing and checkout.
1966 November 3 - . 13:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- OV4-03 - .
Mass: 109 kg (240 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: OV4.
Decay Date: 1967-01-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 2524 . COSPAR: 1966-099A. Apogee: 305 km (189 mi). Perigee: 298 km (185 mi). Inclination: 32.80 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
A Titan IIIC (Vehicle #9), the ninth research and development Titan III and sixth Titan IIIC to be launched from Cape Canaveral, completed the most difficult flight plan and most successful mission to date. The primary objective of injecting a modified Gemini spacecraft into a suborbital trajectory to test the reentry heat shield for the Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) program was accomplished. After dipping down to 80 nautical miles to eject the MOL load, the Transtage pitched up and placed a canister containing 11 experiments into a 160-nautical mile circular orbit. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- OV4-01R - . Mass: 109 kg (240 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: OV4. Decay Date: 1967-01-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 2526 . COSPAR: 1966-099B. Apogee: 292 km (181 mi). Perigee: 289 km (179 mi). Inclination: 32.80 deg. Period: 90.30 min. Whispering gallery experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- OV1-06S - . Mass: 202 kg (445 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1966-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 2527 . COSPAR: 1966-099C. Apogee: 290 km (180 mi). Perigee: 287 km (178 mi). Inclination: 32.80 deg. Period: 90.30 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV4-01T - . Mass: 109 kg (240 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: OV4. Decay Date: 1967-01-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 2528 . COSPAR: 1966-099D. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 289 km (179 mi). Inclination: 32.80 deg. Period: 90.60 min. Whispering gallery experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Gemini B - .
Payload: Gemini SC2. Mass: 1,800 kg (3,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: Gemini.
COSPAR: 1966-099xx.
During the ascent to orbit, the Gemini capsule atop the MOL Cannister was ejected and made a suborbital reentry and splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The spacecraft was the Gemini 2 reentry module, reused to test reentry with hatch cut into the heat shield. The capsule was successfully recovered and it was found that the reentry actually melted hatch shut, indicating that the design was valid for MOL.
- MOL Mockup - .
Payload: MOL Mockup (Titan fuel tank). Mass: 9,680 kg (21,340 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: MOL.
COSPAR: 1966-099xx.
A Titan IIIC (Vehicle #9), the ninth research and development Titan III and sixth Titan IIIC to be launched from Cape Canaveral, completed the most difficult flight plan and most successful mission to date. The primary objective of injecting a modified Gemini spacecraft into a suborbital trajectory to test the reentry heat shield for the Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) program was accomplished. After dipping down to 80 nautical miles to eject the MOL load, the Transtage pitched up and placed a canister containing 11 experiments into a 160-nautical mile circular orbit. This modified Titan 2 propellant tank represented the MOL station itself. It allowed study of the aerodynamic loads associated with launching the MOL into orbit and validated the very long length to diameter core represented by the MOL/Titan 3M configuration. It is possible certain prototype MOL equipment was flown as well.
1966 November 11 - . 20:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC19. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II GLV.
- Gemini 12 - .
Call Sign: Gemini 12. Crew: Aldrin,
Lovell.
Backup Crew: Cernan,
Cooper.
Payload: Gemini SC12. Mass: 3,763 kg (8,295 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Duration: 3.94 days. Decay Date: 1966-11-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 2566 . COSPAR: 1966-104A. Apogee: 289 km (179 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 28.80 deg. Period: 89.90 min.
Two very serious astronauts get it all right to end the program. Docked and redocked with Agena, demonstrating various Apollo scenarios including manual rendezvous and docking without assistance from ground control. Aldrin finally demonstrates ability to accomplish EVA without overloading suit by use of suitable restraints and careful movement.
Major objectives of the mission were to rendezvous and dock and to evaluate extravehicular activities (EVA). Among the secondary objectives were tethered vehicle evaluation, experiments, third revolution rendezvous and docking, automatic reentry demonstration, docked maneuvering for a high-apogee excursion, docking practice, systems tests, and Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) parking. The high-apogee excursion was not attempted because an anomaly was noted in the GATV primary propulsion system during insertion, and parking was not attempted because the GATV's attitude control gas was depleted. All other objectives were achieved. Nine spacecraft maneuvers effected rendezvous with the GATV. The onboard radar malfunctioned before the terminal phase initiate maneuver, but the crew used onboard backup procedures to calculate the maneuvers. Rendezvous was achieved at 3 hours 46 minutes ground elapsed time, docking 28 minutes later. Two phasing maneuvers, using the GATV secondary propulsion system, were accomplished, but the primary propulsion system was not used. The first of two periods of standup EVA began at 19 hours 29 minutes into the flight and lasted for 2 hours 29 minutes. During a more than two-hour umbilical EVA which began at 42 hours 48 minutes, Aldrin attached a 100-foot tether from the GATV to the spacecraft docking bar. He spent part of the period at the spacecraft adapter, evaluating various restraint systems and performing various basic tasks. The second standup EVA lasted 55 minutes, ending at 67 hours 1 minute ground elapsed time. The tether evaluation began at 47 hours 23 minutes after liftoff, with the crew undocking from the GATV. The tether tended to remain slack, although the crew believed that the two vehicles did slowly attain gravity-gradient stabilization. The crew jettisoned the docking bar and released the tether at 51 hours 51 minutes. Several spacecraft systems suffered problems during the flight. Two fuel cell stacks failed and had to be shut down, while two others experienced significant loss of power. At 39 hours 30 minutes ground elapsed time, the crew reported that little or no thrust was available from two orbit attitude and maneuver thrusters.
1966 November 24 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Bubble Girl Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1966 December 14 - . 18:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 8968 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 03 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1966-12-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 2618 . COSPAR: 1966-113A. Apogee: 392 km (243 mi). Perigee: 147 km (91 mi). Inclination: 109.50 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 January 15 - . Launch Site: Little Rock AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Project Yard Fence completed - . Project Yard Fence, the updating of Titan II sites, was completed at Little Rock AFB, Arkansas..
1967 January 18 - . 14:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IDCSP 2-1 - .
Payload: IDCSP 8 / OPS 9321. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 2645 . COSPAR: 1967-003A. Apogee: 33,829 km (21,020 mi). Perigee: 33,518 km (20,827 mi). Inclination: 8.70 deg. Period: 1,329.50 min.
Launched from Cape Canaveral, a Titan IIIC (Vehicle #13) space booster lifted eight 100-pound military communications satellites into synchronous orbits 21,000 miles above the equator. The satellites, together with the seven placed in orbit on 16 June 1966, formed the Initial Defense Satellite Communication System (IDSCS). Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- IDCSP 2-5 - . Payload: IDCSP 12 / OPS 9325. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2652 . COSPAR: 1967-003E. Apogee: 33,935 km (21,086 mi). Perigee: 33,599 km (20,877 mi). Inclination: 8.50 deg. Period: 1,334.20 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 2-7 - . Payload: IDCSP 14 / OPS 9327. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2654 . COSPAR: 1967-003G. Apogee: 34,127 km (21,205 mi). Perigee: 33,622 km (20,891 mi). Inclination: 8.60 deg. Period: 1,339.50 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 2-6 - . Payload: IDCSP 13 / OPS 9326. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2653 . COSPAR: 1967-003F. Apogee: 33,995 km (21,123 mi). Perigee: 33,631 km (20,897 mi). Inclination: 11.80 deg. Period: 1,336.50 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 2-4 - . Payload: IDCSP 11 / OPS 9324. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2651 . COSPAR: 1967-003D. Apogee: 33,873 km (21,047 mi). Perigee: 33,579 km (20,864 mi). Inclination: 8.50 deg. Period: 1,332.10 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 2-3 - . Payload: IDCSP 10 / OPS 9323. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2650 . COSPAR: 1967-003C. Apogee: 33,843 km (21,029 mi). Perigee: 33,549 km (20,846 mi). Inclination: 8.30 deg. Period: 1,330.70 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 2-2 - . Payload: IDCSP 9 / OPS 9322. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2649 . COSPAR: 1967-003B. Apogee: 33,830 km (21,020 mi). Perigee: 33,533 km (20,836 mi). Inclination: 8.50 deg. Period: 1,329.90 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 2-8 - .
Payload: IDCSP 15 / OPS 9328. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 2655 . COSPAR: 1967-003H. Apogee: 34,224 km (21,265 mi). Perigee: 33,666 km (20,919 mi). Inclination: 8.60 deg. Period: 1,343.10 min.
Launched from Cape Canaveral, a Titan IIIC (Vehicle #13) space booster lifted eight 100-pound military communications satellites into synchronous orbits 21,000 miles above the equator. The satellites, together with the seven placed in orbit on 16 June 1966, formed the Initial Defense Satellite Communication System (IDSCS). Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1967 February 24 - . 19:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 4204 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 04 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1967-03-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 2687 . COSPAR: 1967-016A. Apogee: 414 km (257 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 107.00 deg. Period: 90.00 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 March 17 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1967 April 12 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glamour Girl Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1967 April 26 - . 18:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB. FAILURE: Stage 2 engine lost thrust.. Failed Stage: 2.
- OPS 4243 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 05 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1967-04-26 . KH-8 type satellite..
- SRV-1 - . Payload: SRV-1. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8.
- SRV-2 - . Payload: SRV-2. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8.
1967 April 28 - . 10:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Vela 7 - .
Payload: Vela 4A / OPS 6638. Mass: 317 kg (698 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 2765 . COSPAR: 1967-040A. Apogee: 112,627 km (69,983 mi). Perigee: 108,948 km (67,697 mi). Inclination: 32.10 deg. Period: 6,652.10 min.
Two new and heavier Vela Nuclear Detection Satellites and three scientific satellites were placed in orbit by a Titan IIIC (Vehicle #10) launched from Cape Canaveral. The two Vela satellites joined six other Vela spacecraft already on sentry duty 69,000 miles above the earth. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- ERS 18 - . Mass: 9.00 kg (19.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: ERS. USAF Sat Cat: 2767 . COSPAR: 1967-040C. Apogee: 110,842 km (68,873 mi). Perigee: 8,991 km (5,586 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 2,831.30 min. Radiation research. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV5-01 - . Payload: ERS 27. Mass: 9.00 kg (19.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV5. USAF Sat Cat: 2769 . COSPAR: 1967-040E. Apogee: 110,746 km (68,814 mi). Perigee: 8,979 km (5,579 mi). Inclination: 32.80 deg. Period: 2,827.80 min. Materials research; deployed ERS 27. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV5-03 - . Payload: ERS 20. Mass: 9.00 kg (19.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV5. USAF Sat Cat: 2768 . COSPAR: 1967-040D. Apogee: 111,229 km (69,114 mi). Perigee: 8,604 km (5,346 mi). Inclination: 32.80 deg. Period: 2,829.60 min. Radiation research; deployed ERS 20. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Vela 8 - .
Payload: Vela 4B / OPS 6679. Mass: 317 kg (698 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 2766 . COSPAR: 1967-040B. Apogee: 114,578 km (71,195 mi). Perigee: 107,372 km (66,717 mi). Inclination: 33.10 deg. Period: 6,668.10 min.
Two new and heavier Vela Nuclear Detection Satellites and three scientific satellites were placed in orbit by a Titan IIIC (Vehicle #10) launched from Cape Canaveral. The two Vela satellites joined six other Vela spacecraft already on sentry duty 69,000 miles above the earth. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1967 June 20 - . 16:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 4282 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 06 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1967-06-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 2858 . COSPAR: 1967-064A. Apogee: 325 km (201 mi). Perigee: 127 km (78 mi). Inclination: 111.40 deg. Period: 89.00 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 June 23 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Buggy Wheel Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1967 July 1 - . 13:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IDCSP 3-1 - .
Payload: IDCSP 16 / OPS 9331. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 2862 . COSPAR: 1967-066A. Apogee: 33,515 km (20,825 mi). Perigee: 33,030 km (20,520 mi). Inclination: 11.90 deg. Period: 1,309.60 min.
A Titan IIIC booster (Vehicle #14) launched from Cape Canaveral placed a multiple payload of six satellites into orbit. Three of the satellites completed the Pacific link of the Initial Defense Satellite Communication System (IDSCS) program between Washington D.C., and South Vietnam. A fourth was a special communications satellite, the Despun Antenna Test Satellite (DATS), designed to test a despun antenna system for possible use on future communications satellites. DATS was designed to transmit 75 percent of radio signal strength to earth stations compared to the 15 percent for previous systems. Also included in the payload were a Defense Department Gravity Gradient Experiment (DODGE) satellite and a Lincoln Experimental Satellite, LES-5, the first all solid-state Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) band communication satellite intended to test communications with frontline troops. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- IDCSP 3-4 - . Payload: IDCSP 19/DATS / OPS 9334. Mass: 68 kg (149 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2865 . COSPAR: 1967-066D. Apogee: 33,560 km (20,850 mi). Perigee: 33,145 km (20,595 mi). Inclination: 11.90 deg. Period: 1,313.50 min. Antenna tests. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- LES 5 - . Mass: 194 kg (427 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES. USAF Sat Cat: 2866 . COSPAR: 1967-066E. Apogee: 33,609 km (20,883 mi). Perigee: 33,196 km (20,626 mi). Inclination: 12.00 deg. Period: 1,316.00 min. Experimental commsat. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- IDCSP 3-3 - . Payload: IDCSP 18 / OPS 9333. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2864 . COSPAR: 1967-066C. Apogee: 33,547 km (20,845 mi). Perigee: 33,079 km (20,554 mi). Inclination: 11.90 deg. Period: 1,311.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 3-2 - . Payload: IDCSP 17 / OPS 9332. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 2863 . COSPAR: 1967-066B. Apogee: 33,517 km (20,826 mi). Perigee: 33,046 km (20,533 mi). Inclination: 11.90 deg. Period: 1,310.00 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- DODGE 1 - .
Mass: 102 kg (224 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN NASC.
Class: Technology.
Type: Gravity gradient technology satellite. Spacecraft: DODGE.
USAF Sat Cat: 2867 . COSPAR: 1967-066F. Apogee: 33,670 km (20,920 mi). Perigee: 33,257 km (20,664 mi). Inclination: 12.00 deg. Period: 1,319.10 min.
A Titan IIIC booster (Vehicle #14) launched from Cape Canaveral placed a multiple payload of six satellites into orbit. Three of the satellites completed the Pacific link of the Initial Defense Satellite Communication System (IDSCS) program between Washington D.C., and South Vietnam. A fourth was a special communications satellite, the Despun Antenna Test Satellite (DATS), designed to test a despun antenna system for possible use on future communications satellites. DATS was designed to transmit 75 percent of radio signal strength to earth stations compared to the 15 percent for previous systems. Also included in the payload were a Defense Department Gravity Gradient Experiment (DODGE) satellite and a Lincoln Experimental Satellite, LES-5, the first all solid-state Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) band communication satellite intended to test communications with frontline troops. Gravity gradient experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1967 August 16 - . 17:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 4886 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 07 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1967-08-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 2919 . COSPAR: 1967-079A. Apogee: 445 km (276 mi). Perigee: 123 km (76 mi). Inclination: 111.50 deg. Period: 90.10 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 September 11 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glowing Bright GB44 Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1967 September 19 - . 18:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 4941 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 08 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1967-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 2952 . COSPAR: 1967-090A. Apogee: 401 km (249 mi). Perigee: 122 km (75 mi). Inclination: 106.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 October 25 - . 19:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 4995 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 09 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1967-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 3012 . COSPAR: 1967-103A. Apogee: 431 km (267 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 111.50 deg. Period: 90.10 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 October 30 - . Launch Site: Davis-Monthan AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Updated Titan II ICBM sites under Project Yard Fence. - . The last of 18 updated Titan II ICBM sites was returned to the 390th Strategic Missile Wing at Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona. The work was completed as part of the Project Yard Fence update program..
1967 November 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- Titan IIID launch vehicle work begins. - . The Titan III System Program Office (SMVT) of SAMSO's Deputy for Launch Vehicles initiated work on the design, development, and production of the Titan IIID launch vehicle system..
1967 December 5 - . 18:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5000 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 10 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1967-12-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 3058 . COSPAR: 1967-121A. Apogee: 428 km (265 mi). Perigee: 141 km (87 mi). Inclination: 109.50 deg. Period: 90.20 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 January 18 - . 19:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5028 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 11 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-02-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 3098 . COSPAR: 1968-005A. Apogee: 405 km (251 mi). Perigee: 137 km (85 mi). Inclination: 111.50 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 February 28 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glory Trip 04T Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1968 March 13 - . 19:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5057 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 12 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-03-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 3148 . COSPAR: 1968-018A. Apogee: 407 km (252 mi). Perigee: 128 km (79 mi). Inclination: 99.90 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 April 2 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glory Trip 10T Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1968 April 17 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5105 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 13 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-04-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 3199 . COSPAR: 1968-031A. Apogee: 421 km (261 mi). Perigee: 127 km (78 mi). Inclination: 111.40 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 June 5 - . 17:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5138 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 14 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-06-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 3278 . COSPAR: 1968-047A. Apogee: 456 km (283 mi). Perigee: 123 km (76 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 90.30 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 June 12 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glory Trip 08T Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1968 June 13 - . 14:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IDCSP 4-1 - .
Payload: IDCSP 20 / OPS 9341. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 3284 . COSPAR: 1968-050A. Apogee: 33,850 km (21,030 mi). Perigee: 33,725 km (20,955 mi). Inclination: 11.90 deg. Period: 1,335.20 min.
An Air Force Titan IIIC, Vehicle #16, was launched from Cape Canaveral and successfully inserted eight 100-pound communications satellites into near-synchronous orbits. These satellites augmented and completed the deployment of the Initial Defense Satellite Communications System (IDSCS) which now consisted of 26 operational satellites Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- IDCSP 4-6 - . Payload: IDCSP 25 / OPS 9346. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 3289 . COSPAR: 1968-050F. Apogee: 34,118 km (21,199 mi). Perigee: 33,739 km (20,964 mi). Inclination: 9.40 deg. Period: 1,342.20 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 4-5 - . Payload: IDCSP 24 / OPS 9345. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 3288 . COSPAR: 1968-050E. Apogee: 34,035 km (21,148 mi). Perigee: 33,721 km (20,953 mi). Inclination: 7.40 deg. Period: 1,339.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 4-4 - . Payload: IDCSP 23 / OPS 9344. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 3287 . COSPAR: 1968-050D. Apogee: 33,939 km (21,088 mi). Perigee: 33,743 km (20,966 mi). Inclination: 9.20 deg. Period: 1,337.90 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 4-2 - . Payload: IDCSP 21 / OPS 9342. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 3285 . COSPAR: 1968-050B. Apogee: 33,863 km (21,041 mi). Perigee: 33,724 km (20,955 mi). Inclination: 7.40 deg. Period: 1,335.50 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 4-8 - .
Payload: IDCSP 27 / OPS 9348. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 3291 . COSPAR: 1968-050H. Apogee: 34,442 km (21,401 mi). Perigee: 33,752 km (20,972 mi). Inclination: 7.70 deg. Period: 1,350.60 min.
An Air Force Titan IIIC, Vehicle #16, was launched from Cape Canaveral and successfully inserted eight 100-pound communications satellites into near-synchronous orbits. These satellites augmented and completed the deployment of the Initial Defense Satellite Communications System (IDSCS) which now consisted of 26 operational satellites Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- IDCSP 4-7 - . Payload: IDCSP 26 / OPS 9347. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 3290 . COSPAR: 1968-050G. Apogee: 34,256 km (21,285 mi). Perigee: 33,721 km (20,953 mi). Inclination: 7.50 deg. Period: 1,345.20 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- IDCSP 4-3 - . Payload: IDCSP 22 / OPS 9343. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: IDCSP. USAF Sat Cat: 3286 . COSPAR: 1968-050C. Apogee: 33,901 km (21,065 mi). Perigee: 33,722 km (20,953 mi). Inclination: 9.40 deg. Period: 1,336.40 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1968 August 6 - . 16:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5187 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 15 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-08-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 3335 . COSPAR: 1968-064A. Apogee: 395 km (245 mi). Perigee: 142 km (88 mi). Inclination: 110.00 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 August 21 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glory Trip 18T Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1968 September 10 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5247 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 16 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-09-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 3375 . COSPAR: 1968-074A. Apogee: 404 km (251 mi). Perigee: 125 km (77 mi). Inclination: 106.10 deg. Period: 89.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 September 26 - . 07:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- OV2-05 - .
Mass: 204 kg (449 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV2.
Completed Operations Date: 1968-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3428 . COSPAR: 1968-081A. Apogee: 35,745 km (22,210 mi). Perigee: 35,113 km (21,818 mi). Inclination: 12.30 deg. Period: 1,417.90 min.
A Titan ITIC space booster (Vehicle #5) was launched from Complex 41 at the Eastern Test Range and inserted four satellites into separate earth orbits. The primary payload was the Lincoln Experimental Satellite (LES-6) which was the second all-solid-state ultrahigh frequency (UHF) band communication satellite to be placed into a synchronous orbit. It was designed to test communications with aircraft, ships, and ground forces. The other three satellites were Office of Aerospace Research (OAR) payloads - two Experimental Research Satellites (ERS-21 and ERS-28) and an Orbiting Vehicle (OV 2-5) research satellite. Environmental research. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). As of 22 August 2001 located at 128.37 deg E drifting at 4.618 deg E per day. As of 2007 Feb 27 located at 91.48E drifting at 4.631E degrees per day.
- LES 6 - .
Mass: 163 kg (359 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES.
Completed Operations Date: 1976-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3431 . COSPAR: 1968-081D. Apogee: 35,839 km (22,269 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 12.80 deg. Period: 1,437.20 min.
A Titan ITIC space booster (Vehicle #5) was launched from Complex 41 at the Eastern Test Range and inserted four satellites into separate earth orbits. The primary payload was the Lincoln Experimental Satellite (LES-6) which was the second all-solid-state ultrahigh frequency (UHF) band communication satellite to be placed into a synchronous orbit. It was designed to test communications with aircraft, ships, and ground forces. The other three satellites were Office of Aerospace Research (OAR) payloads - two Experimental Research Satellites (ERS-21 and ERS-28) and an Orbiting Vehicle (OV 2-5) research satellite. Experimental commsat. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 38 deg W in 1968-1975 As of 26 August 2001 located at 61.90 deg W drifting at 0.101 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 73.59W drifting at 0.201E degrees per day.
- OV5-02 - . Payload: ERS 28. Mass: 10 kg (22 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV5. Decay Date: 1971-02-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 3429 . COSPAR: 1968-081B. Apogee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 26.40 deg. Period: 630.80 min. Particle radiation data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV5-04 - . Payload: ERS 21. Mass: 13 kg (28 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV5. Completed Operations Date: 1968-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3430 . COSPAR: 1968-081C. Apogee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 3.00 deg. Period: 1,435.80 min. Examined heat transfer in liquids in zero-g. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). Last known longitude (19 July 1995) 138.85 deg E drifting at 0.103 deg W per day..
1968 November 6 - . 19:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5296 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 17 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-11-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 3532 . COSPAR: 1968-099A. Apogee: 390 km (240 mi). Perigee: 130 km (80 mi). Inclination: 106.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 November 19 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glory Trip 26T Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi).
1968 December 4 - . 19:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 6518 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 18 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1968-12-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 3594 . COSPAR: 1968-108A. Apogee: 735 km (456 mi). Perigee: 137 km (85 mi). Inclination: 106.20 deg. Period: 93.30 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1969 January 22 - . 19:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 7585 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 19 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1969-02-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 3665 . COSPAR: 1969-007A. Apogee: 1,090 km (670 mi). Perigee: 142 km (88 mi). Inclination: 106.20 deg. Period: 97.00 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1969 February 9 - . 21:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Tacsat 1 - .
Mass: 730 kg (1,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 308.
Spacecraft: Tacsat.
Completed Operations Date: 1977-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3691 . COSPAR: 1969-013A. Apogee: 36,044 km (22,396 mi). Perigee: 35,939 km (22,331 mi). Inclination: 1.00 deg. Period: 1,446.60 min.
Air Force Titan IIIC, Vehicle #17, was launched from Cape Canaveral and placed the 1,600-pound experimental Tactical Communications Satellite, TACSAT I, into a near-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 19,300 nautical miles above the equator. TACSAT I, built by Hughes Aircraft Company under SAMSO management, was the largest communications satellite yet launched and placed in orbit by the United States. It was to determine the feasibility of using satellite communications repeaters with small mobile ground tactical communications equipment. In addition, using the technology already developed with earlier Despun Antenna Test System (DATS) and Lincoln Experimental Satellites (LES) test spacecraft, TACSAT I would test the feasibility of satellite communications over great distances while also testing the new gyrostat stabilization system. The satellite could handle transmission of television or multiple telephone/ teletype communications channels. Experimental commsat. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 107 deg W in 1969?-1970; over the Pacific Ocean 173 deg W in 1970; over the Pacific Ocean 179 deg W in 1971-1972; over the Pacific Ocean170 deg E in 1972 Last known longitude (9 June 1995) 176.44 deg E drifting at 0.150 deg E per day.
1969 March 4 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 4248 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 20 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1969-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 3772 . COSPAR: 1969-019A. Apogee: 461 km (286 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 92.00 deg. Period: 90.50 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1969 April 15 - . 17:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 5310 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 21 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1969-04-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 3895 . COSPAR: 1969-039A. Apogee: 410 km (250 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 108.80 deg. Period: 90.00 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1969 April 27 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- First static test firing of Titan 3M SRB. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: MOL. First test firing of seven segment solid rocket booster motor for Titan 3M for MOL. The test at Coyote Canyon, California, generated 0.7 million kgf for two minutes..
1969 May 20 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-B. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Glory Trip 39T Follow-On Operational Test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). SAC's launch of Titan II (#63-07738) completed its Follow-on Operational Test (FOT) program launches of the Titan II (LGM-25C)..
1969 May 23 - . 07:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- OV5-05 - .
Payload: ERS 29. Mass: 259 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV5.
USAF Sat Cat: 3950 . COSPAR: 1969-046A. Apogee: 69,130 km (42,950 mi). Perigee: 59,630 km (37,050 mi). Inclination: 33.00 deg. Period: 3,121.90 min.
The 13th, and final, Titan IIIC research and development booster (Vehicle #15) lifted two Vela satellites, the fifth pair of such nuclear detection spacecraft, and three experimental satellites into orbit from Cape Canaveral. This launch concluded the highly successful Titan III research and development program initiated in 1962. Out of 13 Titan IIIC and four Titan IITA vehicles launched, 10 Titan IITCs were complete successes, two were partial successes, and only one was a failure, while three of the four Titan IITA launches were rated successful. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- OV5-09 - . Mass: 11 kg (24 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV5. USAF Sat Cat: 3952 . COSPAR: 1969-046C. Apogee: 69,011 km (42,881 mi). Perigee: 59,543 km (36,998 mi). Inclination: 33.50 deg. Period: 3,115.10 min. VLF plasma wave detection. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Vela 9 - . Payload: Vela 5A / OPS 6909. Mass: 317 kg (698 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Vela. Decay Date: 1992-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 3954 . COSPAR: 1969-046D. Apogee: 145,638 km (90,495 mi). Perigee: 77,082 km (47,896 mi). Inclination: 61.60 deg. Period: 6,700.90 min. Solar flare particle detectors. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Vela 10 - .
Payload: Vela 5B / OPS 6911. Mass: 317 kg (698 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Vela.
Decay Date: 1992-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 3955 . COSPAR: 1969-046E. Apogee: 150,633 km (93,598 mi). Perigee: 72,080 km (44,780 mi). Inclination: 61.00 deg. Period: 6,700.70 min.
The 13th, and final, Titan IIIC research and development booster (Vehicle #15) lifted two Vela satellites, the fifth pair of such nuclear detection spacecraft, and three experimental satellites into orbit from Cape Canaveral. This launch concluded the highly successful Titan III research and development program initiated in 1962. Out of 13 Titan IIIC and four Titan IITA vehicles launched, 10 Titan IITCs were complete successes, two were partial successes, and only one was a failure, while three of the four Titan IITA launches were rated successful. Radiation, low-energy particle, solar flare data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- OV5-06 - . Payload: ERS 26. Mass: 259 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV5. USAF Sat Cat: 3951 . COSPAR: 1969-046B. Apogee: 69,022 km (42,888 mi). Perigee: 59,540 km (36,990 mi). Inclination: 33.60 deg. Period: 3,115.40 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1969 June 3 - . 16:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- OPS 1077 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 22 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1969-06-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 3984 . COSPAR: 1969-050A. Apogee: 414 km (257 mi). Perigee: 137 km (85 mi). Inclination: 110.00 deg. Period: 90.00 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1969 June 10 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- MOL Program cancelled - .
Nation: USA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned space station. Spacecraft: MOL.
Deputy Secretary of Defense David Packard announced the cancellation of the Air Force's Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) program because of the need to reduce defense spending. The cancellation was expected to save $ 1.5 billion of the projected total $ 3.0 billion program costs. The SLC-6 launch facility at Vandenberg, 90% complete, would be finished and mothballed. MOL reconnaisance systems useful on unmanned satellites would be completed for a total cost of $ 225 million. Ten thousand aerospace workers were laid off as a result of the cancellation. The program was initiated in 1965 to advance the development of both manned and unmanned defense-oriented space equipment and to ascertain the full extent of man's utility in space for defense purposes. Following MOL termination, NASA requested that the MOL food and diet contract with Whirlpool Corporation and the space suit development contract with Hamilton Standard Division, United Aircraft Corporation, be transferred to NASA.
1969 August 23 - . 16:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 7807 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 23 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1969-09-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 4078 . COSPAR: 1969-074A. Apogee: 377 km (234 mi). Perigee: 138 km (85 mi). Inclination: 108.10 deg. Period: 89.60 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1969 October 24 - . 18:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 8455 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 24 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1969-11-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 4186 . COSPAR: 1969-095A. Apogee: 740 km (450 mi). Perigee: 136 km (84 mi). Inclination: 108.00 deg. Period: 93.40 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1970 January 14 - . 18:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 6531 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 25 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1970-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 4296 . COSPAR: 1970-002A. Apogee: 383 km (237 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 110.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. The 25th Air Force Titan IIIB/Agena D space booster was launched from Vandenberg AFB. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1970 February 13 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Spacecraft Environment Enclosure for Titan IIIC - .
Work was completed on the new, highly sophisticated spacecraft Environment Enclosure for the Titan IIIC facilities at Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral. The $1.6 million enclosure on the Mobile Service Tower (MST) would provide a temperature and humidity controlled environment for a variety of spacecraft to be orbited by the Titan IIIC. This would allow crews to adjust or repair spacecraft without removing them from the MST. Official Air Force acceptance was announced on 12 March 1970.
1970 March 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Titan Ill/Centaur for Viking. - .
Spacecraft: Viking.
SAMSO and NASA signed a Memorandum of Understanding that defined the roles and responsibilities for a Titan Ill/Centaur coordinating group which would acquire Titan III launch vehicles for Viking. SAMSO and NASA signed a Memorandum of Understanding that defined the roles and responsibilities for a Titan Ill/Centaur coordinating group which would acquire Titan III launch vehicles for Viking.
1970 April 8 - . 10:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Vela 12 - . Payload: Vela 6A / OPS 7044. Mass: 317 kg (698 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Vela. Decay Date: 1992-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 4366 . COSPAR: 1970-027A. Apogee: 121,227 km (75,326 mi). Perigee: 101,261 km (62,920 mi). Inclination: 61.20 deg. Period: 6,691.00 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- Vela 11 - . Payload: Vela 6B / OPS 7033. Mass: 317 kg (698 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Vela. Decay Date: 1992-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 4368 . COSPAR: 1970-027B. Apogee: 119,313 km (74,137 mi). Perigee: 103,570 km (64,350 mi). Inclination: 57.40 deg. Period: 6,707.90 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1970 April 15 - . 15:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 2863 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 26 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1970-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 4375 . COSPAR: 1970-031A. Apogee: 388 km (241 mi). Perigee: 130 km (80 mi). Inclination: 111.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1970 May 15 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Construction completed at SLC-4E - .
Facility construction was completed at the Titan III launch pad, Space Launch Complex 4 East (SLC-4E) at Vandenberg. The new facilities provided a temperature and humidity controlled environment for payloads that were to be flown aboard the Titan III launch vehicles.
1970 June 25 - . 14:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 6820 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 27 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1970-07-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 4422 . COSPAR: 1970-048A. Apogee: 393 km (244 mi). Perigee: 144 km (89 mi). Inclination: 108.90 deg. Period: 89.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1970 August 18 - . 14:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 7874 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 28 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1970-09-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 4492 . COSPAR: 1970-061A. Apogee: 377 km (234 mi). Perigee: 149 km (92 mi). Inclination: 111.10 deg. Period: 89.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1970 October 23 - . 17:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 7568 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 29 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1970-11-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 4596 . COSPAR: 1970-090A. Apogee: 396 km (246 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 111.10 deg. Period: 89.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1970 November 6 - . 10:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC. FAILURE: Partial Failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- IMEWS 1 - .
Payload: DSP Phase 1 s/n 1 / OPS 5960. Mass: 900 kg (1,980 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1973-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 4630 . COSPAR: 1970-093A. Apogee: 36,128 km (22,448 mi). Perigee: 25,840 km (16,050 mi). Inclination: 16.40 deg. Period: 1,197.90 min.
An Air Force Titan IIIC launched the 500th satellite to be placed in orbit successfully by a vehicle launched from Cape Canaveral. First generation geosynchronous ballistic missile launch detection satellite; placed in incorrect subsynchronous orbit. One account claimed that it exhausted its propellant before it could be put into operation, but a 2007service history chart showed that is was considered operational for three years, well beyond its planned life.
1970 Late - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL 1 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: MOL. The first unmanned Gemini-B/Titan 3M qualification flight was planned for late 1970 at the time the program was cancelled..
1971 January 21 - . 18:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 7776 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 30 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1971-02-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 4874 . COSPAR: 1971-005A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 139 km (86 mi). Inclination: 110.90 deg. Period: 90.10 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1971 March 21 - . 03:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 33B.
- Jumpseat 1 - . Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Jumpseat. USAF Sat Cat: 5053 . COSPAR: 1971-021A. Apogee: 33,800 km (21,000 mi). Perigee: 390 km (240 mi). Inclination: 63.20 deg. Period: 596.70 min.
1971 April 22 - . 15:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 23B.
- OPS 7899 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 31 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1971-05-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 5171 . COSPAR: 1971-033A. Apogee: 403 km (250 mi). Perigee: 132 km (82 mi). Inclination: 110.60 deg. Period: 89.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1971 May 5 - . 07:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 2 - .
Payload: DSP Phase 1 s/n 2 / OPS 3811. Mass: 900 kg (1,980 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1983-01-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 5204 . COSPAR: 1971-039A. Apogee: 36,527 km (22,696 mi). Perigee: 36,156 km (22,466 mi). Inclination: 10.50 deg. Period: 1,464.60 min.
First generation geosynchronous ballistic missile launch detection satellite. First completely sucessful operational satellite, remained in service for nearly 12 years. Positioned over the Indian Ocean at 75 deg E in 1979-1982. As of 1983 May 11 located at 73.28W drifting at 7.684W degrees per day.
1971 June 1 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Go ahead for two Titan Ill/Centaur launch vehicles. - .
The Martin Marietta Corporation was given the go ahead to build two Titan Ill/Centaur launch vehicles. This included authority to design, build, and install required aerospace ground equipment (AGE) to activate Eastern Test Range Launch Complex 41 in support of NASA Titan Ill/Centaur missions.
1971 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL 2 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: MOL. The second unmanned Gemini-B/Titan 3M qualification flight would have taken place in 1971 and set the stage for the first manned mission in 1971..
1971 June 15 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- Initial launch of a Titan IIID space booster - . Nation: USA. Initial launch of a Titan IIID space booster from Vandenberg AFB..
1971 June 15 - . 18:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 01 (Big Bird) - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1971-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 5297 . COSPAR: 1971-056A. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi). Perigee: 180 km (110 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 89.30 min. The 6595th Space Test Group at Vandenberg AFB launched the first Titan HID space booster (Vehicle D-l). KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1971 June 20 - . 22:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- SSTTP M1-17 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Safeguard System Test Target..
1971 August 12 - . 15:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 8607 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 32 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1971-09-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 5409 . COSPAR: 1971-070A. Apogee: 424 km (263 mi). Perigee: 137 km (85 mi). Inclination: 111.00 deg. Period: 90.10 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1971 August 28 - . 02:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- SSTTP M2-1 test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Safeguard System Test Target..
1971 October 23 - . 17:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 7616 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 33 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1971-11-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 5575 . COSPAR: 1971-092A. Apogee: 369 km (229 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 110.90 deg. Period: 89.50 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- SRV-2 - . Payload: SRV-2 / OPS 7616 DEB. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1971-11-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 5606 . COSPAR: 1971-092B. Apogee: 330 km (200 mi). Perigee: 93 km (57 mi). Inclination: 110.90 deg. Period: 88.73 min.
1971 November 3 - . 03:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- DSCS II-01 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-1 / OPS 9431. Mass: 520 kg (1,140 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1979-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 5587 . COSPAR: 1971-095A. Apogee: 35,815 km (22,254 mi). Perigee: 35,765 km (22,223 mi). Inclination: 13.80 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
A Titan IIIC, launched from Cape Canaveral, placed into synchronous orbits the first pair of 1,200-pound advanced communications satellites of the Defense Satellite Communication System Phase II (DSCS II). After some initial difficulties with the satellites, telemetry and command links were established with both satellites by 5 November. Under SAMSO program management, TRW Systems Group manufactured these second generation communications satellites that were intended as replacements for the 26-satellite Initial Defense Satellite Communication Systems (IDSCS). Each of the DSCS II (Program 777) satellites would be able to handle voice, teletype, computerized digital data, and video transmissions. Defense Satellite Communications System. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 106 deg W in 1972-?; over the Americas at 81 deg W in 1977-1979; over the Americas at 100-110 deg W in drift 1979-1998 As of 1 September 2001 located at 103.05 deg W drifting at 0.044 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 110.10W drifting at 0.035W degrees per day.
- DSCS II-02 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-2 / OPS 9432. Mass: 520 kg (1,140 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1972-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 5588 . COSPAR: 1971-095B. Apogee: 35,824 km (22,259 mi). Perigee: 35,819 km (22,256 mi). Inclination: 13.60 deg. Period: 1,437.90 min.
Defense Satellite Communications System. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 112 deg W in 1972. As of 30 August 2001 located at 146.34 deg E drifting at 0.101 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 5 located at 36.33W drifting at 0.201E degrees per day.
1972 January 20 - . 18:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 02 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1972-02-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 5769 . COSPAR: 1972-002A. Apogee: 330 km (200 mi). Perigee: 153 km (95 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 89.30 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 7719 - . Payload: SSF-B No. 22. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1979-04-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 5772 . COSPAR: 1972-002D. Apogee: 545 km (338 mi). Perigee: 474 km (294 mi). Inclination: 96.00 deg. Period: 94.80 min. Radar monitoring..
1972 Early - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL 3 (cancelled) - . Crew: Crews, Taylor. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Crews, Taylor. Flight: MOL 3. Spacecraft: MOL. At the time of the cancellation of the MOL program in June 1969, the first manned mission was planned for early 1972. A crew of two would have spent thirty days in orbit operating sophisticated military reconnaisance equipment and other experiments..
1972 February 16 - . 09:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 33B. FAILURE: Failure.
- Jumpseat 2 - . Payload: OPS 1844. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Jumpseat.
1972 March 1 - . 09:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 3 - . Payload: DSP Phase 1 s/n 3 / OPS 1570. Mass: 900 kg (1,980 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP. Completed Operations Date: 1981-08-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 5851 . COSPAR: 1972-010A. Apogee: 35,962 km (22,345 mi). Perigee: 35,416 km (22,006 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,429.90 min. First generation geosynchronous ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for over nine years. Positioned over the Pacific Ocean at 165 deg E in 1979-1980. As of 2003 Mar 5 located at 74.63E drifting at 0.712W degrees per day..
1972 March 17 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 1678 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 34 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1972-04-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 5888 . COSPAR: 1972-016A. Apogee: 409 km (254 mi). Perigee: 131 km (81 mi). Inclination: 111.00 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1972 May 20 - . 15:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: U.
- OPS 6574 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 35 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8.
- SRV-2 - . Payload: SRV-2. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8.
- SRV-1 - . Payload: SRV-1. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8.
1972 May 24 - . 23:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- SSTTP M2-10 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Safeguard System Test Target..
1972 July 7 - . 17:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 03 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1972-09-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 6094 . COSPAR: 1972-052A. Apogee: 254 km (157 mi). Perigee: 176 km (109 mi). Inclination: 96.00 deg. Period: 88.70 min. KH-9 type satellite. Investigation of the upper atmosphere and outer space. .
- OPS 7803 - . Payload: SSF-B No. 23. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1978-05-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 6096 . COSPAR: 1972-052C. Apogee: 504 km (313 mi). Perigee: 498 km (309 mi). Inclination: 96.20 deg. Period: 94.70 min. Radar monitoring..
1972 September 1 - . 17:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 8888 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 36 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1972-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 6172 . COSPAR: 1972-068A. Apogee: 381 km (236 mi). Perigee: 142 km (88 mi). Inclination: 110.40 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1972 October 10 - . 18:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 04 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1973-01-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 6227 . COSPAR: 1972-079A. Apogee: 281 km (174 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 8314/2 - . Payload: SSF-C No. 3 / OPS 8314. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 6822 . COSPAR: 1972-079C. Apogee: 1,464 km (909 mi). Perigee: 1,420 km (880 mi). Inclination: 95.60 deg. Period: 114.70 min. ABM monitoring..
1972 October 11 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- SSTTP M2-14 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Safeguard System Test Target..
1972 Late - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL 4 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Flight: MOL 4. Spacecraft: MOL. Planned date of second manned MOL mission at time of the program cancellation..
1972 December 21 - . 17:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 3978 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 37 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1973-01-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 6321 . COSPAR: 1972-103A. Apogee: 378 km (234 mi). Perigee: 139 km (86 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1973 Feb - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Large HEAO satellite split into three smaller spacecraft. - . Spacecraft: HEAO. NASA cancelled Air Force procurement of a Titan IIIC launch vehicle for the planned 1975 launch of its High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO) satellite (cancelled in favor of smaller satellites)..
1973 March 9 - . 21:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 05 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1973-05-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 6382 . COSPAR: 1973-014A. Apogee: 262 km (162 mi). Perigee: 150 km (90 mi). Inclination: 95.70 deg. Period: 88.70 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1973 May 14 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- DOD to develop the shuttle's Interim Upper Stage. - . An Air Force Program Memorandum on DOD Space Shuttle Utilization was completed that assumed the DOD would develop the shuttle's Interim Upper Stage (IUS) needed for high energy missions..
1973 May 16 - . 16:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 2093 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 38 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1973-06-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 6640 . COSPAR: 1973-028A. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 136 km (84 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 89.40 min. The 40th Titan IIIB/Agena D was launched from Vandenberg AFB by the Space and Missile Test Center's 6595th Space Test Group. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1973 June 12 - . 07:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 4 - .
Payload: DSP Phase 1 s/n 4 / OPS 6157. Mass: 900 kg (1,980 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1980-11-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 6691 . COSPAR: 1973-040A. Apogee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.30 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
First generation geosynchronous ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for over seven years. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 75E in 1973; over the Americas at 105 deg W in 1979-1980. As of 1983 Jan 3 located at 73.21W drifting at 1.648W degrees per day.
1973 June 22 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Air Force accepted the first Titan IIIE. - .
The Air Force accepted the first Titan IIIE (E-1) from the Martin Marietta Corporation. The vehicle was then shipped to the Eastern Test Range for final assembly, checkout, and mating with Centaur upper stage prior to the planned proof launch in January 1974. SAMSO procured the Titan HIE, a Titan HID modified to accept a Centaur upper stage, for NASA's use in its Viking Mars Lander program and other future projects.
1973 June 26 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B. FAILURE: Agena upper stage failed to orbit.. Failed Stage: U.
- OPS 4018 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 39 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1973-06-26 .
- SRV-2 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8.
- SRV-1 - . Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8.
1973 July 13 - . 20:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 06 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1973-10-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 6727 . COSPAR: 1973-046A. Apogee: 291 km (180 mi). Perigee: 143 km (88 mi). Inclination: 96.20 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1973 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL 5 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Flight: MOL 5. Spacecraft: MOL. Planned date of third manned MOL mission at time of the program cancellation..
1973 August 21 - . 16:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 33B.
- Jumpseat 3 - . Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Jumpseat. USAF Sat Cat: 6791 . COSPAR: 1973-056A. Apogee: 39,296 km (24,417 mi). Perigee: 460 km (280 mi). Inclination: 63.30 deg. Period: 705.70 min.
1973 September 27 - . 17:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 6275 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 40 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1973-10-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 6837 . COSPAR: 1973-068A. Apogee: 385 km (239 mi). Perigee: 131 km (81 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1973 October 6 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- SSTTP M2-27 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Safeguard System Test Target..
1973 October 15 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- NASA buys three additional Titan HIE vehicles - . NASA decided to procure three additional Titan HIE (Titan/Centaur) launch vehicles for future space missions..
1973 November 10 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- Titan 23D no. 8 stage - . Payload: SSF 32. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1973-11-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 6929 . COSPAR: 1973-088C. Apogee: 508 km (315 mi). Perigee: 486 km (301 mi). Inclination: 96.30 deg. Period: 94.50 min. ABM monitoring. .
- KH-9 no. 07 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1974-03-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 6928 . COSPAR: 1973-088A. Apogee: 275 km (170 mi). Perigee: 158 km (98 mi). Inclination: 96.90 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6630 P/L 2 - . Payload: SSF-C No. 4 / OPS 6630. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 6938 . COSPAR: 1973-088D. Apogee: 1,457 km (905 mi). Perigee: 1,414 km (878 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 114.60 min.
- OPS 7705 - . Payload: SSF-B No. 24. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1978-12-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 6931 . COSPAR: 1973-088B. Apogee: 505 km (313 mi). Perigee: 488 km (303 mi). Inclination: 96.30 deg. Period: 94.50 min. Radar monitoring..
1973 December 13 - . 23:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- DSCS II-03 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-3 / OPS 9433. Mass: 566 kg (1,247 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1982-08-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 6973 . COSPAR: 1973-100A. Apogee: 36,661 km (22,780 mi). Perigee: 36,413 km (22,625 mi). Inclination: 13.90 deg. Period: 1,474.60 min.
An Air Force Titan IIIC, launched by the 6555th Aerospace Test Group from the Eastern Test Range, boosted two Program 777 Defense Satellite Communications Systems; 13 deg W. A new inertial guidance system, manufactured by Delco Electronics for the Titan IIIC made its first flight. The new system consisted of an inertial measurement unit and a missile guidance computer. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 13 deg W in 1974-1977; over the Atlantic Ocean 57-66 deg W in 1977-1979 As of 3 September 2001 located at 104.01 deg E drifting at 9.429 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 148.24W drifting at 9.427W degrees per day.
- DSCS II-04 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-4 / OPS 9434. Mass: 566 kg (1,247 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-12-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 6974 . COSPAR: 1973-100B. Apogee: 36,837 km (22,889 mi). Perigee: 36,300 km (22,500 mi). Inclination: 13.50 deg. Period: 1,476.30 min.
Defense Satellite Communications System; 175 deg E. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 175 deg E in 1974-1977; over the Indian Ocean 65 deg E in 1977-1980; over the Indian Ocean 60-61 deg E in 1980-1984; over the Indian Ocean 66 deg E in 1984-1987; over the Americas at 56-62 deg W in 1989-1993 As of 5 September 2001 located at 138.02 deg W drifting at 9.919 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 3 located at 146.85E drifting at 9.914W degrees per day.
1974 February 11 - . 13:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE. FAILURE: Centaur LOX pump failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Sphinx - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft: Sphinx. Decay Date: 1974-02-12 . Space Plasma High Voltage Interaction Experiment. Payload carried on test flight of Titan 3E booster..
- Viking Dynamic Simulator - .
Payload: VDS. Mass: 3,399 kg (7,493 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Spacecraft: Viking.
The newest addition to the Titan III series, the Titan IIIE/Centaur - a meld of Air Force and NASA technology, suffered a partial failure in its first flight test from Cape Canaveral. The Titan/Centaur vehicle will be used as the launch vehicles for NASA's Viking Mars Lander in 1975 and for the United States-German Helios program.
1974 February 13 - . 18:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 6889 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 41 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1974-03-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 7121 . COSPAR: 1974-007A. Apogee: 396 km (246 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 110.40 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1974 March 1 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- SSTTP M2-31 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Safeguard System Test Target..
1974 April 10 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 08 Capsule - . Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. COSPAR: 1974-020xx. Apogee: 830 km (510 mi). Perigee: 786 km (488 mi). Inclination: 94.60 deg. Period: 101.10 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- KH-9 no. 08 - . Payload: OPS 6245. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1974-07-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 7242 . COSPAR: 1974-020A. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 153 km (95 mi). Inclination: 94.50 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 4547 - . Payload: OPS 4547 / SSF-B No. 25. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1980-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 7247 . COSPAR: 1974-020C. Apogee: 531 km (329 mi). Perigee: 503 km (312 mi). Inclination: 94.00 deg. Period: 95.00 min. Radar monitoring..
- S73-7 Cal Balloon - . Payload: OPS 6935 / P 73-7. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: Space Test Program Payloads. Spacecraft: S73-7 Cal Balloon. Decay Date: 1974-07-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 7244 . COSPAR: 1974-020B. Apogee: 247 km (153 mi). Perigee: 148 km (91 mi). Inclination: 94.40 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Space Test Program flight S73-7 was launched. The launch was successful but the mission failed when the payload -an infrared calibration balloon - failed to deploy..
1974 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL 6 (cancelled) - . Crew: Crippen, Truly. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Crippen, Truly. Flight: MOL 6. Spacecraft: MOL. Planned date of fourth manned MOL mission at time of the program cancellation. From the beginning of the project, the Navy had demanded that this be an all-Navy crew..
1974 May 30 - . 13:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- ATS 6 - .
Payload: ATS F. Mass: 930 kg (2,050 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: ATS.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: ATS.
Spacecraft: ATS-6.
Completed Operations Date: 1979-08-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 7318 . COSPAR: 1974-039A. Apogee: 35,444 km (22,023 mi). Perigee: 35,184 km (21,862 mi). Inclination: 13.10 deg. Period: 1,412.00 min.
An Air Force Titan IIIC boosted NASA's Applications Technology Satellite (ATS-F) into orbit from Cape Canaveral. Built by Application Technology Satellite; experimental communications satellite. The purpose of the ATS-6 flight experiment was to demonstrate north-south stationkeeping of a geosynchronous satellite using two cesium ion engine systems. Thruster development tests included a life test of 2614 hours and 471 cycles. Thruster input power was 0.15 kW, which resulted in a thrust of 4.5 mN at a specific impulse of 2500 s. One of the ion engines operated for about one hour and the other for 92 hours. Both of the engines failed to provide thrust on restart due to discharge chamber cesium flooding. The feed system flooding problem caused overloading of the discharge and high voltage power supplies. This failure mechanism was verified through a series of ground tests. However engine operation demonstrated an absence of EMI related to spacecraft systems, verified predictions of spacecraft potential with engines operating, and demonstrated compatibility with the spacecraft's star tracker. It was found that the ion engines or just the neutralizer could discharge large negative spacecraft potentials at all times. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 94 deg W in 1974-1975; over the Indian Ocean 35 deg E in 1975-1976; over the Americas at 140 deg W in 1976-1979. As of 2 September 2001 located at 172.56 deg W drifting at 6.144 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 29.12W drifting at 6.125E degrees per day.
1974 June 6 - . 16:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 1776 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 42 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1974-07-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 7330 . COSPAR: 1974-042A. Apogee: 394 km (244 mi). Perigee: 136 km (84 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 89.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1974 August 14 - . 15:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 3004 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 43 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1974-09-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 7416 . COSPAR: 1974-065A. Apogee: 402 km (249 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 89.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1974 October 1 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS studies begun. - .
The Air Force awarded firm-fixed-price (FFP) level of effort contracts of about $635,000 to $640,000 each to Martin Marietta Corporation, Lockheed Missiles and Space Company, General Dynamics Convair Division, The Boeing Company, and McDonnell Douglas Astronautics Company for nine-month IUS System Study efforts.^ These companies had in-production, existing operational upper stages and the studies would provide baseline data for future acquisition efforts.
1974 October 29 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 09 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1975-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 7495 . COSPAR: 1974-085A. Apogee: 272 km (169 mi). Perigee: 115 km (71 mi). Inclination: 96.70 deg. Period: 88.40 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6239 - . Payload: SSF-B No. 26. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1980-01-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 7498 . COSPAR: 1974-085B. Apogee: 531 km (329 mi). Perigee: 521 km (323 mi). Inclination: 96.00 deg. Period: 95.10 min. Radar monitoring; may or may not have existed!!!..
- SESP 73-5 - . Payload: P 73 5 / OPS 8452. Mass: 260 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Space Test Program Payloads. Spacecraft: SESP. Decay Date: 1975-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 7499 . COSPAR: 1974-085C. Apogee: 2,888 km (1,794 mi). Perigee: 150 km (90 mi). Inclination: 96.90 deg. Period: 116.30 min. Space Test Program flight S73-5 was successfully launched. This was the first of three launches to be made under the Small Secondary Satellite (S3) project. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1974 December 10 - . 07:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Helios 1 - .
Mass: 370 kg (810 lb). Nation: Germany.
Agency: DFVLR.
Class: Astronomy.
Type: Solar satellite. Spacecraft: Helios.
USAF Sat Cat: 7567 . COSPAR: 1974-097A.
A Titan IIIE/Centaur launched from Cape Canaveral boosted the United States-West German HELIOS spacecraft into heliocentric orbit as a solar probe to investigate the properties and processes of solar/terrestrial relationships. This was the first completely successful flight of the Titan IIIE/Centaur booster combination. Solar probe. Solar Orbit (Heliocentric). Launched by the United States and the Federal Republic of Germany. Helios A (Helios I). Heliocentric orbit 190 days, 0.309 x 0.985 AU x 0 deg. Exploration of the interplanetary space between the earth and the sun and study of solar influences on that area.
1975 January 10 - . 02:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1975 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3M.
- MOL 7 (cancelled) - . Nation: USA. Flight: MOL 7. Spacecraft: MOL. Planned date of fifth manned MOL mission. This mission was already deleted from the FY 1970 budget request in April 1969, two months before the entire project was cancelled..
1975 March 10 - . 04:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- Jumpseat 4 - . Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Jumpseat. USAF Sat Cat: 7687 . COSPAR: 1975-017A. Apogee: 39,337 km (24,442 mi). Perigee: 295 km (183 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 702.00 min.
1975 April 18 - . 16:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 4883 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 44 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1975-06-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 7747 . COSPAR: 1975-032A. Apogee: 398 km (247 mi). Perigee: 133 km (82 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 89.80 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1975 May 20 - . 14:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC. FAILURE: Transtage gyro platform lost power; attitude control lost; orbit too low.. Failed Stage: U.
- DSCS II-05 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-5 / OPS 9435. Mass: 566 kg (1,247 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Decay Date: 1975-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 7807 . COSPAR: 1975-040A. Apogee: 256 km (159 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 28.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
The third pair of Defense Satellite Communications System II satellites was launched; the launch failed due to a malfunction in the Transtage of the Titan IIIC launch vehicle. Unusable orbit. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- DSCS II-06 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-6 / OPS 9436. Mass: 566 kg (1,247 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Decay Date: 1975-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 7808 . COSPAR: 1975-040B. Apogee: 256 km (159 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 28.60 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
The third pair of Defense Satellite Communications System II satellites was launched; the launch failed due to a malfunction in the Transtage of the Titan IIIC launch vehicle. Unusable orbit. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1975 June 8 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 10 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1975-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 7918 . COSPAR: 1975-051A. Apogee: 272 km (169 mi). Perigee: 157 km (97 mi). Inclination: 96.30 deg. Period: 88.70 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1975 August 7 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1975 August 20 - . 21:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Viking 1 Orbiter - .
Payload: Viking 1. Mass: 3,399 kg (7,493 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft: Viking.
USAF Sat Cat: 8108 . COSPAR: 1975-075A.
A Titan HIE carrying a Viking payload was successfully launched from LC-41, Eastern Test Range. This was the first flight of a new oxydizer accumulator developed for the HIE. Combined Mars orbiter and lander mission; orbiter inserted in Mars orbit 6/19/76; lander soft landed on Martian surface 7/20/76Mars. Mars Orbit. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B).
- Viking 1 Lander - .
Payload: Viking 1. Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Langley.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft: Viking.
Decay Date: 1976-07-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 9024 . COSPAR: 1975-075C.
A Titan HIE carrying a Viking payload was successfully launched from LC-41, Eastern Test Range. This was the first flight of a new oxydizer accumulator developed for the HIE. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B).
1975 September 4 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Interim Upper Stage for use with the Space Transportation System. - . Dr. Walter LaBerge, Assistance Secretary of the Air Force for Research and Development, announced an Interim Upper Stage to be developed for use with the Space Transportation System..
1975 September 9 - . 18:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Viking 2 Orbiter - .
Mass: 3,399 kg (7,493 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft: Viking.
USAF Sat Cat: 8199 . COSPAR: 1975-083A.
A Titan HIE carrying a Viking payload was successfully launched from LC-41, Eastern Test Range. This was the first flight of a new Command Receiver Set. A fire occurred at the launch site following launch and caused $2 million damage to the Aerospace Ground Equipment building. Combined Mars orbiter and lander mission; orbiter inserted in Mars orbit 8/7/76; lander soft landed on Martian surface 9/3/76Mars. Mars Orbit. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B).
- Viking 2 Lander - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Langley.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft: Viking.
Decay Date: 1976-08-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 9408 . COSPAR: 1975-083C.
A Titan HIE carrying a Viking payload was successfully launched from LC-41, Eastern Test Range. This was the first flight of a new Command Receiver Set. A fire occurred at the launch site following launch and caused $2 million damage to the Aerospace Ground Equipment building. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B).
1975 October 9 - . 19:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 5499 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 45 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1975-11-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 8360 . COSPAR: 1975-098A. Apogee: 274 km (170 mi). Perigee: 145 km (90 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 88.60 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1975 December 4 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
1975 December 4 - . 20:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 11 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1976-04-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 8467 . COSPAR: 1975-114A. Apogee: 234 km (145 mi). Perigee: 157 km (97 mi). Inclination: 96.30 deg. Period: 88.40 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- KH 9-11 Subsatellite - . Payload: SSF 9 / OPS 5547. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1978-05-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 8468 . COSPAR: 1975-114B. Apogee: 1,558 km (968 mi). Perigee: 236 km (146 mi). Inclination: 96.30 deg. Period: 103.00 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
1975 December 14 - . 05:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 5 - . Payload: DSP Phase 2 s/n 7 / OPS 3165. Mass: 1,040 kg (2,290 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP. Completed Operations Date: 1987-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 8482 . COSPAR: 1975-118A. Apogee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Perigee: 35,671 km (22,164 mi). Inclination: 3.00 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Second generation geosynchronous ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for over twelve years. As of 1982 Dec 16 located at 34.61E drifting at 0.823E degrees per day..
1976 January 15 - . 05:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Helios 2 - .
Mass: 376 kg (828 lb). Nation: Germany.
Agency: DFVLR.
Class: Astronomy.
Type: Solar satellite. Spacecraft: Helios.
USAF Sat Cat: 8582 . COSPAR: 1976-003A.
A Titan HIE carrying a West German Helios payload was successfully launched from LC-41, Eastern Test Range. Solar probe. Solar Orbit (Heliocentric). Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
1976 February 27 - . LV Family: Titan, Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/IUS.
- Interim Upper Stage to be used with the Titan III - .
A joint DOD/NASA study was carried out on the consolidation of expendable launch vehicles during transition to the space shuttle. The study recommended that the Interim Upper Stage, being developed for the space shuttle, be used with the Titan III during the transition period.
1976 March 15 - . 01:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- LES 8 - .
Mass: 454 kg (1,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES.
Completed Operations Date: 1992-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 8746 . COSPAR: 1976-023A. Apogee: 35,835 km (22,266 mi). Perigee: 35,728 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 11.40 deg. Period: 1,435.80 min.
A Titan IIIC carrying a Space Test Program payload, Flight P74-1, was successfully launched from LC-40, Eastern Test Range. Flight P74-1 was made up of Lincoln Experimental Satellite 8 and 9 (LES 8/9) and Solar Radiation satellites 11A and B (SOLRAD 11A/B). Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication. Also tested pulsed plasma engines. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 1976-77; over the Americas at 106-110 deg W in 1978-1986; over the Atlantic Ocean 60-70 deg W in 1987-1991;over the Americas at 94-106 deg W in 1991-1992. As of 6 September 2001 located at 105.16 deg W drifting at 0.010 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 107.51W drifting at 0.001E degrees per day.
- LES 9 - .
Mass: 454 kg (1,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: LES.
Completed Operations Date: 1992-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 8747 . COSPAR: 1976-023B. Apogee: 35,825 km (22,260 mi). Perigee: 35,745 km (22,210 mi). Inclination: 17.00 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication. Also tested pulsed plasma engines. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 30-40 deg W in 1976-78; over the Americas at 90-100 deg W in 1980-81; over the Americas at 100-106 deg W in 1981-1990; over the Atlantic Ocean 10 deg W in 1991; over the Americas at 105 deg W in 1992-on. As of 1 September 2001 located at 103.85 deg W drifting at 0.023 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 107.07W drifting at 0.018W degrees per day.
- Solrad 11A - . Mass: 181 kg (399 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Astronomy. Type: Solar satellite. Spacecraft: Solrad. USAF Sat Cat: 8748 . COSPAR: 1976-023C. Apogee: 119,180 km (74,050 mi). Perigee: 118,383 km (73,559 mi). Inclination: 25.70 deg. Period: 7,344.30 min. Solar radiation data. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
- Solrad 11B - . Mass: 181 kg (399 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Astronomy. Type: Solar satellite. Spacecraft: Solrad. USAF Sat Cat: 8749 . COSPAR: 1976-023D. Apogee: 116,645 km (72,479 mi). Perigee: 115,720 km (71,900 mi). Inclination: 25.60 deg. Period: 7,116.70 min. Solar radiation data. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1976 March 22 - . 18:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 7600 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 46 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1976-05-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 8770 . COSPAR: 1976-027A. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 125 km (77 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 89.30 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1976 June 2 - . 20:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- SDS no. 1 - . Payload: SDS no. 1 / OPS 7837. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 8871 . COSPAR: 1976-050A. Apogee: 39,315 km (24,429 mi). Perigee: 380 km (230 mi). Inclination: 63.30 deg. Period: 703.80 min.
1976 June 26 - . 03:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 6 - .
Payload: DSP Phase 2 s/n 8 / OPS 2112. Mass: 1,040 kg (2,290 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1984-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 8916 . COSPAR: 1976-059A. Apogee: 35,860 km (22,280 mi). Perigee: 35,620 km (22,130 mi). Inclination: 0.50 deg. Period: 1,433.30 min.
Second generation geosynchronous ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for over eight years. Positioned over the Atlantic Ocean from 1976 to 1981: at 35 deg W in 1976-1977; at 65 deg W in 1977-1979; and 35 deg W in 1979-1980; and 65 deg W in 1980-1981. Then moved over the Pacific Ocean at 125 deg W, then 140 deg W in 1981-1982; then over the Indian Ocean at 75 deg E in 1982-1984.
1976 June 28 - . 02:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 395-C. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- ITF-1 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,300 km (800 mi). Last launch of a Titan II ICBM (first West Coast launch on 16 February 1963). Demonstrated new Universal Space Guidance System for launch vehicle variant..
1976 June 30 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Improved injector for the Titan IIIC Transtage. - . A contract for the development of an improved injector for the Titan IIIC Transtage was distributed to the Aerojet Liquid Rocket Company; it carried a target price of $4.82 million..
1976 July 2 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for Titan III launch services. - . A contract was distributed to Martin Marietta for Titan III launch services from July 1976 to September 1978; the value of the contract was $80.47 million..
1976 July 8 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 12 - . Mass: 13,000 kg (28,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1976-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 9006 . COSPAR: 1976-065A. Apogee: 242 km (150 mi). Perigee: 159 km (98 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 88.50 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- SESP 74-2 - . Payload: P 74-2 / OPS 3986. Mass: 260 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft: SESP. Decay Date: 1986-04-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 9007 . COSPAR: 1976-065B. Apogee: 8,048 km (5,000 mi). Perigee: 236 km (146 mi). Inclination: 97.50 deg. Period: 179.00 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 5366 - . Payload: SSF-D No. 1. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 9008 . COSPAR: 1976-065C. Apogee: 632 km (392 mi). Perigee: 628 km (390 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 97.30 min. Radar monitoring..
1976 July 23 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for five sets of Titan III solid rocket motors. - . A contract was distributed to Chemical Systems Division of United Technologies Corporation for five sets of Titan III solid rocket motors to be delivered at a price of $50.31 million..
1976 August 6 - . 22:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- SDS no. 2 - . Payload: SDS no. 2 / OPS 7940. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 9270 . COSPAR: 1976-080A. Apogee: 39,315 km (24,429 mi). Perigee: 380 km (230 mi). Inclination: 63.30 deg. Period: 703.80 min. Satellite Data Systems 2..
1976 September 3 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Contract for validation phase of the Interim Upper Stage. - . A contract was distributed to the Boeing Aerospace Company for the validation phase of the Interim Upper Stage development program. The contract carried a target price of $21 million..
1976 September 15 - . 18:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 8533 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 47 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1976-11-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 9426 . COSPAR: 1976-094A. Apogee: 337 km (209 mi). Perigee: 142 km (88 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 89.20 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1976 October 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for three Transtage engines and ten sets of Titan III Stage I and Stage II engines. - . A contract was distributed to Aerojet Liquid Rocket Company for three Transtage engines and ten sets of Titan III Stage I and Stage II engines, to be delivered at a price of $36.57 million..
1976 Dec - . LV Family: Titan, Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC, Shuttle.
- Process selected for manufacturing hydrazine fuels for the Titan III and the space shuttle. - . SAMSO selected the Sisler process as the best of three competing methods for manufacturing hydrazine fuels for the Titan III and the space shuttle..
1976 December 3 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Negotiations for eight new Titan III launch vehicles. - . Negotiations were completed between SAMSO and Martin Marietta for procurement of eight new Titan III launch vehicles.These were to be delivered by 30 September 1980 at a price of $79.35 million..
1976 December 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Three Titan IIIC payload fairings contracted - . SAMSO completed negotiations with McDonnell Douglas for the procurement of three Titan IIIC payload fairings at a price of $3.25 million..
1976 December 19 - . 18:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-11 no. 1 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 1 / OPS 5705. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. Decay Date: 1979-01-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 9627 . COSPAR: 1976-125A. Apogee: 531 km (329 mi). Perigee: 246 km (152 mi). Inclination: 96.90 deg. Period: 92.30 min. KH-11 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1977 Jan - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for three payload fairings for Titan IIIC. - . The McDonnell Douglas Astronautics Company went on contract to provide three payload fairings for the Titan IIIC..
1977 February 6 - . 06:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 7 - . Payload: DSP Phase 2 s/n 9 / OPS 3151. Mass: 1,040 kg (2,290 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP. Completed Operations Date: 1984-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 9803 . COSPAR: 1977-007A. Apogee: 35,860 km (22,280 mi). Perigee: 35,620 km (22,130 mi). Inclination: 0.50 deg. Period: 1,433.30 min. Second generation geosynchronous ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for nearly seven years. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 135 deg W in 1977-1979; over the Indian Ocean 70 deg E in 1979-1984..
1977 March 13 - . 18:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 4915 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 48 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1977-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 9863 . COSPAR: 1977-019A. Apogee: 329 km (204 mi). Perigee: 141 km (87 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 89.10 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1977 May 12 - . 14:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- DSCS II-07 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-7 / OPS 9437. Mass: 565 kg (1,245 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1981-12-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 10000 . COSPAR: 1977-034A. Apogee: 36,894 km (22,924 mi). Perigee: 36,759 km (22,840 mi). Inclination: 15.80 deg. Period: 1,489.60 min.
A Titan IIIC launched a pair of DSCS II satellites into orbit from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 12 deg W in 1977-1979; over the Atlantic Ocean 5 deg W in 1979; over the Pacific Ocean 140 deg E in 1980-1981 As of 28 August 2001 located at 152.07 deg W drifting at 12.959 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 47.37W drifting at 12.959W degrees per day.
- DSCS II-08 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-8 / OPS 9438. Mass: 565 kg (1,245 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1990-02-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 10001 . COSPAR: 1977-034B. Apogee: 37,343 km (23,203 mi). Perigee: 37,061 km (23,028 mi). Inclination: 15.50 deg. Period: 1,509.00 min.
A Titan IIIC launched a pair of DSCS II satellites into orbit from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 175 deg E in 1977-1979 over the Atlantic Ocean 12 deg W in 1979-80 over the Pacific Ocean 175 deg E in 1980-1983 over the Pacific Ocean180 deg E in 1983-1986 over the Atlantic Ocean 1 deg W in 1986-1989 As of 3 September 2001 located at 143.55 deg W drifting at 17.451 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 13.13E drifting at 17.445W degrees per day.
1977 Jun - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Contract for five sets of solid rocket motors for the Titan III. - . Chemical Systems Division of United Technologies Corporation went on contract to provide five sets of solid rocket motors for the Titan III..
1977 June 10 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS 85-second test firing. - . A rocket nozzle for the IUS was subjected to an 85 second test firing at the Rocket Propulsion Laboratory. The test was successful. A second successful test took place on 15 July..
1977 June 20 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Titan 34D/IUS launch vehicle begun. - . HQ USAF directed AFSC to begin developing the Titan 34D/IUS launch vehicle..
1977 June 27 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 13 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1977-12-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 10111 . COSPAR: 1977-056A. Apogee: 239 km (148 mi). Perigee: 155 km (96 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 88.50 min. KH-9 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1977 August 20 - . 14:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Voyager 2 - .
Payload: Voyager 2 [Star-37E]. Mass: 800 kg (1,760 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL.
Class: Outer planets.
Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft: Voyager.
USAF Sat Cat: 10271 . COSPAR: 1977-076A.
A Titan HIE launched NASA's Voyager I spacecraft from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Jupiter flyby 7/9/79, Saturn flyby 8/26/81, Uranus flyby 1/24/86, Neptune flyby 8/25/89. Solar system escape trajectory. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B).
1977 September 5 - . 12:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIE.
- Voyager 1 - . Payload: Voyager 1 [Star-37E]. Mass: 800 kg (1,760 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL. Class: Outer planets. Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft: Voyager. USAF Sat Cat: 10321 . COSPAR: 1977-084A. A Titan HIE launched NASA's Voyager I spacecraft from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Jupiter flyby 3/5/79, Saturn flyby 11/12/80. Solar system escape trajectory. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1977 September 23 - . 18:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 7471 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 49 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1977-12-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 10374 . COSPAR: 1977-094A. Apogee: 335 km (208 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 89.10 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1977 October 7 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Rocket nozzle for the IUS tested - . A rocket nozzle for the IUS was subjected to a 145 second test firing at the Rocket Propulsion Laboratory. The test was successful..
1977 November 11 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Launch services for Titan III solid rocket motors. - . Chemical Systems Division of United Technologies Corporation was awarded a contract to provide launch services for Titan III solid rocket motors..
1977 November 16 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Launch services for Titan III liquid rocket engines. - . The Aerojet Liquid Rocket Company was awarded a contract to provide launch services for Titan III liquid rocket engines..
1977 December 15 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS program status - . The status of the IUS program was briefed to the Air Force Systems Acquisition Review Council. The Council requested additional information on funding, requirements and costs, and program alternatives.
1977 December 19 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- IUS motor test fired - . A full scale IUS motor was successfully test fired at the Arnold Engineering Development Center..
1978 Jan - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB, Titan 34D.
- Contract for two Titan IIIB and five Titan III 34D - . SAMSO awarded a contract to Martin Marietta for the production of two Titan IIIB airframes and five Titan III 34D airframes..
1978 February 25 - . 05:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- Jumpseat 5 - . Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Jumpseat. USAF Sat Cat: 10688 . COSPAR: 1978-021A. Apogee: 39,377 km (24,467 mi). Perigee: 311 km (193 mi). Inclination: 63.20 deg. Period: 703.70 min. Or Quasar..
1978 March 16 - . 18:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 14 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1978-09-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 10733 . COSPAR: 1978-029A. Apogee: 240 km (140 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 88.50 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 7858 - . Payload: SSF-D No. 2. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 10734 . COSPAR: 1978-029B. Apogee: 645 km (400 mi). Perigee: 639 km (397 mi). Inclination: 95.80 deg. Period: 97.60 min. Radar monitoring..
1978 March 25 - . 18:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC. FAILURE: Second stage hydraulic pump failure.. Failed Stage: 2.
- DSCS II-09 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-9. Mass: 550 kg (1,210 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Decay Date: 1978-03-25 .
A Titan IIIC was launched from Cape Canaveral carrying DSCS II satellites F-9 and F-10. The vehicle suffered a failure in its second stage hydraulic system about eight minutes after liftoff, and both the vehicle and its payload were lost. Launched with DSCS F10.
- DSCS II F-10 - . Payload: DSCS II F-10. Mass: 562 kg (1,238 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Program: DSCS. Spacecraft: DSCS II. A Titan IIIC was launched from Cape Canaveral carrying DSCS II satellites F-9 and F-10. The vehicle suffered a failure in its second stage hydraulic system about eight minutes after liftoff, and both the vehicle and its payload were lost. .
1978 April 6 - . LV Family: Titan, Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Titan III 34D/IUS not to be used as backup for launch of a Tracking and Data Relay Satellite. - . Spacecraft: TDRS. NASA withdrew its requirement for a Titan III 34D/IUS to be used as backup for a space shuttle launch of a Tracking and Data Relay Satellite in 1980..
1978 April 21 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Cost growth in the Titan III 34D/IUS development program. - . SAMSO representatives briefed HQ AFSC officials on possible alternatives to deal with the cost growth problem in the Titan III 34D/IUS development program..
1978 May 2 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Report on Titan IIIC launch failure of 25 March 1978. - . Spacecraft: DSCS II. The AFSC Missile Mishap Investigation Board, investigating the failure of a Titan IIIC launch of DSCS II satellites on 25 March, submitted its final report..
1978 June 6 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral, Vandenberg. LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Radio guidance for Titan 34D. - .
SAMSO was authorized by the Office of the Secretary of the Air Force to develop a radio guidance system for Titan III34Ds launched from Vandenberg instead of the IUS inertial guidance system. This program change would reduce development costs for the Titan III34D program.
1978 June 10 - . 19:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Chalet 1 - . Payload: Chalet 1 (Vortex 1) / OPS 9454. Mass: 820 kg (1,800 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Chalet. USAF Sat Cat: 10941 . COSPAR: 1978-058A. Apogee: 42,039 km (26,121 mi). Perigee: 29,929 km (18,596 mi). Inclination: 12.00 deg. Period: 1,446.30 min. First launch of the heavier, mored advanced CHALET ELINT satellites. (the project was renamed VORTEX when the code name CHALET appeared in the New York Times)..
1978 June 14 - . 18:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-11 no. 2 - .
Payload: KH-11 no. 2 / OPS 4515. Mass: 13,000 kg (28,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: CIA,
NRO.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11.
Decay Date: 1981-08-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 10947 . COSPAR: 1978-060A. Apogee: 509 km (316 mi). Perigee: 223 km (138 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 91.90 min.
SAMSO held a successful preliminary design review with Martin Marietta on the radio guidance system equipment for Titan III34Ds launched from Vandenberg AFB. KH-11 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1978 Jul - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Improved transtage injectors. - . Aerojet Liquid Rocket Company delivered the first three Titan IIIC Transtage engines fitted with improved transtage injectors..
1978 August 5 - . 05:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- SDS no. 3 - . Payload: SDS no. 3 / OPS 7310. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. Decay Date: 2001-02-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 10993 . COSPAR: 1978-075A. Apogee: 39,053 km (24,266 mi). Perigee: 315 km (195 mi). Inclination: 62.50 deg. Period: 697.10 min. Or Jumpseat..
1978 August 24 - . Launch Site: McConnell AFB. Launch Complex: McConnell AFB. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Accident at Titan 2 Silo kills 2 and injures 25 - . Nation: USA. Large scale oxidizer spill during fueling operation caused extensive damage to the silo and resulted in death and injuries. Repairs were started but the silo complex was never returned to alert status..
1978 September 18 - . LV Family: Titan, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Minuteman 3, Titan 2.
- Minuteman restructured communications program. - . Minuteman Program Management Directive 0-02047(26) and Titan PMD X-08071(l) provided direction for a restructured command and control communications integration program..
1978 September 26 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Production of a new rocket motor test set for the Titan III. - . SAMSO initiated production of a new rocket motor test set for the Titan III. The rocket motor test set was developed by Chemical Systems Division..
1978 Oct - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III launch support - . SAMSO awarded a contract for Titan III launch support to Martin Marietta's Denver Division..
1978 November 2 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- Critical design review of Titan III 34D structures - . SAMSO held a successful critical design review of Titan III 34D structures with Martin Marietta..
1978 November 10 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- Titan 34D launch facilities at Cape Canaveral. - . Design work was completed on Titan III 34D launch facilities at Cape Canaveral. The design work for east coast facilities was done by the firm of H.J. Ross in Miami, Florida..
1978 November 11 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Titan III ground control computers replaced - . Final checkout of Programmable Aerospace Control Equipment (PACE) installed at Cape Canaveral took place. PACE was developed by Martin Marietta to replace obsolete Titan III ground control computers..
1978 December 5 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- Critical design review of Titan III 34D avionics - . SAMSO held a successful critical design review of Titan III 34D avionics with Martin Marietta..
1978 December 6 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- Critical design review of Titan III 34D ground equipment - . SAMSO held a successful critical design review of Titan III 34D ground equipment with Martin Marietta..
1978 December 14 - . 00:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- DSCS II-11 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-11 / OPS 9441. Mass: 550 kg (1,210 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 11144 . COSPAR: 1978-113A. Apogee: 37,749 km (23,456 mi). Perigee: 37,515 km (23,310 mi). Inclination: 9.80 deg. Period: 1,531.40 min.
A Titan IIIC was launched from Cape Canaveral carrying DSCS II satellites F-ll and F-12. The vehicle placed the satellites in the proper orbit, and the satellites performed normally once there. They were expected to go into operation in mid-January 1979, at which point the DSCS II system would have a full, four-satellite constellation at its disposal for the first time in its history. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 135 deg W in 1979-1983 over the Pacific Ocean 129 deg W in 1983-1989 As of 5 September 2001 located at 62.62 deg W drifting at 22.467 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 96.59E drifting at 22.469W degrees per day.
- DSCS II-12 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-12 / OPS 9442. Mass: 550 kg (1,210 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-12-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 11145 . COSPAR: 1978-113B. Apogee: 36,332 km (22,575 mi). Perigee: 36,283 km (22,545 mi). Inclination: 9.80 deg. Period: 1,462.80 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 175 deg E in 1979-1981 over the Indian Ocean 66 deg E in 1981-1983 over the Indian Ocean 60 deg E in 1983-1987 over the Pacific Ocean177 deg E in 1988-1989 over the Indian Ocean 71 deg E in 1990-1992 As of 1 September 2001 located at 93.28 deg E drifting at 6.600 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 143.60E drifting at 6.589W degrees per day.
1979 February 13 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle, Titan 34D.
- A Critical Design Review was held for the Inertial Upper Stage. - .
SAMSO felt that the design presented at this Review was not really complete, and it directed the contractor, Boeing, to do further work in the areas of software, rocket motors, and interface with the space shuttle and the Satellite Control Facility. Boeing was to present the results of its efforts at a follow-on design review to be held later in the year.
1979 March 6 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D, Shuttle.
- Improved IUS performance - . A change order was added to the IUS contract, directing the contractor to take various steps to improve the performance of the vehicle.
1979 March 16 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle, Titan 34D.
- Large rocket motor for the Inertial Upper Stage was fired - .
The large rocket motor for the Inertial Upper Stage was test fired at the Arnold Engineering Development Center. The firing lasted 145 seconds and generated more than 50,000 pounds of thrust. This was the first development test firing of the large motor, and it was entirely successful.
1979 March 16 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 15 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1979-09-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 11305 . COSPAR: 1979-025A. Apogee: 258 km (160 mi). Perigee: 170 km (100 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6675 - . Payload: SSF-D No. 3. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 11306 . COSPAR: 1979-025B. Apogee: 628 km (390 mi). Perigee: 621 km (385 mi). Inclination: 95.80 deg. Period: 97.20 min.
1979 May 28 - . 18:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 7164 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 50 / Agena D. Mass: 4,000 kg (8,800 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1979-08-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 11372 . COSPAR: 1979-044A. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 131 km (81 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 88.70 min. KH-8 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1979 June 10 - . 13:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 10 - .
Payload: DSP MOS/PIM s/n 11 / OPS 7484. Mass: 1,170 kg (2,570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1984-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11397 . COSPAR: 1979-053A. Apogee: 35,854 km (22,278 mi). Perigee: 35,712 km (22,190 mi). Inclination: 1.80 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
First Multi-Orbit Satellite / Performance Improvement ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for nearly six years. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 135 deg W in 1979-1982; 85 deg W in 1982-1984; 135 deg W in 1984; 125 deg W in 1985..
1979 June 25 - . LV Family: Shuttle, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Shuttle, Titan 34D.
- First test firing of the small motor for the Inertial Upper Stage . - . The small rocket motor for the Inertial Upper Stage was test fired at the Arnold Engineering Development Center. This was the first development test firing of the small motor..
1979 August 25 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- 5 1/2 segment solid rocket motor test fired - .
Chemical Systems Division of United Technologies Corporation test fired a 5 1/2 segment solid rocket motor at its Coyote Test Facility at San Jose, California. This was the first test of the motor, and it was entirely successful. The 5 1/2 segment motor was to be used with the new Titan III 34D launch vehicle.
1979 October 1 - . 11:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Chalet 2 - . Payload: Chalet 2 (Vortex 2) / OPS 1948. Mass: 820 kg (1,800 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Chalet. USAF Sat Cat: 11558 . COSPAR: 1979-086A. Apogee: 41,497 km (25,784 mi). Perigee: 30,443 km (18,916 mi). Inclination: 7.50 deg. Period: 1,445.50 min. Chalet ELINT satellite..
1979 November 21 - . 21:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- DSCS II-13 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-13 / OPS 9443. Mass: 611 kg (1,347 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1994-07-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 11621 . COSPAR: 1979-098A. Apogee: 37,195 km (23,111 mi). Perigee: 37,104 km (23,055 mi). Inclination: 13.60 deg. Period: 1,506.30 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 12 deg W in 1980-1981; 131 deg W in 1981-1983; 179 deg W in 1983; 175 deg E in 1983-1989;179 deg W in 1989-1993 As of 3 September 2001 located at 21.08 deg E drifting at 16.828 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 37.50W drifting at 16.828W degrees per day.
- DSCS II-14 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-14 / OPS 9444. Mass: 611 kg (1,347 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-06-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 11622 . COSPAR: 1979-098B. Apogee: 36,351 km (22,587 mi). Perigee: 36,316 km (22,565 mi). Inclination: 13.30 deg. Period: 1,464.10 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 66 deg E in 1980-1981; 12 deg W in 1981-1986; 179 deg W in 1986-1990; 174 deg E in 1990; 65 deg E in 1991-1994 As of 31 August 2001 located at 27.01 deg W drifting at 6.916 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 50.79E drifting at 6.926W degrees per day.
1980 February 7 - . 21:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-11 no. 3 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 3 / OPS 2581. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. Decay Date: 1982-10-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 11687 . COSPAR: 1980-010A. Apogee: 498 km (309 mi). Perigee: 220 km (130 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 91.70 min. KH-11 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1980 June 18 - . 18:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 16 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1981-03-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 11850 . COSPAR: 1980-052A. Apogee: 262 km (162 mi). Perigee: 164 km (101 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-9 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 1292 - . Payload: SSF-C No. 6. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 11852 . COSPAR: 1980-052C. Apogee: 1,333 km (828 mi). Perigee: 1,331 km (827 mi). Inclination: 96.60 deg. Period: 112.30 min. ABM monitoring; may or may not have existed!!!..
1980 September 19 - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II.
- Titan 2 explodes in silo. - .
Nation: USA.
An Air Force repairman doing routine maintenance in a Titan II ICBM silo dropped a wrench socket, which rolled off a work platform and fell to the bottom of the silo. The socket struck the missile, causing a leak from a pressurized fuel tank. The missile complex and surrounding areas were evacuated. Eight and a half hours later, the fuel vapors ignited, causing an explosion which killed an Air Force specialist and injured 21 others. The explosion also blew off the 670-tonne reinforced concrete-and-steel silo door and catapulted the warhead 200 m into the air. The silo was later filled in with gravel.
1980 December 13 - . 16:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- SDS no. 4 - . Payload: SDS no. 4 / OPS 5805. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 12093 . COSPAR: 1980-100A. Apogee: 39,130 km (24,310 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 63.80 deg. Period: 697.40 min.
1981 February 28 - . 19:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 1166 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 51 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1981-06-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 12315 . COSPAR: 1981-019A. Apogee: 336 km (208 mi). Perigee: 138 km (85 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 89.30 min. KH-8 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1981 March 16 - . 19:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 11 - .
Payload: DSP MOS/PIM s/n 10 / OPS 7350. Mass: 1,170 kg (2,570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1992-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 12339 . COSPAR: 1981-025A. Apogee: 35,527 km (22,075 mi). Perigee: 35,463 km (22,035 mi). Inclination: 2.00 deg. Period: 1,421.20 min.
Multi-Orbit Satellite / Performance Improvement ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for nearly eleven years. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 69 deg W in 1981-1982; 135 deg W in 1982-1984; 75 deg E in 1984-1985. As of 2003 Mar 6 located at 40.27E drifting at 0.598E degrees per day.
1981 April 24 - . 21:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- Jumpseat 6 - . Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Jumpseat. USAF Sat Cat: 12418 . COSPAR: 1981-038A. Apogee: 708 km (439 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 62.70 deg. Period: 93.00 min. SDS 4 not deployed..
1981 September 3 - . 18:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-11 no. 4 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 4 / OPS 3984. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. Decay Date: 1984-11-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 12799 . COSPAR: 1981-085A. Apogee: 526 km (326 mi). Perigee: 244 km (151 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 92.30 min. KH-11 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1981 October 31 - . 09:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Chalet 3 - . Payload: Chalet 3 (Vortex 3) / OPS 4029. Mass: 820 kg (1,800 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Chalet. USAF Sat Cat: 12930 . COSPAR: 1981-107A. Apogee: 382 km (237 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 29.30 deg. Period: 90.40 min. Chalet ELINT satellite..
1982 January 21 - . 19:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 2849 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 52 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1982-04-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 13040 . COSPAR: 1982-006A. Apogee: 527 km (327 mi). Perigee: 137 km (85 mi). Inclination: 97.30 deg. Period: 91.20 min. Possible test of KH-12 systems. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1982 March 6 - . 19:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- IMEWS 13 - .
Payload: DSP MOS/PIM s/n 13 / OPS 8701. Mass: 1,170 kg (2,570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 13086 . COSPAR: 1982-019A. Apogee: 35,598 km (22,119 mi). Perigee: 35,520 km (22,070 mi). Inclination: 2.00 deg. Period: 1,424.40 min.
Multi-Orbit Satellite / Performance Improvement ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for over sixteen years. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 68 deg W in 1982; 35 deg W in 1983-1988; 165 deg W in 1988-1989; 35 deg W in 1989-1991.
1982 May 11 - . 18:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-9 no. 17 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1982-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 13170 . COSPAR: 1982-041A. Apogee: 262 km (162 mi). Perigee: 177 km (109 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-9 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
- OPS 6553 - . Payload: SSF-D No. 4. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 13172 . COSPAR: 1982-041C. Apogee: 707 km (439 mi). Perigee: 701 km (435 mi). Inclination: 96.00 deg. Period: 98.90 min. Radar monitoring; may or may not have existed!!!..
1982 October 30 - . 04:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/IUS.
- DSCS II-15 - .
Payload: DSCS II F-15. Mass: 562 kg (1,238 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS II.
Completed Operations Date: 1997-05-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 13636 . COSPAR: 1982-106A. Apogee: 37,332 km (23,196 mi). Perigee: 37,277 km (23,162 mi). Inclination: 11.30 deg. Period: 1,514.40 min.
Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 15 deg W in 1983-1987; 66 deg E in 1987; 60 deg E in 1987-1994; 65 deg E in 1994-1997 As of 5 September 2001 located at 114.00 deg W drifting at 18.661 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 172.94E drifting at 18.658W degrees per day. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
- DSCS III-01 - . Payload: DSCS III F-1. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 13637 . COSPAR: 1982-106B. Apogee: 36,171 km (22,475 mi). Perigee: 36,132 km (22,451 mi). Inclination: 8.80 deg. Period: 1,454.80 min. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 105 deg W in 1982-1983; 135 deg W in 1983-1989; 130 deg W in 1989-1999. As of 2006 Sep 9 located at 94.39E drifting at 5.469W degrees per day..
1982 November 17 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- Final launch of a Titan IIID - . Nation: USA. Final launch of a Titan IIID from Vandenberg AFB (first launch on 1 5 June 1971)..
1982 November 17 - . 21:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIID.
- KH-11 no. 5 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 5 / OPS 9627. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. Decay Date: 1985-08-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 13659 . COSPAR: 1982-111A. Apogee: 520 km (320 mi). Perigee: 280 km (170 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 92.60 min. KH-11 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1983 April 15 - . 18:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 2925 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 53 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1983-08-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 14001 . COSPAR: 1983-032A. Apogee: 305 km (189 mi). Perigee: 131 km (81 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1983 June 20 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- First of seven Titan 34D launches - . Nation: USA. First of seven Titan 34D launches from the West Coast..
1983 June 20 - . 18:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- KH-9 no. 18 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1984-03-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 14137 . COSPAR: 1983-060A. Apogee: 259 km (160 mi). Perigee: 159 km (98 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-9 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
- OPS 3899 - . Payload: SSF-C No. 7. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 14139 . COSPAR: 1983-060C. Apogee: 1,296 km (805 mi). Perigee: 1,278 km (794 mi). Inclination: 96.60 deg. Period: 111.31 min. ABM monitoring; may or may not have existed!!!. .
1983 July 31 - . 15:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- Jumpseat 7 - . Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Jumpseat. USAF Sat Cat: 14237 . COSPAR: 1983-078A. Apogee: 39,321 km (24,432 mi). Perigee: 1,028 km (638 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 717.10 min. Or Quasar.
1984 January 31 - . 03:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/Transtage.
- Chalet 4 - . Payload: OPS 0441. Mass: 1,043 kg (2,299 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Chalet. USAF Sat Cat: 14675 . COSPAR: 1984-009A. Apogee: 1,023 km (635 mi). Perigee: 146 km (90 mi). Inclination: 29.40 deg. Period: 96.40 min. Chalet ELINT satellite..
1984 April 14 - . 16:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/Transtage.
- DSP - .
Payload: DSP MOS/PIM s/n 12 / OPS 7641. Mass: 1,170 kg (2,570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 2002-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 14930 . COSPAR: 1984-037A. Apogee: 35,530 km (22,070 mi). Perigee: 35,530 km (22,070 mi). Inclination: 1.30 deg. Period: 1,423.00 min.
Multi-Orbit Satellite / Performance Improvement ballistic missile launch detection satellite, remained in service for nearly eighteen years. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 135 deg W in 1984-1985; 65 deg E in 1985-1988; as of 31 December 1990 at 99.16 deg W drifting at 0.050 deg W per day.
1984 April 17 - . 18:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 24B.
- OPS 8424 - . Payload: KH-8 no. 54 / Agena D. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-8. Decay Date: 1984-08-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 14935 . COSPAR: 1984-039A. Apogee: 311 km (193 mi). Perigee: 127 km (78 mi). Inclination: 96.40 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-8 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1984 June 25 - . 18:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- USA 2 - . Payload: KH-9 no. 19. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1984-10-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 15063 . COSPAR: 1984-065A. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 170 km (100 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 88.50 min. KH-9 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
- USA 3 - . Payload: SSF-D No. 5. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. USAF Sat Cat: 15071 . COSPAR: 1984-065C. Apogee: 710 km (440 mi). Perigee: 690 km (420 mi). Inclination: 96.10 deg. Period: 98.80 min. Radar monitoring..
1984 August 28 - . 18:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- USA 4 - . Payload: SDS no. 5. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: SDS. USAF Sat Cat: 15226 . COSPAR: 1984-091A. Apogee: 39,975 km (24,839 mi). Perigee: 380 km (230 mi). Inclination: 63.30 deg. Period: 717.80 min. Satellite Data Systems 2..
1984 December 4 - . 18:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- USA 6 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 6. Mass: 13,000 kg (28,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. Decay Date: 1990-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 15423 . COSPAR: 1984-122A. Apogee: 650 km (400 mi). Perigee: 300 km (180 mi). Inclination: 97.10 deg. Period: 93.50 min. KH-11 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1984 December 22 - . 00:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/Transtage.
- USA 7 - .
Payload: DSP Phase 2 Upgrade s/n 6R. Mass: 1,670 kg (3,680 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1994-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 15453 . COSPAR: 1984-129A. Apogee: 35,915 km (22,316 mi). Perigee: 35,619 km (22,132 mi). Inclination: 3.40 deg. Period: 1,445.80 min.
Reserve Phase 2 DSP ballistic missile launch detection satellite fitted with Block 14 sensors, remained in service for nearly eighteen years. Observed Scud launches during Gulf War. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 155 deg W in 1985-1988; 65 deg E in 1988-1991; 145 deg E in 1991-1992; 105 deg E in 1992-1993; 5 deg E in 1993-1994.
1985 February 8 - . 06:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- USA 9 - . Payload: SDS no. 6. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: SDS. USAF Sat Cat: 15546 . COSPAR: 1985-014A. Apogee: 39,775 km (24,714 mi). Perigee: 400 km (240 mi). Inclination: 63.00 deg. Period: 717.80 min. Satellite Data Systems 2..
1985 August 28 - . 21:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D. FAILURE: Stage 1 propellant feed system failure forced premature engine shutdown.. Failed Stage: 1.
- KH-11 no. 7 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 7. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. Decay Date: 1985-08-28 . KH-11 type satellite..
1986 April 18 - . 17:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D. FAILURE: SRM case insulation burned through, causing case burn-through and catastrophic explosion over pad at T+8.5 seconds.. Failed Stage: 0.
- KH-9 no. 20 - . Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-9. Decay Date: 1986-04-18 . KH-9 type satellite..
- SRV-1 - . Payload: SRV-1. Mass: 11,400 kg (25,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: KH-9.
- SRV-4 - . Payload: SRV-4. Mass: 11,400 kg (25,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: KH-9.
- SRV-3 - . Payload: SRV-3. Mass: 11,400 kg (25,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: KH-9.
- SSF-D No. 6 - . Payload: SSF-D No. 6. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1986-04-18 .
- SRV-2 - . Payload: SRV-2. Mass: 11,400 kg (25,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: KH-9.
1987 February 11 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIB.
- Last launch of the Titan IIIB/Agena - . Nation: USA. Last launch of the Titan IIIB/Agena (first launch on 29 July 1966)..
1987 February 12 - . 06:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34B.
- USA 21 - . Payload: SDS no. 7. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 17506 . COSPAR: 1987-015A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 610 km (370 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
1987 October 26 - . 21:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- USA 27 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 8. Mass: 13,300 kg (29,300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. Decay Date: 1992-05-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 18441 . COSPAR: 1987-090A. Apogee: 1,029 km (639 mi). Perigee: 153 km (95 mi). Inclination: 97.80 deg. Period: 96.50 min. KH-11 type satellite. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1987 November 29 - . 03:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/Transtage.
- USA 28 - .
Payload: DSP Phase 2 Upgrade s/n 5R. Mass: 1,670 kg (3,680 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
Completed Operations Date: 1987-12-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 18583 . COSPAR: 1987-097A. Apogee: 35,558 km (22,094 mi). Perigee: 35,514 km (22,067 mi). Inclination: 2.90 deg. Period: 1,423.30 min.
Reserve DSP ballistic missile launch detection satellite fitted with Block 14 sensors, remained in service for only five years.. Observed Scud launches during Gulf War. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 35 deg W in 1988-1989; 10 deg E in 1989-1992; 35 deg W in 1992-1993; 105 deg E in 1993; 165 deg W in 1999.
1988 September 2 - . 12:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/Transtage. FAILURE: Broken Transtage pressurization feed lines prevented the geosynchronous orbit apogee burn from taking place.. Failed Stage: U.
- USA 31 - . Payload: Chalet 5. Mass: 1,045 kg (2,303 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Chalet. USAF Sat Cat: 19458 . COSPAR: 1988-077A. Apogee: 14,103 km (8,763 mi). Perigee: 151 km (93 mi). Inclination: 29.30 deg. Period: 99.80 min. Chalet ELINT satellite; upper stage failure left in lower than planned orbit..
1988 September 5 - . 09:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- USA 32 - . Payload: SBWASS R1. Mass: 1,700 kg (3,700 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Singleton. USAF Sat Cat: 19460 . COSPAR: 1988-078A. Apogee: 292 km (181 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 85.00 deg. Period: 89.30 min. New class of signals intelligence satellite; possibly some kind of imaging also done. On-board propulsion boosts spacecraft to 800 km operating orbit. First Titan 2 standard launch vehicle launch..
1988 November 6 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- Final Titan 34D launch from Vandenberg AFB - . Nation: USA. Final Titan 34D launch from Vandenberg AFB (first launch on 20 June 1983)..
1988 November 6 - . 18:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D.
- USA 33 - . Payload: KH-11 no. 9. Mass: 13,500 kg (29,700 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: KH-11. USAF Sat Cat: 19625 . COSPAR: 1988-099A. Apogee: 1,012 km (628 mi). Perigee: 156 km (96 mi). Inclination: 97.90 deg. Period: 96.40 min. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1989 May 10 - . 19:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/Transtage.
- USA 37 - . Payload: Chalet 6. Mass: 1,045 kg (2,303 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Chalet. USAF Sat Cat: 19976 . COSPAR: 1989-035A. Apogee: 40,073 km (24,900 mi). Perigee: 455 km (282 mi). Inclination: 27.50 deg. Period: 720.00 min. Chalet ELINT satellite..
1989 June 14 - . 13:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402A/IUS.
- USA 39 - .
Payload: DSP-1 Block 14 F14. Mass: 2,360 kg (5,200 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 20066 . COSPAR: 1989-046A. Apogee: 35,614 km (22,129 mi). Perigee: 35,699 km (22,182 mi). Inclination: 3.10 deg. Period: 1,421.80 min.
First DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite; first Titan 4 launch. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 165 deg W in 1990-1994; 145 deg W in 1999; 166 deg W in 2000.. Still in service as of March 2007. As of 2007 Feb 5 located at 145.23W drifting at 0.014W degrees per day.
1989 September 4 - . 05:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 34D/Transtage.
- USA 43 - . Payload: DSCS II F-16. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 20202 . COSPAR: 1989-069A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 6.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit; at 57 deg E in 1995..
- USA 44 - . Payload: DSCS III F-4. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 20203 . COSPAR: 1989-069B. Apogee: 35,808 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 5.00 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit; at 60 deg E in 1995..
1989 September 6 - . 01:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- USA 45 - . Payload: SBWASS R2. Mass: 1,700 kg (3,700 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Singleton. USAF Sat Cat: 20220 . COSPAR: 1989-072A. Signals intelligence. Reentered from initial parking orbit of 200 km after failure of on-board boost motor..
1990 January 1 - . 00:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Commercial Titan 3.
- Skynet 4A - .
Payload: Skynet 4A [PAM-D2] / JCSat 2 [Orbus-7S]. Mass: 1,463 kg (3,225 lb). Nation: UK.
Agency: MoD.
Program: Skynet.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: ECS/OTS.
USAF Sat Cat: 20401 . COSPAR: 1990-001A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 5.50 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
British military communications; 6 deg E. Military communications. Expected life approx 7 years. Owner/operator: Ministry of Defence, Main Building, Whitehall, London SW1A 2HB. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 6 deg E in 1990; 29 deg E in 1991; 65 deg E in 1991; 34 deg W in 1992-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 34.01 deg W drifting at 0.003 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 63.46W drifting at 4.595W degrees per day.
- JCSAT 2 - .
Payload: JCSat 2 / Orbus-7S. Mass: 2,280 kg (5,020 lb). Nation: Japan.
Agency: JCSAT.
Program: JCSAT.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 393.
USAF Sat Cat: 20402 . COSPAR: 1990-001B. Apogee: 35,877 km (22,292 mi). Perigee: 35,868 km (22,287 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,440.50 min.
Japanese domestic communications; 154 deg E. Domestic communications. Launching organization Martin Marietta. Launch time 0007 GMT. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 154 deg E in 1990-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 154.04 deg E drifting at 0.006 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 116.78W drifting at 6.255W degrees per day.
1990 March 14 - . 11:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Commercial Titan 3. FAILURE: Second stage failed to separate due to a wiring error in the stage separation electronics, stranding the payload in low earth orbit.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Intelsat 6 F-3 - .
Payload: Intelsat 603 / Orbus-21S. Mass: 4,215 kg (9,292 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: INTELSAT.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 393.
USAF Sat Cat: 20523 . COSPAR: 1990-021A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
38 C-band and 10 Ku-band transponders. Placed in unusable low earth orbit after second stage separation failure. In May 1992 shuttle STS-49 snared the satellite, and in three EVA's the crew attached a new perigee boost motor, which then reboosted the satellite to geosynchrounous orbit. Positioned at 34 deg W in 1992-1997; 24 deg W in 1997-2001. Later assigned to Intelsat spin-off New Skies, which positioned it at 340º East, from where it provided C-band coverage of the entire Atlantic region, including virtually all of Latin America, Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and the eastern half of North America. As an inclined orbit satellite, IS-603 was best suited for voice/data trunking and video contribution, but could also be used for carrier-scale IP services, notably network bridging and expansion. It supplemented the prime Atlantic region coverage provided by the station-kept NSS 7 satellite, located at 338º East. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 19.96W drifting at 0.012W degrees per day.
1990 June 8 - . 05:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 405A.
- USA 59 - . Payload: Intruder 1. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 20641 . COSPAR: 1990-050A. Apogee: 284 km (176 mi). Perigee: 268 km (166 mi). Inclination: 61.00 deg. Period: 90.00 min. First launch by Titan 4 of new generation of NOSS naval reconnaissance satellites. However earlier NOSS weighed only 2,000 kg; Titan 4 booster has seven times this capacity. What else was launched?.
- USA 60 - . Payload: Intruder 1. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 20682 . COSPAR: 1990-050B. Apogee: 1,146 km (712 mi). Perigee: 1,071 km (665 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.45 min.
- USA 62 - . Payload: Intruder 1. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 20692 . COSPAR: 1990-050D. Apogee: 1,303 km (810 mi). Perigee: 920 km (572 mi). Inclination: 63.42 deg. Period: 107.44 min.
- USA 61 - . Payload: Intruder 1. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 20691 . COSPAR: 1990-050C. Apogee: 1,304 km (810 mi). Perigee: 920 km (571 mi). Inclination: 63.43 deg. Period: 107.44 min.
1990 June 23 - . 11:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Commercial Titan 3.
- Intelsat 6 F-4 - .
Payload: Intelsat 604 / Orbus-21S. Mass: 4,215 kg (9,292 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: INTELSAT.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 393.
USAF Sat Cat: 20667 . COSPAR: 1990-056A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
International communications; 63 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 38 deg W in 1990; 27 deg W in 1990-1992; 60 deg E in 1992-1999 As of 3 September 2001 located at 60.04 deg E drifting at 0.000 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 61.81E drifting at 6.628W degrees per day.
1990 November 13 - . 00:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402A/IUS.
- USA 65 - . Payload: DSP-1 Block 14 F15. Mass: 2,360 kg (5,200 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP. Completed Operations Date: 2006-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 20929 . COSPAR: 1990-095A. Apogee: 35,699 km (22,182 mi). Perigee: 35,614 km (22,129 mi). Inclination: 3.10 deg. Period: 1,421.80 min. DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 105 deg E in 1991; 70 deg E in 1991-1992; 5 deg E in 1992-1993; 35 deg W in 1993; 38 deg W in 1999-2004. Believed to have been taken out of service in 2006..
1991 March 8 - . 12:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 403A.
- USA 69 - . Payload: Lacrosse 2. Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Manufacturer: Martin. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military Radarsat. Spacecraft: Lacrosse satellite. USAF Sat Cat: 21147 . COSPAR: 1991-017A. Apogee: 662 km (411 mi). Perigee: 420 km (260 mi). Inclination: 68.00 deg. Period: 95.50 min. Still operating December 1997. First West Coast launch of a Titan 4..
1991 November 8 - . 07:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 403A.
- USA 72 - . Payload: Intruder 2. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 21775 . COSPAR: 1991-076A. Apogee: 1,321 km (820 mi). Perigee: 799 km (496 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 106.40 min. Second launch by Titan 4 of new generation of NOSS naval reconnaissance satellites. However earlier NOSS weighed only 2,000 kg; Titan 4 booster has seven times this capacity. What else was launched?.
- USA 77 - . Payload: Intruder 2. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 21809 . COSPAR: 1991-076E. Apogee: 1,270 km (789 mi). Perigee: 954 km (593 mi). Inclination: 63.43 deg. Period: 107.44 min.
- USA 76 - . Payload: Intruder 2. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 21808 . COSPAR: 1991-076D. Apogee: 1,270 km (789 mi). Perigee: 954 km (593 mi). Inclination: 63.43 deg. Period: 107.44 min.
- USA 74 - . Payload: Intruder 2. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 21799 . COSPAR: 1991-076C. Apogee: 1,270 km (789 mi). Perigee: 954 km (593 mi). Inclination: 63.43 deg. Period: 107.44 min.
1992 April 25 - . 08:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- USA 81 - . Payload: SBWASS R3. Mass: 1,700 kg (3,700 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Singleton. USAF Sat Cat: 21949 . COSPAR: 1992-023A. Apogee: 175 km (108 mi). Perigee: 145 km (90 mi). Inclination: 84.90 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Signals intelligence satellite; possibly some kind of imaging also done. On-board propulsion boosts spacecraft to 800 km operating orbit..
1992 September 25 - . 17:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Commercial Titan 3.
- Mars Observer - . Payload: Mars Observer [TOS-21H]. Mass: 2,573 kg (5,672 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL. Class: Mars. Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft: Mars Observer. USAF Sat Cat: 22136 . COSPAR: 1992-063A. Planned Mars orbiter; lost contact during orbit insertion burn. Solar Orbit (Heliocentric). Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1992 November 28 - . 21:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 404A.
- USA 86 - . Payload: EIS-1. Mass: 19,600 kg (43,200 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: EIS. Decay Date: 2000-06-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 22251 . COSPAR: 1992-083A. Apogee: 911 km (566 mi). Perigee: 256 km (159 mi). Inclination: 97.70 deg. Period: 96.40 min. Optical reconnaisance satellite built for the US National Reconnaissance Office..
1993 August 2 - . 19:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 403A. FAILURE: Radial cut inadvertently made in SRM during repairs resulted in explosion of SRM and vehicle at T+101 seconds.. Failed Stage: 0.
- NOSS 19 - . Payload: Intruder 3. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. Decay Date: 1993-08-02 . Apogee: 33 km (20 mi). Third attempted launch by Titan 4 of new generation of NOSS naval reconnaissance satellites. No known launches of this system thereafter..
- SSU - . Payload: Intruder 3. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFMC. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. Apogee: 33 km (20 mi).
- SSU - . Payload: Intruder 3. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFMC. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. Apogee: 33 km (20 mi).
1993 October 5 - . 17:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV. FAILURE: Star-37XFP-ISS kick-motor malfunction.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Landsat 6 - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFMC. Program: Landsat. Class: Earth. Type: Earth resources satellite. Spacecraft: Landsat 6. Decay Date: 1993-05-10 . Apogee: 724 km (449 mi).
1994 January 25 - . 16:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- Clementine 1 - .
Payload: Clementine 1 / DSPSE-ISA [Star-37FM]. Mass: 424 kg (934 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: BMDO.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Clementine.
USAF Sat Cat: 22973 . COSPAR: 1994-004A. Apogee: 409,890 km (254,690 mi). Perigee: 804 km (499 mi). Inclination: 63.80 deg. Period: 16,158.80 min.
SDIO sensor technology demonstration; mapped lunar surface; planned asteroid flyby cancelled due to spacecraft failure. After two Earth flybys, lunar insertion was achieved on February 21. Lunar mapping took place over approximately two months, in two parts. The first part consisted of a 5 hour elliptical polar orbit with a perilune of about 400 km at 28 degrees S latitude. After one month of mapping the orbit was rotated to a perilune of 29 degrees N latitude, where it remained for one more month. This allowed global imaging as well as altimetry coverage from 60 degrees S to 60 degrees N. After leaving lunar orbit, a malfunction in one of the on-board computers on May 7 at 14:39 UTC (9:39 AM EST) caused a thruster to fire until it had used up all of its fuel, leaving the spacecraft spinning at about 80 RPM with no spin control. This made the planned continuation of the mission, a flyby of the near-Earth asteroid Geographos, impossible. The spacecraft remained in geocentric orbit and continued testing the spacecraft components until the end of mission. Additional Details: here....
- ISA - . Payload: ISA. Nation: USA. Agency: BMDO. Class: Technology. Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: ISA Interstage Adapter. Decay Date: 1994-06-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 22987 . COSPAR: 1994-004C. Apogee: 126,958 km (78,887 mi). Perigee: 396 km (246 mi). Inclination: 65.80 deg. Period: 3,075.57 min. ISA (Interstage Adapter) satellite launched with Clementine placed in a highly eccentric Earth orbit. It carried a set of space environment experiments..
1994 February 7 - . 21:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 99 - . Payload: Milstar 1-01 / DFS 1. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Milstar. USAF Sat Cat: 22988 . COSPAR: 1994-009A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,733 km (22,203 mi). Inclination: 12.00 deg. Period: 1,434.00 min. Air Force Space Command launches the first Milstar satellite, a new generation military satellite communications system. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg W in 1994; 120 deg W in 1995-1999..
1994 May 3 - . 15:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 103 - . Payload: Raven 1. Mass: 5,200 kg (11,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval signals intelligence satellite. Spacecraft: Raven satellite. USAF Sat Cat: 23097 . COSPAR: 1994-026A. Apogee: 537 km (333 mi). Perigee: 518 km (321 mi). Inclination: 55.10 deg. Period: 95.20 min. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
1994 August 27 - . 08:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 105 - . Payload: Mercury ELINT 1. Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Mercury ELINT. USAF Sat Cat: 23223 . COSPAR: 1994-054A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. First launch of Mercury ELINT satellite..
1994 December 22 - . 22:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402A/IUS.
- USA 107 - . Payload: DSP-1 Block 14 F17. Mass: 2,360 kg (5,200 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP. USAF Sat Cat: 23435 . COSPAR: 1994-084A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 103 deg E in 1999. Still in service as of March 2007..
1995 May 14 - . 13:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 110 - . Payload: Orion 3. Mass: 5,200 kg (11,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Advanced Orion. USAF Sat Cat: 23567 . COSPAR: 1995-022A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min. First launch of 'Advanced Orion' (real code name unknown) new model geostationary ELINT satellite..
1995 July 10 - . 12:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 112 - . Payload: Raven 2. Mass: 5,200 kg (11,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval signals intelligence satellite. Spacecraft: Raven satellite. USAF Sat Cat: 23609 . COSPAR: 1995-034A. Apogee: 39,000 km (24,000 mi). Perigee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Inclination: 64.00 deg. Period: 720.00 min.
1995 November 6 - . 05:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 115 - . Payload: Milstar DFS 2. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Milstar. USAF Sat Cat: 23712 . COSPAR: 1995-060A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 10.00 deg. Secure military communication. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 4 deg E in 1995-2001. As of 2005 Mar 14 located at 10.26E drifting at 0.012E degrees per day..
1995 December 5 - . 21:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 404A.
- USA 116 - . Payload: EIS-2. Mass: 26,000 kg (57,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: EIS. USAF Sat Cat: 23728 . COSPAR: 1995-066A. Apogee: 976 km (606 mi). Perigee: 250 km (150 mi). Inclination: 98.70 deg. Optical reconnaisance satellite built for the US National Reconnaissance Office. Instruments said to include a large telescope with visual and near infrared wavelength CCD sensors and the ICMS mapping system..
1996 April 24 - . 23:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 118 - . Payload: Mercury ELINT 2. Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Mercury ELINT. USAF Sat Cat: 23855 . COSPAR: 1996-026A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Second launch of Mercury ELINT satellite..
1996 May 12 - . 21:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 403A.
- USA 119 - . Payload: SDS B-2. Mass: 6,300 kg (13,800 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 381 / HS 386. Spacecraft: SDS-2. USAF Sat Cat: 23893 . COSPAR: 1996-029A. Apogee: 1,165 km (723 mi). Perigee: 1,051 km (653 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.44 min. Unknown orbit.
- USA 123 - . Payload: TIPS Ralph. Mass: 54 kg (119 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Technology. Type: Tether technology satellite. Spacecraft: TIPS. USAF Sat Cat: 23936 . COSPAR: 1996-029E. Apogee: 1,032 km (641 mi). Perigee: 1,010 km (620 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. ??? .
- USA 124 - . Payload: TIPS Norton. Mass: 54 kg (119 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Technology. Type: Tether technology satellite. Spacecraft: TIPS. USAF Sat Cat: 23937 . COSPAR: 1996-029F. Apogee: 1,032 km (641 mi). Perigee: 1,010 km (620 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg.
- USA 122 - . Payload: Intruder 4. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 23862 . COSPAR: 1996-029D. Apogee: 1,156 km (718 mi). Perigee: 1,060 km (650 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
- USA 121 - . Payload: Intruder 4. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 23908 . COSPAR: 1996-029C. Apogee: 1,160 km (720 mi). Perigee: 1,055 km (655 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
- USA 120 - . Payload: Intruder 4. Nation: USA. Agency: NRL, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 23907 . COSPAR: 1996-029B. Apogee: 1,157 km (718 mi). Perigee: 1,058 km (657 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
1996 July 3 - . 00:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 405A.
- USA 125 - . Payload: SDS B-4. Mass: 6,300 kg (13,800 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar. USAF Sat Cat: 23945 . COSPAR: 1996-038A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min. Unknown orbit.
1996 December 20 - . 18:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 404A.
- USA 129 - . Payload: EIS-3. Mass: 19,600 kg (43,200 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: EIS. USAF Sat Cat: 24680 . COSPAR: 1996-072A. Apogee: 949 km (589 mi). Perigee: 153 km (95 mi). Inclination: 97.90 deg. Optical reconnaisance satellite built for the US National Reconnaissance Office..
1997 February 23 - . 20:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402B/IUS.
- USA 130 - . Payload: DSP-1 Block 18 F18. Mass: 2,380 kg (5,240 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: TRW. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP. USAF Sat Cat: 24737 . COSPAR: 1997-008A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 70 deg E in 1999. Still in service as of March 2007..
1997 April 4 - . 16:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- USA 131 - . Payload: DMSP 5D-2 F-14. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: RCA. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 24753 . COSPAR: 1997-012A. Apogee: 855 km (531 mi). Perigee: 842 km (523 mi). Inclination: 98.90 deg. Period: 101.90 min.
1997 October 15 - . 08:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401B/Centaur.
- Cassini - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Manufacturer: JPL. Class: Outer planets. Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft: Cassini. USAF Sat Cat: 25008 . COSPAR: 1997-061A. En route Venus.
- Huygens - . Nation: Europe. Agency: NASA Cleveland. Manufacturer: Cannes. Class: Outer planets. Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft: Huygens. USAF Sat Cat: 25009 . COSPAR: 1997-061B. Attached to Cassini.
1997 October 24 - . 02:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 403A.
- USA 133 - . Payload: Lacrosse 3. Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Manufacturer: Martin. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military Radarsat. Spacecraft: Lacrosse satellite. USAF Sat Cat: 25017 . COSPAR: 1997-064A. Apogee: 679 km (421 mi). Perigee: 666 km (413 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Still operating December 1997..
1997 November 8 - . 02:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur.
- USA 136 - . Payload: Raven 3. Mass: 5,200 kg (11,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Manufacturer: Kent. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval signals intelligence satellite. Spacecraft: Raven satellite. USAF Sat Cat: 25034 . COSPAR: 1997-068A. Apogee: 39,059 km (24,270 mi). Perigee: 1,100 km (600 mi). Inclination: 63.60 deg. Period: 720.00 min.
1998 May 9 - . 01:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401B/Centaur.
- USA 139 - . Payload: Orion 4. Mass: 5,200 kg (11,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, NSA. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Advanced Orion. USAF Sat Cat: 25336 . COSPAR: 1998-029A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
1998 May 13 - . 15:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- NOAA 15 - .
Payload: NOAA K. Mass: 3,775 kg (8,322 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Manufacturer: RCA.
Program: Tiros.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N .
USAF Sat Cat: 25338 . COSPAR: 1998-030A. Apogee: 824 km (512 mi). Perigee: 807 km (501 mi). Inclination: 98.70 deg. Period: 101.20 min.
NOAA K carried a new microwave sensor in addition to the standard optical/near-infrared radiometers and imagers and the SARSAT search and rescue package. It was the first NOAA launch to use the Titan 23G launch vehicle, a refurbished ICBM. Titan 23G-12 placed NOAA K into a suborbital trajectory 6 minutes after launch. A Star 37XFP solid motor on the satellite fired at apogee to put NOAA K in orbit.
1998 August 12 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401A/Centaur. FAILURE: Due to guidance system loss of heading after power interrupt, booster pitched over 40 seconds after launch, and was destroyed by range safety.. Failed Stage: G.
- Mercury ELINT - . Payload: Mercury ELINT 3. Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, NSA. Manufacturer: TRW. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Mercury ELINT. Third launch of Mercury ELINT satellite..
1999 April 9 - . 17:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402B/IUS. FAILURE: IUS first and second stages failed to separate.. Failed Stage: U.
- USA 142 - .
Payload: DSP-1 Block 18 F19. Mass: 2,380 kg (5,240 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: TRW.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 25669 . COSPAR: 1999-017A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 720 km (440 mi). Inclination: 28.00 deg.
The Titan 4B placed the IUS upper stages and DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite. payload into a 188 km x 718 km x 28.6 deg parking orbit. The first stage of the IUS burned at 18:14 GMT and put the second stage and payload into a geosynchronous transfer orbit. The IUS second stage fired at 23:34 GMT in order to place the spacecraft in geosynchronous orbit. However, at least one connector remained attached between the stages, and the second stage motor nozzle did not extend properly. When the stage fired, the vehicle tumbled wildly during the burn. Separation of the DSP was achieved. Although it could not perform its primary mission, it did provide a good test case in that the effects of radiation on its systems could be monitored as they underwent twice-daily passages of the Van Allen Radiation Belts. However after some weeks the hydrazine propellant aboard the satellite vented into space due to a broken fuel line. It was believed this had been induced by the wild ride aboard the IUS-2 stage.
1999 April 30 - . 16:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401B/Centaur. FAILURE: Centaur software programming error.. Failed Stage: U.
- USA 143 - .
Payload: Milstar-2 F1 / DFS 3. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Milstar.
USAF Sat Cat: 25724 . COSPAR: 1999-023A. Apogee: 5,149 km (3,199 mi). Perigee: 1,097 km (681 mi). Inclination: 28.20 deg.
The Titan core vehicle operated correctly, but a software error in the Centaur stage resulted in all three planned burns being made at the wrong times, during the first orbit instead of over a six hour period. The three burns planned to place Milstar successively in a 170 x 190 km parking orbit, a geostationary transfer orbit, and finally geosynchronous orbit. Instead, at 19:00 GMT, several hours before the scheduled third burn, Milstar separated into a useless 740 km x 5000 km orbit. Milstar-2 F1 was the first upgraded Milstar with an extra Medium Data Rate payload with a higher throughput. The payload included EHF (44 GHz), SHF (20 GHz) and UHF communications transponders and satellite-to-satellite crosslinks, with narrow beams to avoid jamming.
1999 May 22 - . 09:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 404B.
- USA 144 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Misty.
USAF Sat Cat: 25744 . COSPAR: 1999-028A. Apogee: 3,100 km (1,900 mi). Perigee: 2,700 km (1,600 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg.
This classified National Reconnaissance Office satellite represented the first successful Titan launch in four attempts. The payload had been reported to be a Lacrosse radar imaging reconnaissance satellite. However the short 50 foot Titan fairing was used instead of the 66 foot fairing used by Lacrosse. This only seems to be used previously for an Improved Crystal photo-reconnaissance satellite in November 1992. The payload therefore could be related to the ocean surveillance triplets, or be an Improved CRYSTAL derivative. Veteran amateur satellite-watchers believed it was the second launch of 'Misty', a stealthy optical reconnaisance satellite (the first launch being USA 53 in February 1990).
1999 June 20 - . 02:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- QuikScat - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Manufacturer: Ball.
Class: Earth.
Type: Sea satellite. Spacecraft: BCP-2000.
USAF Sat Cat: 25789 . COSPAR: 1999-034A. Apogee: 802 km (498 mi). Perigee: 802 km (498 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 100.90 min.
NASA's QuikScat carried the SeaWinds scatterometer for remote sensing of ocean winds. The Titan 2's second stage shut down at 02:20 GMT and then coasted to apogee still attached to the QuikScat. The Titan second stage vernier thrusters ignited at apogee to raise perigee, leaving QuikScat in a 280 km x 813 km x 98.7 degree parking orbit. The QuikScat's own hydrazine propulsion system then fired to raise the perigee over a period of weeks.
1999 December 12 - . 17:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- USA 147 - . Payload: DMSP 5D-3 F-15. Mass: 1,154 kg (2,544 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: RCA. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-3. USAF Sat Cat: 25991 . COSPAR: 1999-067A. Apogee: 846 km (525 mi). Perigee: 830 km (510 mi). Inclination: 98.50 deg. Period: 101.70 min. First launch of the Block 5D-3 military weather satellite. Satellite F-15 was placed in an initial suborbital trajectory. The Star 37S kick motor on the satellite fired 13 minutes after launch for orbit insertion..
2000 May 8 - . 16:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402B/IUS.
- USA 149 - .
Payload: DSP-1 Block 18 F20. Mass: 2,380 kg (5,240 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: TRW.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 26356 . COSPAR: 2000-024A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg.
DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite. Delivered by the two-stage IUS-22 solid rocket into geostationary orbit. Fullfilled mission of DSP 19 launched in 1999 into the wrong orbit when its IUS stage failed. Still in service as of March 2007. As of 2005 Apr 2 located at 8.05E drifting at 0.166E degrees per day.
2000 August 17 - . 23:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 403B.
- USA 152 - .
Payload: Onyx F1. Mass: 14,500 kg (31,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Manufacturer: Martin.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military Radarsat. Spacecraft: Lacrosse satellite.
USAF Sat Cat: 26473 . COSPAR: 2000-047A. Apogee: 695 km (432 mi). Perigee: 689 km (428 mi). Inclination: 68.00 deg. Period: 98.53 min.
The National Reconnaissance Office satellite was reported to be an Onyx (formerly Lacrosse) radar imaging spacecraft built by Lockheed Martin. The Titan second stage reached a 572 x 675 km x 68.0 deg orbit and separated from the payload. Amateur observers reported the payload has made two small maneuvers and by Aug 23 was in a 681 x 695 km x 68.1 deg orbit.
2000 September 21 - . 10:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- NOAA 16 - .
Payload: NOAA-L. Mass: 1,476 kg (3,254 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Tiros.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N.
USAF Sat Cat: 26536 . COSPAR: 2000-055A. Apogee: 867 km (539 mi). Perigee: 853 km (530 mi). Inclination: 98.79 deg. Period: 102.06 min.
Launch attempt on September 20 scrubbed. The NOAA polar orbit weather satellite, an Advanced Tiros N with a suite of imaging and sounding instruments. The two-stage Titan II launch vehicle, serial 23G-13, put NOAA-L into a suborbital -2500 x 800 km x 98.0 deg trajectory. The spacecraft's Thiokol Star 37XFP solid motor fired at apogee to circularize the sun-synchronous orbit at 800 km.
2001 February 27 - . 21:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: SLC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401B/Centaur.
- USA 157 - .
Payload: Milstar-2 DFS 4. Mass: 4,670 kg (10,290 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Milstar.
USAF Sat Cat: 26715 . COSPAR: 2001-009A. Apogee: 35,768 km (22,225 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 4.50 deg. Period: 1,435.05 min.
Military Communications satellite. Launch delayed from October 30, December 14, 2000, and February 2 and February 24, 2001. The Milstar DFS 4 satellite (the second Milstar Block 2) provided secure communications for the US Department of Defense, with UHF, EHF and SHF band transmitters. Titan 4B-41 with core stage K-30 took off from Cape Canaveral and placed Milstar and the Centaur TC-22 upper stage in a suborbital trajectory. TC-22 then ignited to enter a 200 km parking orbit, and after two more burns delivered Milstar to geosynchronous drift orbit. Small engines on board the Milstar placed it at its targeted geostationary position. USA 157, a 4.5 tonne spacecraft, was the first in the Milstar 2 series which was capable of higher data rates and was more secure against disabling efforts.
2001 August 6 - . 07:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: SLC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402B/IUS.
- USA 159 - .
Payload: DSP-1 Block 18 F21. Mass: 2,380 kg (5,240 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: TRW.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 26880 . COSPAR: 2001-033A. Apogee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 2.90 deg. Period: 1,435.76 min.
Launch postponed from February, then delayed from July 27. USA 159 was a US Air Force Defense Support Program infrared missile early warning satellite was placed by the Titan core into a 328 x 663 km x 28.7 deg parking orbit. The Boeing IUS-16 upper stage then fired its first solid motor to enter geostationary transfer orbit. The second IUS solid motor fired at around 14:00 GMT placing DSP Flight 21 in near-geosynchronous orbit. Still in service as of March 2007.
2001 October 5 - . 21:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 404B.
- USA 161 - .
Payload: EIS-4. Mass: 16,650 kg (36,700 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: EIS.
USAF Sat Cat: 26934 . COSPAR: 2001-044A. Apogee: 1,050 km (650 mi). Perigee: 150 km (90 mi). Inclination: 97.90 deg.
Launch delayed from September 25, October1. National Reconnaissance Office payload that was placed into a sun-synchronous orbit. It was speculated that the payload was an Improved Crystal imaging satellite. That would imply an operational orbit of 150 x 1050 km x 97.9 deg orbit. The satellite belonged to the National Reconnaissance Office's fleet of Earth Imaging System (EIS) satellites. A BBC website reported a resolution of 10 cm in the images. (A commonly used name for the EIS satellites was Advanced Keyhole.) The first member of the EIS fleet was USA 144 (1999-028A), launched in May 1999.
2002 January 16 - . 00:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: SLC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401B/Centaur.
- USA 164 - .
Payload: Milstar 2-F3 / Milstar FLT-5 / DFS-5. Mass: 4,550 kg (10,030 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Milstar.
USAF Sat Cat: 27168 . COSPAR: 2002-001A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 1.46 deg. Period: 1,436.12 min.
Military Communications satellite. Launch delayed from December 2001. The Titan core stage shut down 9 min after launch on a suborbital trajectory, and separated from the upper stage, Centaur TC-19. TC-19 made three burns to parking orbit, geostationary transfer orbit, and finally geostationary orbit. It then released Milstar Flt-5. Milstar provided secure communications in the EHF, SHF and UHF bands and would be stationed over European longitudes. As of 2007 Feb 16 located at 29.98E drifting at 0.014W degrees per day.
2002 June 24 - . 18:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- NOAA 17 - .
Payload: NOAA-M. Mass: 1,475 kg (3,251 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Tiros.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Tiros N.
USAF Sat Cat: 27453 . COSPAR: 2002-032A. Apogee: 820 km (500 mi). Perigee: 802 km (498 mi). Inclination: 98.40 deg. Period: 101.10 min.
Launch delayed from August 2001. The refurbished Titan 2 missile put the NOAA M satellite on a suborbital trajectory of about -2500 x 820 km x 98 deg. at 1829 UTC. At 1837 UTC the NOAA M propulsion module fired its ATK/Thiokol Star 37XFP solid motor for the orbit insertion burn, followed by a hydrazine trim burn to put the satellite in an 807 x 822 km x 98.8 deg operational orbit. NOAA M became NOAA 17 on entering service with the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as the primary morning weather satellite, supplementing the NOAA 16 afternoon satellite. Built by Lockheed Martin, NOAA M carried weather imagers and microwave and infrared sounders, as well as a SARSAT search-and-rescue package. It had an on-orbit mass of 1475 kg.
2003 January 6 - . 14:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- Coriolis - .
Payload: SA-200HP, P98-2. Mass: 828 kg (1,825 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Gilbert.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: SA-200.
Spacecraft: Coriolis.
USAF Sat Cat: 27640 . COSPAR: 2003-001A. Apogee: 936 km (582 mi). Perigee: 742 km (461 mi). Inclination: 98.74 deg. Period: 101.55 min.
Coriolis was an Air Force Space Test Program three-year meteorological science mission to demonstrate the viability of using polarimetry to measure ocean surface wind speed and direction from space, and to demonstrate predictions of geomagnetic disturbances through continuous observation of Coronal Mass Ejections. Launch delayed from August 22, November 15, December 15, 16, 17 and 18, 2002 and January 5, 2003.
2003 April 8 - . 13:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: SLC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401B/Centaur.
- USA 169 - . Payload: Milstar 6 / Milstar 2-F4. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Lockheed. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Milstar. USAF Sat Cat: 27711 . COSPAR: 2003-012A. Apogee: 35,811 km (22,251 mi). Perigee: 35,762 km (22,221 mi). Inclination: 0.91 deg. Period: 1,436.13 min. Delayed from November 4, 2002, and January 21, February 2 and 4, March 5, 8 and 21, and April 6, 2003. As of 2007 Feb 4 located at 89.84W drifting at 0.014W degrees per day..
2003 September 9 - . 04:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: SLC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 401B/Centaur.
- USA 171 - .
Payload: Orion 5. Mass: 5,200 kg (11,400 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Advanced Orion.
USAF Sat Cat: 27937 . COSPAR: 2003-041A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
American signals intelligence satellite placed into geostationary orbit. It was believed the payload was a successor to the USA-110 and USA-139 satellites launched in May 1995 and May 1998, referred to as 'Advanced ORION' by those not in the know. They were thought to be successors to the RHYOLITE missions of the 1970s. The satellite was originally to have launched April 28, 2002. Launch delayed seven times.
2003 October 18 - . 16:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan II SLV.
- USA 172 - . Payload: DMSP-16. Mass: 1,154 kg (2,544 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-3. USAF Sat Cat: 28054 . COSPAR: 2003-048A. Apogee: 853 km (530 mi). Perigee: 843 km (523 mi). Inclination: 98.90 deg. Period: 101.90 min. Final Titan 2 launch, LV dubbed "Cindy Marie". Originally to have launched January 2001. Launch postponed 12 times due to spacecraft and launch vehicle problems..
2004 February 14 - . 18:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: SLC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 402B/IUS.
- USA 176 - .
Payload: DSP-1 Block 18 F22. Mass: 2,380 kg (5,240 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NSA.
Manufacturer: TRW.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft: DSP.
USAF Sat Cat: 28158 . COSPAR: 2004-004A. Apogee: 36,105 km (22,434 mi). Perigee: 35,852 km (22,277 mi). Inclination: 0.68 deg. Period: 1,445.94 min.
DSP-1 Block 14 ballistic missile launch detection satellite. Last flight of the IUS upper stage. Launch delayed from November 4, 2003, and January 17, 2003. Planned IMEX piggyback payload cancelled. Still in service as of March 2007, expected to remain operational until 2017-2022. As of 2004 Feb 15 located at 96.66W drifting at 2.464W degrees per day.
2005 April 30 - . 00:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: SLC40. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 405B.
- USA 182 - . Mass: 14,500 kg (31,900 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military Radarsat. Spacecraft: Lacrosse satellite. USAF Sat Cat: 28646 . COSPAR: 2005-016A. Apogee: 705 km (438 mi). Perigee: 481 km (298 mi). Inclination: 57.00 deg. Last East Coast Titan launch. Delayed from December 18, 2001; July 3, 2002; October 2004; February 20, April 6, 10 and 11, 2005. Amateur observors believed this to be the fifth in the Lacrosse/Onyx radar spy satellite series built by Lockheed Martin..
2005 October 19 - . 18:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 404B.
- USA 186 - .
Payload: EIS-5 / NROL-20. Mass: 20,000 kg (44,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: EIS.
USAF Sat Cat: 28888 . COSPAR: 2005-042A. Apogee: 1,050 km (650 mi). Perigee: 264 km (164 mi). Inclination: 97.90 deg.
Delayed from 2003; February 2004; and June 30, July 10, September 9, 2005. Last launch of the Titan series put a classified National Reconnaisance Office satellite into polar orbit. Its orbital parameters, as determined by amateur observors, suggested it was an Improved Crystal electronic imaging reconnaissace satellite, replacing USA 129, which was launched in 1996.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use