
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
TACSAT
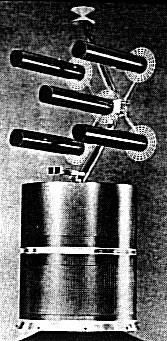 Tacsat Credit: USAF |
Status: Operational 1969. First Launch: 1969-02-09. Last Launch: 1969-02-09. Number: 1 . Gross mass: 730 kg (1,600 lb). Height: 3.40 m (11.10 ft).
As part of an Air Force program aimed at eventual development of a military tactical communications system to complement the IDCSP system, Hughes built the largest experimental communications satellite ever constructed to that time. The mission evaluated the feasibility of using satellite communication repeaters with small surface terminal communication equipment for highly mobile land, sea and air forces. The project was led by the USAF Space and Missile Systems Organization (SAMSO). The satellite featured a then-unique antenna array extending from the top of the drum-shaped spacecraft. The five-element antenna array consisted of UHF antennas, each nearly 2.5 m long. Beneath them were 2 microwave horns. At the extreme top was a biconic horn used for telemetry and command. Technology and concepts originating in this satellite would later make Hughes the leader in commercial communications satellites.
The satellite was spin-stabilized, with the solar panels rotating while the antennas and inner structure remain in a fixed position. The spacecraft was a cylindrical shaped aluminum structure with passive thermal control, spin stabilized (54 rpm) to 0.1 deg using a new gyrostat technique. Body mounted solar cells generated 980 W max and recharged three NiCd batteries of 6 AHr capacity each. The vehicle carried two transponders, one at X-band and one at UHF. The X-band transponder had a bandwidth of 10 MHz and a maximum RF power of 30 watts. The UHF transponder had a bandwidth of 10 MHz and a maximum RF output of 230 watts. Provision was made for cross strapping the UHF and X-band up and downlinks with a reduced usable bandwidth of 425 kHz. Earth coverage horn antennas were used at X-band, bifilar helices were used at UHF.
More at: TACSAT.
Family: Communications technology sat, Geosynchronous orbit, Technology. Country: USA. Launch Vehicles: Titan, Titan IIIC. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral, Cape Canaveral LC41. Agency: USAF SAMSO, Hughes. Bibliography: 2, 405, 6, 13246.
 | Tacsat 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Tacsat 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1967 January 11 - .
- Hughes selected for TACSAT. - .
Spacecraft Bus: HS 308.
Spacecraft: TACSAT.
Space Systems Division selected the Hughes Aircraft Company as the contractor to proceed with research and development of the experimental communications satellite for the U. S. military services. With a target price of $23.5 million, the contract called for design, engineering, assembly, and testing of what became the Tactical Communication Satellite (TACSAT I).
1969 February 9 - . 21:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Tacsat 1 - .
Mass: 730 kg (1,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 308.
Spacecraft: Tacsat.
Completed Operations Date: 1977-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 3691 . COSPAR: 1969-013A. Apogee: 36,044 km (22,396 mi). Perigee: 35,939 km (22,331 mi). Inclination: 1.00 deg. Period: 1,446.60 min.
Air Force Titan IIIC, Vehicle #17, was launched from Cape Canaveral and placed the 1,600-pound experimental Tactical Communications Satellite, TACSAT I, into a near-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 19,300 nautical miles above the equator. TACSAT I, built by Hughes Aircraft Company under SAMSO management, was the largest communications satellite yet launched and placed in orbit by the United States. It was to determine the feasibility of using satellite communications repeaters with small mobile ground tactical communications equipment. In addition, using the technology already developed with earlier Despun Antenna Test System (DATS) and Lincoln Experimental Satellites (LES) test spacecraft, TACSAT I would test the feasibility of satellite communications over great distances while also testing the new gyrostat stabilization system. The satellite could handle transmission of television or multiple telephone/ teletype communications channels. Experimental commsat. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 107 deg W in 1969?-1970; over the Pacific Ocean 173 deg W in 1970; over the Pacific Ocean 179 deg W in 1971-1972; over the Pacific Ocean170 deg E in 1972 Last known longitude (9 June 1995) 176.44 deg E drifting at 0.150 deg E per day.
1970 July 1 - .
- Tactical Satellite Communication (TACSATCOM) reached interim operational capability. - .
Spacecraft Bus: HS 308.
Spacecraft: TACSAT.
Tactical Satellite Communication (TACSATCOM) reached interim operational capability, consisting of the Tactical Communications Satellite (TACSAT I) and the Lincoln Experimental Satellite LES-6. TACSAT I was initially designed to demonstrate the feasibility of handling tactical communications by satellite. The tests had been so successful with both satellites that tri-service traffic was added for relay through the system.
2006 December 16 - . 12:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Wallops Island. Launch Complex: Wallops Island LA0B. LV Family: Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Minotaur 1.
- Tacsat-2 - .
Mass: 370 kg (810 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF RL.
Manufacturer: MicroSats.
Program: Tacsat.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Road Runner.
Spacecraft: Tacsat ORS.
Decay Date: 2011-02-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 29653 . COSPAR: 2006-058A. Apogee: 426 km (264 mi). Perigee: 410 km (250 mi). Inclination: 40.01 deg. Period: 92.93 min.
Tacsat-2 was a prototype rapid development/rapid deployment tactical military satellite that provided American Joint Task Force commanders direct control of a satellite providing both SIGINT and imagery with a resolution of better than 1-m. The known communications payload used an 8 GHz (X-band) downlink. This was the first orbital launch from Wallops Island since 1985. TacSat-2 was to have been launched by a Falcon-1 from Vandenberg into a sun-synchronous orbit. However, the failure of Falcon-1 on its long-delayed maiden in March 2006 caused AFRL to award a new launch contract for TacSat-2 and TacSat-3 to OSC in May 2006. The launch was achieved using OSC's Minotaur launch vehicle only seven months after contract award.
2009 May 19 - . 23:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Wallops Island. Launch Complex: Wallops Island LA0B. LV Family: Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Minotaur 1.
- Tacsat 3 - . Mass: 400 kg (880 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: Tacsat. Class: Technology. Type: Surveillance jtechnology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Road Runner. Spacecraft: Tacsat ORS. Decay Date: 2012-04-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 35001 . COSPAR: 2009-028A. Apogee: 465 km (288 mi). Perigee: 433 km (269 mi). Inclination: 40.50 deg. Period: 93.60 min. USAF experimental imaging satellite..
2011 September 27 - . 15:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Kodiak. LV Family: Peacekeeper. Launch Vehicle: Minotaur IV-Plus.
- Tacsat 4 - .
Mass: 460 kg (1,010 lb). Nation: USA.
Program: Tacsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Road Runner.
Spacecraft: Tacsat ORS.
USAF Sat Cat: 37818 . COSPAR: 2011-052A. Apogee: 12,010 km (7,460 mi). Perigee: 742 km (461 mi). Inclination: 63.60 deg. Period: 238.90 min.
Naval Research Laboratory UHF communications satellite, equipped with a 3.7-meter-diameter communications antenna to support military handheld satellite telephones. Launch used an uprated Minotaur IV with an ATK Star 48V motor replacing the Orion 38 upper stage.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use