
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Redstone
 Redstone Credit: via Andreas Parsch |
AKA: Hermes C;M8;M9;PGM-11;PGM-11A;PTM-11B;SSM-A-14;SSM-G-14. Status: Retired 1967. First Launch: 1953-08-20. Last Launch: 1965-12-01. Number: 53 . Payload: 3,580 kg (7,890 lb). Thrust: 367.50 kN (82,617 lbf). Gross mass: 27,980 kg (61,680 lb). Height: 21.13 m (69.32 ft). Diameter: 1.83 m (6.00 ft). Span: 3.66 m (12.00 ft). Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
In November 1944 the US Army funded General Electric Malta under Project Hermes to develop German rocket technology. The GE team made only desultory progress, and with the outbreak of the Korean War the Army discovered an urgent need to field a ballistic missile. The program was shifted to von Braun's German team in New Mexico in 1950, then in 1951 von Braun's team and the project were shifted to the Redstone Arsenal in Alabama. Von Braun's team completed design of the 400 km (250 mile) range missile in 1952. The Redstone combined proven V-2 technology (aerodynamic fins, exhaust diverters for pitch control, liquid oxygen/alcohol propellant) with some new concepts (inertial navigation, separable warhead). The rocket was powered by a version of the Rocketdyne XLR43-NA-1 engine, an evolution of the V-2's powerplant for the USAF Navaho program. As was von Braun's practice, his team built the prototype rockets, with production being handled by an outside contractor. The first test launch was in August 1953, the first Chrysler production missile flew in July 1956, and Redstone became operational with US Army units in Germany in June 1958. Redstone missiles were used to test technology for von Braun's Jupiter IRBM program, designated Jupiter A and Jupiter C, to the eternal confusion of space journalists. Redstone played a vital role in the space race. A Jupiter C put the first American satellite into orbit in 1958 after the Navy's Vanguard (powered by a GE Malta engine) failed. Redstone was also used to put the first Americans into space on two suborbital Mercury-Redstone missions. The military Redstone was retired in 1964, replaced by the much more operationally suitable solid-propellant Pershing. Surplus missiles were used as anti-ballistic missile targets and transferred to Australia, where they put that country's first satellite into orbit.
Redstone could carry the heavy W-39 4 MT W-39 nuclear warhead to a range of 325 km (175 nm) with a CEP of 300 m (1000 ft). It was certainly capable, as demonstrated by Jupiter A, of carrying lighter military payloads to much greater ranges, but during initial development only the Air Force was allowed to develop long-range missiles. The Redstone's drawback was the extensive logistics required for launch. Although mobile, a Redstone battalion comprised 20 heavy vehicles. After reaching a launch position, it took eight hours to survey the site, assemble the missile, mount it on the launch table, align the inertial navigation system, and check it out for launch. Once a launch order was given, it took another 15 minutes to fill the oxidizer tank with cryogenic liquid oxygen before the launch button could be pushed.
Development Cost $: 92.500 million. Recurring Price $: 4.934 million in 1959 dollars. Flyaway Unit Cost: 1.994 million in 1956 dollars. Maximum range: 320 km (190 mi). Number Standard Warheads: 1. Standard warhead: W39. Warhead yield: 3,750 KT. Boost Propulsion: Liquid rocket, Lox/Kerosene. Maximum speed: 5,650 kph (3,510 mph). Initial Operational Capability: 1958. Total Number Built: 120. Total Development Built: 35. Total Production Built: 85.
Stage Data - Redstone
- Stage 1. 1 x Redstone. Gross Mass: 28,440 kg (62,690 lb). Empty Mass: 3,125 kg (6,889 lb). Thrust (vac): 414.340 kN (93,147 lbf). Isp: 265 sec. Burn time: 155 sec. Isp(sl): 235 sec. Diameter: 1.77 m (5.80 ft). Span: 4.19 m (13.74 ft). Length: 17.58 m (57.67 ft). Propellants: Lox/Alcohol. No Engines: 1. Engine: A-6. Status: Out of Production.
More at: Redstone.
| Juno-1 (5 stage) American orbital launch vehicle variant. |
| Jupiter A American orbital launch vehicle. The Jupiter A was a modified Redstone missile fitted with Jupiter inertial navigation and control system elements. It also tested Hydyne fuel and other engine modifications for the Jupiter C re-entry vehicle test booster. |
| Jupiter C American orbital launch vehicle. Re-entry vehicle test booster and satellite launcher derived from Redstone missile. The Jupiter A version of the Redstone missile was modified with upper stages to test Jupiter re-entry vehicle configurations. Von Braun's team was ordered to ballast the upper stage with sand to prevent any 'inadvertent' artificial satellites from stealing thunder from the official Vanguard program. Korolev's R-7 orbited the first earth satellite instead. The Jupiter C was retroactively named the 'Juno I' by Von Braun's team. |
| Jupiter C Juno I American short range ballistic missile. Four stage orbital launch version consisting of 1 x Redstone + 1 x Cluster stage 2 + 1 x Cluster stage 3 + 1 x RTV Motor. The fourth stage allowed the Explorer payload to be placed into orbit. |
| Redstone MRLV American suborbital launch vehicle. Greatly modified Redstone rocket used to launch the Mercury manned spacecraft on a suborbital trajectory, typically 380 km downrange, 220 km altitude, and a speed of 6800 kph. |
| SPARTA American orbital launch vehicle. Three stage vehicle consisting of 1 x Redstone + 1 x Antares 2 + 1 x BE-3 |
Family: pad-launched, short range ballistic. People: von Braun. Country: USA. Engines: A-6. Spacecraft: Explorer A, Explorer B, Adam, Explorer C, Beacon 1, Mercury, Wresat. Launch Sites: White Sands, Cape Canaveral, Cape Canaveral LC4, Cape Canaveral LC6, Cape Canaveral LC5, San Nicolas, Cape Canaveral LC26A, White Sands LC36, Johnston Island, Johnston Island LC1, Johnston Island LC2, Fort Wingate. Stages: Jupiter C stage. Agency: Chrysler. Bibliography: 126, 17, 18, 2, 222, 26, 281, 366, 45, 483, 563, 59, 6, 86.
 | Redstone Missile Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Redstone Credit: NASA |
 | Wresat launch |
 | Redstone Redstone Day We Launched the Tower Credit: NASA |
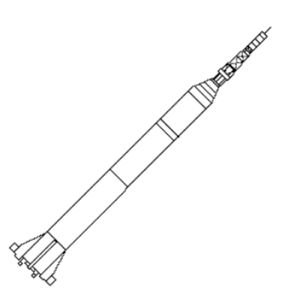 | Mercury Redstone Credit: © Mark Wade |
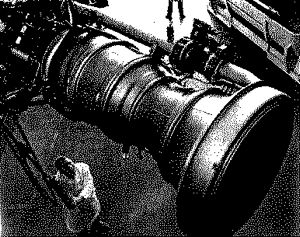 | Redstone engine Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Redstone Adam Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Jupiter C launch Credit: NASA |
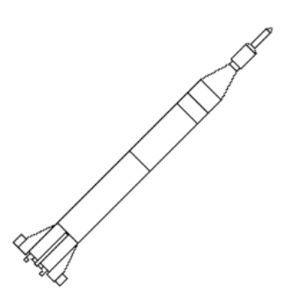 | Jupiter Cc Credit: © Mark Wade |
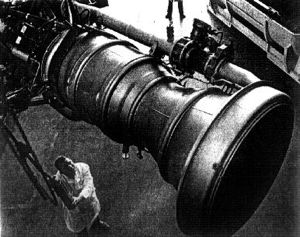 | Redstone engine Credit: NASA |
 | Jupiter C Credit: NASA |
 | Wresat Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Sparta Sparta - COSPAR 1967-118 |
November 1943 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Development of ballistic missiles authorized. - . Nation: Germany. Gen. H. H. Arnold, Chief of Air Staff, directed and authorized emphasis on research, development, and procurement of guided missiles, as indicated by known German advances..
1944 November 20 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Project Hermes - .
Nation: USA.
Ordnance Department entered into a research and development contract with the General Electric Company for study and development of long-range missiles that could be used against ground targets and high-altitude aircraft. This was the beginning of the Hermes project.
1946 June 1 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes C1 - . Nation: USA. General Electric began a feasibility study of the Hermes C1 which later formed the basis for early Redstone missile research..
1947 January 23 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes telemetry system test. - . Nation: USA. Telemetry operated successfully in a V-2 firing at WSPG, Army Ordnance's Hermes telemetry system..
1948 September 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes project extended to cover satellite launch. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: von Braun.
Committee on Guided Missiles of the Research and Development Board approved recommendation that Army Hermes project "be given the task of providing the National Military Establishment with a continuing analysis of the long-range rocket problem as an expansion of their task on an earth satellite vehicle."
1949 June 1 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Redstone Arsenal selected for rocket research. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Redstone Arsenal was reactivated from standby status as the site of the Ordnance Rocket Center..
1949 October 28 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Von Braun team moved to Huntsville. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. The Secretary of the Army approved the transfer of the Ordnance Research and Development Division, Sub-Office (Rocket) at Fort Bliss, Texas, to Redstone Arsenal. Among those transferred were Dr. Wernher von Braun and his team of German scientists..
1950 July 10 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes production version studied. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: von Braun.
Office, Chief of Ordnance directed that the Ordnance Guided Missile Center conduct a preliminary study of the technical requirements and possibilities of developing a 500-mile tactical missile that would be used principally in providing support for the operations of the Army Field Forces.
1950 September 11 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes work transferred from General Electric to Von Braun team. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Ordnance Department directed that the Hermes contract with General Electric Company be amended to transfer responsibility for the Hermes C1 project to the Ordnance Guided Missile Center..
1951 July 10 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes work transferred to Redstone arsenal. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. The Office, Chief of Ordnance formally transferred the responsibility for conducting the research and development phase of the HERMES Cl project to Redstone Arsenal.
1951 October 31 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes project transferred to Redstone Arsenal. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Responsibility for Hermes II transferred to Army Ordnance Guided Missile Center at Redstone Arsenal; Hermes II redesignated the RVA-A-3 test vehicle..
1952 April 1 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Contractor to build Redstone rocket. - .
Nation: USA.
The Office, Chief of Ordnance (OCO) disapproved Redstone Arsenal's proposed development plan for what would become the Redstone missile. The arsenal had intended to implement the manufacturing program for these missiles by creating an assembly line in its own development shops. The OCO, however, required that the development effort be done by a prime contractor. Nonetheless, delays in the acquisition of production facilities for the prime contractor caused Redstone Arsenal to fabricate and assemble the first 12 Redstone missiles along with missiles 18 through 29.
1952 April 8 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Redstone rocket named. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. The Redstone missile system officially received its popular name. Previously, this missile was known at various times and places as the Hermes C1, Major, Ursa, XSSM-G-14, and XSSM-A-14..
1952 October 1 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Chrysler receives Redstone contract. - . Nation: USA. Chrysler Corporation issued a letter order contract to proceed with active work as the prime contractor on the Redstone missile system. This contract was definitized on 19 Jun 53. .
1953 August 20 - . 14:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC4. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Control System malfunction followed by Power Plant malfunction at approximately 80 sec. Ground cut-off command given... Failed Stage: G.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 6.00 km (3.70 mi). Redstone missile No. 1 was fired by Army Redstone Arsenal personnel at AFMTC, Cape Canaveral. Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 240,000 m..
1954 January 27 - . 15:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC4. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 8,400 m..
1954 May 5 - . 17:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC4. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Ejector burnout immediately following lift-off.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 0 km (0 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 277,000 m..
1954 June 25 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Project Orbiter begun. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: von Braun.
Spacecraft Bus: Explorer.
Spacecraft: Explorer A.
In a meeting, Dr. Wernher von Braun, Frederick C. Durant III, Alexander Satin, David Young, Dr. Fred L. Whipple, Dr. S. Fred Singer, and Commander George W. Hoover agreed that a Redstone rocket with a Loki cluster as the second stage could launch a satellite into a 200-mile orbit without major new developments. This became a joint Army-Navy study project after meeting at Redstone Arsenal on August 3. Project Orbiter was a later outgrowth of this proposal and resulted in the launching of Explorer I on January 31, 1958.
1954 August 15 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Von Braun proposes launch of US satellite. - . Payload: Explorer A. Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer. Spacecraft: Explorer A. Von Braun report 'A Minimum Satellite Vehicle Based on Components Available from Developments of the Army Ordnance Corps' in response to June Pentagon meeting proposes $ 100,000 to launch satellite by Redstone..
1954 August 18 - . 14:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC4. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Steam generator regulator malfunction caused drop in combustion pressure..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 19,200 m..
1954 September 29 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Redstone contract awarded. - . Nation: USA. Army Ordnance awarded contract for Redstone missile to Chrysler Corp..
1954 November 17 - . 18:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC4. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Ground programmed yaw maneuver caused missile control loss at 80 sec causing power plant erratic behavior. Human error in selection of yaw maneuver impulse.. Failed Stage: G.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 0 km (0 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 166,300 m..
1954 December 31 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Hermes program terminated. - . Nation: USA. Army Ordnance terminated the Hermes project, during which development of high-performance liquid-fuel rocket and first stabilized platform inertial guidance equipment had been accomplished..
1955 February 9 - . 20:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC4. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Separation bolt No. 3 failure. Inverter frequency shift.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 0 km (0 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 23,400 m..
1955 April 20 - . 06:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Guidance system malfunction at 310 sec due to air pressure loss. ST-80 lateral guidance only..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 7,000 m..
1955 May 23 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Project Orbiter plans. - . Nation: USA. Project Orbiter Conference was held at Redstone Arsenal and at Cape Canaveral..
1955 May 25 - . 04:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Guidance system malfunction at 155, sec due to wiring error..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 17,200 m..
1955 June 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- First Redstone production contract. - . Nation: USA. Chrysler Corporation received the first industrial contract for the Redstone..
1955 August 24 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Redstone recommended as satellite launcher. - .
Payload: Explorer A. Nation: USA.
Related Persons: von Braun.
Program: Explorer.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer.
Spacecraft: Explorer A.
Research and development Policy Council (DOD) unanimously recommended that the time-risk factor in the scientific satellite program be brought to the attention of the Secretary of the Defense for determination as to whether a Redstone backup program was indicated.
1955 August 31 - . 00:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Excessive temperature in tail section caused malfunction of jet vane control..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 540 m..
1955 September 22 - . 05:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Excessive temperature in tail section caused malfunction of control.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 10 km (6 mi).
RS-11 was launched at 0051 hours EST from AMR after a three-hour hold. The flight was unsuccessful. The LOX container pressure and the combustion chamber decreased 50 seconds after lift-off. The temperature of Fin Number 1 went out of measuring range 72 seconds after lift-off. The servo battery current dropped to zero and the stabilised platform lost its reference. The range safety officer gave the emergency cut-off signal at 79 seconds. Impact occurred approximately 21,000 yards from the launch pad. The RS-11 was the first flight with the complete guidance system. Missed aimpoint by 118,800 m.
1955 December 6 - . 00:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
RS-12 was launched from AMR at 1946 hours EST. The flight was successful. The actual range was 144.79 nm; .31 nm over; and 200 meters right of the intended impact point, The primary test objective was to test the complete guidance system. This was the first successful flight with the inertial guidance system. Missed aimpoint by 228,800 m.
1956 February 1 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- ABMA established. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Army activated the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) at Redstone Arsenal, Huntsville, Ala., to weaponize the Redstone and to develop the Jupiter IRBM..
1956 March 15 - . 00:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Early cut-off caused by Incorrect guidance cut-off equation pre-setting. ST-80 gyro spilled at 310 sec..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
The first Jupiter A launching, by ABMA at Cape Canaveral. RS-18 was launched at 1936 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful. The scheduled launching date of this missile was 13 March. Three holds were called because of LOX difficulties, telemetry difficulties, and replacement of a gate valve. The actual range was 133.58 nm; 10.3 nm under; and 5.66 nm right of the intended impact point. Separation occurred before the missile gained its correct velocity. Improper assumption of propellant flow for the trajectory calculation was primarily responsible for the incorrect cut-off. The primary test objectives were to test the complete guidance and control system to establish the performance qualities of the complete missile system. Missed aimpoint by 19,100 m.
1956 April 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- First Redstone batallion formed. - . Nation: USA. The first Redstone missile battalion, the 217th Field Artillery Missile Battalion, was formally activated at Redstone Arsenal..
1956 April 23 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Army proposes Redstone satellite launch. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Army informed the OSD that a Jupiter missile could be fired in an effort to orbit a small satellite in January 1957..
1956 May 16 - . 04:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Missile programmed to cut-off at fuel depletion - this combined with known stability problems caused excessive miss distance..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
RS-19 was launched at 2322 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful. The actual range was 169.4 nm; 13 nm over the intended impact point. Cut-off wee given by the alcohol depletion switch that sensed alcohol injector pressure drop-off. Takeoff occurred 0.156 seconds after firing. The missile followed the correct trajectory with no obvious deviation. Missile cut-off occurred later than predicted and caused the missile to impact approximately 6.5 nm long, During descent the warhead turned left, causing impact to be several miles to the left of the aiming azimuth line. The primary test objectives were to test the angle-of-attack meter hardware (Jupiter control). Missed aimpoint by 25,100 m.
1956 July 19 - . 08:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: ST-80 malfunction at theta switch operation - 310 sec..
- Jupiter A - . Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). CC-13 was launched at 0345 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful. The actual range was 142.457 nm; .780 nm over the intended impact point. This was the first Chrysler fabricated and assembled missile. Missed aimpoint by 1,071 m..
1956 August 8 - . 08:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
RS-20 was launched at 0325 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful. The actual range was 139.72 nm; 0.3 nm over the intended impact point. The primary teat objectives were to test the accuracy of the guidance system and to acquire data for the establishment of design criteria for the Jupiter. This was the first time that the combustion chamber pressure was controlled. Missed aimpoint by 175 m.
1956 September 20 - . 06:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C. FAILURE: Early cut-off due to human error in tanking ..
- Jupiter C re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 1,097 km (681 mi).
First Jupiter C (a three-stage ABMA-JPL Redstone missile) was launched at Cape Canaveral, Fla., attained an altitude of 1096 km and traveled 5,300 km downrange. The first three-stage re-entry missile, was fired at 0145 hours EST from AMR. This missile attained an estimated range of 3,335 ST miles, an altitude of 682 ST miles, and reached Mach 18 velocity. The primary objective of the firing was the propulsion and separation tart of a multi-stage vehicle. The missile was a four-stage configuration with the last stage inactive. The first stage was an elongated Redstone missile, the second and third stages were up of 11 and 3 six-inch scaled SERGEANT rockets, respectively. The payload consisted of approximately 20 pounds of instrumentation attached to the inactive fourth stage. The flight was successful and the sequence of operations occurred as programmed. This vehicle could have obtained sufficient velocity to place it in orbit, if the last stage had been activated. First deep penetration of space. Serial number coding for early Redstones and related vehicles used the following substitution cipher: 1234567890 = HUNTSVILLEX
1956 October 18 - . 09:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
CC-14 was launched at 0405 hours EST from AMR after a series of short holds. The flight was successful. The actual range was 137.870 nm; 72 meters over and 338 meters right: of the intended impact point. The primary objectives were to test the accuracy of the guidance system and to test angle of-attack meters for the Jupiter. Missed aimpoint by 346 m.
1956 October 31 - . 02:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Malfunction of yaw gyro at approximately 10 sec. Ground cut-off command given.. Failed Stage: G.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 0 km (0 mi).
RS-25 was launched at 2104 hours EST from AMR. The flight was not successful. The behaviour of the missile appeared normal for the first 13 seconds, an early roll disturbance having been smoothly eliminated. Starting at 13 seconds after range zero, the gyro yaw signal indicated increasing yaw for a few seconds and the tracking devices at the same time showed increased displacement to the left of the standard trajectory. The malfunction apparently occurred between the yaw gyro potentiometer output and the outputs of the yaw amplifier of the mixing computer. The primary test objective was to test power plant performance. Missed aimpoint by 264,900 m.
1956 November 14 - . 02:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Human error in propellant loading plus programmed fuel depletion cut-off..
- Jupiter A/Sandia PL - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
RS-28 was launched at 2105 EST from AMR. The flight was successful. Actual range was 152.4 nm; 9.51 nm over; and 1.5 kilometres left of the intended impact point. The missile carried the LEV-3 rather than the ST-80 guidance system and used fuel depletion cut-off. The primary test objective was to test the Sandia payload. Missed aimpoint by 19,500 m.
1956 November 26 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, Thor, Jupiter, Redstone, Pershing.
- All missiles over 200 miles range assigned to USAF. - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson issued a memo to the Armed Forces Policy Council to end the argument between the Air Force and Army on responsibility for missile programs. In an effort to settle the areas of jurisdiction for the services, Secretary Wilson ruled that all long-range missiles, ICBMs as well as IRBMs, with a range of more than 200 miles, would be given to the Air Force.
1956 November 29 - . 13:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at 0823 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful. Actual range was 138.969 nm; .137 nm over and 122 meters left of the intended impact point, a radial miss distance of 260 meters. The primary test objectives were to test the accuracy of the complete guidance system and to test Jupiter control components. Missed aimpoint by 255 m.
1956 December 19 - . 02:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: First experimental flight with Hydyne. Specific impulse exceeded predicted values. Re-entry system intentionally unstable to test Jupiter alpha control..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
The flight was successful, Actual range was 401.6 nm; 84.9 nm over the intended impact point. The missile used Hydyne fuel. The primary test objective was to test the control of an unstable missile configuration by using an angle-of-attack meter (boom type) in the ascending phase (Jupiter control). Missed aimpoint by 157,200 m.
1957 January 19 - . 01:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Platform roll control malfunction at 310 sec..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at 2037 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful. Actual range was 61.6 nm; 400 meters left; and 0.21 nm over the intended impact point. The primary objective was to test the accuracy of the guidance system when the missile is fired in a short range trajectory at an extreme attitude to range ratio. The missile closely followed the predicted trajectory for a successful flight which terminated 70 meters beyond and 360 meters to the Left of the expected impact point at 61.553 nm range. The short range trajectory was programmed with an extreme altitude-to-range ratio so the guidance system would be subjected to the most difficult short range expected in future tactical application. Missed aimpoint by 400 m.
1957 March 14 - . 08:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Platform interference caused control malfunction at re-entry..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
The first missile shipped directly from the Chrysler Factory to the test site to be flight tested was launched at 0312 hours EST from AMR The flight was successful. Actual range was 138.178 nm; 2.2 nm under; and 1250 meters left of the intended impact point. The missile functioned properly until 182 seconds when an unexplainable pitch deviation caused a slow tilting of the missile top section. The cut-off function at 120 seconds and the separation function at 135 seconds, after flight zero time, were both satisfactory. Missed aimpoint by 4,183 m.
1957 March 28 - . 01:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at 2022 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful from the standpoint of missions accomplished, with cut-off time 112 seconds and separation time 126 seconds after range zero time. Impact point was 220 meters short and 320 meters to the right, a radial miss distance of 390 meters, primary objective was to test the accuracy of the guidance system when the missile was fired in a short range trajectory at an extreme altitude to range ratio. Missed aimpoint by 390 m.
1957 May 15 - . 07:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C. FAILURE: Loss of instrument compartment pressure at 134 seconds causing failure of pitch gyro prior to cut-off..
- Jupiter re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 655 km (406 mi).
The second three-stage re-entry missile, was launched at 0255 hours EST from AMR to test the thermal behaviour of a scaled-down version of the Jupiter nose cone during re-entry. The separated nose cone, which weighed 314 pounds, should have reached a nominal range of 1,212 nm. The missile began. to pitch up at 134 seconds, and impact was 420 nm short of the intended impact point. The composite missile consisted of three stages. The first stage was an elongated Redstone using alcohol and liquid oxygen as propellant. The second and third stages were made up of clusters of 11 and 3 scaled-down Sergeant solid propellant rockets, respectively. The nose cone was not recovered; however, instrument contact with the nose cone through re-entry indicated that the ablative-type heat protection for warheads was successful. Nose Cone Recovery Test
1957 June 26 - . 11:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Human error in calculation of takeoff weight..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at 0609 hours EST from AMR to test performance of the inertial guidance system, angle-of-attack meters, separation of explosive screws, and impact and radar fusing systems. Range instrumentation difficulties and deteriorating weather delayed the firing from the initially scheduled time of 0230 hours EST. The flight was successful. Actual range was 135.425 nm; 0.42 nm over; and 389 meters left of the intended impact point. Missed aimpoint by 785 m.
1957 July 12 - . 06:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Control system malfunction at re-entry..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at 0130 hours EST from AMR. The primary test objective was to test the accuracy of the guidance system. The flight was successful. Actual range was 130.125 nm; 0.15 nm over; and 285 meters left of the intended impact point. All missions were successfully accomplished. The missile followed the predicted trajectory very closely. Survey of the impact crater indicated a miss distance of 50 meters over and 284 meters to the left of the predicted impact point, giving a radial miss distance of 389.5 meters. Missed aimpoint by 289 m.
1957 July 26 - . 04:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at 2317 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful. Actual range was 126.227 nm; 147 meters under; and 182 meters left of the intended impact point. The primary test objective was to flight test warhead and fuse functioning as a system. A survey of the warhead impact point: indicated a miss distance of 147 meters short, 182 meters to the left of the predicted impact point, or a radial miss distance of 234 meters. Missed aimpoint by 235 m.
1957 August 8 - . 06:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Jupiter re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 460 km (280 mi).
First Nose Cone Recovery. Army-JPL Jupiter-C fired a scale-model nose cone 1,200 miles down range from AMR with a summit altitude of 600 miles. Recovery the next day of aerodynamic nose cone using ablation, resolved reentry heating problem for Jupiter missile. Nose cone was shown to the Nation on TV by President Eisenhower on November 7.
Fired from AMR at 0159 hours EST, impacted at the predicted range. This success proved conclusively that the planned ablative-type heat protection for Jupiter warheads was satisfactory. The missile was a three-stage configuration--the first stage an elongated Redstone missile, the second and third stages 11 and 3 six-inch scaled Sergeant rockets, respectively. The one-third scale Jupiter nose cone was attached to the final stage with scheme for separation provided. The nose cone travelled to a 1,168 nm range, reached a velocity of 4,004 m/sec, and experienced a total heat input at stagnation point at 95% of that for the full scale nose cone at 1,500 nm. Naval units recovered the scaled nose cone according to plan.
1957 September 9 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- First US Army heavy missile group. - . Nation: USA. The 40th Field Artillery Missile Group, the first heavy missile group organized in the U.S. Army, was transferred from Fort Carson, Colorado, to Redstone Arsenal..
1957 September 11 - . 02:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: ST-80 pitch program malfunction..
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at: 2141 hours EST from AMR. The flight was unsuccessful, The missile impacted 14.77 nm from the launch pad. Mechanical failure of the guidance tilt program caused the missile to assume a very steep trajectory which resulted La. a short range flight. Missed aimpoint by 111,000 m.
1957 October 2 - . 19:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Launched at 1429 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful, the impact point was 445 metres long and 452 meters to the right of the predicted impact point, giving a radial miss distance of. 634 meters. This was the first flight test of the NAA A-6 engine with a sea level thrust of 78,000 pounds. Missed aimpoint by 572 m.
1957 October 5 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Von Braun promises first US satellite in 60 days. - . Payload: Explorer A. Nation: USA. Related Persons: McElroy, Medaris, von Braun. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer. Spacecraft: Explorer A. Von Braun briefs Secretary of Defence McElroy on Jupiter-C/Redstone for immediate US satellite launch. Promises launch in 60 days. Medaris says 90..
1957 October 31 - . 04:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A. FAILURE: Loss of inter-compartment pressure at 68 sec. Ground cut-off command given.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 40 km (24 mi).
Launched at 2352 hours EST from AMR. The flight was unsuccessful. Actual range was 48 nm, whereas the predicted range wee 130.588 nm. At 68 seconds, a disturbance occurred in the lateral accelerometer and computer systems. Erroneous guidance instructions were transmitted to the control systems, causing a sharp yaw at 70 seconds. Cut-off was initiated at 98.1 seconds. One of the objectives was to indoctrinate troops for participation in the tactical portions of the countdown. Missed aimpoint by 151,000 m.
1957 November 7 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Eisenhower enunciates science policy. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Eisenhower,
von Braun.
President Eisenhower in major address on science and security announced that scientists had solved the problem of ballistic missile reentry and showed the nose cone of an Army Jupiter-C missile which was intact after a flight through space. He announced the creation of the office of Special Assistant to the President for Science and Technology and the appointment of James R. Killian, president of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, to the new post.
1957 November 8 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Von Braun ordered to launch satellite. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: McElroy,
von Braun.
Program: Explorer.
Secretary of Defense Neil McElroy directed the Army to proceed with the launching of the Explorer earth satellites. This order, in effect, resumed the Orbiter project that had been eliminated from the IGY satellite planning program on September 9, 1955. Von Braun was to modify two Jupiter-C missiles (modified Redstones) and attempt to place an artificial earth satellite in orbit by March 58.
1957 December 11 - . 00:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Jupiter A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Successfully fired at 1936 hours EST from AMR. The missile followed the trajectory very closely and impacted on target. All missions were successfully accomplished. The predicted impact range was 141.895 nm. The miss distance has bean certified as 153 meters radial, 94 meters over, and 121 meters to the left of the predicted impact point. The primary objective of the rest was to flight test Hardtack adaptation kit components as passengers. Missed aimpoint by 209 m.
1958 January 15 - . 01:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
- Hardtack pod test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Successfully fired at 2024 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful in that all missions were accomplished.. The missile followed its predicted trajectory closely. Impact was 370 meters over and 86 meters to the tight of the predicted impact point, a radial miss distance of 380 meters. This wee the fifth complete flight test of warhead and fuse system. Missed aimpoint by 286 m.
1958 February 1 - . 03:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC26A. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Explorer 1 - .
Payload: Explorer A. Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: von Braun.
Agency: US Army.
Program: Explorer.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer.
Spacecraft: Explorer A.
Decay Date: 1970-03-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 4 . COSPAR: 1958-Alpha-1. Apogee: 1,859 km (1,155 mi). Perigee: 347 km (215 mi). Inclination: 33.20 deg. Period: 107.20 min.
Explorer I, the first U.S. earth satellite, was launched by a modified Army Ballistic Missile Agency Jupiter-C. Explorer I, developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, carried the U.S.-IGY (International Geophysical Year) experiment of James A. Van Allen and resulted in the discovery of the radiation belt around the earth.
1958 February 12 - . 00:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Successfully fired at 1954 hours EST from AMR. The flight was successful in that all missions were accomplished, with the exception of the Hardtack adaptation kit mission. Impact was 258 meters over and 172 meters to the left of the predicted impact point, a radial miss distance of 310 meters. The primary objectives of the test were to test the warhead and fuse system and the guidance system. Missed aimpoint by 310 m.
1958 February 27 - . 19:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Successfully fired at 1459 hours EST from the AMR. The flight was successful in that all missions were accomplished. Impact was 461 meters over end 64 meters to the left of the predicted impact point, a radial miss distance of 466 meters. Missed aimpoint by 245 m.
1958 March 5 - . 18:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC26A. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C. FAILURE: Fourth Stage failed to ignite.. Failed Stage: 4.
- Explorer 2 - . Payload: Explorer A. Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Agency: US Army. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer. Spacecraft: Explorer A. Decay Date: 1958-03-05 .
1958 March 26 - . 17:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Explorer 3 - . Payload: Explorer A. Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Agency: US Army. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer. Spacecraft: Explorer A. Decay Date: 1958-06-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 6 . COSPAR: 1958-Gamma-1. Apogee: 2,799 km (1,739 mi). Perigee: 186 km (115 mi). Inclination: 33.40 deg. Period: 115.70 min. Radiation, micrometeoroid data. .
1958 March 27 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- ARPA assigned space project role. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Eisenhower,
McElroy.
President Eisenhower gave his approval to the plans for outer space exploration announced by Secretary of Defense Neil H. McElroy. The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) was to undertake several space projects including the launching of certain earth satellites and five space probes as a part of this country's contribution to the IGY program. The Air Force Ballistic Missile Division was authorized by ARPA to carry out three lunar probes with a Thor-Vanguard system, and lunar probes utilizing the Jupiter-C rocket were assigned to the Army Ballistic Missile Agency.
1958 May 17 - . 00:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 578 m..
1958 June 1 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- First Redstone deployment to Europe. - . Nation: USA. The Redstone became the first large U.S. ballistic missile to be deployed overseas, joining the NATO Shield Force. .
1958 June 3 - . 04:50 GMT - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 409 m..
1958 June 12 - . 01:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter A.
1958 June 25 - . 03:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Human error - thrust controller not connected..
- Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 90 km (55 mi).
Successfully fired at 2059 hours EST from AMR. The flight was a success in that all missions were accomplished with the exception of failure of the thrust governor. This failure was caused by human error before firing which caused excess velocity, thereby exceeding the predicted impact point by 8.36 nm. Programmed range to impact was 137.31 nm. All other missions were satisfactorily completed. Missed aimpoint by 14,917 m.
1958 July 26 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C.
- Explorer 4 - . Payload: Explorer B. Mass: 8.00 kg (17.60 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Agency: DARPA. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer. Spacecraft: Explorer B. Decay Date: 1959-10-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 9 . COSPAR: 1958-Epsilon-1. Apogee: 1,352 km (840 mi). Perigee: 257 km (159 mi). Inclination: 50.20 deg. Period: 100.90 min. Mapped project Argus radiation. .
1958 August 1 - . 09:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Johnston Island. Launch Complex: Johnston Island LC1. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Failure of tilt program device at lift-off causing vertical night flight did not preclude subsequent system operations and successful mission accomplishment..
- Hardtack Teak Nuclear test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 76 km (47 mi).
Teak was a rocket-launched test of a live W-39 nuclear warhead. Purpose was to measure the effects of high altitude nuclear explosions in order to design warheads for the Nike-Zeus anti-ballistic missile system. The Hardtack Configuration Redstone shot the 3.8 megaton warhead to an altitude of 77.8 km. This was the first rocket-launched nuclear test by the United States.
1958 August 12 - . 09:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Johnston Island. Launch Complex: Johnston Island LC2. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Guidance system malfunction at 70 seconds which did not preclude subsequent system operations and successful mission accomplishment..
- Hardtack Orange Nuclear test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Apogee: 41 km (25 mi).
Orange was a rocket-launched test of the W-39 warhead. Purpose was to measure the effects of high altitude nuclear explosions in order to design warheads for Nike-Zeus anti-ballistic missile system. The Hardtack Configuration Redstone shot the 3.8 megaton warhead to an altitude of 43 km.
1958 August 24 - . 06:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C. FAILURE: First Stage collided with upper stages. Second Stage ignited in wrong direction.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Explorer 5 - . Payload: Explorer C. Mass: 17 kg (37 lb). Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Agency: DARPA. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Explorer. Spacecraft: Explorer C. Decay Date: 1958-08-24 .
1958 September 17 - . 18:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Programmed maneuver at re-entry and impact in deep water. Accurate survey not possible. CC-57.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 990 m..
1958 October 23 - . 03:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Jupiter C. FAILURE: Upper stages separated prior to burnout. Structural failure after 149 sec due to vibration disturbances generated by the spinning payload.. Failed Stage: 2.
- Beacon 1 - .
Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Beacon 1.
Decay Date: 1958-10-22 .
NASA¾with the Army as executive agent¾attempted to launch a 12-foot-diameter inflatable satellite of micro-thin plastic covered with aluminum foil known as BEACON. Launched from AMR by a Juno I¾a modified Redstone, the payload prematurely separated prior to booster burnout.
1958 October 24 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Redstone static firing at White Sands. - . Nation: USA. The Redstone underwent static firing at White Sands Missile Range, the first time such a test had been conducted there..
1958 November 6 - . 00:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Boost phase normal. Space phase malfunction..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Redstone final development test. Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 5,010 m..
1959 January 8 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Redstones ordered for Mercury suborbital launches. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: von Braun. Spacecraft: Mercury. NASA requested eight Redstone-type launch vehicles from the Army to be used in Project Mercury development flights..
1959 January 19 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Human error in connecting separation system..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 1,189 m..
1959 February 16 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Improper setting of thrust controller and malfunction of tilt program at 17 sec.. Failed Stage: G.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 10 km (6 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 17,942 m..
1959 March 10 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Army Redstone ejected miniature TV camera which transmitted pictures of its target impact area. Missed aimpoint by 144 m..
1959 May 12 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Known initial laying error of approximately 26 min..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 1,091 m..
1959 June 5 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury-Redstone inflight abort sensing system. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
The Army Ballistic Missile Agency submitted a proposal (Report No. DG-TR-7-59) for a Mercury-Redstone inflight abort sensing system. This system would monitor performance of the control system (attitude and angular velocity), electrical power supply, and launch vehicle propulsion. If operational limits were exceeded, the spacecraft would be ejected from the launch vehicle and recovered by parachute.
1959 June 24 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Eight Mercury Redstone launch vehicles final cost $20.1 million. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Against an original estimated cost of $15.5 million for eight Redstone launch vehicles in support of Project Mercury, the final negotiated figure was $20.1 million..
1959 July 22 - . 04:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC26A. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Control system malfunction during re-entry at 380 sec..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 684 m..
1959 August 5 - . 02:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC26A. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Pre-launch tanking error caused early cut-off by fuel depletion..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 2,707 m..
1959 September 18 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 228 m..
1959 November 20 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Open-circuit television system in the Mercury-Redstone MR-2 and MR-3 flights - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Mercury MR-3.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
At the fifth Mercury Coordination Meeting, the Army Ballistic Missile Agency proposed the installation of an open-circuit television system in the Mercury-Redstone second and third flights (MR-2 and MR-3). The purpose of the system was to observe and relay launch vehicle and spacecraft separation data.
1959 December 22 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Redstone for Mercury MR-1 installed on the interim test stand. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Redstone launch vehicle for the first Mercury-Redstone mission (MR-1) was installed on the interim test stand at the Army Ballistic Missile Agency for static testing..
1960 January 18 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury-Redstone Coordination Committee - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Walter C. Williams proposed the establishment of a Mercury-Redstone Coordination Committee to monitor and coordinate activities related to Mercury-Redstone flight tests..
1960 January 26 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Capsule operational test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test with capsule. Missed aimpoint by 277 m..
1960 February 8 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Tests started for the mission abort sensing program for Mercury-Redstone - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Tests were started by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency for the mission abort sensing program to be integrated in the Mercury-Redstone phase of Project Mercury..
1960 March 15 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- T-1 Capsule operational test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test with T-1 Capsule. Missed aimpoint by 295 m..
1960 March 22 - . 01:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Control system malfunction during re-entry at 373 sec..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 315 m..
1960 April 15 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- T-1 Capsule - . Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 17 m..
1960 June 2 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC36. Launch Pad: ALA3. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 75 km (46 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 336 m..
1960 July 6 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 176 m..
1960 July 23 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury spacecraft No. 2 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury spacecraft No. 2 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone 1-A (MR-1A) mission..
1960 August 1 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Final Trajectory for Mercury MR-1 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Marshall Space Flight Center published the 'Final Standard Trajectory for MR-1 (Mercury-Redstone).'.
1960 August 3 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Redstone launch vehicle No. 1 delivered - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Redstone launch vehicle No. 1 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the MR-1 (Mercury-Redstone)..
1960 August 10 - . 01:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Erroneously destroyed during boost by range personnel.. Failed Stage: G.
1960 September 19 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Format of first Mercury-Redstone postlaunch report - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The format of subject matter coverage for the first Mercury-Redstone postlaunch (MR-1) report was issued. This report, covering a full range of topics related to the mission, was to be submitted within 5 days after the launch..
1960 October 6 - . 03:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Control system malfunction during re-entry at 375 sec..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 221 m..
1960 October 18 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mission rules for Mercury-Redstone 1 (MR-1) issued. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. A revision was published on Nov. 1, 1960..
1960 November 21 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- An attempt was made to launch Mercury-Redstone 1 (MR-1) from Cape Canaveral. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury,
Mercury Escape Tower.
This unmanned mission was unsuccessful because premature cut-off of the launch vehicle engines activated the emergency escape system when the vehicle was only about 1 inch off the pad. Engine cut-off was caused by premature loss of electrical ground power to the booster. The launch vehicle settled back on the pad with only slight damage. Since the spacecraft received a cut-off signal, the escape tower and recovery sequence was initiated. The undamaged spacecraft was recovered for reuse.
1960 November 21 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV. FAILURE: Engine cut off after 1 sec, vehicle fell back to the pad from a few centimeters height, but did not explode. This faulty ground-support circuitry had not been noted on some 60 previous Redstone firings.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Mercury MR-1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Apogee: 0 km (0 mi). Suborbital launch attempt. After a four- or five-inch liftoff, MR-1 launched its escape tower but not the capsule. The undamaged spacecraft was recovered for reuse..
1960 December 3 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury Redstone launch vehicle No. 3 shipped to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Redstone launch vehicle No. 3 was shipped to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone 1A (MR-1A) mission..
1960 December 9 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury spacecraft No. 7 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-3. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft No. 7 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) manned ballistic mission (Shepard)..
1960 December 19 - . 16:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-1A - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Apogee: 210 km (130 mi).
Mercury-Redstone 1A (MR-1A) was launched from Cape Canaveral in a repeat of the November 21, 1960, mission and was completely successful. This was the third attempt to accomplish the objectives established for this flight. The first attempt on November 7, 1960, was canceled as a result of a helium leak in the spacecraft reaction control system relief valve, and on November 21, 1960, the mission could not be completed because of premature cut-off of the launch vehicle engines. Objectives of the MR-1A flight were to qualify the spacecraft for space flight and to qualify the flight system for a primate flight scheduled shortly thereafter. Close attention was given to the spacecraft-launch vehicle combination as it went through the various flight sequences: powered flight; acceleration and deceleration; performance of the posigrade rockets; performance of the recovery system; performance of the launch, tracking, and recovery phases of the operation; other events of the flight including retrorocket operation in a space environment; and operation of instrumentation. Except that the launch vehicle cut-off velocity was slightly higher than normal, all flight sequences were satisfactory; tower separation, spacecraft separation, spacecraft turnaround, retrofire, retropackage jettison, and landing system operation occurred or were controlled as planned. The spacecraft reached a maximum altitude of 130.68 statute miles, a range of 234.8 statute miles, and a speed of 4,909.1 miles per hour. Fifteen minutes after landing in the Atlantic Ocean, the recovery helicopter picked up the spacecraft to complete the successful flight mission.
1960 December 20 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury Redstone launch vehicle No. 2 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Redstone launch vehicle No. 2 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone 2 (MR-2) mission (chimpanzee 'Ham' flight)..
1961 January 16 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-1A postlaunch system evaluation tests - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Mercury-Redstone 1A (MR-1A) postlaunch system evaluation tests were completed at Cape Canaveral. Data disclosed that the instrumentation system, communication system, and other components had operated satisfactorily during the flight mission..
1961 January 22 - . 02:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Control system malfunction during re-entry at 370 sec..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 788 m..
1961 January 31 - . 16:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-2 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Apogee: 251 km (155 mi).
Ham, a 37-pound chimpanzee, was aboard the spacecraft. The over-acceleration of the launch vehicle coupled with the velocity of the escape rocket caused the spacecraft to attain a higher altitude and a longer range than planned. In addition, the early depletion of the liquid oxygen caused a signal that separated the spacecraft from the launch vehicle a few seconds early. However spacecraft recovery was effected, although there were some leaks and the spacecraft was taking on water. Ham appeared to be in good physiological condition, but sometime later when he was shown the spacecraft it was visually apparent that he had no further interest in cooperating with the space flight program. Despite the over-acceleration factor, the flight was considered to be successful.
1961 February 10 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mission rules for the Mercury MR-3 - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-3. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mission rules for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3 - Shepard's flight) were published. Revisions were issued on February 27, and April 28, 1961..
1961 March 7 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury spacecraft No. 11 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-4. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft No. 11 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) ballistic manned (Grissom) flight..
1961 March 7 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury Redstone launch vehicle No. 5 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Redstone launch vehicle No. 5 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone, Booster Development flight (MR-BD)..
1961 March 9 - . 02:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Control system malfunction during re-entry at 374 sec..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 358 m..
1961 March 24 - . 17:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-BD - . Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Apogee: 181 km (112 mi). Suborbital test of Redstone modifications using a boilerplate Mercury capsule. The test was done at von Braun's insistence against Shepard's wishes, thereby putting the first US manned flight after Gagarin's..
1961 March 30 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury Redstone launch vehicle No. 7 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-3. Spacecraft: Mercury. Redstone launch vehicle No. 7 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) mission..
1961 April 4 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Glenn, Grissom, and Shepard refresher course on centrifuge for Mercury - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Glenn,
Grissom,
Shepard.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Glenn, Grissom, and Shepard began refresher course on centrifuge in preparation for the first manned Mercury-Redstone suborbital flight. John Glenn, Virgil Grissom, and Alan Shepard began a refresher course on the Aviation Medical Acceleration Laboratory centrifuge in preparation for the first manned Mercury-Redstone suborbital flight.
1961 April 20 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) readiness review. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-3. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft, mission, and launch vehicle flight safety were reviewed by Space Task Group personnel in preparation for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) mission..
1961 April 28 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Simulated countdown for Mercury MR-3 - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-3. Spacecraft: Mercury. A simulated countdown for the first Mercury-Redstone manned suborbital flight (MR-3) was successfully completed..
1961 May 1 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Webb warns of Mercury failures. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Webb.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
NASA Administrator Webb issued a statement concerning the 2-year Mercury manned space flight program, which said, in part: "NASA has not attempted to encourage press coverage of the first Mercury-Redstone manned flight. It has responded to press and television requests, with the result that over 100 representatives of the press, radio, and TV are now at Cape Canaveral. . . . We must keep the perspective that each flight is but one of the many milestones we must pass. Some will completely succeed in every respect, some partially, and some will fail. From all of them will come mastery of the vast new space environment on which so much of our future depends."
1961 May 2 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-3 postponed. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-3. Spacecraft: Mercury. Manned Mercury-Redstone (MR-3) launch postponed because of rain squalls in the recovery area..
1961 May 5 - . 14:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-3 - .
Call Sign: Freedom 7. Crew: Shepard.
Backup Crew: Grissom.
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MR-3.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Duration: 0.0107 days. Apogee: 187 km (116 mi).
Astronaut Alan B. Shepard, Jr., made the first United States manned space flight in a Mercury spacecraft launched from Cape Canaveral atop the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) vehicle. "Freedom 7" completed the suborbital, ballistic flight without incident in this historical first mission of NASA's Project Mercury. Alan Shepard first American in space, less than a month after Gagarin and only on a 15 minute suborbital flight. Only manned flight with original Mercury capsule design (tiny round porthole and periscope a la Vostok). If NASA had not listened to Von Braun, Shepard would have flown on the MR-BD flight of 24 March, beating Gagarin by three weeks and becoming the first man in space (though not in orbit). Shepard's capsule reached an altitude of 115.696 miles, range of 302 miles,and speed of 5,100 miles per hour. He demonstrated control of a vehicle during weightlessness and high G stresses. Recovery operations were perfect; there was no damage to the spacecraft; and Astronaut Shepard was in excellent condition.
1961 May 9 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Kennedy decision to allow MR-3 flight defended. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Kennedy.
Flight: Mercury MR-3.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Senator Robert S. Kerr, chairman of the Senate Aeronautical and Space Sciences Committee, told a group at the National Radio and Television Convention that President Kennedy accepted the views of NASA and congressional leaders in approving the manned Mercury-Redstone flight of May 5.
1961 May 18 - . 02:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 304 m..
1961 June 12 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury Redstone launch vehicle No. 8 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-4. Spacecraft: Mercury. Redstone launch vehicle No. 8 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) suborbital flight mission..
1961 June 22 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-4 recovery requirements - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-4. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) recovery requirements were forwarded by the Space Task Group to the Navy..
1961 June 22 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Redstone for Mercury MR-4 manned suborbital flight erected - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-4. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Redstone booster for the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) manned suborbital flight mission was erected on Pad 5, at Cape Canaveral..
1961 June 27 - . 02:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC6. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Air vane actuator malfunction at 262 sec..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 1,044 m..
1961 July 6 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 266 m..
1961 July 13 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-6 static engine test - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-6. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury-Redstone 6 was static tested for 30 seconds at Marshall Space Flight Center to ensure satisfactory operation of the turbopump assembly..
1961 July 13 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) manned suborbital flight mission rules were published. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-4. Spacecraft: Mercury.
1961 July 19 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-4 launch scrubbed. - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MR-4. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury-Redstone (MR-4) with manned Liberty Bell 7 capsule canceled within minutes of launch because of adverse weather..
1961 July 21 - . 12:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC5. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-4 - .
Call Sign: Liberty Bell 7. Crew: Grissom.
Backup Crew: Glenn.
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MR-4.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Duration: 0.0108 days. Apogee: 189 km (117 mi).
The Mercury capsule, Liberty Bell 7, manned by Astronaut Virgil I. Grissom, boosted by a Redstone rocket, reached a peak altitude of 190.3 km and a speed of 8,335 km per hour. After a flight of 15 minutes and 37 seconds, the landing was made 487 km downrange from the launch site. The hatch blew while still in water, and the capsule sank; Grissom saved, though his suit was filling up with water through open oxygen inlet lines.
This was the second and final manned suborbital Mercury Redstone flight, and the first flight with trapezoidal window. Further suborbital flights (each astronaut was to make one as a training exercise) were cancelled. An attempt to recover the capsule in very deep water in 1994 not successful. It was finally raised in the summer of 1999.
1961 August 1 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Human error in laying launch azimuth. Drop in inter-compartment pressure suspected..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 5,085 m..
1961 August 18 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Further Mercury suborbital flights cancelled. - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MR-5. Spacecraft: Mercury. NASA announced that analysis of Project Mercury suborbital data indicated that all objectives of that phase of the program had been achieved, and that no further Mercury-Redstone flights were planned..
1961 August 30 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Investigation of the Mercury MR-4 explosive egress hatch. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Mercury MR-4.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
An investigation was conducted as a result of the premature activation of the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) explosive egress hatch. Tests were initiated in an environment more severe than had been conducted in prelaunch activities and tests, but no premature firings occurred. As a backup, McDonnell was asked to design a mechanical-type hatch. The model weighed some 60 pounds more than the explosive type, so other methods had to be sought to prevent any recurrence of the incident. A procedure was initiated which stipulated that the firing plunger safety pin would be left in place until the helicopter hook was attached to the spacecraft and tension was applied to the recovery cable.
1961 Late summer - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-5 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Glenn.
Backup Crew: Slayton.
Payload: Mercury SC15. Nation: USA.
Flight: Mercury MR-5.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
The original Mercury project plan envisioned all of the astronauts making an initial suborbital hop aboard a Redstone booster before making an orbital flight aboard an Atlas. But Gherman Titov was launched on a full-day orbital flight in August 1961, making NASA's suborbital hops look pathetic. Further suborbital Mercury flights after that of Grissom were cancelled.
1961 September 1 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 196 m..
1961 October 1 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 197 m..
1961 October 23 - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury Freedom 7 presented to the Smithsonian - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MR-3. Spacecraft: Mercury. Freedom 7, the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) spacecraft, was presented by NASA to the National Air Museum of the Smithsonian Institution..
1961 Autumn - . LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: Redstone MRLV.
- Mercury MR-6 (cancelled) - . Crew: Slayton. Payload: Mercury SC16. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Slayton, Webb. Flight: Mercury MR-6. Spacecraft: Mercury. After the Russians began orbiting cosmonauts, NASA cancelled further suborbital flights. The MR-6 mission was cancelled by NASA administrator James Webb at the beginning of July, 1961..
1961 December 15 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 82 m..
1962 June 1 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 378 m..
1962 July 1 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 390 m..
1962 August 1 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Human error in repair of pitch .potentiometer..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 3,191 m..
1962 August 1 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 167 m..
1963 August 5 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 216 m..
1963 August 19 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 267 m..
1963 September 10 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone. FAILURE: Control system malfunction immediately prior to impact..
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Missile test failure. Missed aimpoint by 4,393 m..
1963 September 23 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 63 m..
1963 October 5 - . Launch Site: Fort Wingate. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Apogee: 90 km (55 mi). Successful missile test. Missed aimpoint by 131 m..
1964 June 25 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Redstone obsolete. - . Nation: USA. The Redstone missile was classified as obsolete. .
1964 October 30 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Redstone leaves Army service. - . Nation: USA. In a ceremony on the parade field at Redstone Arsenal, the Redstone missile was ceremonially retired..
1964 December 1 - . Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Redstone support contract terminated. - . Nation: USA. The initial Redstone production contract awarded to Chrysler in October 1952 was closed out..
1965 November 29 - . Launch Site: San Nicolas. Launch Complex: San Nicolas. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- Project Defender Redstone launch. - . Nation: USA. Redstone launched as ballistic missile target and was successfully intercepted by a US Navy Terrier surface-to-air missile launched from Point Mugu, California..
1965 November 30 - . Launch Site: San Nicolas. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
- DAT-371 Target mission - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: DARPA,
US Army.
Apogee: 50 km (31 mi).
Redstone launched as ballistic missile target for a US Navy Terrier surface-to-air missile launched from Point Mugu, California. It was reported that there were two Redstone launches as part of Project Defender from November 30 to December 13, 1965, but details of the second launch are not known.
1965 December 1 - . 01:28 GMT - . Launch Site: San Nicolas. Launch Vehicle: Redstone.
1966 November 28 - . 12:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1966 December 13 - . 11:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 April 20 - . 08:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 July 4 - . 23:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 July 24 - . 16:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 August 17 - . 19:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 September 15 - . 16:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 October 11 - . 16:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 October 31 - . 13:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
1967 November 29 - . 04:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Woomera. Launch Complex: Woomera LA8. LV Family: Redstone. Launch Vehicle: SPARTA.
- Wresat 1 - . Payload: Wresat / BE-3. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: Australia. Agency: WRE. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft: Wresat. Decay Date: 1968-01-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 3054 . COSPAR: 1967-118A. Apogee: 1,252 km (777 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 83.30 deg. Period: 99.30 min. Weapons Research Establishment Satellite; solar radiation, upper atmosphere data. WRESAT 1 launched for upper atmosphere and space research at 1419 h central standard time, from Woomera, South Australia. Launch vehicle based on Redstone. .
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use