
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Atlas
Atlas
Credit: (c) Mark Wade
AKA: B-65;CGM/HGM-16D/E/F;CTM-16D/E;HGM-16;SM-65;X-11;X-12. Status: Retired 2004.
Atlas began with a US Army Air Corps request for proposal in October 1945 for long-range missile designs. By 10 January 1946, Consolidated-Vultee's engineers, under the leadership of Belgian-born Karel Bossart, submitted their proposals for two 6,000-nautical mile missiles: one subsonic, winged, and jet powered; the other supersonic, ballistic, and rocket powered. New technologies proposed for the ballistic missile included extremely low structural weight through use of steel monocoque single-wall construction tanks, kept rigid by internal tank pressure; gimbaled rocket engines; a detachable warhead section; and nearly single-stage to orbit performance through the ‘stage-and-a-half' approach of jettisoning the booster engines during the ascent.
On 19 April Convair received a contract for $1,893,000 to fabricate and test ten MX-774 Hiroc missiles to verify Bossart's innovative ballistic missile concepts. Captive testing of the MX-774 research rockets began in San Diego in 1947. In June, Consolidated Vultee was notified that it had lost the cruise missile competition; Northrop and Martin received contracts for development of their subsonic jet-powered cruise missile designs. Defense cutbacks forced the Air Force to terminate the MX-774 contract in July 1947, only three months before the first scheduled flight. The remaining contract funds allowed three MX-774's to be test-launched at White Sands Proving Ground in July-December 1947. Further work at Convair was reduced to ‘Mafia' low-level design activity using company funds.
The outbreak of the Korean war and the beginning of the cold war loosened the federal purse strings. Convair received a new contract (MX-1593) in September 1951 to begin design of a ballistic missile incorporating the design features validated by the MX-774. In 1953 the now-Convair Division of General Dynamics presented a plan to the Air Force for an accelerated program.
A major propulsion problem in the early 1950's was that liquid rocket motor ignition reliability was less than 50 percent. This led to the stage-and-a-half concept, with all engines ignited prior to lift-off and the booster engines jettisoned during flight. This allowed confirmation that all engines were functioning correctly before releasing the missile for flight.
A full go-ahead for the Atlas design was ordered in January 1955 as Weapon System WS107A-l. At Convair the project was known the Model 7 (in Russia, Korolev was working on the competing R-7 ICBM - evidently both sides wanted to use the lucky number). In September 1955, faced with intelligence reports of Russian progress on their ICBM, the Atlas received the highest national development priority. The project became one of the largest and most complex production, testing, and construction programs ever undertaken. The first propulsion system and component tests were conducted in June 1956; the first captive and flight-test missiles were completed later the same year.
The first Atlas A flight took place on 11 June 1957. In a tremendous national effort, by 1959 a peak of 33,000 personnel were working on the project. Total cost of the Atlas ICBM program to the United States was $8 billion. About a quarter of this went to Convair to design and develop the missile and launch facilities. The balance was for the tremendous cost of the ICBM launch facilities. For all of this effort, the Atlas was quickly obsolete, and the facilities were closed by 1966 after five years of service. However surplus ICBM's were stored, refurbished, and used as space launch vehicles until the last was flown in 1995 - 33 years after it was manufactured.
The first operational missile, the Atlas D, was the basis for launching the Mercury manned spacecraft into orbit. By use of Agena and Centaur upper stages, the Atlas became the medium-lift workhorse of American manned, reconnaissance, planetary, and geosynchronous-orbit space programs. After the retirement of the Atlas-Agena in 1978, the Centaur stage became standard on Atlas launch vehicles.
Centaur began with a contract awarded to General Dynamics by the Advanced Research Project Agency in 1958. The first space vehicle to use liquid hydrogen, Centaur was a pioneering project that solved the many technical problems of using the super-cryogenic and highly volatile fuel. Pratt & Whitney Aircraft was awarded the contract to develop Centaur's RL-10 engines. The US Air Force had already built the first large-quantity liquid hydrogen production facility for the deep black Suntan reconnaissance program.
In 1962, with the hydrogen propulsion technology being vital to the success of the Apollo program, Centaur management was transferred to NASA's Lewis Research Center. Lewis had fired their first experimental Lox/LH2 engine of 5,000 pounds thrust in 1953. The Centaur project was given the highest DX priority, but suffered delays due to management problems at both NASA and Convair. The first successful flight of Centaur atop Atlas occurred in November 1963. However thereafter von Braun's Saturn S-IV stage, using six of the RL-10 motors, leapfrogged the Centaur program . By the time of the first operational Centaur mission in May 1966, the S-IV had already completed its test series of six orbital flights. Yet thirty years later, the Saturn was long gone, and the Centaur continued, having been launched or planned for launch from Atlas, Titan, Delta, and Shuttle vehicles. Production continued into the 21st century, and no replacement for the RL-10 engine, the ultimate engine using the ultimate propellants, was ever put into production.
Development Cost $: 2,230.000 million. Recurring Price $: 8.309 million in 1965 dollars. Flyaway Unit Cost 1985$: 1.800 million in 1965 dollars.
More at: Atlas.
| Atlas 3A American orbital launch vehicle. The Atlas IIIA was a development of the Atlas using Russian engines in place of the Rocketdyne MA-5 booster/sustainer group used on all previous models. It was the centerpiece of Lockheed Martin's strategy to remain a leader in the commercial launch services industry. However customers never materialized, and it was used for only two launches in 2002-2004 before being replaced by the Atlas V. |
| Atlas 3B American orbital launch vehicle. This was the first version of the Atlas to fly using Russian RD-180 engines; and the last version to fly using the original balloon-tank concept for the first stage. It differed from the Atlas IIIA in use of a stretched, two-engine upper stage, and had a brief three-year operational career in 2002-2005 before being superseded by the Atlas V. |
| Atlas 3B DEC American orbital launch vehicle variant, Atlas IIIB with dual-engine Centaur upper stage. |
| Atlas A American test vehicle. First test model of Atlas ICBM. Two booster engines, no sustainer, dummy warhead. 50% reliability in 8 flight tests. |
| Atlas Able American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas with upper stage based on Vanguard second stage. |
| Atlas Agena A American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas D + 1 x Agena A upper stage. Agena originally called 'Hustler', based on engine for cancelled rocket-propelled nuclear warhead pod for B-58 Hustler bomber. |
| Atlas Agena B American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas D with improved, enlarged Agena upper stage. |
| Atlas Agena D American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas D with further improved and lightened Agena upper stage. |
| Atlas B American test vehicle. First all-up test version of the Atlas ICBM, with jettisonable booster engines and a single engine sustainer on core - a '1 1/2' stage launch vehicle. |
| Atlas Burner 2 American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas SLV-3 + 1 x Star 37B upper stage. |
| Atlas C American test vehicle. Last development version of Atlas. Never deployed operationally or used for space launches. |
| Atlas C Able American orbital launch vehicle. Version with Atlas C first stage, Able AJ10-101A second stage, Altair solid third stage. |
| Atlas Centaur American orbital launch vehicle. First test version of Atlas with Centaur upper stage. |
| Atlas Centaur D American orbital launch vehicle. Version with Centaur D upper stage. |
| Atlas Centaur LV-3C American orbital launch vehicle. Version with basic Centaur upper stage. |
| Atlas D American intercontinental ballistic missile. Rocket used both as a space launcher and ICBM. |
| Atlas D Able American orbital launch vehicle. Version with Atlas D first stage, Able AJ10-101A second stage, Altair solid third stage. |
| Atlas D CGM-16 American intercontinental ballistic missile. ICBM version. |
| Atlas E American intercontinental ballistic missile. Initial fully operational version of Atlas ICBM. Differed in guidance system from Atlas F. Deployed as missiles from 1960 to 1966. After retirement, the ICBM's were refurbished and used over twenty years as space launch vehicles. |
| Atlas E Altair American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas E + 1 x Star 20 upper stage. |
| Atlas E CGM-16E American intercontinental ballistic missile. ICBM version |
| Atlas E/MSD American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas E + 1 x MSD upper stage. |
| Atlas E/OIS American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas E + 1 x OIS upper stage. |
| Atlas E/SGS-2 American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas E + 1 x Star 48 + 1 x Star 48 upper stages. |
| Atlas E/SVS American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas E + 1 x Star 37E + 1 x Star 37E upper stages. |
| Atlas E/Trident Atlas E + 1 x Trident upper stage. |
| Atlas F American intercontinental ballistic missile. Final operational version of Atlas ICBM. Differed in guidance systems. Deployed as missiles from 1961 to 1966. After retirement, the ICBM's were refurbished and used for over thirty years as space launch vehicles. |
| Atlas F Burner 2A American intercontinental ballistic orbital launch vehicle. Atlas F + 1 x Star 37B + 1 x Star 26B upper stages. |
| Atlas F HGM-16F American intercontinental ballistic missile. ICBM version. Also CGM-16F |
| Atlas F/Agena D Atlas F + 1 x Agena D upper stage. |
| Atlas F/MSD American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas F + 1 x MSD upper stage. |
| Atlas F/OIS American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas F + 1 x OIS upper stage. |
| Atlas F/PTS American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas F + 1 x Star 37E upper stage. |
| Atlas F/SVS American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas F + 1 x Star 37E + 1 x Star 37E upper stages. |
| Atlas F/Trident Atlas F + 1 x Trident upper stage. |
| Atlas G American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas-Centaur launch vehicles using stretched, uprated Atlas core. |
| Atlas G Centaur Atlas-Centaur launch vehicles using stretched, uprated Atlas core. |
| Atlas H American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas H used the Atlas first stage developed for the Atlas G vehicle. It was flown without the Centaur upper stage. |
| Atlas I American orbital launch vehicle. The Atlas I launch vehicle was derived from the Atlas G, and included the same basic vehicle components (Atlas booster and Centaur upper stage). Significant improvements in the guidance and control system were made with an emphasis on replacing analog flight control components with digital units interconnected with a digital data bus. |
| Atlas II American orbital launch vehicle. The Atlas II booster was 2.7-meters longer than an Atlas I and included uprated Rocketdyne MA-5A engines. The Atlas I vernier engines were replaced with a hydrazine roll control system. The Centaur stage was stretched 0.9-meters compared to the Centaur I stage. Fixed foam insulation replaced Atlas I's jettisonable insulation panels. The original Atlas II model was developed to support the United States Air Force Medium Launch Vehicle II program. Its Centaur used RL10A-3-3A engines operating at an increased mixture ratio. The first Atlas II flew on 7 December 1991, successfully delivering AC-102/Eutelsat II F3 to orbit. |
| Atlas IIA American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas IIA was a commercial derivative of the Atlas II developed for the US Air Force. Higher performance RL10A-4 (or RL10A-4-1) engines replaced Atlas II's RL10A-3-3A engines. |
| Atlas IIAS American orbital launch vehicle. The Atlas II booster was 2.7-meters longer than the Atlas I and included uprated Rocketdyne MA-5A engines. The Atlas I vernier engines were replaced with a hydrazine roll control system. The Centaur stage was stretched 0.9-meters compared to the Centaur I stage. Fixed foam insulation replaced Atlas I's jettisonable insulation panels. Higher performance RL10A-4 or RL10A-4-1 engines replaced Atlas II's RL10A-3-3A. The Atlas IIAS model added four Thiokol Castor IVA solid rocket boosters (SRBs) to the core Atlas stage to augment thrust for the first two minutes of flight. |
| Atlas LV-3A / Agena B American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas D with improved, enlarged Agena upper stage. |
| Atlas LV-3B American orbital launch vehicle. First operational version of Atlas ICBM and used as launch vehicle for Project Mercury. |
| Atlas LV-3B / Mercury American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas D modified for use in Project Mercury. |
| Atlas SLV-3 American orbital launch vehicle. Standardized Atlas booster with no or small solid upper stage. |
| Atlas SLV-3 Agena B American orbital launch vehicle. Standardized Atlas booster with Agena B upper stage. |
| Atlas SLV-3 Agena D Standardized Atlas booster with Agena D upper stage. |
| Atlas SLV-3A Agena D Uprated Atlas booster with Agena D upper stage. |
| Atlas SLV-3C Centaur Standardized SLV-3C Atlas booster with Centaur D upper stage. |
| Atlas SLV-3D Centaur Fully developed version of Atlas with Centaur D-1A upper stage. |
| Atlas Vega American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas-Vega consisted of an Atlas booster with a storable propellant upper stage. It was planned by NASA at its inception for deep space and planetary missions before the Atlas Centaur was available. Work had already begun when NASA discovered that the CIA and the US Air Force had an essentially identical launch vehicle (Atlas-Hustler, later called Atlas-Agena) in development for the highly classified Corona reconnaissance satellite program. Atlas-Vega was accordingly cancelled. |
| Atlas-B (mod.) American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas B test ICBM modified to orbit the Score satellite. |
| Atlas-D Antares-2 American orbital launch vehicle variant with Atlas D first stage, Antares-2 solid propellant second stage. |
| Atlas-D OV1 American orbital launch vehicle variant with Atlas D first stage, OV1 package. |
| Atlas-E/-F Burner-2 American orbital launch vehicle. Atlas E + Burner-2 upper stage. |
| Atlas-E/-F OV1 American orbital launch vehicle variant. Atlas E + OV1 upper stage. |
| Atlas-E/-F Star-17A American orbital launch vehicle variant. Atlas E + Star 17 upper stage. |
| Atlas-E/-F Star-37S ISS American orbital launch vehicle variant. Atlas E + Star 37S upper stage. |
| Atlas-SLV3B Agena-D Uprated Atlas booster with Agena D upper stage. |
| Atlas-SLV3C Centaur-D Star-37E Atlas booster with Centaur D upper stage and Star 37E final stage. |
| Atlas-SLV3D Centaur-D1A Atlas booster with Centaur D1A upper stage. |
| Atlas-SLV3D Centaur-D1A Star-37E Atlas booster with Centaur D1A upper stage and Star 37E final stage. |
| Atlas-SLV3D Centaur-D1AR Atlas booster with Centaur D1AR upper stage. |
| Concept ICBM American orbital launch vehicle. The January 1951 design for the Atlas used seven main engines plus two vernier engines to hurl the 3600 kg nuclear warhead over a 9300 km range. CEP was optimistically estimated as 460 m. |
| Contracted Atlas American orbital launch vehicle. The 1954 design for the Atlas as contracted for by the Air Force used three main engines to power a 110 metric ton rocket able to send a 1400 kg nuclear warhead over a 10,200 km range. CEP was 3700 m. The missile actually delivered six years later would have the same dimensions and launch mass, but 63% more range and four times better accuracy. |
| Hiroc American test vehicle. Project MX-774 inaugurated by AAF with Consolidated-Vultee to study rocket capabilities with an ICBM as a final objective. Limited funds permitted a few test launches. These rockets demonstrated technologies that would later be applied to the Atlas. |
| MX-1593 American orbital launch vehicle. The September 1951 design for the Atlas used seven main engines to hurl the 3600 kg nuclear warhead over a 9300 km range. CEP was 1850 m. |
| Proposed Atlas American orbital launch vehicle. The April 1953 design for the Atlas at the time of Convair's proposal used five main engines to power a 200 metric tone rocket able to send a 1400 kg nuclear warhead over a 10,200 km range. CEP was 1850 m. |
| World Series American orbital launch vehicle. In May 1956 the Air Force proposed mating an Atlas A with an Aerobee-Hi upper stage in order to launch a satellite during the International Geophysical Year (1957-1958). The Eisenhower administration selected the Vanguard instead. After Sputnik, an Atlas B with no upper stage orbited the Score satellite as a reply to the Soviet's Sputnik 3. |
Family: orbital launch vehicle. Country: USA. Spacecraft: Intruder, Quasar, SAINT, Score, Aeronutronics Project 7969, Convair Project 7969, Lockheed Project 7969, McDonnell Project 7969, Outpost, Project Mer, Mercury, Pioneer P 3, Mercury Space Suit, Midas, Samos, Gemini, Ranger 1-2, Westford Needles, Mariner R, SECOR, Ranger 3-4-5, Mariner 1-2, ERS, Orbital Workshop, SSF, Dash, TRS, KH-7, Vela, Surveyor, Ranger 6-7-8-9, FIRE, OGO, Calsphere, Surveyor Block II, Mariner 3-4, OV1, Surveyor Lunar Rover, Snapshot, LCS, Surveyor Orbiter, Gemini Agena Target Vehicle, Bluebell, OAO, Atlas Target Docking Adapter, Lunar Orbiter, ATS-1, Prime, ATS-2, Research Payload Module 481, OV5, Mariner 5, ATS-3, Canyon, ATS-4, Orbiscal, RADCAT, RM, Boost Glide Re-entry Vehicle, Mariner 6-7, ATS-5, Rhyolite, Intelsat 4, Mariner 8-9, Cannonball, Gridsphere, Musketball, Mylar, Rigidsphere, NOSS, Pioneer 10-11, Radsat, Mariner 10, NTS, P 72, Spacebus 100, Intelsat 4A, NOSS-Subsat, HEAO, FLTSATCOM, GPS Block 1, Pioneer 12, Seasat, Pioneer 13, Tiros N, Solwind, HS 376, Intelsat 5, LIPS, AS 3000, DSCS III, DMSP Block 5D-2, Advanced Tiros N, Geosat, Intelsat 5A, AS 4000, Eurostar 2000, FS-1300, HS 601, Stacksat P87-2, CRRES, AS 5000, AS 7000, GOES-Next, SOHO, SAX, Spacebus 3000, AS 2100, Falcon Gold, CAPRICORN, Terra, SDS-3, NOSS-3. Agency: Convair. Bibliography: 126, 1269, 16, 17, 171, 172, 18, 2, 26, 276, 278, 279, 281, 296, 33, 34, 42, 4460, 45, 48, 480, 483, 498, 552, 554, 563, 567, 59, 6, 60, 61, 88.
 | New Generation LVs From left: 3 versions of Atlas 5, 5 versions of Delta 4, 3 versions of Chinese NGLV, Ariane 5. Vertical scale is 10 m intervals. Credit: © Mark Wade |
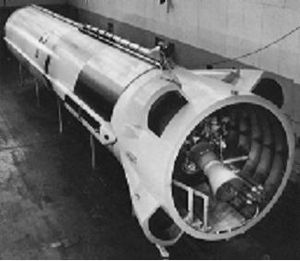 | WS-107 WS-107 Concept 1. Before the Tea Pot report, Atlas was to have five thrust chambers and double the throw weight. Credit: Ronald Wade |
 | WS-107 WS-107 Concept 2. First mock-up of the Atlas missile in the three-chamber configuration. Credit: Ronald Wade |
 | Atlas Family From left - MX-774 of 1946; MX-1593 of 1953; Atlas A, B, D; Atlas Agena D; Atlas Centaur; Atlas I, IIA, IIAS, IIIA, IIIB, V Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | MX-774 Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | MX-774 MX-774 in its gantry. Credit: Ronald Wade |
 | Atlas 1953 5-engine Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas B Credit: US Air Force |
 | Atlas B Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas D OV Atlas D OV-1 (2x) - COSPAR 1966-111 |
 | Atlas manned lab |
 | Atlas D ICBM Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Atlas D Mercury BW Credit: NASA |
 | Atlas D Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas D Mercury Credit: NASA |
 | Mercury Atlas 9 Credit: NASA |
 | Mercury Atlas 5 Credit: NASA |
 | Atlas E Atlas E - COSPAR 1991-032 |
 | Atlas E Credit: US Air Force |
 | Atlas F Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas D Able Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Atlas Burner 2A Atlas Burner 2A - COSPAR 1972-076 |
 | Atlas D Midas Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Atlas Agena A Credit: US Air Force |
 | Atlas Agena A Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas D Samos Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Atlas D Agena B Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Atlas Agena B Atlas Agena B - COSPAR 1962 Eta |
 | Atlas D Mercury Lab Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Atlas Agena D Credit: © Mark Wade |
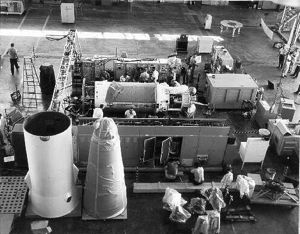 | Agenhgre Agena D stages in process, Hangar E, Cape Canaveral |
 | Atlas ATDA Credit: US Air Force |
 | Atlas Agena D Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas Agena Last Atlas Agena - Agena s/n P113 - 6 April 1978 |
 | Atlas Agena First Atlas Agena - Agena s/n 1008 - Midas 1 |
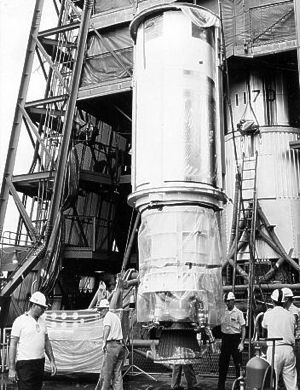 | Agena D Agena D rocket stage being raised for mating with Atlas launch vehicle |
 | Atlas Agena Atlas Agena / Ranger C launch vehicle |
 | Atlas D ATS Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | SLV-3C Centaur SLV-3C Centaur AC-17 - COSPAR 1968-068 |
 | Atlas Centaur Atlas Centaur at Sunrise Credit: Lockheed Martin |
 | Atlas Centaur SLV-3D Credit: © Thomas Kladiva - Thomas Kladiva |
 | Atlas Centaur No. 40 Credit: Lockheed Martin |
 | Atlas 2 Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas Centaur Centaur Launch Vehicle Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas Centaur No.69 Credit: Lockheed Martin |
 | Atlas 2AS Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Atlas LV Atlas LV-3C s/n AC-3 - 1964-06-30 |
 | Atlas Centaur C Credit: © Mark Wade |
1946 January 11 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- Strategic Missile Proposals - .
Nation: USA.
Bids were received in response to the USAAF request for proposal of the previous October. Vultee submitted proposals for two types (glide and ballistic) of 8000-km range missiles. North American proposed a three-year development program for a supersonic 800-km range missile, culminating in a production run of 50 missiles.
1946 April 2 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- MX-774 strategic missile study contract awarded - . Nation: USA. Convair received contract W33-038-AC-14168 for a $1.4 million, one-year study of two missile designs..
1946 December - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- MX-774 Azusa tracking - . Nation: USA. Study report submitted to Air Force on proposed Azusa tracking/guidance system. MX-774 funding cut back..
Early 1947 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- MX-774 Azusa tracking tests - . Nation: USA. Tracking tests started with experimental Azusa equipment.
1947 July 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- MX-774 cancelled. - .
Nation: USA.
Contract with Convair for the MX-774 "Upper Air Test Vehicle," predecessor of the Atlas ICBM, was cancelled by the AAF. However the service approves Convair use of unexpended MX-774 funds to launch the MX-774 test vehicles already built. The decision made to move Vultee operations to San Diego.
1947 October - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- First complete MX-774 moved to Pt. Loma for test - . Nation: USA.
1947 November 20 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- First static firing of MX-774 - . Nation: USA. Unsuccessful, small fire..
1948 January - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- Second MX-774 static firing - . Nation: USA. Successful, at Point Loma..
1948 May 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- MX-774 static firing tests at Pt Loma completed. - . Nation: USA.
1948 June - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- First MX-774 arrives at White Sands Proving Ground - . Nation: USA.
1948 July 14 - . 01:05 GMT - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC33. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc. FAILURE: Cutoff after half of the propellants were used.. Failed Stage: 1.
- MX-774 Flight 1 - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1.00 km (0.60 mi). First Convair MX-774 (RTV-A-2) test rocket was successfully launched, first demonstrating use of gimballed engines and design features later incorporated in the Atlas ICBM. This was the first of three Convair-sponsored test flights..
1948 September 27 - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC33. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc. FAILURE: Cutoff at 16 km altitude.. Failed Stage: 1.
- MX-774 Flight 2 - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 47 km (29 mi). Second Corvair MX-774 test rocket fired. Shut down at 15 km; reached 65 km before malfunction of unknown origin caused self-destruction..
1948 December 2 - . 22:01 GMT - . Launch Site: White Sands. Launch Complex: White Sands LC33. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc. FAILURE: Vibration closed valve early..
- MX-774 Flight 3 - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 50 km (31 mi). Third (last) MX-774 launched, WSPG; shut down at 51 seconds attaining an altitude of 48 km. Self-destructed at high altitude..
1949 February - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- All MX-774 work shut off by Air Force - . Nation: USA.
During 1949 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Hiroc.
- MX-774 unexpended funds run out in 1950. - . Nation: USA. Convair allocated R&D funds to ICBM studies and marketing, running into 1950.
1950 October 1 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- RAND studies ICBM's. - . Nation: USA. Rand Corp. completed missile feasibility studies begun in 1949, which confirmed the military practicability of long-range rocket weapons..
1951 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas tracking system. - . Nation: USA. Azusa tracking system reaching advanced stage of development.
1951 January 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Concept ICBM.
- Project MX-1593 (Project Atlas) begins. - .
Nation: USA.
Air Force established Project MX-1593 (Project Atlas), study phase for an intercontinental missile. Requirements included 8000-pound warhead, 5000 nautical mile range, to hit within 1500 ft. CEP. $1.5 million study contract was awarded to Consolidated-Vultee Aircraft on January 23. This was the follow-on to Project MX-774 terminated in 1947. Several test vehicles had been fired using residual funds in 1948 and 1949, after which the Convair MX-774 (Atlas) missile project had been shelved. The company, however, had continued to fund a research program.
1951 August - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas to be accelerated. - . Nation: USA. AF Gen. John Sessums proposes Atlas acceleration.
1951 August - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: MX-1593.
- Atlas XB-65 configuration. - . Nation: USA. MX-1593 named "Project Atlas" as XB-65; 120 feet long, 12-foot diameter, 7 engines, 8000-pound warhead, CEP 1 nautical mile.
1951 September 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: MX-1593.
- Atlas project to concentrate on ballistic missile. - . Nation: USA. MX-1593 glide missile cancelled. USAF directed all work in Project MX-1593 (Atlas) be for development of a rocket-powered ballistic missile..
Late 1951/early 1952 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Reports of large Russian rocket engines - . Nation: USA.
During 1952 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Proposed Atlas.
- Reduced thermonuclear warhead size will allow American ICBM's to be smaller. - . Nation: USA. Atlas 3000-pound warhead anticipated, 1500-foot CEP.
1952 March - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Gen. Joseph McNarney joins Convair - . Nation: USA.
1953 January - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Millikan Committee Report - . Nation: USA. Millikan Committee report issued, saying Atlas could be operational by 1963.
Spring 1953 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Proposed Atlas.
- Atlas size reduced. - . Nation: USA. Atlas 12-foot diameter, 110 feet long, 440,000 pounds, 3000-pound warhead, 5500 nautical mile range, 1500-foot CEP.
1953 June - . LV Family: Atlas.
- US guided missile status review - . Nation: USA. Defense Secretary Wilson institutes reviews of guided missiles' status.
1953 July - . LV Family: Atlas.
- J.R. Dempsey joins Convair - . Nation: USA.
1953 September - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Von Neumann's "Teapot Committee" established - . Nation: USA.
1953 October - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Contracted Atlas.
- Teapot Committee's first output - . Nation: USA. ICBM could use smaller warhead.
1953 December 3 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Convair leases test facility. - . Nation: USA. A five-year Pt. Loma lease was approved..
1954 January 27 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Reorganization of USAF ballistic missile programs. - .
Mr. Trevor Gardner, Special Assistant to the Secretary of the Air Force for Research and Development, recommended to Air Force Chief of Staff General Nathan Twining, that the Air Force ballistic missile programs be reorganized.The "new" program would be provided with centralized management authority. The change was recommended to minimize the existing complexities and to focus attention on the importance of the program.
1954 February 8 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas) operational by the early 1960s. - .
A Rand Corporation memorandum by Dr. Bruno W. Augenstein indicated that the Atlas ballistic missile (Project MX-1593) could be operational by the early 1960s. The missile, then , then under development by Consolidated-Vultee Aircraft Corporation (Convair), could make that date if the existing stringent performance criteria were relaxed while funding and program priority were increased.
1954 February 10 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Teapot Report - .
The Strategic Missiles Evaluation ("Teapot") Committee, established in October 1953 and chaired by Professor John von Neumann, submitted its report on intercontinental strategic missiles. Convair's ICBM design was feasible, as was acceleration of the program. The von Neumann Committee recommended changes similar to those outlined in the Rand study of 8 February. In addition, the report urged the establishment of a development-management group with sufficient authority, funds, and priority to reorient and accelerate the ballistic missile program.
1954 February 26 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
- Atlas sustainer rocket engine contract - . The Air Force issued a contract to North American Aviation for continued development of a liquid-fueled sustainer rocket engine for Convair's Project Atlas..
1954 February 26 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas management structure outlined - .
Trevor Gardner, Special Assistant to the Secretary of the Air Force for Research and Development, held a meeting in Washington. Included were representatives of the Air Research and Development Command (ARDC). Headquarters USAF, certain former members of the von Neumann Committee, and concerned contractor personnel. Among the problems discussed was the manner of meshing the scientific and technical operations in ballistic missile development with the prime contractor who would actually build the missiles. Finally it was agreed that the scientific-technical group recommended by the Strategic Missiles Evaluation Committee would be placed under an industrial contractor or university and would be balanced by an Air Force organization set up to supervise the whole show.
1954 March - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Proposed Atlas.
- First Atlas hardware. - . Nation: USA. 12-foot diameter Atlas tank completed by Solar.
1954 March 1 - . LV Family: Atlas, Navaho. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas booster propulsion system work begins. - . Nation: USA. Work on MA-2 propulsion system for Atlas by Rocketdyne was begun, drawing upon the experience in developing the regeneratively cooled chamber developed for the Navaho..
1954 March - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Contracted Atlas.
- US tests confirm feasibility of small thermonuclear warheads - .
Nation: USA.
The United States exploded its first "droppable" hydrogen bomb in the Marshall Islands. A second U.S. thermonuclear device was successfully tested on 20 March. These tests as part of Operation Castle confirmed the feasibility of the development of lightweight, high-yield thermonuclear weapons. This advance allowed the previously restrictive performance characteristics of the Atlas to be relaxed to the point where continued development was within the existing "state-of-the-art."
1954 March 8 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- First public indication that Project Atlas exists - . Nation: USA.
1954 March 11 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Plan for accelerating the intercontinental ballistic missile program. - .
Related Persons: Schriever.
As a result of the 26 February meeting, Trevor Gardner submitted a plan for accelerating the intercontinental ballistic missile system (IBMS) program. This was sent to Secretary of the Air Force Harold E Talbott and Air Force Chief of Staff General Nathan Twining. The plan called for emergency funding and an operational capability as early as 1958-60. Mr. Gardner also recommended that high-ranking military officers be placed in charge of the revised program and specifically named Major General James McCormack, Jr., Vice Commander of ARDC, and Brigadier General Bernard A. Schriever, then Assistant for Development Planning, Deputy Chief of Staff/Development, Headquarters USAF, for the top positions.
1954 March 16 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas performance specifications relaxed so that the program could be accelerated. - .
The Air Force Council recommended to the Chief of Staff that the Atlas missile's performance specifications be relaxed so that the program could be accelerated as much as possible. It also recommended the use of Air Force funds to finance the program, a reorientation of the program to achieve the earliest possible operational capability, the assignment of program responsibility to Air Research and Development Command, and the establishment of a special development-management organization to recommend further measures to accelerate the entire Atlas program.
1954 March 19 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas acceleration ordered. - . Air Force Secretary Harold E. Talbott directed General Twining to take all necessary actions to implement the Strategic Missiles Evaluation Committee's recommendations of 10 February..
1954 March 23 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas acceleration measures approved. - . General Nathan Twining, Chief of Staff of the Air Force, approved the Air Force Council's recommendations of 16 March..
1954 Apr - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF established the Atlas Scientific Advisory Committee - .
Due to the continuing need for the best available scientific advice for the reorientation and acceleration of the Atlas program, Headquarters USAF established the Atlas Scientific Advisory Committee. Subsequently redesignated the ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee, this Committee was essentially a reconstitution of the former von Neumann Committee (Strategic Missiles Evaluation Committee) which had disbanded following the submission of its report on 10 February. The new Committee was also chaired by John von Neumann, but its membership was expanded and slightly different from the old "Teapot" Committee.
1954 April 8 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF Assistant Chief of Staff for Guided Missiles - . Headquarters USAF established the new office of Assistant Chief of Staff for Guided Missiles (AFCGM) - a clear indication of the importance now attached to the missile program..
1954 April 9 - . LV Family: Atlas, Thor.
- Ballistic missiles to move forward with all practicable speed. - .
In a memorandum to Secretary of the Air Force Harold E. Talbott, Deputy Secretary of Defense Roger M. Keyes stressed that the plans for the ballistic missile program "be formulated with a thoroughly realistic appraisal of the capabilities of our contractors to meet their commitments." He then emphasized that the program was to move forward "with all practicable speed."
1954 April 14 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Agreement on the proposed plan to accelerate Atlas. - .
Trevor Gardner informed General Twining, Air Force Chief of Staff, that the 19 March memorandum from Secretary of the Air Force Harold E. Talbott and the Air Force Council's actions of 16 March were substantially in agreement on the proposed plan to accelerate Atlas. The program was to be reoriented, and its acceleration was to proceed at maximum possible effort with no limitation on funding. The accomplishment of the new program was to be the direct responsibility of a field office under a general officer who would have authority and control over all aspects of the program.
1954 May - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Schriever named head of Atlas program. - . Related Persons: Schriever. In addition to his other duties, Brigadier General Bernard A. Schriever was appointed Assistant for Project Atlas to the Director of Research and Development..
1954 May - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas receives high priority. - . Lt General Donald L. Putt, DCS/Development, Headquarters USAF, informed his subordinates that Project Atlas had the highest program priority in the Air Force..
1954 May 3 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Ramo-Wooldridge contracted for Atlas technical support. - .
Development Command gave the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation a new contract to continue research and experimental investigations that had been begun in support of the original von Neumann Committee. Part of Ramo-Wooldridge's work involved technical evaluations and systems analyses of Project Atlas to be performed over a 12-month period and to be used for the redefinition of the program prior to its acceleration. In addition, conclusions and recommendations resulting from research completed under previous contracts were to be analyzed for possible future applications.
1954 May 14 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas program accelerated to the maximum extent that technology would permit. - .
General Thomas D. White, Air Force Vice Chief of Staff, informed Headquarters USAF offices and personnel that the Atlas program would be accelerated to the maximum extent that technology would permit. To insure the necessary support, the program was given the highest research and development priority in the Air Force (1-A), while it received a 1-2 category and precedence rating and a S-l supply priority. Field responsibility for the Atlas program during development and test would be assigned to Air Research and Development Command which would establish a field office on the west coast commanded by a general officer.
1954 May 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Ramo-Woolridge contracted for Atlas systems integration. - . Nation: USA. Ramo-Wooldridge given letter contract as Technical Director and Systems Integrator for Atlas program.
1954 Jun - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF Western Development Division established. - . Related Persons: Schriever. In June 1954, the Air Force established the Western Development Division under the direction of BrigGen Bernard A. Schriever. Early planning and development of the Atlas ICBM was conducted from there..
1954 Jun - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Responsibility for accelerating Atlas program given to USAF ARDC. - .
Lt General Donald L. Putt officially assigned the responsibility for reorienting and accelerating the Atlas program to Headquarters, Air Research and Development Command. The general officer appointed to command the office was to be given authority and control over the entire Atlas program which already had been granted the highest priority in the Air Force on 14 May.
1954 June 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Schriever named head of Atlas program. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: Schriever. Brigadier-General Bernard A. Schriever, ARDC, assigned to head Atlas program.
1954 July - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Scientific Advisory Board recommendations rejected. - . Nation: USA. Scientific Advisory Board recommendations differing from Teapot Committee rejected.
1954 Jul - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Western Development Division (WDD) established by USAF - .
Related Persons: Power.
By verbal orders of LtGeneral Thomas S. Power, Commander, ARDC, the Western Development Division (WDD), Headquarters ARDC, was established at 409 East Manchester Boulevard, Inglewood, California, under the command of Brigadier General Bernard A. Schriever. Headquarters ARDC General Order Number 42 confirmed LtGeneral Power's verbal orders of 1 July establishing the Western Development Division of Headquarters ARDC. Rocketdyne put on contract for Atlas engines.
1954 July 20 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Reorientation of the Atlas program - .
The Air Force Atlas Scientific Advisory Committee (the former von Neumann Committee as reconstituted in April) met at the Western Development Division to discuss the reorientation of the Atlas program. The Committee expressed its dissatisfaction with Convair's lack of progress and noted some serious flaws in the company's technical and managerial approaches. After examining the project management structure proposed by WDD, the Committee unanimously concluded that it was weak and confused and that Convair was not strong enough to be given systems responsibility over the Atlas project. It was recommended that the project management structure, and especially Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation's role therein, be reevaluated and that a new, stronger approach be worked out. In addition, the Committee recommended that a second propulsion system contractor be introduced into the program as a back-up for North American.
1954 July 29 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Schriever assigned full authority for the Atlas project - . Related Persons: Schriever. Brigadier General Schriever was assigned full authority, responsibility, and accountability for the Atlas project and given status and prerogatives for a Deputy Commander, Air Research and Development.
1954 August - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- First USAF WDD Facility - . Nation: USA. Inglewood "Schoolhouse" WDD facility established.
1954 August 2 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- General Schriever in command of the Western Development Division - . Related Persons: Schriever. General Schriever personally assumed command of the Western Development Division, Headquarters ARDC..
1954 August 3 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Early action to accelerate the Atlas program. - . Western Development Division gave North American Aviation the go-ahead to proceed with their rocket development program, including engine test stand construction and erection of an engine pilot plant..
1954 August 6 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas contracting function colocated with Western Development Division. - .
Headquarters Air Materiel Command (AMC) announced the establishment of the Special Aircraft Project Office (SAPO) under the command of Colonel Harold T. Morris. SAPO was to begin operations in Inglewood, California, on 15 August, and would perform all procurement and contracting functions for the Western Development Division.
1954 August 11 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF issues GOR 21 for an intercontinental ballistic missile - .
Headquarters USAF issued a "skeleton" general operational requirements, GOR Number 21 (SA-IC), for an intercontinental bombardment weapon system ballistic missile replacing the previous GOR Number 1. The weapon system to satisfy this GOR was expected to emerge from the redefinition and acceleration of the Atlas program.
1954 August 18 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Proposal that Ramo-Wooldridge manage the Atlas program. - .
Related Persons: Schriever.
After completing an evaluation of possible management approaches, a special WDD study group recommended to General Schriever that the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation manage the Atlas program. In this position, the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation would provide and be responsible for systems engineering and technical direction (SE/TD) for the entire Atlas project and for monitoring hardware development accomplished under Air Force contracts with industry.
1954 August 23 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Atlas alternate propulsion system contractor. - .
Related Persons: Schriever.
General Schriever forwarded two important recommendations to Headquarters ARDC. First, he recommended that an alternate propulsion system contractor be introduced into the Atlas program as a back-up. Second, he presented the results of the Atlas management study of 18 August and recommended Ramo-Wooldridge for the SE/TD role in the project.
1954 September 8 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Technical direction functions for Project Atlas. - .
Related Persons: Power.
Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation selected to perform systems engineering and technical direction functions for Project Atlas. Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation selected to perform systems engineering and technical direction functions for Project Atlas. Following approval by General Power, ARDC Commander, and General E.W. Rawlings, AMC Commander, Assistant Secretary of the Air Force for Materiel Roger Lewis approved the selection of the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation to perform systems engineering and technical direction functions for Project Atlas under the overall control of the Western Development Division.
1954 October 25 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Convair group to become the nucleus for the Atlas development team. - .
Related Persons: Schriever.
After further study, General Schriever recommended that the Convair program be continued because the company had the experience and could become the nucleus for the Atlas development team. Convair would handle airframe structural and aerodynamic aspects of the program along with the assembly of the vehicle and its components. The Western Development Division and the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation would provide SE/TD for the Atlas contractor.
1954 October 28 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Contract for development of the Atlas liquid oxygen/RP-1 rocket engine. - . Western Development Division and Special Aircraft Projects Office awarded a letter contract to North American Aviation for continued research and development of the liquid oxygen/RP-1 rocket engine..
Late 1954 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas further reduced in size - . Nation: USA. Atlas size reduced from 12-foot to 10-foot diameter, with 3 large engines.
1954 December - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas full-scale development - . Nation: USA. First major Atlas WS107A1 development and construction contract awarded Convair; CEP 2-3 NM, IOC by 1960-62.
1954 December 13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- First production funding for Atlas. - . Air Force Procurement Authorization 54-GM-3 authorized $3.6 million in P-150 production funding for Atlas. This was the first production funding for Atlas..
1954 December 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas publicly announced. - . Nation: USA. USAF announced Atlas ICBM under construction by Convair..
1955 January 4 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan begins as alternate configuration and staging approach to the Atlas missile. - . The Air Force ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee recommended that an alternate configuration and staging approach to the present Atlas missile be introduced into the ballistic missile program..
1955 January 6 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas contract award. - .
A contract was awarded to the Convair Division of the General Dynamics Corporation for the development and fabrication of the Atlas (XSM-65) airframe and control system. Included were the integration and assembly of the various subsystems with the airframe and control system, and for checkout and testing.
1955 January 12 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Titan proposed as a competitor and backup to the Atlas program. - . Related Persons: Schriever. General Schriever formally proposed to Hq ARDC that an alternate, two-stage configuration intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) be developed as a competitor and backup to the Atlas program..
1955 January 14 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Contract for Titan liquid oxygen-hydrocarbon ICBM engines. - .
The Western Development Division (WDD) and the Special Aircraft Project Office (SAPO) awarded a contract to Aerojet-General Corporation for development of liquid oxygen-hydrocarbon ICBM engines. The contract covered design and fabrication of booster, sustainer, and vernier engines and was intended to provide an alternate propulsion system should the North American Aviation effort encounter delays.
1955 January 29 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Definitive to Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation for technical support for ICBMs. - .
A formal, definitive contract between the Air Force and the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation fixed the firm's responsibility for systems engineering and technical direction (SE/TD) support for ICBMs. A formal, definitive contract between the Air Force and the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation fixed the firm's responsibility for systems engineering and technical direction (SE/TD) support for ICBMs.
1955 January 31 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- AVCO to conduct research on nose cones for missiles. - . The Western Development Division and the Special Aircraft Project Office selected AVCO Manufacturing to conduct research needed for the design of nose cones for missiles..
Early 1955 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas fabrication begins - . Nation: USA.
1955 February 14 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Contract for 12 propulsion systems for Atlas A. - . The Air Force awarded the Rocketdyne Division of North American Aviation a contract to fabricate and deliver 12 rocket engine propulsion systems for the Series A Atlas flight test missiles..
1955 February 16 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, . Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Contract for ballisitc missile all-inertial guidance system. - . Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) was awarded a contract for the research and development of an all-inertial guidance system. AC Spark Plug Company was to work with MIT and would fabricate and test the completed guidance system..
1955 February 24 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Radio guidance system for Atlas. - . The General Electric Company (GE) was given a contract to design, develop, and fabricate three complete ground-based tracking and command elements of the radio guidance system for Atlas..
1955 March 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas given top development priority. - . Nation: USA. USAF Chief of Staff, Nathan F. Twining, reported that ICBM's were receiving priority in the AF program because of known Soviet progress. Navaho, Snark, and Atlas programs accelerated..
1955 April - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- New WDD complex - . Nation: USA. New WDD complex activated on Arbor Vitae Blvd. in Los Angeles.
1955 April 12 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Contract for all-inertial guidance for a ballistic missile. - . The Arma Division of American Bosch Arma Corporation received a contract to design, develop, fabricate, and test a complete airborne all-inertial guidance system for a ballistic missile system..
1955 April 21 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Development Plan for Atlas - . The Western Development Division published the first Development Plan for Atlas (WS107A)..
1955 May 25 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- Contract for a prototype nose cone for the Atlas. - . The Air Force awarded a contract to General Electric for research, design, and development of a prototype, full-scale nose cone for the Atlas reentry system..
1955 June 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
- Quarles Committee studies best method of furnishing the United States with a sattelite by end of 1958. - .
Related Persons: Quarles,
Schriever.
Spacecraft Bus: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
SCORE.
Quarles Committee studies best method of furnishing the United States with a sattelite by end of 1958. A committee, appointed by Secretary of the Air Force, D. A. Quarles, to recommend the best method of furnishing the United States with a satellite between the dates of June and December 1958, was briefed at Western Development Division (WDD). The Atlas project was reviewed and the potential of Atlas as a booster vehicle in a selected satellite system was presented. The committee was advised that WDD was qualified to manage the program if so directed but that such a program would interfere, to some extent with the high priority of the Atlas development effort. (Memo, Col C. H. Terhune, Dep Cmdr Tech Opns, WDD, to Brig Gen B. A. Schriever, Cmdr WDD, 28 Jun 55, subj: Visit of DOD Satellite Committee, 28 Jun 55.)
1955 July 5 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Back-up reentry vehicle for Atlas. - . Western Development Division gave the AVCO Manufacturing Corporation a contract to research, design, and develop a second, or back-up, reentry vehicle (nose cone) prototype for Atlas..
1955 July 12 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Requirement for an intercontinental ballistic missile. - . General Operational Requirement (GOR) Number 104 was issued for a long-range intercontinental ballistic missile..
1955 July 27 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Maximum acceleration of the Atlas program. - . Development Directive 76 was issued for an ICBM weapon system. The directive called for maximum acceleration of the Atlas program and confirmed the assignment of the highest Air Force priority..
1955 July 28 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Eisenhower given a complete briefing on the Atlas. - .
Related Persons: Schriever,
Eisenhower.
President Dwight D. Eisenhower and the National Security Council (NSC) were given a complete briefing on the Atlas program. Briefers were Assistant Secretary of the Air Force Trevor Gardner, Professor John von Neumann, and Brigadier General Bernard A. Schriever, Commander of the Western Development Division.
1955 September 8 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Eisenhower declared that the Atlas missile had the highest priority in the nation. - . Related Persons: , Eisenhower. President Eisenhower and the National Security Council (NSC) declared that the Atlas missile, Weapon System 107A-1, had the highest research and development priority in the nation..
1955 September 13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- Acceleration of ballistic missile program. - .
Related Persons: ,
Eisenhower.
Trevor Gardner, Assistant Secretary of the Air Force for Research and Development, requested that a working group be formed to evaluate the ballistic missile program. Such an evaluation was necessary to assure that the administrative management and control procedures of the program would allow the full project acceleration as directed by President Eisenhower and the National Security Council on 8 September. Accordingly, a committee was established under Hyde Gillette, Deputy for Budget and Program Management, to evaluate these procedures and to recommend means for reducing administrative delays that might impede attainment of the earliest possible operational capability of Atlas.
1955 Oct - . LV Family: Atlas.
- First Atlas sustainer engine fired - . North American Aviation test fired the first 60,000-pound thrust Atlas sustainer engine..
Late 1955 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas program assigned top priority in the nation - . Nation: USA. Atlas program assigned top priority in the nation (was highest priority only for AF).
1955 November 8 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Gillette Committee report - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson approved the report of the Gillette Committee on simplifying administrative procedures for ICBM development programs. In accordance with the Committee's recommendations, Wilson established the Office of the Secretary of Defense Ballistic Missile Committee (OSD/BMC) with exclusive Department of Defense (DoD) authority to review and approve all ballistic missile program requirements. The existing Air Force ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee was also to advise the Secretary of Defense on ballistic missile matters. In addition, the Air Force was later authorized to undertake all actions necessary for the construction of ICBM operational bases.
1955 Dec - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Complete Atlas booster propulsion package fired for the first time. - . North American Aviation test fired the complete two-engine, 270,000-pound thrust Atlas booster propulsion package for the first time..
1955 December 1 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, . Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Highest priority for both ICBMs and IRBMs. - . Related Persons: , Eisenhower. President Eisenhower officially assigned highest and equal priority to the development of the Atlas and Titan ICBMs and the Thor and Jupiter IRBMs. This decision led to the resignation of ICBM program advocate Gardner..
1955 December 14 - . LV Family: Atlas, Thor.
- Thor given second priority after Atlas. - .
Related Persons: Power.
On the basis of the Hq USAF directive of 18 November, General Thomas S. Power, ARDC Commander, amended the Western Development Division's mission to include responsibility for ICBM initial operation capability (IOC) and for the development of IRBM Number 1 on a priority second only to that of the ICBM program.
1956 January 20 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- The Air Force ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee transferred to the Office of the Secretary of Defense. - .
The Air Force ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee was transferred to the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) to assure common interchange of technical information on all DoD missile programs. The Committee continued to act in an advisory capacity for the Western Development Division and the Air Force ballistic missile program.
1956 January 30 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- ICBM and IRBM equal priority. - . Headquarters ARDC directed WDD to treat the ICBM and IRBM with equal priority..
1956 February 10 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Trevor Gardner resigned as Assistant Secretary of the Air Force. - .
Trevor Gardner, who was instrumental in the actions leading to the acceleration of the Air Force ballistic missile program two years earlier, resigned as Assistant Secretary of the Air Force. He protested the Pentagon's policies concerning missiles and lack of stronger emphasis on the programs.
1956 Mar - . LV Family: Atlas.
- First Atlas Series A booster engines delivered. - . North American Aviation delivered the first research and development, Series A booster engines to the Convair plant in San Diego, California, where the first Atlas missile was produced..
1956 March 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- Ballistic Missiles Office established. - . The AMC Special Aircraft Project Office (SAPO) was redesignated the Ballistic Missiles Office (BMO), and Brigadier General Ben I. Funk assumed command..
1956 April 13 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Production funding for guided missiles increased. - . As per authority of the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee (AF/BMC), Procurement Authorization 56-GM-20 increased the production funding for guided missiles to $279.05 million..
1956 May - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able.
- Lunar instrument carrier using the Atlas - . Spacecraft: Explorer. The Rand Corporation reported on the feasibility of a lunar instrument carrier using the Atlas as a booster vehicle..
1956 May 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able.
- Rand Corporation studies a lunar instrument carrier, based on use of an Atlas booster. - . Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest. Rand Corporation issued a series of reports on the feasibility of a lunar instrument carrier, based on use of an Atlas booster. (Early BMD-ARDC General Space Chronology, II Feb 59, prep by AFBMD Hist Ofc.).
1956 May 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able.
- Lunar instrument carrier based on Atlas booster. - . Spacecraft: Explorer. Rand Corporation issued a series of reports on the feasibility of a lunar instrument carrier, based on use of an Atlas booster..
1956 May - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas production plant at Kearney Mesa - . Nation: USA. New Astronautics plant announced—$20 million funding by General Dynamics, with the Air Force to match, for tooling and special equipment.
1956 May 3 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Convair announced as the prime contractorfor the Atlas - . Nation: USA. The Air Force disclosed that a $41 million guided missile production facility would be built at Sorrento, California, for the Atlas launch vehicle. Convair was announced as the prime contractor..
1956 May 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able.
- RAND lunar instrument carrier based on the Atlas booster - .
Nation: USA.
The RAND Corporation issued the first of a series of reports on the feasibility of a lunar instrument carrier, based on the use of an Atlas booster. A braking rocket would decelerate the vehicle before lunar landing, and a penetration spike on the forward point of the instrument package would help to absorb the 500 feet per second impact velocity. Instruments would then transmit information on the lunar surface to earth.
1956 June 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- First Atlas production engine delivered. - . North American Aviation delivered the first production type, Series A XSM-65 Atlas engine to Convair. The early Series A booster engines had a nominal thrust of 270,000-pounds..
1956 June 21 - . Launch Site: Edwards. Launch Complex: Edwards. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas ICBM first test firing - .
Nation: USA.
First captive Atlas first test firing. The 'battleship' missile was installed at test stand 1-4, Edwards Air Force Base. The test was a failure due to inadvertant closure of the fuel prevalve, leading to duct collapse, and a turbine overspeed cutoff. No damage was sustained and the first successful firing came the next day. Atlas, First successful captive test firing, June 22, 1956, Edwards Rocket Base, duration - 4 seconds. Successful.
1956 Jul - . LV Family: Atlas.
- First test firing of the MA-1 engine for the Atlas missile. - . The Rocketdyne Division of North American Aviation completed the first test firing of the 360,000-pound thrust, three-engine propulsion cluster (MA-1) for the Atlas missile..
1956 July 3 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF missile program reductions - .
Related Persons: ,
Quarles,
Eisenhower.
The Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee (AF/BMC) withheld approval of WDD's proposed initial operational capability (IOC) program until a further review was completed. Austerity in facilities and reductions in military objectives were recommended. Secretary of the Air Force Donald Quarles and the AF/BMC directed the Western Development Division to adopt a "poor man's approach" when working out the alternate IOC program.
1956 July 9 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, .
- Hardened bases for ICBMs studied - . The Western Development Division began studying hardened bases for ICBM operational deployment..
1956 September 1 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. LV Family: Thor, Atlas.
- Vandenberg chosen as location for USAF ICBM and IRBM operations and training. - . Related Persons: , Quarles. Secretary of the Air Force Donald Quarles approved the location of ICBM and IRBM operational and training facilities at Camp Cooke, California, contingent upon approval by higher authorities..
1956 September - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas 1A delivered - . Nation: USA. Atlas missile 1A was conditionally accepted by the Air Force and delivered to the Convair Sycamore Canyon Test Site for checkout prior to captive testing..
1956 September 27 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Ballistic missile program budget cut - .
Related Persons: Schriever,
Quarles.
Secretary of the Air Force Donald Quarles rejected WDD's FY 1958 ballistic missile program budget submitted to the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee by Major General Schriever. Secretary Quarles directed a cut from the recommended $1,672 billion on a maximum of $1.3 billion and advised a restudy of IOC planning.
1956 September 28 - . Launch Site: Edwards. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas missile 2A delivered to Edwards AFB - . Atlas missile 2A was accepted by the Air Force and delivered to Edwards AFB, Test Stand 1-A, for checkout prior to captive test firings scheduled for early 1957..
1956 November 10 - . LV Family: Atlas, .
- Revised WDD ballistic missile development plan - .
Related Persons: ,
Quarles.
The revised WDD ballistic missile development plan was submitted to Secretary of the Air Force Donald Quarles and the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee. Cuts were made in force structure, and the budget was reduced to $1,335 billion as already approved by the Air Council. AFBMC also approved the new submission and passed it on to the Office of the Secretary of Defense Ballistic Missile Committee (OSD/ BMC) for consideration.
1956 November 16 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Vandenberg selected as first ICBM base. - .
Nation: USA.
Department of Defense transferred northern portion of Camp Cooke, Calif. (now Vandenberg AFB), to the Air Force to be used as first ICBM base. The Secretary of Defense directed the United States Army to transfer 64,000 acres of Camp Cooke's 86,000 acres to the Air Force.
1956 November 26 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, Thor, Jupiter, Redstone, Pershing.
- All missiles over 200 miles range assigned to USAF. - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson issued a memo to the Armed Forces Policy Council to end the argument between the Air Force and Army on responsibility for missile programs. In an effort to settle the areas of jurisdiction for the services, Secretary Wilson ruled that all long-range missiles, ICBMs as well as IRBMs, with a range of more than 200 miles, would be given to the Air Force.
1956 November 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas first flight test vehicle delivered - . Atlas missile 4A, the first flight test vehicle, was delivered to the USAF at Convair's San Diego plant. It was then transported by truck to the Missile Test Center in Florida..
1956 December - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Scheduled design complete (95%) for Atlas A-series missiles - . Nation: USA.
1956 Dec - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF missile development budget - .
Related Persons: ,
Quarles.
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson, Secretary Quarles, and the OSD/BMC approved the $1,335 billion budget submitted by WDD for FY 1958. Subsequently, however, this approved budget was cut to $1,135 billion by OSD in an effort to reduce the overall FY 1958 funding requirements of the Air Force.
1956 December 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Atlas 1A destroyed in test. - . Atlas missile 1A made its first captive test firing at Convair's Sycamore Canyon captive test facility. It burned on second run at S-l with stand damage.
1957 January 10 - . LV Family: Atlas, Titan, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Highest priority for ICBM/IRBM contracts - . The Defense Department assigned the highest priority to ICBM/IRBM contracts and purchase orders to expedite the programs..
Spring 1957 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- First flight Atlas missile delivered - . Nation: USA. First flight Atlas missile, 4A, delivered, and shipped to AMR.
1957 March - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- First flight Atlas missile erected - . Nation: USA. Atlas 4A erected on AMR LC-14.
1957 May 6 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . The Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee approved the use of Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, as the second operational prototype base in the Atlas initial operational capability (IOC) program..
1957 June - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- WDD renamed Ballistic Missiles Division (BMD) - . Nation: USA.
1957 June 11 - . 19:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A. FAILURE: Failure in the booster fuel system.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 3.00 km (1.80 mi).
The first Atlas Series A flight test missile (4A) had to be destroyed shortly after launch from Cape Canaveral due to a booster engine shutdown and loss of thrust. From a technical standpoint, however, this first booster-only launch successfully demonstrated the launching mechanism, structural integrity of the airframe, subsystems performance, and operating procedures for launch crew personnel. First test flight of prototype WS-107A Atlas was detonated by command signal at 10,000 feet following a failure in the booster fuel system. The 23-second flight was considered a partial success.
1957 July 1 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- First Atlas wing activated at Cooke AFB. - . Nation: USA. Air Research and Development Command activated the 704th Strategic Missile Wing (Atlas) at Cooke AFB..
1957 August 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas IOC delayed. - . Nation: USA. Estimated operational capability date for Atlas changed from March 1959 to June 1959..
1957 August 1 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Ballistic missile programs reoriented. - .
The National Security Council approved a Defense Department recommendation to reorient and cut back the ballistic missile programs. Atlas retained its priority, but the Titan program was reduced to second priority. The Thor and Jupiter IRBM programs were to be combined and evaluated by a joint Office of the Secretary of Defense-Air Force-Army Committee that would choose between them for future development.
1957 August 9 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor.
- Missile production rates curtailed. - .
In an attempt to reduce program costs, Defense Secretary Charles E. Wilson curtailed the planned production rates for Atlas, Titan, and Thor missiles to four missile each per month for the ICBMs. He also requested a study of the effects of a monthly production rate of 2-2-2 for the three programs.
1957 August 16 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E, Titan I.
- US ICBM production limited to four Atlas and two Titan missiles per month - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson directed that the ICBM program be limited to a maximum monthly production of four Atlas and two Titan missiles rather than the "4-4" program ordered on 9 August. With other areas also reduced, the Titan program became essentially a research and development effort.
1957 September - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
- Scheduled design complete (95%) for Atlas B-series missiles - . Nation: USA.
1957 September 11 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E, Titan I, Thor.
- Air Force Ballistic Missile program cuts - .
The Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee reviewed the revised AFBMD FY 1958 program that resulted from OSD decisions and directives of August that cut the program from $1,135 billion to $944 million. A 4-4-2 monthly production rate was approved for Atlas, Titan, and Thor missiles, and program slippages were accepted in response to Secretary Wilson's guidance of 9 August. The program was later submitted to OSD/BMC and approved on 5 October 1957.
1957 September 25 - . 19:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A. FAILURE: Failure in the booster fuel system.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 4.00 km (2.40 mi).
The second Atlas flight test missile (6A) was destroyed 32 seconds into the flight because of an engine shutdown. Atlas was again destroyed by command signal at three minutes into flight following a failure in the booster fuel system. The 50-second active flight was considered a partial success.
1957 October 5 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter.
- Studies to accelerate missile programs. - . In anticipation of directives to revise the objectives of the United States missile programs in light of the Russian success with Sputnik, AFBMD began studies for accelerating its programs..
1957 October 5 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Atlas, Thor, Titan.
- Approval of the revised AFBMD ballistic missile program. - .
Secretary of Defense Charles E. Wilson approved the revised AFBMD ballistic missile program submitted to the Air Force Ballistic Missile Committee on 12 September. A total of $991 million was approved; $437 million for Atlas, $335 million for Titan, and $148 million for Thor. AFBMD's original FY58 budget submission of October 1956 had requested $1,672 billion for the ballistic missile programs.
1957 October 6 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, .
- Restrictions on US missile production removed. - . The Defense Department removed the restrictions placed on missile production on 16 August, while the production rates and operational deployment schedules were revised..
1957 November 14 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D, Atlas E, Titan I.
- USAF augmented program for ballistic missiles - .
Headquarters USAF presented its revised and augmented program for ballistic missile development to the Secretary of Defense and the Armed Forces Policy Council. Nine Atlas squadrons were proposed, the first to become operational in June 1959 and the ninth in June 1963 and eight Titan squadrons, the first to be operational in March 1961 and the last in June 1963.
1957 November 21 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . The Air Force announced that the first Atlas ICBM operational base and strategic missile squadron would be located at Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming..
1957 December 17 - . 17:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 120 km (70 mi).
The third flight test missile (12A) became the first successful Atlas Series A missile flight. A short-range, booster-only flight was completed with the booster impacting 575 miles down range from Cape Canaveral. During the flight, all systems performed satisfactorily. First successful test firing of USAF Atlas ICBM, the missile landing in the target area after a flight of 600 miles.
1957 December 26 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- SAC made responsible for operational ballistic missile program. - . Headquarters AEDC notified AFBMD that the responsibility for the IOC phase of the ballistic missile program was to be transferred to SAC effective 1 January 1958..
1958 January - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C.
- Scheduled design complete (95%) for Atlas C-series missiles - . Nation: USA.
1958 - During the year - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Outpost four-man space station. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Ehricke.
Spacecraft: Outpost.
In 1958, the year after Sputnik 1, Krafft Ehricke, then with General Dynamics' Convair Division, designed a four-man space station known as Outpost. Ehricke proposed that the Atlas ICBM being developed by Convair could be adapted as the station's basic structure. The Atlas, 3 m in diameter and 22.8 m long, was America's largest rocket at the time.
During 1958 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Vega.
- NASA sketches two-crew Mercury follow-on spacecraft - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Johnson, Caldwell.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
In 1958 H. Kurt Strass and Caldwell C. Johnson of NASA's Space Task Group at Langley Field, Virginia.sketched a spacecraft design concept for a two-man orbiting laboratory to be launched by an Atlas-Vega booster. This was one of the earliest sketches of a two-crew Mercury follow-on. The Vega stage was dropped in favour of the Agena a year later, and a similar one-crew Mercury-Agena space station was proposed by McDonnell some years later.
1958 January 6 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Centaur proposed - . Hq ARDC proposed to Hq USAF the initiation of a program for development of an experimental exploratory space vehicle. This subsequently became the Centaur high-energy upper stage program..
1958 January 10 - . 15:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 120 km (70 mi). A successful limited flight was made by the fourth Atlas fired from Cape Canaveral..
1958 January 29 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas.
- Pacific Missile Range announced - . The Defense Department announced plans to establish the Pacific Missile Range (PMR) as part of the Naval Air Missile Test Center at Point Magu, California, and as a national range..
1958 February 3 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Thor, Atlas E, Jupiter.
- Highest priority to ballistic missiles, spy satellites, and ballistic missile early detection. - .
Related Persons: ,
Eisenhower.
Spacecraft: WS-117.
President Eisenhower directed the highest and equal national priority for Atlas, Titan, Thor, Jupiter, the WS 117L advanced military satellite system, and WS 224A BMEWS. This action returned the Titan program to its previous highest national priority status.
1958 February 7 - . 19:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1958 February 11 - . LV Family: Thor, Atlas, Titan, Navaho. Launch Vehicle: Thor Able, Thor Agena A.
- 14 Thor boosters to be used during year for space and ICBM missions. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
The ballistic missile division informed command headquarters that as many as 14 Thor boosters would be available during the calendar year for special purpose flights. These were tentatively allocated as follows: three were assigned to Phase I "Able" series flights, six were assigned to the program for recoverable satellites, and five were assigned to Phase II "Able" for continued development leading to a Thor ICBM capability. (For a time Thor plus a second stage and warhead was considered as a means of acquiring an early emergency ICBM inventory well ahead of Atlas and Titan.) However, only eight additional launchings could be scheduled through 1958--three for Phase I "Able", three for recoverable satellites to be launched one a month beginning in October, and two in support of Phase II "Able" precisely guided reentry vehicles. Thus this appeared to be the maximum effort possible in the category of space related experimental flights essential to a more advance program. If a greater effort was desirable it would be necessary to obtain additional launching facilities, a problem that might be quickly and easily solved by modifying Navaho launch stands to accept Thor vehicles. (Msg, WDT 2-7E, AFBMD to ARDC, 11 Feb 58.)
1958 February 20 - . 17:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1958 March 5 - . LV Family: Thor, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Thor Agena A, Atlas Agena A.
- USAF lead role in space reaffirmed. WS 117L to be prioritized. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
KH-1,
WS-117.
The Office of the Secretary of Defense, in the first significant forward step to accelerate development of a space capability, reiterated the space role of the Air Force. In addition to its missile programs the Air Force was responsible for the 117L system and "... has a recognized long term development responsibility for manned space flight capability with the primary objective of accomplishing satellite flight as soon as technology permits." Furthermore, the Air Force was told it was to carry forward and accelerate the Atlas 117L project "under the highest national priority in order to attain an initial operational capability in the earliest possible date," But the proposed interim system using a Thor booster combined with a second stage and recoverable capsule "should not be pursued. " The Department of Defense did agree that a Thor booster with a suitable second stage "may be the most promptly and readily available device for experimental flights with laboratory animals" and development of such hardware including a system for recovery of animals was authorized. (Msg 03-014, Cmdr ARDC, to Cmdr AFBMD, 5 Mar 58.)
1958 April 5 - . 17:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). USAF Atlas A ICBM was flown from Cape Canaveral, Fla., to the impact area some 600 miles away..
1958 April 10 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter.
- Equal priority for all ICBM and IRBM programs - . Related Persons: , Eisenhower. President Dwight D. Eisenhower reaffirmed the highest and equal national priority for Atlas, Titan, Thor, and Jupiter..
1958 April 30 - . Launch Vehicle: Thor, Atlas.
- AVCO-Convair proposal for a manned satellite at the earliest possible date. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
An AVCO-Convair contractor team submitted to the Air Force an unsolicited proposal for development of a manned satellite at the earliest possible date. The proposed system was built around an Atlas booster, no second stage, mounting a light double walled capsule which would rely on a steel mesh drag chute for deceleration and recovery. The proposal was analyzed by Air Force space specialists who concluded that the plan was feasible but offered little margin for error. Furthermore, weight estimates were optimistic, its orbital endurance and altitude were low and it possessed no growth potential although use of Atlas as a booster appeared to have merit. Air Force Ballistic Missile Division felt adoption of the proposal would only gain three or four months over the much more versatile Thor-fluorine combination vehicle which would also be free from the major limitations inherent in the AVCO-Convair proposal. (Memo, Col J. D. Lowe, AFBMD. to Col H. Evans, AFBMD, 16 May 1958, no subject.)
1958 May - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Centaur program begun - . Spacecraft: WS-117. Headquarters ARDC recommended initiation of a development program for a liquid hydrogen fueled rocket engine (Centaur program) that would be incorporated in the WS 117L advanced satellite program..
1958 May 20 - . Launch Vehicle: Thor, Atlas.
- Man-In-Space Soonest plan presented to LeMay. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
The ballistic missile division briefing on Man-In-SpaceSoonest was presented at Air Research and Development Command headquarters. Present were General C. E. LeMay and "members of the Air Staff, and to Air Force Undersecretary M. A. Maclntyre and Assistant Secretary R. E. Horner. Favorable reception was accorded the briefings and the command was assured that adequate funding, "somewhere between seventy-five and one hundred million dollars" would be allocated the program for fiscal year 1959. The briefing to Maclntyre and Horner evoked a specific suggestion that an ICBM be used as a booster in lieu of developing a second stage for the Thor. The division was allowed two weeks to prepare a plan using an Atlas booster and bring it to Washington for secretarial review. (Memo, Col H. L. Evans, Asst Dep Cmdr, Space Sys, to Col C. H. Terhune, 23 May 58, subj: Trip Report.)
1958 May 26 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Inertial guidance system transferred from the Titan to Atlas. - .
American Bosch Arma Corporation's contract for an all-inertial guidance system was transferred from the Titan (XSM-68) development program to Atlas (XSM-65) that was to become operational sooner. The Bell Telephone Laboratories (BTL) radio-guidance system would be used on all Titan research and development missiles and for the first four Titan operational squadrons.
1958 May 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas production facility opens. - . Nation: USA. Open house, new Astronautics facility on Kearny Mesa.
1958 May 28 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF fourth Man-In-Space Development Plan. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division completed its fourth Man-In-Space Development Plan.This, in the form of charts rather than a formal publication, proposed use of the Atlas booster plus a second stage consisting of a Lockheed Hustler (second stage of the 117L, later called Agena) to place a man in a 150 nautical mile orbit during October 1960. Cost for this project was estimated to be $106.11 million for fiscal 1959. The plan was briefed at command and Air Force headquarters, as well as the Air Force secretariat level. (Chronological Space Hist, 1958.)
1958 June 3 - . 21:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas A.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 120 km (70 mi).
The final Series A Atlas missile (16A) was launched from Cape Canaveral. Of the eight research and development launches, five had been failures, but each had provided vast quantities of important data. Last Atlas A flight, considered fully successful. Four of the eight flights were considered successful.
1958 June 12 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Configuration for last seven Atlas squadrons - .
The Air Force recommended to the OSD Ballistic Missile Committee that the last seven Atlas squadrons be in a dispersed 3x3 configuration and that the last five squadrons be hardened to 25 psi.The Air Force also recommended that the missiles in the last five squadrons be equipped with an all-inertial guidance system. The Committee approved these recommendations on 19 August.
1958 June 13 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- BMD opposes reduction 100 nm manned spacecraft orbit - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
The ballistic missile division informed command headquarters that reducing the orbit of a manned spacecraft from 150 to 100 nautical miles would either significantly (by 50 percent) increase the number of -stations needed for tracking and control of the manned satellite or decrease the reliability and length of contact appreciably. Also on this same date, the missile division agreed to prepare a revised manned space program which scheduled its first manned flight in April 1960--moving the date up from October by six months -by using an Atlas D booster (Chronological Space Hist, 1958..)
1958 June 13 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF conference on manned satellite program - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
Mercury,
Project 7969.
A conference was scheduled at Air Force headquarters on 25-26 Jun 1958 to discuss the "over-all problems of the manned satellite development program." The conference was sponsored by the Advanced Research Projects Agency with representatives of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Air Research and Development Command, Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, Space Technology Laboratories, and Convair invited to the meeting. Questions to be attacked were: Could the booster be an Atlas without a second stage? What would be the subsystem distribution of payload weight? What was Atlas maximum payload weight performance? question of ablation or heat sink capsule design was to be resolved before the conference. If it was concluded that Atlas weight lifting performance was inadequate an alternate choice would be the Atlas with a 117L second stage. Complete funding plans covering program options were to be available to the conferees. (Msg, AFDRD 51947, Hq USAF, to Hq ARDC, 13 Jun 58.)
1958 June 13 - . LV Family: Atlas, .
- Man-In-Space-Soonest to use of Atlas D booster for first manned spacecraft during April 1960. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
In an agreed draft revision of its "Man-In-Space-Soonest" development plan, AFBMD proposed the use of an Atlas D booster to put the first manned spacecraft into a 115-NM orbit during April 1960. If Atlas D performance were not sufficient, an Agena or Vanguard second stage would be added.
1958 June 15 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Draft revision of USAF Man-In-Space-Soonest plan - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
This plan proposed use of an Atlas booster to place a man in 115 nautical milt, orbit during April 1960. In event the performance was not up to lifting the required payload weight, a 1177L or a Vanguard second stage would be added. Costs were estimated at $99.3 million for Atlas alone, $139.51 million if a 117L vehicle were used as the second stage. (Chronological Space Hist, 1958.)
1958 June 16 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF fifth Man-In-Space-Soonest plan - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division presented its fifth Man-In-Space-Soonest development plan to Washington decision points in the Air Force and Office of the Secretary of Defense. The division was instructed to complete its plans for an Atlas vehicle plus a second stage as a backup in the event the Atlas could not handle the job alone. (Chronological Space Mist, 1958.)
1958 June 19 - . Launch Vehicle: Thor, Atlas.
- No "go ahead" for the man in space program. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
Mercury,
Project 7969.
The Advanced Research Projects Agency had not yet directed a "go ahead" for the man in space program. However, Air Force headquarters considered it a certainty that direction of an Atlas boosted manned space flight would be given to the Air Force at an early date, that funds for the project would probably total $66 million and that a series of Thor boosted, instrument and animal capsule flights would precede the Atlas full sized instrumented capsule, chimpanzee, and manned shots. The Air Force would probably re-program to obtain whatever additional funds were required to support the program. The ballistic missile division was advised that while waiting for an authoritative "go ahead" it should continue preparation of work statements for industry competition and contractor selection so they might be coordinated with the Advanced Research iProjects Agency and the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics. (Ltr, Maj Gen J. E. Smart, Asst V/CS, to Lt Gen S. E. Anderson, Cmdr ARDC, 19 Jun 58, no subject given, quoted in TWX, RDZGW6-33-K, Hq ARDC, to Hq AFBMD, 27 Jun 58.)
1958 June 24 - . Launch Vehicle: Thor, Atlas.
- Secretary of the Air Force authorized an increase in missile production. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
,
KH-1.
Inasmuch as availability of basic booster units threatened to limit selection of the most desirable space programs, the Secretary of the Air Force authorized an increase in missile production as follows: four more Thor boosters, delivery to begin in December 1958 at a rate of one a month; four more Atlas boosters, delivery to begin in May 1959 at a rate of one a month; and $8 million budgeted to the Advanced Research Projects Agency for procurement of four additional Lockheed 117L vehicles, delivery to begin January 1959 at a rate of one a month. (Memo, SAF to C/S USAF, 24 Jun 58, no subject.)
1958 July - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas ICBM soft pad design complete. - . Nation: USA. Design of vertical initial operational capability ground support equipment.
1958 July 10 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Advanced Research Projects Agency questions - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
The Advanced Research Projects Agency addressed two questions to the research and development command: Would the Air Force accept a 110 nautical mile orbit instead of 150 nautical miles for the manned space flight? What degree of program accomplishment could be obtained with a fiscal 1959 program of $50 million based on an Atlas-117L second stage? (Chronological "Space Hi't, 1958.)
1958 July 19 - . 17:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B. FAILURE: Flight Control Failure. Failed Stage: G.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 10 km (6 mi).
The initial Atlas Series B missile flight test vehicle (3B) malfuncticr.ed and broke up 60 seconds after launch from the Air Force Missile Test Center at Cape Canaveral. To the basic Series A airframe, the Series B missiles added the complete North American Aviation MA-1 propulsion cluster of booster and sustainer engines, General Electric's Mod II airborne radio inertial guidance system (open loop), and GE's Mark II nose cone. First full-powered flight of USAF Atlas B ICBM using both the sustainer and booster engines. 'Marginally successful'.
1958 July 24 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF sixth Manned Military Space System Development plan. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division published its sixth Manned Military Space System Development plan. This proposed a single Atlas booster, but with a back-up program for a second stage (either 117L or AJ 10), to place a man in a 150 nautical mile orbit in June 1960. The cost to carry out this plan was estimated at $106.66 million for fiscal 1959. (Chronological Space Hist, 1958.)
1958 August - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Scheduled design complete (95%) for Atlas D-series missiles - . Nation: USA.
1958 August 2 - . 22:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 900 km (550 mi).
The first successful flight test of a Series B Atlas missile. This was also the first successful staging of a long-range missile. (AF Ballistic Missiles Program Status Report.) Flight test missile 4B was the first Atlas Series B missile to be launched successfully and the first ICBM to complete staging. Its 2,500-mile powered flight was the first time that the MA-1 propulsion cluster operated for the planned duration of flight. Second full-powered flight of USAF Atlas ICBM traveled 2,500 miles with radio-inertial guidance, fully successful.
1958 August 22 - . LV Family: Atlas, Thor, Minuteman, .
- Largely as a result of the successful Thor/Able reentry tests, Brigadier General Osmond J. - .
Ritland, AFBMD Vice Commander, reoriented the Division's reentry vehicle research and development program. Avco was directed to cancel its work on a y copper "heat sink" reentry vehicle. General Electric's Mark II copper "heat sink" nose con^ would be used on Thor IRBMs and early model Atlas ICBMs. Moreover, GE was assigned to start work on lightweight, second generation nose cones for heavier warheads.
1958 August 26 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- USAFstrategic communications satellite plan. - . Spacecraft: Advent. After examining contractor proposals for a communications satellite relay project since September 1957, Headquarters ARDC presented its original strategic communications satellite development plan..
1958 August 29 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Centaur upper stage to be used with either Atlas or Titan boosters. - .
ARPA issued order Number 19-59 establishing the Centaur program that would provide a high energy, liquid-fuel upper stage for use with either the Atlas or Titan boosters. Pratt and Whitney was to develop the liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen engines for the upper stage vehicle to be developed by Convair/Astronautics. The development goal was to produce an upper stage vehicle that could place a satellite into a 24-hour, synchronous orbit 23,000 miles above the equator.
1958 August 29 - . 04:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
1958 September 14 - . 05:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
1958 September 18 - . 21:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1958 October 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- Centaur engine contract awarded. - . Nation: USA. Air Force awarded contract Pratt & Whitney for Centaur vehicle with hydrogen-burning chamber based on research of Lewis Research Center between 1953 and 1957. Centaur project later transferred to NASA..
1958 October 17-18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Negotiations for Mercury Atlas launch vehicles - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Langley Research Center personnel visited the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, Inglewood, California, to open negotiations for procuring Atlas launch vehicles for the manned satellite project..
1958 November 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Joint Army-Air Force synchronous orbit communications satellite. - .
Spacecraft: Advent.
ARPA requested a joint Army-Air Force development plan for a 24-hour, synchronous equatorial orbit communications satellite. The Army Signal Corps was to be responsible for the ground and satellite communications while the Air Force (AFBMD) was to handle satellite spacecraft, booster, and launch services. The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) made the Army Signal Research and Development Laboratory (ASRDL) and the Air Research and Development Command (ARDC) responsible for milcomsats. This covered communications and vehicular aspects of the first U.S. military communications satellite program. Booster and spacecraft development were assigned to AFBMD.
1958 November 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- AFBMD responsible for booster and spacecraft for Advent. - . Spacecraft: Advent, . Headquarters ARDC informed AFBMD that it would be responsible for the booster and spacecraft portions of the 24-hour communications satellite program..
1958 November 18 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
1958 November 24 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Space Task Group orders first Mercury Atlas missile. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
The Space Task Group placed an order for one Atlas launch vehicle with the Air Force Missile Division, Inglewood, California, as part of a preliminary research program leading to manned space flight. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration Headquarters requested that the Air Force construct and launch one Atlas C launch vehicle to check the aerodynamics of the spacecraft. It was the intention to launch this missile about May 1959 in a ballistic trajectory. This was to be the launch vehicle for the Big Joe reentry test shot, but plans were later changed and an Atlas Model D launch vehicle was used instead.
1958 November 25 - . Launch Vehicle: Thor, Atlas.
- USAF receives request for booster support of NASA manned space program. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
Mercury.
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division received its first specific request from the civilian space agency to support a "preliminary research program leading to manned space flight." The division was requested to procure one Atlas C ballistic missile booster with its associated control and guidance equipment." '... This request was a forerunner of a support effort for a program "requiring approximately thirteen (13) ballistic missile boosters of the Thor and Atlas class."' The space agency would procure the payload, scheduled for May 1959 delivery. The missile division was to furnish detailed plans, subject to the approval of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, for the design, construction and launching of this vehicle. One million dollars was immediately transferred to the Air Force with more money to be supplied as it was requested. (Msg, no cite number, Hq NASA, to Cmds. AFBMD, 25 Nov 58.)
1958 November 29 - . 02:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
- Research and development / AFSWC-3 test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 900 km (550 mi). Less than 18 months after the first flight, a USAF Atlas made its first successful full-range operational test flight in a 6,325 statute-mile flight, landed close to its target..
1958 December 1 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAF support role only in US manned space program. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest.
While the probability of the ballistic missile division developing a military manned space system was rapidly diminishing, military and civilian demand for space boosters was accelerating. Except for certain strictly military applications it was plain the Air Force would play mainly a supporting role in the nation's space program, supplying boosters and launch facilities to the civilian .space agency and the Advanced Research Projects Agency. On this date there were approximately 11 scheduled programs, several only in the planning stage. One of the firm programs was the civilian agency's man in space which was scheduled to launch its first experimental Atlas C payload in May 1959 and start a series of nine Atlas D launches beginning December 1959. (Ltr, Col L. D. Ely, Asst Dep Cmdr, Military Space Sys, AFBMD, to Col C. H. Terhune, 1 Dec 58, subj: Atlas Boosters for Space Projects.)
1958 December 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Nine Atlas launch vehicles ordered for Project Mercury - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Space Task Group indicated that nine Atlas launch vehicles were required in support of the Project Mercury manned and unmanned flights and these were ordered from the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division..
1958 December 18 - . 23:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
- Score - .
Mass: 70 kg (154 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DARPA.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft: Score.
Decay Date: 1959-01-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 10 . COSPAR: 1958-Zeta-1. Apogee: 1,484 km (922 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 32.30 deg. Period: 101.50 min.
Signal Communication by Orbiting Relay Equipment; first commsat; transmitted taped messages for 13 days. Project Score, Atlas rocket placed in orbit carrying communications equipment which relayed President Eisenhower's Christmas message to the world from outer space. (AF Ballistic Missiles Program Status Report.)
1958 December 20 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- NASA-USAF modalities for Atlas - .
Spacecraft: Mercury.
One of the most important Project Mercury meetings between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the missile division took place. A series of agreements was approved controlling administrative arrangements and procedural channels essential to coordinated, efficient management of the joint phases of the program. Cost of the Atlas booster was set at $3.5 million, Space Technology Laboratories systems engineering and technical direction of the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division's part in the program was agreed upon, revision of program requirements was accomplished, regular technical and management meetings were arranged, and the missile division promised to prepare a development plan for the first Mercury booster (HS-24) by February 1959. (Ref .J file, AFBMD Support, Proj Mercury, Dec 60.)
1958 December 24 - . 04:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 900 km (550 mi). First Atlas C flight (3C), successful..
1959 January - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Strategic Air Command takes over Atlas ICBM facilities. - . Nation: USA. VAFB SMS 576A facilities turned over to SAC.
1959 January 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- Centaur first contract. - . Nation: USA. Centaur project (Atlas upper stage) contracted for $7 million in its first year.
1959 January 16 - . 04:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1959 January 27 - . 23:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C.
- Mod II re-entry vehicle research and development mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 990 km (610 mi).
1959 February - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NASA/USAF responsibilities for the first two Mercury Atlas firings. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
During a meeting between personnel of the Space Task Group and the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, the responsibilities of the two organizations were outlined for the first two Atlas firings. Space Technology Laboratories, under Air Force Ballistic Missile Division direction, would select the design trajectories according to the specifications set forth by the Space Task Group. These specifications were to match a point in the trajectory at about 450,000 feet, corresponding to a normal reentry condition for the manned spacecraft after firing of the retrorockets at an altitude of 120 nautical miles. Space Technology Laboratories would also provide impact dispersion data, data for range safety purposes, and the necessary reprograming of the guidance computers. The spacecraft for the suborbital Atlas flights would be manufactured under the deriction of the Lewis Research Center, based on Space Task Group designs. Space Task Group was developing the spacecraft instrumentation, with a contingent of personnel at the Lewis Research Center. The attitude control system was being developed by Lewis.
1959 February - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas ICBM coffin launcher design completed. - . Nation: USA. Design of horizontal operational ground support equipment (coffin configuration) completed.
1959 February 4 - . 08:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas B.
- Research and development / AFSWC-4? test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 990 km (610 mi). Last Atlas B flight, fully successful.
1959 February 12-13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas launch vehicles in Project Mercury. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Discussions were held at Langley Field between the Space Task Group and the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division covering aspects of the use of Atlas launch vehicles in Project Mercury. Specifically discussed were technical details of the first Atlas test flight (Big Joe), the abort sensing capability for later flights, and overall program objectives.
1959 February 20 - . 05:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1959 February 28 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- The first operational Atlas missile accepted by the Air Force - . The first operational Atlas missile, 6D, was accepted by the Air Force from Convair. Subsequently, 6D was installed in the first Atlas complex, 65-1, at Vandenberg AFB during the first week of March..
1959 Mar - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas squadrons five to nine to have nine launchers each. - . Atlas squadrons five through nine were approved for a 1x9 configuration - each squadron to consist of nine individual launchers..
1959 Mar - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . Construction began on the Atlas D operational sites assigned to Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, and Offutt AFB, Nebraska..
1959 March - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C.
- Atlas 6C blows up. - . Nation: USA. Missile 6C blows up, destroying ERB Stand 1-A..
1959 March 11 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- NASA Atlas plan - .
Spacecraft: Mercury,
.
The civilian space agency acknowledged receipt of the missile division development plan for the first booster scheduled to start the man in space effort. Except for two revisions, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration declared the plan to be "satisfactory." One of the revisions was suggested in this statement: "NASA prefers not to be committed to the specified sum of $3,556,000, but reserves the right to negotiate the costs." (Ltr, T. K. Glennan, NASA Administrator, to Cmdr, ARDC, 11 Mar 59, no subject.)
1959 March 19 - . 00:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- RVX-2 re-entry vehicle research and development mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 200 km (120 mi).
1959 April - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Scheduled design complete (95%) for Atlas E-series missiles - . Nation: USA.
1959 April 14 - . 21:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development launch - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1.00 km (0.60 mi).
The first Atlas D model flight test missile (3D) had to be destroyed 36 seconds into flight due to a severe engine malfunction and explosions. In addition to other changes, the D series replaced the MA-1 engine package with the Rocketdyne MA-2. The booster engines in the MA-2 produced 309,000 pounds of thrust versus 300,000 pounds for the MA-1. Sustainer engine thrust remained 57,000 pounds. With verniers, total thrust for the MA-2 was 368,000 pounds compared to 357,000 for the MA-1 engine package.
1959 April 26 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- USAf-NASA Atlas cost dispute - .
Spacecraft: Mercury,
.
Air Force Ballistic Missile Division replied to the 11 March 1959 letter in which the civilian agency demurred at accepting the charge of $3.55 million without the right to negotiate the cost. The missile division reminded National Aeronautics and Space Administration that it had already committed $2.761 million to the space agency's Order HS-24 and in the immediate future additional funds were required up to $3.556 million to cover the cost of the basic Atlas booster and additional work schedule through the launching sequence as stipulated in the development plan. (Msg, WDPP-4-4, Cmdr AFBMD, to NASA, 24 Apr 59.)
1959 May 9 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Vega.
- High-resolution photographs of the moon using Vega rocket - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Rosen, Milton.
Program: Apollo.
Spacecraft: Lunar Orbiter.
Milton W. Rosen of NASA Headquarters proposed a plan for obtaining high-resolution photographs of the moon. A three-stage Vega would place the payload within a 500-mile diameter circle on the lunar surface. A stabilized retrorocket fired at 500 miles above the moon would slow the instrument package sufficiently to permit 20 photographs to be transmitted at a rate of one picture per minute. Additional Details: here....
1959 May 14 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NASA combines Atlas booster orders - .
Spacecraft: Mercury.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration instructed the missile division to combine its first order for an Atlas booster (HS-24) with a later order for nine Atlas boosters. This action would also combine fund allocations of $2,761 000 for the first booster and $6 million for the nine boosters to a fund total of $8,761, 000 for Mercury booster procurement. therefore, the missile division was requested to prepare a development and funding plan covering the amended HS-36 order and forward the plan to NASA by 15 June 1959, (Msg, no cite number, NASA to AFBMD, 14 May 1959.)
1959 May 19 - . 04:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1959 May 20 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Project Steer - .
Spacecraft: Advent.
At last realizing the importance of the ground-to-aircraft communications requirements for control of the SAC bomber force, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) initiated Project Steer. The defense communication satellite effort now had three distinct elements - Steer; Tackle, for an advanced polar communication satellite; and Decree for a 24-hour synchronous communication satellite to be put in orbit by the as yet undeveloped Atlas-Centaur. Priority was assigned to Project Steer, and project supervision was given to AFBMD. However, ARPA retained control and did not delegate authority and responsibility for systems integration.
1959 June - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas 2D blows up. - . Nation: USA. Missile 2D blows up on Sycamore stand S-2, after a total of 1486 seconds running time.
1959 June 5 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Flight instrumentation for Mercury-Atlas program. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Space Technology Laboratories and Convair completed an analysis of flight instrumentation necessary to support the Mercury-Atlas program. The primary objective of the study was to select a light-weight telemetry system. A system weighing 270 pounds was recommended, and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration concurred with the proposal.
1959 June 6 - . 17:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1959 June 30 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Centaur transferred to NASA. - . The Centaur high-energy upper stage development program was transferred from the Air Force (ARDC) to NASA..
1959 July 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Instrumentation to measure noise level during the Mercury Big Joe-Atlas launching. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
An agreement was made with the Air Force for Space Task Group to place microphone pickups on the skin of the Atlas launch vehicle as a part of the instrumentation to measure noise level during the Big Joe-Atlas launching. Distribution of the microphones was as follows: one inside the Mercury spacecraft, three externally about midway of the launch vehicle, and one on the Atlas skirt.
1959 July 21 - . 05:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C.
- Research and development / AFSWC-5 test / particles mission - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 900 km (550 mi).
The first full-scale test of an ablation reentry vehicle (RVX-2) was conducted with the launch and successful flight of Atlas 8C. Following the 4,385 NM flight into the South Atlantic, the reentry vehicle was recovered. A full-scale USAF Atlas ICBM nose cone recovered for the first time after flight down the AMR.
1959 July 28 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- First successful Series D Atlas missile flight test. - . Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest. (Air Force Ballistic Missiles Program Status Report.).
1959 July 29 - . 04:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). First Atlas successful D missile flight.After three consecutive failures (3D, 7D, and 5D), Atlas missile 11D became the first Series D flight test missile to complete a successful launch from Cape Canaveral..
1959 August 11 - . 18:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1959 August 24 - . 15:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C.
- Research and development / AFSWC-6 test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
The final Atlas Series C missile, 11C, was fired from Cape Canaveral. Three of the six Atlas C research and development test missiles were successful, while the other three were failures. Last successful Atlas C flight (11C); 9C exploded one month later during the Able static firing.
1959 August 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Additional Atlas launch vehicles in support of Project Mercury. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
NASA Headquarters authorized the Space Task Group to enter into negotiations with the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division for the procurement of additional Atlas launch vehicles in support of Project Mercury. The authorization was to be incorporated into Contract No. HS-36.
1959 August 31 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas.
- LC 576A at Vandenberg first fully operational ICBM complex. - . Complex 576A (65-1) at Vandenberg AFB was transferred to SAC and thus became the first fully operational ICBM complex..
1959 September 1 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas D ICBM operational. - . Nation: USA. USAF Atlas ICBM officially declared operational and taken over by the Strategic Air Command, at Vandenberg AFB..
1959 September 9 - . 08:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Mercury BJ-1 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 153 km (95 mi).
A NASA boilerplate model of the Mercury capsule was launched atop Atlas 10D from Cape Canaveral. Although the range was less than planned due to failure of the Atlas booster engine section to separate, the capsule was recovered in the South Atlantic after surviving reentry heat of more than 10,000°F.
1959 September 9 - . 17:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas ICBM initial operational capability demonstration launch - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF SAC.
Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
A SAC crew conducted the first west coast launch of an Atlas operational configuration missile, 12D, from Vandenberg AFB, to a target near Wake Island, Afterward, General Thomas S. Power, CINCSAC, declared the Atlas system to be operational. This marked the attainment of operational status for the Atlas one year earlier than the six years that the von Neumann Committee had projected in its February 1954 report.
1959 September 17 - . 02:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1959 September 21 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor.
- USAF responsible for all military spacecraft. - .
Related Persons: ,
LeMay.
General Curtis E. LeMay, Vice Chief of Staff, USAF, informed Headquarters ARDC that the Secretary of Defense had assigned responsibility to the Air Force for developing and launching all military spacecraft. The Air Force was also to perform all required systems integration for military space systems. The decision was made for reasons of efficiency and economy.
1959 September 23 - . LV Family: Polaris, Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Responsibility for military space programs assigned to USAF - .
Spacecraft: WS-117,
Transit,
Midas,
Samos.
Once again, the Defense Department reorganized its space program. Primary responsibility for military space programs was assigned to the Air Force. ARPA retained responsibility for advanced research on missile defense, solid propellants, and several other projects. Existing projects were reassigned to the military services from ARPA - MIDAS and SAMOS to the Air Force,the Transit navigation satellite to the Navy, and NOTUS to the Army. These reassignments were not immediately effective, but the move toward Air Force development, production, and launching of military space vehicles was quite clear.
1959 September 24 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas C Able. FAILURE: Vehicle exploded on pad.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Atlas C Able explodes on pad during static test. - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: Pioneer.
A participant remembers:
I live near the Cape on Merritt Island and have been here for about 41 years. I worked for the ARMA Corp that developed the Atlas Inertial Guidance System. I was in the Blockhouse at Complex 11 while a static test was performed on an Atlas Able on Complex 12. It did explode. Did it ever! After a couple of hours the six of us were allowed out of the blockhouse and saw all the damage to our complex...I had a tiny piece of that missile for a long time that somehow wound up on my person...labeled 9C.
The next Atlas Able would not fly until over a year later, using the Atlas D as the booster stage.
1959 October 2 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . The first Atlas missile was delivered to Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, and was used to check out missile installation and launch facilities..
1959 October 6 - . 05:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mk 3 Mod 1 re-entry vehicle research and development mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1959 October 10 - . 03:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1959 October 29 - . 07:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). USAF Atlas successfully launched from Cape Canaveral carrying a nose-cone camera which took a series of photographs of the earth's cloud cover from a 300-mile altitude..
1959 November 4 - . 21:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1959 November 24 - . 19:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1959 November 26 - . 07:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able. FAILURE: Payload shroud failed after 45 sec, broke away prematurely.. Failed Stage: S.
- Pioneer (P 3) - .
Payload: Pioneer P 3 / Able IVB. Mass: 168 kg (370 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Pioneer.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer P 3.
Decay Date: 1959-11-26 . Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
An intended lunar probe launched from the Atlantic Missile Range by an Atlas-Able booster disintegrated about 45 seconds later when the protective sheath covering the payload detached prematurely. The probe was sponsored by NASA, developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and launched by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division.
1959 November 27 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Headquarters USAF directed an Atlas program of 13 squadrons. - .
1959 Dec - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas.
- First American ICBM put on strategic offensive alert - . One Atlas D missile at Vandenberg complex 576A was maintained in a state of operational readiness during the month. This marked the introduction of the ICBM into the U.S. strategic offensive alert..
1959 December 9 - . 00:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1959 December 19 - . 00:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Atlas ICBM made second successful 6,325-mile flight at AMR..
1960 Jan - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Ablestar second stage completed - .
Aerojet-General Corporation completed development of the Ablestar second stage for use with Atlas, Titan, or Thor boosters. Primary improvements over the previous Able vehicles were increased propellant capacity, multiple restart capability, and full-time attitude control.
1960 January 7 - . 01:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). 43D achieved a 6300 NM (7200 SM) flight from AMR with enough residual fuel for an additional 2000 miles.
1960 January 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury-Atlas flight test working group - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
A proposal was made by Walter C. Williams, Associate Director of Project Mercury Operations, that the Mercury-Atlas flight test working group become an official and standing coordination body. This group brought together representation from the Space Task Group, Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, Convair Astronautics, McDonnell Aircraft Corporation, and the Atlantic Missile Range. Personnel from these organizations had met informally in the past on several occasions.
1960 January 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- 15 Atlas launch vehicles and 26 Mercury spacecraft purchased. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. At a meeting to draft fiscal year 1962 funding estimates, the total purchase of Atlas launch vehicles was listed as 15, and the total purchase of Mercury spacecraft was listed as 26..
1960 January 26 - . 23:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure.
- Initial operational capability demonstration launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Two Atlas ICBMs launched within two hours - one by SAC at VAFB, one by GD/A at AMR; both successful..
1960 January 27 - . 01:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1960 February 12 - . 04:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1960 February 15 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able. FAILURE: Vehicle exploded in static firing.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Pioneer (P 31) - . Payload: Pioneer P 31. Nation: USA. Program: Pioneer. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer P 3. Decay Date: 1960-02-15 . COSPAR: F600215A.
1960 February 26 - . 17:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena A. FAILURE: Second stage failed to separate.. Failed Stage: U.
- Midas 1 - .
Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1008. Mass: 2,025 kg (4,464 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: Midas.
Decay Date: 1960-02-26 .
The Air Force MIDAS I satellite was launched from Cape Canaveral in the first successful launch of the Atlas D/Agena A booster-upper stage combination. MIDAS I, however, failed to achieve orbit because an accident at the Atlas-Agena staging damaged the Agena. The entire vehicle reentered and burned up about 2,500 miles downrange. Missile Defense Alarm System.
1960 February 29 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- USAF selects Advent as sole military communication satellite. - .
Spacecraft: Advent.
Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) issued an interim directive cancelling the three-phase development program for a military communication satellite system. Pending a Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) and OSD review, Projects Steer, Tackle, and Decree were replaced by a single synchronous communications satellite system subsequently designated Project Advent. AFBMD was directed to conduct a single integrated research and development program for a 24-hour synchronous equatorial global communication satellite system. The Army was to develop the communications equipment while AFBMD handled the booster and spacecraft.
1960 Mar - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Three Atlas missiles in semi-readiness - . Three Atlas missiles were placed in semi-readiness at Vandenberg AFB..
1960 March-April - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury-Atlas working panels - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
The Mercury-Atlas working panels were reorganized into four groups: coordination, flight test, trajectory analysis, and change control. Each panel was composed of at least one representative from NASA (Space Task Group), McDonnell, Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, Space Technology Laboratory, and Convair-Astronautics.
1960 March 8 - . 13:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). First USAF Atlas R&D flight using all-inertial guidance system..
1960 March 11 - . 00:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1960 March 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Recovery requirements for Mercury MA-1. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Space Task Group published recovery requirements for the Mercury-Atlas 1 (MA-1) flight test..
1960 Apr - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas squadrons 8 through 13 to have 12 launchers each. - . Headquarters USAF approved a 1 x 12 configuration for Atlas squadrons 8 through 13 - each squadron would have 12 individual launch facilities..
1960 April 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E, Atlas F.
- Atlas E/F silo-based squadrons increased by one silo each. - . Atlas E/F silo-lift strategic missile squadrons were enlarged from 9-12 launchers to 10-13 each. In these units, the Atlas missiles would be maintained in hardened underground silos..
1960 April 8 - . 02:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1.00 km (0.60 mi). Atlas 48D, intended to be the first closed-loop test of the Arma all-inertial guidance system, exploded immediately after launch release as a result of combustion instability in the MA-2 engine..
1960 April 22 - . 19:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Initial operational capability operational readiness test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). SAC crews successfully fired the first Atlas missile (25D) to be launched from an operational horizontal "coffin" missile storage/launcher facility at Vandenberg AFB. .
1960 May 6 - . 16:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Initial operational capability operational readiness test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 2.00 km (1.20 mi).
1960 May 20 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
Atlas 56D carried a 3,000-pound payload 7,859 nautical miles (9,040 statute miles) from Cape Canaveral to the target area in the Indian Ocean. This was the longest U.S. missile flight to date. Payload was an operational weight nose cone plus instrumentation. Missile attained an apogee of about 1,000 miles.
1960 May 24 - . 17:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena A.
- Midas 2 - .
Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1007. Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: Midas.
Decay Date: 1974-02-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 43 . COSPAR: 1960-Zeta-1. Apogee: 494 km (306 mi). Perigee: 473 km (293 mi). Inclination: 33.00 deg. Period: 94.30 min.
Missile Defense Alarm System. Test launch with W-17 sensor. The last Atlas D/Agena A booster to be used by the Air Force placed into orbit the MIDAS II infrared scanning satellite designed to detect and give early warning of missile launchings. Although intended to function for 40 months, the satellite's telemetry system failed on 26 May. MIDAS II was the first early warning satellite system placed in orbit.
1960 June 11 - . 06:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Atlas flight test missile 54D completed the first successful demonstration of accuracy and reliability of the closed-loop Arma all-inertial guidance system. .
1960 June 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-1 launch vehicle delivered - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle 50-D was delivered for the first Mercury-Atlas mission (MA-1)..
1960 June 22 - . 14:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Electrical Failure.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). 50th Atlas to be flown at AMR, successful.
1960 June 28 - . 02:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development / ionosphere mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1960 July 2 - . 06:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1960 July 11 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Ballistic missile site activation moved to Air Materiel Command. - .
Headquarters USAF assigned responsibility for management of all ballistic missile operational site activation work to Air Materiel Command. ARDC retained responsibility for activation of Atlas D squadrons - the 564th and 565th Strategic Missile Squadrons at F.E. Warren and the 566th at Offutt AFB - and for first-of-a-kind installations at Vandenberg AFB. Under these arrangements, AMC was to have responsibility for contractor direction and performance while AFBMD retained control of site installation design and some facets of technical engineering and configuration control.
1960 July 11 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas operational plans given high priority - . Nation: USA. M. Gen. Tom Gerrity appointed head of new BMC for operational site selection through turnover.
1960 July 15 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas F squadron 576A activated at Vandenberg AFB. - . The 576A Strategic Missile Squadron (Atlas F) was activated at Vandenberg AFB and assigned to SAC's First Missile Division..
1960 July 22 - . 23:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Initial operational capability operational readiness test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 20 km (12 mi).
1960 July 25 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas D squadron 576B activated at Vandenberg AFB. - .
1960 July 29 - . 13:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Structural failure of Atlas.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Mercury MA-1 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Apogee: 13 km (8 mi).
The first Mercury-Atlas -D (MA-1) was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral to test the Mercury capsule and Atlas D booster for future use in NASA's Project Mercury manned orbital flight program. Mercury-Atlas 1 (MA-1) was launched from the Atlantic Missile Range in a test of spacecraft structural integrity under maximum heating conditions. After 58.5 seconds of flight, MA-1 exploded and the spacecraft was destroyed upon impact off-shore. None of the primary capsule test objectives were met. The mission objectives were to check the integrity of the spacecraft structure and afterbody shingles for a reentry associated with a critical abort and to evaluate the open-loop performance of the Atlas abort-sensing instrumentation system. The spacecraft contained no escape system and no test subject. Standard posigrade rockets were used to separate the spacecraft from the Atlas, but the retrorockets were dummies. The flight was terminated because of a launch vehicle and adapter structural failure. The spacecraft was destroyed upon impact with the water because the recovery system was not designed to actuate under the imposed flight conditions. Later most of the spacecraft, the booster engines, and the liquid oxygen vent valve were recovered from the ocean floor. Since none of the primary flight objectives was achieved, Mercury-Atlas 2 (MA-2) was planned to fulfill the mission.
1961 August 1960 to February - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Exhaustive review of Mercury-Atlas after dual Atlas failures. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Because of the failure of the Big Joe Atlas test flight and the Mercury-Atlas 1 (MA-1) flight to attain all its mission objectives, the overall Mercury-Atlas program underwent an exhaustive review. . Additional Details: here....
1960 August 5 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . Complex 564A, designed to house three Atlas D missiles in horizontal "coffin" storage/launcher facilities, was completed at Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, and transferred to SAC..
1960 August 9 - . 18:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development / aeronomy mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1960 August 11 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-1 malfunction discussed. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: Chamberlin. Spacecraft: Mercury. Representatives of NASA, McDonnell, Ballistic Missile Division, Space Technology Laboratories, and Convair met at Cape Canaveral and later at Convair Astronautics (Aug. 30, 1960) to discuss the Mercury-Atlas 1 (MA-1) mission malfunction. . Additional Details: here....
1960 August 12 - . 13:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1960 August 30 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - .
The transfer of the three-missile Complex 564B, the first operational Atlas D (CGM-16D) squadron at Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming. With this the 564th Strategic Missile Squadron, was turned over to the Strategic Air Command's 706th Strategic Missile Wing.
1960 September 12 - . 20:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Initial operational capability demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi).
1960 September 17 - . 00:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1960 September 19 - . 18:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Atlas ICBM fired 9030 statute miles, from Cape Canaveral to the Indian Ocean off the Cape of Good Hope in 50 minutes, the second record distance flight..
1960 September 20 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-3 launch vehicle delivered - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Atlas launch vehicle 67-D was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 2 (MA-2) reentry test mission..
1960 September 25 - . 15:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able. FAILURE: Second stage exploded.. Failed Stage: U.
- Pioneer (P 30) - . Payload: Pioneer P 30 / Able VA. Mass: 175 kg (385 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Pioneer. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer P 3. Decay Date: 1960-09-25 . Apogee: 1,290 km (800 mi). An attempt to launch a Pioneer satellite into lunar orbit failed when one of the upper stages of the Atlas- Able rocket malfunctioned..
1960 September 26 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Roll-out of Mercury MA-3 launch vehicle - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The roll-out inspection of Mercury Atlas launch vehicle 77-D was conducted at Convair-Astronautics. This launch vehicle was allocated for the Mercury-Atlas 3 (MA-3) mission, but was later canceled and Atlas booster 100-D was used instead..
1960 September 29 - . 20:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Initial operational capability demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 500 km (310 mi).
1960 October 11 - . 19:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,000 km (600 mi). First E missile flown with MA-3 engine, unsuccessful.
1960 October 11 - . 20:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena A. FAILURE: Second stage failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Samos 1 - . Payload: Samos E-1 no. 1. Mass: 1,845 kg (4,067 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1960-10-11 . First generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images; Satellite and Missile Observation Satellite..
1960 October 13 - . 04:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Initial operational capability demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 20 km (12 mi).
1960 October 13 - . 09:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). USAF Atlas launched at AMR placed nose cone containing three black mice 650 miles up and 5,000 miles downrange at 17,000 mph. Nose cone was recovered in target area near Ascension Island, the three mice surviving the flight in "good condition.".
1960 October 17 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Air Force gives up on separate military man in space program. - .
Spacecraft: Man-In-Space-Soonest,
Mercury,
Lunex.
The Air Force no longer seriously entertained the prospect of a separate military man in space program. Instead the ballistic missile division became deeply involved in support activity for the civilian space agency, especially developing and supplying hardware for the Mercury program. As of this date, Air Force Ballistic Missile Division participation included the following: providing 16 Atlas D boosters to accept Mercury capsules and adapters, to be provided by the space agency, a modified guidance structure, an installed abort system to insure pilot safety, and telemetry. Air Force Ballistic Missile Division also furnished launch facilities at the Atlantic Missile Range Complex 14, and one-half of Hangar J and the necessary modifications thereto as requested and made necessary by booster requirements. Such work included installation of capsule umbilical and checkout cabling, telemetry, communications, and data transfer equipment required by the payload. The missile division also provided the guidance site and use of the range Atlas guidance computer (Mod III) for powered trajectory guidance and the special computations requested by the space agency. Air Force Ballistic Missile Division and several Air Force contractors provided, as of this date, 401 military and civilian personnel to the program. Much of the cost of this support activity was reimbursed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, but some was not. Air Force personnel costs, military and civilian; office space and equipment; and normal base support functions were provided at Air Force expense. Cost of a 14 booster "program (the additional two boosters were ordered too late to be included in this summary) was as follows:(Millions of Dollars)
Prior Years FY 61 FY 62 Total Booster Hardware and Launch Service 19.769 15.324 5.924 41.017 Engineering Modifications and Studies, Technical Direction, Booster Safety Program, etc. 3.436 6.367 1.362 11.165 Miscellaneous, Propellant, Transportation, Travel, etc. .466 1.133 .122 1.721 Total Estimate 23.671 22.824 7.408 53.903
(Msg, WDGP 17-10-5, AFBMD to Hq ARDC, 17 Oct 1960)
1960 October 22 - . 05:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
November 1960-August 1961 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Crash program instigated to get Atlas sites operational. - . Nation: USA. Golden Ram program accomplished at SMS 576-B2 & B3.
1960 November 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- Centaur tracking network test. - .
Nation: USA.
Under arrangements of the AACB (Aeronautics and Astronautics Coordinating Board), NASA will utilize existing NASA tracking stations for initial Centaur development vehicles and switch to the Advent network (which is to be planned, funded, and constructed by DOD) when Centaur is operational, perhaps as early as the fourth of 10 development launchings of Centaur.
1960 November 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas D/AIG All Inertial Guidance - . Nation: USA. Atlas D/AIG (All Inertial Guidance) scheduled design 95 % complete.
1960 November 15 - . 05:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1960 November 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-3 spacecraft delivered - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft No. 8 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 3 (MA-3) unmanned orbital mission..
1960 November 30 - . 01:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1960 December 15 - . 09:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Able. FAILURE: Atlas exploded 70 seconds after liftoff.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Pioneer (P 31) - . Payload: Pioneer P 31 / Able VB. Mass: 175 kg (385 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Pioneer. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer P 3. Decay Date: 1960-12-15 . Apogee: 13 km (8 mi). The final launch in the Pioneer lunar probe program was unsuccessful; the Atlas-Able booster rocket went out of control and exploded at an altitude of 12,200 m off Cape Canaveral..
1960 December 16 - . 20:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). The first ICBM operational reentry vehicle ever recovered was fished out of the Eniwetok Lagoon five days later..
1960 December 21 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas.
- Operational ICBM RV recovered. - . The first ICBM operational reentry vehicle ever recovered was fished out of the Eniwetok Lagoon. It had been launched by an Atlas D from Vandenberg AFB on 16 December..
1961 January 9 - . LV Family: Atlas, Saturn I, Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan 3.
- USAF need for a space launch vehicle with 15,000 lb payload - . Headquarters USAF instructed AFBMD to continue its efforts to define the need for a space launch vehicle with a payload capacity between the Atlas/Centaur (9,000 lbs) and the early Saturn (19,000 lbs).
1961 January 23 - . 21:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
The flight testing of the Series D Atlas missiles was completed with the successful launch and flight of Atlas 90D from Cape Canaveral. This was the 32d Atlas D to be launched in the research and development series and the 55th Atlas missile to be flown since the first attempted launch on 11 June 1957. During the flight test series to date, 35 missiles were flown successfully and 20 were rated failures. Final test flight of USAF Atlas D traveled 5,000 miles to target down Atlantic Missile Range, representing 35 successes, 8 partials, and 6 failures in 49 test launchings for D model. 75th Atlas launched at AMR, successful
1961 January 24 - . 21:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1961 January 31 - . 20:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena A.
- Samos 2 - .
Payload: Samos E-1 no. 2. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: Samos.
Decay Date: 1973-10-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 70 . COSPAR: 1961-Alpha-1. Apogee: 557 km (346 mi). Perigee: 474 km (294 mi). Inclination: 97.40 deg. Period: 95.00 min.
An Air Force Atlas D/Agena A was launched from Vandenberg and successfully placed the SAMOS II satellite into orbit. This was the last Air Force use of an Agena A upper stage vehicle. First generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images; micrometeoroid impact data. Poor results.
1961 February 7 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- Centaur development milestones set. - . Nation: USA. Meeting of NASA and contractor personnel held at NASA headquarters to review Centaur development program..
1961 February 17 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Atlas Weapon System Project Office transferred to Norton AFB - . AFBMD's WS 107A-1 (Atlas) Weapon System Project Office was transferred to Norton AFB, California..
1961 February 17-20 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Rules for the Mercury MA-2 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft, mission, and launch vehicle flight safety rules for the Mercury-Atlas 2 (MA-2) mission were reviewed by Space Task Group personnel..
1961 February 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Space Task Group selected severe flight trajectory for Mercury MA-2 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Information was released by NASA Headquarters that Space Task Group engineers directing Project Mercury had selected the flight trajectory for the Mercury-Atlas 2 (MA-2) mission. . Additional Details: here....
1961 February 21 - . 14:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-2 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Apogee: 182 km (113 mi).
Mercury-Atlas 2 (MA-2) was launched from Cape Canaveral in a test to check maximum heating and its effects during the worst reentry design conditions. The flight closely matched the desired trajectory and attained a maximum altitude of 114.04 statute miles and a range of 1,431.6 statute miles. Inspection of the spacecraft aboard the recovery ship some 55 minutes after launch (actual flight time was 17.56 minutes) indicated that test objectives were met, since the structure and heat protection elements appeared to be in excellent condition. The flight control team obtained satisfactory data; and the complete launch computing and display system, operating for the first time in a flight, performed satisfactorily.
1961 February 24 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-5 spacecraft delivered - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft No. 9 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 5 (MA-5) orbital primate (Enos) mission..
1961 February 24 - . 18:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,500 km (900 mi). Atlas missile 9E made the first successful flight test of the Series E Atlas missile. First successful Atlas E flight..
1961 March 3 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-3 launch vehicle rolled out. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Factory roll-out inspection of Atlas launch vehicle No. 100-D was conducted at Convair-Astronautics. This launch vehicle was allocated for the Mercury-Atlas 3 (MA-3) mission..
1961 March 4 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . The second Atlas D (horizontal storage/ launcher) squadron at Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming - the 565th Strategic Missile Squadron was transferred to SAC's 706th Strategic Missile Wing..
1961 March 14 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-3 launch vehicle delivered - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle 100-D was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 3 (MA-3) mission..
1961 March 14 - . 04:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1961 March 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- The Mercury-Atlas Missile Range Projects Office designated as a staff function - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Mercury-Atlas Missile Range Projects Office, headed by Elmer H. Buller, was designated as a staff function of the Space Task Group Director's office..
1961 March 25 - . 01:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1961 March 30 - . Launch Site: Offutt AFB. Launch Complex: Offutt AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas SMS 566 operational. - . Nation: USA. Offutt AFB SMS 566 operational. The third and last Series D Atlas complex of nine missiles was turned over to SAC's 549th Strategic Missile Squadron at Offutt AFB, Nebraska..
1961 April 25 - . 16:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Destroyed by range safety.. Failed Stage: G.
- Mercury MA-3 - .
Payload: Mercury SC8. Mass: 1,355 kg (2,987 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: Mercury.
Decay Date: 1961-04-25 .
Mercury-Atlas 3 (MA-3) was launched from Cape Canaveral in an attempt to orbit the spacecraft with a 'mechanical astronaut' aboard. After lift-off, the launch vehicle failed to roll to a 70 degree heading and to pitch over into the proper trajectory. The abort-sensing system activated the escape rockets prior to the launch vehicle's destruction by the range safety officer after approximately 40 seconds of flight that had attained an altitude of 16,400 feet. The spacecraft then coasted up to 24,000 feet, deployed its parachutes, and landed in the Atlantic Ocean 2,000 yards north of the launch pad. The spacecraft was recovered and was found to have incurred only superficial damage; it was then shipped to McDonnell for refitting.
1961 May 11 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- MA-4 spacecraft delivered - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury spacecraft 8A was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 4 (MA-4) orbital unmanned (mechanical astronaut) mission..
1961 May 13 - . 02:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1961 May 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-3 investigation board - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. An Atlas investigation board was convened to study the cause of the Mercury-Atlas 3 (MA-3) mission launch vehicle failure. Several possible areas were considered, and three were isolated as probable causes based on a review of test data..
1961 May 24 - . 21:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1961 May 26 - . 02:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1961 May 29 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena B.
- Ranger 1 booster erected. - . Nation: USA. Program: Ranger. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger. Spacecraft: Ranger 1-2. Atlas booster 111-D, to be used for Ranger I, was erected on the launch pad at Cape Canaveral..
1961 May 29 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Centrifuge training for Mercury-Atlas orbital missions. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. A 30 day centrifuge training program was conducted at the Aviation Medical Acceleration Laboratory directed entirely toward training the astronauts for the Mercury-Atlas orbital missions..
1961 June 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1961 June 7 - . 21:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development Category II test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Atlas 27E was to be the first Series E operational test launch (OTL) from Vandenberg. However, the missile self-destructed over the launch pad due to a first stage engine failure at T+4 seconds. First E launched at SMS 576 from OSTF-1, unsuccessful.
1961 June 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1961 June 23 - . 03:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1961 June 29-30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- MA-4 vehicle roll-out - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Factory roll-out inspection of Atlas launch vehicle 88-D, designated for the Mercury-Atlas 4 (MA-4) mission, was conducted at Convair..
1961 June 30 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- First Atlas E operational complex - .
Complex 576C (576C Strategic Missile Squadron), the first Atlas E operational complex, was transferred to SAC at Vandenberg AFB. The 576C consisted of one above ground horizontal coffin storage/launcher hardened to withstand 25 pounds per-square inch (psi).
1961 July 7 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- McDonnell studies of the redesigned Mercury spacecraft. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Ejection,
Gemini Parachute.
Walter F. Burke of McDonnell summarized the company's studies of the redesigned Mercury spacecraft for Space Task Group's senior staff. McDonnell had considered three configurations: (1) the minimum-change capsule, modified only to improve accessibility and handling, with an adapter added to carry such items as extra batteries; (2) a reconfigured capsule with an ejection seat installed and most of the equipment exterior to the pressure vessel on highly accessible pallets; and (3) a two-man capsule, similar to the reconfigured capsule except for the modification required for two rather than one-man operation. The capsule would be brought down on two Mercury-type main parachutes, the ejection seat serving as a redundant system. In evaluating the trajectory of the two-man capsule, McDonnell used Atlas Centaur booster performance data.
1961 July 7 - . 04:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,500 km (900 mi). Atlas missile 22E completed a flight of 7,863 nautical miles (9,050 statute miles), with the nose cone landing 1,000 miles southeast of Capetown, South Africa..
1961 July 12 - . 15:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Midas 3 - .
Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1201. Mass: 1,600 kg (3,500 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: Midas.
USAF Sat Cat: 163 . COSPAR: 1961-Sigma-1. Apogee: 3,540 km (2,190 mi). Perigee: 3,343 km (2,077 mi). Inclination: 91.20 deg. Period: 161.40 min.
MIDAS III (Missile Defense Alarm System) satellite was launched into polar orbit from Vandenberg AFB by the first Atlas D/Agena B booster (97D/#1201). This vehicle achieved a record 1,850-mile orbit and was the heaviest U.S. satellite put up to date. Missile Defense Alarm System.
1961 July 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Atlas launch vehicle 88-D delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle 88-D was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 4 (MA-4) mission..
1961 July 31 - . 21:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1961 August 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- Centaur operational contracts initiated. - . Nation: USA. NASA directed Marshall Space Flight Center to enter contract negotiations with contractors for procurement of five operational Atlas-Centaur vehicles. These launchings were planned to begin in second quarter of 1964..
1961 August 9 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Key personnel operational assignments for the Mercury MA-4 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Key personnel operational assignments for the Mercury-Atlas 4 (MA-4) unmanned orbital mission were made by the Space Task Group..
1961 August 9 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Retrofire-from-orbit mission rules for Mercury MA-4 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury, Mercury Retrorockets. Retrofire-from-orbit mission rules were published for the unmanned Mercury-Atlas 4 (MA-4) orbital flight..
1961 August 9 - . 04:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The first Series F Atlas missile (2F) was successfully launched from Complex 13 at Cape Canaveral and completed its test flight. First F flight, at AMR), successful.
1961 August 23 - . 01:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Research and development launch - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
The launch of Atlas 101D from Vandenberg AFB completed the initial operational capability (IOC) launch series for the Atlas D ICBM. In 11 launches, only five missiles were successful. The launch of Atlas 101D from Vandenberg AFB completed the initial operational capability (IOC) launch series for the Atlas D ICBM. In 11 launches, only five missiles were successful.
1961 August 23 - . 10:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Agena B second stage failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Ranger 1 - .
Payload: NASA P-32 (RA-1). Mass: 306 kg (674 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 1-2.
Decay Date: 1961-08-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 173 . COSPAR: 1961-Phi-1. Apogee: 446 km (277 mi). Perigee: 179 km (111 mi). Inclination: 32.90 deg. Period: 90.60 min.
Lunar probe; failed to leave Earth orbit. Ranger 1, a test version of the spacecraft which would attempt an unmanned crash landing on the moon, was launched from the Atlantic Missile Range by an Atlas-Agena B booster. The 306 kg spacecraft did not attain the scheduled extremely elongated orbit because of the misfiring of the Agena B rocket. Although the spacecraft systems were tested successfully, only part of the eight project experiments could be carried out. Ranger 1 reentered on August 29 after 111 orbits. Ranger 1's primary mission was to test the performance of those functions and parts that are necessary for carrying out subsequent lunar and planetary missions using essentially the same spacecraft design.
1961 August 24 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1961 August 25 - . LV Family: Thor, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D, Thor Agena D.
- Lockheed contracted for the Agena D upper stage. - . Lockheed was awarded an Air Force letter contract to develop and manufacture the first 12 flight models of the standardized configuration Agena D (Standard Stage OlA, SS-01A)..
1961 September 9 - . 01:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1961 September 9 - . 19:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Exploded on launch pad.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Samos 3 - . Payload: Samos E-2 no. 1. Mass: 1,890 kg (4,160 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1961-09-09 . First generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images..
1961 September 13 - . 14:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-4 - .
Payload: Mercury SC8A. Mass: 1,200 kg (2,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: Mercury.
Decay Date: 1961-09-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 183 . COSPAR: 1961-A-Alpha-1. Apogee: 248 km (154 mi). Perigee: 156 km (96 mi). Inclination: 32.80 deg. Period: 88.40 min.
Mercury-Atlas 4 (MA-4) was launched from Cape Canaveral with special vibration and noise instrumentation and a mechanical crewman simulator aboard in addition to the normal spacecraft equipment. This was the first Mercury spacecraft to attain an earth orbit. The orbital apogee was 123 nautical miles and the perigee was 86 nautical miles. After one orbit, the spacecraft's orbital timing device triggered the retrograde rockets, and the spacecraft splashed in the Atlantic Ocean 161 miles east of Bermuda. Recovery was made by the USS Decatur. During the flight, only three slight deviations were noted - a small leak in the oxygen system; loss of voice contact over Australia; and the failure of an inverter in the environmental control system. Overall, the flight was highly successful: the Atlas booster performed well and demonstrated that it was ready for the manned flight, the spacecraft systems operated well, and the Mercury global tracking network and telemetry operated in an excellent manner and was ready to support manned orbital flight.
1961 September 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mission rules for the Mercury-Atlas 5 (MA-5) orbital flight. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mission rules for the Mercury-Atlas 5 (MA-5) orbital flight were published. Revisions were issued on October 16 and 25, 1961, and November 11, 1961..
1961 September 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- Mariner moved to Atlas-Agena due to Centaur delay. - . Nation: USA. Program: Mariner. Class: Venus. Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner. Spacecraft: Mariner 1-2. NASA announced that instrumented Venus probe to be launched next year would be launched by an Atlas-Agena B rather than a Centaur rocket as originally planned..
1961 September 28 - . Launch Site: Fairchild AFB. LV Family: Atlas.
- First Series E Atlas squadron operational - . The first Series E Atlas squadron became operational at Fairchild AFB, Washington (567th Strategic Missile Squadron, SAC)..
1961 September 28 - . Launch Site: Fairchild AFB. Launch Complex: Fairchild AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Atlas SMS 567 operational. - . Nation: USA. Fairchild AFB SMS 567 operational.
1961 October 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Factory roll-out inspection of Mercury Atlas booster No. 93-D - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Factory roll-out inspection of Atlas booster No. 93-D was conducted at Convair. This booster was designated for the Mercury-Atlas 5 (MA-5) mission..
1961 October 2 - . 18:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1961 October 3 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Cancellation of the Advent program. - . Spacecraft: Advent, IDCSP, . Because of delays in the Centaur upper stage development program and increasing management difficulties, Headquarters USAF recommended cancellation of the Advent program..
1961 October 5 - . 13:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,500 km (900 mi). USAF Atlas fired 9,000 miles for Atlantic Missile Range into Indian Ocean, carrying dummy nuclear warhead and a data capsule which was recovered..
1961 October 9 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Atlas booster No. 93-D delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas booster No. 93-D was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 5 (MA-5) orbital flight mission..
1961 October 10 - . Launch Site: Forbes AFB. Launch Complex: Forbes AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Atlas SMS 548 operational. - . Nation: USA. Forbes AFB SMS 548 operational.
1961 October 10 - . Launch Site: Forbes AFB. LV Family: Atlas.
- Second Atlas Series E squadron operational - . The 548th Strategic Missile Squadron, the second Atlas Series E (CGM-16E) missile squadron, became operational at Forbes AFB, Kansas..
1961 October 21 - . 13:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Midas 4 - . Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1202. Mass: 1,800 kg (3,900 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. USAF Sat Cat: 192 . COSPAR: 1961-A-Delta-1. Apogee: 3,763 km (2,338 mi). Perigee: 3,482 km (2,163 mi). Inclination: 95.90 deg. Period: 165.90 min. Missile Defense Alarm System. Deployed subsatellites..
- Westford - . Payload: Westford. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft: WestFord Needles. USAF Sat Cat: 194 . COSPAR: 1961-A-Delta-3. Apogee: 3,963 km (2,462 mi). Perigee: 3,252 km (2,020 mi). Inclination: 95.85 deg. Period: 165.51 min.
1961 November 10 - . 14:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Sustainer engine failed 15 seconds after launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test / Pod 13 chemical release - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 10 km (6 mi). USAF Atlas with capsule containing squirrel monkey destroyed by range safety officer at Atlantic Missile Range when main sustainer engine failed 15 seconds after launch..
1961 November 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury 5 launch postponed - . Nation: USA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury-Atlas 5, scheduled for launch no earlier than November 14, ran into technical difficulties, postponing launch for several days..
1961 November 18 - . 08:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Agena B Second Stage failed to restart.. Failed Stage: U.
- Ranger 2 - .
Payload: NASA P-33 (RA-2). Mass: 304 kg (670 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 1-2.
Decay Date: 1961-11-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 206 . COSPAR: 1961-A-Theta-1. Apogee: 242 km (150 mi). Perigee: 150 km (90 mi). Inclination: 33.30 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
This was a flight test of the Ranger spacecraft system designed for future lunar and interplanetary missions. The spacecraft was launched into a low earth parking orbit, but an inoperative roll gyro prevented Agena restart resulting in Ranger 2 being stranded in low earth orbit. The orbit decayed and the spacecraft reentered Earth's atmosphere on 20 November 1961.
1961 November 19 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur LV-3C.
- RL-10 flight rating complete. - .
Nation: USA.
NASA announced the completion of the preliminary flight rating test of the Nation's first liquid-hydrogen rocket engine. The engine, the RL-10, was designed and developed by Pratt and Whitney, of United Aircraft, for the Marshall Space Flight Center, and 20 captive firings were competed within 5 days under simulated space conditions, consistently producing 15,000 pounds of thrust. RL-10, previously known as XLR-115, was initiated in October 1958 and over 700 firings were conducted in its development.
1961 November 20 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. Launch Complex: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Atlas SMS 549 operational. - . Nation: USA. Warren-3 AFB SMS 549 operational.
1961 November 22 - . 20:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Samos 4 - . Payload: Samos E-5 no. 1. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1961-11-22 . Apogee: 200 km (120 mi). First generation photo surveillance; return of camera and film by capsule; SAMOS type satellite..
1961 November 22 - . 21:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). Pod 3, 22 test / ionosphere / aeronomy mission.
1961 November 23 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Warren AFB - .
The third and final Series E Atlas missile squadron of nine missiles, the 566th Strategic Missile Squadron of the 706th Strategic Missile Wing at Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, became operational. The wing now had three squadrons - two Atlas D and one Atlas E - and a total of 24 missile launchers.
1961 November 29 - . 15:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-5 - .
Payload: Mercury SC9. Mass: 1,300 kg (2,800 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft: Mercury.
Decay Date: 1961-11-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 208 . COSPAR: 1961-A-Iota-1. Apogee: 237 km (147 mi). Perigee: 158 km (98 mi). Inclination: 32.60 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
Atlas D (53D) was the first missile to be launched by SAC from Vandenberg in the operation test (Category III) launch program. Mercury-Atlas 5 (MA-5), the second and final orbital qualification of the spacecraft prior to manned flight was launched from Cape Canaveral with Enos, a 37.5 pound chimpanzee, aboard. Scheduled for three orbits, the spacecraft was returned to earth after two orbits due to the failure of a roll reaction jet and to the overheating of an inverter in the electrical system. Both of these difficulties could have been corrected had an astronaut been aboard. The spacecraft was recovered 255 miles southeast of Bermuda by the USS Stormes. During the flight, the chimpanzee performed psychomotor duties and upon recovery was found to be in excellent physical condition. The flight was termed highly successful and the Mercury spacecraft well qualified to support manned orbital flight.
1961 November 29 - . 23:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Operational missile test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Atlas D (53D) was the first missile to be launched by SAC from Vandenberg in the operation test (Category III) launch program. .
1961 November 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Atlas launch vehicle 109-D delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle 109-D was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) first manned orbital mission..
1961 December 1 - . 20:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1961 December 7 - . 21:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1961 December 12 - . 20:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1961 December 20 - . 03:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Research and development/Pod Test/Chemical release mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1961 December 21 - . 03:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 500 km (310 mi). Pod 15, 25 chemical release / ionosphere / meteorite mission.
1961 December 22 - . 19:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Samos 5 - .
Payload: Samos E-5 no. 2. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: Samos.
Decay Date: 1962-01-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 218 . COSPAR: 1961-A-Lambda-2. Apogee: 310 km (190 mi). Perigee: 187 km (116 mi). Inclination: 89.60 deg. Period: 89.40 min.
First generation photo surveillance; return of camera and film by capsule; SAMOS type satellite. Reached orbit but failed to deorbit and be recovered. In his memoirs Sergei Khrushchev recounts recovery of what he believed to be a recoverable Samos, except the date given is the winter before tests of this configuration actually started. He relates that a second American capsule was recovered in the spring of 1961. It was equipped with a 30 cm lens and 100's of metres of 10 cm wide film. Also recovered were a pear-shaped module made of fibreglass, and an inertial orientation system powered by electric motors. It may have been a SAMOS prototype. The capsule was found by tractor drivers, who disassembled it and used the film to wrap around the frame of their outhouse to provide some privacy in the treeless area. Unfortunately this ruined the film, preventing the Russians from developing it and discovering the technical capabilities of the system.
1962 January 15-17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Recovery swimmers trained for Mercury MA-6. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Recovery area swimmers were trained at the Pensacola Naval Air Station, Florida, for use in the Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) manned orbital mission. Instruction included films, briefings, auxiliary flotation collar deployment, and jumps from a helicopter..
1962 January 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury spacecraft 16 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft 16 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the third manned (Schirra) orbital flight, Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8)..
1962 January 17 - . 21:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1962 January 23 - . 21:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1962 January 26 - . 20:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Agena B second stage guidance system failure. Failed Stage: U.
- Ranger 3 - .
Payload: NASA P-34 (RA-3). Mass: 327 kg (720 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 3-4-5.
USAF Sat Cat: 221 . COSPAR: 1962-Alpha-1.
Lunar impact probe; missed the moon by 36,874 km and went into solar orbit. A malfunction in the booster guidance system resulted in excessive spacecraft speed. Reversed command signals caused the telemetry antenna to lose earth acquisition, and mid-course correction was not possible. Some useful data were obtained from the flight. Of four scientific experiments only one was partially completed: gamma-ray readings of the lunar surface. Attempts to relay television pictures of the moon and to bounce radar signals off the moon at close range were unsuccessful.
1962 January 27 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-6 postponed at T-minus 29 minutes - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) manned orbital flight was postponed at T-minus 29 minutes due to weather conditions..
1962 January 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-6 postponed - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. The Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) mission was postponed because of technical difficulties with the launch vehicle..
1962 February 13 - . 20:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 1,600 km (900 mi).
Atlas 40E, the 18th and last Atlas E research and development flight test missile to be launched from the Atlantic Missile Range, completed its programmed 7,000-mile flight downrange. Of the 18 missiles launched, nine were successes, seven partials, and two failures. Last Atlas E R&D flight.
1962 February 14 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-6 postponed. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Unfavorable weather conditions caused the Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) manned orbital mission to be postponed..
1962 February 16 - . 23:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1962 February 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NASA announced Project Fire - .
Nation: USA.
Program: Apollo.
Spacecraft Bus: Apollo CSM.
Spacecraft: FIRE.
NASA announced Project Fire, a high-speed reentry heat research program to obtain data on materials, heating rates, and radio signal attenuation on spacecraft reentering the atmosphere at speeds of about 24,500 miles per hour. Information from the program would support technology for manned and unmanned reentry from lunar missions. Under the management of the Langley Research Center, Project Fire would use Atlas D boosters and the reentry package would be powered by an Antares solid-fuel motor (third stage of the Scout).
1962 February 20 - . 14:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-6 - .
Call Sign: Friendship 7. Crew: Glenn.
Backup Crew: Carpenter.
Payload: Mercury SC13. Mass: 1,355 kg (2,987 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MA-6.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Duration: 0.21 days. Decay Date: 1962-02-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 240 . COSPAR: 1962-Gamma-1. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 159 km (98 mi). Inclination: 32.50 deg. Period: 88.60 min.
The 6555th Aerospace Test Wing launched the Mercury/Atlas D (MA-6), "Friendship 7," that placed the Mercury capsule containing LtColonel John Glenn, USMC, into orbit for the first Project Mercury manned orbital flight. "Friendship 7" completed three orbits before successful reentry and recovery in the Atlantic Ocean. First US manned orbital mission. John Glenn finally puts America in orbit. False landing bag deploy light led to reentry being started with retropack left in place on heat shield. It turned out that indicator light was false and a spectacular reentry ensued, with glowing chunks of the retropack whizzing by the window. After four hours and 43 minutes the spacecraft reentered the atmosphere and landed at 2:43 pm EST in the planned recovery area NE of the Island of Puerto Rico. All flight objectives were achieved. Glenn was reported to be in excellent condition. Beause of failure of one of the automatic systems, the astronaut took over manual control of the spacecraft during part of the flight. With this flight, the basic objectives of Project Mercury had been achieved.
1962 February 21 - . 22:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1962 February 25 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Factory roll-out inspection of Mercury Atlas launch vehicle 107-D. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-7. Spacecraft: Mercury. Factory roll-out inspection of Atlas launch vehicle 107-D, designated for the Mercury-Atlas 7 (MA-7) manned orbital mission, was conducted at Convair..
1962 March 1 - . 00:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1962 March 5 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Rendezvous radar and transponder system for the Gemini spacecraft. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Radar,
Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Baltimore, Maryland, received a $6.8 million subcontract from McDonnell to provide the rendezvous radar and transponder system for the Gemini spacecraft. Purpose of the rendezvous radar, sited in the recovery section of the spacecraft, was to locate and track the target vehicle during rendezvous maneuvers. The transponder, a combined receiver and transmitter designed to transmit signals automatically when triggered by an interrogating signal, was located in the Agena target vehicle.
1962 March 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Atlas launch vehicle 107-D delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle 107-D was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 7 (MA-7) mission..
1962 March 7 - . 22:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Samos 6 - . Payload: Samos E-5 no. 3. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1963-06-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 259 . COSPAR: 1962-Eta-3. Apogee: 686 km (426 mi). Perigee: 236 km (146 mi). Inclination: 90.90 deg. Period: 93.90 min. First generation photo surveillance; return of camera and film by capsule; SAMOS type satellite. Failed to return camera and film. Samos film return project cancelled; remaining 4 cameras placed in warehouse and later used on KH-6 Lanyard..
1962 March 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Carpenter replaces Slayton on Mercury-Atlas 7 (MA-7) - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-7. Spacecraft: Mercury. NASA Headquarters publicly announced that Scott Carpenter would pilot the Mercury-Atlas 7 (MA-7) manned orbital mission replacing Donald Slayton. The latter, formerly scheduled for the flight, was disqualified because of a minor erratic heart rate..
1962 March 24 - . 00:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF SAC.
Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
An Air Force crew launched Atlas 134D during the visit of President John F. Kennedy to Cape Canaveral. This was the first time that a President had witnessed a live ICBM launch. President John F. Kennedy visited Vandenberg AFB and witnessed the launch of Atlas 134D.
1962 April - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Crash program completed to clear Atlas configuration problems. - . Nation: USA. Golden Ram follow-on completed at all Atlas D operational bases.
1962 April - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas F training facility activated. - . Nation: USA. VAFB Atlas F training facility turned over to SAC.
1962 April 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Symposium on the results of Mercury MA-6 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. NASA sponsored a 1-day symposium in Washington on the results of the Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) three-orbit flight of John Glenn. One of the items of particular interest was Glenn's 'fire-flies,' or luminous particles, and their possible origin..
1962 April 9 - . 15:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Midas 5 - . Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1203. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. USAF Sat Cat: 271 . COSPAR: 1962-Kappa-1. Apogee: 3,405 km (2,115 mi). Perigee: 2,784 km (1,729 mi). Inclination: 86.70 deg. Period: 152.90 min. Missile Defense Alarm System..
- West Ford Drag - . Payload: West Ford Drag Experiment. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft: WestFord Needles. Decay Date: 1962-05-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 272 . COSPAR: 1962-Kappa-2. Apogee: 2,729 km (1,695 mi). Perigee: 99 km (61 mi). Inclination: 86.64 deg. Period: 114.09 min.
1962 April 9 - . 20:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1962 April 12 - . 01:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1962 April 23 - . 20:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Ranger 4 - .
Mass: 328 kg (723 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 3-4-5.
Decay Date: 1962-04-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 280 . COSPAR: 1962-Mu-1.
The 6555th Aerospace Test Wing launched an Atlas D/Agena B vehicle that carried NASA's Ranger IV to the moon. This was the first U.S. instrument package to impact on the moon. Ranger IV was launched by an Atlas-Agena B booster from the Atlantic Missile Range, attained a parking orbit, and was fired into the proper lunar trajectory by the restart of the Agena B engine. Failure of a timer in the spacecraft payload caused loss of both internal and ground control over the vehicle. The Goldstone Tracking Station maintained contact with the spacecraft until it passed behind the left edge of the moon on April 26. It impacted at a speed of 9,617 km per hour, the first American spacecraft to land on the lunar surface. The Agena B second stage passed to the right of the moon and later went into orbit around the sun. Lunar photography objectives were not achieved.
1962 April 26 - . 18:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Samos 7 - . Payload: Samos E-6 no. 1 / Agena B 2401. Mass: 1,588 kg (3,500 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1962-04-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 286 . COSPAR: 1962-Pi-1. Second generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images; Satellite and Missile Observation Satellite. Poor results..
- FTV 2401 RV - . Payload: E-6 RV. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. COSPAR: 1962-Pi-xx.
1962 April 27 - . 23:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1962 April 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Swimmer training for Mercury MA-7 - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Swimmer training was started for the Mercury-Atlas 7 (MA-7) manned orbital mission recovery area. Instruction consisted of films, briefings, exercises in deploying the auxiliary flotation collar, and jumps from a helicopter..
1962 May 1 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. LV Family: Atlas, Thor.
- Contract to the Thor DSV-2C. - .
Space Systems Division awarded a letter contract to the Douglas Aircraft Company for the design, development, fabrication, assembly, and pre-flight testing of one Douglas Space Vehicle 2C (DSV-2C). This was originally proposed by the company in June 1961. The DSV-2C, later SLV-2A in Air Force nomenclature, was the Thrust Augmented Thor (TAT) that was the first attempt to combine solid and liquid fuel engines in a single space booster. Intended to fill the gap between the basic Thor booster (LV-2) and the Atlas (SLV-3), the TAT was to use three TX-33-52 solid-pro-pellant Sergeant rocket motors installed around the engine section and attached to the three main thrust beams. Each of the solid-rocket motors would generate 54,500 pounds of thrust for 27 seconds after lift-off. This increased the total thrust of the vehicle to over 330,000 pounds, vastly improving its payload capabilities. The new TAT would have a 50 percent improvement in payload capacity since it could place 1,450 pounds into a 300-NM circular orbit when launched from Cape Canaveral - a 500-pound increase over the present Thor/Agena booster.
1962 May 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Small working group to discuss the feasibility of making the Gemini telemetry system a full PCM system. - .
Nation: USA.
Small working group to discuss the feasibility of making the Gemini telemetry system a full PCM system. Following a Lockheed briefing on pulse-code-modulation (PCM) instrumentation systems, representatives of Goddard Space Flight Center and Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) formed a small working group to discuss the feasibility of making the Gemini telemetry system a full PCM system. PCM was a digital telemetry system which could provide more channels of information, faster data rates, improved accuracy, and less weight of equipment per data channel. Goddard had already reviewed several PCM ground station proposals and had concluded that such a system could handle future NASA programs. All who attended the meeting agreed that a full PCM telemetry system, airborne and ground, could be implemented in time to support the Gemini program. Gemini Project Office approved the formation of an MSC-Gemini PCM Instrumentation Working Group to be responsible for the implementation and compatibility of the airborne and ground PCM system for Gemini. On June 27, Walter C. Williams, MSC Associated Director, notified Goddard of NASA's decision 'to utilize a PCM telemetry system for Gemini and Agena real time data.' Ten sites were selected for the installation of PCM equipment; each of these also received dual acquisition equipment, dual digital command system, and pulse coders for distinguishing between the manned Gemini spacecraft and the Agena target when both were in orbit.
1962 May 8 - . 19:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur. FAILURE: Vehicle exploded due to insulation problems on the Atlas.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Apogee: 6.00 km (3.70 mi).
The first attempt to launch an Atlas/Centaur from the Atlantic Missile Range was unsuccessful when the Centaur stage blew up at T+55 seconds due to a second stage structural failure. Despite this failure, the launch marked the first U.S. use of a space vehicle fueled by a liquid hydrogen engine. First Centaur flight (unsuccessful).
1962 May 12 - . 00:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1962 May 24 - . 12:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-7 - .
Call Sign: Aurora 7. Crew: Carpenter.
Backup Crew: Schirra.
Payload: Mercury SC18. Mass: 1,349 kg (2,974 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MA-7.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Duration: 0.21 days. Decay Date: 1962-05-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 295 . COSPAR: 1962-Tau-1. Apogee: 260 km (160 mi). Perigee: 154 km (95 mi). Inclination: 32.50 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
BSD's 6555th Aerospace Test Wing launched Mercury/Atlas 7 (MA-7), "Aurora 7", into orbit carrying Navy Commander M. Scott Carpenter. This was the second U.S. manned orbital flight mission. Scott Carpenter in Aurora 7 is enthralled by his environment but uses too much orientation fuel. Yaw error and late retrofire caused the landing impact point to be over 300 km beyond the intended area and beyond radio range of the recovery forces. Landing occurred 4 hours and 56 minutes after liftoff. Astronaut Carpenter was later picked up safely by a helicopter after a long wait in the ocean and fears for his safety. NASA was not impressed and Carpenter left the agency soon thereafter to become an aquanaut.
1962 May 29 - . LV Family: Atlas, Thor. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D, Thor Agena D.
- Standardized Agena D upper stage for use with Atlas and Thor. - .
The Defense Department and NASA signed a joint agreement that authorized the Defense Department to develop a standardized Agena D upper stage for joint use with Atlas and Thor booster stages. The Agena would use present flight-proven equipment, stress simplification of vehicle design, permit adaptability to advanced components without any basic changes, and permit production at lower costs.
1962 June 17 - . 18:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Samos 8 - . Payload: Samos E-2 no. 2 / Agena B 2402. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1962-06-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 307 . COSPAR: 1962-Psi-1. Apogee: 198 km (123 mi). Perigee: 198 km (123 mi). Inclination: 96.20 deg. Period: 88.40 min. First generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images; Satellite and Missile Observation Satellite. Poor results..
- FTV 2402 RV - . Payload: E-6 RV. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. COSPAR: 1962-Psi-xx.
1962 June 26 - . 10:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-1 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). K-1 Nike-Zeus intercept of Atlas ICBM. First launch of an Atlas from Vandenberg AFB as a target for an Army Nike-Zeus from Kwajalein..
1962 July 12 - . 16:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1962 July 13 - . 21:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Research and development Category II test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). After two consecutive failures, the first successful launch and flight by an Atlas E (67E) from Vandenberg AFB took place. .
1962 July 18 - . 20:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Samos 9 - . Payload: Samos E-2 no. 3 / Agena B 2403. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1962-07-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 342 . COSPAR: 1962-A-Zeta-1. Apogee: 234 km (145 mi). Perigee: 184 km (114 mi). Inclination: 96.00 deg. Period: 88.60 min. First generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images; Satellite and Missile Observation Satellite. Poor results..
- FTV 2403 RV - . Payload: E-6 RV. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1962-07-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 343 . COSPAR: 1962-A-Zeta-2. Apogee: 215 km (133 mi). Perigee: 163 km (101 mi). Inclination: 96.10 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
1962 July 19 - . 11:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-2 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). K-2 Nike-Zeus intercept of Atlas ICBM. Date differs in records..
1962 July 22 - . 09:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Destroyed by range safety.. Failed Stage: U.
- Mariner 1 - . Payload: Mariner R-1. Mass: 200 kg (440 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mariner. Class: Venus. Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner. Spacecraft: Mariner 1-2. Decay Date: 1962-07-22 . Venus probe..
1962 July 27 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Atlas launch vehicle No. 113-D accepted - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle No. 113-D was inspected at Convair and accepted for the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) manned orbital mission..
1962 August 1 - . 21:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The first Atlas F missile (15F) was launched from Vandenberg on an operational test flight. First successful Atlas F flight at operational site, SMS 576E (15F).
1962 August 5 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Samos 10 - . Payload: Samos E-6 no. 2 / Agena B 2404. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1962-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 361 . COSPAR: 1962-A-Lambda-2. Apogee: 203 km (126 mi). Perigee: 201 km (124 mi). Inclination: 96.20 deg. Period: 88.50 min. Second generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images; Satellite and Missile Observation Satellite. Poor results..
- FTV 2404 - . Payload: AFP-201 PVP 854. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1962-08-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 361 . COSPAR: 1962-A-Lambda-1. Apogee: 203 km (126 mi). Perigee: 203 km (126 mi). Inclination: 96.30 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
- FTV 2404 RV - . Payload: E-6 RV. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. COSPAR: 1962-A-Lambda-xx.
1962 August 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Atlas launch vehicle 113-D delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle 113-D was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) manned orbital mission..
1962 August 9 - . 22:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1962 August 9 - . 23:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1962 August 10 - . 21:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1962 August 13 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
1962 August 27 - . 06:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Mariner 2 - .
Payload: Mariner R-2. Mass: 201 kg (443 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Mariner.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner.
Spacecraft: Mariner 1-2.
USAF Sat Cat: 374 . COSPAR: 1962-A-Rho-1.
Mariner 2 was the first spacecraft to successfully flyby another planet. It was a backup for the Mariner 1 mission which failed shortly after launch to Venus. After launch and termination of the Agena first burn, the Agena-Mariner was in a 118 km altitude Earth parking orbit. The Agena second burn injected the Mariner 2 spacecraft into a geocentric escape hyperbola at 26 minutes 3 seconds after lift-off. Solar panel extension was completed about 44 minutes after launch. On 29 August 1962 cruise science experiments were turned on. A midcourse maneuver was initiated at 22:49:00 GMT on 4 September and completed at 2:45:25 GMT 5 September. On 8 September at 17:50 GMT the spacecraft suddenly lost its attitude control, which was restored by the gyroscopes 3 minutes later. The cause was unknown but may have been a collision with a small object. On October 31 the output from one solar panel deteriorated abruptly, and the science cruise instruments were turned off. A week later the panel resumed normal function and instruments were turned back on. The panel permanently failed on 15 November, but Mariner 2 was close enough to the Sun that one panel could supply adequate power. On December 14 the radiometers were turned on. Mariner 2 approached Venus from 30 degrees above the dark side of the planet, and passed below the planet at its closest distance of 34,773 km at 19:59:28 GMT 14 December 1962. After encounter, cruise mode resumed. Spacecraft perihelion occurred on 27 December at a distance of 105,464,560 km. The last transmission from Mariner 2 was received on 3 January 1963 at 07:00 GMT. Mariner 2 remains in heliocentric orbit. Scientific discoveries made by Mariner 2 included a slow retrograde rotation rate for Venus, hot surface temperatures and high surface pressures, a predominantly carbon dioxide atmosphere, continuous cloud cover with a top altitude of about 60 km, and no detectable magnetic field. It was also shown that in interplanetary space the solar wind streams continuously and the cosmic dust density is much lower than the near-Earth region. Improved estimates of Venus' mass and the value of the astronomical unit were made.
1962 September - . Launch Site: Schilling AFB. Launch Complex: Schilling AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas SMS 560 operational. - . Nation: USA. Schilling AFB SMS 550 operational.
1962 September 7 - . Launch Site: Schilling AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- The first Atlas F (HGM-16AF) missile squadron, the 550th Strategic Missile Squadron at Schilling AFB, Kansas, was turned over to SAC. - .
The first Atlas F (HGM-16AF) missile squadron, the 550th Strategic Missile Squadron at Schilling AFB, Kansas, was turned over to SAC. This was the first Atlas unit to feature the silo-lift storage/launcher configuration for improved hardness and survivability.
1962 September 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Atlas vehicle 113-D static-fired - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Atlas launch vehicle 113-D for the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) manned orbital mission was static-fired at Cape Canaveral. This test was conducted to check modifications that had been made to the booster for the purpose of smoother engine combustion..
1962 September 15 - . Launch Site: Lincoln AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- The second silo-lift Atlas F squadron turned over to SAC. - . The second silo-lift Atlas F squadron, the 551st Strategic Missile Squadron at Lincoln AFB, Nebraska, was turned over to SAC..
1962 September 15 - . Launch Site: Lincoln AFB. Launch Complex: Lincoln AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas SMS 551 operational. - . Nation: USA. Lincoln AFB SMS 551 operational.
1962 September 19 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Research and development / Pod 17 test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). Atlas 8F, the seventh Series F R&D missile, was the 100th to be launched from Cape Canaveral since the first abortive launch on 11 June 1957 and the 145th Atlas to be launched from both Cape Canaveral and Vandenberg. .
1962 September 25 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- A preliminary design criteria review conference for complex 14, held in Los Angeles, resulted in ground rules for all contractors. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
A preliminary design criteria review conference for complex 14, held in Los Angeles, resulted in ground rules for all contractors. Target dates established were (1) stand availability, July 1, 1963; (2) estimated beneficial occupancy date, November 1, 1963; and (3) vehicle on-stand date, February 1, 1964. Complex 14 would be used for launching the Gemini-Agena target vehicle and Mariner spacecraft, but basic modifications would be primarily for the Gemini program. On November 15, 1962, Air Force Space Systems Division reviewed the criteria summary report for complex 14 modifications and suggested only minor engineering changes.
1962 October 2 - . 11:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1962 October 3 - . 12:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-8 - .
Call Sign: Sigma 7. Crew: Schirra.
Backup Crew: Cooper.
Payload: Mercury SC16. Mass: 1,374 kg (3,029 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MA-8.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Duration: 0.38 days. Decay Date: 1962-10-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 433 . COSPAR: 1962-B-Delta-1. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 153 km (95 mi). Inclination: 32.50 deg. Period: 88.80 min.
The Sigma 7 spacecraft with Astronaut Walter M. Schirra, Jr., as pilot was launched into orbit by a Mercury-Atlas vehicle from Atlantic Missile Range. In the most successful American manned space flight to date, Schirra traveled nearly six orbits, returning to earth at a predetermined point in the Pacific Ocean 9 hours, 13 minutes after liftoff. Within 40 minutes after landing, he and his spacecraft were safely aboard the aircraft carrier U.S.S. Kearsarge. Schirra attempted and achieved a nearly perfect mission by sticking rigorously to mission plan.
1962 October 7 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- The Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) press conference was held at the Rice University, Houston, Texas. - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: Schirra. Spacecraft: Mercury. Astronaut Schirra expressed his belief that the spacecraft was ready for the 1-day mission, that he experienced absolutely no difficulties with his better than 9 hours of weightlessness, and that the flight was of the 'textbook' variety..
1962 October 9 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury spacecraft 20 delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft 20 was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) 1-day mission flight..
1962 October 9 - . Launch Site: Altus AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Third Atlas F squadron turned over to SAC at Altus AFB. - . The 577th Strategic Missile Squadron at Altus AFB, Oklahoma, was the third Atlas F squadron turned over to SAC by Ballistic Systems Division site activation task forces (SATAFs)..
1962 October 9 - . Launch Site: Altus AFB. Launch Complex: Altus AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas SMS 577 operational. - . Nation: USA. Altus AFB SMS 577 operational.
1962 October 18 - . 16:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Ranger 5 - .
Mass: 340 kg (740 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 3-4-5.
USAF Sat Cat: 439 . COSPAR: 1962-B-Eta-1.
The Ranger V lunar probe was launched from Atlantic Missile Range by an Atlas-Agena B launch vehicle. The Agena B stage attained parking orbit and 25 minutes later reignited to send Ranger V toward the moon. A malfunction in the Agena B guidance system resulted in excessive spacecraft velocity. The spacecraft's solar cells did not provide power and reversed command signals caused the telemetry antenna to lose earth acquisition. This made reception of the flight-path correction signal impossible and rendering its television cameras useless. Reversed command signals caused the telemetry antenna to lose earth acquisition, and mid-course correction was not possible. The spacecraft missed the Moon by 725 km and went into solar orbit. Gamma-ray data were collected for 4 hours prior to the loss of power. Ranger V was to have relayed television pictures of the lunar surface and rough-landed an instrumented capsule containing a seismometer. The spacecraft was tracked for 8 hours, 44 minutes, before its small reserve battery went dead. Additional Details: here....
1962 October 19 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- NASA Headquarters' recent decision to cut the MSC budget for fiscal year 1963 from $687 million to $660 million. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Chamberlin.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Paraglide.
NASA Headquarters' recent decision to cut the MSC budget for fiscal year 1963 from $687 million to $660 million. Wesley L. Hjornevik, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Assistant Director for Administration, described to members of MSC's senior staff the implications of NASA Headquarters' recent decision to cut the MSC budget for fiscal year 1963 from $687 million to $660 million, the entire reduction to be borne by the Gemini program. Hjornevik feared that the Gemini budget, already tight, could absorb so large a cut only by dropping the paraglider, Agena, and all rendezvous equipment from the program. Gemini Project Office (GPO) reported that funding limitations had already forced Martin and McDonnell to reduce their level of activity. The first Gemini flight (unmanned) was rescheduled for December 1963, with the second (manned) to follow three months later, and subsequent flights at two-month intervals, with the first Agena (fifth mission) in August or September 1964. This four-month delay imposed by budget limitations required a large-scale reprogramming of Gemini development work, reflected chiefly in drastic reduction in the scale of planned test programs. Details of the necessary reprogramming had been worked out by December 20, when GPO Manager James A. Chamberlin reported that December 1963 was a realistic date for the first Gemini flight. Gemini funding for fiscal year 1963 totaled $232.8 million.
1962 October 19 - . 18:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
1962 October 25 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Manned Spacecraft Center informed Lockheed that Gemini program budget readjustments required reprogramming the Gemini-Agena program. - .
Nation: USA.
Manned Spacecraft Center informed Lockheed that Gemini program budget readjustments required reprogramming the Gemini-Agena program. Subsequent meetings on November 2 and November 20 worked out the changes necessary to implement the Agena program at minimum cost. The overall test program for the Agena and its propulsion systems was significantly reduced, but in general neither the scope nor the requirements of the Agena program were altered. The major result of the reprogramming was a four-month slip in the scheduled launch date of the first Agena (to September 1964); this delay was about a month and a half less than had been anticipated when reprogramming began. In addition, Lockheed was to continue its program at a reduced level through the rest of 1962, a period of about six weeks, and to resume its normal level of activity on January 1, 1963.
1962 October 26 - . 10:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-5 / Pod 20 Target - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Atlas 159D was launched from Vandenberg AFB carrying the first payload in the Ballistic Systems Division's Nike Targets program in support of the Army's Nike-X anti-ballistic missile development effort. .
1962 November 4 - . Launch Site: Dyess AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas F missile squadron turned over to SAC. - . The Atlas F missile squadron located at Dyess AFB, Texas - the 578th Strategic Missile Squadron - was turned over to SAC..
1962 November 7 - . 19:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
1962 November 11 - . 20:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Samos 11 - . Payload: Samos E-6 no. 3 / TRS 1 / Agena B 2405. Mass: 1,860 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. Decay Date: 1962-11-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 455 . COSPAR: 1962-B-Pi-1. Apogee: 292 km (181 mi). Perigee: 128 km (79 mi). Inclination: 96.00 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Second generation photo surveillance; radio relay of images; Satellite and Missile Observation Satellite. Poor results. SAMOS project cancelled..
- FTV 2405 RV - . Payload: E-6 RV. Mass: 1,900 kg (4,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Samos. COSPAR: 1962-B-Pi-xx.
- TRS 1 - . Payload: ERS 1. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: ERS. COSPAR: 1962-B-Pi-xx.
1962 November 13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Cooper named for Mercury MA-9 1-day orbital mission - . Nation: USA. Related Persons: Cooper, Shepard. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft: Mercury. Gordon Cooper was named as the pilot for Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) 1-day orbital mission slated for April 1963. Alan Shepard, pilot of Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) was designated as backup pilot..
1962 November 14 - . 22:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1962 November 15 - . Launch Site: Dyess AFB. Launch Complex: Dyess AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas SMS 578 operational. - . Nation: USA. Dyess AFB SMS 578 operational.
1962 November 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury spacecraft 15A delivered to Cape Canaveral - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-10. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury spacecraft 15A was delivered to Cape Canaveral for the Mercury-Atlas 10 (MA-10) orbital manned 1-day mission..
1962 November 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- "T-back" pod proposed as the Gemini rendezvous target instead of the Agena. - .
Nation: USA.
Andre J. Meyer, Jr., of Gemini Project Office reported that Space Technology Laboratories was conducting a study for NASA Headquarters on a 'T-back' pod to be used in the spacecraft adapter as the rendezvous target instead of the Agena. The pod would be stabilized but would have no translation capabilities. Although it would be almost as expensive as the Agena, it would avoid separate launch problems.
1962 November 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Retrofire initiated 2 seconds late during Mercury MA-8 - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Retrofire was reported to have initiated 2 seconds late during the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) mission. Because of this, the mechanics and tolerances of the Mercury orbital timing device were reviewed for the benefit of operational personnel, and the procedural sequence for Mercury retrofire initiation was outlined.
1962 November 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Simulator 2 modified to the 1-day configuration. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft: Mercury. Mercury Simulator 2 was modified to the 1-day Mercury orbital configuration in preparation for the Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) flight..
1962 November 30 - . Launch Site: Walker AFB. Launch Complex: Walker AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas SMS 579 operational. - . Nation: USA. Walker AFB SMS 579 operational.
1962 November 30 - . Launch Site: Walker AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- The Atlas F silo-lift squadron at Walker AFB turned over to SAC - . The Atlas F silo-lift squadron at Walker AFB, New Mexico, was turned over to SAC (579th SMS) and was declared fully operational 8 December..
By the end of 1962 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-9A (cancelled) - .
Call Sign: Faith 7. Crew: Cooper.
Backup Crew: Shepard.
Payload: Mercury SC19. Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Kennedy.
Flight: Mercury MA-9A.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
NASA's Mercury orbital operations plan of July 19, 1961 had four spacecraft equipped for three-orbit flights. However by Schirra's flight the seven-astronaut corps was down to four. So even thought the flight-ready SC19 had been delivered to Cape Canaveral on March 20, 1962, the decision was taken to cancel the remaining short-duration mission and move directly to an 18 orbit mission.
1962 December 5 - . 21:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Research and development test - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
The final Atlas F research and development flight test missile (21F) was launched down the Atlantic Missile Range. Ten missiles were launched in this series - seven were successes and three failures. The launch of Atlas 21F brought flight testing of Atlas operational missiles from Cape Canaveral to an end after almost five and one-half years. Since the first R&D Atlas was launched on 11 June 1957, 83 Atlas Series A through F missiles had been fired from the Cape - 52 of them successes or partials and 31 failures. Last Atlas F R&D flight.
1962 December 7 - . Launch Site: Plattsburgh AFB. LV Family: Atlas.
- Activation of the Atlas ICBM force completed. - .
With the transfer of the 556th Strategic Missile Squadron at Plattsburgh AFB, New York, to SAC, the activation of the Atlas ICBM force was completed. The 556th was declared fully operational on 20 December. Between 7 September and 7 December 1962, Ballistic Systems Division had turned over 72 Atlas F missile launchers to SAC. Since August 1959, a total of 132 Atlas D, E, and F missile sites had been turned over to SAC.
1962 December 12 - . 11:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-6 Target mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). K-6 Nike-Zeus intercept of Atlas ICBM..
1962 December 17 - . 20:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: U.
- Midas 6 - . Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1205. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. Decay Date: 1962-12-17 . Missile Defense Alarm System. Carried ERS-3, ERS-4 subsatellites..
- TRS 4 - . Payload: ERS 4. Mass: 1,840 kg (4,050 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas.
- TRS 3 - . Payload: ERS 3. Mass: 1,840 kg (4,050 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas.
1962 December 18 - . 17:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1962 December 20 - . Launch Site: Plattsburgh AFB. Launch Complex: Plattsburgh AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas SMS 556 - last Atlas squadron - operational. - . Nation: USA. Plattsburgh AFB SMS 556 (last Atlas squadron) operational.
1962 December 22 - . 09:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-7 / Pod 4 ABM sensor test / plume characterization mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 2,259 km (1,403 mi). K-7 Nike-Zeus intercept of Atlas ICBM..
1963 January 3 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-9 flight to go 22 orbits. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Mercury. Tentative plans were made by NASA to extend the Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) flight from 18 to 22 orbits..
1963 January 9 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Flight Operations Division outlined detailed requirements for the remote stations of the worldwide tracking network. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight Operations Division outlined detailed requirements for the remote stations of the worldwide tracking network. Each station would need five consoles: Gemini system, Agena system, command, aeromedical, and maintenance and operations. The Gemini and Agena consoles would have 42 analog display meters and 40 on/off indicators.
1963 January 14 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- MSC assumed complete responsibility for the Gemini target vehicle program. - .
Nation: USA.
Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) assumed complete responsibility for the Gemini target vehicle program from Marshall Space Flight Center following a meeting between MSC and Marshall on January 11 establishing procedures for the transfer. Marshall was to continue to participate actively in an advisory capacity until March 1 and thereafter as technical consultant to MSC upon request. All other NASA Atlas-Agena programs were transferred to Lewis Research Center in a move aimed at freeing Marshall to concentrate on Saturn launch vehicle development and consolidating Atlas launch vehicle technology at Lewis. NASA Headquarters had decided to effect the transfer on October 12, 1962.
1963 January 25 - . 10:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1963 January 31 - . 08:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1963 February 5-6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Rendezvous and Reentry Panel meeting. - . Nation: USA. At a Gemini Rendezvous and Reentry Panel meeting, it was reported that attempts to obtain information on flight controller procedures to command the Agena in orbit had been delayed by the Air Force Agena security program. .
1963 February 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- The Manned Spacecraft Center announced a mid-May flight for Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9). - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft: Mercury. Originally scheduled for April, the launch date was delayed by a decision to rewire the Mercury-Atlas flight control system, as a result of the launch vehicle checkout at the plant inspection meeting..
1963 February 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Objectives of the Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) manned 1-day mission were published. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft: Mercury. This was the ninth flight of a production Mercury spacecraft to be boosted by an Atlas launch vehicle and the sixth manned United States space flight. . Additional Details: here....
1963 February 13 - . 11:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-8 / NC20.133 ABM test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). K-8 Nike-Zeus intercept of Atlas ICBM..
1963 February 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Agena target vehicle checkout plans were presented at a meeting of the Gemini Management Panel. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Radar.
Upon receipt at Cape Canaveral, the target vehicle would be inspected and certified. After this action, mechanical mate and interface checks with the target docking adapter would be accomplished. Agena-Gemini spacecraft compatibilty tests would then be conducted, and the Agena would undergo validation and weight checks. Subsequently, a joint checkout of the spacecraft and Agena would be conducted with tests on the Merritt Island radar tower.
1963 February 28 - . 09:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-10 ABM test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). K-10 Nike-Zeus intercept of Atlas ICBM..
1963 March 1 - . 21:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES REX-I / Pod 1 Re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1963 March 5 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Project Office discussed with contractors the establishment of a philosophy for the final phase of the rendezvous mission. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Radar.
Gemini Project Office discussed with contractors the establishment of a philosophy for the final phase of the rendezvous mission. They agreed on the following general rules: (1) when the launch was on time, the terminal maneuver would be initiated when the Agena came within range of the spacecraft's sensors, which would occur between spacecraft insertion and first apogee; (2) automatic and optical terminal guidance techniques would always back each other up, one method being selected as an objective for each mission and the other serving as a standby; (3) during early rendezvous missions, the terminal phase would be initiated by the third spacecraft apogee or delayed until the twelfth because of range radar tracking limitations; (4) for the same reason, no midcourse corrections should be made during orbits 4 through 11; (5) in case of extreme plane or phase errors, the Agena would be maneuvered to bring it within the spacecraft's maneuver capability; and (6) after such gross Agena maneuvers, the Agena orbit would be recircularized and two orbits of spacecraft catchup would precede the initiation of terminal rendezvous plan.
1963 March 10 - . 02:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1963 March 12 - . 05:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1963 March 15 - . 11:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1963 March 16 - . 02:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576D. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- OT TALL TREE 5 operational test launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1963 March 16 - . 08:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- NTMP K-14/NC20.145 Target/Aeronomy mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi).
1963 March 21 - . 21:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
1963 March 24 - . 00:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1963 April - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Bell Aerosystems successfully completed initial firing of the Gemini Agena Model 8247 engine at its Buffalo plant early in the month. - .
Nation: USA.
Bell Aerosystems successfully completed initial firing of the Gemini Agena Model 8247 engine at its Buffalo plant early in the month. The Model 8247 engine for the Gemini Agena's primary propulsion system was developed from the Model 8096 currently being flown in satellite and probe programs for NASA and the Air Force. Unlike the operational engine, the new engine was capable of being restarted several times in orbit, a Gemini program requirement. The principle change in the new engine was the substitution of liquid propellants for solid pyrotechnic 'starter cans' to start the gas generator. The unit tested was the development engine that had been assembled in March. In mid-April, the test engine was shipped to Arnold Engineering Development Center (AEDC), Tullahoma, Tennessee, for further development tests. At AEDC, test cell arrangements were completed April 12, with testing scheduled to begin in May.
1963 April 22 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury Spacecraft 20 mated to Atlas launch vehicle - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft: Mercury. Spacecraft 20 was moved from Hanger S at Cape Canaveral to Complex 14 and mated to Atlas launch vehicle 130-D in preparation for the Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) mission. The first simulated flight test was begun immediately..
1963 April 22 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- First management review of the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV). - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Representatives of Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD), Manned Spacecraft Center, and Lockheed met in Sunnyvale for the first management review of the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV). Patterned after similar meetings regularly held between SSD, Lewis Research Center, and Lockheed on medium space vehicle satellite and probe programs, the Gemini Target Management Review Meetings encompassed a comprehensive monthly review of the status of the GATV program.
1963 April 24 - . 20:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Research and development test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,600 km (900 mi). First successful E missile from OSTF-1, SMS 576.
1963 April 27 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- LC 14 modifications - .
Nation: USA.
Final design review of complex 14 modifications and activation of facilities was held under the aegis of Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) in Los Angeles. All drawings and specifications were accepted. SSD's activation of the complex was scheduled to begin January 1, 1964, with an estimated 10 months required to prepare complex 14 for Project Gemini Atlas-Agena launches.
1963 April 27 - . 02:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES REX-II re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1963 April 29 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Rescheduling of the Gemini flight program - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Parachute,
Gemini Paraglide.
NASA Headquarters approved rescheduling of the Gemini flight program as proposed by Gemini Project Office (GPO). Late delivery of the spacecraft systems coupled with the unexpectedly small number of Mercury systems incorporated in the Gemini spacecraft had forced GPO to review the flight program critically. In the revised program, the first flight was still set for December 1963 and was still to be unmanned, but it was now to be orbital rather than suborbital to flight-qualify launch vehicle subsystems and demonstrate the compatibility of the launch vehicle and spacecraft; no separation or recovery was planned. The second mission, originally a manned orbital flight, now became an unmanned suborbital ballistic flight schedule for July 1964. Its primary objection was to test spacecraft reentry under maximum heating-rate reentry conditions; it would also qualify the launch vehicle and all spacecraft systems required for manned orbital flight. The third flight, formerly planned as a manned orbital rendezvous mission, became the first manned flight, a short-duration (probably three-orbit) systems evaluation flight scheduled for October 1964. Subsequent flights were to follow at three-month intervals, ending in January 1967. Rendezvous terminal maneuvers were planned for missions 3 (if flight duration permitted) and 4, a seven-day mission using a rendezvous pod. The sixth flight was to be a 14-day long-duration mission identical to 4 except that no rendezvous maneuver missions with the Atlas-launched Agena D target vehicle. Water landing by parachute was planned for the first six flights and land landing by paraglider from flight 7 on.
1963 April 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Improvements to the Mercury pressure suit for Mercury MA-9 - . Nation: USA. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft Bus: Mark IV Model 3 Type I. Spacecraft: Mercury Space Suit. A number of improvements had been made to the Mercury pressure suit for the Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) flight. . Additional Details: here....
1963 May 9 - . 20:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Midas 7 - . Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1206. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. USAF Sat Cat: 574 . COSPAR: 1963-014A. Apogee: 3,680 km (2,280 mi). Perigee: 3,609 km (2,242 mi). Inclination: 87.30 deg. Period: 166.40 min. MIDAS 7 was the first operational MIDAS mission and the first equipped with the W-37 sensor. During its six weeks of operation, MIDAS 7 recorded nine US ICBM launches, including the first missile launch ever detected from space..
- TRS 3 - . Payload: ERS 6. Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: TRS. USAF Sat Cat: 608 . COSPAR: 1963-014C. Apogee: 3,691 km (2,293 mi). Perigee: 3,591 km (2,231 mi). Inclination: 87.30 deg. Period: 166.40 min. Solar cells damage data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Westford - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Communications. Type: Passive communications satellite. Spacecraft: Westford Needles. COSPAR: 1963-014xx.
- TRS 2 - . Payload: ERS 5. Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: TRS. Decay Date: 1973-07-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 579 . COSPAR: 1963-014B. Apogee: 4,902 km (3,045 mi). Perigee: 2,269 km (1,409 mi). Inclination: 87.20 deg. Period: 165.00 min. Solar cells damage data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Dash 1 - . Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft: Dash. USAF Sat Cat: 589 . COSPAR: 1963-014D. Apogee: 3,724 km (2,313 mi). Perigee: 3,558 km (2,210 mi). Inclination: 87.30 deg. Period: 166.30 min.
1963 May 15 - . 13:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-9 - . Call Sign: Faith 7. Crew: Cooper. Backup Crew: Shepard. Payload: Mercury SC20. Mass: 1,376 kg (3,033 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Flight: Mercury MA-9. Spacecraft: Mercury. Duration: 1.43 days. Decay Date: 1963-05-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 576 . COSPAR: 1963-015A. Apogee: 265 km (164 mi). Perigee: 163 km (101 mi). Inclination: 32.50 deg. Period: 88.70 min. Final Mercury mission, Faith 7, was piloted by Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper, Jr..
1963 May 24 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Titan I.
- Atlas D,E, and Titan I missiles to be phased out 1965 - 1968. - .
Headquarters USAF recommended that Atlas D,E, and Titan I missiles be phased out of SAC's active operational inventory between 1965 and 1968. The older liquid-fueled ICBMs were expensive to operate, required a large manpower commitment, were slow-reacting and thus vulnerable when compared to the more advanced Minuteman and Titan II missile that were being deployed.
1963 June 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas F propellant loading accident. - . Nation: USA. Exploded during propellant loading (Walker AFB 1).
1963 June 2 - . 00:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Walker AFB. Launch Complex: Walker AFB. Launch Pad: Walker AFB Missile Site 579. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
1963 June 4 - . 20:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1963 June 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-10 environmental control system changes - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Mercury MA-10.
Spacecraft: Mercury,
Mercury ECS.
In preparation for the Mercury-Atlas 10 (MA-10) mission, should the flight be approved by NASA Headquarters, several environmental control system changes were made in spacecraft 15B. Particularly involved were improvements in the hardware and flexibility of the urine and condensate systems. With regard to the condensate portion, Gordon Cooper, in his press conference, indicated that the system was not easy to operate during the flight of Faith 7 (MA-9).
1963 June 12 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: U.
- Midas 8 - . Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1204. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. Decay Date: 1963-06-12 . Missile Defense Alarm System. Carried ERS-7, ERS-8 subsatellites..
- TRS 8 - . Payload: ERS 8. Mass: 1,840 kg (4,050 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas.
- TRS 7 - . Payload: ERS 7. Mass: 1,840 kg (4,050 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas.
1963 June 12 - . 09:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP K-15 Atlas intercept - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). K-15 Nike-Zeus intercept of Atlas ICBM..
1963 June 19 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- The Cape Gemini/Agena Test Integration Working Group met to define "Plan X" test procedures and responsibilities. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Radar,
Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
The Cape Gemini/Agena Test Integration Working Group met to define "Plan X" test procedures and responsibilities. The purpose of Plan X was to verify the Gemini spacecraft's ability to command the Agena target vehicle both by radio and hardline; to exercise all command, data, and communication links between the spacecraft, target vehicle, and mission control in all practical combinations, first with the two vehicles about six feet apart, then with the vehicles docked and latched but not rigidized; and to familiarize the astronauts with operating the spacecraft/target vehicle combination in a simulated rendezvous mission. Site of the test was to be the Merritt Island Launch Area Radar Range Boresight Tower ('Timber Tower'), a 65 x 25 x 50-foot wooden structure.
1963 June 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Atlas E weapon system - . Responsibility for the Atlas E weapon system was transferred from BSD (AFSC) to the Air Force Logistics Command (AFLC)..
1963 July 3 - . 21:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576C. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,600 km (900 mi). Atlas 69E successfully led off the seven-missile Atlas E operational program launch series from Vandenberg. .
1963 July 12 - . 20:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-01 (Gambit) - .
Payload: KH-7 no. 1 / OPS 1467. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO,
USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: KH-7.
Decay Date: 1963-07-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 618 . COSPAR: 1963-028A. Apogee: 212 km (131 mi). Perigee: 173 km (107 mi). Inclination: 95.30 deg. Period: 88.30 min.
The Air Force launched its first Atlas D/Agena D from Vandenberg. This was the 100th Agena (Number 4702) space vehicle used since 28 February 1959. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1963 July 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Development tests of the Agena 8247 engine ended in an emergency shutdown. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Development tests of the Agena Model 8247 main engine at Arnold Engineering Development Center ended when the latch-type gas generator valve failed in testing, making an emergency shutdown of the engine necessary. The wrong choice of emergency shutdown procedures caused turbine overspeed and total failure of the engine's turbine pump assembly. As a result of this failure, the valve was redesigned. Because success of the new design was doubtful, a parallel program was initiated to design and develop an alternative valve configuration, solenoid-operated rather than latch-type. Intensive development testing followed; and in a meeting at Bell Aerosystems on November 15, the solenoid type was selected for use in the first flight system of the Agena target vehicle. The new valve allowed significant reductions in engine complexity and increased reliability, but the development effort imposed a serious delay in Preliminary Flight Rating Tests, which had been scheduled to begin in September 1963.
1963 July 19 - . 03:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Midas 9 - . Payload: Midas / Agena TV 1207. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. USAF Sat Cat: 622 . COSPAR: 1963-030A. Apogee: 3,726 km (2,315 mi). Perigee: 3,676 km (2,284 mi). Inclination: 88.40 deg. Period: 167.90 min. The final Air Force Atlas D/Agena B (75D/1207) was launched from Vandenberg AFB. Missile Defense Alarm System. Did not eject ERS 10 subsatellite..
- TRS 10 - . Payload: ERS 10. Mass: 45 kg (99 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: ERS. COSPAR: 1963-030xx.
- TRS 4 - . Payload: ERS 9. Mass: 2.00 kg (4.40 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: TRS. USAF Sat Cat: 635 . COSPAR: 1963-030B. Apogee: 3,736 km (2,321 mi). Perigee: 3,661 km (2,274 mi). Inclination: 88.40 deg. Period: 167.80 min. Radiation damage data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Dash 2 - . Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft: Dash. Decay Date: 1971-04-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 624 . COSPAR: 1963-030D. Apogee: 3,839 km (2,385 mi). Perigee: 3,573 km (2,220 mi). Inclination: 88.50 deg. Period: 168.00 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1963 July 26 - . 19:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi).
1963 July 30 - . 18:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576C. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,600 km (900 mi).
1963 July 31 - . 20:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1963 August 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Centaur first firing using both RL-10 engines. - . General Dynamics' Convair/Astronautics fired the Centaur liquid hydrogen/ liquid oxygen upper stage for the first time using both RL-10 engines..
1963 August 24 - . 09:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1963 August 28 - . 23:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1963 September 5 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lockheed's contract for the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) was amended. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
As a result of the seven-and-one-half-month relaxation of the required launch date for the first GATV, Lockheed was directed to use the improved version of the standard Agena, the AD-62 block of vehicles, instead of AD-13. The AD-62 block originally included the multistart engine, subsequently slipped to the AD-71 block. Lockheed accordingly was directed in January 1964 to substitute the AD-71 for AD-62. The combined effect of these changes was to use up much of the seven-and-one-half-month leeway. The change to AD-62 caused a two-month slip, and changing to AD-71 added a five-week slip. With much of the contingency time gone, the Agena schedule was now tight, and further slippage threatened to cause launch delays.
1963 September 6 - . LV Family: Atlas, Thor.
- NASA and DoD announced a new agreement for NASA's use of Air Force-developed Agena vehicles. - .
Space Systems Division was to be responsible for design, engineering, and acceptance testing of basic Atlas and Thor vehicles and the Agena D upper stages. NASA would buy these from the Air Force, modify them as needed, and launch the Atlas/Agenas from the Atlantic Missile Range while the Air Force conducted all Atlas/Agena and Thor/Agena launches from Vandenberg.
1963 September 6 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-02 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 2 / OPS 1947. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1963-09-13 . USAF Sat Cat: 641 . COSPAR: 1963-036A. Apogee: 243 km (150 mi). Perigee: 171 km (106 mi). Inclination: 94.40 deg. Period: 88.70 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1963 September 6 - . 21:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1963 September 11 - . 21:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1963 September 25 - . 11:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576C. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi).
1963 September 27 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini and Agena compatible with NASA ground stations. - .
Nation: USA.
Electro-Mechanical Research successfully tested the compatibility of airborne and ground station PCM (pulse code modulated) telemetry equipment. The tests demonstrated that Gemini spacecraft and Agena telemeter and recorder formats were compatible with NASA ground stations.
1963 October - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-10 (cancelled) - .
Call Sign: Freedom 7 II. Crew: Shepard.
Backup Crew: Cooper.
Payload: Mercury SC15B. Nation: USA.
Flight: Mercury MA-10.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
Alan Shepard, and others pushed for a six day Mercury 10 endurance mission. This would give America the manned space endurance record for the first time and also cover the biological objectives of the first two Gemini missions. The Mercury 15B capsule had already been modified for long-duration flight and Shepard had the name 'Freedom 7 II' painted on the side. But the risk and work pending on Gemini persuaded NASA managers not to undertake another mission.
1963 October 4 - . 05:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1963 October 7 - . 21:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
By the end of 1963 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-11 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Grissom.
Backup Crew: Schirra.
Payload: Mercury SC12B. Nation: USA.
Flight: Mercury MA-11.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
From October 25, 1961 until April 1962 NASA's Mercury program plan included four one-day flights in 1963. By October 1962 the decision had been quietly taken to limit the long-duration flights to only MA-9 and MA-10. MA-10 was fnally cancelled in turn after the successful MA-9 mission.
1963 October 17 - . 02:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Vela 2 - .
Payload: Vela 1B. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 674 . COSPAR: 1963-039A. Apogee: 116,582 km (72,440 mi). Perigee: 101,081 km (62,808 mi). Inclination: 38.70 deg. Period: 6,486.20 min.
Space Systems Division, acting.as program manager for the Defense Department, launched two Vela nuclear radiation detection satellites from Cape Canaveral aboard the first Atlas D/Agena D (SLV-3/SS-01A) launch vehicle (197D). The Vela satellites were developed and produced by the TRW Systems and were the first pair in a series of satellites designed to provide information on nuclear detonations in the atmosphere or in outer space to a distance of 100 million miles. The 297-pound satellites were placed in near-circular orbits approximately 70,000 miles above the Earth's surface. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- Vela 1 - . Payload: Vela 1A. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela. USAF Sat Cat: 692 . COSPAR: 1963-039C. Apogee: 116,528 km (72,407 mi). Perigee: 101,925 km (63,333 mi). Inclination: 37.80 deg. Period: 6,519.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- TRS 5 - . Payload: ERS 12. Mass: 2.00 kg (4.40 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: TRS. Decay Date: 1963-06-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 675 . COSPAR: 1963-039B. Apogee: 102,372 km (63,610 mi). Perigee: 953 km (592 mi). Inclination: 35.90 deg. Period: 2,319.40 min. Decay date suspect Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1963 October 25 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Agena D - . Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1963-10-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 678 . COSPAR: 1963-041B. Apogee: 276 km (171 mi). Perigee: 116 km (72 mi). Inclination: 99.00 deg. Period: 88.41 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- KH 7-03 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 3 / OPS 2196. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1963-10-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 677 . COSPAR: 1963-041A. Apogee: 312 km (193 mi). Perigee: 123 km (76 mi). Inclination: 99.00 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1963 October 28 - . 03:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- ABRES WAC-1 / Pod 21 Reentry test / plume mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 500 km (310 mi).
1963 November - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Milestone schedule for the Gemini Agena target vehicle - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Lockheed included a milestone schedule for the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) in its monthly progress report for the first time since January 1963. The new schedule reflected the revised Gemini flight program of April 29 and the corresponding revision of the Agena program which followed. It displayed key events in the progress of the first GATV taking place between five and six months later than the January schedule. Engineering development was now scheduled to be completed by May 15, 1964, rather than by December 11, 1963. Completion of modification and final assembly was now planned for June 12 rather than January 10, 1964; preliminary vehicle systems testing was rescheduled from April 10 to September 11, 1964. Special tests, including a Radio frequency Interference Test in the later schedule in addition to the hot-firing scheduled earlier, were to end November 20 instead of May 22, 1964. Final Vehicle Systems Tests were to be completed December 18 instead of June 19, 1964, with shipment to follow on January 6, 1965, rather than June 30, 1964. Launch was now expected on April 15, 1965, seven and one-half months later than the September 1, 1964, date that had been planned in January 1963.
1963 November 4 - . 09:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES REX-III re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). The first Advanced Ballistic Reentry System (ABRES) program launch from Vandenberg was successfully completed when SAC's Atlas D booster (232D) carried the Chrysler-built REX-3 reentry vehicle down the Pacific Missile Range. .
1963 November 13 - . 22:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- ST COOL WATER VI test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi). SAC launched Atlas D (158) in the final Atlas D operational program launch from Vandenberg. The missile was a failure, making the final tally for the 26 launches nine failures and 17 successes. .
By the end of 1963 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Mercury MA-12 (cancelled) - .
Crew: Schirra.
Payload: Mercury SC17. Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Schirra.
Flight: Mercury MA-12.
Spacecraft: Mercury.
From October 25, 1961 until April 1962 NASA's Mercury program plan included four one-day flights in 1963. By October 1962 the decision had been quietly taken to limit the long-duration flights to only MA-9 and MA-10. MA-10 was fnally cancelled in turn after the successful MA-9 mission.
1963 November 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Tests to demonstrate structural integrity of the Gemini target docking adapter (TDA). - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Douglas Aircraft Corporation, Tulsa, Oklahoma, began a series of tests to demonstrate the structural integrity of the Gemini target docking adapter (TDA) during shroud separation. The shroud, which protected the TDA during the launch and ascent of the Agena target vehicle, was tested under simulated altitude conditions to show proper operation of pyrotechnic devices and adequate clearance between shroud and TDA during separation. Successfully concluded on November 21, and tests demonstrated the compatibility of the TDA with the shroud system during operational performance, with no indication of damage or failure of the TDA structure.
1963 November 20 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas.
- Point Arguello and Navy tracking stations in the Pacific transferred to the Air Force. - .
The Defense Department announced that the Naval Missile Facility at Point Arguello, California, and the Navy tracking stations in the Pacific would be transferred to the Air Force. This would include control of the Atlantic Missile Range, the Pacific Missile Range, and the satellite control facilities at Sunnyvale, California, and combine them under a single component of the Air Force.
1963 November 27 - . 19:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Atlas Centaur 2 - .
Payload: Centaur 2B. Mass: 4,620 kg (10,180 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Cleveland.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor.
USAF Sat Cat: 694 . COSPAR: 1963-047A. Apogee: 1,478 km (918 mi). Perigee: 469 km (291 mi). Inclination: 30.40 deg. Period: 104.60 min.
Launched from Cape Canaveral, Atlas/Centaur (AC-2) was the first successful use of the high-energy liquid hydrogen/ liquid oxygen Centaur upper stage vehicle developed for NASA by General Dynamics. The spent Centaur stage entered orbit. Launch vehicle test. Launch vehicle put dummy payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit. First successful Centaur (liquid hydrogen-fueled) flight.
1963 December 18 - . 09:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES LORV-8 re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF SAC.
Spacecraft: ABRES.
Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
Atlas 109F was the final Atlas research and development flight test missile to be launched. Since the first attempted launch of a Series A Atlas on 11 June 1957, 95 Atlas missiles had been used in the R&D program - eight As, nine Bs, six Cs, 32 Ds, 24 Es, and 16 Fs. All but 12 of these were launched from Cape Canaveral. Of the 95 launches, 57 were considered successful while 38 were failures.
1963 December 18 - . 21:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-04 - .
Payload: KH-7 no. 4 / OPS 2372. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO,
USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: KH-7.
Decay Date: 1963-12-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 711 . COSPAR: 1963-051A. Apogee: 266 km (165 mi). Perigee: 122 km (75 mi). Inclination: 97.90 deg. Period: 88.50 min.
Atlas 109F was the final Atlas research and development flight test missile to be launched. Since the first attempted launch of a Series A Atlas on 11 June 1957, 95 Atlas missiles had been used in the R&D program - eight As, nine Bs, six Cs, 32 Ds, 24 Es, and 16 Fs. All but 12 of these were launched from Cape Canaveral. Of the 95 launches, 57 were considered successful while 38 were failures. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1963 December 18 - . 22:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Research and development launch - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
Atlas 109F was the final Atlas research and development flight test missile to be launched. Since the first attempted launch of a Series A Atlas on 11 June 1957, 95 Atlas missiles had been used in the R&D program - eight As, nine Bs, six Cs, 32 Ds, 24 Es, and 16 Fs. All but 12 of these were launched from Cape Canaveral. Of the 95 launches, 57 were considered successful while 38 were failures.
1964 January 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Update program for Atlas F begun - . The update program for the Atlas F missile sites began on schedule..
1964 January 30 - . 15:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Ranger 6 - .
Payload: RA-6. Mass: 362 kg (798 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 6-7-8-9.
Decay Date: 1964-02-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 747 . COSPAR: 1964-007A.
Impacted Moon but TV camera malfunctioned. A midcourse trajectory correction was accomplished early in the flight by ground control. On February 2, 1964, 65.5 hours after launch, Ranger 6 impacted the Moon on the eastern edge of Mare Tranquillitatis (Sea of Tranquility). No camera data were obtained, probably because of failure due to an arc-over in the TV power system when it inadvertently turned on during the period of booster-engine separation.
1964 February 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Atlas F missile responisibility transferred to AFLC. - . Ballistic Systems Division transferred system and engineering responsibility for the Atlas F missile to AFLC's San Bernardino Air Materiel Area (SBAMA), Norton AFB, Califoria..
1964 February 5 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Bell Aerosystems began Preliminary Flight Rating Tests (PFRT) of the Agena primary propulsion system (PPS). - .
Nation: USA.
Bell Aerosystems began Preliminary Flight Rating Tests (PFRT) of the Agena primary propulsion system (PPS). Tests were expected to be completed April 24 but were not actually concluded until late June. Testing proceeded with only minor problems through the first week of April. But in the following week PPS testing encountered what proved to be a six-week delay when the test unit's fuel and oxidizer start tanks failed. The two start tanks, stainless steel canisters with an internal bellows arrangement, supplied the propellants required to initiate the main engine start sequence. Visible longitudinal cracks in the outer shell allowed the gas which forced the propellants out of the tank to escape. Investigation revealed that the cracks had resulted from intergranular corrosion of the stainless steel tanks. The defective tanks were replaced by start tanks with a new heat-treated shell (delivered April 24), and PFRT resumed early in May.
1964 February 12 - . 19:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1964 February 13 - . 18:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Walker AFB. Launch Complex: Walker AFB. Launch Pad: Walker AFB Missile Site 579. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Exploded during propellant loading..
1964 February 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Bell Aerosystems delivered the first Gemini Agena Model 8247 main engine to Lockheed. - .
Nation: USA.
This engine was installed in the propulsion test vehicle assembly (PTVA), a unit to be used for a series of tests on the Agena primary and secondary propulsion systems at Lockheed's Santa Cruz Test Base. Bell delivered the two secondary propulsion system modules for the PTVA on March 6 and 14. Installation was completed and the PTVA delivered to Santa Cruz Test Base on March 26.
1964 February 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Bell Aerosystems began Preliminary Flight Rating Tests (PFRT) of the Agena secondary propulsion system (SPS). - .
Nation: USA.
Bell Aerosystems began Preliminary Flight Rating Tests (PFRT) of the Agena secondary propulsion system (SPS). After proceeding through the acceleration and vibration test phases of PFRT without incident, the SPS began calibration firings early in April. The failure of a propellant valve in Unit I (the 16-pound thrust chamber fired prior to starting the main engine in order to orient propellant) of the SPS imposed a minor delay, but a more serious problem emerged late in April during high-temperature firings. The wall of the Unit II 200-pound thrust chamber burned through near the injector face after an accumulated PFRT firing time of 354 seconds, below the specification limit of 400 seconds although well in excess of the maximum orbital useful time of 200 seconds. The thrust chamber was replaced and testing continued, but PFRT, originally scheduled to end June 19, was first slipped to July 8, and finally completed in mid-August. To resolve the burn-through problem, Bell began a test program in September to determine the cause of failure.
1964 February 25 - . 18:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-05 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 5 / OPS 2423. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-03-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 754 . COSPAR: 1964-009A. Apogee: 135 km (83 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 95.60 deg. Period: 87.20 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1964 February 25 - . 20:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- ABRES WAC-3 / Pod 18 Re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,600 km (900 mi). The first and only Atlas E (5E) ABRES vehicle to be launched from Cape Canaveral completed a successful flight down the Atlantic Missile Range..
1964 February 28 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Tighter control of Gemini spacecraft weight and configuration. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Gemini Project Manager Charles W. Mathews informed Manned Spacecraft Center senior staff of efforts to control Gemini spacecraft weight and configuration more tightly. Mathews had assigned Lewis R. Fisher of his office to head a Systems Integration Office within Gemini Project Office to oversee these efforts by keeping very precise accounts of spacecraft weight, interface actions between the spacecraft and launch vehicle, and interface actions between the spacecraft and the Agena target vehicle.
1964 March 9 - . 21:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Walker AFB. Launch Complex: Walker AFB. Launch Pad: Walker AFB Missile Site 579. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Exploded during propellant loading..
1964 March 11 - . 20:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-06 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 6 / OPS 3435. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-03-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 764 . COSPAR: 1964-012A. Apogee: 203 km (126 mi). Perigee: 163 km (101 mi). Inclination: 95.70 deg. Period: 88.20 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1964 March 20 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Test program to increase confidence in critical components of the Gemini Agena target vehicle. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) approved Air Force Space Systems Division's (SSD) recommendations for a test program to increase confidence in 16 critical electronic and electrical components of the Gemini Agena target vehicle. The program included complete electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing of all components peculiar to the Gemini mission, as well as elevated stress tests and extended life tests. SSD had also recommended subsystem-level, as well as component-level, EMI testing, but this part of the program MSC disapproved. SSD directed Lockheed to proceed with the program on March 23. EMI tests were scheduled to be completed by July 1, stress and life tests by September 1, 1964.
1964 March 25 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini mission plans for the first Agena rendezvous flight. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Aldrin.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Radar.
At a meeting of the Gemini Project Office's Trajectories and Orbits Panel, members of Flight Operations Division described two mission plans currently under consideration for the first Agena rendezvous flight. One was based on the concept of tangential Agena and spacecraft orbits, as proposed by Howard W. Tindall, Jr., and James T. Rose when they were members of Space Task Group. The second plan, based on a proposal by Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., then of Air Force Space Systems Division, involved orbits which were concentric rather than tangential. The most significant advantage of the second plan was that it provided the greatest utilization of onboard backup techniques; that is, it was specifically designed to make optimum use of remaining onboard systems in the event of failure in the inertial guidance system platform, computer, or radar.
1964 March 26 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- The propulsion test vehicle assembly (PTVA) arrived at Santa Cruz Test Base. - .
Nation: USA.
It consisted of a basic Agena structure with propellant pressurization, feed-and-load system, the primary propulsion system (PPS), and two secondary propulsion system (SPS) modules attached to the aft rack. The test program called for loading operations and hot firings of both propulsion systems to establish the adequacy of PPS and SPS propellant loading systems and associated ground equipment, to demonstrate proper overall system operation, and to provide engineering data on systems operation and the resulting environment. Start of testing was delayed by the PPS start tank problems which showed up during Preliminary Flight Rating Tests at Bell Aerosystems during April. Lockheed returned the PTVA main engine start tanks to Bell, where they were inspected and found to be defective. New tanks were ready by mid-May, but additional minor problems delayed the initiation of hot-firing until June 16.
1964 April 1 - . 20:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC11. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES WAC-2 / Pod 2 Reentry test / plume mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The last of four Atlas F (137F) ABRES test missiles was flown down the Atlantic Missile Range from Cape Canaveral. .
1964 April 3 - . 20:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 0 km (0 mi).
1964 April 13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena launch on a nonrendezvous mission proposed. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) recommended a Gemini Agena launch on a nonrendezvous mission to improve confidence in target vehicle performance before undertaking a rendezvous mission. Gemini Project Office (GPO) rejected this plan, regarding it as impractical within current schedule, launch sequence, and cost restraints. Additional Details: here....
1964 April 14 - . 21:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- FIRE 1 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Apogee: 837 km (520 mi).
FIRE was a subscale model of the Apollo capsule used to verify the spacecraft's hypersonic flight and thermal characteristics. An Atlas D launch vehicle lifted a Project Fire spacecraft from Cape Kennedy in the first test of the heat that would be encountered by a spacecraft reentering the atmosphere at lunar-return velocity. During the spacecraft's fall toward earth, a solid-fuel Antares II rocket behind the payload fired for 30 seconds, increasing the descent speed to 40,501 kilometers (25,166 miles) per hour. Instruments in the spacecraft radioed temperature data to the ground. The spacecraft exterior reached an estimated temperature of 11,400 K (20,000 degrees F). About 32 minutes after launch, the spacecraft impacted into the Atlantic Ocean. The mission, sponsored by Langley Research Center, provided reentry heating measurements needed to evaluate heatshield materials and information on the communications blackout during reentry.
1964 April 23 - . 16:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-07 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 7 / OPS 3743. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-04-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 786 . COSPAR: 1964-020A. Apogee: 336 km (208 mi). Perigee: 150 km (90 mi). Inclination: 103.60 deg. Period: 89.40 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1964 April 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- First Agena D for the Gemini program. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Radar,
Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) accepted the first Agena D (AD-71) for the Gemini program. The Agena D was a production-line vehicle procured from Lockheed by SSD for NASA through routine procedures. Following minor retrofit operations, the vehicle, now designated Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001, entered the manufacturing final assembly area at the Lockheed plant on May 14. There began the conversion of the Agena D into a target vehicle for Gemini rendezvous missions. Major modifications were installation of a target docking adapter (supplied by McDonnell), an auxiliary equipment rack, external status displays, a secondary propulsion system, and an L-band tracking radar.
1964 May 11 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Sea trials of the tracking ship, Rose Knot, were begun on Chesapeake Bay to study the effects of shock vibrations on Gemini equipment. - .
Nation: USA.
Sea trials of the tracking ship, Rose Knot, were begun on Chesapeake Bay to study the effects of shock vibrations on Gemini equipment. A few vibration problems with the pulse-code-modulation system were reported. Gemini-Agena systems were simulated by an instrumented Lockheed Super Constellation aircraft.
1964 May 13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini plan for the first Agena rendezvous flight. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight Operations Division presented the Gemini Program Office's proposed mission plan No. 3 for the first Agena rendezvous flight to the Trajectories and Orbits Panel. Plan No. 3, as yet incomplete, provided for rendezvous at first apogee on a perfectly nominal mission.
1964 May 14 - . Launch Site: Altus AFB. Launch Complex: Altus AFB 577-6. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Exploded during propellant loading..
- Accident - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Apogee: 0 km (0 mi). Operational missile test at Altus AFB..
1964 May 16 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- Phase out plan for Atlas and Titan I ICBM's. - . The Defense Department tentatively established phase out of the Atlas E and Titan I missiles during the third and fourth quarters of FY1965 (January-June 1965) and that of the Atlas F in FY1968..
1964 May 19 - . 19:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-08 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 8 / OPS 3592. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-05-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 799 . COSPAR: 1964-024A. Apogee: 380 km (230 mi). Perigee: 141 km (87 mi). Inclination: 101.10 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1964 May 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- Atlas E update program completed - . The Atlas E update program was completed nearly two months ahead of schedule..
1964 June 3 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lockheed inaugurated the Gemini Extra Care Program to reduce the incidence of equipment failures and discrepancies. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Lockheed inaugurated the Gemini Extra Care Program to reduce the incidence of equipment failures and discrepancies. In cooperation with Air Force and NASA, Lockheed inaugurated the Gemini Extra Care Program to reduce the incidence of equipment failures and discrepancies resulting from poor or careless workmanship during the modification and assembly of the Agena target vehicle. The program included increased inspection, exhortation, morale boosters, special awards, and other activities aimed at fostering and maintaining a strong team spirit at all levels. Results of the program were evidenced in a drastic decline in the number of FEDRs (Failed Equipment and Discrepancy Reports) recorded in the Gemini final manufacturing area on successive vehicles.
1964 June 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Test-firing the Gemini Agena D propulsion test vehicle begins. - .
Nation: USA.
Lockheed began test-firing the propulsion test vehicle assembly at its Santa Cruz Test Base, after a delay caused primarily by problems with the Agena main engine start tanks. The program, undertaken because of extensive changes in the propulsion system required to adapt the standard Agena D for use in Gemini missions, comprised three series of static-firing tests. The first series, in addition to providing base line performance for both primary and secondary propulsion systems (PPS and SPS), also subjected one SPS module to the dynamic and acoustic environment created by 55 seconds of PPS firing. The second series, successfully completed July 16, simulated a possible Gemini mission profile, including multiple firings and various coast and burn times on both PPS and SPS units. The third series, which concluded the test program on August 7, involved a maximum number of starts and minimum-impulse firings on both PPS and SPS. All firings were successful, and review of test data revealed only minor anomalies. The entire test program comprised 27 PPS firings for a run time totaling 545 seconds, 30 SPS Unit I firings totaling 286 seconds, and 11 SPS Unit II firings totaling 268 seconds. Post-test disassembly revealed no physical damage to any equipment.
1964 June 18 - . 14:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES LORV-1 / Pod 31 Re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1964 June 24 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Construction of Gemini-Agena facilities at complex 14 was completed. - . Nation: USA. General Dynamics finished the installation and checkout of equipment in the Launch Operations Building on July 20. Lockheed equipment in the Launch Operations Building was installed and checked out by July 31..
1964 June 30 - . 14:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur. FAILURE: Centaur hydraulics failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Centaur AC-3 - . Payload: Centaur 1C. Mass: 4,815 kg (10,615 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Decay Date: 1964-06-30 . Apogee: 500 km (310 mi). Centaur test. Launch vehicle was to have put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1964 July 6 - . 18:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-09 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 9 / OPS 3684. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-07-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 825 . COSPAR: 1964-036A. Apogee: 345 km (214 mi). Perigee: 121 km (75 mi). Inclination: 92.90 deg. Period: 89.10 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 4923 - . Payload: EHH A3. Mass: 80 kg (176 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1965-01-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 826 . COSPAR: 1964-036B. Apogee: 505 km (313 mi). Perigee: 156 km (96 mi). Inclination: 92.90 deg. Period: 91.10 min. Radar monitoring..
1964 July 17 - . 08:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Vela 3 - .
Payload: Vela 2A / OPS 3662. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 836 . COSPAR: 1964-040A. Apogee: 104,101 km (64,685 mi). Perigee: 102,500 km (63,600 mi). Inclination: 39.10 deg. Period: 6,024.80 min.
An Atlas D/Agena D launch vehicle (Atlas 216D), carrying the second set of Vela Nuclear Detection Satellites, was launched from Cape Canaveral and placed the satellites in their prescribed orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- Vela 4 - .
Payload: Vela 2B / OPS 3674. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 837 . COSPAR: 1964-040B. Apogee: 114,000 km (70,000 mi). Perigee: 92,103 km (57,230 mi). Inclination: 40.80 deg. Period: 6,004.30 min.
An Atlas D/Agena D launch vehicle (Atlas 216D), carrying the second set of Vela Nuclear Detection Satellites, was launched from Cape Canaveral and placed the satellites in their prescribed orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- TRS 6 - . Payload: ERS 13. Mass: 12 kg (26 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: TRS. Decay Date: 1966-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 838 . COSPAR: 1964-040C. Apogee: 104,665 km (65,035 mi). Perigee: 217 km (134 mi). Inclination: 36.70 deg. Period: 2,366.20 min. Decay date suspect Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1964 July 28 - . 16:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Ranger 7 - .
Mass: 362 kg (798 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 6-7-8-9.
Decay Date: 1964-07-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 842 . COSPAR: 1964-041A.
First successful Ranger; returned 4,308 photos before lunar impact. The Atlas- Agena B inserted the Agena and Ranger into a 192 km altitude Earth parking orbit. Half an hour after launch a second burn of the Agena engine injected the spacecraft into a lunar intercept trajectory. After separation from the Agena, the solar panels were deployed, attitude control activated, and spacecraft transmissions switched from the omniantenna to the high-gain antenna. The next day the planned mid-course maneuver was successfully initiated at 10:27 GMT. The only anomaly during flight was a brief loss of two-way lock on the spacecraft by the DSIF tracking station at Cape Kennedy following launch.
Ranger 7 reached the Moon on 31 July. The F-channel began its one minute warm up 18 minutes before impact. The first image was taken at 13:08:45 GMT at an altitude of 2110 km. Transmission of 4,308 photographs of excellent quality occurred over the final 17 minutes of flight. The final image taken before impact had a resolution of 0.5 meters. The spacecraft encountered the lunar surface in direct motion along a hyperbolic trajectory, with an incoming asymptotic direction at an angle of -5.57 degrees from the lunar equator. The orbit plane was inclined 26.84 degrees to the lunar equator. After 68.6 hours of flight, Ranger 7 impacted in an area between Mare Nubium and Oceanus Procellarum (subsequently named Mare Cognitum) at approximately 10.35 S latitude, 339.42 E longitude. Impact occurred at 13:25:48.82 GMT at a velocity of 2.62 km/s.
1964 July 29 - . 09:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1964 August 7 - . 20:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1964 August 14 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-10 - .
Payload: KH-7 no. 10 / OPS 3802. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO,
USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117.
Spacecraft: KH-7.
Decay Date: 1964-08-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 850 . COSPAR: 1964-045A. Apogee: 300 km (180 mi). Perigee: 165 km (102 mi). Inclination: 95.40 deg. Period: 89.10 min.
The first Atlas/Agena D standard launch vehicle (SLV-3, 7100 Series) was successfully launched from Vandenberg AFB. This vehicle, Number 7101, was the first Atlas booster to be designed and produced to fully standardized specifications. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- OPS 3316 - . Payload: P-11 s/n 4202. Mass: 79 kg (174 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1979-03-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 851 . COSPAR: 1964-045B. Apogee: 3,751 km (2,330 mi). Perigee: 272 km (169 mi). Inclination: 95.70 deg. Period: 127.40 min. The first Atlas/Agena D standard launch vehicle (SLV-3, 7100 Series) was successfully launched from Vandenberg AFB. This vehicle, Number 7101, was the first Atlas booster to be designed and produced to fully standardized specifications. .
1964 August 27 - . 09:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
1964 August 31 - . 15:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576D. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Demonstration and shakedown operations launch - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1964 September 1 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . The first Atlas D squadron, the 564th Strategic Missile Squadron at Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, was inactivated..
1964 September - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas SMS 564 deactivated. - . Nation: USA. Warren-1 AFB SMS 564 deactivated.
1964 September 5 - . 01:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- OGO 1 - .
Payload: OGO A. Mass: 487 kg (1,073 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OGO.
Decay Date: 1980-08-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 879 . COSPAR: 1964-054A. Apogee: 112,657 km (70,001 mi). Perigee: 36,262 km (22,532 mi). Inclination: 88.92 deg. Period: 3,812.21 min.
Two experiment booms failed to properly deploy, with one of the booms obscuring a horizon scanner's view of earth. As a result, the spacecraft attitude could not be earth oriented and OGO 1 remained spin stabilized at 5 rpm. Nevertheless, data from all 20 experiments on board was received, although at a 'less than expected capacity' from some of them. Twelve of the experiemnts were particle studies and two were magnetic field studies. In addition, there was one experiment for each of the following types of studies: interplanetary dust, VLF, Lyman-alpha, Gegenschein, atmospheric mass, and radio astronomy. During September 1964, acceptable data were received over 70% of the orbital path. By June 1969, data acquisition was limited to 10% of the orbital path. Spacecraft operation was restricted to Spring and Fall due to power supply limitations. There were 11 such 3-month periods prior to the spacecraft being put into stand-by mode on 25 November 1969. By April 1970 the spacecraft perigee had increased to 46,000 km and the inclination had increased to 58.8 deg. All support was terminated November 1, 1971.
1964 September 15 - . 15:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES LORV-3 / Pod 26 Re-entry vehicle test - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1964 September 22 - . 13:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1964 September 23 - . 20:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-11 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 11 / OPS 4262. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-09-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 884 . COSPAR: 1964-058A. Apogee: 303 km (188 mi). Perigee: 143 km (88 mi). Inclination: 92.90 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1964 September 24 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Final assembly of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Lockheed completed the modification and final assembly of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 and transferred it to systems test complex C-10 at the Lockheed plant. Lockheed began the task of hooking the vehicle up for systems testing the next day, September 25.
1964 October 8 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: U.
- KH-7 12 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 12. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-10-08 . KH-7 type satellite..
- SRV - . Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7.
1964 October 22 - . Launch Site: Offutt AFB. LV Family: Atlas.
- Last Atlas D at Offutt AFB removed. - . The last Atlas D missile of the 549th Strategic Missile Squadron at Offutt AFB, Nebraska, was dispatched from the base in preparation for final inactivation of the unit in December..
1964 October 23 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- KH 7-13 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 13 / OPS 4384. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-10-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 912 . COSPAR: 1964-068A. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 140 km (80 mi). Inclination: 95.50 deg. Period: 88.50 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 5063 - . Payload: EHH A4. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-02-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 914 . COSPAR: 1964-068B. Apogee: 344 km (213 mi). Perigee: 311 km (193 mi). Inclination: 95.50 deg. Period: 91.10 min. Radar monitoring..
- SRV - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1965-02-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 914 . COSPAR: 1964-068xx. Apogee: 185 km (114 mi). Perigee: 185 km (114 mi). Inclination: 95.40 deg. Period: 88.20 min.
1964 October 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Bell Aerosystems successfully fired the Agena secondary propulsion system (SPS) in a test of the system's ability to survive a launch hold. - .
Nation: USA.
Bell Aerosystems successfully fired the Agena secondary propulsion system (SPS) in a test of the system's ability to survive a launch hold. The SPS had first gone through a 20-day dry (unloaded) period, followed by a 20-day wet (loaded) period. The system reverted to hold condition and was successfully refired November 2.
1964 November 5 - . 19:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D. FAILURE: Launch fairing failure. Failed Stage: S.
- Mariner 3 - . Payload: Mariner C-2. Mass: 260 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Program: Mariner. Class: Mars. Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner. Spacecraft: Mariner 3-4. USAF Sat Cat: 923 . COSPAR: 1964-073A. Mars probe; launch fairing failure prevented Mars flyby. Solar Orbit (Heliocentric). Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1964 November 10 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 competed a simulated flight (ascent and orbit) at Lockheed test complex C-10. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 competed a simulated flight (ascent and orbit) at Lockheed test complex C-10. Minor anomalies required portions of the test to be rerun. This concluded GATV 5001 systems tests in preparation for captive-firing tests to be conducted at Lockheed's Santa Cruz Test Base. The vehicle was shipped November 30.
1964 November 19 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- Atlas E,F, and Titan I ICBMs to be retired from the active operational inventory. - .
Related Persons: ,
McNamara.
Secretary of Defense Robert S. McNamara officially announced his decision to retire Atlas E,F, and Titan I ICBM weapon systems from the active operational inventory. They were said to be no longer supportable from requirements, cost, or manpower use standpoints. Moreover, the relative slow-reacting, liquid-fueled Atlas and Titan I missiles had provided the initial deterrent that was necessary and would now be replaced by the less vulnerable, more easily maintained Minuteman and Titan II ICBMs.
1964 November 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Phase out of the Atlas F from the operational force by June 1965. - . Headquarters USAF issued Atlas System Program Directive 107A-65-1 announcing the scheduled phase out of the Atlas F from the operational force by the end of FY1965 (30 June 1965)..
1964 November 28 - . 14:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Mariner 4 - .
Payload: Mariner C-3. Mass: 260 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Mariner.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner.
Spacecraft: Mariner 3-4.
USAF Sat Cat: 938 . COSPAR: 1964-077A.
Mariner 4 provided the first up close pictures of Mars. The protective shroud covering Mariner 4 was jettisoned and the Agena D/Mariner 4 combination separated from the Atlas D booster at 14:27:23 GMT on 28 November 1964. The Agena D first burn from 14:28:14 to 14:30:38 put the spacecraft into an Earth parking orbit and the second burn from 15:02:53 to 15:04:28 injected the craft into a Mars transfer orbit. Mariner 4 separated from the Agena D at 15:07:09 and began cruise mode operations. The solar panels deployed and the scan platform was unlatched at 15:15:00 and Sun acquisition occurred 16 minutes later. A midcourse maneuver made on 5 December 1964.
After a 228 day cruise, the spacecraft flew by Mars on July 14 and 15, 1965. Planetary science mode was turned on at 15:41:49 GMT on 14 July. The camera sequence started at 00:18:36 GMT on July 15 and 21 pictures plus 21 lines of a 22nd picture were taken. The images covered a discontinuous swath of Mars starting near 40 N, 170 E, down to about 35 S, 200 E, and then across to the terminator at 50 S, 255 E, representing about 1% of the planet's surface. The closest approach was 9,846 km from the Martian surface at 01:00:57 GMT 15 July 1965. The images taken during the flyby were stored in the onboard tape recorder. At 02:19:11 GMT Mariner 4 passed behind Mars as seen from Earth and the radio signal ceased. The signal was reacquired at 03:13:04 GMT when the spacecraft reappeared. Cruise mode was then re-established. Transmission of the taped images to Earth began about 8.5 hours after signal reacquisition and continued until 3 August. All images were transmitted twice to insure no data was missing or corrupt.
The spacecraft performed all programmed activities successfully and returned useful data from launch until 22:05:07 GMT on 1 October 1965, when the distance from Earth (309.2 million km) and the antenna orientation temporarily halted signal acquisition. In 1967 Mariner 4 returned to the vicinity of Earth again and engineers decided to use the ageing craft for a series of operational and telemetry tests to improve their knowledge of the technologies that would be needed for future interplanetary spacecraft. The cosmic dust detector registered 17 hits in a 15 minute span on 15 September, part of an apparent micrometeoroid shower which temporarily changed the spacecraft attitude and probably slightly damaged the thermal shield. On 7 December the gas supply in the attitude control system was exhausted, and on December 10 and 11 a total of 83 micrometeoroid hits were recorded which caused perturbation of the attitude and degradation of the signal strength. On 21 December 1967 communications with Mariner 4 were terminated.
Results
The total data returned by the mission was 5.2 million bits. All experiments operated successfully with the exception of the ionization chamber/Geiger counter which failed in February, 1965 and the plasma probe, which had its performance degraded by a resistor failure on 6 December 1964. The images returned showed a Moon-like cratered terrain (which later missions showed was not typical for Mars, but only for the more ancient region imaged by Mariner 4). A surface atmospheric pressure of 4.1 to 7.0 mb was estimated and no magnetic field was detected.
1964 November 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lockheed shipped Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 to its Santa Cruz Test Base for captive-firing tests. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Lockheed shipped Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 to its Santa Cruz Test Base for captive-firing tests. Primary test objective was verifying the operational capabilities of the GATV during actual firing of the primary and secondary propulsion systems. Additional Details: here....
1964 December 1 - . Launch Site: Warren AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Warren AFB - . The 565th Strategic Missile Squadron (Atlas D) of SAC's 389th Strategic Missile Wing at Francis E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, was inactivated..
1964 December - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas SMS 565 deactivated. - . Nation: USA. Warren-2 AFB SMS 565 deactivated.
1964 December 1 - . 08:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES LORV-5 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1964 December 4 - . 11:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1964 December 4 - . 18:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-14 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 14 / OPS 4439. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1964-12-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 946 . COSPAR: 1964-079A. Apogee: 357 km (221 mi). Perigee: 158 km (98 mi). Inclination: 97.00 deg. Period: 89.70 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1964 December 11 - . 14:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur.
- Surveyor SD-1 - . Payload: Surveyor SD-1. Mass: 2,944 kg (6,490 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1964-12-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 951 . COSPAR: 1964-082A. Apogee: 178 km (110 mi). Perigee: 165 km (102 mi). Inclination: 30.70 deg. Period: 87.80 min. Launch vehicle test. Centaur AC-4 put dummy Surveyor payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1964 December 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Deletion of the eighth Agena from the Gemini Agena target vehicle program. - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Gemini Program Office (GPO) reported that it had initiated contractual action to delete the eighth Agena from the Gemini Agena target vehicle program. On March 6, 1965, GPO reported its decision to eliminate the seventh Agena as well..
1964 December 15 - . Launch Site: Offutt AFB. LV Family: Atlas.
- Last Atlas D squadron inactivated. - . The last of the three SAC Atlas D squadrons, the 549th Strategic Missile Squadron at Offutt AFB, Nebraska, was inactivated..
1964 December 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- Atlas SMS 566 deactivated. - . Nation: USA. Offutt AFB SMS 566 deactivated.
1964 December 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Air Force Space Systems Division officially accepted Agena D (AD-82) for the Gemini program. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 6. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Lockheed then transferred it to the vehicle final assembly area for modification to Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002. Work was scheduled to begin in mid-January 1965..
1964 December 22 - . 19:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
1965 January 8 - . 18:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg OSTF2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ST - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF SAC.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
Atlas 106F concluded SAC's Atlas F operational test launch program from Vandenberg AFB that had begun on 9 September 1959. During the series, 51 Atlas missiles were launched by SAC crews to verify the operational missiles, with 30 of them ruled successes.
1965 January 12 - . 14:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1965 January 13 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas, Minuteman. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- By June 1965, 150 more ICBM sites would be inactivated. - .
The Defense Department announced that by the end of FY1965 (June 1965), 150 more ICBM sites would be inactivated and the Atlas E, F, and Titan I missiles removed and placed in storage. The missiles werer stored at San Bernardino Air Materiel Area (SBAMA) facilities at Norton AFB, California. The retired missiles would be replaced by more advanced Minuteman missiles whose annual combat-ready costs were $100,000 per missile compared to nearly $1.0 million for each of the older, more complicated liquid-fueled ICBMs.. In addition, manpower savings would be substantial since only 12 men were required for support of each Minuteman versus approximately 80 for each Atlas or Titan.
1965 January 20 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 underwent a successful hot-firing test at Lockheed's Santa Cruz Test Base. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 underwent a successful hot-firing test at Lockheed's Santa Cruz Test Base. The test simulated a full 20,000-second mission, including multiple firings of both the primary and secondary propulsion systems and transmission of operational data in real time to two PCM (pulse-code-modulated) telemetry ground stations, one at the test site and one in Sunnyvale. Major test anomaly was a series of command programmer time-accumulator jumps, seven of which totaled 77,899 seconds. The vehicle was removed from the test stand on February 1 and returned to Sunnyvale.
1965 January 21 - . 21:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- OV1-01 - . Payload: ABRES MTV-1. Mass: 85 kg (187 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1965-01-21 . Failure..
1965 January 23 - . 20:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-15 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 15 / OPS 4703. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-01-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 980 . COSPAR: 1965-005A. Apogee: 291 km (180 mi). Perigee: 146 km (90 mi). Inclination: 102.50 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1965 February - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lockheed initiated a "Ten-point Plan for C&C Equipment." - .
Nation: USA.
The Agena command and communication (C and C) system comprised the electronic systems for tracking the vehicle, for monitoring the performance of its various subsystems, and for verifying operating commands for orbital operations. Because of the unique requirements of the Gemini mission, in particular rendezvous and docking, Lockheed had had to design and develop a new C and C system for the Gemini target vehicle. Numerous failures and problems calling for rework during the initial manufacturing stages of the C and C system suggested the existence of mechanical and electronic design deficiencies. Aerospace, which had assumed technical surveillance functions for the Gemini Agena in the fall of 1964, was instrumental in bringing these problems to the attention of Air Force and Lockheed top management. Among the results of the 10-point plan were several redesigned programmer circuits and packaging changes, closer monitoring of vendor work, expedited failure analysis, and improved quality control.
1965 February 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 was removed from the test stand at Santa Cruz Test Base and returned to Sunnyvale. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 was removed from the test stand at Santa Cruz Test Base and returned to Sunnyvale. After a brief stopover in systems test complex C-10, the vehicle was transferred to the anechoic chamber for elecromagnetic interference and radio-frequency-interference tests. Additional Details: here....
1965 February 17 - . 17:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Ranger 8 - .
Payload: RA-8. Mass: 366 kg (806 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 6-7-8-9.
Decay Date: 1965-02-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 1086 . COSPAR: 1965-010A.
Returned 7137 photos before lunar impact. The Atlas- Agena B booster injected the Agena and Ranger 8 into an Earth parking orbit at 185 km altitude 7 minutes after launch. Fourteen minutes later a 90 second burn of the Agena put the spacecraft into lunar transfer trajectory, and several minutes later the Ranger and Agena separated. The Ranger solar panels were deployed, attitude control activated, and spacecraft transmissions switched from the omni-directional antenna to the high-gain antenna by 21:30 GMT. On 18 February at a distance of 160,000 km from Earth the planned mid-course manoeuvre took place, involving reorientation and a 59 second rocket burn. During the 27 minute manoeuvre, spacecraft transmitter power dropped severely, so that lock was lost on all telemetry channels. This continued intermittently until the rocket burn, at which time power returned to normal. The telemetry dropout had no serious effects on the mission. A planned terminal sequence to point the cameras more in the direction of flight just before reaching the Moon was cancelled to allow the cameras to cover a greater area of the Moon's surface.
Ranger 8 reached the Moon on 20 February 1965. The first image was taken at 9:34:32 GMT at an altitude of 2510 km. Transmission of 7,137 photographs of good quality occurred over the final 23 minutes of flight. The final image taken before impact has a resolution of 1.5 meters. The spacecraft encountered the lunar surface in a direct hyperbolic trajectory, with incoming asymptotic direction at an angle of -13.6 degrees from the lunar equator. The orbit plane was inclined 16.5 degrees to the lunar equator. After 64.9 hours of flight, impact occurred at 09:57:36.756 GMT on 20 February 1965 in Mare Tranquillitatis at approximately 2.67 degrees N, 24.65 degrees E. Impact velocity was slightly less than 2.68 km/s.
1965 February 27 - . 11:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES LORV-4 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 March 2 - . 09:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1965 March 2 - . 13:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: U.
- Surveyor SD-1 - . Payload: Surveyor SD-1. Mass: 951 kg (2,096 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1965-03-02 . Launch vehicle test. Launch vehicle was to have put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1965 March 9 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 completed electromagnetic compatibility tests in the anechoic chamber at Sunnyvale. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 completed electromagnetic compatibility tests in the anechoic chamber at Sunnyvale. It remained in the chamber, however, until March 17 while Lockheed verified the corrective action that had been taken to eliminate programmer time-accumulator jumps and telemetry synchronization problems. The vehicle was then transferred to systems test complex C-10 for final Vehicle Systems Tests on March 18.
1965 March 12 - . 19:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-16 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 16 / OPS 4920. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-03-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 1247 . COSPAR: 1965-019A. Apogee: 358 km (222 mi). Perigee: 223 km (138 mi). Inclination: 107.50 deg. Period: 90.30 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1965 March 12 - . 23:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES MTV-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF SAC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 March 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 was transferred from the anechoic chamber to systems test complex C-10. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 was transferred from the anechoic chamber to systems test complex C-10. Six days were scheduled for vehicle modifications before beginning final systems tests. . Additional Details: here....
1965 March 21 - . 21:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena B.
- Ranger 9 - .
Payload: RA-9. Mass: 366 kg (806 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Ranger.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft Bus: Ranger.
Spacecraft: Ranger 6-7-8-9.
Decay Date: 1965-03-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 1294 . COSPAR: 1965-023A.
Ranger 9, last of the series, returned 5814 images before lunar impact. The target was Alphonsus, a large crater about 12 degrees south of the lunar equator. The probe was timed to arrive when lighting conditions would be at their best. The Atlas- Agena B booster injected the Agena and Ranger 9 into an Earth parking orbit at 185 km altitude. A 90 second Agena 2nd burn put the spacecraft into lunar transfer trajectory. This was followed by the separation of the Agena and Ranger. The initial trajectory was highly accurate; uncorrected, the craft would have landed only 650 km north of Alphonsus. 70 minutes after launch the command was given to deploy solar panels, activate attitude control, and switch from the omni-directional antenna to the high-gain antenna. The accuracy of the initial trajectory enabled delay of the planned mid-course correction from 22 March to 23 March when the manoeuvre was initiated at 12:03 GMT. After orientation, a 31 second rocket burn at 12:30 GMT, and reorientation, the manoeuvre was completed at 13:30 GMT. Ranger 9 reached the Moon on 24 March 1965. At 13:31 GMT a terminal manoeuvre was executed to orient the spacecraft so the cameras were more in line with the flight direction to improve the resolution of the pictures. Twenty minutes before impact the one-minute camera system warm-up began. The first image was taken at 13:49:41 at an altitude of 2363 km. Transmission of 5,814 good contrast photographs was made during the final 19 minutes of flight. The final image taken before impact has a resolution of 0.3 meters. The spacecraft encountered the lunar surface with an incoming asymptotic direction at an angle of -5.6 degrees from the lunar equator. The orbit plane was inclined 15.6 degrees to the lunar equator. After 64.5 hours of flight, impact occurred at 14:08:19.994 GMT at approximately 12.83 S latitude, 357.63 E longitude in the crater Alphonsus. Impact velocity was 2.67 km/s. Millions of Americans followed the spacecraft's descent via real time television coverage provided to the three networks of many of the F-channel images (primarily camera B but also some camera A pictures) were provided for this flight.
The pictures showed the rim and floor of the crater in fine detail: in those just prior to impact, objects less than a foot in size were discernible.
A panel of scientists presented some preliminary conclusions from Ranger IX at a press conference that same afternoon. Crater rims and ridges inside the walls, they believed, were harder and smoother than the moon's dusty plains, and therefore were considered likely sites for future manned landings. Generally, the panel was dubious about landing on crater floors however. Apparently, the floors were solidified volcanic material incapable of supporting a spacecraft. Investigators believed several types of craters were seen that were of nonmeteoric origin. These findings reinforced arguments that the moon at one time had experienced volcanic activity. Later the images were shown to the press as a continuous-motion movie, leading astronaut Wally Schirra to yell 'bail out you fool!' just before the final frame.
1965 March 25 - . Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- Six Atlas squadrons deactivated. - . Nation: USA. Forbes AFB SMS 548, Warren-3 AFB SMS 549, Altus AFB SMS 577, Dyess AFB SMS 578, Walker AFB SMS 579, and Plattsburgh AFB SMS 556 all deactivated.
1965 March 25 - . LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- Atlas and Titan I ICBMs to be retired - .
These were: two Atlas E units, the 566th Strategic Missile Squadron (SMS) at Warren and the 548th SMS at Forbes AFB, Kansas; three Atlas F squadrons, the 577th SMS at Altus, the 578th SMS at Dyess, and the 579th SMS at Walker; and three Titan I squadrons, the 851st SMS at Beale, the 850th SMS at Ellsworth, and the 568th SMS at Larson AFB, Washington.
1965 March 26 - . 09:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES LORV-7 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 April 3 - . 21:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Snapshot - .
Payload: SNAP 10A / Agena D / OPS 4682. Mass: 440 kg (970 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: AEC,
USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Ion engine technology satellite. Spacecraft: Snapshot.
USAF Sat Cat: 1314 . COSPAR: 1965-027A. Apogee: 1,314 km (816 mi). Perigee: 1,270 km (780 mi). Inclination: 90.30 deg. Period: 111.40 min.
The 6595th Aerospace Test Wing launched an Atlas/Agena which boosted the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) Snapshot spacecraft into orbit carrying the SNAP-10A satellite nuclear power supply experiment. The onboard nuclear reactor was used to provide electric power for an ion engine, marking the first attempt to test a reactor-ion system in orbit. Only nuclear reactor ever orbited by the United States. The SNAP-10A reactor provided electrical power for an 8.5 mN ion engine using cesium propellant. The engine was shut off after one hour of operation when high-voltage spikes created electromagnetic interference with the satellite's attitude control system sensors. The reactor continued in operation, generating 39 kWt and more than 500 watts of electrical power for 43 days before the spacecraft telemetry failed.
- SECOR 4 - . Payload: EGRS 4. Mass: 40 kg (88 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USA ACE. Class: Earth. Type: Geodetic satellite. Spacecraft: SECOR. USAF Sat Cat: 1315 . COSPAR: 1965-027B. Apogee: 1,316 km (817 mi). Perigee: 1,267 km (787 mi). Inclination: 90.20 deg. Period: 111.40 min. Failed. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1965 April 5 - . Launch Site: Fairchild AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- The final Atlas E missile retired from the operational inventory. - . The final Atlas E missile was removed from its launcher/storage site at Fairchild AFB, Washington, and was retired from the operational inventory..
1965 April 6 - . 13:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES WAC-4 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 April 9 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Gemini/Atlas/Agena Target Vehicle responsibility. - . Spacecraft: Gemini, Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Space Systems Division and NASA signed an agreement for the Gemini/Atlas/Agena Target Vehicle (GAATV) program. NASA had overall management responsibility for the program..
1965 April 13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini - Agena Target Vehicle Responsibilities. - .
Nation: USA.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Manned Spacecraft Center delivered the 'Gemini Atlas Agena Target Vehicle Systems Management and Responsibilities Agreement' to Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) with signatures of Director Robert R. Gilruth and Gemini Program Manager Charles W. Mathews (dated April 9). Major General Ben I. Funk, SSD Commander, and Colonel John B. Hudson, SSD Deputy for Launch Vehicles, had signed for SSD on March 31 and 29 respectively. The agreement, dated March 1965, followed months of negotiation and coordination on management relationships and fundamental responsibilities for the Gemini Agena target vehicle program. It clarified and supplemented the 'Operational and Management Plan for the Gemini Program' (December 29, 1961) with respect to the target vehicle program.
1965 April 20 - . Launch Site: Lincoln AFB. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Final Atlas F missile departed for retirement and storage. - . The final Atlas F missile departed Lincoln AFB, Nebraska (551st Strategic Missile Squadron), for retirement and storage..
1965 April 28 - . 20:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-17 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 17 / OPS 4983. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-05-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 1327 . COSPAR: 1965-031A. Apogee: 259 km (160 mi). Perigee: 180 km (110 mi). Inclination: 95.60 deg. Period: 89.00 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6717 - . Payload: EHH B1. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1969-10-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 1329 . COSPAR: 1965-031B. Apogee: 547 km (339 mi). Perigee: 506 km (314 mi). Inclination: 95.20 deg. Period: 95.10 min. Radar monitoring..
1965 May 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 completed vehicle systems testing with a final simulated flight. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 completed vehicle systems testing with a final simulated flight. The vehicle was disconnected from the test complex on May 14, and data analysis was completed May 19. Meanwhile, the First Article Configuration Inspection on GATV 5001 began on May 10.
1965 May 10 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- First Article Configuration Inspection (FACI) of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 at Sunnyvale. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12,
Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
First Article Configuration Inspection (FACI) of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 at Sunnyvale. A team of representatives from NASA, Air Force Space Systems Division, Aerospace, and Lockheed began the First Article Configuration Inspection (FACI) of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 at Sunnyvale. Additional Details: here....
1965 May 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 completed final assembly - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 completed final assembly and was transferred to systems test complex C-10 at Sunnyvale to begin Vehicle Systems Tests. The transfer had been scheduled for May 5 but was delayed by parts shortages, engineering problems, and considerable work backlog. The major source of delay was correcting a gap between the forward auxiliary rack and the vehicle; machining and aligning the rack and refinishing the scraped surfaces proved time-consuming. GATV 5002 was still short several items of command equipment. Systems testing began May 21.
1965 May 22 - . 21:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- FIRE 2 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Apogee: 817 km (507 mi).
Suborbital reentry heating experiment using the FIRE subscale Apollo capsule. An Atlas D booster propelled the instrumented probe, called a "flying thermometer," into a ballistic trajectory over 805 km (500 mi) high. After 26 minutes of flight, when the spacecraft began its descent, a solid-fueled Antares rocket accelerated its fall.
The probe entered the atmosphere at a speed of 40,877 km (25,400 mph) and generated temperatures of about 11,206K (20,000 degrees F). Data on heating were transmitted to ground stations throughout the descent. Thirty-two minutes after the launch - and but six minutes after the Antares was fired - the device impacted in the Atlantic about 8,256 km (5,130 mi) southeast of the Cape.
1965 May 27 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-18 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 18 / OPS 5236. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-06-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 1386 . COSPAR: 1965-041A. Apogee: 267 km (165 mi). Perigee: 149 km (92 mi). Inclination: 95.60 deg. Period: 88.70 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1965 May 28 - . 02:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- OV1-03 - . Mass: 555 kg (1,223 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1965-05-28 .
1965 May 29 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 arrived at Cape Kennedy following its conditional acceptance by the Air Force on May 27. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 arrived at Cape Kennedy following its conditional acceptance by the Air Force on May 27. It was moved to the Missile Assembly Building (Hanger E) for testing. The target vehicle was mated with target docking adapter No. 1 on June 18, and Combined Interface Tests began June 19. Testing was completed July 8 with secondary propulsion system (SPS) functional and static leak checks, SPS installation and postinstallation checks, and thermal control surface preparation. Target vehicle 5001 was then transferred to complex 14 to be mated to target launch vehicle 5301.
1965 June 3 - . 10:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP RMV-304 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 June 8 - . 15:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES LORV-6 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 June 10 - . 12:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP RMV-303 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 June 25 - . Launch Site: Mountain Home AFB. LV Family: Titan, Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Titan I, Atlas E, Atlas F.
- The remaining seven Atlas and Titan I squadrons assigned to SAC were inactivated. - .
These included the last Atlas E squadron, the 567th Strategic Missile Squadron (SMS) at Fairchild; three Atlas F units at Schilling (550th SMS), Lincoln (551st SMS), and Plattsburgh (556th SMS); and three Titan I squadrons, and the 569th SMS at Mountain Home along with the two units at Lowry, the 724th and 725th SMSs. These actions concluded the phase out of all Atlas and Titan I ICBMs in the SAC operational inventory.
1965 June 25 - . Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- Three Atlas squadrons deactivated. - . Nation: USA. Fairchild AFB SMS 567, Schilling AFB SMS 550, and Lincoln AFB SMS 551 all deactivated.
1965 June 25 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- OPS 6749 - . Payload: EHH B2. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1968-08-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 1422 . COSPAR: 1965-050A. Apogee: 510 km (310 mi). Perigee: 496 km (308 mi). Inclination: 107.60 deg. Period: 94.70 min. Radar monitoring..
- KH 7-19 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 19 / OPS 5501. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-06-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 1424 . COSPAR: 1965-050B. Apogee: 349 km (216 mi). Perigee: 254 km (157 mi). Inclination: 107.60 deg. Period: 90.50 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1965 June 30 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 completed Vehicle Systems Tests at Sunnyvale, and the final acceptance test was conducted. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 completed Vehicle Systems Tests at Sunnyvale, and the final acceptance test was conducted. The vehicle was disconnected from the test complex on July 13, after NASA, Air Force Space Systems Division, Aerospace, and Lockheed representatives agreed that all data discrepancies from the final systems tests had been resolved.
1965 July 1 - . 09:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-32 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 July 12 - . 19:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: U.
- KH-7-20 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 20. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-07-12 . KH-7 type satellite..
- SRV - . Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7.
1965 July 20 - . 08:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Vela 5 - . Payload: Vela 3A / OPS 6577. Mass: 235 kg (518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela. USAF Sat Cat: 1458 . COSPAR: 1965-058A. Apogee: 115,839 km (71,978 mi). Perigee: 106,367 km (66,093 mi). Inclination: 35.20 deg. Period: 6,679.00 min. Air Force Atlas/Agena D lifted the third pair of Vela nuclear detection satellites into their 70,000-mile, nearly circular orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- Vela 6 - . Payload: Vela 3B / OPS 6564. Mass: 235 kg (518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela. USAF Sat Cat: 1459 . COSPAR: 1965-058B. Apogee: 121,281 km (75,360 mi). Perigee: 101,715 km (63,202 mi). Inclination: 34.20 deg. Period: 6,712.70 min. An Air Force Atlas/Agena D lifted the third pair of Vela nuclear detection satellites into their 70,000-mile, nearly circular orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- ORS 3 - . Payload: ERS 17. Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: ERS. Decay Date: 1968-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 1460 . COSPAR: 1965-058C. Apogee: 111,793 km (69,464 mi). Perigee: 566 km (351 mi). Inclination: 36.90 deg. Period: 2,595.40 min. Radiation data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1965 July 23 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5003. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Standard Agena D (AD-108), which had been completed in June and held in storage, was transferred to Building 104 at Sunnyvale for modifications and final assembly as Gemini Agena target vehicle 5003. While in storage, several pieces of AD-108 equipment had been removed for modification to the Gemini configuration. Final assembly began August 8.
1965 July 23 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 completed. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Air Force Space Systems Division formally accepted delivery of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 after the vehicle acceptance team inspection had been completed. The vehicle was then shipped by air to Eastern Test Range on July 24, arriving July 25. Although GATV 5002 was accepted, several items of equipment remained in 'not qualified' status, including the shroud, secondary and primary propulsion systems, and components of both the electrical power and command systems.
1965 August 3 - . 19:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-21 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 21 / OPS 5698. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-08-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 1471 . COSPAR: 1965-062A. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 278 km (172 mi). Inclination: 107.40 deg. Period: 90.80 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6761 - . Payload: EHH B3. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1968-06-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 1472 . COSPAR: 1965-062B. Apogee: 515 km (320 mi). Perigee: 501 km (311 mi). Inclination: 107.40 deg. Period: 94.80 min. Radar monitoring..
1965 August 4 - . 12:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES WAC-5 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 August 5 - . 13:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES LORV-2A re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The first Atlas F (147F) Advanced Ballistic Reentry Systems (ABRES) program launch was conducted at Vandenberg. The four previous Atlas F/ABRES launches were from Cape Canaveral, and the rest would be conducted on the Western Test Range. .
1965 August 11 - . 14:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur D.
- Surveyor; Atlas Centaur 6 - . Payload: Surveyor-SD-2. Mass: 950 kg (2,090 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. USAF Sat Cat: 1503 . COSPAR: 1965-064A. Centaur AC-6 launched dummy Surveyor payload into a barycentric / translunar orbit..
1965 August 23 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 completed preliminary systems testing at Hanger E. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 completed preliminary systems testing at Hanger E and was transferred to Merritt Island Launch Area, where it was joined by spacecraft No. 6 for Plan X testing. After ground equipment checks, Plan X tests proceeded on August 25. No significant interference problems were found, and testing ended on August 31.
1965 August 26 - . 11:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-41 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 September 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Final troubleshooting on Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 after Plan X testing at Merritt Island Launch Area (MILA) was completed. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Final troubleshooting on Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 after Plan X testing at Merritt Island Launch Area (MILA) was completed. The next day GATV 5002 was returned to Hanger E from MILA, where it began a series of tests to verify the operational readiness of all vehicle systems prior to erection and mating with the launch vehicle.
1965 September 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Completion of Agena qualification tests. - .
Nation: USA.
Representatives of Air Force Space Systems Division, Aerospace, and Lockheed attended a technical review of the flight verification test program for the oxidizer gas generator solenoid valve. This was the last remaining component of the Agena primary propulsion system needing test qualification. Testing had been completed August 26; disassembly, inspection, and evaluation were concluded September 3. The consensus of those attending was that the successful test program had demonstrated flightworthiness of this configuration. This concluded qualification of all propulsion system components.
1965 September 29 - . 10:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-45 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 September 30 - . 19:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-22 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 22 / OPS 7208. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-10-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 1609 . COSPAR: 1965-076A. Apogee: 361 km (224 mi). Perigee: 237 km (147 mi). Inclination: 95.60 deg. Period: 90.50 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1965 October 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 was transported to complex 14 and mated to target launch vehicle 5301. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 was transported to complex 14 and mated to target launch vehicle 5301. Preliminary checks were followed, on October 4, by the Joint Flight Acceptance Composite Test (J-FACT). J-FACT was a combined check of all contractors, the range, the vehicles, and aerospace ground equipment in a simulated countdown and flight; propellants and high pressure gases were not loaded, nor was the gantry removed. Simultaneous Launch Demonstration was successfully completed October 7.
1965 October 5 - . 09:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- OV1-02 - . Payload: OV1 Dummy. Mass: 86 kg (189 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 1613 . COSPAR: 1965-078A. Apogee: 2,735 km (1,699 mi). Perigee: 408 km (253 mi). Inclination: 144.20 deg. Period: 117.60 min. Radiation data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- NB20.170 - . Payload: SPP 29. Mass: 555 kg (1,223 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: OV1. COSPAR: 1965-078xx. Apogee: 2,418 km (1,502 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 144.20 deg. Period: 114.00 min.
- OV1-02S - . Mass: 555 kg (1,223 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. COSPAR: 1965-078xx. Apogee: 2,418 km (1,502 mi). Perigee: 401 km (249 mi). Inclination: 144.20 deg. Period: 114.00 min.
1965 October 14 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5003 was transferred to Vehicle Systems Test after completing final assembly on October 9. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 8. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Gemini Agena target vehicle 5003 was transferred to Vehicle Systems Test after completing final assembly on October 9. Testing began October 18..
1965 October 25 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D. FAILURE: Exploded 6 minutes after takeoff. Failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Gemini 6 Agena Target - . Payload: TDA-2. Mass: 3,261 kg (7,189 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 6, Gemini 7. Spacecraft Bus: Agena. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Decay Date: 1965-10-25 . The Agena target vehicle failed to reach orbit. Gemini 6, awaiting launch, was cancelled. In the ashes of this setback, the idea of launching Gemini 6 to rendezvous with Gemini 7 was born..
1965 October 27 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Catastrophic anomaly of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 on October 25 defined as a mission failure. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Catastrophic anomaly of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 on October 25 defined as a mission failure. NASA Associate Administrator Robert C. Seamans, Jr., informed George E. Mueller, Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight, that the catastrophic anomaly of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 on October 25 had been defined as a mission failure. Additional Details: here....
1965 October 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Discrepancies remaining on Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 cleared. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
The major portion of 819 discrepancies remaining from the First Article Configuration Inspection (FACI) of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 in June were cleared; 128 that had not been applied against the acceptance document (DD-250) remained. All subsystem FACI discrepancies were also closed out during October.
1965 November 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- The subpanel for Gemini VI of the Agena Flight Safety Review Board met at Lockheed. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 6. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. The subpanel, chaired by Colonel John B. Hudson, Deputy Commander for Launch Vehicles, Air Force Space Systems Division, reviewed Lockheed's flight safety analysis of the failure of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 on October 25. . Additional Details: here....
1965 November 3 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Investigation of the failure of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
The Agena Flight Safety Review Board met at Lockheed to continue its investigation of the failure of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5002 on October 25. The board, chaired by George E. Mueller, NASA Associate Administrator of Manned Space Flight, reviewed the findings of the subpanel for Gemini VI and reached the same conclusion: the failure resulted from a hard start probably caused by the fuel lead. Additional Details: here....
1965 November 8 - . 19:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-23 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 23 / OPS 8293. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1965-11-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 1727 . COSPAR: 1965-090A. Apogee: 352 km (218 mi). Perigee: 280 km (170 mi). Inclination: 93.90 deg. Period: 90.80 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6232/Agena D - . Payload: Agena Pickaback / OPS 6232. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1965-11-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 1728 . COSPAR: 1965-090B. Apogee: 284 km (176 mi). Perigee: 155 km (96 mi). Inclination: 93.90 deg. Period: 88.90 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
1965 November 12-13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- A symposium on hypergolic rocket ignition at altitude was held at Lockheed. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 6.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Because too little diagnostic information had been obtained from the flight of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5002 to determine the exact nature of the probable hard start, it was not certain that the proposed modification - a return to oxidizer lead - would definitely prevent a recurrence of the malfunctions. Additional Details: here....
1965 November 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) engine modification and test program. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Hohmann, Bernhard.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Lockheed presented its proposed Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) engine modification and test program to Colonel A. J. Gardner, Gemini Target Vehicle Program Director, Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD). The proposal was immediately turned over to a three-man team comprising B. A. Hohmann (Aerospace), Colonel J. B. Hudson (Deputy Commander for Launch Vehicles, SSD), and L. E. Root (Lockheed) for consideration. On November 18, the group decided on a final version of the proposal that called for: (1) modifying the Agena engine to provide oxidizer lead during the start sequence, (2) demonstrating sea-level engine flightworthiness in tests at Bell Aerosystems, and (3) conducting an altitude test program at Arnold Engineering Development Center. The final proposal was presented to the GATV Review Board at Manned Spacecraft Center on November 20.
1965 November 19 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) directed Lockheed to return Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 to Sunnyvale. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) directed Lockheed to return Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 to Sunnyvale. The GATV was still being stored in Hanger E, Eastern Test Range, minus its main engine which SSD had directed Lockheed to ship to Bell Aerosystems on November 9 for modification. Additional Details: here....
1965 November 24 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lockheed submitted an engineering change proposal to Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) for Project Surefire. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8,
Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Lockheed submitted an engineering change proposal to Air Force Space Systems Division (SSD) for Project Surefire. Surefire was the code name for the Gemini Agena Target Vehicle (GATV) Modification and Test Program designed to correct the malfunction which had caused the failure of GATV 5002 on October 25. Additional Details: here....
1965 November 26 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- McDonnell proposed building a backup target vehicle for Gemini rendezvous missions. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini,
Gemini Radar,
Atlas Target Docking Adapter.
The augmented target docking adapter (ATDA) would serve as an alternative to the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) if efforts to remedy the GATV problem responsible for the October 25 mission abort did not meet the date scheduled for launching Gemini VIII. Additional Details: here....
1965 November 29 - . 14:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-33 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1965 December 2 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A, Atlas SLV-3C.
- Atlas SLV-3A and SLV-3 approved - . NASA approved the development of new standard launch vehicles, the Atlas/Agena (SLV-3A) and the Atlas/Centaur (SLV-3C). Both Atlas boosters were to be of improved design to provide higher performance .
1965 December 14 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Disassembly and inspection of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 to determine the extent of refurbishment. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Air Force Space Systems Division authorized Lockheed to begin the disassembly and inspection of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 to determine the extent of refurbishment needed. The vehicle was stripped down to its major structural components to expose all areas of possible contamination.
1965 December 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 main engine - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
The Air Force accepted the main rocket engine for Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 after Bell Aerosystems had completed Project Surefire modifications. The engine was shipped immediately and arrived at Lockheed December 18. Lockheed completed reinstalling the engine on December 20. GATV 5003 systems retesting began December 27 after other equipment modifications had been installed.
1965 December 20 - . 13:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-31 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 January 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 completed its final acceptance tests. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 completed its final acceptance tests at Sunnyvale, after an elusive command system problem had made it necessary to rerun the final systems test (January 4). No vehicle discrepancy marred the rerun. Air Force Space Systems Division formally accepted GATV 5003 on January 18, after the vehicle acceptance team inspection. It was shipped to Eastern Test Range the same day, but bad weather delayed delivery until January 21. GATV 5003 was to be the target vehicle for Gemini VIII.
1966 January 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Project Surefire verification testing began at Bell Aerosystems. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Bell's part in the test program was to demonstrate the sea-level flightworthiness of the modified Agena main engine. Bell completed testing on March 4 with a full 180-second mission simulation firing. The successful completion of this phase of the test program gave the green light for the launch of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5003, scheduled for March 15.
1966 January 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Program Office review of possible future mission activities. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 8,
Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
At a NASA-McDonnell Management Panel meeting, W. B. Evans of Gemini Program Office reviewed possible future mission activities. Gemini VIII would have three periods of extravehicular activity (EVA) - two in daylight, one in darkness - and would undock during EVA with the right hatch snubbed against the umbilical guide and the astronaut strapped into the adapter section. Additional Details: here....
1966 January 19 - . 20:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-24 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 24 / OPS 7253. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-01-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 1939 . COSPAR: 1966-002A. Apogee: 259 km (160 mi). Perigee: 138 km (85 mi). Inclination: 93.80 deg. Period: 88.40 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 3179/Agena D - . Payload: Agena Pickaback / OPS 3179. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1966-01-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 1940 . COSPAR: 1966-002B. Apogee: 149 km (92 mi). Perigee: 120 km (70 mi). Inclination: 93.80 deg. Period: 87.20 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
1966 January 22 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 was mated to target docking adapter (TDA) 3. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
McDonnell had delivered TDA-3 to Cape Kennedy on January 8. The GATV/TDA interface functional test was completed January 24, and the vehicle was transferred to Merritt Island Launch Area for integrated tests with spacecraft No. 8 and extravehicular equipment, which were completed January 28.
1966 January 26 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5004 was transferred to the vehicle systems test area at Sunnyvale. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5004 was transferred to the vehicle systems test area at Sunnyvale. Its modified main engine had been received on schedule from Bell Aerosystems January 12 and installed by January 20. Because of GATV 5003 priority, however, several main electronic assemblies, including the command system, had been removed from GATV 5004 and used in GATV 5003 final acceptance tests. As a result, GATV 5004 had fallen eight days behind its scheduled transfer date, January 18.
1966 January 28 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 was returned to Hanger E after completing Plan X tests at Merritt Island Launch Area. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 was returned to Hanger E after completing Plan X tests at Merritt Island Launch Area. Systems Verification and Combined Interface Tests were conducted through February 18, followed by functional checks of the primary and secondary propulsion systems. Hanger E testing ended February 28, and the GATV was transferred to complex 14.
1966 February 2 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Mission planning for Gemini flights IX through XII. - .
Nation: USA.
A mission planning meeting for Gemini flights IX through XII, held at McDonnell, was attended by members of the Gemini Program Office and Flight Operations Division. The last item on the agenda was a reminder from McDonnell that the Gemini spacecraft was capable of flying to a relatively high elliptic orbit from which it could safely reenter under certain circumstances. The type of orbit McDonnell suggested had an apogee of 500-700 nautical miles. This would involve using the Agena primary propulsion system both to get into this orbit and to return to a 161-mile circular orbit for nominal reentry.
1966 February 2 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Agena D (AD-129) was accepted by the Air Force for delivery to the Gemini program. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 10. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. It was transferred to the final assembly area at Sunnyvale for modification to Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005..
1966 February 4 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- The augmented target docking adapter (ATDA) arrived at Cape Kennedy. Modifications, testing, and troubleshooting were completed March 4. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Atlas Target Docking Adapter,
Gemini.
The augmented target docking adapter (ATDA) arrived at Cape Kennedy. Modifications, testing, and troubleshooting were completed March 4. The ATDA, which was intended to back up the Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV), was then placed in storage (March 8) where it remained until May 17, when the failure of target launch vehicle 5303 prevented GATV 5004 from achieving orbit. The ATDA became the target for Gemini IX-A.
1966 February 10 - . 09:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-38 / Pod 32 Reentry test / plume mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 February 11 - . 13:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-51 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 February 15 - . 20:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-25 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 25 / OPS 1184. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 2012 . COSPAR: 1966-012A. Apogee: 290 km (180 mi). Perigee: 142 km (88 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Bluebell 2C (Cylinder) - . Payload: OPS 3011. Mass: 9.00 kg (19.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: Bluebell. Decay Date: 1966-02-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 2014 . COSPAR: 1966-012B. Apogee: 253 km (157 mi). Perigee: 115 km (71 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 88.10 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Bluebell 2S (Sphere) - . Payload: OPS 3031. Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: Bluebell. Decay Date: 1966-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 2015 . COSPAR: 1966-012C. Apogee: 268 km (166 mi). Perigee: 147 km (91 mi). Inclination: 96.50 deg. Period: 88.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 February 19 - . 09:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1966 February 27 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5004 completed systems testing at Sunnyvale. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 9. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. It was formally accepted by the Air Force on March 11, following the vehicle acceptance team inspection. The next day (March 12), GATV 5004 was shipped by air to Eastern Test Range, arriving March 14..
1966 March 4 - . 12:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- NTMP KX-35 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 500 km (310 mi).
1966 March 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5003 systems exercised. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Following the early termination of Gemini VIII, Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 remained in orbit, where its various systems were extensively exercised. The main engine was fired nine times, four more than required by contract, and 5000 commands were received and executed by the command and communications system, as against a contractural requirement of 1000. Additional Details: here....
1966 March 16 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini 8 Agena Target - . Payload: TDA 3/Agena D 5003 GATV. Mass: 3,175 kg (6,999 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 8. Spacecraft Bus: Agena. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Decay Date: 1967-09-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 2104 . COSPAR: 1966-019A. Apogee: 299 km (185 mi). Perigee: 285 km (177 mi). Inclination: 28.90 deg. Period: 90.40 min. Target vehicle for Gemini 8..
1966 March 18 - . 20:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-26 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 26 / OPS 0879. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-03-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 2109 . COSPAR: 1966-022A. Apogee: 308 km (191 mi). Perigee: 162 km (100 mi). Inclination: 101.00 deg. Period: 89.30 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
- OPS 0974/Agena D - . Payload: NRL PL137 / OPS 0974. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1966-03-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 2112 . COSPAR: 1966-022B. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 149 km (92 mi). Inclination: 101.00 deg. Period: 88.80 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 March 19 - . 12:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-43 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 March 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5004 and spacecraft No. 9 began Plan X compatibility tests at Merritt Island Launch Area Radar Range. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 9. Spacecraft: Gemini, Gemini Radar, Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Gemini Agena target vehicle 5004 and spacecraft No. 9 began Plan X compatibility tests at Merritt Island Launch Area Radar Range. .
1966 March 22 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Agena D (AD-130) accepted by the Air Force. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 11. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Agena D (AD-130) was formally accepted by the Air Force for the Gemini program and moved to Building 104 at Sunnyvale for modification and final assembly as Gemini Agena target vehicle 5006. .
1966 March 24 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Project Surefire test program not to be curtailed. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 8. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Air Force Space Systems Division and Lockheed agreed not to curtail the Project Surefire test program despite the excellent performance of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5003 during the Gemini VIII mission. . Additional Details: here....
1966 March 30 - . 09:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- OV1-04 - . Mass: 88 kg (194 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 2121 . COSPAR: 1966-025A. Apogee: 1,008 km (626 mi). Perigee: 884 km (549 mi). Inclination: 144.50 deg. Period: 104.00 min. Thermal control experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-04S - . Mass: 555 kg (1,223 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. COSPAR: 1966-025xx. Apogee: 1,002 km (622 mi). Perigee: 879 km (546 mi). Inclination: 144.50 deg. Period: 103.80 min.
- OV1-05S - . Payload: BORE. Mass: 114 kg (251 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 2122 . COSPAR: 1966-025B. Apogee: 1,056 km (656 mi). Perigee: 985 km (612 mi). Inclination: 144.60 deg. Period: 105.60 min. Optical radiation test. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 April - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Final active Atlas squadron deactivated. - . Nation: USA. VAFB SMS 576 deactivated.
1966 April 8 - . 01:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur D. FAILURE: Centaur propellant leak.. Failed Stage: U.
- Surveyor Model - . Payload: Surveyor SD-3. Mass: 784 kg (1,728 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1966-05-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 2139 . COSPAR: 1966-030A. Apogee: 336 km (208 mi). Perigee: 182 km (113 mi). Inclination: 30.70 deg. Period: 89.70 min. Launch vehicle test. Payload was dummy Surveyor spacecraft..
1966 April 8 - . 19:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- OAO 1 - . Payload: OAO A1. Mass: 1,774 kg (3,911 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: OAO. USAF Sat Cat: 2142 . COSPAR: 1966-031A. Apogee: 793 km (492 mi). Perigee: 783 km (486 mi). Inclination: 35.00 deg. Period: 100.60 min. Orbiting Astronomical Observatory. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
1966 April 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5004 began tests. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5004 began the Combined Interface Test (CIT) at Hanger E, Eastern Test Range, after completing Plan X tests March 24. CIT ended April 22 and engine functional tests of both the primary and secondary propulsion systems followed. Hanger E testing was completed May 1.
1966 April 15 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Space probes could be launched from AAP stations in space. - .
Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Mueller,
Seamans.
Spacecraft Bus: Skylab.
Spacecraft: Orbital Workshop,
Skylab.
Evaluation of a Lockheed proposal to launch space probes from orbit using Agena rockets launched from AAP stations in space. Associate Administrator for Manned Space Fight George E. Mueller informed Deputy Administrator Robert C. Seamans, Jr., of the Saturn/Apollo Applications Program Office's evaluation of a Lockheed proposal to launch space probes from orbit using Agena rockets launched from AAP stations in space. The proposal was feasible, Mueller advised, but did not seem a desirable mission for inclusion in the AAP. Additional Details: here....
1966 April 19 - . 19:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-27 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 27 / OPS 0910. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-04-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 2146 . COSPAR: 1966-032A. Apogee: 375 km (233 mi). Perigee: 139 km (86 mi). Inclination: 116.90 deg. Period: 89.60 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 May 3 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lockheed completed Combined Systems Acceptance Test on Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 in test complex C-10 at Sunnyvale. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 10. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Lockheed completed Combined Systems Acceptance Test on Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 in test complex C-10 at Sunnyvale. The vehicle was formally accepted by the Air Force on May 14 and delivered to Eastern Test Range on May 16..
1966 May 3 - . 10:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- NTMP KX-37 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 500 km (310 mi).
1966 May 8 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Refurbishing of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Lockheed established a task force to handle the refurbishing of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 and announced a GATV 5001 Reassembly Plan. The task force's function was to see that GATV 5001 reached a flightworthy condition on time and as economically as possible. The reassembly plan provided an operational base line as well as guidelines for reassembling the vehicle, which was completely disassembled down to the level of riveted or welded parts. GATV 5001 was scheduled for acceptance on September 20 and would be the target vehicle for Gemini XII.
1966 May 13 - . 11:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES WAC-5A re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 May 14 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-28 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 28 / OPS 1950. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-05-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 2171 . COSPAR: 1966-039A. Apogee: 319 km (198 mi). Perigee: 130 km (80 mi). Inclination: 110.50 deg. Period: 89.00 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6785 - . Payload: EHH B4. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1970-10-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 2172 . COSPAR: 1966-039B. Apogee: 555 km (344 mi). Perigee: 519 km (322 mi). Inclination: 110.00 deg. Period: 95.40 min. Radar monitoring..
1966 May 17 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Launch of Gemini IX was postponed when Agena target vehicle failed to achieve orbit. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
The scheduled launch of Gemini IX was postponed when target launch vehicle 5303 malfunctioned and, as a result, Gemini Agena target vehicle 5004 failed to achieve orbit. Launch and flight were normal until about 120 seconds after liftoff, 10 seconds before booster engine cutoff. Additional Details: here....
1966 May 17 - . 15:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D. FAILURE: Control system failure.. Failed Stage: G.
- Gemini 9 Agena Target - .
Payload: TDA 5. Mass: 3,248 kg (7,160 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft Bus: Agena.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle,
Atlas Target Docking Adapter.
Decay Date: 1966-05-17 .
The Gemini 9 mission was scrubbed when the Atlas booster launched from Cape Canaveral failed to place the Gemini Agena Target Vehicle (GATV) in its planned circular orbit. A malfunction of the number 2 booster engine of the Atlas caused both the Atlas and Agena to fall into the ocean. The Gemini 9-Atlas/Agena mission was later rescheduled to 1 June using the Augmented Target Docking Adapter (ATDA).
1966 May 25 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 was mated to the target docking adapter (TDA) in Hanger E at Cape Kennedy. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 was mated to the target docking adapter (TDA) in Hanger E at Cape Kennedy. McDonnell had delivered the TDA on May 4. After mating, interface functional tests were performed, May 25-27. Preparations then began for Plan X testing with spacecraft No. 10 at Merritt Island Launch Area.
1966 May 26 - . 12:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
1966 May 30 - . 14:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur D.
- Surveyor 1 - .
Payload: Surveyor SC-1. Mass: 269 kg (593 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor.
Decay Date: 1966-06-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 2185 . COSPAR: 1966-045A.
The first operational Atlas/Centaur (AC-10) carried the NASA Surveyor I spacecraft to the moon in a direct ascent lunar transfer trajectory. This was the first in a series of seven Surveyors designed to develop soft-landing technology and to provide basic scientific and engineering data in support of Project Apollo. On 2 June, Surveyor I became the first U.S. spacecraft to soft-land on the moon and transmit television pictures Surveyor 1 soft landed on the moon in the Ocean of Storms and began transmitting the first of more than 11,150 clear, detailed television pictures to Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Deep Space Facility, Goldstone, Calif. The landing sequence began 3,200 kilometers above the moon with the spacecraft traveling at a speed of 9,700 kilometers per hour. The spacecraft was successfully slowed to 5.6 kilometers per hour by the time it reached 4-meter altitude and then free-fell to the surface at 13 kilometers per hour. The landing was so precise that the three footpads touched the surface within 19 milliseconds of each other, and it confirmed that the lunar surface could support the LM. It was the first U.S. attempt to soft land on the moon.
1966 June 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 completed preliminary testing. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 completed preliminary testing at Hanger E, Eastern Test Range, and was moved to Merritt Island Launch Area for Plan X tests with spacecraft No. 10. Plan X tests had first been scheduled for May 23 but were rescheduled for June 2-3. Additional Details: here....
1966 June 1 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3.
- Gemini 9 ATDA - .
Payload: TDA 4. Mass: 794 kg (1,750 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 9.
Spacecraft: Atlas Target Docking Adapter,
Gemini.
Decay Date: 1966-06-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 2186 . COSPAR: 1966-046A. Apogee: 296 km (183 mi). Perigee: 292 km (181 mi). Inclination: 28.80 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
The first and only Atlas/Augmented Target Docking Adapter (ATDA) Gemini Agena (#5304) was launched from the Eastern Test Range as part of the Gemini 9 mission. The ATDA was a back-up for the Gemini Agena Target Vehicle (GATV) and similar to it except that it lacked the capability to maneuver in space. The ATDA achieved a near-circular orbit (apogee 161.5, perigee 158.5 nautical miles). One hour and 40 minutes later, the scheduled launch of Gemini IX-A was postponed by a ground equipment failure which prevented the transfer of updating information from Cape Kennedy mission control center to the spacecraft computer. The mission was recycled for launch on June 3, following a prepared 48-hour recycle plan. Anomalous telemetry indicated some sort of problem with the target, but it was not until Gemini IX rendezvoused with it in orbit that it was seen that fairing separation had failed.
1966 June 3 - . 19:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-29 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 29 / OPS 1577. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-06-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 2192 . COSPAR: 1966-048A. Apogee: 288 km (178 mi). Perigee: 143 km (88 mi). Inclination: 87.00 deg. Period: 88.90 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 1856/Agena D - . Payload: [AAS 6] / OPS 1856. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1966-06-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 2194 . COSPAR: 1966-048B. Apogee: 230 km (140 mi). Perigee: 148 km (91 mi). Inclination: 86.90 deg. Period: 88.20 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
1966 June 6 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5006 completed modification and final assembly and was transferred to Vehicle Systems Test (VST) at Sunnyvale. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5006 completed modification and final assembly and was transferred to Vehicle Systems Test (VST) at Sunnyvale. Although the vehicle lacked the flight control electronics package and guidance module, testing began immediately. The guidance module was received June 7 and the flight control electronics package June 9. Preliminary VST was completed June 17. The Air Force Plant Representative Office at Sunnyvale authorized final acceptance test to begin on June 20.
1966 June 7 - . 02:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena B.
- OGO 3 - .
Payload: OGO B. Mass: 634 kg (1,397 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OGO.
Decay Date: 1981-09-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 2195 . COSPAR: 1966-049A. Apogee: 102,806 km (63,880 mi). Perigee: 19,519 km (12,128 mi). Inclination: 77.60 deg. Period: 2,911.50 min.
Orbiting Geophysical Observatory 3. All 21 experiments returned good data. At the time, this was the largest experimental complement ever put into orbit. There were 4 cosmic ray instruments (1 of which included a gamma-ray spectrometer), 4 plasma, 2 trapped radiation, 2 magnetic fields, 5 ionosphere, 3 radio/optical, and 1 micrometeoroid detectors. OGO 3 maintained 3-axis stabilization for 46 days. At that point, an attitude controller failed and the spacecraft was put into a spin on 23 July 1966. The spin period varied from 90-125 seconds. By June 1969, data acquisition was limited to 50% of the orbital path. Routine spacecraft operation was discontinued on December 1, 1969, after which only data from Heppner's experiment (Rubidium + Fluxgate magnetometer) was acquired. By March 1971 spacecraft perigee had increased to 16,400 km and the inclination had increased to 75.8 deg. All spacecraft support terminated on February 29, 1972.
1966 June 9 - . 20:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Midas 10 - . Payload: Midas RTS 1 / Agena TV 1351 / Agena D 1351 / OPS 1. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. Decay Date: 1966-12-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 2200 . COSPAR: 1966-051A. Apogee: 3,678 km (2,285 mi). Perigee: 154 km (95 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 125.20 min. The first Atlas SLV-3/Agena D (7200 Series, Vehicle #7201) standard booster was successfully launched from Vandenberg. Missile Defense Alarm System. Left in transfer orbit..
- SECOR 6 - . Payload: EGRS 6. Mass: 17 kg (37 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USA ACE. Class: Earth. Type: Geodetic satellite. Spacecraft: SECOR. Decay Date: 1967-07-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 2205 . COSPAR: 1966-051B. Apogee: 3,646 km (2,265 mi). Perigee: 168 km (104 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 125.00 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- ORS 2 - . Payload: ERS 16. Mass: 15 kg (33 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: ERS. Decay Date: 1967-03-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 2202 . COSPAR: 1966-051C. Apogee: 3,641 km (2,262 mi). Perigee: 178 km (110 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 125.10 min. The first Atlas SLV-3/Agena D (7200 Series, Vehicle #7201) standard booster was successfully launched from Vandenberg. Metal-to-metal bonding experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 June 10 - . 11:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-42 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 June 13 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Combined Interface Tests(CIT) of Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5005 began. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 10. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. CIT was completed June 22, with no significant anomalies detected. Primary and secondary propulsion system functional checks were completed June 30. The GATV was then moved to complex 14..
1966 June 19 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini X prime crew to be Young and Collins. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 8.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
NASA announced that the Gemini X mission had been scheduled for no earlier than July 18, with John W. Young, command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot, as the prime crew. Alan L. Bean, command pilot, and Clifton C. Williams, pilot, would be the backup crew. Mission plans would include rendezvous, docking, and extravehicular activity. The spacecraft was scheduled to rendezvous and dock with an Agena target vehicle which was to be launched the same day. If possible, Gemini X would also rendezvous with the Agena launched in the March 16 Gemini VIII mission.
1966 June 26 - . 15:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-20 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 June 27 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Final acceptance test of Gemini Agena target vehicle 5006 was completed at Sunnyvale. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini.
The vehicle was disconnected from the test complex July 6 and formally accepted by the Air Force on July 13, two days ahead of schedule. Shipment of the vehicle to Eastern Test Range (ETR), planned for July 13, was delayed until July 14 by wind conditions. It arrived at ETR in the early morning of July 15.
1966 June 30 - . 10:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- NTMP KX-39 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1966 July 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 was transferred to complex 14 and mated to target launch vehicle 5305. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle 5005 was transferred to complex 14 and mated to target launch vehicle 5305. Joint Flight Acceptance Composite Test was completed July 8. Complex 14 systems tests were completed July 12 with the Simultaneous Launch Demonstration.
1966 July 12 - . 17:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-30 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 30 / OPS 1850. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-07-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 2322 . COSPAR: 1966-062A. Apogee: 261 km (162 mi). Perigee: 150 km (90 mi). Inclination: 95.50 deg. Period: 88.70 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 July 14 - . 02:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Partial Failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- OV1-07 - . Payload: PasComSat. Mass: 10 kg (22 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1978-01-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 2324 . COSPAR: 1966-063A. Apogee: 1,022 km (635 mi). Perigee: 985 km (612 mi). Inclination: 144.20 deg. Period: 105.20 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-08 PasComSat - . Mass: 555 kg (1,223 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1978-01-04 . USAF Sat Cat: 2324 . COSPAR: 1966-063xx. Apogee: 410 km (250 mi). Perigee: 393 km (244 mi). Inclination: 144.20 deg. Period: 92.60 min.
1966 July 18 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5006 was mated to target docking adapter (TDA) 6. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 10, Gemini 11, Gemini 8. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. McDonnell had delivered TDA-6 to Cape Kennedy July 7. The interface functional test was completed July 21. The next day GATV 5006 was moved to the Merritt Island Launch Area for integrated tests with spacecraft No. 11 and extravehicular equipment..
1966 July 18 - . 20:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini 10 Agena Target - .
Payload: TDA 1A/Agena D 5005 GATV. Mass: 3,175 kg (6,999 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 10.
Spacecraft Bus: Agena.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Decay Date: 1966-12-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 2348 . COSPAR: 1966-065A. Apogee: 296 km (183 mi). Perigee: 290 km (180 mi). Inclination: 28.90 deg. Period: 90.40 min.
An Air Force Titan Gemini Launch Vehicle placed the Gemini 10 (GT-10) spacecraft into orbit for the three-day mission of Astronauts John Young and Michael Collins. Rendezvous and docking were accomplished with the Gemini Agena Target Vehicle (GATV) that had been launched from Cape Kennedy aboard an Atlas Booster just ahead of GT-10. Using the GATV-10 Primary Propulsion System (PPS), the docked vehicles achieved a manned-flight altitude record of 476 miles. Reentry was accomplished on 21 July and recovery was made 544 miles east of Cape Canaveral. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1966 July 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle made three orbital maneuvers under ground control. - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 10,
Gemini 11.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Following the reentry of spacecraft No. 10, Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5005 made three orbital maneuvers under ground control. Its primary propulsion system (PPS) fired to put the vehicle in a 750.5 by 208.6 nautical mile orbit in order to determine the temperature effects of such an orbit on the vehicle. Additional Details: here....
1966 July 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 was transferred to systems test complex. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 was transferred to systems test complex C-10 at Sunnyvale, after the long process of refurbishing it had been completed; however, it was still short several pieces of equipment. .
1966 August 8 - . 17:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- ABRES MBRV-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 500 km (310 mi).
1966 August 10 - . 19:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lunar Orbiter 1 - .
Payload: Lunar Orbiter A. Mass: 386 kg (850 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Langley.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Lunar Orbiter.
Decay Date: 1966-10-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 2394 . COSPAR: 1966-073A.
Lunar Orbiter I was launched from Cape Kennedy Launch Complex 13 at 3:26 p.m. EDT August 10 to photograph possible Apollo landing sites from lunar orbit. The Atlas-Agena D launch vehicle injected the spacecraft into its planned 90-hour trajectory to the moon. A midcourse correction maneuver was made at 8 p.m. the next day; a planned second midcourse maneuver was not necessary. A faultless deboost maneuver on August 14 achieved the desired initial elliptic orbit around the moon, and one week later the spacecraft was commanded to make a transfer maneuver to place it in a final close-in elliptic orbit of the moon.
During the spacecraft's stay in the final close-in orbit, the gravitational fields of the earth and the moon were expected to influence the orbital elements. The influence was verified by spacecraft tracking data, which showed that the perilune altitude varied with time. From an initial perilune altitude of 58 kilometers, the perilune decreased to 49 kilometers. At this time an orbit adjustment maneuver began an increase in the altitude, which was expected to reach a maximum after three months and then begin to decrease again. The spacecraft was expected to impact on the lunar surface about six months after the orbit adjustment.
During the photo-acquisition phase of the flight, August 18 to 29, Lunar Orbiter I photographed the 9 selected primary potential Apollo landing sites, including the one in which Surveyor I landed; 7 other potential Apollo landing sites; the east limb of the moon; and 11 areas on the far side of the moon. Lunar Orbiter I also took photos of the earth, giving man the first view of the earth from the vicinity of the moon (this particular view has been widely publicized). A total of 207 frames (sets of medium- and high-resolution pictures) were taken, 38 while the spacecraft was in initial orbit, the remainder while it was in the final close-in orbit. Lunar Orbiter I achieved its mission objectives, and, with the exception of the high-resolution camera, the performance of the photo subsystem and other spacecraft subsystems was outstanding. At the completion of the photo readouts, the spacecraft had responded to about 5,000 discrete commands from the earth and had made about 700 maneuvers.
Photographs obtained during the mission were assessed and screened by representatives of the Lunar Orbiter Project Office, U.S. Geological Survey, DOD mapping agencies, MSC, and Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The spacecraft was deliberately crashed into moon after the mission was completed.
1966 August 16 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 completed final acceptance testing. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini. Analysis of test data was completed by August 24 and the vehicle was disconnected from the test complex..
1966 August 16 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-31 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 31 / OPS 1832. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-08-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 2396 . COSPAR: 1966-074A. Apogee: 330 km (200 mi). Perigee: 143 km (88 mi). Inclination: 93.20 deg. Period: 89.20 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6810 - . Payload: SSF-B No. 5. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1970-03-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 2397 . COSPAR: 1966-074B. Apogee: 522 km (324 mi). Perigee: 511 km (317 mi). Inclination: 93.20 deg. Period: 94.90 min. Radar monitoring..
1966 August 19 - . 19:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Midas 11 - . Payload: Midas RTS 2 / Agena TV 1352 / Agena D / OPS 0856. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. USAF Sat Cat: 2403 . COSPAR: 1966-077A. Apogee: 3,708 km (2,304 mi). Perigee: 3,658 km (2,272 mi). Inclination: 89.70 deg. Period: 167.40 min. Missile Defense Alarm System..
- SECOR 7 - . Payload: EGRS 7. Mass: 17 kg (37 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USA ACE. Class: Earth. Type: Geodetic satellite. Spacecraft: SECOR. USAF Sat Cat: 2411 . COSPAR: 1966-077B. Apogee: 3,700 km (2,200 mi). Perigee: 3,671 km (2,281 mi). Inclination: 89.70 deg. Period: 167.50 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- ORS 1 - . Payload: ERS 15. Mass: 5.00 kg (11.00 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: ERS. USAF Sat Cat: 2412 . COSPAR: 1966-077C. Apogee: 3,700 km (2,200 mi). Perigee: 3,680 km (2,280 mi). Inclination: 89.70 deg. Period: 167.60 min. Cold welding experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 August 22 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5006 was mated to target launch vehicle 5306. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 11. Spacecraft: Gemini. Joint Flight Acceptance Composite Test was performed August 26, Simultaneous Launch Demonstration on August 31..
1966 September 2 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 was formally accepted by the Air Force after vehicle acceptance team inspection. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 was formally accepted by the Air Force after vehicle acceptance team inspection. It was shipped from Sunnyvale on September 3 and arrived at Eastern Test Range on September 4..
1966 September 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 was mated to target docking adapter (TDA) 7A at Cape Kennedy. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 11, Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini. McDonnell had delivered TDA 7A to the Cape August 19. After functional verification tests (September 13-15), the vehicle was moved (September 19-20) to the Merritt Island Launch Area for Plan X integrated tests with spacecraft No. 12..
1966 September 12 - . 13:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini 11 Agena Target - . Payload: TDA 6/Agena D 5006 GATV. Mass: 3,175 kg (6,999 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 11. Spacecraft Bus: Agena. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Decay Date: 1966-12-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 2414 . COSPAR: 1966-080A. Apogee: 298 km (185 mi). Perigee: 298 km (185 mi). Inclination: 28.80 deg. Period: 90.40 min. Docking target for Gemini 11..
1966 September 16 - . 17:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-32 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 32 / OPS 1686. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-09-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 2419 . COSPAR: 1966-083A. Apogee: 328 km (203 mi). Perigee: 146 km (90 mi). Inclination: 93.90 deg. Period: 89.20 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 6874 - . Payload: EHH B5. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1968-05-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 2420 . COSPAR: 1966-083B. Apogee: 501 km (311 mi). Perigee: 461 km (286 mi). Inclination: 94.10 deg. Period: 94.20 min. Radar monitoring..
1966 September 20 - . 12:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur D.
- Surveyor 2 - .
Payload: Surveyor SC-2. Mass: 292 kg (643 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor.
Decay Date: 1966-09-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 2425 . COSPAR: 1966-084A.
Soft lunar landing attempt failed. Surveyor II was launched from Cape Kennedy at 8:32 a.m. EDT. The Atlas-Centaur launch vehicle placed the spacecraft on a nearly perfect lunar intercept trajectory that would have missed the aim point by about 130 kilometers. Following injection, the spacecraft successfully accomplished all required sequences up to the midcourse thrust phase. This phase was not successful because of the failure of one of the three vernier engines to ignite, causing eventual loss of the mission. Contact with the spacecraft was lost at 5:35 a.m. EDT, September 22, and impact on the lunar surface was predicted at 11:18 p.m. on that day.
1966 September 21 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 began systems test - .
Nation: USA.
Flight: Gemini 12.
Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle.
Gemini Agena target vehicle (GATV) 5001 was returned to Hanger E and began systems test after completing Plan X tests at the Merritt Island Launch Area. Systems testing was completed September 29. The Combined Interface Test (September 29-October 13) was followed by functional tests of the primary and secondary propulsion systems, completed October 22. GATV 5001 was then moved to complex 14.
1966 October 5 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Midas 12 - . Payload: Midas RTS 3 / Agena TV 1353 / Agena D / OPS 1920. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Early warning satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: Midas. USAF Sat Cat: 2481 . COSPAR: 1966-089A. Apogee: 3,724 km (2,313 mi). Perigee: 3,657 km (2,272 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 167.60 min. Missile Defense Alarm System..
- SECOR 8 - . Payload: EGRS 8. Mass: 17 kg (37 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USA ACE. Class: Earth. Type: Geodetic satellite. Spacecraft: SECOR. USAF Sat Cat: 2520 . COSPAR: 1966-089B. Apogee: 3,707 km (2,303 mi). Perigee: 3,674 km (2,282 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 167.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 October 11 - . 19:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- ABRES SBGRV-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 50 km (31 mi).
1966 October 12 - . 19:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-33 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 33 / OPS 2055. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-10-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 2489 . COSPAR: 1966-090A. Apogee: 287 km (178 mi). Perigee: 155 km (96 mi). Inclination: 91.00 deg. Period: 89.00 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 5345/Agena D - . Payload: SGLS 1 / OPS 5345. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1966-10-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 2490 . COSPAR: 1966-090B. Apogee: 258 km (160 mi). Perigee: 181 km (112 mi). Inclination: 90.90 deg. Period: 89.00 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
1966 October 23 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini Agena target vehicle 5001 was mated to target launch vehicle 5307 on complex 14. - . Nation: USA. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft: Gemini. Joint Flight Acceptance Composite Test was completed October 28, Simultaneous Launch Demonstration on November 1..
1966 October 26 - . 11:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur D.
- Surveyor SD-4 - . Payload: Surveyor SD-4. Mass: 951 kg (2,096 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1966-11-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 2512 . COSPAR: 1966-095A. Apogee: 406,200 km (252,400 mi). Perigee: 166 km (103 mi). Inclination: 29.60 deg. Period: 15,912.00 min. Launch vehicle test. Centaur D AC-9 put Surveyor spacecraft payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1966 November 2 - . 20:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-34 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 34 / OPS 2070. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-11-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 2523 . COSPAR: 1966-098A. Apogee: 305 km (189 mi). Perigee: 159 km (98 mi). Inclination: 91.00 deg. Period: 89.20 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 5424/Agena D - . Payload: Agena Pickaback / OPS 5424. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1966-11-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 2525 . COSPAR: 1966-098B. Apogee: 324 km (201 mi). Perigee: 208 km (129 mi). Inclination: 91.00 deg. Period: 89.90 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
1966 November 6 - . 23:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lunar Orbiter 2 - .
Payload: Lunar Orbiter B. Mass: 390 kg (850 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Langley.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Lunar Orbiter.
Decay Date: 1967-10-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 2534 . COSPAR: 1966-100A.
Lunar Orbiter II was launched at 6:21 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 13 at Cape Kennedy, to photograph possible landing sites on the moon for the Apollo program. The Atlas-Agena D booster placed the spacecraft in an earth-parking orbit and, after a 14-minute coast, injected it into its 94-hour trajectory toward the moon. A midcourse correction maneuver on November 8 increased the velocity from 3,051 to 3,133 kilometers per hour. At that time the spacecraft was 265,485 kilometers from the earth.
The spacecraft executed a deboost maneuver at 3:26 p.m., November 10, while 352,370 kilometers from the earth and 1,260 kilometers from the moon and traveling at a speed of 5,028 kilometers per hour. The maneuver permitted the lunar gravitational field to pull the spacecraft into the planned initial orbit around the moon. On November 15, a micrometeoroid hit was detected by one of the 20 thin-walled pressurized sensors.
The spacecraft was transferred into its final close-in orbit around the moon at 5:58 p.m. November 15 and the photo-acquisition phase of Lunar Orbiter II's mission began November 18. Thirteen selected primary potential landing sites and a number of secondary sites were to be photographed. By the morning of November 25, the spacecraft had taken 208 of the 211 photographs planned and pictures of all 13 selected potential landing sites. It also made 205 attitude change maneuvers and responded to 2,421 commands.
The status report of the Lunar Orbiter II mission as of November 28 indicated that the first phase of the photographic mission was completed when the final photo was taken on the afternoon of November 25. On November 26, the developing web was cut with a hot wire in response to a command from the earth. Failure to achieve the cut would have prevented the final readout of all 211 photos. Readout began immediately after the cut was made. One day early, December 6, the readout terminated when a transmitter failed, and three medium-resolution and two high-resolution photos of primary site 1 were lost. Full low-resolution coverage of the site had been provided, however, and other data continued to be transmitted. Three meteoroid hits had been detected.
1966 November 11 - . 19:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC14. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Gemini 12 Agena Target - . Payload: TDA 7A/Agena D 5001R GATV. Mass: 3,175 kg (6,999 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Houston. Class: Manned. Type: Manned logistics spacecraft. Flight: Gemini 12. Spacecraft Bus: Agena. Spacecraft: Gemini Agena Target Vehicle. Decay Date: 1966-12-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 2565 . COSPAR: 1966-103A. Apogee: 310 km (190 mi). Perigee: 243 km (150 mi). Inclination: 28.80 deg. Period: 89.90 min. Docking target for Gemini 12..
1966 December 5 - . 21:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-35 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 35 / OPS 1890. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1966-12-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 2606 . COSPAR: 1966-109A. Apogee: 341 km (211 mi). Perigee: 137 km (85 mi). Inclination: 104.60 deg. Period: 89.20 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 December 7 - . 02:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- ATS 1 - .
Payload: ATS B. Mass: 352 kg (776 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: ATS.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 306.
Spacecraft: ATS-1.
Completed Operations Date: 1985-04-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 2608 . COSPAR: 1966-110A. Apogee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Perigee: 35,728 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 12.50 deg. Period: 1,434.50 min.
Applications Technology Satellite; communications and meteorological experiments. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 151 deg W in 1966-1968?; over the Americas at 149 deg W in 1968-1982; over the Pacific Ocean 170 deg E in 1982-1985 As of 3 September 2001 located at 167.30 deg E drifting at 0.065 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 59.28W drifting at 0.332E degrees per day.
1966 December 11 - . 21:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- OV1-09 - . Mass: 230 kg (500 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 2610 . COSPAR: 1966-111A. Apogee: 4,582 km (2,847 mi). Perigee: 475 km (295 mi). Inclination: 99.10 deg. Period: 139.40 min. Radiation bio-hazard experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-10 - . Mass: 130 kg (280 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 2002-11-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 2611 . COSPAR: 1966-111B. Apogee: 604 km (375 mi). Perigee: 541 km (336 mi). Inclination: 93.40 deg. Period: 96.10 min. Radiation data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1966 December 21 - . 22:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3.
- Prime 1 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,500 km (900 mi).
The first SV-5D Precision Recovery Including Maneuvering Entry (PRIME) maneuverable reentry vehicle was launched from Vandenberg by the first Series 7000 Atlas standard launch vehicle (SLV-3, Vehicle #7001). Managed by Space Systems Division, PRIME was designed to explore and advance the development of possible future manned and unmanned lifting body vehicles that would have the capability of operating like a spacecraft in orbit and of flying and maneuvering like an aircraft in the sensible atmosphere. Research was to be applicable to later Space Transportation System (STS) technology. The first test of the X-23A SV-5D lifting body re-entry shape. It was a zero cross-range suborbital flight, with recovery 6935 km downrange. The ballute deployed at 30.440 m, followed by the main parachute at 13,700 m, and the vehicle was descending within 275 m of the target point. Nevertheless the air-snatch was unsuccessful, and the vehicle sank. However 90% of the planned telemetry was successfully transmitted by radio.
1967 January 18 - . 01:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES TVX-13 (21) re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1967 January 22 - . 15:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES Mk 12R PDV re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1967 February 2 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Agena D - . Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1967-02-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 2665 . COSPAR: 1967-007B. Apogee: 285 km (177 mi). Perigee: 126 km (78 mi). Inclination: 102.70 deg. Period: 88.61 min.
- KH 7-36 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 36 / OPS 4399. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1967-02-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 2664 . COSPAR: 1967-007A. Apogee: 357 km (221 mi). Perigee: 136 km (84 mi). Inclination: 103.00 deg. Period: 89.50 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 February 5 - . 01:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lunar Orbiter 3 - . Payload: Lunar Orbiter C. Mass: 385 kg (848 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Langley. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Lunar Orbiter. Decay Date: 1967-10-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 2666 . COSPAR: 1967-008A. Crashed into Moon; returned 182 photos of lunar surface. Selenocentric orbit. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1967 February 13 - . 22:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES TX-22 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1967 March 5 - . 23:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3.
- Prime 2 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,500 km (900 mi).
The second SV-5D Precision Recovery Including Maneuvering Reentry (PRIME) lifting body was successfully launched from Vandenberg by an Atlas booster. Although the SV-5D was not recovered, its on-board sensors provided excellent data on the effects of reentry. This was also the first spacecraft to perform cross-range maneuvers during reentry. The X-23A SV-5D lifting body vehicle demonstrated a 1055 km cross-range manoeuvre, but again air snatch failed.
1967 March 16 - . 17:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES MBRV-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The second Maneuvering Ballistic Reentry Vehicle (MBRV-2) was launched down the Western Test Range by Atlas 151F. Performance of the launch vehicle was satisfactory, but the MBRV failed to accomplish its planned reentry. .
1967 April 6 - . 03:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D. FAILURE: Partial Failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- ATS 2 - . Payload: ATS A. Mass: 370 kg (810 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: ATS. Class: Technology. Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: ATS. Spacecraft: ATS-2. Decay Date: 1969-09-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 2743 . COSPAR: 1967-031A. Apogee: 11,119 km (6,909 mi). Perigee: 177 km (109 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 218.80 min. Launch vehicle failure left in useless orbit; communications tests..
- Research Payload Module 481 - . Payload: Module 481. Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Cleveland. Program: ATS. Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle Attached Payloads. Spacecraft: Research Payload Module 481. Decay Date: 1968-06-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 2744 . COSPAR: 1967-031B. Apogee: 10,732 km (6,668 mi). Perigee: 160 km (90 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 213.28 min.
1967 April 7 - . 11:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES AX-1 / Pod 30 Reentry test / ionosphere mission - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1967 April 17 - . 07:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur D.
- Surveyor 3 - . Payload: Surveyor SC-3. Mass: 283 kg (623 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1967-04-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 2756 . COSPAR: 1967-035A. Soft landed on Moon; perrformed soil sample tests and imaged lunar surface..
1967 April 20 - . 01:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3.
- Prime 3 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,500 km (900 mi).
The third and last SV-5D Precision Recovery Including Maneuvering Entry (PRIME) flight vehicle, essentially a small maneuverahle reentry spacecraft, successfully performed cross-range maneuvers after being launched from Vandenberg on an Atlas booster. The series of three flights was so successful in demonstrating that a maneuverable spacecraft could survive reentry that the planned fourth flight test was cancelled. The full design 1145 km cross range was demonstrated, and the X-23A SV-5D lifting body vehicle was successfully snatched at 3700 m altitude, 8 km from the target point. With this success the rest of the project was cancelled, and the two remaining unflown X-22A's were sent to the USAF Museum at Wright Patterson Air Force Base.
1967 May 4 - . 22:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lunar Orbiter 4 - . Payload: Lunar Orbiter D. Mass: 390 kg (850 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Langley. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Lunar Orbiter. Decay Date: 1967-10-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 2772 . COSPAR: 1967-041A. Returned 163 photos of lunar surface before impacting Moon. Selenocentric orbit. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1967 May 19 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES SBGRV-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1967 May 22 - . 18:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-37 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 37 / OPS 4321. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1967-05-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 2813 . COSPAR: 1967-050A. Apogee: 293 km (182 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 91.50 deg. Period: 88.80 min. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OPS 5557/Agena D - . Payload: LOGACS / OPS 5557. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: P 11. Spacecraft: SSF. Decay Date: 1967-05-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 2816 . COSPAR: 1967-050B. Apogee: 240 km (140 mi). Perigee: 148 km (91 mi). Inclination: 91.50 deg. Period: 88.40 min. Not identified as a subsatellite ferret by McDowell..
1967 June 4 - . 18:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC4E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- KH 7-38 - . Payload: KH-7 no. 38 / OPS 4360. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Military surveillance satellite. Spacecraft Bus: WS-117. Spacecraft: KH-7. Decay Date: 1967-06-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 2831 . COSPAR: 1967-055A. Apogee: 456 km (283 mi). Perigee: 149 km (92 mi). Inclination: 104.90 deg. Period: 90.60 min. The final Air Force Atlas/Agena D (SLV-3 #7128/SS-01B #4837) was successfully launched from Vandenberg AFB. KH-7 type satellite. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1967 June 9 - . 10:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- ABRES SPDS (RMP-B-1) re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1967 June 14 - . 06:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Mariner 5 - .
Payload: Mariner 67-2. Mass: 244 kg (537 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Mariner.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner.
Spacecraft: Mariner 5.
USAF Sat Cat: 2845 . COSPAR: 1967-060A.
Mariner 5 flew by Venus on October 19, 1967 at an altitude of 3,990 kilometres. With more sensitive instruments than its predecessor Mariner 2, Mariner 5 was able to shed new light on the hot, cloud-covered planet and on conditions in interplanetary space. Operations of Mariner 5 ended in November 1967. The spacecraft instruments measured both interplanetary and Venusian magnetic fields, charged particles, and plasmas, as well as the radio refractivity and UV emissions of the Venusian atmosphere.
1967 July 6 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES PDV re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1967 July 14 - . 11:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Centaur D.
- Surveyor 4 - . Payload: Surveyor SC-4. Mass: 283 kg (623 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1967-07-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 2875 . COSPAR: 1967-068A. Soft lunar landing attempt failed..
1967 July 22 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
1967 July 27 - . 19:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D. FAILURE: Partial Failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- OV1-08S - . Mass: 118 kg (260 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1972-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 2893 . COSPAR: 1967-072A. Apogee: 557 km (346 mi). Perigee: 529 km (328 mi). Inclination: 101.60 deg. Period: 95.50 min. Carried cosmic ray telescope. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-12S - . Mass: 140 kg (300 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1980-07-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 2901 . COSPAR: 1967-072D. Apogee: 579 km (359 mi). Perigee: 497 km (308 mi). Inclination: 101.70 deg. Period: 95.40 min. Solar flare observations. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-11 - . Mass: 555 kg (1,223 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1972-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 2893 . COSPAR: 1967-072xx. Apogee: 146 km (90 mi). Perigee: 144 km (89 mi). Inclination: 101.70 deg. Period: 87.40 min. OV-1 11 did not reach orbit..
1967 July 29 - . 08:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES MBRV-3 re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Spacecraft: ABRES.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
Launched from Vandenberg AFB atop Atlas booster 150F, the third Maneuvering Ballistic Reentry Vehicle (MBRV-3) achieved the first successful flight and reentry of a maneuvering ballistic reentry vehicle in the Advanced Ballistic Reentry Systems (ABRES) program. MBRV-3 successfully accomplished its planned terminal maneuver during reentry, and all objectives were achieved.
1967 August 1 - . 22:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- Lunar Orbiter 5 - .
Payload: Lunar Orbiter E. Mass: 389 kg (857 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Langley.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Lunar Orbiter.
Decay Date: 1968-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 2907 . COSPAR: 1967-075A.
Lunar Orbiter V was launched from the Eastern Test Range at 6:33 p.m. EDT August 1. The Deep Space Net Tracking Station at Woomera, Australia, acquired the spacecraft about 50 minutes after liftoff. Signals indicated that all systems were performing normally and that temperatures were within acceptable limits. At 12:48 p.m. EDT August 5, Lunar Orbiter V executed a deboost maneuver that placed it in orbit around the moon. The spacecraft took its first photograph of the moon at 7:22 a.m. EDT August 6. Before it landed on the lunar surface on January 31, 1968, Lunar Orbiter V had photographed 23 previously unphotographed areas of the moon's far side, the first photo of the full earth, 36 sites of scientific interest, and 5 Apollo sites for a total of 425 photos.
1967 September 8 - . 07:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Surveyor 5 - . Payload: Surveyor SC-5. Mass: 279 kg (615 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1967-09-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 2937 . COSPAR: 1967-084A. Soft lunar landing; returned 19,000 photos, soil data..
1967 October 11 - . 11:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES TVX-13 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
1967 October 14 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES MBRV-4 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1967 October 27 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1967 November 5 - . 23:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC12. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- ATS 3 - .
Payload: ATS C. Mass: 365 kg (804 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: ATS.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: ATS.
Spacecraft: ATS-3.
USAF Sat Cat: 3029 . COSPAR: 1967-111A. Apogee: 35,837 km (22,268 mi). Perigee: 35,736 km (22,205 mi). Inclination: 14.50 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications tests. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 45 deg W in-100 deg W in 1968-1970; over the Americas at 69 deg W in 1971-1976; over the Americas at 105 deg W in 1977-1998 As of 4 September 2001 located at 105.90 deg W drifting at 0.003 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 105.23W drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
1967 November 7 - . 07:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Surveyor 6 - .
Payload: Surveyor SC-6. Mass: 280 kg (610 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Class: Moon.
Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor.
Decay Date: 1967-11-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 3031 . COSPAR: 1967-112A.
Atlas 94D was the 91st, and last, D series missile to be launched from Vandenberg AFB since 12D was launched on 9 September 1959. Soft landed on lunar Moon; photographed lunar surface; sampled lunar soil; used propulsion system to briefly lift off of lunar surface.
1967 November 7 - . 13:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576B2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas D.
- ABRES Mk 11 AX-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Atlas 94D was the 91st, and last, D series missile to be launched from Vandenberg AFB since 12D was launched on 9 September 1959. Final launch of an Atlas D missile (first operational at Vandenberg on 9 September 1959)..
1967 November 10 - . 12:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES BGRV-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1967 December 21 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
1968 January 7 - . 06:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Surveyor 7 - . Payload: Surveyor SC-7. Mass: 1,036 kg (2,283 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: JPL, NASA. Class: Moon. Type: Lunar probe. Spacecraft: Surveyor. Decay Date: 1968-01-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 3091 . COSPAR: 1968-001A. Soft landed on lunar Moon; photographed lunar surface; sampled lunar soil..
1968 January 31 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
1968 February 26 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES BGRV-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The Boost Glide Re-entry Vehicle was launched from Vandenberg AFB, California to the area of Wake Island in the Pacific Ocean. It was launched from an Atlas missile booster and served to provide data on hypersonic manoeuvring flight characteristics..
1968 March 4 - . 13:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- OGO 5 - .
Payload: OGO E. Mass: 634 kg (1,397 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OGO.
Decay Date: 2011-07-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 3138 . COSPAR: 1968-014A. Apogee: 111,034 km (68,993 mi). Perigee: 36,021 km (22,382 mi). Inclination: 50.30 deg. Period: 3,746.50 min.
OGO 5 carried 25 experiments, 17 of which were particle studies, and two were magnetic field studies. In addition, there was one each of the following types of experiments: radio astronomy, UV spectrum, Lyman-alpha, solar X ray, plasma waves, and electric field. By April 1971, spacecraft perigee had increased to 26,400 km and inclination had increased to 54 deg. The spacecraft attitude control failed on August 6, 1971, after 41 months of normal operation. The spacecraft was placed in a standby status on October 8, 1971. Four experiments (Meyer, Blamont, Thomas, and Simpson) were reactivated for the period from June 1 to July 13, 1972, after which all operational support terminated. Spacecraft orbit parameters changed significantly over the spacecraft life.
1968 March 6 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/Trident.
- RMP-B-6 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,600 km (900 mi). The Air Force Western Test Range supported the initial west coast use of an Atlas E (74E) as a booster in an Advanced Ballistic Reentry Systems (ABRES) reentry vehicle development program. .
1968 April 6 - . 09:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- OV1-13 - . Mass: 107 kg (235 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 3173 . COSPAR: 1968-026A. Apogee: 9,214 km (5,725 mi). Perigee: 587 km (364 mi). Inclination: 100.00 deg. Period: 198.70 min. Radiation, engineering experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-14 - . Mass: 101 kg (222 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 3174 . COSPAR: 1968-026B. Apogee: 9,858 km (6,125 mi). Perigee: 568 km (352 mi). Inclination: 100.00 deg. Period: 207.00 min. Radiation data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 April 16 - . Launch Site: Kwajalein, Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas.
- Last Atlas E launch from Vandenberg AFB. - . Atlas 68E, the 16th and last E model to be launched from Vandenberg AFB, completed its mission to Kwajalein as part of the SAMSO-Army Reentry Measurements Program Phase B (RMP-B)..
1968 April 18 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- ABRES RVTO-1A-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,600 km (900 mi).
1968 April 27 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/Trident.
1968 May 3 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- ABRES Penaid TVX re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 100 km (60 mi).
1968 June 1 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES PDV re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1968 June 22 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
1968 June 29 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES RVTO-1A-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1968 July 11 - . 19:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- OV1-15S - . Payload: Spades. Mass: 470 kg (1,030 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1968-11-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 3318 . COSPAR: 1968-059A. Apogee: 1,800 km (1,100 mi). Perigee: 153 km (95 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 104.60 min. Studied relationship between atmospheric density and solar radiation. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-16 Cannonball 1 - . Payload: Loads. Mass: 600 kg (1,320 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1968-08-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 3319 . COSPAR: 1968-059B. Apogee: 556 km (345 mi). Perigee: 145 km (90 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 91.50 min. Ionospheric drag tests. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1968 August 6 - . 11:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- Canyon 1 - .
Payload: Canyon 1 / Agena D / OPS 2222. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO,
USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Canyon.
USAF Sat Cat: 3334 . COSPAR: 1968-063A. Apogee: 39,860 km (24,760 mi). Perigee: 31,680 km (19,680 mi). Inclination: 9.90 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
The first "stretched" Atlas SLV-3A/ Agena D was launched from the Eastern Test Range. The "stretched" Atlas had an additional 117-inch tank section to provide more fuel, a longer burn time, and increased payload capability. First launch in a communications intelligence program operated by the USAF within the National Reconnaissance Office, on behalf of the National Security Agency. The first generation series, CANYON, was based on the Agena vehicle. The Agena D remained attached to the spacecraft. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean. Last known longitude (30 December 1968) 98.50 deg W drifting at 0.166 deg E per day.
1968 August 10 - . 22:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur. FAILURE: Centaur oxidizer leak. No restart.. Failed Stage: U.
- ATS 4 - .
Payload: ATS D. Mass: 391 kg (862 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: ATS.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 306.
Spacecraft: ATS-4.
Decay Date: 1968-08-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 3344 . COSPAR: 1968-068A. Apogee: 769 km (477 mi). Perigee: 220 km (130 mi). Inclination: 29.10 deg. Period: 94.50 min.
Applications Technology Satellite that was to have been put into a geosynchronous transfer orbit, instead was left in a nearly-useless LEO orbit. ATS-4 included two cesium contact ion engines. Flight test objectives were to measure thrust and to examine electromagnetic compatibility with other spacecraft subsystems. The 5 cm diameter thrusters were designed to operate at 0.02 kW and provide about 89 microN thrust at about 6700 s specific impulse. The thrusters had the capability to operate at 5 setpoints from 18 to 89 microN. Thrusters were configured so they could be used for East-West station-keeping. Prior to launch, a 5 cm cesium thruster was life tested for 2245 hours at the 67 microN thrust level. However the Centaur upper stage did not achieve a second burn and the spacecraft remained attached to the Centaur in a 218 km by 760 km orbit. It was estimated that the pressure at these altitudes was between 10^-6 and 10^-8 Torr. Each of the two engines was tested on at least two occasions each over the throttling range. Combined test time of the two engines was about 10 hours over a 55 day period. The spacecraft re-entered the atmosphere on October 17, 1968. TheATS-4 flight was the first successful orbital test of an ion engine. There was no evidence of IPS electromagnetic interference related to spacecraft subsystems. Measured values of neutralizer emission current were much less than the ion beam current, implying inadequate neutralization. The spacecraft potential was about -132V which was much different than the anticipated value of about -40V.
1968 August 16 - . 20:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Burner 2. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- LCS 3 - .
Payload: LCS 3. Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF,
USN.
Class: Earth.
Type: Ionosphere satellite. Spacecraft: Orbiscal.
Decay Date: 1968-08-16 .
An Atlas/Burner II (SLV-3, #7004), the first Atlas to be launched with a Burner II upper stage, was launched from Space Launch Complex 3 East (SLC-3E) at Vandenberg but failed to place its payload in orbit due to a malfunction of the nose-fairing heat shield separation system. First of two Atlas/Burner II space launches. 1 of 13 satellite launch attempts; investigate effects of ionosphere on radio signals.
- LIDOS - . Payload: LIDOS. Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: Orbiscal.
- EGRS 11 - . Payload: EGRS 11. Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: Orbiscal.
- EGRS 12 - . Payload: EGRS 12. Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: Orbiscal.
- Orbiscal 1 - . Payload: Orbiscal 1. Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: Orbiscal.
- Radcat - . Payload: Radcat. Mass: 208 kg (458 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: Radcat.
- AVL-802 Grid Sphere 7-1 - . Payload: AVL-802. Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: Orbiscal.
- AVL-802 Grid Sphere 7-2 - . Payload: AVL-802. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: Calsphere.
- AVL-802 Rigid Sphere - .
Payload: AVL-802. Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Spacecraft: Calsphere.
An Atlas/Burner II (SLV-3, #7004), the first Atlas to be launched with a Burner II upper stage, was launched from Space Launch Complex 3 East (SLC-3E) at Vandenberg but failed to place its payload in orbit due to a malfunction of the nose-fairing heat shield separation system.
1968 September 25 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
1968 September 27 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- RVTO-1A-3 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1968 November 16 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1968 November 24 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- RVTO-1A-4 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1968 December 7 - . 08:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- OAO 2 - .
Payload: OAO A2. Mass: 2,012 kg (4,435 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Class: Astronomy.
Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: OAO.
USAF Sat Cat: 3597 . COSPAR: 1968-110A. Apogee: 758 km (470 mi). Perigee: 749 km (465 mi). Inclination: 35.00 deg. Period: 99.90 min.
Orbiting Astronomical Observatory; carried 11 telescopes; performed X-ray, UV, IR observations of stars. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit
1969 January 16 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- RMP-B-11 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1969 February 25 - . 01:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Mariner 6 - .
Payload: Mariner 69-3. Mass: 412 kg (908 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Mariner.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner.
Spacecraft: Mariner 6-7.
USAF Sat Cat: 3759 . COSPAR: 1969-014A.
Mars flyby 31 July 1969; returned 75 images of Martian surface. Ten days before the scheduled launch, a faulty switch opened the main valves on the Atlas stage. This released the pressure which supported the Atlas structure, and as the booster deflated it began to crumple. Two ground crewman started pressurizing pumps, saving the structure from further collapse. The two ground crewman, who had acted at risk of the 12-story rocket collapsing on them, were awarded Exceptional Bravery Medals from NASA.
The Mariner 6 spacecraft was removed, put on another Atlas/Centaur, and launched on schedule. The main booster was jettisoned 4 min. 38 sec. after launch, followed by a 7.5 minute Centaur burn to inject the spacecraft into Mars direct trajectory. After Mariner 6 separated from the Centaur the solar panels were deployed. A midcourse correction involving a 5.35 second burn of the hydrazine rocket occurred on 1 March 1969. A few days later explosive valves were deployed to unlatch the scan platform. Some bright particles released during the explosion distracted the Canopus sensor, and attitude lock was lost temporarily. It was decided to place the spacecraft on inertial guidance for the Mars flyby to prevent a similar occurrence.
On 29 July, 50 hours before closest approach, the scan platform was pointed to Mars and the scientific instruments turned on. Imaging of Mars began 2 hours later. For the next 41 hours, 49 approach images (plus a 50th fractional image) of Mars were taken through the narrow-angle camera. At 05:03 UT on 31 July the near-encounter phase began, including collection of 26 close-up images. Due to a cooling system failure, channel 1 of the IR spectrometer did not cool sufficiently to allow measurements from 6 to 14 micrometers so no infrared data were obtained over this range. Closest approach occurred at 05:19:07 UT at a distance of 3431 km from the martian surface. Eleven minutes later Mariner 6 passed behind Mars and reappeared after 25 minutes. X-band occultation data were taken during the entrance and exit phases. Science and imaging data were played back and transmitted over the next few days. The spacecraft was then returned to cruise mode which included engineering and communications tests, star photography TV tests, and UV scans of the Milky Way and an area containing comet 1969-B. Periodic tracking of the spacecraft in its heliocentric orbit was also done.
Science Results
Mariner 6 returned 49 far encounter and 26 near encounter images of Mars. Close-ups from the near encounter phases covered 20% of the surface. The spacecraft instruments measured UV and IR emissions and radio refractivity of the Martian atmosphere. Images showed the surface of Mars to be very different from that of the Moon, in some contrast to the results from Mariner 4. The south polar cap was identified as being composed predominantly of carbon dioxide. Atmospheric surface pressure was estimated at between 6 and 7 mb. Radio science refined estimates of the mass, radius and shape of Mars.
1969 March 18 - . 07:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- OV1-17S - .
Mass: 142 kg (313 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF OAR.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1.
Decay Date: 1970-03-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 3823 . COSPAR: 1969-025A. Apogee: 466 km (289 mi). Perigee: 400 km (240 mi). Inclination: 99.10 deg. Period: 93.20 min.
Atlas 104F was launched from Vandenberg AFB and placed 41 scientific experiments into orbit as part of SAMSO's Space Experiments Support Program (SESP). Solar radiation experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- OV1-17A Orbiscal 2 - . Payload: OV1-17P. Mass: 221 kg (487 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1969-03-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 3826 . COSPAR: 1969-025D. Apogee: 309 km (192 mi). Perigee: 175 km (108 mi). Inclination: 99.10 deg. Period: 89.40 min. Radio beacon mountedon OV17 propulsion module. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-19S - . Mass: 124 kg (273 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 3825 . COSPAR: 1969-025C. Apogee: 5,551 km (3,449 mi). Perigee: 483 km (300 mi). Inclination: 104.80 deg. Period: 151.10 min. Radiation experiments. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- OV1-18S - . Mass: 125 kg (275 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF OAR. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. Decay Date: 1972-08-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 3824 . COSPAR: 1969-025B. Apogee: 583 km (362 mi). Perigee: 466 km (289 mi). Inclination: 98.90 deg. Period: 95.20 min. Ionospheric, radiation, electric field data. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1969 March 27 - . 22:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Mariner 7 - .
Payload: Mariner 69-2. Mass: 412 kg (908 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Mariner.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner.
Spacecraft: Mariner 6-7.
USAF Sat Cat: 3837 . COSPAR: 1969-030A.
Mars flyby 5 August 1969; returned 126 images of Martian surface. Mariner 7 was launched on a direct-ascent trajectory to Mars 31 days after Mariner 6. On 8 April 1969 a midcourse correction was made by firing the hydrazine moter for 7.6 seconds. On 8 May Mariner 7 was put on gyro control to avoid attitude control problems which were affecting Mariner 6. On 31 July telemetry from Mariner 7 was suddenly lost and the spacecraft was commanded to switch to the low-gain antenna. It was later successfully switched back to the high-gain antenna. It was thought that leaking gases, perhaps from the battery which later failed a few days before encounter, had caused the anomaly.
At 09:32:33 GMT on 2 August 1969 Mariner 7 bagan the far-encounter sequence involving imaging of Mars with the narrow angle camera. Over the next 57 hours, ending about 5 hours before closest approach, 93 images of Mars were taken and transmitted. The spacecraft was reprogrammed as a result of analysis of Mariner 6 images. The new sequence called for the spacecraft to go further south than originally planned, take more near-encounter pictures, and collect more scientific data on the lighted side of Mars. Data from the dark side of Mars were to be transmitted directly back to Earth but there would be no room on the digital recorder for backup due to the added dayside data. At closest approach, 05:00:49 GMT on 5 August, Mariner 7 was 3430 km above the martian surface. Over this period, 33 near-encounter images were taken. About 19 minutes after the flyby, the spacecraft went behind Mars and emerged roughly 30 minutes later. X-band occultation data were taken during the entrance and exit phases. Science and imaging data were played back and transmitted over the next few days. The spacecraft was then returned to cruise mode which included engineering and communications tests, star photography TV tests, and UV scans of the Milky Way and an area containing comet 1969-B. Periodic tracking of the spacecraft in its heliocentric orbit was also done.
Science Results
The total data return for Mariners 6 and 7 was 800 million bits. Mariner 7 returned 93 far and 33 near encounter images. Close-ups from the near encounter phases covered 20% of the surface. The spacecraft instruments measured UV and IR emissions and radio refractivity of the Martian atmosphere. Images showed the surface of Mars to be very different from that of the Moon, in some contrast to the results from Mariner 4. The south polar cap was identified as being composed predominantly of carbon dioxide. Atmospheric surface pressure was estimated at between 6 and 7 mb. Radio science refined estimates of the mass, radius and shape of Mars.
1969 April 13 - . 02:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- Canyon 2 - . Payload: Canyon 2 / Agena D / OPS 3148. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Canyon. USAF Sat Cat: 3889 . COSPAR: 1969-036A. Apogee: 39,270 km (24,400 mi). Perigee: 32,670 km (20,300 mi). Inclination: 9.90 deg. Period: 1,445.00 min. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean. Last known longitude (31 December 1969) 99.24 deg W drifting at 2.246 deg W per day..
1969 August 12 - . 11:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- ATS 5 - .
Payload: ATS E. Mass: 821 kg (1,809 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: ATS.
Class: Technology.
Type: Communications technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: ATS.
Spacecraft: ATS-5.
Completed Operations Date: 1984-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 4068 . COSPAR: 1969-069A. Apogee: 36,024 km (22,384 mi). Perigee: 35,992 km (22,364 mi). Inclination: 14.50 deg. Period: 1,447.40 min.
Applications Technology Satellite; communications tests. Launch vehicle successfully put the payload into a geosynchronous transfer orbit. The spacecraft maneuvered into geostationary orbit at 108 degrees W. The purpose of this flight was to demonstrate North-South Stationkeeping of a geosynchronous satellite. ATS-5 was equipped with an ion engine package identical to that on ATS-4. Once in geosynchronous orbit the spacecraft could not be despun as planned, and thus the spacecraft gravity gradient stabilization could not be implemented. The spacecraft spin rate was about 76 revolutions per minute, and this caused an effective 4g acceleration on the cesium feed system. The high g-loading on the cesium feed system caused flooding of the discharge chamber, and normal operation of the thruster with ion beam extraction could not be performed. The IPS was instead be operated as a neutral plasma source, without high-voltage ion extraction, along with the wire neutralizer to examine spacecraft charging effects. The neutralizer was also operated by itself to provide electron injection for the spacecraft charging experiments. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 105 deg W in 1969-1977; over the Americas at 70 deg W in 1977-1983. As of 1 September 2001 located at 15.48 deg E drifting at 2.807 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 111.70E drifting at 2.819W degrees per day.
1969 August 20 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES RVTO-1A-5 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1969 September 16 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- RMP-B-12 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1969 October 10 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
1969 December 3 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES RVTO-1A-6 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1969 December 12 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- RMP-B-14 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1970 February 8 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- RMP-B-15 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1970 March 13 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- RMP-B-16 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1970 May 30 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- RMP-B-17 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1970 June 9 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES RVTO-1A-7 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1970 June 19 - . 11:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- OPS 5346 - . Payload: AFP-720 Rhyolite 1. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Rhyolite. USAF Sat Cat: 4418 . COSPAR: 1970-046A. Apogee: 33,685 km (20,930 mi). Perigee: 178 km (110 mi). Inclination: 28.20 deg. Period: 588.90 min. First launch of Rhyolite geostationary ELINT satellite. Reportedly left in transfer orbit; other sources indicate a successful mission. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean..
1970 September 1 - . 01:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- Canyon 3 - . Payload: Canyon 3 / Agena D / OPS 7329. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Canyon. USAF Sat Cat: 4510 . COSPAR: 1970-069A. Apogee: 39,855 km (24,764 mi). Perigee: 31,947 km (19,850 mi). Inclination: 10.30 deg. Period: 1,441.90 min. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean. Last known longitude (31 December 1970) 99.01 deg W drifting at 1.490 deg W per day..
1970 November 30 - . 22:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur. FAILURE: Shroud failed to separate.. Failed Stage: S.
- OAO-B - . Payload: OAO B. Mass: 2,121 kg (4,676 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: OAO. Decay Date: 1970-11-30 . COSPAR: F701130A. Orbiting Astronomical Observatory. Launch vehicle was to have put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1970 December 22 - . 08:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- ABRES RVTO-2A-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1971 January 26 - . 00:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Intelsat 4 F-2 - .
Mass: 706 kg (1,556 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4.
Completed Operations Date: 1983-05-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 4881 . COSPAR: 1971-006A. Apogee: 36,236 km (22,515 mi). Perigee: 36,151 km (22,463 mi). Inclination: 15.30 deg. Period: 1,457.00 min.
Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit; the satellite performed the apogee burn and positioned itself in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 24.5 deg W. Subsequently at 23 deg W in 1971-1975; over the Atlantic Ocean 1-6 deg W in 1976-1980; over the Atlantic Ocean 0-5 deg E in 1980-1983. As of 3 September 2001 at 31.91 deg E drifting at 5.168 deg W per day. As of 2006 Dec 18 located at 133.93E drifting at 5.166W degrees per day. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
1971 April 5 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES LAR-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1971 May 9 - . 01:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur. FAILURE: Inadvertent Centaur electronic signal shut down stage early.. Failed Stage: U.
- Mariner H - . Payload: Mariner 71H. Mass: 996 kg (2,195 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Program: Mariner. Class: Mars. Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner. Spacecraft: Mariner 8-9. Decay Date: 1971-05-08 . Intended Mars flyby..
1971 May 30 - . 22:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Mariner 9 - .
Payload: Mariner 71J. Mass: 974 kg (2,147 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Mariner.
Class: Mars.
Type: Mars probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner.
Spacecraft: Mariner 8-9.
USAF Sat Cat: 5261 . COSPAR: 1971-051A.
The first spacecraft to orbit another planet. The Mariner Mars 71 mission was planned to consist of two spacecraft on complementary missions. Mariner 8 was to map 70 % of the Martian surface and Mariner 9 was to study temporal changes in the Martian atmosphere and on the Martian surface. The launch failure of Mariner 8 forced Mariner 9 to combine the mission objectives of both. For the survey portion of the mission, the planetary surface was to be mapped with the same resolution as planned for the original mission, although the resolution of pictures of the polar regions would be decreased due to the increased slant range. The variable features experiments were changed from studies of six given areas every 5 days to studies of smaller regions every 17 days. Mariner 9 was launched on a direct trajectory to Mars. Separation from the booster occurred at 22:36 GMT. The four solar panels were deployed at 22:40 GMT. The sensors locked onto the Sun at 23:16, shortly after the spacecraft left the Earth's shadow and Canopus acquisition was achieved at 02:26 GMT 31 May. A planned midcourse maneuver was executed on 5 June. Mariner 9 arrived at Mars on 14 November 1971 after a 167 day flight. A 15 minute 23 second rocket burn put the spacecraft into Mars orbit. The insertion orbit had a periapsis of 1398 km and a period of 12 hr, 34 min. Two days later a 6 second rocket burn changed the orbital period to just under 12 hours with a periapsis of 1387 km. A correction trim maneuver was made on 30 December on the 94th orbit which raised the periapsis to 1650 km and changed the orbital period to 11:59:28 so that synchronous data transmissions could be made to the Goldstone 64-m DSN antenna.
Imaging of the surface of Mars by Mariner 9 was delayed by a dust storm which started on 22 September 1971 in the Noachis region. The storm quickly grew into one of the largest global storms ever observed on Mars. By the time the spacecraft arrived at Mars no surface details could be seen except the summits of Olympus Mons and the three Tharsis volcanoes. The storm abated through November and December and normal mapping operations began. The spacecraft gathered data on the atmospheric composition, density, pressure, and temperature and also the surface composition, temperature, gravity, and topography of Mars. A total of 54 billion bits of scientific data were returned, including 7329 images covering the entire planet. After depleting its supply of attitude control gas, the spacecraft was turned off on 27 October 1972. Mariner 9 was left in an orbit which should not decay for at least 50 years, after which the spacecraft will enter the Martian atmosphere.
The Mariner 9 mission resulted in a global mapping of the surface of Mars, including the first detailed views of the martian volcanoes, Valles Marineris, the polar caps, and the satellites Phobos and Deimos. It also provided information on global dust storms, the gravity field as well as evidence for surface aeolian activity.
1971 June 29 - . 13:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Trident.
- ABRES RVTO-2A-3 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1971 August 7 - . 00:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A2. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- OV1-20P - .
Mass: 70 kg (154 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF STP.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1.
Decay Date: 1971-08-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 5394 . COSPAR: 1971-067A. Apogee: 1,932 km (1,200 mi). Perigee: 136 km (84 mi). Inclination: 92.00 deg. Period: 105.90 min.
Atlas 76F, with two upper stage Orbital Vehicle propulsion modules, OV1-20 and 0V1-21, was launched from Vandenberg as part of SAMSO's Space Test Program (STP). This mission, STP 70-2, successfully placed six spacecraft with nine separate payloads into polar orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- OV1-21P - . Mass: 70 kg (154 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF STP. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: OV1. USAF Sat Cat: 5397 . COSPAR: 1971-067B. Apogee: 896 km (556 mi). Perigee: 778 km (483 mi). Inclination: 87.60 deg. Period: 101.70 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Cannonball 2 - . Payload: LOADS 2. Mass: 364 kg (802 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF STP. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: Cannonball. Decay Date: 1972-01-31 . USAF Sat Cat: 5382 . COSPAR: 1971-067C. Apogee: 1,970 km (1,220 mi). Perigee: 133 km (82 mi). Inclination: 92.00 deg. Period: 106.30 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Musketball 1 - . Payload: RTDS. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF STP. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Musketball. Decay Date: 1971-09-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 5383 . COSPAR: 1971-067D. Apogee: 859 km (533 mi). Perigee: 134 km (83 mi). Inclination: 87.60 deg. Period: 94.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Gridsphere 1 - . Payload: AVL-802 Grid Sphere 7-1. Mass: 37 kg (81 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Gridsphere. USAF Sat Cat: 5398 . COSPAR: 1971-067E. Apogee: 856 km (531 mi). Perigee: 756 km (469 mi). Inclination: 87.60 deg. Period: 101.00 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- LCS 4 - . Mass: 1.00 kg (2.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: US Army. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: LCS. Decay Date: 1972-06-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 5396 . COSPAR: 1971-067F. Apogee: 910 km (560 mi). Perigee: 779 km (484 mi). Inclination: 87.60 deg. Period: 101.80 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Gridsphere 2 - . Payload: AVL-802 Grid Sphere 7-2. Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Gridsphere. Decay Date: 1979-03-18 . USAF Sat Cat: 5401 . COSPAR: 1971-067G. Apogee: 915 km (568 mi). Perigee: 783 km (486 mi). Inclination: 87.60 deg. Period: 101.90 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Rigidsphere - . Payload: AVL-802 Rigid Sphere. Mass: 6.00 kg (13.20 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Radar calibration target. Spacecraft: Rigidsphere. Decay Date: 1979-11-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 5406 . COSPAR: 1971-067H. Apogee: 916 km (569 mi). Perigee: 781 km (485 mi). Inclination: 87.60 deg. Period: 101.80 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
- Mylar Balloon - . Payload: AVL-802 Mylar Sphere. Mass: 2.00 kg (4.40 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Mylar. Decay Date: 1981-09-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 5410 . COSPAR: 1971-067P. Apogee: 912 km (566 mi). Perigee: 791 km (491 mi). Inclination: 87.60 deg. Period: 101.90 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). .
1971 September 1 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- ABRES LAR-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Spacecraft: ABRES. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1971 December 4 - . 22:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D. FAILURE: First stage failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- AFP-827 / Canyon 4 - . Payload: Canyon 4 / Agena D. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Canyon. Decay Date: 1971-12-04 .
1971 December 20 - . 01:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Intelsat 4 F-3 - .
Mass: 1,410 kg (3,100 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4.
Completed Operations Date: 1984-02-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 5709 . COSPAR: 1971-116A. Apogee: 36,009 km (22,374 mi). Perigee: 35,930 km (22,320 mi). Inclination: 11.10 deg. Period: 1,445.50 min.
Over Atlantic. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 20-25 deg W in 1972-1976; over the Atlantic Ocean 34 deg W in 1976-1977; over the Atlantic Ocean 18-22 deg W in 1977-1980; over the Atlantic Ocean 53 deg W in 1981-1982; over the Atlantic Ocean 38-44 deg W in 1982-1983 As of 4 September 2001 located at 90.58 deg E drifting at 2.365 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 54.69E drifting at 2.365W degrees per day.
1972 January 23 - . 00:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Intelsat 4 F-4 - .
Mass: 1,410 kg (3,100 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4.
Completed Operations Date: 1983-05-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 5775 . COSPAR: 1972-003A. Apogee: 35,917 km (22,317 mi). Perigee: 35,905 km (22,310 mi). Inclination: 10.50 deg. Period: 1,442.50 min.
Over Pacific. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 174 deg E in 1972-1974; over the Pacific Ocean 179 deg E in 1975-1982; over the Atlantic Ocean 1 deg W in 1982-1983 As of 28 August 2001 located at 178.00 deg E drifting at 1.569 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 7 located at 155.84W drifting at 1.593W degrees per day.
1972 March 3 - . 01:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Pioneer 10 - .
Payload: Pioneer F. Mass: 259 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Ames.
Program: Pioneer.
Class: Outer planets.
Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 10-11.
USAF Sat Cat: 5860 . COSPAR: 1972-012A.
Jupiter flyby December 1973; first man-made object to leave solar system. The spacecraft achieved its closest approach to Jupiter on December 3, 1973, when it reached approximately 2.8 Jovian radii (about 200,000 km). As of Jan. 1, 1997 Pioneer 10 was at about 67 AU from the Sun near the ecliptic plane and heading outward from the Sun at 2.6 AU/year and downstream through the heliomagnetosphere towards the tail region and interstellar space. Additional Details: here....
1972 June 13 - . 21:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- Intelsat 4 F-5 - .
Mass: 1,410 kg (3,100 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4.
Completed Operations Date: 1983-02-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 6052 . COSPAR: 1972-041A. Apogee: 35,847 km (22,274 mi). Perigee: 35,811 km (22,251 mi). Inclination: 11.30 deg. Period: 1,438.30 min.
Over Indian Ocean. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 61 deg E in 1972-1975; over the Indian Ocean 60 deg E in 1976-1980; over the Pacific Ocean 179 deg E in 1980-1981 As of 2 September 2001 located at 8.61 deg E drifting at 0.536 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 73.10W drifting at 0.625W degrees per day.
1972 August 21 - . 10:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3C Centaur.
- OAO 3 - . Payload: OAO-C. Mass: 2,204 kg (4,858 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: OAO. USAF Sat Cat: 6153 . COSPAR: 1972-065A. Apogee: 724 km (449 mi). Perigee: 713 km (443 mi). Inclination: 35.00 deg. Period: 99.20 min. UV observations of stellar objects. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1972 October 2 - . 20:09 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Burner 2.
- RADCAT - .
Payload: Radsat / Radcat / OPS 8180. Mass: 208 kg (458 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: US Army.
Class: Technology.
Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft: RADCAT.
Decay Date: 2012-08-02 . USAF Sat Cat: 6212 . COSPAR: 1972-076A. Apogee: 638 km (396 mi). Perigee: 627 km (389 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 97.40 min.
An Atlas F/Burner IIA launch vehicle, carrying SAMSO's Space Test Program Flight 72-1, was launched from Vandenberg. This was the first use of this booster/upper stage combination. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- Radsat - .
Payload: P 72-1 / OPS 8180. Mass: 726 kg (1,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft: Radsat.
USAF Sat Cat: 6217 . COSPAR: 1972-076B. Apogee: 705 km (438 mi). Perigee: 688 km (427 mi). Inclination: 98.70 deg. Period: 98.70 min.
An Atlas F/Burner IIA launch vehicle, carrying SAMSO's Space Test Program Flight 72-1, was launched from Vandenberg. This was the first use of this booster/upper stage combination. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1972 December 20 - . 22:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- Canyon 5 - . Payload: Canyon Improved / OPS 9390. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Canyon. USAF Sat Cat: 6317 . COSPAR: 1972-101A. Apogee: 40,728 km (25,307 mi). Perigee: 31,012 km (19,269 mi). Inclination: 9.70 deg. Period: 1,440.40 min. First launch of improved ELINT satellite. In comparison to earlier Canyon ELINT satellites, Improved Canyon had a similar but heavier payload which separated from the Agena D final stage..
1973 Mar - . LV Family: Atlas, Minuteman, Trident. Launch Vehicle: Minuteman 1.
- HAVE FLY to also use Minuteman boosters. - .
A SAMSO-Navy Strategic System Program Office Memorandum of Agreement was amended to provide Minuteman I boosters in addition to the Atlas vehicles already scheduled. These were for HAVE FLY, the Trident Supplemental Flight Test (SFT) program managed by the Deputy for Reentry Systems.
1973 March 6 - . 09:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- OPS 6063 - . Payload: AFP-720 Rhyolite 2. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Rhyolite. USAF Sat Cat: 6380 . COSPAR: 1973-013A. Apogee: 35,855 km (22,279 mi). Perigee: 35,679 km (22,169 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,435.10 min. Second launch of Rhyolite geostationary ELINT satellite..
1973 April 6 - . 02:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Pioneer 11 - .
Payload: Pioneer G. Mass: 259 kg (570 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Ames.
Program: Pioneer.
Class: Outer planets.
Type: Outer planets probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 10-11.
USAF Sat Cat: 6421 . COSPAR: 1973-019A.
NASA's Atlas/Centaur was launched from Cape Canaveral carrying Pioneer 11 (Jupiter-Saturn). This was the first SLV-3D Atlas booster (vehicle 5011D), and the first SLV-3 to use the new 370,000-pound thrust MA-5 booster package for improved payload performance. Jupiter flyby December 1974; Saturn flyby September 1979. Solar system escape trajectory. Pioneer 11 was the second mission to investigate Jupiter and the outer solar system and the first to explore the planet Saturn and its main rings. Pioneer 11, like Pioneer 10, used Jupiter's gravitational field to alter its trajectory radically. It passed close to Saturn and then it followed an escape trajectory from the solar system. During its closest approach, December 4, 1974, Pioneer 11 passed to within 34,000 km of Jupiter's cloud tops. It passed by Saturn on September 1, 1979, at a distance of 21,000 km from Saturn's cloud tops. The spacecraft has operated on a backup transmitter since launch. Instrument power sharing began in February 1985 due to declining RTG power output. Science operations and daily telemetry ceased on September 30, 1995 when the RTG power level was insufficient to operate any experiments. As of the end of 1995 the spacecraft was located at 44.7 AU from the Sun at a nearly asymptotic latitude of 17.4 degrees above the solar equatorial plane and was heading outward at 2.5 AU/year. Routine tracking and project data processing operations were terminated on March 31, 1997 for budget reasons.
1973 Jul - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- First SLV-3A standard Atlas delivered. - . The first SLV-3A standard Atlas booster (Vehicle 5506A) with the 370,000-pound thrust MA-5 propulsion system was delivered to the Air Force by Convair/Astronautics..
1973 August 23 - . 22:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4 F-7 - .
Mass: 1,410 kg (3,100 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4.
Completed Operations Date: 1984-02-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 6796 . COSPAR: 1973-058A. Apogee: 36,132 km (22,451 mi). Perigee: 36,080 km (22,410 mi). Inclination: 10.40 deg. Period: 1,452.50 min.
Over Atlantic Ocean. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 30 deg W in 1973-1976 over the Atlantic Ocean 1 deg W in 1976-1980; over the Indian Ocean 56 deg E in 1980-1981; over the Pacific Ocean179 deg E in 1981-1982; over the Atlantic Ocean 53 deg W in 1982-1983 As of 31 August 2001 located at 74.52 deg W drifting at 4.067 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 19.61E drifting at 4.058W degrees per day.
1973 August 29 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS RVTO-3A-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1973 September 30 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS ACE-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Spacecraft: ABRES.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
Atlas 108F, carrying the Advanced Control Experiment 1 (ACE 1) vehicle, was launched from Vandenberg AFB and impacted in the Kwajalein area. The ACE 1 vehicle was to test the development of a preprototype of maneuvering reentry vehicle (MaRV) as part of the Advanced Ballistic Reentry Systems (ABRES) program.
1973 November 3 - . 05:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Mariner 10 - .
Payload: Mariner 73J. Mass: 526 kg (1,159 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Program: Mariner.
Class: Mercury.
Type: Mercury probe. Spacecraft Bus: Mariner.
Spacecraft: Mariner 10.
USAF Sat Cat: 6919 . COSPAR: 1973-085A.
An Atlas/Agena D launched Mariner 10 (Mariner Venus-Mercury) from the Eastern Test Range. The spacecraft was scheduled for Venus f lyby in February 1974 and Mercury in March 1974 - it would be the first space probe ever to approach Mercury. Mariner 10 was the first spacecraft to reach Mercury. Mariner 10 was placed in a parking orbit for 25 minutes after launch, then accelerated to a trans-Venus escape trajectory. The television and ultraviolet experiments were trained on the comet Kohoutek while the spacecraft was en route to its destination. The vehicle's first planetary encounter was with Venus on February 5, 1974, at a distance of 4200 km. Mariner 10 took 4,000 photos of Venus, which revealed a nearly round planet enveloped in smooth cloud layers. The gravity of Venus bent the orbit of the spacecraft and sent it towards Mercury. It crossed the orbit of Mercury on March 29, 1974, at 20:46 GMT, at a distance of 704 km from the surface. Photographs taken during the pass revealed an intensely cratered, Moon-like surface and a faint atmosphere of mostly helium. After the first flyby, Mariner 10 entered solar orbit, which permitted two more rendezvous with Mercury. On September 21, 1974, the second Mercury rendezvous, at an altitude of about 47,000 km, provided another opportunity to photograph the sunlit side of the planet and the south polar region. The third and final Mercury encounter on March 16, 1975, at an altitude of 327 km, yielded 300 photographs and magnetic field measurements. The vehicle was turned off March 24, 1975 when the supply of attitude-control gas was depleted.
1974 March 6 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS SFT-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
Atlas 73F was launched from Vandenberg and was the first mission in the Trident Supplemental Flight Test program (SFT-1), designated HAVE FLY. Managed by SAMSO's Deputy for Reentry Systems (RS), this reentry vehicle research and development program was conducted for the Navy's Strategic System Program Office (SSPO). The SFT missions were for the Trident missile system and were part of the joint-service Advanced Ballistic Reentry System (ABRES) program.
1974 March 23 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS ACE-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The second Advanced Control Experiment (ACE) vehicle was flight tested and all objectives were met..
1974 May 1 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS SFT-2 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1974 June 1 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3 Agena D.
- USAF transferred responsibility for Atlas SLV-3 to NASA - . HQ SAMSO formally transferred management responsibility for Standard Launch Vehicle-3 (SLV-3) vehicle to National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
1974 June 28 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS SFT-3 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
1974 July 14 - . 05:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/PTS.
- NTS 1 - .
Payload: Timation 3 / OPS 7518 / P73-3. Mass: 293 kg (645 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: Navstar.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: NTS.
USAF Sat Cat: 7369 . COSPAR: 1974-054A. Apogee: 13,774 km (8,558 mi). Perigee: 13,446 km (8,354 mi). Inclination: 125.20 deg. Period: 468.70 min.
Space Test Program flight P73-3 was launched from the Western Test Range, and the payload - Navy Navigation Technology Satellite #1 (NTS-1) - was successfully placed into orbit. Demonstrated navigation technologies leading eventually to Navstar/GPS system. Operated for 5 years.
1974 September 8 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A1. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS ACE-3 re-entry vehicle test flight - . Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi). The third Advanced Control Experiment (ACE) reentry vehicle was launched but malfunctioned and the mission objectives were not met..
1974 October 14 - . 04:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg 576A3. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- BMRS RVTO-3A-1 re-entry vehicle test flight - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF AFSC.
Spacecraft: ABRES.
Apogee: 1,400 km (800 mi).
Surplus Atlas 31F was launched from Vanden-berg AFB carrying a Reentry Vehicles Technology and Observables (RVT0-3A-1) payload. This successful launch and flight marked the apparent end of the use of Atlas D,E, and F ICBMs in support of various Advanced Ballistic Reentry Systems (ABRES) and other governmental agency programs. Since Atlas 159D was launched from Vandenberg AFB on 26 October 1962 in support of the Nike Targets Program, a total of 113 Atlas missiles - 54Ds, 4Es, and 55Fs - have been launched with only 11 failures.
1974 November 21 - . 23:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4 F-8 - .
Mass: 1,410 kg (3,100 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4.
Completed Operations Date: 1985-08-20 . USAF Sat Cat: 7544 . COSPAR: 1974-093A. Apogee: 35,944 km (22,334 mi). Perigee: 35,907 km (22,311 mi). Inclination: 8.80 deg. Period: 1,443.20 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean at 174 deg E in 1974-1982; over the Pacific Ocean 179 deg E in 1982; over the Atlantic Ocean 1 deg W in 1983-1985 As of 1 September 2001 located at 139.80 deg W drifting at 1.762 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 61.11W drifting at 1.754W degrees per day.
1975 February 20 - . 23:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur. FAILURE: Staging electrical disconnect.. Failed Stage: U.
- Intelsat 4 F-6 - . Mass: 1,410 kg (3,100 lb). Nation: International. Agency: Intelsat. Program: Intelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353. Spacecraft: Intelsat 4. Decay Date: 1975-02-20 . Staging electrical disconnect. Launch vehicle was to have put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1975 April 13 - . 00:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: First stage failure due to explosion in flame pit at lift-off.. Failed Stage: 1.
- P 72-2 - .
Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Military technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: P.
Spacecraft: P 72.
Decay Date: 1975-04-12 .
Space Test Program flight P72-2 was launched; it carried two infrared radiometers and three other payloads. The launch failed when the Atlas F launch vehicle malfunctioned. A lack of deluge water and collection in the flame bucket of a kerosene/liquid oxygen gel led to the explosion of the gel on lift-off, damaging one of the Atlas engines and leading to complete engine failure during the ascent.
1975 May 22 - . 22:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4 F-1 - .
Mass: 727 kg (1,602 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4.
Completed Operations Date: 1987-10-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 7815 . COSPAR: 1975-042A. Apogee: 36,128 km (22,448 mi). Perigee: 36,016 km (22,379 mi). Inclination: 8.90 deg. Period: 1,450.70 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 63 deg E in 1976-1978; over the Atlantic Ocean 17.0 deg W in 1978; over the Atlantic Ocean 18.5 deg W in 1979-1981; over the Pacific Ocean 174 deg E in 1982; over the Atlantic Ocean 53 deg W in 1983-1984; over the Atlantic Ocean 50 deg W in 1984-1987 As of 30 August 2001 located at 111.08 deg W drifting at 3.657 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 95.13E drifting at 3.657W degrees per day.
1975 June 18 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- Canyon 6 - . Payload: Canyon Improved / OPS 4966. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Canyon. USAF Sat Cat: 7963 . COSPAR: 1975-055A. Apogee: 40,800 km (25,300 mi). Perigee: 30,200 km (18,700 mi). Inclination: 9.00 deg. Period: 1,422.00 min.
1975 September 26 - . 00:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4A F-1 - .
Mass: 1,500 kg (3,300 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1986-07-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 8330 . COSPAR: 1975-091A. Apogee: 35,910 km (22,310 mi). Perigee: 35,860 km (22,280 mi). Inclination: 8.90 deg. Period: 1,441.10 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 25 deg W in 1975-1981; over the Atlantic Ocean 18.5 deg W in 1982-1983; over the Atlantic Ocean 30 deg W in 1983-1986 As of 30 August 2001 located at 4.05 deg E drifting at 1.213 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 28.51E drifting at 1.239W degrees per day.
1975 December 18 - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Funding for the activation of SLC-3E - . Congress approved funding for the activation of SLC-3E, Vandenberg AFB, and its conversion to an Atlas F configuration..
1976 January 29 - . 23:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4A F-2 - .
Mass: 1,500 kg (3,300 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1985-12-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 8620 . COSPAR: 1976-010A. Apogee: 35,981 km (22,357 mi). Perigee: 35,924 km (22,322 mi). Inclination: 9.00 deg. Period: 1,444.60 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 29.5 deg W in 1976-79; over the Atlantic Ocean 27.5 deg W in 1979-1980; over the Atlantic Ocean 21.5 deg W in 1980-1983; over the Indian Ocean 57 deg E in 1983-1984; over the Atlantic Ocean 2-4 deg W in 1984-1985 As of 3 September 2001 located at 151.88 deg E drifting at 2.088 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 130.98W drifting at 2.123W degrees per day.
1976 Mar - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Construction began on SLC-3E, Vandenberg - . Construction began on the activation of SLC-3E, Vandenberg AFB, and its conversion to an Atlas F configuration..
1976 April 30 - . 19:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/MSD.
- NOSS 1 (Whitecloud 1) - . Payload: PARCAE 1 / OPS 6431. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 8818 . COSPAR: 1976-038A. Apogee: 1,128 km (700 mi). Perigee: 1,092 km (678 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 107.50 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- SSU 2 (NOSS 1) - . Payload: NOSS-Subsat 1-2. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 8836 . COSPAR: 1976-038D. Apogee: 1,286 km (799 mi). Perigee: 931 km (578 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Deployed from NOSS 1..
- SSU 1 (NOSS 1) - . Payload: NOSS-Subsat 1-1. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 8835 . COSPAR: 1976-038C. Apogee: 1,284 km (797 mi). Perigee: 932 km (579 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Deployed from NOSS 1..
- SSU 3 (NOSS 1) - . Payload: NOSS-Subsat 1-3. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 8884 . COSPAR: 1976-038J. Apogee: 1,324 km (822 mi). Perigee: 893 km (554 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Deployed from NOSS 1..
1976 May 13 - . 22:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Comstar 1 - .
Payload: Comstar 1A. Mass: 792 kg (1,746 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Comsat.
Program: Comstar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1984-10-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 8838 . COSPAR: 1976-042A. Apogee: 35,925 km (22,322 mi). Perigee: 35,903 km (22,309 mi). Inclination: 12.70 deg. Period: 1,442.60 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 128 deg W in 1976-1981 over the Americas at 95 deg W in 1981-1983 over the Atlantic Ocean 76 deg W in 1983-1984 As of 4 September 2001 located at 48.64 deg E drifting at 1.641 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 31.21E drifting at 1.624W degrees per day.
1976 July 22 - . 22:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Comstar 2 - .
Payload: Comstar 1B. Mass: 792 kg (1,746 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Comsat.
Program: Comstar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-12-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 9047 . COSPAR: 1976-073A. Apogee: 35,887 km (22,299 mi). Perigee: 35,855 km (22,279 mi). Inclination: 12.60 deg. Period: 1,440.40 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 95 deg W in 1976-1983 over the Americas at 76 deg W in 1983-1993 As of 28 August 2001 located at 172.63 deg W drifting at 1.031 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 150.18W drifting at 1.064W degrees per day.
1977 Mar - . Launch Site: , Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Space Launch Complex 3 East completed. - . The task of activating Space Launch Complex 3 East, Vandenberg AFB, and converting it to an Atlas F configuration was completed..
1977 May 23 - . 18:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- Canyon 7 - . Payload: Canyon Improved / OPS 9751. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO, USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Canyon. USAF Sat Cat: 10016 . COSPAR: 1977-038A. Apogee: 35,855 km (22,279 mi). Perigee: 35,679 km (22,169 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,435.10 min.
1977 May 26 - . 21:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4A F-4 - .
Mass: 1,500 kg (3,300 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1989-08-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 10024 . COSPAR: 1977-041A. Apogee: 36,075 km (22,415 mi). Perigee: 35,969 km (22,350 mi). Inclination: 7.80 deg. Period: 1,448.20 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Atlantic Ocean at 34.5 deg W in 1977-1983 over the Atlantic Ocean 21.5 deg W in 1983-1989 As of 28 August 2001 located at 153.30 deg E drifting at 2.976 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 121.69W drifting at 3.003W degrees per day.
1977 June 23 - . 09:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/SVS.
- NTS 2 - .
Mass: 431 kg (950 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF,
USN.
Program: Navstar.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: NTS.
USAF Sat Cat: 10091 . COSPAR: 1977-053A. Apogee: 20,256 km (12,586 mi). Perigee: 20,115 km (12,498 mi). Inclination: 63.90 deg. Period: 718.10 min.
An Atlas booster and a Global Positioning System Stage Vehicle launched Navigation Technology Satellite 2 into orbit from Vandenberg AFB, California. This was the first use of the GPS Stage Vehicle. Navigation Technical Satellite; GPS precursor. Operated 50% satisfactorily -- still operating 25 years later.
1977 August 12 - . 06:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- HEAO 1 - . Payload: HEAO A. Mass: 2,720 kg (5,990 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Huntsville. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: HEAO. Decay Date: 1979-03-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 10217 . COSPAR: 1977-075A. Apogee: 447 km (277 mi). Perigee: 429 km (266 mi). Inclination: 22.70 deg. Period: 93.40 min. High Energy Astronomical Observatory; surveyed sky in X-ray band. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1977 September 30 - . 01:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur. FAILURE: Atlas failure - gas generator hot gas leak.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Intelsat IVA F-5 - . Mass: 1,500 kg (3,300 lb). Nation: International. Agency: Intelsat. Program: Intelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353. Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A. Decay Date: 1977-09-29 .
1977 December 8 - . 17:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/MSD.
- NOSS 2 - . Payload: PARCAE 2 / OPS 8781. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 10502 . COSPAR: 1977-112A. Apogee: 1,169 km (726 mi). Perigee: 1,054 km (654 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.50 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- SS 1 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 10529 . COSPAR: 1977-112D. Apogee: 1,169 km (726 mi). Perigee: 1,054 km (654 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.50 min. Deployed from NOSS 2..
- SS 3 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 10594 . COSPAR: 1977-112F. Apogee: 1,168 km (725 mi). Perigee: 1,055 km (655 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.50 min. Deployed from NOSS 2..
- SS 2 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 10544 . COSPAR: 1977-112E. Apogee: 1,168 km (725 mi). Perigee: 1,055 km (655 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.50 min. Deployed from NOSS 2..
1977 December 11 - . 22:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- OPS 4258 - . Payload: AFP-472 AQUACADE 3. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Rhyolite. USAF Sat Cat: 10508 . COSPAR: 1977-114A. Apogee: 35,855 km (22,279 mi). Perigee: 35,679 km (22,169 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,435.10 min. Third launch of Rhyolite geostationary ELINT satellite. Code name changed to Aquacade after Rhyolite name came out in trial of spy Boyce..
1978 January 7 - . 00:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4A F-3 - .
Mass: 1,511 kg (3,331 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1988-11-16 . USAF Sat Cat: 10557 . COSPAR: 1978-002A. Apogee: 35,909 km (22,312 mi). Perigee: 35,874 km (22,291 mi). Inclination: 7.20 deg. Period: 1,441.50 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 60 deg E in 1978-1982 over the Pacific Ocean 179 deg E in 1982-1986 over the Pacific Ocean 177 deg E in 1986-1988 As of 2 September 2001 located at 156.51 deg W drifting at 1.304 deg W per day. As of 2007 Feb 27 located at 107.90E drifting at 1.326W degrees per day.
1978 February 9 - . 21:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Fltsatcom 1 - .
Mass: 1,884 kg (4,153 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom.
USAF Sat Cat: 10669 . COSPAR: 1978-016A. Apogee: 36,170 km (22,470 mi). Perigee: 36,119 km (22,443 mi). Inclination: 14.60 deg. Period: 1,454.40 min.
An Atlas booster was launched from Cape Canaveral carrying the first FLTSATCOM satellite. The launch was successful, and the satellite functioned normally once in orbit. It was declared operational on 4 April. Fleet Satellite Communications. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 100 deg W in 1978-1987; over the Pacific Ocean 177 deg W in 1987-1992; over the Atlantic Ocean 15 deg W in 1992-1996;over the Indian Ocean 72 deg E in 1996-2001. Last known longitude (26 July 1999) 71.17 deg E drifting at 0.004 deg W per day.
1978 February 22 - . 23:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/SVS.
- Navstar 1 - .
Payload: GPS SVN 1 / OPS 5111. Mass: 759 kg (1,673 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Seal Beach.
Program: Navstar.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar.
Spacecraft: GPS Block 1.
USAF Sat Cat: 10684 . COSPAR: 1978-020A. Apogee: 20,560 km (12,770 mi). Perigee: 20,249 km (12,582 mi). Inclination: 64.50 deg. Period: 727.00 min.
An Atlas booster was launched from Vandenberg AFB carrying the first NAVSTAR Satellite. The launch was successful, and the satellite functioned normally once in orbit. It was declared operational on 31 March. Also known as Navigational Development Satellite 1. Technology prototype of Navstar satellite.
1978 March 31 - . 23:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 4A F-6 - .
Mass: 826 kg (1,821 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1986-12-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 10778 . COSPAR: 1978-035A. Apogee: 35,823 km (22,259 mi). Perigee: 35,758 km (22,218 mi). Inclination: 11.60 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean at 63 deg E in 1978-1982; over the Pacific Ocean 174 deg E in 1982-1986; over the Pacific Ocean 170 deg E in 1986 As of 26 August 2001 located at 92.43 deg E drifting at 0.407 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 75.50E drifting at 0.437W degrees per day.
1978 April 7 - . 00:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3A Agena D.
- OPS 8790 - . Payload: AFP-472 AQUACADE 4. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: CIA, NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Rhyolite. USAF Sat Cat: 10787 . COSPAR: 1978-038A. Apogee: 35,855 km (22,279 mi). Perigee: 35,679 km (22,169 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,435.10 min. Fourth and final launch of Rhyolite geostationary ELINT satellite. Code name changed to Aquacade after Rhyolite name came out in trial of spy Boyce..
1978 May 13 - . 10:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/SVS.
- Navstar 2 - .
Payload: GPS SVN 2 / OPS 5112. Mass: 759 kg (1,673 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Seal Beach.
Program: Navstar.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar.
Spacecraft: GPS Block 1.
USAF Sat Cat: 10893 . COSPAR: 1978-047A. Apogee: 20,653 km (12,833 mi). Perigee: 19,523 km (12,131 mi). Inclination: 63.60 deg. Period: 714.20 min.
An Atlas booster was launched from Vandenberg AFB with the second NAVSTAR satellite. Launch was successful and the satellite functioned normally once in orbit. It began operating at its final station on 27 June. Also known as Navigational Development Satellite 2. Technology prototype of Navstar satellite.
1978 May 20 - . 13:13 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Pioneer Venus Orbiter - .
Payload: Pioneer-Venus 1. Mass: 582 kg (1,283 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Ames.
Program: Pioneer.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 12.
Decay Date: 1992-10-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 10911 . COSPAR: 1978-051A.
The Pioneer Venus Orbiter was inserted into an elliptical orbit around Venus on December 4, 1978. After entering orbit around Venus in 1978, the spacecraft returned global maps of the planet's clouds, atmosphere and ionosphere, measurements of the atmosphere-solar wind interaction, and radar maps of 93 percent of the planet's surface. Additionally, the vehicle made use of several opportunities to make systematic UV observations of several comets. From Venus orbit insertion to July 1980, periapsis was held between 142 and 253 km (at 17 degrees north latitude) to facilitate radar and ionospheric measurements. The spacecraft was in a 24 hour orbit with an apoapsis of 66,900 km. Thereafter, the periapsis was allowed to rise (to 2290 km at maximum) and then fall, to conserve fuel. In 1991 the Radar Mapper was reactivated to investigate previously inaccessible southern portions of the planet. In May 1992 Pioneer Venus began the final phase of its mission, in which the periapsis was held between 150 and 250 km until the fuel ran out and atmospheric entry destroyed the spacecraft. With a planned primary mission duration of only eight months, the spacecraft remained in operation until October 8, 1992 when it finally burned up in Venus' atmosphere after running out of propellant.
1978 June 27 - . 01:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/Agena D.
- Seasat 1 - .
Payload: Seasat A. Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: JPL,
NASA.
Class: Earth.
Type: Civilian Radarsat. Spacecraft: Seasat.
USAF Sat Cat: 10967 . COSPAR: 1978-064A. Apogee: 765 km (475 mi). Perigee: 761 km (472 mi). Inclination: 108.00 deg. Period: 100.10 min.
An Atlas booster launched SEASAT-A, a NASA satellite. The purpose of the mission was to evaluate the use of microwave instruments to obtain oceanographic data. The launch was successful, but the satellite ceased functioning because of an electrical short after 99 days of operation. Oceanographic. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
1978 June 29 - . 22:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Comstar 3 - .
Payload: Comstar 1C. Mass: 1,520 kg (3,350 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Comsat.
Program: Comstar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
Completed Operations Date: 1986-05-21 . USAF Sat Cat: 10975 . COSPAR: 1978-068A. Apogee: 36,172 km (22,476 mi). Perigee: 36,007 km (22,373 mi). Inclination: 11.50 deg. Period: 1,451.60 min.
US domestic telephone service. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit over the Americas at 87 deg W in 1978-1984 over the Americas at 76 deg W in 1984-1986 As of 1 September 2001 located at 101.79 deg W drifting at 3.884 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 4 located at 39.19E drifting at 3.878W degrees per day.
1978 August 8 - . 07:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Pioneer Venus 2 - .
Payload: Pioneer-Venus 2. Mass: 904 kg (1,992 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Ames.
Program: Pioneer.
Class: Venus.
Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 13.
Decay Date: 1978-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 11001 . COSPAR: 1978-078A.
The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe consisted of a bus which carried one large and three small `atmospheric probes. The large probe was released on November 16, 1978 and the three small probes on November 20. All four probes entered the Venus atmosphere on December 9, followed by the bus. The small probes were each targeted at different parts of the planet and were named accordingly. The North probe entered the atmosphere at about 60 degrees north latitude on the day side. The night probe entered on the night side. The day probe entered well into the day side, and was the only one of the four probes which continued to send radio signals back after impact, for over an hour. With no heat shield or parachute, the bus survived and made measurements only to about 110 km altitude before burning up. It afforded the only direct view of the upper Venus atmosphere, as the probes did not begin making direct measurements until they had decelerated lower in the atmosphere.
- Pioneer Venus Probe 3 - . Payload: Pioneer-Venus 2. Mass: 90 kg (198 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Ames. Program: Pioneer. Class: Venus. Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 13. Decay Date: 1978-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 12105 . COSPAR: 1978-078F.
- Pioneer Venus Probe 1 - . Payload: Pioneer-Venus 2. Mass: 315 kg (694 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Ames. Program: Pioneer. Class: Venus. Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 13. Decay Date: 1978-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 12103 . COSPAR: 1978-078D.
- Pioneer Venus Probe 2 - . Payload: Pioneer-Venus 2. Mass: 90 kg (198 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Ames. Program: Pioneer. Class: Venus. Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 13. Decay Date: 1978-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 12104 . COSPAR: 1978-078E.
- Pioneer Venus Probe 4 - . Payload: Pioneer-Venus 2. Mass: 90 kg (198 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Ames. Program: Pioneer. Class: Venus. Type: Venus probe. Spacecraft: Pioneer 13. Decay Date: 1978-12-09 . USAF Sat Cat: 12106 . COSPAR: 1978-078G.
1978 October 7 - . 00:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/SVS.
- Navstar 3 - .
Payload: GPS SVN 3 / OPS 5113. Mass: 759 kg (1,673 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Seal Beach.
Program: Navstar.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar.
Spacecraft: GPS Block 1.
USAF Sat Cat: 11054 . COSPAR: 1978-093A. Apogee: 20,941 km (13,012 mi). Perigee: 20,706 km (12,866 mi). Inclination: 63.30 deg. Period: 744.20 min.
The third NAVSTAR satellite was launched from Vandenberg AFB on board an Atlas booster. Both the booster and the satellite itself functioned normally, and the satellite began operating at its final station on 31 October. Technology prototype of Navstar satellite.
1978 October 13 - . 11:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- Tiros N - .
Mass: 734 kg (1,618 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Program: Tiros.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Tiros N.
USAF Sat Cat: 11060 . COSPAR: 1978-096A. Apogee: 845 km (525 mi). Perigee: 829 km (515 mi). Inclination: 98.70 deg. Period: 101.70 min.
An Atlas booster launched a TIROS-N prototype weather satellite designed and funded by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The launch took place at Vandenberg AFB and was successful. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
1978 November 13 - . 05:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- HEAO 2 - . Payload: HEAO B. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Huntsville. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: HEAO. Decay Date: 1982-03-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 11101 . COSPAR: 1978-103A. Apogee: 548 km (340 mi). Perigee: 526 km (326 mi). Inclination: 23.50 deg. Period: 95.40 min. High Energy Astronomy Observatory. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1978 December 11 - . 03:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/SVS.
- Navstar 4 - . Payload: GPS SVN 4 / OPS 5114. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. USAF Sat Cat: 11141 . COSPAR: 1978-112A. Apogee: 21,012 km (13,056 mi). Perigee: 20,750 km (12,890 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 746.50 min. The fourth NAVSTAR satellite was successfully launched from Vandenberg AFB on board an Atlas booster. The satellite was due to begin operating at its final station in early January 1979. Global Positioning System. First pre-opertional Navstar satellite..
1978 December 12 - . LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- More powerful upper stage for GPS satellites. - . Spacecraft: Navstar. SAMSO released a draft RFP for a more powerful stage vehicle to be used on the Atlas F in launching GPS satellites..
1979 February 24 - . 08:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/OIS.
- Solwind (P 78-1) - .
Payload: P 78-1. Mass: 1,331 kg (2,934 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Space Test Program Payloads.
Spacecraft: Solwind.
Decay Date: 1985-09-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 11278 . COSPAR: 1979-017A. Apogee: 317 km (196 mi). Perigee: 310 km (190 mi). Inclination: 97.80 deg. Period: 90.80 min.
Atlas booster 27F successfully launched Space Test Program Flight P78-1 from Space Launch Complex 3W, Vandenberg AFB, California. The primary payload on the spacecraft was a gamma spectrometer sponsored by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). Ionosphere and magnetosphere studies; destroyed on 13 September 1985 (while still functioning) as part of an American ASAT test.
1979 May 4 - . 18:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Fltsatcom 2 - .
Mass: 1,884 kg (4,153 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom.
Completed Operations Date: 1992-02-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 11353 . COSPAR: 1979-038A. Apogee: 36,331 km (22,574 mi). Perigee: 36,227 km (22,510 mi). Inclination: 13.50 deg. Period: 1,461.30 min.
The second FLTSATCOM satellite was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on board an Atlas/Centaur booster. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 23 deg W in 1979-1980; 72 deg E in 1980-1992 As of 5 September 2001 located at 90.48 deg W drifting at 6.234 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 12.01W drifting at 6.223W degrees per day.
1979 June 14 - . LV Family: Atlas.
- Contract for SGS-II upper stage vehicles for use with Atlas boosters to launch GPS. - .
Spacecraft: Navstar.
SAMSO awarded the McDonnell Douglas Astronautics Company a contract for two SGS-II upper stage vehicles, with an option for five more. The vehicles would be used with Atlas boosters to launch GPS. SAMSO awarded the McDonnell Douglas Astronautics Company a contract for two SGS-II upper stage vehicles, with an option for five more. The vehicles would be used with Atlas boosters to launch GPS.
1979 June 27 - . 15:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- NOAA 6 - . Payload: NOAA A. Mass: 723 kg (1,593 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 11416 . COSPAR: 1979-057A. Apogee: 800 km (490 mi). Perigee: 785 km (487 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 100.70 min. Atlas booster 25F successfully launched NASA's NOAA-A satellite from Vandenberg AFB, California. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1979 September 20 - . 05:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- HEAO 3 - . Payload: HEAO C. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: HEAO. Decay Date: 1981-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 11532 . COSPAR: 1979-082A. Apogee: 503 km (312 mi). Perigee: 487 km (302 mi). Inclination: 43.60 deg. Period: 94.50 min. High Energy Astronomy Observatory; cosmic, gamma ray measurements. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1980 January 18 - . 01:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Fltsatcom 3 - .
Mass: 1,884 kg (4,153 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom.
Completed Operations Date: 1991-01-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 11669 . COSPAR: 1980-004A. Apogee: 35,851 km (22,276 mi). Perigee: 35,669 km (22,163 mi). Inclination: 9.10 deg. Period: 1,434.80 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 22 deg W in 1980-1990 As of 28 August 2001 located at 174.83 deg W drifting at 0.082 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 84.20W drifting at 0.376E degrees per day.
1980 February 9 - . 23:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/SVS.
- Navstar 5 - . Payload: GPS SVN 5 / OPS 5117. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. USAF Sat Cat: 11690 . COSPAR: 1980-011A. Apogee: 20,560 km (12,770 mi). Perigee: 19,805 km (12,306 mi). Inclination: 64.90 deg. Period: 718.00 min. Global Positioning System..
1980 March 3 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/MSD.
- EP-2 (NOSS 3) - . Payload: Plume shield / OPS 7245 DEB. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 11733 . COSPAR: 1980-019E. Apogee: 1,166 km (724 mi). Perigee: 1,048 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
- NOSS 3 - . Payload: PARCAE 3 / OPS 7245. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 11720 . COSPAR: 1980-019A. Apogee: 1,150 km (710 mi). Perigee: 1,035 km (643 mi). Inclination: 63.00 deg. Period: 107.10 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- EP 3 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 11745 . COSPAR: 1980-019G. Apogee: 1,166 km (724 mi). Perigee: 1,048 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Deployed from NOSS 3. .
- EP 1 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 11731 . COSPAR: 1980-019C. Apogee: 1,166 km (724 mi). Perigee: 1,048 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Deployed from NOSS 3..
- EP 2 - . Payload: SSU. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 11732 . COSPAR: 1980-019D. Apogee: 1,484 km (922 mi). Perigee: 730 km (450 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.41 min.
1980 April 26 - . 22:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F/SVS.
- Navstar 6 - . Payload: GPS SVN 6 / OPS 5118. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. USAF Sat Cat: 11783 . COSPAR: 1980-032A. Apogee: 20,471 km (12,720 mi). Perigee: 19,387 km (12,046 mi). Inclination: 62.80 deg. Period: 707.80 min. Global Positioning System..
1980 May 29 - . 10:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F. FAILURE: Atlas sustainer engine under-thrust resulted in 50 second extended burn time, and spacecraft attempted to separate and fired apogee kick motor while booster was still thrusting.. Failed Stage: P.
- NOAA B - .
Payload: NOAA B. Mass: 1,405 kg (3,097 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Program: Tiros.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Tiros N.
Decay Date: 1981-05-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 11819 . COSPAR: 1980-043A. Apogee: 1,445 km (897 mi). Perigee: 264 km (164 mi). Inclination: 92.20 deg. Period: 102.10 min.
Unusable orbit; would have been NOAA 7. At engine start up, one of the booster engines suffered an internal fuel leak, causing it to run at about 80% thrust. As a result the booster was low on velocity and heavy on propellant over much of its flight and ran an incredible 50 seconds longer than the nominal burn. The NOAA Advanced TIROS payload was designed with no direct communication with the booster, and unaware of the booster problem, at 375 sec after liftoff attempted to separate with the booster still firing. The booster's continued thrusting defeated the payload's attempt to perform the required pitch maneuver. When the payload fired its apogee kick motor, it blew the top of the booster's liquid oxygen tank off. The spacecraft survived all this, but the resultant orbit was highly elliptical rather than the desired circular sun-synchronous. The mission was a total loss. Officially: Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).>
1980 October 31 - . 03:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Fltsatcom 4 - .
Mass: 1,800 kg (3,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom.
USAF Sat Cat: 12046 . COSPAR: 1980-087A. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,769 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 9.20 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 171 deg E from 1981. Last known longitude (25 July 1999) 172.61 deg E drifting at 0.001 deg W per day.
1980 December 6 - . 23:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 5 F-2 - .
Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Intelsat 5.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-04-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 12089 . COSPAR: 1980-098A. Apogee: 36,242 km (22,519 mi). Perigee: 36,118 km (22,442 mi). Inclination: 9.70 deg. Period: 1,456.20 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 21 deg W in 1981; 27 deg W in 1981-1983; 34 deg W in 1983-1985; 27 deg W in 1985; 1 deg W in 1985-1989; 21 deg W in 1989-1994; 40 deg W in 1994-1998 As of 2 September 2001 located at 103.82 deg W drifting at 5.004 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 81.84W drifting at 5.000W degrees per day.
1980 December 9 - . 07:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/MSD. FAILURE: Premature shut down of one of the Atlas booster engines turned the vehicle around, thereafter the sustainer thrust it back toward the earth.. Failed Stage: 1.
- NOSS - .
Payload: PARCAE 4. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS.
Decay Date: 1980-12-08 . COSPAR: F801209A.
Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE. Other sources give the payload designation ABSAD. The failure was caused by a loss of lubricating oil to one of the booster engines, causing the engine to fail approx 200 milliseconds before it was to have shut down on guidance command. The asymmetric thrust pivoted the booster around approximately 180 degrees, where it stabilized in a retrofire attitude with the sustainer engine still firing. It descended back toward earth through its own exhaust flame and exploded a couple of minutes later.
- SSU - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. COSPAR: F801209D.
- SSU - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. COSPAR: F801209C.
- SSU - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF AFSC. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. COSPAR: F801209B.
1981 February 21 - . 23:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Comstar 4 - .
Payload: Comstar 1D. Mass: 1,520 kg (3,350 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Comsat.
Program: Comstar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: HS 312 / HS 351 / HS 353.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 4A.
USAF Sat Cat: 12309 . COSPAR: 1981-018A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 7.20 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 142 deg W in 1981; 127 deg W in 1981-1985; 76 deg W in 1985-on. As of 31 August 2001 located at 25.65 deg W drifting at 1.067 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 78.95E drifting at 0.039W degrees per day.
1981 May 23 - . 22:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 5 F-1 - .
Payload: Intelsat 501. Mass: 1,928 kg (4,250 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Intelsat 5.
Completed Operations Date: 1997-02-08 . USAF Sat Cat: 12474 . COSPAR: 1981-050A. Apogee: 36,224 km (22,508 mi). Perigee: 36,151 km (22,463 mi). Inclination: 10.10 deg. Period: 1,456.60 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1981; 60 deg E in 1982-1984; 57 deg E in 1984-1986; 174 deg E in 1986-1988; 177 deg E in 1988-1990; 177 deg W in 1990-1992; 91 deg E in 1993-1996; 72 deg E in 1996-1997 As of 4 September 2001 located at 169.69 deg W drifting at 5.095 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 13.28E drifting at 5.096W degrees per day.
1981 June 23 - . 10:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- NOAA 7 - . Payload: NOAA C. Mass: 1,405 kg (3,097 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 12553 . COSPAR: 1981-059A. Apogee: 847 km (526 mi). Perigee: 828 km (514 mi). Inclination: 98.90 deg. Period: 101.70 min. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1981 August 6 - . 08:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur. FAILURE: Failure of the fiberglass fairing during ascent.. Failed Stage: S.
- Fltsatcom 5 - .
Mass: 1,884 kg (4,153 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom.
Completed Operations Date: 1986-07-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 12635 . COSPAR: 1981-073A. Apogee: 36,300 km (22,500 mi). Perigee: 36,221 km (22,506 mi). Inclination: 8.90 deg. Period: 1,460.40 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit. The Atlas G Centaur delivered a badly damaged but operating FLTSATCOM spacecraft to its correct orbit. Investigation showed that the most likely cause was failure of the fiberglass fairing during ascent. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg W in 1981; 90-114 deg W in 1982; 44 deg W in 1982-1986 As of 5 September 2001 located at 140.32 deg W drifting at 6.003 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 31.85E drifting at 6.002W degrees per day.
1981 December 15 - . 23:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 5 F-3 - .
Mass: 1,870 kg (4,120 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Intelsat 5.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-01-19 . USAF Sat Cat: 12994 . COSPAR: 1981-119A. Apogee: 36,129 km (22,449 mi). Perigee: 35,894 km (22,303 mi). Inclination: 9.40 deg. Period: 1,447.60 min.
Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1982-1985; 27 deg W in 1985; 53 deg W in 1985-1988; 174 deg E in 1988-1990; 177 deg E in 1990-1992; 177 deg W in 1992-1995; 157 deg E in 1995-1998 As of 5 September 2001 located at 57.52 deg W drifting at 2.890 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 101.94W drifting at 2.904W degrees per day.
1981 December 19 - . 01:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/SVS. FAILURE: Failure.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Navstar 7 - . Payload: GPS SVN 7. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. Decay Date: 1981-12-18 . Global Positioning System..
1982 March 5 - . 00:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 5 F-4 - .
Mass: 1,928 kg (4,250 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Intelsat 5.
Completed Operations Date: 1995-11-28 . USAF Sat Cat: 13083 . COSPAR: 1982-017A. Apogee: 36,243 km (22,520 mi). Perigee: 35,920 km (22,310 mi). Inclination: 9.40 deg. Period: 1,451.20 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 32 deg E in 1982; 63 deg E in 1982; 27 deg W in 1983-1985; 34 deg W in 1985-1992; 40 deg W in 1992; 31 deg W in 1993-1995; 29 deg W in 1995 As of 1 September 2001 located at 4.64 deg W drifting at 3.747 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 7 located at 4.34W drifting at 3.748W degrees per day.
1982 September 28 - . 23:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 5 F-5 - .
Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Intelsat 5.
USAF Sat Cat: 13595 . COSPAR: 1982-097A. Apogee: 36,404 km (22,620 mi). Perigee: 36,228 km (22,510 mi). Inclination: 9.00 deg. Period: 1,463.30 min.
Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 63 deg E in 1982-1990; 66 deg E in 1991-1996; 33 deg E in 1996; 72 deg E in 1997-on. As of 3 September 2001 located at 16.28 deg E drifting at 6.707 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 163.88W drifting at 6.709W degrees per day.
1982 December 21 - . 02:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- AMS 5 - . Payload: DMSP S-6 / OPS 9845. Mass: 750 kg (1,650 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 13736 . COSPAR: 1982-118A. Apogee: 810 km (500 mi). Perigee: 797 km (495 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 100.90 min. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program..
1983 February 9 - . 13:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas H.
- NOSS 4 - . Payload: PARCAE 5 / OPS 0252. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 13791 . COSPAR: 1983-008A. Apogee: 1,186 km (736 mi). Perigee: 1,063 km (660 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.80 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- LIPS 2 - . Payload: LIPS 2. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Spacecraft: LIPS. USAF Sat Cat: 13792 . COSPAR: 1983-008B. Apogee: 1,399 km (869 mi). Perigee: 822 km (510 mi). Inclination: 63.30 deg. Period: 107.49 min.
- SSB - . Payload: SSU. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 13845 . COSPAR: 1983-008F. Apogee: 1,489 km (925 mi). Perigee: 733 km (456 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.42 min.
- SSD (NOSS 4) - . Payload: NOSS-Subsat 4-4. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 13834 . COSPAR: 1983-008C. Apogee: 1,419 km (881 mi). Perigee: 796 km (494 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.42 min. Released from NOSS 4. .
- SSA (NOSS 4) - . Payload: NOSS-Subsat 4-1 / OPS 0252 DEB. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 13835 . COSPAR: 1983-008D. Apogee: 1,164 km (723 mi). Perigee: 1,051 km (653 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Released from NOSS 4..
- SSA - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 13844 . COSPAR: 1983-008E. Apogee: 1,166 km (724 mi). Perigee: 1,051 km (653 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Released from NOSS 4..
- SSC - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 13874 . COSPAR: 1983-008H. Apogee: 1,173 km (728 mi). Perigee: 1,043 km (648 mi). Inclination: 63.50 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Released from NOSS 4..
1983 March 28 - . 15:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- NOAA 8 - . Payload: NOAA E. Mass: 3,775 kg (8,322 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 13923 . COSPAR: 1983-022A. Apogee: 817 km (507 mi). Perigee: 793 km (492 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 101.00 min. Carried search and rescue package. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1983 May 19 - . 22:26 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- Intelsat 5 F-6 - .
Mass: 1,928 kg (4,250 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Intelsat 5.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-07-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 14077 . COSPAR: 1983-047A. Apogee: 36,125 km (22,446 mi). Perigee: 36,076 km (22,416 mi). Inclination: 8.30 deg. Period: 1,452.10 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 29 deg E in 1983; 18 deg W in 1983-1992; 34 deg W in 1992; 50 deg W in 1992-1995; 31 deg W in 1995-1998 As of 4 September 2001 located at 47.96 deg E drifting at 3.999 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 62.15W drifting at 3.995W degrees per day.
1983 June 9 - . 23:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas H.
- NOSS 5 - . Payload: PARCAE 6 / OPS 6432. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 14112 . COSPAR: 1983-056A. Apogee: 1,167 km (725 mi). Perigee: 1,049 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- GB1 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 14143 . COSPAR: 1983-056C. Apogee: 1,167 km (725 mi). Perigee: 1,049 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Deployed from NOSS 5..
- GB2 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 14144 . COSPAR: 1983-056D. Apogee: 1,167 km (725 mi). Perigee: 1,049 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Deployed from NOSS 5..
- GB3 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 14180 . COSPAR: 1983-056G. Apogee: 1,166 km (724 mi). Perigee: 1,049 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
1983 July 14 - . 10:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/SGS-2.
- Navstar 8 - . Payload: GPS SVN 8 / OPS 9794. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. USAF Sat Cat: 14189 . COSPAR: 1983-072A. Apogee: 21,229 km (13,191 mi). Perigee: 20,757 km (12,897 mi). Inclination: 64.20 deg. Period: 751.10 min. Global Positioning System..
1983 November 18 - . 06:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- DMSP-Block-5B5D2-2 - . Payload: DMSP S-7 / OPS 1294. Mass: 750 kg (1,650 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 14506 . COSPAR: 1983-113A. Apogee: 818 km (508 mi). Perigee: 801 km (497 mi). Inclination: 98.40 deg. Period: 101.10 min. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program..
1984 February 5 - . 18:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas H.
- NOSS 6 - . Payload: PARCAE 7 / OPS 8737. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 14690 . COSPAR: 1984-012A. Apogee: 1,172 km (728 mi). Perigee: 1,052 km (653 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.00 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- JD3 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 14795 . COSPAR: 1984-012F. Apogee: 1,172 km (728 mi). Perigee: 1,052 km (653 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.00 min.
- JD1 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 14728 . COSPAR: 1984-012C. Apogee: 1,172 km (728 mi). Perigee: 1,052 km (653 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.00 min. Deployed from NOSS 6..
- JD2 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 14729 . COSPAR: 1984-012D. Apogee: 1,172 km (728 mi). Perigee: 1,052 km (653 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.00 min. Deployed from NOSS 6..
1984 June 9 - . 23:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas G Centaur. FAILURE: Centaur structural failure. . Failed Stage: U.
- Intelsat 5 F-9 - . Mass: 1,091 kg (2,405 lb). Nation: International. Agency: Intelsat. Program: Intelsat. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Intelsat 5. Decay Date: 1984-10-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 15034 . COSPAR: 1984-057A. Apogee: 1,227 km (762 mi). Perigee: 180 km (110 mi). Inclination: 29.20 deg. Period: 98.90 min. Failure of Centaur upper stage left stranded in useless orbit. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle was to have put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
1984 June 13 - . 11:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/SGS-2.
- USA 1 - . Payload: GPS SVN 9. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. USAF Sat Cat: 15039 . COSPAR: 1984-059A. Apogee: 21,194 km (13,169 mi). Perigee: 20,681 km (12,850 mi). Inclination: 64.20 deg. Period: 748.80 min. Global Positioning System..
1984 September 8 - . 21:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/SGS-2.
- USA 5 - . Payload: GPS SVN 10. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. USAF Sat Cat: 15271 . COSPAR: 1984-097A. Apogee: 21,203 km (13,174 mi). Perigee: 20,612 km (12,807 mi). Inclination: 61.90 deg. Period: 747.60 min. Global Positioning System..
1984 December 12 - . 10:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- NOAA 9 - . Payload: NOAA F. Mass: 1,712 kg (3,774 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 15427 . COSPAR: 1984-123A. Apogee: 855 km (531 mi). Perigee: 833 km (517 mi). Inclination: 99.10 deg. Period: 101.80 min. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1985 February 6 - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas F.
- USAF - . Nation: USA.
1985 March 13 - . 02:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/OIS.
- Geosat - . Mass: 635 kg (1,399 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Earth. Type: Civilian Radarsat. Spacecraft: Geosat. USAF Sat Cat: 15595 . COSPAR: 1985-021A. Apogee: 779 km (484 mi). Perigee: 775 km (481 mi). Inclination: 108.10 deg. Period: 100.40 min. Ocean sea height mapping. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1985 March 22 - . 23:58 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas G Centaur.
- Intelsat 5A F-10 - .
Mass: 2,013 kg (4,437 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Intelsat 5.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 5A.
USAF Sat Cat: 15629 . COSPAR: 1985-025A. Apogee: 36,468 km (22,660 mi). Perigee: 36,237 km (22,516 mi). Inclination: 7.20 deg. Period: 1,465.10 min.
Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 24 deg W in 1985-1990; 174 deg E in 1990-1994; 66 deg E in 1994-1995; 57 deg E in 1995-1996; 33 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 135.23 deg W drifting at 7.152 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 107.21W drifting at 7.157W degrees per day.
1985 June 30 - . 00:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas G Centaur.
- Intelsat 5A F-11 - .
Mass: 1,098 kg (2,420 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Intelsat 5.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 5A.
USAF Sat Cat: 15873 . COSPAR: 1985-055A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.70 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 27 deg W in 1985-1990; 63 deg E in 1990-1992; 177 deg E in 1992-1994; 180 deg E in 1994-1997; 29 deg W in 1998-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 29.54 deg W drifting at 0.005 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 113.07W drifting at 0.696W degrees per day.
1985 September 28 - . 23:36 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas G Centaur.
- Intelsat 5A F-12 - .
Mass: 1,096 kg (2,416 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Intelsat 5.
Spacecraft: Intelsat 5A.
Completed Operations Date: 1998-06-23 . USAF Sat Cat: 16101 . COSPAR: 1985-087A. Apogee: 36,140 km (22,450 mi). Perigee: 36,086 km (22,422 mi). Inclination: 6.20 deg. Period: 1,452.80 min.
Telephone communications; 31 deg E. Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 60 deg E in 1985-1989; 1 deg W in 1989-1994; 21 deg W in 1994-1996; 56 deg W in 1996-1998 As of 28 August 2001 located at 145.57 deg E drifting at 4.159 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 19.14E drifting at 4.163W degrees per day.
1985 October 9 - . 02:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E/SGS-2.
- USA 10 - . Payload: GPS SVN 11. Mass: 770 kg (1,690 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Seal Beach. Program: Navstar. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft Bus: Navstar. Spacecraft: GPS Block 1. USAF Sat Cat: 16129 . COSPAR: 1985-093A. Apogee: 21,673 km (13,466 mi). Perigee: 20,765 km (12,902 mi). Inclination: 65.00 deg. Period: 760.40 min. Global Positioning System..
1986 February 9 - . 10:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas H.
- USA 15 - . Payload: PARCAE 8. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 16591 . COSPAR: 1986-014A. Apogee: 1,166 km (724 mi). Perigee: 1,049 km (651 mi). Inclination: 63.00 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- USA 18 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 16631 . COSPAR: 1986-014H. Apogee: 1,407 km (874 mi). Perigee: 817 km (508 mi). Inclination: 63.41 deg. Period: 107.44 min.
- USA 16 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 16624 . COSPAR: 1986-014E. Apogee: 1,161 km (721 mi). Perigee: 1,055 km (655 mi). Inclination: 63.00 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
- USA 17 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 16625 . COSPAR: 1986-014F. Apogee: 1,165 km (723 mi). Perigee: 1,055 km (655 mi). Inclination: 63.00 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
1986 September 17 - . 15:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- NOAA 10 - . Payload: NOAA G. Mass: 1,700 kg (3,700 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 16969 . COSPAR: 1986-073A. Apogee: 816 km (507 mi). Perigee: 795 km (493 mi). Inclination: 98.50 deg. Period: 101.00 min. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1986 December 5 - . 02:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas G Centaur.
- USA 20 - .
Payload: Fltsatcom 7. Mass: 2,310 kg (5,090 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom.
USAF Sat Cat: 17181 . COSPAR: 1986-096A. Apogee: 35,832 km (22,264 mi). Perigee: 35,740 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.90 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 100 deg W in 1987-1999 Last known longitude (27 July 1999) 100.33 deg W drifting at 0.027 deg W per day.
1987 March 26 - . 21:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas G Centaur. FAILURE: Lightning strike zapped guidance at T+51 seconds. Fault was directly attributed to a random memory upset that forced rocket to veer off course. Destroyed by range safety.. Failed Stage: G.
- Fltsatcom 6 - . Payload: Fltsatcom 6. Mass: 2,300 kg (5,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom. Decay Date: 1987-03-26 .
1987 May 15 - . 15:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas H.
- USA 22 - . Payload: PARCAE 9. Mass: 700 kg (1,540 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft: NOSS. USAF Sat Cat: 17997 . COSPAR: 1987-043A. Apogee: 1,179 km (732 mi). Perigee: 1,045 km (649 mi). Inclination: 62.90 deg. Period: 107.80 min. Ocean surveillance; aka White Cloud type spacecraft; Navy Ocean Surveillance Satellite; PARCAE..
- USA 24 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 18010 . COSPAR: 1987-043F. Apogee: 1,184 km (735 mi). Perigee: 1,046 km (649 mi). Inclination: 63.20 deg. Period: 107.90 min.
- LIPS 3 - . Payload: LIPS 3. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Spacecraft: LIPS. USAF Sat Cat: 18007 . COSPAR: 1987-043C. Apogee: 1,316 km (817 mi). Perigee: 899 km (558 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.42 min.
- USA 25 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 18025 . COSPAR: 1987-043H. Apogee: 1,178 km (731 mi). Perigee: 1,035 km (643 mi). Inclination: 62.60 deg. Period: 107.60 min.
- USA 23 - . Payload: SSU. Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Class: Surveillance. Type: Naval SIGINT. Spacecraft Bus: NOSS. Spacecraft: NOSS-Subsat. USAF Sat Cat: 18009 . COSPAR: 1987-043E. Apogee: 1,170 km (720 mi). Perigee: 1,039 km (645 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.30 min.
1987 June 20 - . 02:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- USA 26 - . Payload: DMSP S-9/Star 37S S/N 15019. Mass: 750 kg (1,650 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 18123 . COSPAR: 1987-053A. Apogee: 848 km (526 mi). Perigee: 828 km (514 mi). Inclination: 98.80 deg. Period: 101.70 min. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program..
1988 February 3 - . 05:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- USA 29 - . Payload: DMSP S-8/Star 37S S/N 15021. Mass: 750 kg (1,650 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 18822 . COSPAR: 1988-006A. Apogee: 817 km (507 mi). Perigee: 807 km (501 mi). Inclination: 98.50 deg. Period: 101.10 min. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program..
1988 September 24 - . 10:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- NOAA 11 - . Payload: NOAA H. Mass: 1,712 kg (3,774 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 19531 . COSPAR: 1988-089A. Apogee: 854 km (530 mi). Perigee: 838 km (520 mi). Inclination: 99.20 deg. Period: 101.90 min. Carried search & rescue package. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1989 September 25 - . 08:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas G Centaur.
- USA 46 - .
Payload: Fltsatcom 8. Mass: 2,310 kg (5,090 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Fltsatcom.
USAF Sat Cat: 20253 . COSPAR: 1989-077A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 4.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Last in series of 8. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 23 deg W in 1989-1999.
1990 April 11 - . 15:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E Altair.
- USA 56 - .
Payload: POGS & SSR. Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: MAESTRO.
Spacecraft: Stacksat P87-2.
USAF Sat Cat: 20560 . COSPAR: 1990-031A. Apogee: 745 km (462 mi). Perigee: 627 km (389 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 98.48 min.
Polar Orbiting Geomagnetic Survey satellite designed to measure the Earth's magnetic field vector as a function of position. Data from the experiment was used to improve Earth navigation systems, and was stored in an experimental solid state recorder. Six low cost ground stations were designed, built and located around the world to operate the spacecraft flown on this mission.
- USA 58 - . Payload: SCE. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: MAESTRO. Spacecraft: Stacksat P87-2. USAF Sat Cat: 20562 . COSPAR: 1990-031C. Apogee: 741 km (460 mi). Perigee: 627 km (389 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 98.44 min. SCE (Selective Communications Experiment) carried a variable frequency transmitter to study ionospheric effects at various RF frequencies, and was also designed to demonstrate message store and forward techniques..
- USA 57 - . Payload: TEX. Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft Bus: MAESTRO. Spacecraft: Stacksat P87-2. USAF Sat Cat: 20561 . COSPAR: 1990-031B. Apogee: 742 km (461 mi). Perigee: 627 km (389 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 98.45 min. TEX (Transceiver EXperiment) carried a variable power transmitter used to study ionospheric effects on RF transmissions. Data from the experiment was used to determine minimum spacecraft transmitter power levels for transmission to ground receivers..
1990 July 25 - . 19:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- CRRES - . Payload: CRRES (P 86-1). Mass: 1,629 kg (3,591 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: CRRES. USAF Sat Cat: 20712 . COSPAR: 1990-065A. Apogee: 34,739 km (21,585 mi). Perigee: 335 km (208 mi). Inclination: 18.00 deg. Period: 613.40 min. Combined Release and Radiation Effects Satellite. First launch of commercial Atlas-Centaur. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space. Elliptical orbit; MRS trajectory..
1990 December 1 - . 15:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E. FAILURE: Failure of the spacecraft's TEM-364-15 AKM nozzle due to a manufacturing defect led to the satellite being placed into lower than planned orbit.. Failed Stage: P.
- USA 68 - . Payload: DMSP S-10. Mass: 750 kg (1,650 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 20978 . COSPAR: 1990-105A. Apogee: 837 km (520 mi). Perigee: 724 km (449 mi). Inclination: 98.70 deg. Period: 100.50 min. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program; broken nozzle prevented satellite from reaching desired orbit..
1991 April 18 - . 23:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I. FAILURE: RL-10 Centaur engine turbopump failed at T+361 seconds; destroyed by range safety.. Failed Stage: U.
- Yuri 3H - . Payload: BS-3H. Mass: 600 kg (1,320 lb). Nation: Japan. Agency: TSCJ. Manufacturer: Lockheed. Program: BS. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 3000. Decay Date: 1991-04-18 . Apogee: 175 km (108 mi).
1991 May 14 - . 15:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- NOAA 12 - . Payload: NOAA D. Mass: 1,416 kg (3,121 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 21263 . COSPAR: 1991-032A. Apogee: 824 km (512 mi). Perigee: 805 km (500 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 101.20 min. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
1991 November 28 - . 13:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- USA 73 - . Payload: DMSP S-12/Star 37S S/N 15029. Mass: 830 kg (1,820 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 21798 . COSPAR: 1991-082A. Apogee: 852 km (529 mi). Perigee: 835 km (518 mi). Inclination: 99.00 deg. Period: 101.80 min. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program. 500th Atlas launch..
1991 December 7 - . 22:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- Eutelsat II F3 - .
Mass: 1,874 kg (4,131 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: Eutelsat.
Program: Eutelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 100.
USAF Sat Cat: 21803 . COSPAR: 1991-083A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,769 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 2.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Stationed at 16 deg E. Telecommunications satellite. French registration 1991-8. Transfer orbit was 663 min, 200 x 36000 km x 7.0 deg. Registered by France in ST/SG/SER.E/249 until EUTELSAT can register the satellite. EUTELSAT is the European Telecommunications Satellite Organi zation. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 16 deg E in 1992-1998; 36 deg E in 1999. As of 1 September 2001 located at 21.51 deg E drifting at 0.017 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 74.40E drifting at 3.531W degrees per day.
1992 February 11 - . 00:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 78 - . Payload: DSCS III B-14. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 21873 . COSPAR: 1992-006A. Apogee: 35,503 km (22,060 mi). Perigee: 30,675 km (19,060 mi). Inclination: 0.90 deg. Period: 1,300.50 min. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit; at 135 deg W in 1995..
1992 March 14 - . 00:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- Galaxy 5 - . Mass: 1,412 kg (3,112 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: HCI. Program: Galaxy. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376. USAF Sat Cat: 21906 . COSPAR: 1992-013A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,782 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Geostationary at 125 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 125 deg W in 1992-2001. As of 2007 Mar 8 located at 7.46E drifting at 3.538W degrees per day..
1992 June 10 - . 00:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Intelsat K - .
Mass: 2,928 kg (6,455 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 5000.
USAF Sat Cat: 21989 . COSPAR: 1992-032A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Stationed at 21.5 deg W. Intelsat K is a single spacecraft purchased to meet critical requirements for Ku-band capacity over the Atlantic region, driven primarily by international broadcasters. The satellite was purchased from GE Americom while under construction (as Satcom K4) and required extensive payload modifications. Spacecraft: Based on GE 5000 series bus.3-axis stabilised using magnetotorquers. Hydrazine propulsion system. Two large solar panels with 1-axis articulation provide 4800 W BOL.4 50 Ahr NiH batteries. Payload: 16 Ku-band transponders which can be configured into 32 high quality television channels. Permits access from ground antennas 1.2 meters dia. and smaller. Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 21 deg W in 1992-1999 As of 6 September 2001 located at 21.54 deg W drifting at 0.011 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 160.51W drifting at 11.137W degrees per day.
1992 July 2 - . 21:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 82 - .
Payload: DSCS III B-12. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III.
USAF Sat Cat: 22009 . COSPAR: 1992-037A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 12 deg W in 1995-1996. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
1992 August 22 - . 22:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I. FAILURE: Destroyed by range safety. Centaur engine turbopump did not start. Identical to the 18 April 1991 failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Galaxy 1R - . Payload: Galaxy 1R. Mass: 2,800 kg (6,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: HCI. Program: Galaxy. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 376. Decay Date: 1992-08-22 .
1993 March 25 - . 21:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I. FAILURE: Atlas engine failure. Loss of booster engine thrust resulted in a lower-than planned 1560 km x 1900 km orbit. Failed Stage: 1.
- UHF F1 - .
Payload: UHF F/O F1. Mass: 2,866 kg (6,318 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Program: UHF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
Completed Operations Date: 1993-07-01 . USAF Sat Cat: 22563 . COSPAR: 1993-015A. Apogee: 36,098 km (22,430 mi). Perigee: 36,053 km (22,402 mi). Inclination: 21.10 deg. Period: 1,450.90 min.
US Navy communications; Ultra High Frequency Follow On; unusable orbit. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle was to have put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. As of 28 August 2001 located at 45.55 deg W drifting at 3.676 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 95.89E drifting at 3.687W degrees per day.
1993 July 19 - . 22:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 93 - .
Payload: DSCS III B-9. Mass: 2,615 kg (5,765 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III.
USAF Sat Cat: 22719 . COSPAR: 1993-046A. Apogee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Perigee: 183 km (113 mi). Inclination: 26.10 deg. Period: 625.80 min.
Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 175 deg E in 1995-1997.
1993 August 9 - . 10:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- NOAA 13 - . Payload: NOAA I. Mass: 1,712 kg (3,774 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 22739 . COSPAR: 1993-050A. Apogee: 860 km (530 mi). Perigee: 846 km (525 mi). Inclination: 99.20 deg. Period: 102.00 min. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). .
1993 September 3 - . 11:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- USA 95 - .
Payload: UHF F/O F2. Mass: 2,844 kg (6,269 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Program: UHF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 22787 . COSPAR: 1993-056A. Apogee: 35,805 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,767 km (22,224 mi). Inclination: 5.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
US Navy communications. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 72 deg E in 1993-1999.
1993 November 28 - . 23:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 97 - .
Payload: DSCS III B-10. Mass: 2,615 kg (5,765 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III.
USAF Sat Cat: 22915 . COSPAR: 1993-074A. Apogee: 35,501 km (22,059 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 26.40 deg. Period: 625.40 min.
Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 52 deg W in 1995; 60 deg E in 1997. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C).
1993 December 16 - . 00:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Telstar 401 - .
Mass: 3,375 kg (7,440 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: ATT.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Telstar series.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 7000.
Completed Operations Date: 1997-01-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 22927 . COSPAR: 1993-077A. Apogee: 35,821 km (22,258 mi). Perigee: 35,759 km (22,219 mi). Inclination: 4.30 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Stationed at 97 deg W. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C). Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with IFR trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 97 deg W in 1994-1997 As of 5 September 2001 located at 100.42 deg W drifting at 0.039 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 97.36W drifting at 0.024W degrees per day.
1994 April 13 - . 06:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- GOES 8 - .
Payload: GOES I. Mass: 2,105 kg (4,640 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Program: GOES.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: FS-1300.
Spacecraft: GOES-Next.
USAF Sat Cat: 23051 . COSPAR: 1994-022A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,770 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Geostationary Environmental Satellite. Stationed at 75 deg W. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A). Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg W in 1994-1995; 75 deg W in 1995-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 74.78 deg W drifting at 0.019 deg E per day. NASA announced that GOES-8 was "de-orbited" (presumably moved to a sub-synchronous orbit) on May 5, 2004 after 10 years of service. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 87.46E drifting at 4.935W degrees per day.
1994 June 24 - . 13:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- USA 104 - . Payload: UHF F/O F3. Mass: 2,847 kg (6,276 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: HCI. Program: UHF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 23132 . COSPAR: 1994-035A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 4.81 deg. Period: 1,436.05 min. US Navy communications . Stationed at 14.38 deg W 1995-1999. Launch vehicle put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option..
1994 August 3 - . 23:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- DBS 2 - .
Mass: 2,860 kg (6,300 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DirecTV.
Program: DirecTV.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 23192 . COSPAR: 1994-047A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.11 min.
Commercial TV broadcast. Stationed at 100.79 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 101 deg W in 1994-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 100.81 deg W drifting at 0.010 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 91.17W drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
1994 August 29 - . 17:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- USA 106 - . Payload: DMSP 23545/Star 37S S/N 15030 / DMSP 5D-1 F12. Mass: 830 kg (1,820 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 23233 . COSPAR: 1994-057A. Apogee: 860 km (530 mi). Perigee: 840 km (520 mi). Inclination: 98.89 deg. Period: 101.94 min. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program..
1994 October 6 - . 06:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Intelsat 703 - .
Payload: NSS 703. Mass: 3,656 kg (8,060 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 23305 . COSPAR: 1994-064A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0400 deg. Period: 1,436.07 min.
38 C-band and 20 Ku-band transponders. Initially positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 177 deg E in 1994-1996. Then reassigned to Intelsat subsidiary New Skies, redesignated NSS 703, and moved to 57 deg E after 1996. At the crossroads of three continents, NSS-703 provided cross-connectivity for Europe, Africa and Asia. NSS-703 was used for video contribution from Europe to India and Africa, and was capable of bringing signals from London to India and Australia in one hop. NSS-703's coverage included a global beam, and two C-band hemispheric beams, which covered Africa and the triangle from Eastern Iran to Japan and Australia, including all of India and China. Three steerable Ku-band spot beams targeted Europe and Iran, Central Asia and Afghanistan-Pakistan-North India. Expected end of life March 2009. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 56.96E drifting at 0.001E degrees per day.
1994 November 29 - . 10:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Orion 1 - .
Mass: 2,358 kg (5,198 lb). Nation: USA.
Manufacturer: Toulouse.
Program: Orion.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 2000.
USAF Sat Cat: 23413 . COSPAR: 1994-079A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
34 Ku-band transponders for TV. Stationed at 37.48 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 37 deg W in 1994-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 37.54 deg W drifting at 0.010 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 37.60W drifting at 0.015W degrees per day.
1994 December 30 - . 10:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- NOAA 14 - . Payload: NOAA K. Mass: 1,712 kg (3,774 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NOAA. Program: Tiros. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: Advanced Tiros N. USAF Sat Cat: 23455 . COSPAR: 1994-089A. Apogee: 861 km (534 mi). Perigee: 847 km (526 mi). Inclination: 98.88 deg. Period: 102.02 min.
1995 January 10 - . 06:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Intelsat 704 - .
Mass: 3,656 kg (8,060 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 23461 . COSPAR: 1995-001A. Apogee: 36,113 km (22,439 mi). Perigee: 36,075 km (22,415 mi). Inclination: 2.20 deg. Period: 1,451.80 min.
Stationed at 66.0 deg E. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 66 deg E in 1995-1999 As of 29 August 2001 located at 66.03 deg E drifting at 0.005 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 66.03E drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
1995 January 29 - . 01:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 108 - . Payload: UHF F/O F4. Mass: 3,023 kg (6,664 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: HCI. Program: UHF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 23467 . COSPAR: 1995-003A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 2.20 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. UHF Follow-On #4; US Navy communications . Stationed at 177.0 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 177 deg W in 1995-1999..
1995 March 22 - . 06:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Intelsat 705 - .
Mass: 3,669 kg (8,088 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 23528 . COSPAR: 1995-013A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Stationed at 50.1 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 50 deg W in 1995-1996; 18 deg W in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 17.97 deg W drifting at 0.006 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 50.01W drifting at 0.007W degrees per day.
1995 March 24 - . 14:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3W. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas E.
- USA 109 - . Payload: DMSP 24547/Star 37S / DMSP F13. Mass: 750 kg (1,650 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DMSP. Class: Earth. Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: TIROS N. Spacecraft: DMSP Block 5D-2. USAF Sat Cat: 23533 . COSPAR: 1995-015A. Apogee: 854 km (530 mi). Perigee: 845 km (525 mi). Inclination: 98.80 deg. Period: 101.90 min. Last successful Atlas E space launch..
1995 April 7 - . 23:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- AMSC-1 - .
Mass: 2,700 kg (5,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: AMSC.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 23553 . COSPAR: 1995-019A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Mobile communicaitons. Stationed at 101.1 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 101 deg W in 1995-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 101.01 deg W drifting at 0.024 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 100.99W drifting at 0.003W degrees per day.
1995 May 23 - . 05:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- GOES 9 - .
Payload: GOES J. Mass: 2,105 kg (4,640 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Program: GOES.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: FS-1300.
Spacecraft: GOES-Next.
USAF Sat Cat: 23581 . COSPAR: 1995-025A. Apogee: 35,911 km (22,314 mi). Perigee: 35,809 km (22,250 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,435.90 min.
Stationed at 135 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 90 deg W in 1995; 135 deg W in 1996-1998; 98-105 deg W in 1998-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 103.62 deg W drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 159.81E drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
1995 May 31 - . 15:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 111 - . Payload: UHF F/O F5-EHF. Mass: 3,015 kg (6,646 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: UHF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 23589 . COSPAR: 1995-027A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 4.80 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. UHF Follow-On #5; US Navy communications . Stationed at 72.3 deg E. Launch vehicle put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 72 deg E in 1995-1999..
1995 June 16 - . Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- General Dynamics Space Division bought by Martin - . Nation: USA.
1995 June 17 - . Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- Lockheed Aircraft Corporation merged with Martin to form Lockheed Martin - . Nation: USA. Atlas assembly line moved from Kearney Mesa, California, to Littleton, Colorado.
1995 July 31 - . 23:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- USA 113 - . Payload: DSCS III B-7. Mass: 2,610 kg (5,750 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 23628 . COSPAR: 1995-038A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit; located at 53 deg W in 1997..
1995 August 29 - . 00:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- JCSAT 3 - .
Mass: 1,841 kg (4,058 lb). Nation: Japan.
Agency: JSAT.
Program: JCSAT.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 23649 . COSPAR: 1995-043A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
8 transponders for digital TV. Stationed at 128.1 deg E. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 128 deg E in 1995-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 128.05 deg E drifting at 0.005 deg E per day. As of 2007 Feb 20 located at 126.99E drifting at 0.144W degrees per day.
1995 September 27 - . Launch Vehicle: Atlas.
- Final Atlas produced in California. - . Nation: USA. Ceremony commemorating final Atlas (AC-126) produced at Kearny Mesa plant.
1995 October 22 - . 08:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 114 - . Payload: UHF F/O F6-EHF. Mass: 3,015 kg (6,646 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: UHF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 23696 . COSPAR: 1995-057A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 5.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. UHF Follow-On #6; US Navy communications. Stationed at 105.3 deg W. Launch vehicle put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 105 deg W in 1995-1999..
1995 December 2 - . 08:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- SOHO - . Mass: 1,850 kg (4,070 lb). Nation: Europe. Agency: ESA. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: SOHO. USAF Sat Cat: 23726 . COSPAR: 1995-065A. Apogee: 671,400 km (417,100 mi). Perigee: 8,973 km (5,575 mi). Inclination: 29.60 deg. Period: 29,196.30 min. Solar and Heliospheric Observatory; orbiting at L1 Lagrange point; solar physics. En route Earth-Sun L1 point Earth-Sun L1 libration point transfer trajectory. Inertial trajectory option..
1995 December 15 - . 00:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Galaxy 3R - .
Payload: HS 376. Mass: 2,980 kg (6,560 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: HCI.
Program: Galaxy.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 23741 . COSPAR: 1995-069A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,774 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Stationed at 95 deg W; 24 C-band, 24 Ku-band transponders; TV for Caribbean and Central America. Launch vehicle put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 95 deg W in 1996-1999 As of 3 September 2001 located at 95.05 deg W drifting at 0.008 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 132.80W drifting at 0.084W degrees per day.
1996 February 1 - . 01:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Palapa C-1 - .
Payload: Palapa C1. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: Indonesia.
Agency: Satelind.
Program: Palapa.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 23779 . COSPAR: 1996-006A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
30 C-band, 6 Ku-band transponders. Geostationary at 150.4E. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 113 deg E in 1996; 150 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 50.03 deg E drifting at 0.006 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 38.04E drifting at 0.007E degrees per day.
1996 April 3 - . 23:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Inmarsat 3 F1 - .
Mass: 2,068 kg (4,559 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Inmarsat.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Inmarsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 4000.
USAF Sat Cat: 23839 . COSPAR: 1996-020A. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,767 km (22,224 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geostationary at 64.1E. Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with RAAN Cntl trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 64 deg E in 1996-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 63.98 deg E drifting at 0.003 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 64.52E drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
1996 April 30 - . 04:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- Beppo SAX - . Payload: BeppoSAX. Nation: Italy. Agency: ASI. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: SAX. Decay Date: 2003-04-29 . USAF Sat Cat: 23857 . COSPAR: 1996-027A. Apogee: 601 km (373 mi). Perigee: 584 km (362 mi). Inclination: 4.00 deg. Period: 96.50 min. LEO. Satellite per Astronomia a raggi X; X-ray celestial observatory Launch vehicle put payload into low earth orbit with IFR trajectory option. 100th Atlas-Centaur flight..
1996 July 25 - . 12:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 127 - . Payload: UHF F/O F7-EHF. Mass: 3,015 kg (6,646 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: HCI. Program: UHF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 23967 . COSPAR: 1996-042A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 4.90 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 170 deg W in 1996; 23 deg W in 1996-1999; 100 deg W in 1999. As of 29 July 1999) 99.21 deg W drifting at 0.011 deg W per day. As of 2007 Feb 22 located at 21.85W drifting at 0.014W degrees per day..
1996 September 8 - . 21:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- GE 1 - .
Payload: A2100A. Mass: 2,783 kg (6,135 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: GE Americom.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 24315 . COSPAR: 1996-054A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geostationary at 103.0W. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 103 deg W in 1996-1999 As of 4 September 2001 located at 103.06 deg W drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 103.03W drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
1996 November 21 - . 20:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Hot Bird 2 - .
Payload: Eurostar 2000+. Mass: 2,900 kg (6,300 lb). Nation: France.
Agency: Eutelsat.
Manufacturer: Toulouse.
Program: Eutelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 2000.
USAF Sat Cat: 24665 . COSPAR: 1996-067A. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,768 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geostationary at 13.0E. Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 13 deg E in 1997-1999 As of 3 September 2001 located at 12.95 deg E drifting at 0.024 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 4 located at 13.07E drifting at 0.011E degrees per day.
1996 December 18 - . 01:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Inmarsat 3 F3 - .
Mass: 1,021 kg (2,250 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Inmarsat.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Inmarsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 4000.
USAF Sat Cat: 24674 . COSPAR: 1996-070A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Geostationary at 157.6E. Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with RAAN Cntl trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 178 deg E in 1997-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 178.02 deg E drifting at 0.006 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 178.19E drifting at 0.002E degrees per day.
1997 February 17 - . 01:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- JCSAT 4 - .
Mass: 3,105 kg (6,845 lb). Nation: Japan.
Agency: JSAT.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: JCSAT.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 24732 . COSPAR: 1997-007A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 150.0E Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 150 deg E in 1997-1998; 124 deg E in 1998-1999; 127 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 127.02 deg E drifting at 0.015 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 7 located at 150.01E drifting at 0.008W degrees per day.
1997 March 8 - . 06:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Tempo 2 - .
Mass: 3,640 kg (8,020 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: TCI.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Tempo.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 24748 . COSPAR: 1997-011A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 118.7W Launch vehicle put payload into subsynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 119 deg W in 1997-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 118.82 deg W drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 42.64E drifting at 4.479W degrees per day.
1997 April 25 - . 05:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas I.
- GOES 10 - .
Payload: GOES K. Mass: 2,105 kg (4,640 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: GOES.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft Bus: FS-1300.
Spacecraft: GOES-Next.
USAF Sat Cat: 24786 . COSPAR: 1997-019A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.40 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 105.7W Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 105 deg W in 1997-1998; 135 deg W in 1998-1999 As of 6 September 2001 located at 135.09 deg W drifting at 0.037 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 59.64W drifting at 0.009W degrees per day.
1997 July 28 - . 01:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Superbird C - .
Mass: 3,130 kg (6,900 lb). Nation: Japan.
Agency: SCC.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Superbird.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 24880 . COSPAR: 1997-036A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 144.0E Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 144 deg E in 1997-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 144.00 deg E drifting at 0.014 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 143.94E drifting at 0.009W degrees per day.
1997 September 4 - . 12:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- GE 3 - .
Payload: A2100A. Mass: 2,845 kg (6,272 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: GE Americom.
Manufacturer: RCA.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 24936 . COSPAR: 1997-050A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 87.1W Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 87 deg W in 1997-1999 As of 3 September 2001 located at 87.12 deg W drifting at 0.002 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 86.99W drifting at 0.010W degrees per day.
1997 October 5 - . 21:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Echostar 3 - .
Mass: 3,415 kg (7,528 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Echostar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 25004 . COSPAR: 1997-059A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 61.4W Launch vehicle put payload into supersynchronous earth orbit with IFR/MRS trajectory option. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 61 deg W in 1997-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 61.53 deg W drifting at 0.017 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 61.50W drifting at 0.007W degrees per day.
1997 October 25 - . 00:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- USA 135 - . Payload: DSCS III B-13. Mass: 2,613 kg (5,760 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Valley Forge. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 25019 . COSPAR: 1997-065A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,770 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Geosynchronous. Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option..
- Falcon Gold - . Nation: USA. Agency: Lockheed. Manufacturer: USAF Colorado Springs. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: Falcon Gold. Decay Date: 1998-09-27 . USAF Sat Cat: 25020 . COSPAR: 1997-065B. Apogee: 34,457 km (21,410 mi). Perigee: 151 km (93 mi). Inclination: 26.20 deg. Period: 185.80 min. US Air Force Academy experiment to demonstrate use of GPS navigation in geosynchronous orbit..
1997 December 8 - . 23:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Galaxy 8i - .
Payload: HS 601HP. Mass: 3,537 kg (7,797 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Galaxy.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25086 . COSPAR: 1997-078A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Geosynchronous. Stationed over 79.2W Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with MRS trajectory option. Used HS-601 XIPS ion engine for station keeping. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 95 deg W in 1998-1999 As of 3 September 2001 located at 94.92 deg W drifting at 0.000 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 37.58W drifting at 2.053W degrees per day.
1998 January 29 - . 18:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- USA 137 - .
Payload: CAPRICORN?. Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar.
USAF Sat Cat: 25148 . COSPAR: 1998-005A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
Classified satellite for the National Reconnaissance Office. It was likely that it was a technology test satellite combining equipment for several future projects, including a prototype COBRA BRASS infrared early warning satellite sensor. The project seemed to have been several years behind schedule (based on the launch vehicle serial number.
1998 February 28 - . 00:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Intelsat 806 - .
Payload: NSS 806. Mass: 3,415 kg (7,528 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Manufacturer: RCA.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 7000.
USAF Sat Cat: 25239 . COSPAR: 1998-014A. Apogee: 35,799 km (22,244 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Initially positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 40 deg W in 1998-2001. 36 C-band and 6 Ku-band transponders. Later assigned to Intelsat spin-off New Skies, redesignated NSS-806, and moved to 319.5º East, giving it an optimum view of Latin American markets while also reaching the Iberian peninsula, the Canary Islands, Western Europe and much of Eastern Europe. Its tailored, high-powered hemispheric beam provided simultaneous coverage of both Europe and the Americas, with virtually complete coverage of North, Central and South America, therefore ensuring the maximum reach throughout Spanish and Portuguese speaking markets. Expected end of life July 2016. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 40.47W drifting at 0.007W degrees per day.
1998 March 16 - . 21:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas II.
- USA 138 - .
Payload: UHF F/O F8-EHF. Mass: 3,206 kg (7,068 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: UHF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25258 . COSPAR: 1998-016A. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,771 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 3.30 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
UHF Follow-On F8 was the first Block III UHF Follow-On satellite, replacing the old FLTSATCOM satellites. It carried UHF, EHF and Ka-band transponders, including a video broadcast payload. This was the last Atlas II launch; future Atlas launches would use the Atlas IIA, IIAS and III models. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 172 deg E in 1998-1999.
1998 June 18 - . 22:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Intelsat 805 - .
Mass: 3,520 kg (7,760 lb). Nation: International.
Agency: Intelsat.
Manufacturer: RCA.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 7000.
USAF Sat Cat: 25371 . COSPAR: 1998-037A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Satellite had 28 C-band and 3 Ku-band transponders, and initially served the Atlantic Ocean region for INTELSAT. Launch vehicle put payload into geosynchronous transfer orbit with GCS trajectory option. Geostationary at 55.5 degrees W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 55 deg W in 1998-1999 As of 5 September 2001 located at 55.52 deg W drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 55.54W drifting at 0.012W degrees per day.
1998 October 9 - . 22:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- Hot Bird 5 - . Payload: Eurostar 2000+. Mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Nation: France. Agency: Eutelsat. Manufacturer: Toulouse. Program: Eutelsat . Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Eurostar 2000. USAF Sat Cat: 25495 . COSPAR: 1998-057A. Apogee: 35,807 km (22,249 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Geostationary at 10.0 degrees E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 13 deg E in 1998-1999 As of 3 September 2001 located at 12.97 deg E drifting at 0.010 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 25.56E drifting at 0.014W degrees per day..
1998 October 20 - . 07:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- USA 140 - .
Payload: UHF F/O F9. Mass: 3,200 kg (7,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: UHF.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25501 . COSPAR: 1998-058A. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 3.80 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
The orbit at burnout of the Centaur was 286 km x 25866 km x 27.0 degree. Modification of the orbit to a geostationary 38,300 km circular x 0.0 degree inclination was accomplished by the Marquardt R-4D liquid propellant motor on the HS-601 spacecraft. The satellite carried UHF and EHF transponders for naval communications, and a Ka-band Global Broadcast Service video relay package. Launch mass of 3200 kg dropped to 1550 kg once geostationary orbit was reached. UHF F/O F9 was placed over the Atlantic Ocean in geosynchronous orbit at 174 deg W in 1998; 22 deg W in 1999. Additional Details: here....
1999 February 16 - . 01:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- JCSAT-6 - .
Mass: 2,900 kg (6,300 lb). Nation: Japan.
Agency: JSAT.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: JCSAT.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 25630 . COSPAR: 1999-006A. Apogee: 35,791 km (22,239 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
JCSAT-6 carried a Ku-band relay system. It was operated by Japan Satellite Systems, Inc., Tokyo, provided communications and data relay for Japan and the Pacific Rim. Two burns of the Centaur upper stage placed it into a supersynchronous transfer orbit of 258 km x 96736 km x 24.1 degrees. JCSAT-6's on-board R-4D engine would maneuver it into its final geostationary location. Dry mass of the spacecraft was 1230 kg. Stationed at 124 deg E Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 123 deg E in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 124.00 deg E drifting at 0.014 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 124.01E drifting at 0.011W degrees per day.
1999 April 12 - . 22:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Eutelsat W3 - .
Payload: Spacebus 3000B2. Mass: 3,183 kg (7,017 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: Eutelsat.
Manufacturer: Cannes.
Program: Eutelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 25673 . COSPAR: 1999-018A. Apogee: 35,803 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,770 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications satellite is for the European Telecommunications Satellite Organization. The vehicle entered a 153 km x 385 km x 27.4 deg parking orbit nine minutes after launch. The second Centaur stage burn delivered the satellite to a 166 km x 46,076 km x 19.7 deg super-synchronous transfer orbit. The satellite was stationed at 7 deg E and carried 24 Ku-band transponders with a wide beam covering Europe, North Africa and Asia, and a spot beam for digital TV to Turkey. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 7 deg E in 1999. As of 26 August 2001 located at 7.01 deg E drifting at 0.004 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 7 located at 21.59E drifting at 0.003E degrees per day.
1999 September 23 - . 06:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Echostar 5 - .
Mass: 3,602 kg (7,941 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: Echostar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 25913 . COSPAR: 1999-050A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
The Centaur second stage put Echostar 5 into a supersynchronous transfer orbit of 131 km x 45526 km x 26.6 degrees. The satellite's own engine put it into the final geosynchronous orbit. Echostar 5 was a Ku-band satellite, part of the Dish Network. Stationed at 110 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 110 deg W in 1999. As of 5 September 2001 located at 110.01 deg W drifting at 0.003 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 128.86W drifting at 0.001E degrees per day.
1999 November 23 - . 04:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- USA 146 - . Payload: UHF F/O F10. Mass: 3,206 kg (7,068 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: UHF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 25967 . COSPAR: 1999-063A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,777 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 3.90 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. UHF Follow-on satellite providing UHF and EHF communications, and Global Broadcast Service television for the US Navy. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 173 deg W in 1999; 72 deg E in 2000-2003..
1999 December 18 - . 18:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Terra - . Payload: EOS-AM1. Mass: 4,854 kg (10,701 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Manufacturer: Valley Forge. Class: Earth. Type: Seismology satellite. Spacecraft: Terra. USAF Sat Cat: 25994 . COSPAR: 1999-068A. Apogee: 703 km (436 mi). Perigee: 702 km (436 mi). Inclination: 98.20 deg. Period: 98.80 min. First launch in NASA's Earth Observing System program. Terra carried multispectral imagers, a radiation budget instrument, a detector to measure CO and methane pollution, and an instrument to study cloud top and vegetation properties..
2000 January 21 - . 01:03 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- USA 148 - . Payload: DSCS III B-8. Mass: 1,232 kg (2,716 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Manufacturer: Valley Forge. Program: DSCS. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III. USAF Sat Cat: 26052 . COSPAR: 2000-001A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Part of the US Air Force Defense Satellite Communications System. To be stationed in geosynchronous orbit over the Pacific Ocean..
2000 February 3 - . 23:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Hispasat 1C - .
Payload: Spacebus 3000B2. Mass: 3,112 kg (6,860 lb). Nation: Spain.
Agency: Hispasat.
Manufacturer: Cannes.
Program: Hispasat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 26071 . COSPAR: 2000-007A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Spanish domestic geosynchronous communications satellite. Stationed at 30 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 30 deg W in 2000. As of 3 September 2001 located at 30.14 deg W drifting at 0.013 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 30.01W drifting at 0.005W degrees per day.
2000 May 3 - . 07:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- GOES 11 - .
Payload: GOES L. Mass: 2,217 kg (4,887 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: GOES.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 26352 . COSPAR: 2000-022A. Apogee: 35,796 km (22,242 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.40 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
US civilian geostationary weather satellite in the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite series. It was the first GOES launch on the Atlas II launch vehicle (the Atlas I having been phased out). Built by SS/Loral, based on the FS-1300 bus. It was equipped with one solar panel array and a counter-boom with a solar sail. The satellite carried well as an imaging radiometer and an X-ray detector to monitor solar activity. Stationed at 106 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 104 deg W in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 108.58 deg W drifting at 0.018 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 135.52W drifting at 0.001E degrees per day.
2000 May 24 - . 23:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas 3A.
- Eutelsat W4 - .
Payload: Spacebus 3000B2. Mass: 3,190 kg (7,030 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: Eutelsat.
Manufacturer: Cannes.
Program: Eutelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 26369 . COSPAR: 2000-028A. Apogee: 35,804 km (22,247 mi). Perigee: 35,770 km (22,220 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications satellite. Maiden flight of Atlas IIIA with Russian RD-180 main engine; scrubbed four times. European Telecommunications Satellite Organization (Eutelsat) satellite equipped with 32 Ku-band transponders, and antennae covering Russia and Africa. It will be stationed at 36 deg E. This was the third of the high power Eutelsat W series to be launched (W1 was destroyed in a ground accident). Stationed at 36 deg E. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 32 deg E in 2000. As of 4 September 2001 located at 35.98 deg E drifting at 0.003 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 36.08E drifting at 0.005E degrees per day.
2000 June 30 - . 12:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- TDRS 8 - .
Payload: TDRS-H. Mass: 3,180 kg (7,010 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 26388 . COSPAR: 2000-034A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,773 km (22,228 mi). Inclination: 5.40 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from June 29. First Advanced Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, using a Hughes HS 601 satellite bus. It included an S-band phased array antenna and two Ku/Ka band reflectors 4.6 meters in diameter. The satellite was launched into a a 167 x 577 km x 28.3 deg parking orbit at 13:05 GMT. The Centaur upper stage made a second burn at 13:21 GMT, releasing the satellite into a subsynchronous transfer orbit of 237 x 27,666 km x 27.0 deg. The satellite's own Primex/Marquardt R4D liquid apogee engine would be used to maneuver the satellite into its final geosynchronous orbit. Stationed at 151 deg W. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 150 deg W in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 149.99 deg W drifting at 0.014 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 145.38E drifting at 3.007W degrees per day.
2000 July 14 - . 05:21 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Echostar 6 - . Mass: 3,700 kg (8,100 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: PanAmSat. Manufacturer: Palo Alto. Program: Echostar. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 26402 . COSPAR: 2000-038A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,776 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Communications satellite, positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 149 deg W. By 5 September 2001 located at 119.07 deg W drifting at 0.002 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 110.39W drifting at 0.006W degrees per day..
2000 October 20 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- USA 153 - .
Payload: DSCS III B-11. Mass: 1,235 kg (2,722 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Manufacturer: Valley Forge.
Program: DSCS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: DSCS III.
USAF Sat Cat: 26575 . COSPAR: 2000-065A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg.
Military Communications satellite. Launch delayed from October 12 by spacecraft problem. The US Air Force Defense Satellite Communications System satellite was placed by the Centaur upper stage into a 148 km x 898 km x 29.3 deg parking orbit. A second burn put it into a 218 km x 35,232 km x 26.0 deg transfer orbit. The DSCS III B-11 IABS-8 apogee stage, with two Primex R4D liquid apogee engines, circularised the orbit at geostationary altitude on October 21 and then separated from the DSCS.
2000 December 6 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- USA 155 - .
Payload: Capricorn 2? / MLV-11 'Great Bear'. Mass: 3,600 kg (7,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar.
USAF Sat Cat: 26635 . COSPAR: 2000-080A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,780 km (22,230 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
Classified satellite. Launch delayed 24 hours by RL10 engine problem in upper stage. USA 155 was a classified National Reconnaissance Office satellite. The Centaur placed the payload in a 176 x 831 km parking orbit and then in a 270 x 37490 km x 26.5 deg geostationary transfer orbit. The spacecraft was probably either a data relay satellite (to relay spy satellite imagery and data to the ground) and/or a signals intelligence satellite.
2001 June 19 - . 04:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- ICO F-2 - .
Mass: 2,750 kg (6,060 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: ICO.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 26857 . COSPAR: 2001-026A. Apogee: 10,389 km (6,455 mi). Perigee: 10,385 km (6,452 mi). Inclination: 45.00 deg. Period: 360.10 min.
Launch delayed from June 5. The ICO-2 satellite was launched by British New ICO (formerly ICO Global Communications) to provide mobile communications and data/Internet services at S-band, supporting 4500 simultaneous calls. The Boeing BSS-601M satellite was similar to the standard geostationary 601 model except that it omitted the R-4D apogee engine and associated fuel, and had a larger payload section. Launch mass was 2700 kg; dry mass was around 2200-2400 kg with the remainder being station-keeping fuel. The AC-156 launch vehicle's Centaur stage reached a 167 x 10099 km x 44.6 deg transfer orbit 10 minutes after launch. A second burn 1.5 hours later put ICO-2 into a circular 10,100 km orbit. The first ICO satellite was launched in March 2000 but failed to reach orbit. ICO-2 was used for testing of the ICO system before the remaining satellites would be launched. Unlike the Iridium and Globalstar constellations, ICO proposed to use a small number of large satellites. The ICO fleet, anticipated to consist of 10 satellites, was to enable relay in S- and C-bands of voice and internet communications from/to land and ocean based mobile telephones. With a total power of 5 kW, ICO F2 was to enable a simultaneous capacity in 4,500 channels.
2001 July 23 - . 07:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- GOES 12 - .
Payload: GOES-M. Mass: 2,105 kg (4,640 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NOAA.
Manufacturer: Palo Alto.
Program: GOES.
Class: Earth.
Type: Weather satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300.
USAF Sat Cat: 26871 . COSPAR: 2001-031A. Apogee: 35,813 km (22,253 mi). Perigee: 35,769 km (22,225 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.30 min.
Launch delayed from July 12, 15 and 22. The GOES-M weather satellite was placed by the Atlas AC-142 Centaur stage into a 164 x 505 km parking orbit and then a super synchronous transfer orbit of 274 x 42275 km x 20 deg. GOES-M was a Loral 1300-series satellite with a single solar array and a solar attitude control sail. Launch mass was 2279 kg and dry mass 1042 kg. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites were developed by NASA-Goddard and were transferred to the NOAA weather agency when operational. In addition to the usual weather imager/sounder, GOES-M carried a new solar soft X-ray imager. Earlier GOES satellites carried simple X-ray collimator detectors, but the new SXI was a full-fledged grazing incidence telescope similar to the SXT on Japan's Yohkoh satellite. The GOES-M satellite was redesignated GOES 12 once in orbit.
GOES 12 was a 980 kg, 973 W spacecraft that carried an IR imager, a "sounder", and an X-ray imager. The IR imager was a Cassegrain telescope covering five wavelength channels, 0.55-0.75, 3.80-4.00, 6.50-7.00, 10.20-11.20, and 11.50-12.50 microns. It provided images covering 3,000 km x 3,000 km every 41 seconds, by scanning the area in 16 square kilometer sections. The "sounder" provided vertical distribution of temperature, moisture and ozone, by passive monitoring in 18 depth-dependent wavelengths. (Long wave IR: 14.71, 14.37, 14.06, 13.64, 13.37, 12.66, and 12.02 microns. Medium wave IR: 11.03, 9.71, 7.43, 7.02, and 6.51 microns. Short wave IR: 4.57, 4.52, 4.45, 4.13, 3.98, and 3.74 microns. There was also another band at visible wavelength 0.7 microns, to provide pictures of cloud tops.) The sounder covered an area of 3,000 km x 3,000 km in about 42 minutes. Another instrument package named SEM (Space Environment Monitor) monitored the energetic electrons and protons in the magnetosphere and the X-rays from the Sun. The above three had been carried on the earlier GOES missions, but GOES 12 carried also an X-ray imager providing an X-ray (about 0.1-1.0 nm wavelength) picture of the solar disk. For some months, the spacecraft was to be on standby, to be activated and moved to a desired longitude. As of 5 September 2001 located at 89.93 deg W drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 74.73W drifting at 0.014E degrees per day.
2001 September 8 - . 15:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- USA 160 - .
Payload: Intruder 5 / MLV-10. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Manufacturer: Martin.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder.
USAF Sat Cat: 26905 . COSPAR: 2001-040A. Apogee: 1,200 km (700 mi). Perigee: 1,060 km (650 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
Launch delayed from July 31. Move of launch of the Intruder naval electronic intelligence satellites for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) from the Titan to the Atlas launch vehicle. The Lockheed Martin Atlas IIAS AC-160 put the vehicle in a transfer orbit. The phrasing of the launch commentary implied that the second burn left the payload in 'transfer orbit', but several observers saw the bright Centaur in the typical final deployment orbit of the earlier NOSS satellites. Therefore it seemed the first burn was to a transfer orbit of around 180 x 1100 km x 63 deg. The second burn at 1629 GMT put the Centaur and payload into an 1100 x 1100 km x 63 deg orbit. The design was apparently different from earlier generation NOSS satellites since only one companion satellite was deployed rather than two, in line with the lower payload capability of the Atlas. Prime contractor for the new satellites was again believed to be Lockheed Martin Astronautics at Denver. The NRL probably continued to have a management and technical role in the program under overall NRO auspices.
- USA 160 companion - . Payload: Intruder 5 / MLV-10. Mass: 5,000 kg (11,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NRO. Manufacturer: Martin. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 26907 . COSPAR: 2001-040C. Apogee: 1,200 km (700 mi). Perigee: 1,060 km (650 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
2001 October 11 - . 02:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- USA 162 - .
Payload: Aquila / MLV-12. Mass: 3,600 kg (7,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar.
USAF Sat Cat: 26948 . COSPAR: 2001-046A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
The Atlas AC-162 Centaur entered a 176 x 907 km x 28.2 deg parking orbit at 0242 GMT and then made a second burn to deploy its payload in a 274 x 37538 km x 26.5 deg geostationary transfer orbit at 0301 GMT. USA 162 was rumoured to be a data relay satellite used to return data from imaging satellites similar to the one launched on October 5 2001. It was also possible that the satellite is a signals intelligence payload. The satellite is owned and operated by the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO).
2002 February 21 - . 12:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas 3B.
- Echostar 7 - .
Payload: A2100AX. Mass: 690 kg (1,520 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: Lockheed,
Motorola.
Program: Echostar.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 27378 . COSPAR: 2002-006A. Apogee: 35,794 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Direct Broasdcasting satellite. The first launch of the Atlas 3B, with the Common Centaur stretched two-engine upper stage. Launch delayed from December 19, 2001 and January 22. The Echostar 7 communications satellite was placed into geostationary transfer orbit. The first burn of the Centaur put the stack into a 185 x 193 km x 28.1 deg parking orbit. At 1305 UTC the Centaur burned again to achieve the final 245 x 57060 km x 22.6 deg transfer orbit and separated from Echostar. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 118.92W drifting at 0.006W degrees per day.
2002 March 8 - . 22:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- TDRS 9 - .
Payload: TDRS-I. Mass: 3,192 kg (7,037 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 27389 . COSPAR: 2002-011A. Apogee: 35,811 km (22,251 mi). Perigee: 35,758 km (22,218 mi). Inclination: 8.30 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Launch delayed from October 31, November 13 and 26, 2001 and February 6 due to contract dispute with Boeing over performance of earlier satellites of the series. The Centaur upper stage entered a 167 x 578 km parking orbit and then placed the payload into a 247 x 29135 km x 27.1 deg subsynchronous transfer orbit. NASA's TDRS-I (TDRS-9) data relay satellite used a Boeing BSS-601 bus and was to provide S, Ku and Ka band communications for the Shuttle and International Space Station. After launch a problem developed with the fuel supply from one of the satellite's four propellant tanks. The tanks were paired, so losing one tank cuts the propellant supply in half. A test burn of the General Dynamics R-4D apogee motor raised the orbit to 433 x 29146 km x 26.4 deg on March 11 and a larger perigee burn raised the apogee to geostationary altitude, 429 x 35800 km, on March 13. A further burn on March 19, raised the orbit to 3521 x 35789 km and lowered the inclination to 21.4 deg. A burn on March 25 raised the orbit further to 8383 x 35811 km and lowered inclination to 17.4 deg. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 62.04W drifting at 0.008W degrees per day.
2002 September 18 - . 22:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Hispasat 1D - .
Payload: Spacebus 3000B2. Mass: 3,250 kg (7,160 lb). Nation: Spain.
Agency: Hispasat.
Manufacturer: Cannes.
Program: Hispasat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: Spacebus 3000.
USAF Sat Cat: 27528 . COSPAR: 2002-044A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from May 28, August 14. Hispasat 1D was a Spanish geostationary communications spacecraft. The 3.3-ton, 7.0-kW satellite carried three antennae looking in different directions to provide video, data, and Internet services to Europe, North America, and North Africa via 28 Ku-band transponders after being parked over 30° W longitude alongside Hispasat 1A, 1B, and 1C. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 29.97W drifting at 0.014W degrees per day.
2002 December 5 - . 02:42 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIA.
- TDRS 10 - .
Payload: TDRS-J. Mass: 3,190 kg (7,030 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NASA Greenbelt.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: STS.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 27566 . COSPAR: 2002-055A. Apogee: 35,804 km (22,247 mi). Perigee: 35,765 km (22,223 mi). Inclination: 7.00 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min.
Delayed from October 29, November 21 and 23. The third and final Advanced Tracking and Data Relay Satellite satellite separated from the Centaur upper stage 30 minutes after launch. This completed the $800 million, three satellite contract. Last launch of the Atlas 2A booster. Flight delayed from October 29, November 21 and 23. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 40.92W drifting at 0.012E degrees per day.
2003 April 12 - . 00:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas 3B.
- AsiaSat 4 - .
Payload: HS 601HP / AsiaSat 1R. Mass: 4,042 kg (8,911 lb). Nation: China.
Agency: AsiaSat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Asiasat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601.
USAF Sat Cat: 27718 . COSPAR: 2003-014A. Apogee: 35,805 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Delayed from May 28, 2002, and January 13, February 5, and April 11, 2003. AsiaSat 4 was designed to provide broadcast, telecommunications and broadband multimedia services to the Asia Pacific region, and direct-to-home broadcast servic-es to Hong Kong, from its orbital position of 122 deg É East longitude.The satellite generated up to 9,600 watts using two sun-tracking four-panel solar wings covered with triple-junction gallium arsenide solar cells. AsiaSat 4 was to operate in C-band and Ku-band. The satellite carried 28 active transponders with six spares in C-band, powered by 55-watt traveling-wave tube amplifiers (TWTAs), and 20 active transponders with four spares in Ku-band, powered by 140-watt TWTAs. The C-band payload was designed to offer pan-Asian coverage, similar to AsiaSat 3S, also a 601HP model. The Ku-band payload provided high power, and spot beams for selected areas in either the Fixed Satellite Service frequency band or in the Broadcast Satellite Service frequency band. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 122.23E drifting at 0.011W degrees per day.
2003 December 2 - . 10:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC3E. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- USA 173 - . Payload: Intruder 6 / NROL-18. Nation: USA. Agency: NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 28095 . COSPAR: 2003-054A. Apogee: 1,210 km (750 mi). Perigee: 1,010 km (620 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min. Second launch of new generation paired satellites used for tracking, characterisation, and intelligence on naval vessels and civilian shipping worldwide..
- USA 173 companion - . Payload: Intruder 6 / NROL-18. Nation: USA. Agency: NRO. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 28097 . COSPAR: 2003-054C. Apogee: 1,210 km (750 mi). Perigee: 1,010 km (620 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
2003 December 18 - . 02:30 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas 3B.
- USA 174 - . Payload: UFO F/O F11. Mass: 3,041 kg (6,704 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: UHF. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 28117 . COSPAR: 2003-057A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 4.20 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min. The last UHF Follow-On communications satellite for the US Navy. The satellite provided fleet communications from geostationary orbit..
2004 February 5 - . 23:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- AMC-10 (GE-10) - .
Payload: A2100A. Mass: 2,340 kg (5,150 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SES Americom.
Manufacturer: Lockheed.
Program: Americom.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100.
USAF Sat Cat: 28154 . COSPAR: 2004-003A. Apogee: 35,798 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min.
Americom 10 (AMC-10) was a replacement satellite for Satcom C3. It was to be located at 135 deg W. The C-band satellite, to be accompanied by AMC-11 later in 2004, were designed to support SES Americom's cable network in the United States, Canada, the Caribbean, and Mexico. The satellite had a design life of 15 years and carried 24 x 36 MHz C-band transponders. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 134.97W drifting at 0.005E degrees per day.
2004 March 13 - . 05:40 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas 3A.
- MBSAT - . Mass: 4,143 kg (9,133 lb). Nation: Japan. Agency: MBC. Manufacturer: Palo Alto. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: FS-1300. USAF Sat Cat: 28184 . COSPAR: 2004-007A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Mobile S-band digital broadcasting services for home and automobile users in Japan. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 144.03E drifting at 0.009W degrees per day..
2004 April 16 - . 00:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- Superbird 6 - . Mass: 3,100 kg (6,800 lb). Nation: Japan. Agency: JSCC. Program: Superbird. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 601. USAF Sat Cat: 28218 . COSPAR: 2004-011A. Apogee: 35,797 km (22,243 mi). Perigee: 35,775 km (22,229 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. The satellite was to provide Ka and Ku band communications for Japan's Space Communications Corporation..
2004 May 19 - . 22:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- AMC-11 (GE-11) - . Payload: A2100A. Mass: 2,316 kg (5,105 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: SES Americom. Manufacturer: Lockheed. Program: Americom. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: AS 2100. USAF Sat Cat: 28252 . COSPAR: 2004-017A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,778 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.00 min. Delayed from May 17. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 131.04W drifting at 0.000E degrees per day..
2004 August 31 - . 23:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36A. Launch Pad: SLC36A. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas IIAS.
- USA 179 - .
Payload: Nemesis / NROL-1). Mass: 3,600 kg (7,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: NRO.
Class: Communications.
Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Quasar.
USAF Sat Cat: 28384 . COSPAR: 2004-034A. Apogee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Perigee: 35,800 km (22,200 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,440.00 min.
63rd and last flight of Atlas IIAS. 576th and final launch of Rocketdyne-powered Atlas rockets. Final launch from LC36A after 42 years of use. Launch delayed from June 24 and 25, July 1 and 27, August 27, 28, 29 and 30. The payload was probably a communications satellite used to relay data from imaging spy satellites.
2005 February 3 - . 07:41 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. Launch Pad: SLC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas 3B.
- USA 181 - .
Payload: Intruder 7. Nation: USA.
Agency: ILS.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder.
USAF Sat Cat: 28537 . COSPAR: 2005-004A. Apogee: 1,209 km (751 mi). Perigee: 1,011 km (628 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
Last launch of an Atlas model using the original, innovative, balloon propellant tanks conceived in 1947. Third launch of new generation paired satellites used for tracking, characterisation, and intelligence on naval vessels and civilian shipping worldwide.
- USA 181 companion - . Payload: Intruder 7. Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Class: Surveillance. Type: SIGINT. Spacecraft: Intruder. USAF Sat Cat: 28541 . COSPAR: 2005-004C. Apogee: 1,209 km (751 mi). Perigee: 1,011 km (628 mi). Inclination: 63.40 deg. Period: 107.40 min.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use