
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Transit
 Transit Credit: APL |
AKA: Navy Navigation Satellite;NNS;Transat. Status: Operational 1959. First Launch: 1959-09-17. Last Launch: 1988-08-25. Number: 46 . Gross mass: 55 kg (121 lb). Height: 0.25 m (0.82 ft).
The program began with several experimental satellites that settled technical issues regarding key features of the operational design. Early Transits carried a variety of piggy-back payloads, many still classified. Following initial problems with production quality, Transit proved so reliable that individual satellites operated for over 10 years. The first run of production satellites was sufficient to keep the constellation operational for 32 years.
A Transit receiver used the known characteristics of the satellite's orbit, measured the Doppler shift of the satellite's radio signal, and thereby calculated the receiver's position on the earth. Technical breakthroughs during the program included gravity gradient stabilization, the use of radio-isotope thermoelectric generators (RTG), and navigation satellite technologies used in the later GPS series. The TRIAD satellite was launched in 1972 to test improvements.
The John Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory designed all aspects of Transit, including the spacecraft, user equipment, and ground control system.
The original requirement was that Transit would be able to provide Polaris submarines equipped with silent passive navigation receivers positional accuracies of 0.1 nautical mile several times a day. As the system developed, the Navy upped the requirements, until the final system provided 0.042 nautical mile positional accuracy, available within four hours at any time, with timing accurate to within 200 milliseconds of absolute Universal Time.
APL made its first fifty-page proposal on Transit to the Navy in the spring of 1958. The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) took over development and authorized APL in October 1958 to proceed with satellite and ground station design. Many initial challenges had to be faced. The Navy itself did not see the necessity for the accuracy requirements; initial assessments of available electronics reliability indicated that each satellite would be operational for only two weeks before failing. But Polaris program managers saw the absolute necessity for the system, and by May 1959 APL issued a program plan, divided into an ARPA-supervised experimental phase and a Navy operational phase. A few years later Transit became an integral part of the Fleet Ballistic Weapon System, and was managed by the Navy Strategic Systems Programs Office.
Richard B Kershner was the program manager at APL. He insisted on a KISS (keep it simple, stupid) approach to solving design problems and obtain a reliable system. He put dedicated subsystem managers in place and made them responsible for seeing out the entire development and production cycle. He also established a parts reliability group to establish and maintain one of the first lists of space-qualified component parts.
Five experimental Transits reached orbit between 13 April 1960 and 15 November 1961 . They proved navigation signal techniques, and settled the technical issue of gravity gradient versus magnetic torque techniques of satellite attitude control. Transit 4A and 4B explored the use of power generation by radioisotope nuclear generators as opposed to solar power on the other experimental satellites.
These were followed by operational prototypes. The Scout rocket was selected as the dedicated launch vehicle due to its low cost. However this meant that the mass of the operational Transits had to be reduced from 136 kg to 55 kg to allow for launch by the Scout. Furthermore, the all-solid rocket booster imposed a more difficult launch vibration environment on the satellite.
There were three series of operational prototypes to finalize other design choices. The Transit 5A and 5C-1 prototypes used solar power, and the 5BN series used nuclear power. The 5E series used solar power but instead of the navigation package had instruments to measure the Transit orbital environment. To accomplish this they were launched piggy-back with the 5B series using Thor Able-Star boosters.
After the failure of Transit 5BN-3 to achieve orbit, it was decided that operational satellites would be solar powered. Not only was the cost lower, but the need to obtain special approvals to launch each nuclear-powered satellite and the operational and publicity issues in case of a failure to orbit were unacceptable.
Operational ("Oscar") Transits closely followed the design of Transit 5C-1, except for the inclusion of hysteresis rods on the solar panels to dampen residual motion after despin in orbit. The first Oscars were built by the Naval Avionics Facility at Indianapolis. But by completion of Oscars 1, 2, 3, 5, and 7 it was clear that NAFI was not able to meet the quality standards - Oscars 1, 2, 5, and 7 were orbited, but none operated more than a few weeks before failing. The Navy decided that APL would refurbish NAFI-built for Oscars 4, 6, 8, 9, and 10. The reworked satellites operated for 7 to 11 months in orbit. APL built Oscars 11 through 17 from scratch, and RCA was selected for further production. Oscar 12 represented the first satellite which incorporated all the lessons learned from earlier failures, and this and subsequent Transits operated from 14 to 20 years before failing.
When RCA received the production contract, the satellite lifetimes were expected to be 14 months. After RCA had completed Oscars 18 through 32, it was clear that the lifetime was actually in excess of 14 years. Therefore production ended. Unlaunched satellites were placed in gray containers - "the long gray line" - in long-term storage at RCA. Ten of these stored satellites proved sufficient to keep Transit operational for the rest of the century.
This remarkable fact was due to the basic satellite design, which allowed improvement of the on-board software. Transit navigational accuracy improved from 120 m in 1964 to 3 m in 1980, using the same basic satellites, largely through improvements in the earth geodesy model. In 1967 Transit signal information was released for public use. By the early 1970's low-cost receivers had been developed, and the system was adopted for oil platforms and supertankers. The cost of Transit receivers was eventually below $1,000.
A Transit Improvement Program (TIP) in 1969-1980 resulted in the Nova production satellite. This was more accurate than the basic Transit through use of rocket motors to correct orbital precession and atmospheric drag, but at a mass twice as much as Transit. Only two TIP and three Nova satellites were launched. These were radiation-hardened and could maintain accurate position fixes for months without ground updates - evidently intended to provide Transit navigation signals to ballistic missile submarines even after a nuclear exchange. But they did not replace Transit. Instead, the decision was taken to replenish the Transit constellation with the satellites that had been in storage for nearly 20 years. The first constellation replenishment launch was made in 1985. The Scout launch vehicle had been so improved that a single launch could put two Transits in orbit ("SOOS"- Stacked Oscars On Scout). Three subsequent dual constellation replenishment launches of Transits that had been stored for nearly 20 years were made in 1987-1989. This established the constellation for the rest of Transit's operational life - 12 satellites, with 7 or 8 operational, and the remaining serving as on-orbit spares.
More at: Transit.
| Transit 1A, 1B Navigation satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1959 - 1960. |
| Transit 2A, 2B Navigation satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1960. |
| Transit 3A, 3B Navigation satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1960 - 1961. |
| Transit 4A, 4B Navigation satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1961. |
| Transit-5A 1, 2, 3 Navigation satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1962 - 1963. Used Transit-Bus. |
| Transit-5BN 1, 2, 3 Navigation satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1963 - 1964. Used Transit-Bus. |
| Transit-5E 1 Experimental satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1963. Used Transit-Bus. |
| Transit-5E 3 Experimental satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1963. Used Transit-Bus. |
| Transit-5E 2 Experimental satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1964. Used Transit-Bus. |
| Transit-5C 1, 2 Navigation satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1964. Used Transit-Bus. |
| Transit-5E 5 Experimental satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN, USA. Launched 1964. Used Transit-Bus. |
| LIDOS Geodetic-research satellite built by JHU/APL for USAF STP (Space Test Program), USA. Launched 1968. Used Transit-Bus. |
| SAS A (Uhuru) Null |
| Triad 1 (TIP 1, NNS) Null |
| SAS B Astronomy, X-Ray, Gamma satellite built by NASA GSFC for NASA, USA. Launched 1972. Used mod. Transit-Bus. |
| SAS C Astronomy, X-Ray, Gamma satellite built by Center for Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Applied Physics Laboratory, Johns Hopkins University for NASA, USA. Launched 1975. Used mod. Transit-Bus. |
| TIP 2, 3 (Triad, NNS) Null |
| Wideband (P76-5) Null |
| Transat (Transit-O 11, NNS 30110) Null |
| Nova (NNS) Null |
| Polar Bear (P87-1) Null |
| Transit-5E 4 Experimental satellite built by Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) for USN. Used Transit-Bus. |
Family: Communications, Earth, Medium earth orbit, Navigation. Country: USA. Spacecraft: Transit, TIP. Launch Vehicles: Thor, Delta, Scout A, Thor Able, Thor Able II, Scout, Thor Ablestar, Scout X-3, Scout X-4, Scout B-1, Scout D-1, Scout A-1, Scout G-1, Scout D. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral, Vandenberg, Cape Canaveral LC17B, Cape Canaveral LC17A, Vandenberg SLC2E, Vandenberg SLC2W, Vandenberg SLC5. Agency: APL, USN, USAF, DARPA, RCA. Bibliography: 126, 2, 279, 405, 4256, 4463, 6, 6994, 13290, 13291, 13292, 13293, 13294, 13295, 13296.
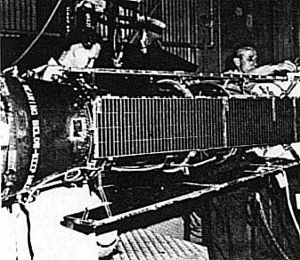 | Transit Operational Credit: USN |
 | Transit 2A Credit: USN |
 | LIDOS Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Polar Bear Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Explorer 53 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
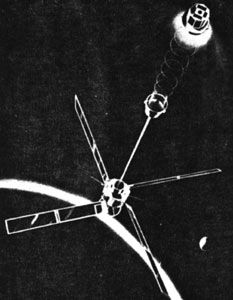 | Transit 5A Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transit-5BN 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transit 5C-1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
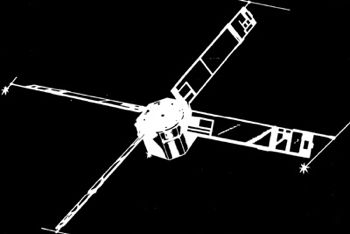 | Transit-5E 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transit-5E 2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
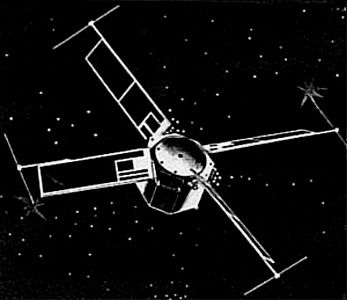 | Transit-5E 3 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transit-5E 5 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transat Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transit O-18 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transit 1A Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Transit 2A Credit: Manufacturer Image |
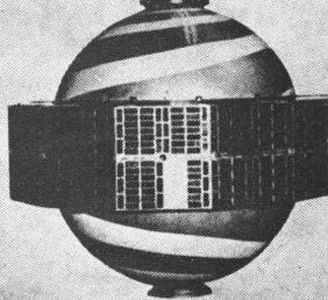 | Transit 3A Credit: Manufacturer Image |
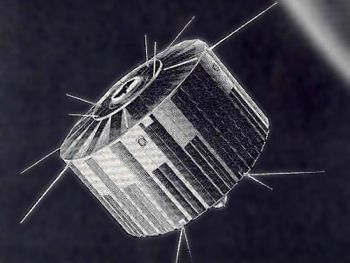 | Transit 4A Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Lofti 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1958 September 4 - .
- Transit and TIROS satellite programs initiated - .
Spacecraft: Transit,
Tiros,
.
The Transit and TIROS satellite programs were initiated with booster responsibilities assigned to AFBMD. Transit was a navigation satellite, while TIROS (Television Infrared Observation Satellite) was to take television pictures of cloud cover and transmit meteorological information for relay to ground stations.
1959 February 20 - .
- Development plans for Transit and TIROS satellites. - . Spacecraft: Transit, Tiros, . As requested by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), AFBMD forwarded its development plans for the Transit navigation satellite and TIROS weather satellite programs to Headquarters USAF..
1959 September 17 - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17A. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Able II. FAILURE: Third stage failed.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Transit 1A - . Payload: Transit 1A. Mass: 119 kg (262 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: DARPA. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. Decay Date: 1959-09-17 . A Thor/Able II booster carrying the Navy's Transit IA navigation satellite was launched from Cape Canaveral. A third stage malfunction prevented the satellite from achieving orbit. First Transit test satellite; failed to reach orbit..
1959 September 23 - . LV Family: Polaris, Titan, Atlas, Thor, Jupiter, .
- Responsibility for military space programs assigned to USAF - .
Spacecraft: WS-117,
Transit,
Midas,
Samos.
Once again, the Defense Department reorganized its space program. Primary responsibility for military space programs was assigned to the Air Force. ARPA retained responsibility for advanced research on missile defense, solid propellants, and several other projects. Existing projects were reassigned to the military services from ARPA - MIDAS and SAMOS to the Air Force,the Transit navigation satellite to the Navy, and NOTUS to the Army. These reassignments were not immediately effective, but the move toward Air Force development, production, and launching of military space vehicles was quite clear.
1960 April 13 - . 12:02 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 1B - .
Mass: 121 kg (266 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DARPA.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
Duration: 89.00 days. Decay Date: 1967-10-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 31 . COSPAR: 1960-Gamma-2. Apogee: 644 km (400 mi). Perigee: 363 km (225 mi). Inclination: 51.20 deg. Period: 94.60 min.
The first Thor/Ablestar launched from Cape Canaveral placed the Navy's Transit IB navigation satellite into orbit. This was the first navigation satellite to be placed in orbit. The Ablestar upper stage demonstrated the first engine restart in space. The Able-Star second stage demonstrated the first engine restart in space and the feasibility of using satellites as navigational aids. The first experimental Transit satellite to achieve orbit operated for 89 days. It transmitted on two frequency pairs to test the technique for refraction correction and to determine if the transmitted frequencies should be close together or far apart. It also tested a magnetic torque device for spacecraft attitude control - the first satellite to do so.
1960 June 22 - . 05:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 2A - .
Mass: 101 kg (222 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
USAF Sat Cat: 45 . COSPAR: 1960-Eta-1. Apogee: 988 km (613 mi). Perigee: 604 km (375 mi). Inclination: 66.70 deg. Period: 100.80 min.
A Thor/Ablestar booster placed a U.S. Navy Transit IIA research and development navigation satellite into orbit using the Ablestar second stage with a restart engine. A smaller parasitic radiation-measuring satellite, the Galactic Radiation Experiment Background (GREB), was also placed into orbit. This was the first time two satellites had been carried in "piggyback" alignment on a single booster. Also returned geodetic data. Similar to Transit 1B, it transmitted until 26 October 1962. A planned Transit 2B was considered redundant and never built.
1960 November 30 - . 19:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: 1.
- Transit 3A - . Mass: 91 kg (200 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. Decay Date: 1960-11-30 . Destroyed by range safety; launched with Solrad 2. Thor shut down too early..
1961 February 22 - . 03:45 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 3B - .
Mass: 112 kg (246 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
Decay Date: 1961-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 87 . COSPAR: 1961-Eta-1. Apogee: 225 km (139 mi). Perigee: 135 km (83 mi). Inclination: 28.40 deg. Period: 88.10 min.
Lofti 1 piggyback payload did not separate. Nevertheless Transit 3B returned useful data needed for design of the operational satellites. It carried a digital clock driven by the same oscillator that drove the transmitters. It transmitted timing signals governed by the clock and a 384-bit memory. This allowed testing of the techniques for loading the memory from the ground, the ability of the memory to hold a message in orbit, and the ability to encode the memory contents by means of a frequency modulation on one of the main transmitters. It was also shown that ±60° phase modulation could be used to transmit the contents of the satellite memory without degradation of the accuracy of the Doppler signal and Doppler measurements.
- Lofti 1 - . Mass: 25 kg (55 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. Decay Date: 1961-03-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 87 . COSPAR: 1961-Eta-2. Apogee: 983 km (610 mi). Perigee: 188 km (116 mi). Inclination: 28.30 deg. Period: 96.40 min. Failed to separate from Transit 3B..
1961 June 29 - . 04:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 4A - . Mass: 79 kg (174 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 116 . COSPAR: 1961-Omicron-1. Apogee: 986 km (612 mi). Perigee: 865 km (537 mi). Inclination: 66.80 deg. Period: 103.50 min. Transits 4A and 4B were drum-shaped instead of spherical to provide more space for solar cells. In addition, operational 150-and 400-MHz frequencies were used for the first time. Carried SNAP-3A nuclear power source..
1961 November 15 - . 22:19 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 4B - .
Mass: 86 kg (189 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
USAF Sat Cat: 202 . COSPAR: 1961-A-Eta-1. Apogee: 1,104 km (685 mi). Perigee: 953 km (592 mi). Inclination: 32.40 deg. Period: 105.70 min.
Together, Transits 4A and 4B allowed the determination of harmonics in the Earth's gravity field that had not yet been evaluated, and they also allowed firm navigational ties to be established from continent to continent as well as to isolated islands. As a result, it was discovered that the position of Hawaii was incorrect by 1 km. Carried SNAP 3 nuclear power source.
1962 December 19 - . 01:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout X-3.
- Transit 5A - . Payload: Transit 5A-1. Mass: 61 kg (134 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. Decay Date: 1986-09-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 509 . COSPAR: 1962-B-Psi-1. Apogee: 347 km (215 mi). Perigee: 336 km (208 mi). Inclination: 90.60 deg. Period: 91.40 min. First operational solar-powered prototype; failed first day. The satellite verified a new technique for deploying the solar panels and for separating from the rocket, but otherwise it was not successful because of trouble with the power system..
1963 April 5 - . 03:01 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout X-3. FAILURE: Failure.. Failed Stage: U.
- Transit 5A-2 - . Payload: Transit 5A-2. Mass: 84 kg (185 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. Decay Date: 1963-04-05 . Replacement for the failed Transit 5A; failed to reach orbit..
1963 June 16 - . 01:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout X-3.
- Transit 5A-3 - .
Payload: Transit 5A-3. Mass: 55 kg (121 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
Decay Date: 1990-08-03 . USAF Sat Cat: 594 . COSPAR: 1963-022A. Apogee: 360 km (220 mi). Perigee: 350 km (210 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 91.60 min.
First operational prototype with a redesigned power supply. A malfunction of the memory occurred during powered flight that kept it from accepting and storing navigation messages, and the oscillator stability was degraded during launch. The satellite could not be used for navigation, but it was the first to achieve gravity-gradient stabilization, and its other subsystems performed well.
1963 September 28 - . 20:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2E. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 5BN-1 - .
Mass: 70 kg (154 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
USAF Sat Cat: 670 . COSPAR: 1963-038B. Apogee: 1,125 km (699 mi). Perigee: 1,066 km (662 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 107.20 min.
The first Thor/Ablestar launch from Vandenberg carried a Navy payload that became the first satellite to be operated completely with nuclear power. A SNAP-9A satellite nuclear power supply, built by the Martin Company and the Atomic Energy Commission, was used to power the satellite. First test of nuclear-powered Transit operational prototype. Carried SNAP-9A nuclear power source. The satellite achieved gravity-gradient stabilization, but upside down, making the signal level too low for operational users with low-gain antennas. However, geodetic and navigational evaluation data were obtained.
- Transit 5E-1 - .
Payload: APL SN 39. Mass: 61 kg (134 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
USAF Sat Cat: 671 . COSPAR: 1963-038C. Apogee: 1,123 km (697 mi). Perigee: 1,065 km (661 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 107.10 min.
The first Thor/Ablestar launch from Vandenberg carried a Navy payload that became the first satellite to be operated completely with nuclear power. A SNAP-9A satellite nuclear power supply, built by the Martin Company and the Atomic Energy Commission, was used to power the satellite. The missions of Satellite 1963-038C were to measure omnidirectional flux of protons and electrons at various energy levels, radiation effects on transistors, and the effectiveness of thermal coatings. The satellite was launched together with a classified Department of Defense spacecraft on September 28, 1963. Its planned orbit was apogee 1120 kilometres, perigee 1070 kilometres, inclination 88.9 degrees. The satellite weighed 62 kg; its body was in the shape of an 0.46 m x 0.25 m octagonal prism. It was powered by four solar blades and transmited on 136, 162, and 324 mcs. The spacecraft was built for the Bureau of Naval Weapons. In 1967 it was still sending usable data from all systems.
1963 December 5 - . 21:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2E. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 5BN-2 - .
Mass: 75 kg (165 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
USAF Sat Cat: 704 . COSPAR: 1963-049B. Apogee: 1,110 km (680 mi). Perigee: 1,061 km (659 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 107.00 min.
Transit operational prototype powered by a SNAP-9A nuclear power source. First operational navigation satellite. It was used regularly by both surface and submarine units of the Navy until November 1964. From this point in time the US Navy had continuous use of satellite navigation.
- Transit 5E-3 - . Mass: 53 kg (116 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 705 . COSPAR: 1963-049C. Apogee: 1,108 km (688 mi). Perigee: 1,060 km (650 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 106.90 min. Radiation monitoring..
1964 April 21 - . 18:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2E. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar. FAILURE: Failure. Failed Stage: U.
- Transit 5BN-3 - . Mass: 75 kg (165 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. Decay Date: 1964-04-21 . COSPAR: F640421A. Carried SNAP-9A nuclear power source. After this launch failure it was decided that operational Transits would be solar-powered only..
- Transit 5E-4 - . Mass: 55 kg (121 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. COSPAR: F640421B. Radiation monitoring..
1964 June 4 - . 03:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout X-4.
- Transit 5C-1 - . Payload: Transit 5C / OPS 4412. Mass: 54 kg (119 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 801 . COSPAR: 1964-026A. Apogee: 898 km (557 mi). Perigee: 825 km (512 mi). Inclination: 90.50 deg. Period: 102.20 min. Operational prototype similar to the 5A series but with some redesign to improve performance. Operated successfully until 23 August 1965..
1964 October 6 - . 17:04 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2W. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit O-1 - . Payload: NNS 30010 / Ablestar 016 / OPS 5798. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 897 . COSPAR: 1964-063B. Apogee: 1,077 km (669 mi). Perigee: 1,046 km (649 mi). Inclination: 90.20 deg. Period: 106.40 min. Naval Avionics Facility-assembled production spacecraft. Failed after a few days operation..
1964 December 13 - . 00:08 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2W. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit 5E-5 - . Payload: APL SN 43 / OPS 6582. Mass: 78 kg (171 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 959 . COSPAR: 1964-083C. Apogee: 1,064 km (661 mi). Perigee: 1,007 km (625 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 105.90 min. Celestial UV, magnetic field data..
- Transit O-2 - . Payload: NNS 30020 / OPS 6582. Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 965 . COSPAR: 1964-083D. Apogee: 1,079 km (670 mi). Perigee: 1,020 km (630 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 106.20 min. Naval Avionics Facility-assembled production spacecraft. Failed after a few days operation..
1965 March 11 - . 13:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2E. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit-O-3 - . Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. Decay Date: 1965-06-14 . USAF Sat Cat: 1303 . COSPAR: 1965-017A. Apogee: 418 km (259 mi). Perigee: 191 km (118 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 90.70 min. Naval Avionics Facility-assembled production spacecraft. Failed after a few weeks operation..
1965 June 24 - . 22:35 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2E. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit O-4 - . Payload: NNS 30040 / OPS 8480. Mass: 61 kg (134 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 1420 . COSPAR: 1965-048A. Apogee: 1,125 km (699 mi). Perigee: 1,016 km (631 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 106.60 min. Spacecraft built by Naval Avionics Facility, but refurbished by APL. Operated for 7 to 11 months, but then failed due to poor workmanship of NAFI components..
1965 August 13 - . 22:11 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2E. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Ablestar.
- Transit O-5 - . Payload: NNS 30050 / OPS 8464. Mass: 61 kg (134 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 1514 . COSPAR: 1965-065F. Apogee: 1,183 km (735 mi). Perigee: 1,078 km (669 mi). Inclination: 89.90 deg. Period: 107.90 min. Naval Avionics Facility-assembled production spacecraft. Failed after a few weeks operation..
1965 December 22 - . 04:33 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-6 - . Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 1864 . COSPAR: 1965-109A. Apogee: 1,059 km (658 mi). Perigee: 891 km (553 mi). Inclination: 89.10 deg. Period: 104.60 min. Spacecraft built by Naval Avionics Facility, but refurbished by APL. Operated for 7 to 11 months, but then failed due to poor workmanship of NAFI components..
1966 January 28 - . 17:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-7 - . Mass: 50 kg (110 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 1952 . COSPAR: 1966-005A. Apogee: 1,180 km (730 mi). Perigee: 850 km (520 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 105.40 min. Naval Avionics Facility-assembled production spacecraft. Failed after a few weeks operation..
1966 March 26 - . 03:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-8 - . Mass: 50 kg (110 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 2119 . COSPAR: 1966-024A. Apogee: 1,099 km (682 mi). Perigee: 879 km (546 mi). Inclination: 89.70 deg. Period: 104.90 min. Spacecraft built by Naval Avionics Facility, but refurbished by APL. Operated for 7 to 11 months, but then failed due to poor workmanship of NAFI components..
1966 May 19 - . 02:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-9 - . Mass: 50 kg (110 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 2176 . COSPAR: 1966-041A. Apogee: 951 km (590 mi). Perigee: 833 km (517 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 102.80 min. Spacecraft built by Naval Avionics Facility, but refurbished by APL. Operated for 7 to 11 months, but then failed due to poor workmanship of NAFI components..
1966 August 18 - . 02:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-10 - .
Mass: 58 kg (127 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
USAF Sat Cat: 2401 . COSPAR: 1966-076A. Apogee: 1,089 km (676 mi). Perigee: 1,038 km (644 mi). Inclination: 88.90 deg. Period: 106.50 min.
Spacecraft built by Naval Avionics Facility, but refurbished by APL. Only partially operational due to a decrease in the number of solar cells available for charging the batteries after thermal working of the solar cell interconnections in day/night cycles.
1967 April 14 - . 03:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-12 - . Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 2754 . COSPAR: 1967-034A. Apogee: 1,064 km (661 mi). Perigee: 1,037 km (644 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 106.20 min. First APL-built Transit Operational satellite. Operational life of this and subsequent Transits was over 14 years..
1967 May 18 - . 09:05 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-13 - . Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 2807 . COSPAR: 1967-048A. Apogee: 1,088 km (676 mi). Perigee: 1,059 km (658 mi). Inclination: 89.60 deg. Period: 106.70 min. Operational life over 20 years..
1967 September 25 - . 08:25 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-14 - . Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 2965 . COSPAR: 1967-092A. Apogee: 1,099 km (682 mi). Perigee: 1,030 km (640 mi). Inclination: 89.20 deg. Period: 106.50 min.
1968 March 2 - . 03:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-18 - . Mass: 60 kg (132 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 3133 . COSPAR: 1968-012A. Apogee: 1,130 km (700 mi). Perigee: 1,014 km (630 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 106.70 min. First RCA-built Transit..
1970 August 27 - . 13:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A.
- Transit O-19 - . Mass: 18 kg (39 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 4507 . COSPAR: 1970-067A. Apogee: 1,201 km (746 mi). Perigee: 946 km (587 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 106.70 min. The last Scout booster to be launched by an all-military crew was fired from Vandenberg AFB. Future Scout operations would be conducted by contractor launch teams under Air Force technical management. .
1972 September 2 - . 17:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout B-1.
- Triad 1 - . Payload: TIP 1. Mass: 94 kg (207 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: TIP. USAF Sat Cat: 6173 . COSPAR: 1972-069A. Apogee: 792 km (492 mi). Perigee: 709 km (440 mi). Inclination: 90.00 deg. Period: 99.80 min. A Scout rocket launched from Vandenberg boosted an improved Navy navigation satellite (TRIAD OI-IX) into orbit. Prototype of improved Transit satellite..
1973 October 30 - . 00:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout A-1.
- Transit O-20 - . Mass: 58 kg (127 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 6909 . COSPAR: 1973-081A. Apogee: 1,120 km (690 mi). Perigee: 885 km (549 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 105.20 min. Operational life over 20 years. SAMSO launched a Transit navigation Satellite into orbit from Vandenberg Air Force Base. It replaced a polar orbiting spacecraft which had ceased to operate..
1975 October 12 - . 06:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout D-1.
- Triad 2 - .
Payload: TIP 2. Mass: 94 kg (207 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: TIP.
Decay Date: 1991-05-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 8361 . COSPAR: 1975-099A. Apogee: 490 km (300 mi). Perigee: 427 km (265 mi). Inclination: 90.40 deg. Period: 93.80 min.
A Scout vehicle carrying a Transit Improvement Program payload was launched from SLC-5, Western Test Range. Launch was successful, but the solar panels of the satellite failed to deploy after the satellite had reached orbit. Prototype of improved Transit satellite. Tested pulsed plasma engine.
1976 September 1 - . 21:14 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout D-1.
- TIP 3 - .
Payload: Triad 3 (TIP 3). Mass: 94 kg (207 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USN.
Program: Transit.
Class: Navigation.
Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: TIP.
Decay Date: 1981-05-30 . USAF Sat Cat: 9403 . COSPAR: 1976-089A. Apogee: 789 km (490 mi). Perigee: 345 km (214 mi). Inclination: 90.30 deg. Period: 95.90 min.
A Scout vehicle carrying a Transit Improvement Program payload was launched from SLC-5, Western Test Range. Launch was successful, but the solar panels of the satellite failed to deploy after the satellite had reached orbit. Prototype of improved Transit satellite. Also tested pulsed plasma engine.
1977 October 28 - . 04:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout D-1.
- Transat O-11 - . Mass: 94 kg (207 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 10457 . COSPAR: 1977-106A. Apogee: 1,097 km (681 mi). Perigee: 1,059 km (658 mi). Inclination: 89.70 deg. Period: 106.80 min. Modification of first APL-built operational Transit for 'related experiments'..
1981 May 15 - . 06:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Nova 1 - . Mass: 170 kg (370 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: TIP. USAF Sat Cat: 12458 . COSPAR: 1981-044A. Apogee: 1,185 km (736 mi). Perigee: 1,165 km (723 mi). Inclination: 90.20 deg. Period: 108.90 min. Improved Transit..
1983 June 27 - . 15:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout D-1.
- HILAT - . Payload: Transit O-16 / P83-1. Mass: 55 kg (121 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF STP. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 14154 . COSPAR: 1983-063A. Apogee: 818 km (508 mi). Perigee: 754 km (468 mi). Inclination: 82.00 deg. Period: 100.60 min. Modification of Transit O-16 for military communications research. Officially: Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1984 October 12 - . 01:43 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Nova 3 - . Mass: 165 kg (363 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: TIP. USAF Sat Cat: 15362 . COSPAR: 1984-110A. Apogee: 1,200 km (700 mi). Perigee: 1,152 km (715 mi). Inclination: 89.90 deg. Period: 108.90 min. Improved Transit. Pulsed plasma engine..
1985 August 3 - . 03:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Transit O-24 - . Mass: 55 kg (121 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 15935 . COSPAR: 1985-066A. Apogee: 1,254 km (779 mi). Perigee: 1,000 km (600 mi). Inclination: 89.90 deg. Period: 107.90 min. First operational Transits launched in 12 years due to reliability of original constellation. First paired Transit launch..
- Transit O-30 - . Mass: 55 kg (121 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 15936 . COSPAR: 1985-066B. Apogee: 1,255 km (779 mi). Perigee: 999 km (620 mi). Inclination: 89.90 deg. Period: 107.90 min.
1986 November 14 - . 00:23 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Polar Bear - .
Payload: Transit O-16 / P 87-1. Mass: 125 kg (275 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF STP.
Class: Earth.
Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: Transit.
USAF Sat Cat: 17070 . COSPAR: 1986-088A. Apogee: 1,013 km (629 mi). Perigee: 955 km (593 mi). Inclination: 89.60 deg. Period: 104.80 min.
Tranist O-17 had been turned over to the National Air and Space Museum in 1976 and was displayed to the public for more than 8 years. In 1984, it was refurbished at APL and launched as the Polar Beacon Experiment and Auroral Research satellite to collect data for studying communications over the Earth's polar regions.
1987 September 16 - . 19:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Transit O-27 - . Mass: 59 kg (130 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 18361 . COSPAR: 1987-080A. Apogee: 1,174 km (729 mi). Perigee: 1,016 km (631 mi). Inclination: 90.30 deg. Period: 107.20 min. Dual launch of operational Transits manufactured in the 1960's to replenish the constellation..
- Transit O-29 - . Mass: 59 kg (130 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 18362 . COSPAR: 1987-080B. Apogee: 1,177 km (731 mi). Perigee: 1,016 km (631 mi). Inclination: 90.30 deg. Period: 107.20 min.
1988 April 26 - . 01:57 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Transit O-23 - . Mass: 64 kg (141 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 19070 . COSPAR: 1988-033A. Apogee: 1,301 km (808 mi). Perigee: 1,016 km (631 mi). Inclination: 90.40 deg. Period: 108.50 min. Dual launch of operational Transits manufactured in the 1960's to replenish the constellation..
- Transit O-32 - . Mass: 64 kg (141 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 19071 . COSPAR: 1988-033B. Apogee: 1,298 km (806 mi). Perigee: 1,017 km (631 mi). Inclination: 90.40 deg. Period: 108.50 min.
1988 June 16 - . 06:54 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Nova 2 - . Mass: 174 kg (383 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: TIP. USAF Sat Cat: 19223 . COSPAR: 1988-052A. Apogee: 1,198 km (744 mi). Perigee: 1,154 km (717 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 108.90 min. Improved Transit. Pulsed plasma thruster.
1988 August 25 - . 06:59 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC5. LV Family: Scout. Launch Vehicle: Scout G-1.
- Transit O-25 - . Mass: 59 kg (130 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 19419 . COSPAR: 1988-074A. Apogee: 1,176 km (730 mi). Perigee: 1,032 km (641 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 107.30 min. Dual launch of operational Transits manufactured in the 1960's to replenish the constellation..
- Transit O-31 - . Mass: 59 kg (130 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USN. Program: Transit. Class: Navigation. Type: Navigation satellite. Spacecraft: Transit. USAF Sat Cat: 19420 . COSPAR: 1988-074B. Apogee: 1,174 km (729 mi). Perigee: 1,032 km (641 mi). Inclination: 89.80 deg. Period: 107.30 min.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use