
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Lunar Rovers
Lunar rovers were studied in a dizzying variety of sizes and shapes by NASA in the 1960's - including crawlers, trains, hoppers, and even worms. Two rovers designed for manned use actually traveled the lunar surface in the 1970's - the American two-man Lunar Rover, and the Soviet Lunokhod, which traveled the moon in robotic mode but was originally designed as emergency cosmonaut transportation.
Subtopics
| Prospector American lunar rover. Study 1961. The Prospector spacecraft was a NASA/JPL unmanned lunar rover of the early 1960's. |
| Bendix Manned Lunar Vehicle 4 Wheel American manned lunar rover. Study 1961. The Bendix Manned Lunar Vehicle was a lunar rover design of November 1961. The vehicle had 4 wheels and a range of 400 km with a crew of 3 on a 14 day traverse. |
| Bendix Manned Lunar Vehicle 3 Wheel American lunar rover. Study 1961. The Bendix Lunar Mobile System was an unmanned lunar rover design of September 1961. The vehicle had 3 wheels, powered separately, and a range of 800 km. |
 | L2-1963 Russian lunar rover. Study 1963. The L2 was a project to land a remote-controlled self-propelled rover on the surface of the moon. It was described in a 23 September 1963 letter setting out the space exploration plan for 1965 to 1975. |
| Bendix Lunar Logistic System American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Bendix Lunar Logistic System was a lunar rover design of January 1963. The vehicle had 4 wheels with alternative front or all-wheel steering and a range of 800 km with a crew of 3 on a 14 day traverse. |
| Boeing LES Rover American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Boeing Lunar Exploration Systems lunar rover design of November 1963 was for a multipurpose rover with a range of 480 km with a crew of 2 on a 8 day traverse. The cabin had a volume of 4.95 cubic meters. |
| Grumman LSS Project 344 Rover - Unmanned American lunar rover. Study 1963. The Grumman Lunar Logistics System Project 344 unmanned rover design of February 1963 had 4 wheels (two equal-weight, 2 wheel modules of 360 cm diameter). The robot had a range of 750 km. |
 | Grumman LSS Project 344 Rover - 1 man American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Grumman Lunar Logistics System Project 344 single-crew rover of January 1963 had 2 x two-wheeled power modules. Each wheel was 360 cm in diameter, and the rover had a range of 300 km on a 3.3 day traverse. |
| Grumman LSS Project 344 Rover - 2 man American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Grumman Lunar Logistics System Project 344 two-man rover design of January 1963 consisted of the basic vehicle, a manned module, and a tanker. This provided a range of 370 km on a 7 day traverse. |
| Grumman LSS Project 344 Rover - 3 man American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Grumman Lunar Logistics System Project 344 three-man lunar rover design of January 1963 used a 3 module vehicle. It had a range of 2340 km on a 28 day traverse. |
| Grumman LSS Project 344 Rover - 2 man 3 kW American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Grumman Lunar Logistics System Project 344 alternate three-crew lunar rover design of February 1963 vehicle had three x two wheeled modules. The rover would have a range of 770 km on a 23.5 day traverse. |
| LSS Site Survey Payload American lunar rover. Study 1963. The BellComm Lunar Logistic System unmanned Site Survey Payload was outlined in a January 1963 study. The 2 x 2 vehicle had articulated wheels, a 1.5 m diameter folded chassis. and a range of 260 km. |
| Lunar Logistic System 13.7 kW American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. This NASA Lunar Logistic System lunar rover design of March 1963 had 4 wheels, rigidly mounted, and a range of 450 km with a crew of 2 on a 30 day traverse. The cabin had a volume of 9.72 cubic meters. |
| Lunar Logistic System 6 kW American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. This NASA Lunar Logistic System lunar rover design of March 1963 had 4 wheel unit, each wheel 1.3 m in diameter and 20 cm wide. It had a range of 370 km with a crew of 2 on a 7 day traverse. |
| Northrop LSS Lunar Rover RV-1 American lunar rover. Study 1963. The Northrop Lunar Logistic System RV-1 unmanned lunar rover design of January 1963 had 3 wheels, rigidly mounted, and a range of 80 km. |
| Northrop LSS Lunar Rover RV3 RV4 American lunar rover. Study 1963. The unmanned portion of the January 1963 Northrop Lunar Logistic System had 4 articulated wheels and a range of 240 km. |
| Northrop LSS Lunar Rover RV5 American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. This Northrop Lunar Logistic System design of January 1963 was a 3 wheel open cart and had a range of 30 km with a crew of 2. It could also tow the RV6 50 kg, 2 to 4 wheeled dolly or trailer. |
| Northrop LSS Lunar Rover RV7 American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Northrop Lunar Logistic System RV7 was a lunar rover design of January 1963. The one-crew vehicle was designed for scooping and dozing operations. |
| Northrop LSS Lunar Rover RV8 American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Northrop Lunar Logistic System RV8 was a lunar rover design of January 1963. Dual single-crew vehicles were designed to be operated separately or together as a system. |
| Northrop LSS Lunar Rover RV-1A American manned lunar rover. Study 1963. The Northrop Lunar Logistic System RV-1A crewed rover of January 1963 had 4 tracks and a range of 2900 km on a 27 day traverse. |
| Northrop Molab American manned lunar rover. Study 1964. The Northrop Molab lunar rover design of March 1964 had 4 wheels, each a flexible torus or controlled flexible disc. It could accommodate a crew of 2 on a 14 day traverse. |
| Northrop ALSS Rover American manned lunar rover. Study 1964. Northrop completed Molab Studies under a Apollo Logistic Support Systems contract in March 1964. |
| Surveyor Lunar Rover American lunar rover. Cancelled 1965. Follow-on Surveyor unmanned lunar landers were to deploy small nuclear-powered rovers (a carry-over from the cancelled Prospector spacecraft). |
| Bendix Molab American manned lunar rover. Study 1965. The Bendix Molab lunar rover design of June 1965 had 4 wheels and a range of 400 km with a crew of 2 on a 14 day traverse. The cabin had a volume of 12.8 cubic meters. |
| Bendix LSSM American manned lunar rover. Study 1965. The Bendix LSSM lunar rover design of October 1965 had 4 wheels. and a range of 400 km with a crew of 2 on a 14 day traverse. |
| Boeing LSSM American manned lunar rover. Study 1965. The Boeing LSSM lunar rover design of June 1965 had 4 wheels of 1.2 or 1.6 m diameter. and a range of 200 km with a crew of 2 on a 14 day traverse. |
| Bendix ALSS Rover American manned lunar rover. Study 1965. The Bendix ALSS Payloads lunar rover design of June 1965 had a range of 400 km with a crew of 2 on a 14 day traverse. A variety of configurations were studied in detail. |
 | MOBEV R1B American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. Early manned operations would utilize the basic Apollo LM or an augmented version of it. The augmented version would a small mobility unit. |
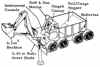 | MOBEV R1CB American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOBEV R1CB Base Support Vehicle -- Special Purpose was a manned lunar tractor, which provided base support capability in terms of earth moving, towing, and general utility within close proximity of the base. |
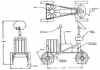 | MOBEV R0AE American lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOBEV R0AE was based on the cancelled Surveyor Lunar Roving Vehicle, originally conceived for the Apollo site selection program. |
| MOBEV R0CE American lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOBEV R0CE utilized a Surveyor probe from a lunar orbiting vehicle. The rover would operate in lunar day or night and have a total range capability of 200 km over a 90-day period. |
| MOBEV R0DE American lunar rover. Study 1966. Robotic vehicle delivered to the lunar surface with a LM-Shelter or a LM-Truck-Shelter and used during and after the manned mission to explore areas prior to committing a man. |
 | MOBEV R1DE American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOBEV R1DE recommended Lunar Station Vehicle was a Cabined LSSM, a manned exploration vehicle designed to provide a shirt-sleeve (open spacesuit faceplate) environment. |
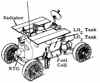 | MOBEV R2C(1)E American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOBEV R2C(1)E manned Mobile Laboratory Vehicle (MOLAB) was to be used for exploration of the moon. The MOLAB provided complete life support capabilities for its two-man crew during a 14-day, 400-km mission. |
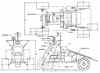 | MOBEV R3DE American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOBEV R3DE Extended Traverse Vehicle was a 90-Day MOBEX, a manned mobile laboratory used for exploration of the moon. |
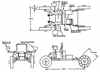 | MOBEV RIB(1)E American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOBEV RIB(1)E recommended Lunar Station Vehicle was a Greater Versatility LSSM, an exploration vehicle designed for both manned and unmanned operation. |
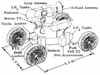 | MOCOM American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. Third generation versions of the CM were studied by North American in 1966 to further modify a CM shelter to provide mobility. Essentially the CM was mounted on a four-wheel chassis. |
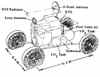 | MOLEM American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. Third generation versions of LM derivative equipment were studied by Grumman in a report delivered on 10 May 1966. |
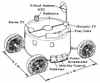 | MOCAN American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. The MOCAN was a manned Lunar Rover using the planned Boeing pressurized Apollo Multipurpose Mission Module (CAN) as the basic structure and MOLAB wheels |
 | LSSM American manned lunar rover. Study 1968. The Bendix Local Science Survey Module was a forerunner of the Lunar Rover. The LSSM was a small size vehicle used to support a local manned survey. It was proposed for delivery with an LM Shelter. |
 | Molab American manned lunar rover. Cancelled 1968. The moderate capacity mobile laboratory (MOLAB) concept was studied in two NASA/MT contracts to determine configurations and capabilities of vehicles in the 2950 to 3850 kg class. |
 | Luna Ye-8 Russian lunar rover. Lunar lander and rover satellite, Russia. Launched 1969 - 1973. |
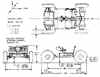 | Apollo LRV American manned lunar rover. The Apollo Lunar Roving Vehicle was one of those sweet pieces of hardware that NASA and its contractors seemed to be able to develop so effortlessly during the short maturity of the Apollo program. The Lunar Rover was the only piece of equipment from NASA's ambitious post-Apollo lunar exploration plans to actually fly in space, being used on Apollo missions 15, 16, and 17 in 1971-1972. The design was based on three years of studies for light, two-crew, open-cockpit 'Local Science Survey Modules'. Although Bendix built a prototype, Boeing ended up with the production contract. |
 | DLB Lunokhod 1 Russian manned lunar rover. Study 1971. One of several conceptual models of Lunokhod or Marsokhod pressurized surface rovers planned for Soviet moon or Mars expeditions. |
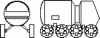 | DLB Lunokhod 2 Russian manned lunar rover. Study 1971. One of several conceptual models of Lunokhod or Marsokhod pressurized surface rovers planned for Soviet moon or Mars expeditions. |
 | DLB Lunokhod 3 Russian manned lunar rover. Study 1971. One of several conceptual models of Lunokhod or Marsokhod pressurized surface rovers planned for Soviet moon or Mars expeditions. |
 | LSV American manned lunar rover. Study 1971. The Lunar Sortie Vehicle (LSV), was a North American Rockwell design of 1971, conceived as a railroad train without the rails. |
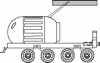 | Lunokhod LEK Russian manned lunar rover. Study 1973. Lunar rover for the Vulkan Lunar Expedition. The rover provided pressurized quarters for 2 crew, allowing trips up to 200 km from the lunar base at a top speed of 5 km/hr. |
| Bendix SLRV American lunar rover. Study 1964. The Bendix SLRV unmanned lunar rover design of April 1964 had a speed up to 25 kph on 4 tracks with floating pivot articulation. It was designed for a 105 day traverse mission. |
 | Lunar Leaper American manned lunar rover. Study 1964. One of the many bizarre modes for lunar transportation proposed in the early 1960's. |
 | Lunar Worm American manned lunar rover. Study 1966. The Aeronutronic Division of Philco Corp. proposed the unique Lunar Worm Planetary Roving Vehicle Concept in 1966. |
 | LOTRAN American manned lunar rover. Study 1989. The LOTRAN (LOcal TRANsportation) two-crew rover was the unpressurized lunar rover intended for local base operations in NASA's 90-Day-Study moon base concept of 1989. |
 | MOSAP American manned lunar rover. Study 1989. MOSAP (MObile Surface APplication traverse vehicle) was the pressurized lunar rover that was the key to NASA's 90-Day-Study moon base concept of 1989. It would greatly extend the range of manned lunar expeditions. |
 | Daylight Rover American manned lunar rover. Study 1990. The Daylight Rover was a Boeing concept of 1990, which consisted of two separate pressure vessels. The forward served as the driving station, and the rear served as a storm shelter and EVA airlock. |
 | DMLRV American manned lunar rover. Study 1990. |
 | Light Utility Rover American manned lunar rover. Study 1990. In 1990, Boeing Advanced Civil Space Systems performed an Advanced Civil Space Systems Piloted Rover Technology Assessment Study, which considered both a large pressurized and a small unpressurized rover. |
| Mega Rover American manned lunar rover. Study 1992. The Mega Rover was conceived to support a crew of six over thousands of kilometers of traverses. Variants had masses as great as 45 metric tons, exclusive of the descent and landing system. |
 | Pressurized Lunar Rover - Dual Hull American manned lunar rover. Study 1992. An alternate April 1992 USRA study by students at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University sketched out a design for a Pressurized Lunar Rover (PLR) using dual hulls. |
| PLR American manned lunar rover. Study 1992. A May 1992 USRA study by students at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University sketched out a design for a Pressurized Lunar Rover (PLR). |
| Rover First American manned lunar rover. Study 1992. Boeing updated their Apollo-era MOLAB pressurized rover concept in 1992. The concept, dubbed "Rover First," was smaller than the traditional pressurized rovers, and did not require a separate landing vehicle. |
| Ratler American earth rover. Tested 1995. Robotic All Terrain Lunar Exploration Rover demonstrated the use of existing technology for lunar exploration missions. |
 | Nomad American earth rover. Tested 1998. NOMAD was an unmanned rover developed by the Robotics Institute of Carnegie Mellon University to evaluate and demonstrate a robot capable of long distance and long duration planetary exploration. |
 | Lunar Polar Rover American manned lunar rover. Study 1999. Pressurized rover concept for a hypothetical lunar polar mission. |
 | MSTS American manned lunar rover. Study 1999. |
 | Habot American manned lunar rover. Study 2000. The Habot (Habitat Robot) modules would land on six articulated legs, which also provided the locomotion. These walking modules could operate autonomously or in a teleoperation mode. |
 | Morphlab American manned lunar rover. Study 2004. Morphlab (Modular Roving Planetary Habitat, Laboratory, and Base) was a lunar exploration system proposed by the University of Maryland. |
 | Athlete American lunar rover. Study 2005. Athlete was a Habot-inspired mobility system for doing cargo handling, assembly, maintenance, and servicing tasks on the moon. Each of the six limbs had a 6-degree-of-freedom manipulator with a wheel at the end. |
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use
