
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
AE
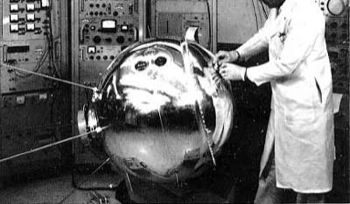 Explorer 17 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
AKA: Atmosphere Explorer. Status: Operational 1963. First Launch: 1963-04-03. Last Launch: 1975-11-20. Number: 5 . Gross mass: 185 kg (407 lb).
NASA NSSDC Master Catalog Description
The purpose of the AE-C mission was to investigate the thermosphere, with emphasis on the energy transfer and processes that govern its state. The study of photochemical processes accompanying the absorption of solar UV radiation in the earth's atmosphere was accomplished by making closely coordinated measurements of reacting constituents and the solar input. The AE-C spacecraft was a multi-sided polyhedron with a diameter of approximately 1.4 m. It weighed about 660 kg including 85 kg of instrumentation. The initial elliptical orbit was altered many times in the first year of life by means of an onboard propulsion system employing a 3.5-lb thruster. The purpose of these changes was to alter the perigee height to 129 km. After this period, the orbit was circularized and was raised periodically to about 390 km when it would decay to 250 km altitude. During the first year, the latitude of perigee moved from about 10 deg up to 68 deg north and then down to about 60 deg south. During this period about two cycles through all local times were completed. The spacecraft could be operated in either of two modes: spinning at a nominal 4 rpm or despun to 1 revolution per orbit. The spin axis was perpendicular to the orbit plane. Power was supplied by a solar cell array. The spacecraft used a PCM telemetry data system that operated in real time or in a tape recorder mode. The payload included instrumentation for the measurement of solar UV; the composition of positive ions and neutral particles; the density and temperature of neutral particles, positive ions and electrons; the measurement of airglow emissions, photoelectron energy spectra, and proton and electron fluxes up to 25 keV. More details can be found in A. Dalgarno et al., Radio Sci.,v. 8, n. 4, p. 263, 1973.
NASA NSSDC Master Catalog Description
The purpose of the AE-E mission was to investigate the chemical processes and energy transfer mechanisms that control the structure and behavior of the earth's atmosphere and ionosphere in the region of high absorption of solar energy at low and equatorial latitudes. The simultaneous sampling at higher latitudes was carried out by the AE-D spacecraft until its failure on January 29, 1976, and then by AE-C, until it reentered on December 12, 1978. The same type of spacecraft as AE-C was used, and the payload consisted of the same types of instruments except that the low-energy electron and UV nitric oxide experiments were deleted and a backscatter UV spectrometer was added to monitor the ozone content of the atmosphere. The two experiments that were deleted were more appropriate for the high-latitude regions. The perigee swept through more than six full latitude cycles and two local time cycles during the first year after launch when the orbit was elliptical and the perigee height was varied between 130 and 400 km. The circularization of the orbit around 390 km was made on November 20, 1976 and the spacecraft was raised to this height whenever it would decay to about 250 km. AE-E reentered on June 10, 1981. More details can be found in A. Dalgarno et al., Radio Sci., v. 8, n. 4, p. 263, 1973.
NASA NSSDC Master Catalog Description
Explorer 17 AE-A was a spin-stabilized sphere 0.95 m in diameter. The spacecraft was vacuum sealed in order to prevent contamination of the local atmosphere. Explorer 17 carried four pressure gauges for the measurement of total neutral particle density, two mass spectrometers for the measurement of certain neutral particle concentrations, and two electrostatic probes for ion concentration and electron temperature measurements. Battery power failed on July 10, 1963. Three of the four pressure gauges and both electrostatic probes operated normally. One spectrometer malfunctioned, and the other operated intermittently.
NASA NSSDC Master Catalog Description
The purpose of the AE-D mission was to continue the investigation begun by AE-C of the chemical processes and energy transfer mechanisms that control the structure and behavior of the earth's atmosphere and ionosphere in the region of high absorption of solar energy. This mission was planned to sample the high latitude regions at the same time that the AE-E mission was sampling the equatorial and low latitude regions. The same type of spacecraft as AE-C was used, and the payload consisted of the same types of instruments except for deletion of the extreme solar UV monitor and the Bennett ion mass spectrometer, which were part of the AE-E payload. The polar orbit provided the sampling of all latitudes and the perigee moved through all latitudes in 3 months and all local times in 4 months. Unfortunately, a failure in the solar power panels resulted in the termination of operations on January 29, 1976, after slightly less than 4 months of useful life. However, all the regions at the perigee altitudes were sampled during this time. The spacecraft re-entered the atmosphere about 1 month after cessation of telemetry. To continue the correlated observations with the AE-E mission, AE-C was reactivated on February 28, 1976, to replace AE-D. More details can be found in A. Dalgarno et al., Radio Sci., v. 8, n. 4, p. 263, 1973.
NASA NSSDC Master Catalog Description
Explorer 32 AE-B was an aeronomy satellite which was designed to directly measure temperatures, composition, densities, and pressures in the upper atmosphere on a global basis. The satellite was a stainless steel, vacuum-sealed sphere, 0.889 m in diameter. The experimental payload included one ion and two neutral mass spectrometers, three magnetron density gauges, and two electrostatic probes. Additional equipment included optical and magnetic aspect sensors, magnetic attitude and spin rate control systems, and a tape recorder for data acquisition at locations remote from ground receiving stations. Power was supplied by silver-zinc batteries and a solar cell array mounted on the satellite exterior. Two identical pulse-modulated telemetry systems and a canted turnstile antenna were employed. The two neutral-particle mass spectrometers failed about 6 days after launch. The remaining experiments operated satisfactorily and provided useful data for most of the 10-month satellite lifetime. The spacecraft ceased to function due to battery failures which resulted from depressurization of the sphere.
More at: AE.
| AE B Null |
| AE C, D, E Atmospheric Research satellite built by RCA, Astro-Electronics Div. for NASA, USA. Launched 1973 - 1975. |
Family: Atmosphere sat, Earth. Country: USA. Launch Vehicles: Thor, Delta, Thor Delta B, Thor Delta C1, Delta 1900, Delta 2910, Delta 1000, Delta C, Delta 2000. Projects: Explorer. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral, Vandenberg, Cape Canaveral LC17B, Cape Canaveral LC17A, Vandenberg SLC2W. Agency: NASA. Bibliography: 2, 279, 3701, 3704, 3729, 6, 10753, 12028, 12029, 12030.
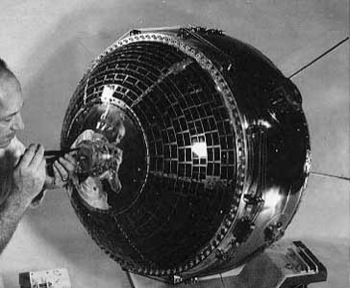 | Explorer 32 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Explorer 51 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1963 April 3 - . 02:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17A. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Delta B.
- Explorer 17 - . Payload: AE A (S-6). Mass: 185 kg (407 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft: AE. Decay Date: 1966-11-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 564 . COSPAR: 1963-009A. Apogee: 891 km (553 mi). Perigee: 254 km (157 mi). Inclination: 57.60 deg. Period: 96.10 min. Atmospheric research. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
1966 May 25 - . 14:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Thor Delta C1.
- Explorer 32 - . Payload: AE B. Mass: 225 kg (496 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft: AE. Decay Date: 1985-02-22 . USAF Sat Cat: 2183 . COSPAR: 1966-044A. Apogee: 2,723 km (1,691 mi). Perigee: 282 km (175 mi). Inclination: 64.60 deg. Period: 116.00 min. Atmospheric Explorer; aeronomy experiments. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
1973 December 16 - . 06:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2W. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Delta 1900.
- Explorer 51 - . Payload: AE C. Mass: 658 kg (1,450 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft: AE. Decay Date: 1978-12-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 6977 . COSPAR: 1973-101A. Apogee: 4,306 km (2,675 mi). Perigee: 155 km (96 mi). Inclination: 68.10 deg. Period: 132.50 min. Atmospheric Explorer; upper atmospheric research. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
1975 October 6 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2W. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Delta 2910.
- Explorer 54 - . Payload: AE D. Mass: 676 kg (1,490 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft: AE. Decay Date: 1976-03-12 . USAF Sat Cat: 8353 . COSPAR: 1975-096A. Apogee: 3,819 km (2,373 mi). Perigee: 151 km (93 mi). Inclination: 90.10 deg. Period: 126.80 min. Atmospheric Explorer; atmospheric research. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
1975 November 20 - . 02:06 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Delta 2910.
- Explorer 55 - . Payload: AE E. Mass: 721 kg (1,589 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Greenbelt. Program: Explorer. Class: Earth. Type: Atmosphere satellite. Spacecraft: AE. Decay Date: 1981-06-10 . USAF Sat Cat: 8440 . COSPAR: 1975-107A. Apogee: 3,002 km (1,865 mi). Perigee: 154 km (95 mi). Inclination: 19.70 deg. Period: 117.70 min. Atmospheric Explorer. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B). .
2014 July 29 - . 23:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA3. LV Family: Ariane 5. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5ES.
- ATV-5 Georges Lemaitre - . Mass: 19,520 kg (43,030 lb). Nation: France. Agency: AE. Spacecraft: ATV. Duration: 201.00 days. Decay Date: 2015-02-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 40103 . COSPAR: 2014-044A. Apogee: 419 km (260 mi). Perigee: 413 km (256 mi). Inclination: 51.65 deg. Period: 92.89 min. ISS resupply mission. Arrived at the ISS on August 12, docking with Zvezda at 13:30 GMT. Undocked from the ISS Zvezda module at 13:42 GMT on February 14 2015 and was deorbited over the Pacific on February 15..
2014 August 22 - . 03:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELS. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-ST-B.
- GalileoSat-5 - .
Payload: Galileo FOC FM01 / Doresa. Mass: 733 kg (1,615 lb). Nation: Europe.
Agency: AE.
Spacecraft: Galileo Navsat.
USAF Sat Cat: 40128 . COSPAR: 2014-050A. Apogee: 25,918 km (16,104 mi). Perigee: 13,721 km (8,525 mi). Inclination: 49.69 deg. Period: 703.33 min.
Europe's first two Galileo FOC (Full Operational Capability) navigation satellites were put on a suborbital trajectory by the booster. The Fregat-MT No. 1039 upper stage made a first burn to put the stack in elliptical transfer orbit, and then began the coast to apogee. At apogee at 16:05 GMT the Fregat made a second burn intended to circularize the orbit at 23500 km x and 55.0 deg inclination. The satellites separated from the Fregat at 16:15 GMT. Unfortunately the Fregat was wrongly oriented and the orbit actually reached was 13,700 x 25,900 km x 49.7 deg. An attitude control thrusters may have failed during the coast, leaving Fregat pointing the wrong way at second main engine ignition.
- GalileoSat-6 - . Payload: Galileo FOC FM02 / Milena. Mass: 733 kg (1,615 lb). Nation: Europe. Agency: AE. Spacecraft: Galileo Navsat. USAF Sat Cat: 40129 . COSPAR: 2014-050B. Apogee: 25,906 km (16,097 mi). Perigee: 13,702 km (8,514 mi). Inclination: 49.69 deg. Period: 702.69 min.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use