
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Radarsat
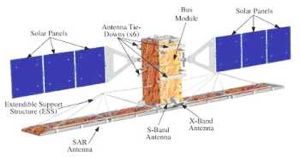 Radarsat Credit: CSA |
Status: Operational 1995. First Launch: 1995-11-04. Last Launch: 2007-12-14. Number: 2 . Gross mass: 2,713 kg (5,981 lb). Height: 1.50 m (4.90 ft). Span: 15.00 m (49.00 ft).
This sophisticated remote sensing satellite was a Canadian-led project involving the United States. It carried a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), a powerful microwave instrument that could transmit and receive signals to "see" through clouds and darkness, obtaining detailed images of the Earth. This would provide significant advantages in viewing under conditions that precluded observation by aircraft or optical satellites. RADARSAT collected data on resource management, ice, ocean and environmental monitoring and Arctic and off-shore surveillance. RADARSAT also supported fishing, shipping, oil exploration, offshore drilling and ocean research. The RADARSAT would provide complete global coverage with the flexibility to support specific requirements.
The spacecraft solar array provided 2.1 kW of power and recharged three NiCd batteries rated at 48 Ah. On the cube shaped bus was mounted the earth facing SAR antenna measuring 15 meters across. Using a single 5.3 GHz C-Band SAR with a wavelength of 5.6 cm, Radarsat had the unique ability to shape and steer its beam over a 500 kilometer range. Beam selections could image swaths from 35 kilometers to 500 kilometers with resolutions from 10 meters to 100 meters respectively. Incidence angles ranged from less than 20 degrees to 60 degrees via a steerable antenna. The RF bandwidth of the system varied between 1.6, 17.3 or 30.0 MHz, with a peak transmitter peak of 5kW. The maximum data rate was 85 Mb/s (recorded) or 105 Mb/s (in real time).
The project had a total cost of $ 475 million. Ball received a contract in 1989 for the satellite frame valued at $ 55 million.
More at: Radarsat.
Family: Earth, Civilian radarsat, Sun synchronous orbit. Country: Canada. Launch Vehicles: Thor, Delta, R-7, Delta 2 7000, Delta 7920-10, Soyuz-FG. Launch Sites: Vandenberg, Baikonur, Vandenberg SLC2W, Baikonur LC31. Agency: CSA, Spar. Bibliography: 2, 6, 6814, 12995, 12996.
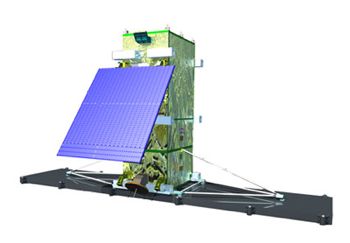 | Radarsat Constellati Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Radarsat Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Radarsat-2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1995 November 4 - . 14:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Vandenberg. Launch Complex: Vandenberg SLC2W. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Delta 7920-10.
- Radarsat - . Mass: 2,713 kg (5,981 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: CSA. Class: Earth. Type: Civilian Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: BCP-4000. Spacecraft: Radarsat. USAF Sat Cat: 23710 . COSPAR: 1995-059A. Apogee: 793 km (492 mi). Perigee: 791 km (491 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 100.70 min. Earth imaging with synthetic aperture radar..
2007 December 14 - . 13:17 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC31. LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz-FG.
- Radarsat-2 - .
Mass: 2,200 kg (4,800 lb). Nation: Canada.
Agency: Starsem.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Civilian Radarsat. Spacecraft Bus: BCP-4000.
Spacecraft: Radarsat.
USAF Sat Cat: 32382 . COSPAR: 2007-061A. Apogee: 793 km (492 mi). Perigee: 791 km (491 mi). Inclination: 98.60 deg. Period: 100.70 min.
Follow-on to Canadian Radarsat-1 launched in 1995. Designed to provide C-band synthetic aperture radar mapping with resolution of 3 m to Canadian government users. Compared to the earlier model had greater resolution, vastly increased on-board data storage capacity, and capability to scan left or right of ground track. Planned lifetime of seven years.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use