Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
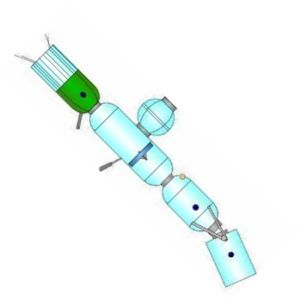
Vostok-Zh
AKA: 3KZh;Vostok-2. Status: Study 1961. Gross mass: 4,700 kg (10,300 lb). Height: 4.50 m (14.70 ft).
The pilot would rendezvous and dock with components of a space station or translunar spacecraft as they reached orbit, then maneuver the component to a docking with the in-assembly spacecraft. Abandoned in favor of the Soyuz.
During the course of 1961 Korolev's OKB-1 worked on design of a reliable manned spacecraft to succeed Vostok. The Soyuz or Sever designs would utilize body lift to reduce G forces and allow the crew to make re-entries at hyperbolic speeds - when returning from the moon, or Mars. On 10 March 1962 Korolev approved the technical project "Complex docking of spacecraft in earth orbit - Soyuz". This draft report envisioned use of an manned orbital tug version of the Vostok capsule to assemble spacecraft in low earth orbit. In one concept a large spacecraft was assembled in earth orbit by a Vostok-Zh (or Vostok-7) maneuverable manned satellite, piloted by a 'cosmonaut assemblyman'. The pilot would rendezvous and dock with each component as it reached orbit, then maneuver the component to the in-assembly spacecraft. Following completion of assembly, the Vostok would retrofire and the assemblyman would return to earth.
The Vostok-Zh could be used on another mission to assemble a 15 metric ton orbital station with the mission of observing the earth. It would consist of three separately-launched blocks: a ZhO living section, BAA scientific apparatus block, and the Soyuz spacecraft itself.
By the end of 1962 the Vostok-Zh approach had been discarded in favor of automatic docking in orbit of the L1 spacecraft and a succession of tankers to fuel a single rocket block.
Crew Size: 1.
Family: Manned spacecraft, Soviet Space Stations. Country: Russia. Launch Vehicles: R-7, Soyuz 11A511. Agency: Korolev bureau. Bibliography: 191, 26, 376.
1961 During the Year - .
- Competing designs for a reliable manned spacecraft to succeed Vostok. - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft: Sever,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz B,
Soyuz V,
Vostok-Zh.
The Soyuz or Sever designs would utilize body lift to reduce G forces and allo the crew to make re-entries at hyperbolic speeds - when returning from the moon, or Mars. An associated design was a manned orbital tug version of the Vostok capsule to assemble spacecraft in low earth orbit.
1961 March 11 - .
- New manned spacecraft - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Vershinin.
Spacecraft: Raketoplan,
Sever,
Vostok-Zh.
The VVS TTZ requirements document for the next generation Soviet manned spacecraft is approved by Vershinin. It is to accommodate two cosmonauts, have a launch mass of 6.5 to 7.0 tonnes, be capable of manoeuvring and changing its orbit at altitudes of 270 to 300 km altitude. The TDU engine is to be restartable, and the spacecraft will have a system to reliably change and hold its orientation in flight. The crew will be returned in a pressurised spherical re-entry capsule, but still be provided with ejection seats for separate landing of the crew in emergencies. The craft will be capable of flights of 15 to 20 days duration and be equipped with redundant communications systems. Kamanin points out the necessity of coordinating the TTZ with OKB-1. Vershinin and Ponomarev fight over whether to consider Chelomei's Raketoplan as meeting the requirement. Kamanin's position is that Korolev's Vostok is now flying reliably, while the Raketoplan is a 'crane in the clouds' - it might come to them some day, but who knows when.
1962 During the Year - . LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Soyuz 11A511.
- Vostok-Zh studies - .
Nation: Russia.
Program: Lunar L1.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Vostok.
Spacecraft: Vostok-Zh.
Vostok-Zh studies conducted for multiple dockings of rocket blocks and payloads in orbit for circumlunar missions, using Vostok rocket. Vostok-Zh spacecraft used to for manual dockings only. Manned reentry vehicle from circumlunar distance is Sever/Soyuz design. Korolev's reaction to Chelomei's exclusive assignment by Khrushchev to circumlunar mission.
1962 January 18 - . LV Family: R-7. Launch Vehicle: Voskhod 11A57.
- Korolev requests new Vostoks - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev.
Program: Vostok.
Spacecraft: Vostok,
Vostok-Zh,
Zenit-4.
Korolev has issued a letter requested eight new Vostok 3A spacecraft to be built in 1962-1963. He recommends that they should be finished as the 1100 to 1300 kg heavier 'Vostok-2', to be boosted by the 11A57 rocket, developed originally for the Zenit-4 spy satellite. These Vostok-2's will be used for docking experiments, to form EO Experimental Orbital stations, and to develop spacecraft systems for flight to the moon. The VVS fully supports these plans. One of the docking spacecraft will be piloted, the other unpiloted.
1962 March 10 - .
- Soyuz Technical Project approved. - .
Nation: Russia.
Related Persons: Korolev.
Spacecraft: L1-1962,
OS-1962,
Vostok-Zh.
Korolev approved the technical project 'Complex docking of spacecraft in earth orbit - Soyuz'. The Soyuz would first be tested using multiple launches of an R-7 derived rocket. In this concept a large spacecraft was assembled in earth orbit by a Vostok-Zh (or Vostok-7) manoeuvrable manned satellite, piloted by a 'cosmonaut assemblyman'. Following completion of assembly, the Vostok would return to earth. The assembled circumlunar craft would put the L1, with a crew of one to three, on a circumlunar trajectory. The Vostok-Zh could be used on another mission to assemble a 15 tonne OS orbital station with the mission of observing the earth.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use