
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
LACE
 USA 51 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
AKA: Low-power Atmospheric Compensation Experiment. Status: Operational 1990. First Launch: 1990-02-14. Last Launch: 1990-02-14. Number: 1 . Gross mass: 1,430 kg (3,150 lb). Height: 2.40 m (7.80 ft).
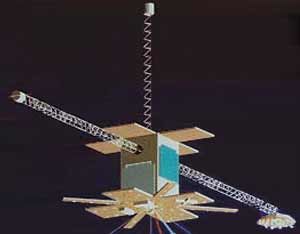
LACE was built by the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to act as a target for ground lasers to investigate atmospheric distortion and compensation methods.
The spacecraft was gravity gradient stabilized with no attitude control thrusters. Low-power lasers were beamed from the Air Force Maui Optical Station (AMOS) and received by on-board IR and phased detectors. A laser locked onto a reflector mounted on a 46 meter boom to acquire the satellite. The sensor array returned data on the laser coverage, allowing the laser's adaptive optics to be adjusted, compensating for atmospheric distortion.
NCST developed, launched and operated the Low-power Atmospheric Compensation Experiment (LACE) satellite. The LACE satellite was integrated with a USAF relay-mirror experiment payload and mounted atop a Delta II rocket for a successful launch in February 1990 from Cape Canaveral. The LACE satellite carried four experiments:
- Sensor field for ground based adaptive optics evaluation in the infrared, visible and pulsed wavelengths (for the Strategic Defense Initiatives Office). LACE carried visible, IR and phased laser sensors. They were on booms and panels extending from the 1.4 x 1.4 x 2.4 meter main body. In total, there were 210 laser sensors.
- Ultra-Violet Plume Imaging (UVPI) tracking experiment (also for SDIO). This tracked rocket plumes and used two CCD cameras.
- Optical Radiation Detection experiment (for Aerospace Corporation)
- Background neutron environment measurements for decoy detection experiment (for the US Army). This instrument monitored background levels of neutron radiation in order to be able to discriminate between warheads and decoys.
More at: LACE.
Family: Military, Military strategic defense sat. Country: USA. Launch Vehicles: Thor, Delta, Delta 2 6000, Delta 6920-8. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral, Cape Canaveral LC17B. Agency: NRL, SDIO. Bibliography: 2, 279, 6, 12751.
1990 February 14 - . 16:15 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. LV Family: Thor. Launch Vehicle: Delta 6920-8.
- USA 51 - .
Payload: LACE. Mass: 1,430 kg (3,150 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SDIO.
Class: Military.
Type: Strategic defense satellite. Spacecraft: LACE.
Decay Date: 2000-05-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 20496 . COSPAR: 1990-015A. Apogee: 480 km (290 mi). Perigee: 463 km (287 mi). Inclination: 43.10 deg. Period: 94.00 min.
Low-power Atmospheric Compensation Experiment for SDIO. Research and exploration of the upper atmosphere and outer space. The McDonnell Douglas Corporation has provided the following information for its launch of the Losat spacecraft on 14 Feb 1990: LACE spacecraft (Losat-L), launch time 1615:00.626 GMT, ETR Launch Complex 17. Programmed orbital parameters 95.6 min, apogee 551 km, inc. 43.1 deg. Evaluate laser beam distortion in space.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use