Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
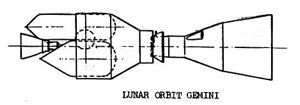
Gemini LORV
Gemini LORV
Gemini Lunar Orbit Rescue Vehicle, studied for rescue of an Apollo crew stranded in lunar orbit. Gemini would be launched by Saturn V. Following lunar orbit insertion it would rendezvous with the disabled Apollo. The three Apollo crew members would transfer by spacewalk to a compartment in the stretched Gemini capsule. It would then boost itself on a transearth trajectory. This was rejected in favour of the more flexible Gemini Lunar Surface Rescue Vehicle.
Credit: McDonnell Douglas
AKA: Gemini Lunar Orbit Rescue Vehicle;McDonnell-Douglas. Status: Study 1967. Thrust: 62.27 kN (13,999 lbf). Gross mass: 15,500 kg (34,100 lb). Unfuelled mass: 5,500 kg (12,100 lb). Specific impulse: 311 s. Height: 7.37 m (24.17 ft).
Following lunar orbit insertion it would automatically rendezvous with the disabled Apollo. The three Apollo crew members would transfer by a spacewalk to the passenger compartment of the stretched Gemini reentry module. It would then boost itself and the rescued crew to a transearth trajectory. This version was rejected in favor of the more flexible Gemini Lunar Surface Rescue Vehicle.
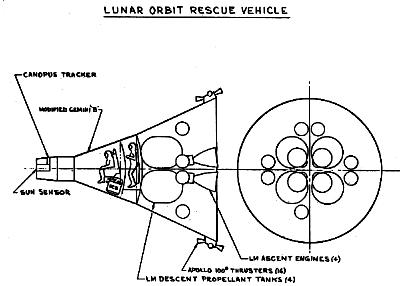
In the wake of the Apollo fire, NASA reexamined many safety aspects of the Apollo project. The Apollo mission profile was inherently risky, and the likelihood of a crew being stranded in lunar orbit or on the lunar surface was relatively high. McDonnell returned to a concept first studied in 1962 - the use of Gemini as a Lunar Rescue Vehicle. Use of the Gemini B capsule, then in construction for use with the US Air Force's Manned Orbiting Laboratory, with various combinations of Apollo lunar module stations, would provide a rescue vehicle that could pick up Apollo astronauts stranded in lunar orbit or on the lunar surface. Three variant rescue schemes were studied, a Gemini Lunar Orbit Rescue Vehicle, Gemini Lunar Surface Survival Shelter and a Gemini Lunar Surface Rescue Spacecraft.
McDonnell summarized the advantages of the various schemes, as contrasted with use of Apollo hardware for the same task, as follows:
- Lunar Orbit Rescue Gemini: Modified Gemini & repackaged LM Ascent Stage. Unmanned to lunar orbit, three man direct return. Advantages: Uses developed equipment. Disadvantages: New spacecraft development. Recommendation: Do not develop-rescue capability too limited. Greatest emergency potential at lunar surface.
- Lunar Orbit Rescue Apollo: Apollo CSM. Unmanned to lunar orbit, three man direct return. Advantages: No new development. Can be accomplished with current acquisitions. Disadvantages: Possibility of same failure mode. Recommendation: Do not develop-rescue capability too limited. Greatest emergency potential at lunar surface.
- Lunar Surface Survival Shelter Gemini: Vehicle Description: Modified Gemini & Modified LM Descent Stage. Mission: Unmanned to lunar surface, 28 day quiescent storage, 28 day 2-man operation. Advantages: Extension of lunar orbit vehicle. Disadvantages: New spacecraft development. Recommendation: Do not develop - need for shelter and total number of Saturn launches reduced by providing an on-station backup return capability.
- Lunar Surface Survival Shelter Apollo: Vehicle Description: Modified SM & Modified LM. Mission: Unmanned to lunar surface, 30 day manned operation. Advantages: Similar to planned post-Apollo exploration shelter. Disadvantages: Requires modifications to existing hardware. Recommendation: Do not develop - need for shelter and total number of Saturn launches reduced by providing an on-station backup return capability.
- Lunar Surface Rescue Gemini: Vehicle Description: Modified Gemini, repackaged LM Ascent Stage & Modified LM Descent Stages. Mission: Unmanned to lunar orbit, 30 day unmanned quiescent stay, 2 man direct return. Advantages: Extension of lunar orbit/shelter vehicle. No rendezvous required. Direct return. Disadvantages: New spacecraft development. Recommendation: Modify to a 'Universal' Rescue Vehicle by improving capability to cover three-man cases.
- Lunar Surface Rescue Apollo: Vehicle Description: Apollo CSM & LM. Mission: Unmanned to lunar orbit, LM to lunar surface, LM to lunar orbit, 2 man return. Advantages: No new development. Same as existing mission. Disadvantages: Rendezvous required. May be difficult to automate transpose docking. Recommendation: Modify to a 'Universal' Rescue Vehicle by improving capability to cover three-man cases.
This last attempt to resuscitate Lunar Gemini failed as well. At that point in the Apollo program cut-backs already had begun. No funds would be forthcoming to build additional launch vehicles and spacecraft beyond those already purchased. There was definitely no money to provide a rescue capability, using either Apollo or Gemini hardware.
Crew Size: 3. Habitable Volume: 5.00 m3. Spacecraft delta v: 3,100 m/s (10,100 ft/sec).
Family: Lunar Orbiters, Moon. People: McDonnell. Country: USA. Spacecraft: Gemini LORV RM, Gemini LORV SM. Launch Vehicles: Saturn V. Propellants: N2O4/UDMH. Agency: NASA. Bibliography: 209.
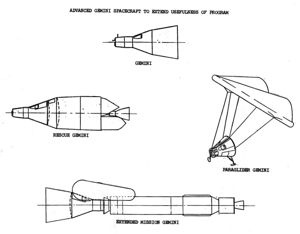 | Gemini Variants Modest modifications of Gemini proposed by McDonnell Douglas as a follow-on to the basic program (927 x 723 pixel version). Credit: McDonnell Douglas |
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use