
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
SJ
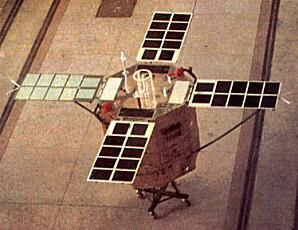 SJ-2A Credit: via Chen Lan |
AKA: QQW;Shi Jian 1. Status: Operational 1979. First Launch: 1979-07-28. Last Launch: 1994-02-08. Number: 7 . Gross mass: 221 kg (487 lb).
China started to explore the upper atmosphere using rockets and balloons in the early 1960s. In the early 1970s, China began to utilize SJ satellites to obtain data on the space environment. The establishment of open state-level laboratories specializing in space physics, micro-gravity and space life science, and the founding of the Space Payload Application Centre provided the basis for public international collaboration on space science.
- The SJ-1 was similar in appearance to the American Telstar and conducted communications technology tests. It used the DFH-1 satellite bus, weighed 221 kg, and monitored the space physics environment. The mission of SJ-2 covered both space technology and space physical measurements. The payloads included a solar X-ray detector, a single cell particle measurement device and a magnetometer. Also known as SKW-2, the spacecraft was a modification of SKW-1, replacing the telemetry music box with space exploration instruments, including a cosmic ray detector, x-ray detector, magnetometer, field effect solid state storage device, louver-type thermal control device, and above all, a solar-cell experimental power supply system with its own long duration telemetry. SJ-l was launched on March 3, 1971, and the long duration telemetry system powered by the experimental solar cells continued to operate normally after more than 8 years in orbit, until June 17, 1979, when the satellite re-entered the atmosphere and burned up. This was much longer than the expected life of one year, and greatly encouraged the design and development team.
- SJ-2 was launched on September 20, 1981, weighed 257 kg, and conducted space physics and environment studies. Also known as SKW-3, the satellite included some technology flight demonstration experiments. It weighed 257 kg, with a hexagonal shape, and was equipped with four deployable solar panels at one end of the body. It was spin stabilized but with active on-board attitude control to keep the spin axis pointed toward the sun, using sun sensors, earth sensors, and hydrazine thrusters. The on-board instruments included a thermal ionization gauge, a solar x-ray sensor, a solar ultraviolet sensor; magnetometers, a scintillation counter, an infra-red radiometer, and an electron detector. The telemetry system was an improved version of that used on the DFH series, using an on-board storage device of sufficient capacity to collect data world-wide and then transmit the stored data when passing through an earth station in China. SJ-2 was successfully launched into orbit on September 20, 1981 by the launch vehicle FB-1, together with two other balloon satellites SJ-2A and SJ-2B. Although SJ-2 was the major item of the mission, the launching of three satellites using a single launch vehicle was considered a big success of space vehicle tracking, separation and control.
- SJ-3 was an earth science satellite cancelled in 1985. It would have weighed 450 kg.
- A Chinese astronomy satellite began development but was also cancelled in 1985. It would have weighed 500 kg and studied solar physics and astronomy.
- The DQ-1A and DQ-1B (also given as DQ-1 and DQ-2) QQW balloon satellites were deployed on September 3, 1990 for studies of the density of the upper atmosphere. They weighed 2.6 kg and 3.3 kg and were deployed from the CZ-4 upper stage using a special adapter for multiple payload ejection.
- SJ-4 was launched on February 8, 1994 and studied magnetospheric physics (particles and fields research). Also known as SKW-4, the satellite was dedicated to the study of the space charged particle environment, radiation effects, and radiation protection techniques. Main instruments included a high energy proton and heavy ion detector, a high energy electron detector, a plasma detector, a spacecraft surface potential meter, and single event upset monitors. SJ-4 weighed 397 kg, and was successfully launched into orbit by the maiden launch of the CZ-3A launcher on February 8, 1994
- SJ-5 studied the radiation belts. The SJ-5 scientific satellite was built by the Chinese Center for Space Science Application Research of the Chinese Academy of Science. SJ-5 was the first satellite based on CAST968 bus and carried 11 science payloads. It weighed 298 kg and had an operational life of about three months. SJ-5 was designed to test a platform with three different attitude control technologies (3-axis, spin and gravity-gradient). It also carried an instrument for space single particle study, space fluid study (by return of images of fluid behavior to earth), S-band high-speed data transmission and large capacity solid storage experiments.
| SJ 1 Technology satellite for CAST (Chinese Academy of Space Technology), China. Launched 1971. |
| SJ 2 Technology satellite, China. Launched 1979 - 1981. |
| SJ 2A Technology satellite, China. Launched 1979 - 1981. |
| SJ 2B Technology satellite, China. Launched 1979 - 1981. |
| SJ 4 Technology satellite, China. Launched 1994. |
| SJ 8 Micro-gravity satellite built by CAST, China. Launched 2006. |
| SJ 3 Earth observation satellite for CAST (Chinese Academy of Space Technology), China. |
Family: Communications, Communications technology sat, Earth, Technology. Country: China. Launch Vehicles: Feng Bao 1, Chang Zheng 4, Chang Zheng 2D, Chang Zheng 3A, Chang Zheng 4B. Launch Sites: Jiuquan, Jiuquan LA2B, Taiyuan, Xichang, Xichang LC2, Jiuquan SLS-2, Taiyuan LC1. Agency: MAI. Bibliography: 119, 2, 276, 279, 424, 532, 6.
 | SJ-2A Chinese satellite. |
 | SJ-1 First Chinese satellite; communications technology tests. Similar in appearance to Telstar 1. |
 | SJ-2C Chinese satellite. Balloon for atmospheric drag experiments. |
 | SJ-4 Credit: via Chen Lan |
 | SJ-5 Credit: via Chen Lan |
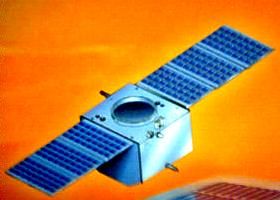 | SJ-5 Credit: © Mark Wade |
 | Shi Jian 16 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SJ-2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SJ-2A Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SJ-2B Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SJ-4 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SJ-5 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SJ 9B Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SJ-1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1979 July 28 - . Launch Site: Jiuquan. Launch Complex: Jiuquan LA2B. LV Family: CZ. Launch Vehicle: Feng Bao 1. FAILURE: Second stage failure.. Failed Stage: 2.
- SJ-1 - . Payload: Shi Jian 1. Mass: 221 kg (487 lb). Nation: China. Agency: PRC. Spacecraft: SJ. The SJ-1 was similar in appearance to the American Telstar and conducted communications technology tests..
1981 September 19 - . 21:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Jiuquan. Launch Complex: Jiuquan LA2B. LV Family: CZ. Launch Vehicle: Feng Bao 1.
- SJ-2A - . Payload: Shi Jian 2B. Mass: 257 kg (566 lb). Nation: China. Agency: MAI. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: SJ. Decay Date: 1981-09-26 . USAF Sat Cat: 12842 . COSPAR: 1981-093A. Apogee: 1,598 km (992 mi). Perigee: 232 km (144 mi). Inclination: 59.50 deg. Period: 103.30 min.
- SJ-2B - . Payload: Shi Jian C. Mass: 28 kg (61 lb). Nation: China. Agency: MAI. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: SJ. Decay Date: 1982-10-06 . USAF Sat Cat: 12843 . COSPAR: 1981-093B. Apogee: 1,615 km (1,003 mi). Perigee: 233 km (144 mi). Inclination: 59.40 deg. Period: 103.50 min. Balloon for drag studies..
- SJ-2 - . Payload: Shi Jian 2. Mass: 483 kg (1,064 lb). Nation: China. Agency: MAI. Class: Technology. Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: SJ. Decay Date: 1982-08-17 . USAF Sat Cat: 12845 . COSPAR: 1981-093D. Apogee: 1,608 km (999 mi). Perigee: 232 km (144 mi). Inclination: 59.40 deg. Period: 103.40 min.
1990 September 3 - . 00:53 GMT - . Launch Site: Taiyuan. Launch Complex: Taiyuan LC1. LV Family: CZ. Launch Vehicle: Chang Zheng 4.
- QQW 1 - . Payload: QQW 1A. Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: China. Agency: MAI. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: SJ. Decay Date: 1991-03-11 . USAF Sat Cat: 20789 . COSPAR: 1990-081B. Apogee: 811 km (503 mi). Perigee: 789 km (490 mi). Inclination: 99.00 deg. Period: 100.90 min. QQW atmospheric balloon..
- QQW 2 - . Payload: QQW 1B. Mass: 4.00 kg (8.80 lb). Nation: China. Agency: MAI. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: SJ. Decay Date: 1991-07-24 . USAF Sat Cat: 20790 . COSPAR: 1990-081C. Apogee: 629 km (390 mi). Perigee: 596 km (370 mi). Inclination: 99.00 deg. Period: 97.00 min. QQW atmospheric balloon..
1994 February 8 - . 08:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Xichang. Launch Complex: Xichang LC2. LV Family: CZ. Launch Vehicle: Chang Zheng 3A.
- SJ-4 - . Payload: Shi Jian 4. Mass: 400 kg (880 lb). Nation: China. Agency: CASC. Class: Earth. Type: Magnetosphere satellite. Spacecraft: SJ. USAF Sat Cat: 22996 . COSPAR: 1994-010A. Apogee: 26,837 km (16,675 mi). Perigee: 195 km (121 mi). Inclination: 28.70 deg. Period: 465.40 min. Particles and fields research. .
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use