
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Mars 1989
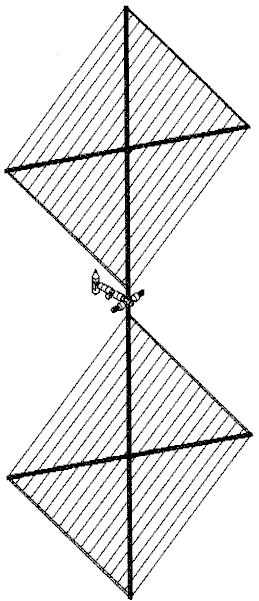
 Mars 1989 NPO Energia solar-powered Mars expedition spacecraft of 1989. The complete extent of the vast 200 m x 200 m solar panels is not shown. Credit: © Mark Wade |
Status: Study 1989. Thrust: 441 N (99 lbf). Gross mass: 355,000 kg (782,000 lb). Specific impulse: 4,000 s. Height: 600.00 m (1,960.00 ft). Span: 280.00 m (910.00 ft).
The spacecraft hardware was essentially that of the 1986 design, in place of the nuclear reactor of previous designs power would be generated by huge farms of solar panels, developed from those on the Salyut 7 and Mir stations.
The spacecraft itself became part of a more logical program with sequential launch of evolving hardware, beginning with unmanned spacecraft and ending with piloted expeditions. Five launches of the huge Energia booster would be required to assemble the spacecraft in low earth orbit. Mission specification was as follows:
- Flight time - 716 days
- Crew - 4
- Crew on surface of Mars - 2
- Time of work on Martian surface - 7 days.
The ship designed to perform this mission would have a mass of 355 metric tons.
This would be apportioned among the modules as follows:
- MOA (Mars Orbital Apparatus) - 80 metric tons, a 4.1 m diameter cylinder, 23 m long, divided into three sections: living section, a spherical airlock/transfer compartment, and a work section. The living compartment contained a cabin for each crew member, a common room, and a rest area. As always, a radiation shelter was included to shield the crew during solar storms. A greenhouse would augment the SZhO life support system. This system was designed around the following daily consumption values per crew member: oxygen - 600 l/day; carbon dioxide to be eliminated - 480 l/day; water to be supplied - 2.5 kg/day; food requirement - 2.0 kg/day. The regenerative design of SZhO meant that only 0.5 kg of water and 1.5 kg of food would have to come from reserve stocks per day. The greenhouse would have an area of 15 square meters and a mass of mass of 500 kg per crew member. Total mass of the life support system was 26 metric tons, including 5.5 metric tons of food reserves, and 1 metric ton of emergency food stocks.
- EA (Expeditionary Apparatus) - the Mars landing craft, 60 metric tons mass, 3.8 m in diameter and 13 m long. Provisions were carried for a stay of one week on the surface and one day in Mars orbit.
- AVNZ (Earth re-entry vehicle), 10 metric tons. This was the same as that designed for MEK in 1969.
- Electric engines, structure, and solar panels, 40 metric tons. The two enormous panels, each 200 m x 200 m would generate a total of 15 MW of power at earth. The use of ultra-thin (less than 50 micrometer) / low mass (0.2 kg per square meter) photovoltaic cells with a high specific power value (up to 200 W per square meter) minimized the mass of these vast arrays. The power generated would be used primarily by two ion engines mounted perpendicular to the living block. In high-power mode these would have a specific impulse of 3500 seconds. Total thrust at normal level, assuming the 4000 second specific impulse of the 11B97 engine, can be calculated as 45 kgf.
- Xenon propellant, 165 metric tons
This evolutionary approach to the exploration of Mars was to be conducted in three phases:
- Phase 1 - A small model spacecraft would be assembled at the Mir station with assistance from Progress re-supply craft. This 'Mars Module' would test the solar panels, ion engines, and other essential systems of the larger manned spacecraft. From its initial low earth orbit it would fly to Mars, arriving in a circular near-Mars orbit with a research apparatus mass of 1.3 metric tons. From this orbit the equipment could have a functional life of two years. It was also possible to return equipment back to low earth orbit. Mass of the spacecraft on departure from Mir would be 5500 kg, with the solar battery generating 180 kW. The apparatus could be refueled in the space station orbit from Progress tankers. After replacement of the research equipment it could then be launched to Mars again. In 1994, during discussions between NASA Administrator D Goldin and RKK Energia Director Y P Semenov on the International Space Station (ISS), Semenov proposed the use of this Mars Module from the ISS. Although Goldin indicated interest in the advantages of the concept, the project was not pursued further.
- Phase 2 - Preparatory delivery of equipment for subsequent piloted expeditions. A solar tug would deliver to Martian orbit two descent craft. One would have the complete equipment for landing and return of the crew. The other would have several Marsokhod rovers (total mass around 20 metric tons), which would be used to conduct detailed investigations of the Martian surface
- Phase 3 - The piloted expedition to Mars.
Of course by the late 1980's all such studies by GKB NPO Energia were only a way to usefully occupy the engineers of the corporation and had no chance of authorization.
Mars 1989 Mission Summary:
- Summary: Revision of 1986 study to use solar electric propulsion.
- Propulsion: Solar Electric
- Braking at Mars: propulsive
- Mission Type: low acceleration
- Split or All-Up: all up
- ISRU: no ISRU
- Launch Year: 2001
- Crew: 4
- Mars Surface payload-metric tons: 60
- Outbound time-days: 408
- Mars Stay Time-days: 30
- Return Time-days: 278
- Total Mission Time-days: 716
- Total Payload Required in Low Earth Orbit-metric tons: 355
- Total Propellant Required-metric tons: 160
- Propellant Fraction: 0.45
- Mass per crew-metric tons: 88
- Launch Vehicle Payload to LEO-metric tons: 88
- Number of Launches Required to Assemble Payload in Low Earth Orbit: 5
- Launch Vehicle: Energia
Crew Size: 4. Electric System: 15,000.00 average kW.
Family: Mars Expeditions. Country: Russia. Launch Vehicles: Mars tactical rocket, Energia. Propellants: Electric/Xenon. Agency: Korolev bureau. Bibliography: 193, 206, 89.
 | Mars 1989 Version of the Mars 1989 shown by RKK Energia in 1990 Credit: via Steven S. Pietrobon |
 | EA Ascent Stage The Ascent Stage of the EA Mars Lander fires to launch the crew back to Mars orbit and rendezvous with the waiting Mars 1986 or 1989 expedition craft. Credit: RKK Energia |
 | Aelita Martian Wishful thinking - a Martian peeks from a crater after the EA Lander departs for orbit. Frame from an RKK Energia film. Credit: RKK Energia |
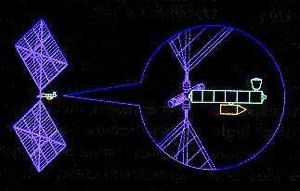 | Mars 1989 NPO Energia solar-powered Mars expedition spacecraft of 1989. Credit: RKK Energia |
1989 During the Year - .
- Manned Mars project proposal - . Nation: Russia. Spacecraft Bus: TMK. Spacecraft: Mars 1989. In 1989 yet another ion engine-powered Mars project was proposed by NPO Energia. In the place of the nuclear reactor of previous designs, solar panels would be deployed in huge farms of panels..
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use

