
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Mars 1986
 Mars 1986 NPO Energia nuclear-powered Mars expedition spacecraft designed in 1978-1986. The reactor system was split into two independent units to provide redundancy. Credit: © Mark Wade |
Status: Study 1978. Thrust: 441 N (99 lbf). Gross mass: 365,000 kg (804,000 lb). Specific impulse: 4,000 s. Height: 210.00 m (680.00 ft). Span: 11.00 m (36.00 ft).
The 1978-1986 study used some of the ideas and technical results of the 1969 study, but modified according to technical developments of the period.
The 15 MW nuclear power requirement was retained, but actual development of the 11B97 rocket stage beginning in 1971 had shown earlier specific impulse projections to be hopelessly unrealistic. This lead to the mass of the spacecraft more than doubling, with the propellant fraction increasing from 17% to 45% of the spacecraft total. Other differences included the use of two reactors in the place of one; reduction of the crew size from six to four; and the use of tested systems developed on the Salyut and Mir orbital stations in placed of the untried TMK hardware. This use of tested hardware guaranteed an increased level of crew safety compared to previous concepts. The original use of a completely separate second reactor and propulsion unit ensured the safe return of the crew even in the event of complete failure of one reactor or engine cluster.
The Mars landing craft was also completely revised. Both conical and pear-shaped lifting bodies were studied, with a hypersonic lift to drag ratio of 0.3 to 0.5. The preferred configuration was a cylindrical 60 metric ton spacecraft with a conical nose, 3.8 m in diameter and 13 m long.
Mars 1986 Mission Summary:
- Summary: First post-Soviet study. Updated 1969 nuclear-electric design for launch by Energia, use of proven Mir station components.
- Propulsion: Nuclear electric
- Braking at Mars: propulsive
- Mission Type: low acceleration
- Split or All-Up: all up
- ISRU: no ISRU
- Launch Year: 2000
- Crew: 4
- Mars Surface payload-metric tons: 60
- Outbound time-days: 408
- Mars Stay Time-days: 30
- Return Time-days: 278
- Total Mission Time-days: 716
- Total Payload Required in Low Earth Orbit-metric tons: 365
- Total Propellant Required-metric tons: 164
- Propellant Fraction: 0.45
- Mass per crew-metric tons: 91
- Launch Vehicle Payload to LEO-metric tons: 88
- Number of Launches Required to Assemble Payload in Low Earth Orbit: 5
- Launch Vehicle: Energia
Crew Size: 4. Electric System: 15,000.00 average kW.
Family: Mars Expeditions. Country: Russia. Spacecraft: Buran. Launch Vehicles: Energia. Propellants: Electric/Xenon. Agency: Korolev bureau. Bibliography: 193, 206, 474, 89.
 | Mars 1986 NPO Energia nuclear-powered Mars expedition spacecraft designed in 1978-1986. Credit: RKK Energia |
 | EA Ascent Stage The Ascent Stage of the EA Mars Lander fires to launch the crew back to Mars orbit and rendezvous with the waiting Mars 1986 or 1989 expedition craft. Credit: RKK Energia |
 | Aelita Martian Wishful thinking - a Martian peeks from a crater after the EA Lander departs for orbit. Frame from an RKK Energia film. Credit: RKK Energia |
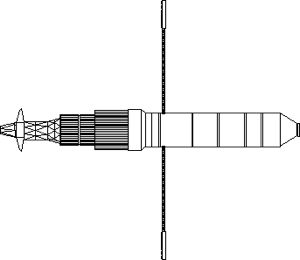 | Gerkules Nuclear Tug Gerkules Nuclear Electric Interorbital Tug with 11B97 engine. Credit: © Mark Wade |
1971 June 8 - .
- Decree authorising design of 11B97 nuclear electric rocket stage - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft Bus: TMK.
Spacecraft: Mars 1986.
Central Committee of the Communist Party and Council of Soviet Ministers Decree 'On work on nuclear rocket engines' was issued. Prior work, mainly on propulsion for manned Mars expeditions, was now concentrated on development of the NEP rocket stage 11B97. This stage would have an electric capacity of 500-600 kW and would use specialised plasma-ion electric engines using standing plasma waves and anodes.
1976 June 15 - . Launch Vehicle: Buran.
- Decree authorising development of 11B97 nuclear electric rocket stage - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft Bus: TMK.
Spacecraft: Mars 1986.
Decree 'On course of work on nuclear rocket engines' was issued. The 11B97 stage would have an electric capacity of 500-600 kW and would use specialised plasma-ion electric engines using standing plasma waves and anodes. It was powered from a reactor with a 200 litre core containing 30 kg of uranium fuel. In 1978 this engine was studied for use as a reusable interorbital space tug for launch by Energia-Buran.
1981 February 5 - . Launch Vehicle: Buran.
- Decree for Gerkules nuclear-electric interorbital tug - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft Bus: TMK.
Spacecraft: Mars 1986.
NPO Energia developed for the Ministry of Defence the interorbital tug Gerkules with 550 kW maximum output and continuous operation in the 50-150 kW range for 3 to 5 years. In 1986 an interorbital tug was studied to solve the specific application of transporting heavy satellites of 100 tonnes to geostationary orbit, launched by Energia.
1986 During the Year - .
- Mars 1986 - .
Nation: Russia.
Spacecraft Bus: TMK.
Spacecraft: Mars 1986.
Having completed design and development work on Energia-launched nuclear-electric upper stages, NPO Energia studied a manned Mars project again. The study revamped the 1969 studies to include launch by Energia and use of two reactors in the place of one and the use of tested systems developed on orbital stations.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use
