
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Juno V-A
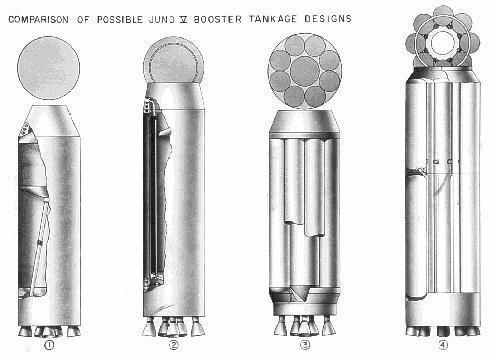
Juno-5 Alternatives
Alternate configurations studied for Juno 5.
Status: Study 1958. Payload: 10,000 kg (22,000 lb). Thrust: 6,690.00 kN (1,503,970 lbf). Gross mass: 549,820 kg (1,212,140 lb). Height: 60.00 m (196.00 ft). Diameter: 6.52 m (21.39 ft). Apogee: 185 km (114 mi).
LEO Payload: 10,000 kg (22,000 lb) to a 185 km orbit at 28.00 degrees. Flyaway Unit Cost 1985$: 57.500 million.
Family: orbital launch vehicle. People: von Braun. Country: USA. Engines: LR87-3, LR91-3, H-1 engine. Stages: Titan 1-2, Titan 1-1, S-I stage.
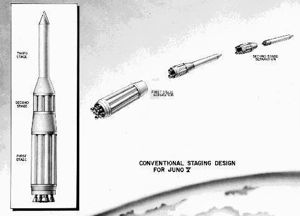 | Juno-5 Staging The selected sequential staging method selected for the Juno-5. |
 | Juno-5 Recovery Full recovery and reuse of the Juno-5 was planned. The structural provisions were retained in the earliest Saturn I test vehicles, but never used. |
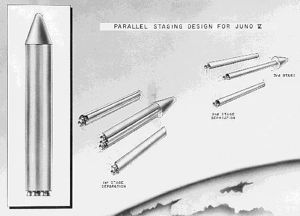 | Juno-5 Parallel Stag A parallel staging scheme was considered for the Juno-5. This would have resulted in a vehicle similar to the Russian R-7 launcher. |
 | Juno-5 on Test Stand The very first Juno-5 test article firing on the stand at the Redstone Arsenal. |
 | Juno-5 Airlift The Juno-5 was designed to be air-transportable and assembled at austere launch pads. |
1958 - . LV Family: Saturn I. Launch Vehicle: Juno V-A.
- Juno V heavy space launch design - . Nation: USA. The Von Braun team's Super-Jupiter evolved into the Juno V. The 4 E-1 engines were abandoned in favor of clustering 8 Jupiter IRBM engines below existing Redstone/Jupiter tankage..
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use