Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
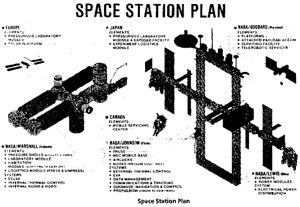
Dual Keel Space Station - 1985
 Dual Keel Station/85 Dual Keel Space Station - 1985 Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
Status: Study 1985.
The new 'Dual Keel' Station was largely based on Lockheed and McDonnell-Douglas designs and its structure was much stiffer and hence easier to stabilize. It would offer additional space for external instruments plus a better microgravity environment than the previous gravity gradient-stabilized 'Power Tower.' The number of crew members was increased to 8 astronauts because scientists were concerned that a crew of six would be too busy with assembly and maintenance tasks and have no time for research. NASA's target date for the launch of the first element was now January 1993 while the initial operational capability had slipped to January 1994 mainly because the Fiscal 1986 budget was reduced from $280 million to just $200 million.
11 Shuttle flights would be required for initial assembly. Officially, the estimated cost of the Station had only increased by $400 million but there were concerns that NASA was once again hiding the true cost of the larger, more complex 'Dual Keel' design.
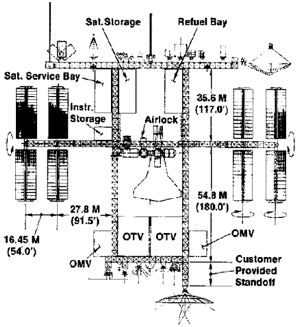
NASA struggled to define a 'Dual Keel' design that met all the various cost, engineering, safety, launch and user requirements. By the time Phase B1 ended in March 1986, the size of the truss structure elements had been increased from 3 x 3 meters to 5 x 5 meters for additional strength and stiffness. Another early 1986 modification involved the power system, which was upgraded to 87.5 kW. By the end of Phase B1 in March 1986, NASA had settled for a hybrid system consisting of 37.5 kW photovoltaic arrays and 50 kW solar thermodynamic generators. The number of American crew modules was also reduced from four to two while European and Japanese laboratories were incorporated in the design for the first time. The habitable volume remained the same, though, since the length of the US modules was increased to 13.3 meters. NASA Space Station Office submitted its recommended final baseline in May 1986 as Phase C/D started. The number of instrument mounting ports was reduced to five, down from an earlier projection of nine. One of the two bays for satellite servicing was also deleted.
According to the May '86 Space Station assembly sequence, the first element would be launched in January 1993. The Station would support man-tended operations after the sixth Shuttle assembly mission in August 1993 and be ready for permanent occupation after the ninth mission in January 1994. Initial Operating Capability (IOC) would be achieved after 21 flights -- twice as many as the 1984 estimate.
By the time of the 'Dual Keel' Space Station's final flight sequence overview in October 1986 NASA had to insert an additional eight Shuttle flights into the manifest. By this time, increased complexity and Shuttle payload capability reductions had increased the required number of assembly flights to more than 30 for an Initial Operating Capability (IOC) vs. 8-10 in 1984.
NASA's new Space Station design was criticized in a widely publicized astronaut office briefing by Shuttle astronaut Gordon Fullerton. The Dual Keel design was found to provide poor access for maintenance, visibility from habitable areas was obstructed, there was no provision for internal vehicle 'hands on' access to EVA equipment. No crew escape vehicle had been added although a small fleet plus lower-than-hoped-for flight rates means astronauts could not be rescued as easily by the Shuttle. The Canadian manipulator was regarded as insufficient for building and maintaining such a complex Station. Fullerton also criticized excessive EVA 'spacewalk' requirements, including a 'long and complex' assembly sequence. 'Basic structure, wire runs, and plumbing are not easily designed for replacement / repair. EVA crew time even for planned maintenance was excessive. Correction of design errors may not be possible; unplanned failures may not be fixable at all...'
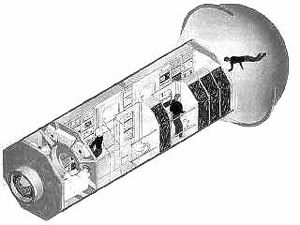
McDonnell-Douglas' redesigned 'Dual Keel' crew modules of this period introduced separate 'node modules' or docking ports which also accommodated many systems that would not have fit inside the original 'Power Tower' crew modules. NASA was still planning to contribute two laboratory modules plus two habitation modules in late 1985. Gordon Fullerton and other observers felt the Station's habitable volume was too limited when the number of US modules was reduced to one lab plus one habitation module. There would be no room for a second shower, commode or 'safe haven' emergency provisions. A Boeing longer 13.3-meter module was introduced in early 1986.
The Space Station was briefly suspended by a major row in the summer of 1986 when NASA tried to reassign some habitation module responsibilities from the Johnson Space Center to the Marshall Space Flight Center. A compromise was reached in September 1986, but it was yet another indication of the Station's Byzantine management structure and turf battles between NASA centers. But Congress still approved the project's $420-million Fiscal 1987 budget while imposing a number of restriction: power levels of at least 37.5 kW, fully outfit the microgravity lab by the sixth assembly flight, attach useful science payload by the third flight, launch all US elements before the foreign modules and restrict ESA's Columbus module to life sciences. The congressional requirements would essentially have forced NASA to change the Station along the lines of a new proposal which then, surprisingly, emerged from JSC. NASA had previously testified in Congress that no Station funds were being spent on alternative design studies. Using funding earmarked for alternate assembly sequence research, the Johnson Space Center nonetheless ordered its main contractors (Rockwell and McDonnell-Douglas) to examine a smaller, more compact configuration while keeping NASA headquarters in the dark about it... This caused additional confusion about who was really in charge of the project: NASA headquarters or Johnson.
NASA's first detailed cost assessment in February 1987 revealed the 'Dual Keel' Space Station would cost at least $14.5 billion in 1984 dollars, or $21 billion in current-year dollars. This caused a political uproar in Congress, where many politicians had started to express doubt about the project. However, NASA and Reagan Administration officials reached a compromise in March 1987 which allowed the agency to proceed with a cheaper $12.2-billion Phase One Station. This design initially omitted the $3.4-billion 'Dual Keel' structure and half of the power generators. It was dubbed 'Freedom'.
Article by Marcus Lindroos
Family: Space station, USA - Space Stations. Country: USA. Agency: NASA.
 | Os1095 Credit: ESA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Os9510I Credit: ESA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Dual Keel Station/85 Dual Keel Space Station - 1985. Rockwell's "Dual Keel" proposal at various stages of the assembly process. Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Dual Keel Station/85 Dual Keel Space Station - 1985. Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Dual Keel Station/85 Dual Keel Space Station - 1986-87 Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | McAir Station-1984 Dual Keel Space Station Crew Module. McDonnell-Douglas illustration of the "Dual Keel" crew modules. Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
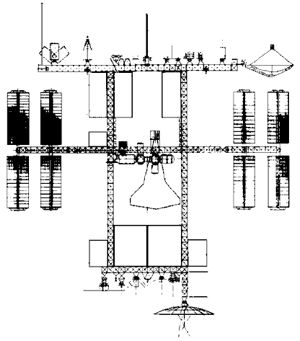 | Dual Keel Station Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Dual Keel Station/85 Dual Keel Space Station - 1985 Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Dual Keel Station/86 Dual Keel Space Station - 1986-87 Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Dual Keel Station/86 Dual Keel Space Station - 1986-87. Rockwell "Dual Keel" Space Station proposal. Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
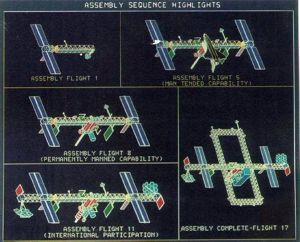 | Dual Keel Assembly Dual Keel Space Station Assembly Sequence - 1987. Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
 | Dual Keel Modules Dual Keel Space Station Crew Module. This Boeing illustration shows the longer 13.3-meter module introduced in early 1986. Credit: NASA via Marcus Lindroos |
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use