
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Cosmopolis 21
 C-21 Spaceplane Credit: Space Adventures, Ltd |
AKA: C-21. Status: Mock-up 2002. Payload: 500 kg (1,100 lb). Gross mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb).
They announced it would be ready to take paying passengers (at $98,000 per ticket) on suborbital flights to 100 km altitude in 2004. The spaceplane, designed by the Myasishchev Design Bureau, would be carried to 27 km altitude by the firm's M-55X Geofizika high altitude aircraft. It would then separate and use its rocket engine to take the pilot and two passengers for a ride to 100 km including three minutes of weightlessness.
The Cosmopolis XXI Aerospace System consisted of the carrier aircraft, the M-55X, and a manned rocket module, the C-21. The C-21 was a lifting body Reusable Launch Vehicle built around a 3-seat passenger capsule. It included an engine unit and an equipment compartment with rescue and environmental control / life support systems. The rocket module would be mounted on top of the M-55 Geofyzika carrier aircraft. A data link between the carrier and the rocket module provided information on propulsion systems status before take off and separation.
The carrier aircraft with the C-21 attached would reach a cruise altitude of 17 kilometers, and then gather speed to perform a vertical climb maneuver. Once the altitude reached 20 kilometers, and the trajectory angle reached 40-60 degrees to the horizon, the locks would be disengaged and the rocket module separated from the M-55X. At a safe distance from the carrier aircraft, the C-21šs expendable solid rocket motor would be ignited automatically. The rocket module would then climb steadily under rocket power, on a gradual trajectory up to maximum altitude, around 100 kilometers. Once the rocket engine burned out, it would separate from the crew compartment. The C-21 then would continue to gain altitude.
During the descent phase back to Earth, control surfaces would be extended for optimal aerodynamic performance. The spaceplane would glide to the landing area and then make a parachute-assisted touch down.
Cosmopolis XXI System Specifications
Combined Take off weight: 27,000 kg
- M-55X: Weight 25,000 kg; Crew 1; Maximum Altitude: 27 km; Maximum Speed: 800 km/h; Max. Flight Duration: 6.5 hours
- C-21: Weight: 2,000 kg; Crew / Passengers: 1 / 2; Maximum Altitude: 100 km
Crew Size: 3.
Family: Spaceplane, Suborbital. Country: Russia. Agency: Myasishchev bureau. Bibliography: 536, 6428.
 | C-XXI / M55 C-21 Spaceplane and M-55 launch aircraft. Credit: Space Adventures, Ltd |
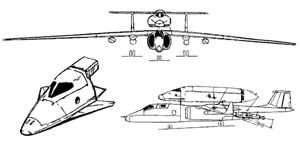 | M-55 / C-21 C-21 Spaceplane and M-55 launch aircraft. Credit: Space Adventures, Ltd |
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use