
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Apollo Direct 2-Man
 Apollo Direct 2-Man |
Status: Study 1961.
Following the preliminary decision to proceed with the lunar orbit rendezvous technique for the Apollo lunar landing mission, there was one final effort to return to the simpler direct landing approach. Lunar orbit rendezvous would require a three-man Apollo capsule, in order for a crew of two to reach the lunar surface while the third crewmember tended the waiting Apollo in lunar orbit. But if the objective was to land two men on the moon, why use the three-man Apollo capsule? Why not use either the two-man Gemini capsule, or a reduced size two-man Apollo-shaped capsule to land directly on the moon? Such a spacecraft could be propelled toward the moon on a single launch of the Saturn C-5 rocket, just like the LOR version.
McDonnell, builders of the Mercury and Gemini spacecraft, were given the contract to make a study of the alternate approach. The result showed it was indeed feasible, at less cost, risk, complexity, and time, then the LOR 3-man Apollo. The only problem was that the existing work done on the North American three-crew Apollo would have to be scrapped, and either a modified Gemini or a new two-crew Apollo developed in its place. Wiesner, Kennedy's science adviser, was an enthusiastic about the approach. NASA, North American, and the competitors for the lunar module contract were distinctly less interested. Webb, the NASA Administrator, finally got the idea spiked once and for all.
Major ground rules for the study were:
- Launch vehicle was the Saturn C-5, injecting 40,800 kg to a lunar transfer orbit.
- Mission duration was eight days (two and one-half days flight time to moon, one day on lunar surface plus one day contingency, two and one-half days return time plus one day contingency) plus seven days post landing (one day habitable environment plus six days survivable environment ).
- Both cryogenic and noncryogenic propulsion systems were to be considered. The final configuration used a LOX/LH2 RL10-powered stage for the major lunar crasher stage, and N2O4/MMH storable propellants for the lunar landing and ascent stages.
- Atmosphere was 5 psi normal, 3.5 psi emergency, 100% oxygen.
- First operational flight during the first half of calendar year 1967 was assumed.
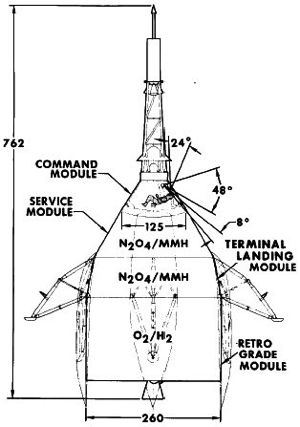
The command module was a 33 decree blunt cone with the same geometry as the Apollo 3-man capsule then in development. But it was 25% smaller, with a 3.18 m diameter base. The module has a hypersonic L/D of 0.45, achieved by offset center of gravity. The two crewmen entered and exited the module through a quick opening hatch in the side wall. A tower mounted launch escape system was attached to the conical end of the command module.
Weight summary was as follows:
- Command Module: 2337 kg
- Service Module Equipment: 520 kg
- Spacecraft Weight Margin: 652 kg
- Service Module: 10,104 kg
- Terminal Landing Module: 2735 kg
- Retrograde Module: 24,393 kg
- Launch Escape System: 1,179 kg
- Landing Gear Fairing: 634 kg
- Gross Weight at Launch: 42,556 kg
- Less (1% effective) Jettisonable Items: 1740 kg
- Effective Launch Weight: 40,816 kg
The guidance and navigation system for Two-Man Apollo was essentially the same as the system developed by MIT for the Three-Man Apollo. It consisted of an inertial system for attitude memory and acceleration measurements, navigation sensors (optical, radar, and DSIF), a computer for computation of guidance and display signals for nominal and abort trajectories, and electronic interface equipment required to drive appropriate displays. Total weight was 176 kg, compared with 200 kg for the Three- Man Apollo.
The environmental control system was identical to the equipment in the Gemini spacecraft with the exception of the volume differences dictated by the requirements for expendables. Normal mission power was supplied from six fuel cell stacks located in the service module. Silver-zinc batteries in the command module provided re-entry and recovery power plus back-up for the fuel cells, as required. Additional silver-zinc batteries provided redundant isolated sources for squibs, relays and other transient producing equipment. Both the fuel cells and the batteries were identical to Gemini equipment. A detailed electrical load analysis indicated that the mission requirements were 900 watts average. Sufficient fuel was provided for the full 8 day mission, two days of which were contingency.
Conventional spacecraft structures were employed in all modules, following the proven materials and concepts demonstrated in the Mercury and Gemini designs. Primary structure of each module consisted of a semimonocoque shell with reinforcements around cut-outs and fittings to distribute localized loads. Titanium was used as the basic shell material in all modules except the service module where beryllium sheet was used for the structural radiator shell.
Re-entry heat protection was conservatively designed for a controlled 17,000 km range, polar re-entry. The ablative material was M.A.C. Thermorad Shield S-3 elastomeric composite, which was being used for the Gemini blunt face heat shield. A 1.15 factor was applied to the predicted heating rates. Nominal material physical properties were used, determined from Project Gemini testing. Total ablative material design weight was 259 kg.
Family: Lunar Landers. Country: USA. Spacecraft: Apollo Direct CM, Apollo Direct RM, Apollo Direct SM, Apollo Direct TLM. Bibliography: 2303, 2304.
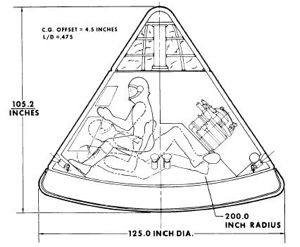 | Apollo 2 Man Layout of Apollo 2-man reduced-size capsule. Credit: NASA |
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use