
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
S5.4
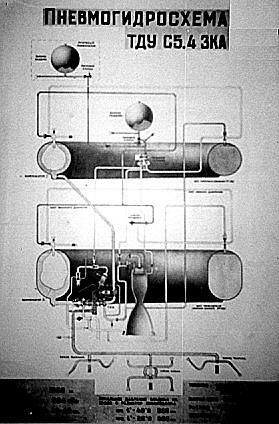 S.5.4 Vostok TDU S.5.4 Vostok TDU engine schematics Credit: © Mark Wade |
AKA: 8D66;TDU-1. Status: Out of Production. Date: 1959. Thrust: 15.83 kN (3,559 lbf). Unfuelled mass: 98 kg (216 lb). Specific impulse: 266 s. Burn time: 45 s. Height: 1.13 m (3.69 ft). Diameter: 0.95 m (3.11 ft).
In the 22 May 1959 government decree that gave the go-ahead for the Vostok program both Isayev's OKB-2 and the NII-125 design bureau of Boris Zhukov were tasked with developing deorbit engines for the various Vostok versions. OKB-2 was to develop a liquid-propellant engine and NII-125 a solid-propellant engine. Korolev decided to use the liquid-propellant engine both on the manned vehicle and the first spy satellite version (Zenit-2). This engine was initially known as S5.4, but received the military index 8D66 after Zenit-2 was declared operational. Series production of the engine was turned over by OKB-2 to the Zlatoust Machine Building Factory, where it was manufactured until 1975. In 1974 forty engines were produced and stored with a storage lifetime of 10 years.
The liquid propellant engine was used by Zenit-2, Zenit-4, Zenit-2M and Zenit-4MKM, with its last flight with Cosmos 1214 in 1985 . A new Isayev engine (11D452) was introduced on Zenit-6 and a slightly modified version of that (11D452A) flew on Zenit-6U and presumably also on Zenit-8.
When OKB-1 finished the preliminary design for Zenit-4 in 1964, the idea was to introduce the NII-125 solid-fuel engine on the series production versions of the satellite. The solid-fuel engine made a test flight on Cosmos 69 (a Zenit-4) in June 1965, but didn't fly again until October 1968 (Cosmos 251, the first Zenit-4M). The solid-propellant engine flew on Zenit-4M, 4MT and 4MK.
Chambers: 1 + 4. Engine: 98 kg (216 lb). Chamber Pressure: 55.50 bar. Propellant Formulation: AK20F/TG-02. Thrust to Weight Ratio: 16.46. Oxidizer to Fuel Ratio: 3.07.
Family: Storable liquid. Country: Russia. Propellants: Nitric acid/Amine. Agency: Isayev bureau. Bibliography: 225, 321, 329.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use