
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Project 921
AKA: China Type E. Status: Design 1992. Payload: 11,000 kg (24,000 lb). Thrust: 4,801.00 kN (1,079,307 lbf). Gross mass: 373,000 kg (822,000 lb). Height: 55.00 m (180.00 ft). Diameter: 4.50 m (14.70 ft). Apogee: 300 km (180 mi).
The stages would be combined and clustered to achieve a wide range of payload capabilities:
| Vehicle | Basic | A | B | C | D | E |
| Booster Stages | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Upper Stages Stages | 1 | none | none | 1 | none | none |
| Lift-off mass (metric tons) | 373 | 944 | 802 | 1,018 | 1,583 | 2,219 |
| Lift-off thrust (kN) | 4 x 1,200 | 12 x 1,200 | 8 x 1,200 +2 x 490* | 12 x 1,200 | 20 x 1,200 | 28 x 1,200 |
| Payload LEO (metric tons) | 11 | 22 | 30 | 38 | 48 | 70 |
* The B vehicle unusually used two of the Lox/LH2 engines to supplement the main engines.
Like Chelomei's UR-700 vehicles, the core booster engines would ignite at lift-off but initially use propellants from the lateral booster stages. At jettison of the lateral stages, the connections would be closed, allowing the core booster to proceed with the next burn with full propellant tanks.
The stages were sized at 4.5 m diameter to allow rail transport from the factory to the launch site at Jiuquan. Lateral clustering of the boosters allowed the height of the vehicle to be kept at no more than 60 m.
The drawings of the rockets provided show an upper stage with dimensions that are not consistent with the use of Lox/LH2 in the usual Western oxidizer:fuel ratio of 6:1. Either the upper stage actually is wider than indicated (e.g. 5.4 m to match the payload shroud of the larger versions) or some exotic cryogenic propellant technologies were envisioned (slush hydrogen, oxygen-rich off-optimum propellant use). The upper stage was equipped with a guidance section and a storable propellant engine unit for on-orbit maneuvering and restart of the main engine. Therefore it could form the basis for a trans-lunar or deep space injection stage for the Type E vehicle.
The original Project 921 proposal was issued by the Shanghai Astronautics Bureau in October 1993 for inclusion in the Eight and Ninth Five Year Economic Plans. Shanghai proposed the development of six large carrier rockets and eight new spacecraft. But the plan was not approved in its entirety. The program for the new liquid oxygen and kerosene rockets was delayed, and resources were put instead into the development of large solid motors for military use. The Project 921-1 spacecraft was approved for launch on a modification of the storable-propellant CZ-2E, called CZ-2F.
However the new Vertical Assembly Building built at Jiuquan was sized to handle vehicles of the new modular series. Basic research work continued on the new launch vehicle. The new Lox/Kerosene engines could possibly incorporate licensed Russian technology (the engine parameters are similar to those of the NK-33 licensed in the USA to Kistler). Therefore it seems likely that production of modern boosters of this type may be authorized later in the 21st Century, when economic conditions permit - or in support of a Chinese lunar base.
LEO Payload: 11,000 kg (24,000 lb) to a 300 km orbit at 60.00 degrees.
Stage Data - Project 921
- Stage 1. 1 x Project 921-1. Gross Mass: 306,000 kg (674,000 lb). Empty Mass: 20,000 kg (44,000 lb). Thrust (vac): 5,406.141 kN (1,215,349 lbf). Isp: 330 sec. Burn time: 170 sec. Isp(sl): 293 sec. Diameter: 4.50 m (14.70 ft). Span: 7.50 m (24.60 ft). Length: 29.00 m (95.00 ft). Propellants: Lox/Kerosene. No Engines: 4. Status: Study 1992. Comments: Engine chamber pressure 13 to 15 Mpa.
- Stage 2. 1 x Project 921-2. Gross Mass: 57,000 kg (125,000 lb). Empty Mass: 7,000 kg (15,400 lb). Thrust (vac): 490.000 kN (110,150 lbf). Isp: 440 sec. Burn time: 430 sec. Diameter: 4.50 m (14.70 ft). Span: 4.50 m (14.70 ft). Length: 10.00 m (32.00 ft). Propellants: Lox/LH2. No Engines: 1. Status: Study 1992. Comments: Additionally 4 vernier Lox/LH2 engines with a total thrust of 4600 kgf and a storable engine package for stage propellant ullage and restart.
| Project 921-1 LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Engine chamber pressure 13 to 15 MPa. |
| Project 921 LV-2 LOx/LH2 propellant rocket stage. Additionally 4 vernier LOx/LH2 engines with a total thrust of 4600 kgf and a storable engine package for stage propellant ullage and restart. |
Family: orbital launch vehicle. Country: China. Stages: Project 921-1, Project 921 LV-2. Agency: Shanghai. Bibliography: 286, 425, 478, 8498.
 | Chinese Type E LV The largest known Chinese launch vehicle, the Type E. This would consist of a cluster of six modular stages around a single module core. Credit: © Mark Wade |
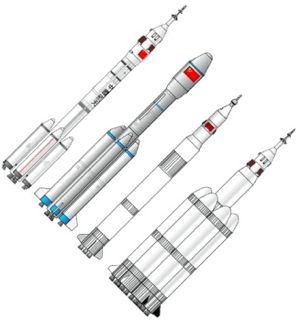 | China Lunar LV's From left to right, existing Chinese manned program vehicles (CZ-2F and CZ-2E(A)) and proposed future vehicles (Type A, and Type C). Credit: © Mark Wade |
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use

