
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Orbital Scanner
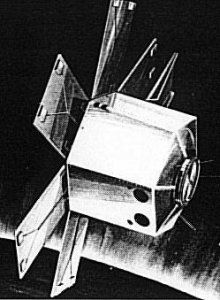 OrbScan Credit: Manufacturer Image |
Status: Study 1969.
Orbital Scanner was an automated research satellite proposed in the late 1960's to map a new artificial horizon on a global basis for use as a more stable reference by future spacecraft guidance, navigation and pointing systems. Apparently the satellite never flew or its sensors were tested on other missions.
The existing reference point, the earth's limb, was not felt to provide the accuracies necessary to conduct all the precision pointing experiments required in planned communications, weather, earth resources observation, reconnaissance and astronomy missions. So preliminary design was begun on spacecraft to map a stable band of infrared energy that exists at 40 to 65 km high in the earth's atmosphere. The satellite would take readings during the early 1970s from a near polar orbit over a year's period to assure complete data in all seasonal conditions. Prime Contractor: Honeywell Inc. Subcontractors: RCA (communications and data handling); Lockheed Missiles and Space Company (radiometer); Control Data Corporation (attitude determination); Gulton Industries Inc. (onboard power); Spectrolab Division of Textron Electronics Inc. (solar panels); Allied Research-Mellonics (data reduction and analysis).
Family: Navigation technology satellite, Technology. Country: USA. Agency: Honeywell. Bibliography: 405.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use