
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
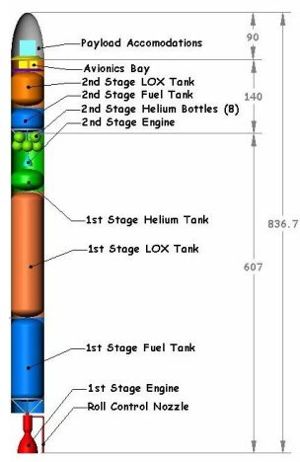
Nanosat Launch Vehicle
 Nanolv |
Status: Development. Payload: 10 kg (22 lb). Apogee: 250 km (150 mi).
Garvey Spacecraft Corporation (GSC), based in Long Beach, California, was a small research and development (R&D) company, focusing on the development of advanced space technologies and launch vehicle systems. As part of the California Launch Vehicle Initiative (CALVEIN), GSC and California State University, Long Beach (CSULB), were jointly conducting preliminary R&D tasks to establish the foundation for development of a two-stage, liquid propellant Nanosat Launch Vehicle (NLV
As part of this initiative, GSC and CSULB were pursuing advanced aerospike engine technology for use on the NLV first stage. Their work built upon the first-ever powered liquid propellant aerospike flight that the team conducted using several of its LOX/ethanol Prospector research vehicles. GSC's most visible accomplishments included the first-ever flight of a composite LOX tank (conducted in partnership with Microcosm, Inc.), the first-ever powered flights of a liquid-propellant aerospike engine, and the launch and 100-percent recovery of several prototype reusable test vehicles.
On May 24, 2005, GSC and CSULB conducted a successful test launch of Prospector 6, a partially-reusable full-scale prototype of the NLV, from the Mojave Test Area in California. The rocket flew to an altitude of approximately 915 meters before parachuting back to Earth. The GSC/CSULB team was planning to refurbish and relaunch the rocket while also working on an improved design. In October 2005, GSC and CSULB conducted two flights in the same day of a single vehicle, the new Prospector 7, to demonstrate RLV-like rapid turnaround operations. Project funding was derived from a series of NLV-related suborbital flight tests that GSC and CSULB were conducting for several U.S. government organizations.
LEO Payload: 10 kg (22 lb) to a 250 km orbit at 90.00 degrees.
Family: LCLVs, low cost, orbital launch vehicle. Country: USA. Agency: Garvey.
 | Nanolv1 |
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use