
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Hyperion 1958
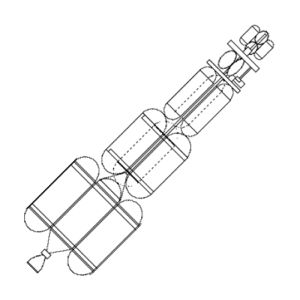 Hyperion Interplanet Hyperion Interplanetary Spacecraft Credit: © Mark Wade |
Status: Study 1959. Payload: 145,000 kg (319,000 lb). Thrust: 10,700.00 kN (2,405,400 lbf). Gross mass: 850,000 kg (1,870,000 lb). Height: 85.40 m (280.10 ft). Diameter: 8.54 m (28.01 ft). Apogee: 485 km (301 mi).
This booster stage surrounded the nuclear core vehicle with its large liquid hydrogen tank. The conventional stage would draw fuel from the main hydrogen tank until burnout. Hyperion would have doubled the translunar trajectory performance of the Saturn V and less than one third of the liftoff mass.
LEO Payload: 145,000 kg (319,000 lb) to a 485 km orbit at 28.00 degrees. Payload: 82,000 kg (180,000 lb) to a earth escape.
Family: nuclear-powered, orbital launch vehicle. Country: USA. Stages: Hyperion Booster, Hyperion Sustainer. Agency: Convair. Bibliography: 45.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use